Arginine Methyltransferases Are Regulated by Epstein-Barr Virus in B Cells and Are Differentially Expressed in Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Protein Arginine Methyltransferases Are Differentially Expressed in Primary HL


| Immunohistochemical staining of 77 cases of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma for PRMT1, CARM1 and PRMT5 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | Intensity of Cytoplasmic Staining | ||||||
| PRMT1 * | intensity of nuclear staining | strong | moderate | weak | negative | Total | |
| strong | 22 (12) | 10 (1) | 3 | 8 | 43 | ||
| moderate | 0 | 25 (11) | 3 | 4 | 32 | ||
| weak | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| negative | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| CARM1 ** | intensity of nuclear staining | strong | 26 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 32 |
| moderate | 11 | 14 | 1 | 0 | 26 | ||
| weak | 4 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 11 | ||
| negative | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4 | ||
| PRMT5 * | intensity of nuclear staining | strong | 4 [2] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| moderate | 2 [2] | 10 [5] | 0 | 0 | 12 | ||
| weak | 7 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 13 | ||
| negative | 25 | 21 | 0 | 1 | 47 | ||
| Influence of EBV Status: Comparison of Immunohistochemical Staining for PRMT1, CARM1 and PRMT5 in EBV Positive (n = 27) and EBV Negative (n = 50) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| intensity of nuclear staining | PRMT1 | CARM1 | PRMT5 | ||||
| EBV negative | EBV positive | EBV negative | EBV positive | EBV negative | EBV positive | ||
| strong | 21 | 22 | 24 | 9 | 3 | 2 | |
| moderate | 27 | 5 | 16 | 9 | 7 | 4 | |
| weak | 1 | 0 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 5 | |
| negative | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 31 | 16 | |
| X23df = 11; p = 0.005 | X23df = 2.9; p = 0.41 | X23df = 0.1; p = 0.99 | |||||
| intensity of cytoplasmic staining | strong | 12 | 10 | 26 | 16 | 25 | 13 |
| moderate | 25 | 10 | 14 | 9 | 23 | 13 | |
| weak | 6 | 1 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| negative | 6 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| X23df = 4.2; p = 0.24 | X23df = 4.4; p = 0.06 | X23df = 3.4; p = 0.3 | |||||
2.2. EBV Infection Modulates the Expression of the Protein Arginine Methyltransferases
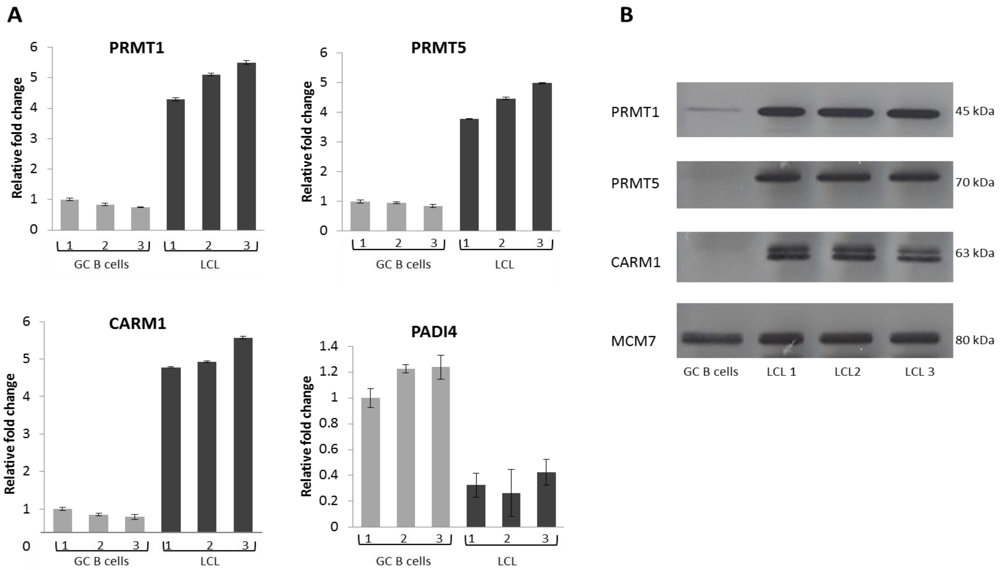
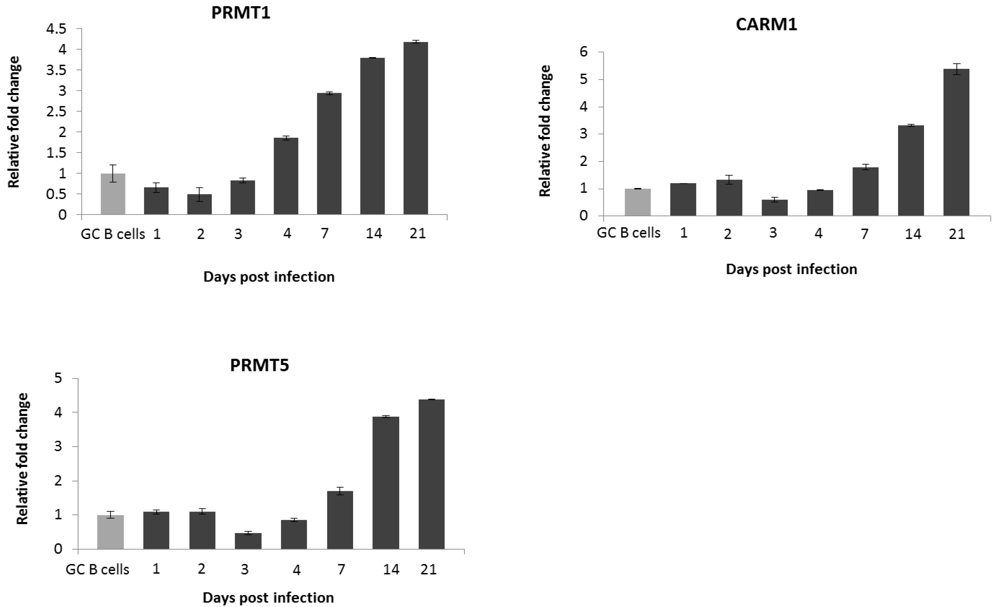
2.3. PRMT1 is Up-Regulated in B Cells by the EBV Oncogene, LMP1

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Isolation and Infection of Tonsillar GC B Cells
3.2. Maintenance of Cell Lines
3.3. Quantitative Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction
3.4. Western Blotting
3.5. Immunohistochemistry
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Bedford, M.T.; Clarke, S.G. Protein arginine methylation in mammals: Who, what, and why. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbert, G.L.; Daujat, S.; Snowden, A.W.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Hagiwara, T.; Yamada, M.; Schneider, R.; Gregory, P.D.; Tempst, P.; Bannister, A.J.; et al. Histone deimination antagonizes arginine methylation. Cell 2004, 118, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wysocka, J.; Sayegh, J.; Lee, Y.H.; Perlin, J.R.; Leonelli, L.; Sonbuchner, L.S.; McDonald, C.H.; Cook, R.G.; Dou, Y.; et al. Human PAD4 regulates histone arginine methylation levels via demethylimination. Science 2004, 306, 279–283. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Shin, B.; Park, E.S.; Yang, S.; Cho, S.; Kang, M. Protein arginine methyltransferase 1 regulates herpes simplex virus replication through ICP27 RGG-box methylation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 1, 322–328. [Google Scholar]
- Koyuncu, O.O.; Dobner, T. Arginine methylation of human adenovirus type 5 L4 100-kilodalton protein is required for efficient virus production. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 4778–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.; Chang, P.C.; Huerta, S.; Izumiya, C.; Davis, R.; Tepper, C.G.; Kim, K.Y.; Shevchenko, B.; Wang, D.H.; Jung, J.U.; et al. Protein arginine methyltransferase 1-directed methylation of Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency-associated nuclear antigen. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 17, 5806–5818. [Google Scholar]
- Shire, K.; Kapoor, P.; Jiang, K.; Hing, M.N.; Sivachandran, N.; Nguyen, T.; Frappier, L. Regulation of the EBNA1 Epstein-Barr virus protein by serine phosphorylation and arginine methylation. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5261–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, H.; Barth, S.; Palermo, R.D.; Mamiani, A.; Hennard, C.; Zimber-Strobl, U.; West, M.J.; Kremmer, E.; Grässer, F.A. Asymmetric Arginine dimethylation of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 promotes DNA targeting. Virology 2010, 397, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.J.; Lu, H.; Cho, W.K.; Park, H.U.; Pise-Masison, C.; Brady, J.N. Coactivator-Associated arginine methyltransferase 1 enhances transcriptional activity of the human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 long terminal repeat through direct interaction with Tax. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 10036–10044. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumaran, H.; van der Horst, A.; Fulcher, A.J.; Apolloni, A.; Lin, M.H.; Jans, D.A.; Harrich, D. Arginine methylation increases the stability of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 11694–11703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, F.H.; Christen, V.; Berke, J.M.; Penna, S.H.; Moradpour, D.; Heim, M.H. Upregulation of protein phosphatase 2Ac by hepatitis C virus modulates NS3 helicase activity through inhibition of protein arginine methyltransferase 1. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 15342–15350. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.H.; Peng, K.L.; Jhang, H.C.; Lin, C.H.; Wu, S.Y.; Chiang, C.M.; Lee, S.C.; Yu, W.C.; Juan, L.J. The HPV E6 oncoprotein targets histone methyltransferases for modulating specific gene transcription. Oncogene 2012, 3, 2335–2349. [Google Scholar]
- Küppers, R. The biology of Hodgkin's lymphoma. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Frankel, A.; Cook, R.J.; Kim, S.; Paik, W.K.; Williams, K.R.; Clarke, S.; Herschman, H.R. PRMT1 is the predominant type I protein arginine methyltransferase in mammalian cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 7723–7730. [Google Scholar]
- Hassa, P.O.; Covic, M.; Bedford, M.T.; Hottiger, M.O. Protein arginine methyltransferase 1 coactivates NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression synergistically with CARM1 and PARP1. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 377, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, P.J.; Ruland, J. Aberrant NF-kappaB signaling in lymphoma: Mechanisms. consequences. and therapeutic implications. Blood 2007, 109, 2700–2707. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Pal, S.; Sif, S. Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 suppresses the transcription of the RB family of tumor suppressors in leukemia and lymphoma cells. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 28, 6262–6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P.; Vaites, L.P.; Kim, J.K.; Mellert, H.; Gurung, B.; Nakagawa, H.; Herlyn, M.; Hua, X.; Rustgi, A.K.; McMahon, S.B.; et al. Nuclear cyclin D1/CDK4 kinase regulates CUL4 expression and triggers neoplastic growth via activation of the PRMT5 methyltransferase. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Y.; Liao, Y.F.; Chang, W.H.; Liu, C.C.; Hsieh, M.C.; Hsu, P.C.; Tsay, G.J.; Hung, H.C. Overexpression of peptidylarginine deiminase IV features in apoptosis of haematopoietic cells. Apoptosis 2006, 11, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vockerodt, M.; Morgan, S.L.; Kuo, M.; Wei, W.; Chukwuma, M.B.; Arrand, J.R.; Kube, D.; Gordon, J.; Young, L.S.; Woodman, C.B.; Murray, P.G. The epstein-barr virus oncoprotein latent membrane protein-1 reprograms germinal centre B cells towards a Hodgkin’s Reed-Sternberg-like phenotype. J. Pathol. 2008, 216, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, S.; Wei, W.; Anderton, J.; Vockerodt, M.; Rowe, M.; Murray, P.G.; Woodman, C.B. Epigenetic and transcriptional changes which follow Epstein-Barr virus infection of germinal centre B cells and their relevance to the pathogenesis of Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 9568–9577. [Google Scholar]
- O’Brien, K.B.; Alberich-Jordà, M.; Yadav, N.; Kocher, O.; Diruscio, A.; Ebralidze, A.; Levantini, E.; Sng, N.J.; Bhasin, M.; Caron, T.; et al. CARM1 is required for proper control of proliferation and differentiation of pulmonary epithelial cells. Development 2010, 137, 2147–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin-Lespinasse, Y.; Sentis, S.; Kolytcheff, C.; Rostan, M.; Corbo, L.; Le Romancer, M. hCAF1, a new regulator of PRMT1-dependent arginine methylation. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 120, 638–647. [Google Scholar]
- Tee, W.W.; Pardo, M.; Theunissen, T.W.; Yu, L.; Choudhary, J.S.; Hajkova, P.; Surani, M.A. Prmt5 is essential for early mouse development and acts in the cytoplasm to maintain ES cell pluripotency. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 2772–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Hoshikawa, Y.; Oh-hara, T.; Koike, S.; Naito, M.; Noda, T.; Arai, H.; Tsuruo, T.; Fujita, N. PRMT5, a novel TRAIL receptor-binding protein, inhibits TRAIL-Induced apoptosis via nuclear factor-κB activation. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floettmann, J.E.; Ward, K.; Rickinson, A.B.; Rowe, M. Cytostatic effect of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane Protein-1 analyzed using tetracycline-regulated expression in B cell lines. Virology 1996, 223, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, V.; Tiacci, E.; Pfeil, I.; Döring, C.; Eckerle, S.; van Noesel, C.J.; Klapper, W.; Falini, B.; von Heydebreck, A.; Metzler, D.; et al. Origin and pathogenesis of nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma as revealed by global gene expression analysis. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2251–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, A.; Jung, K.J.; Jeong, S.J.; Brady, J.N. Inhibition of methyltransferases results in induction of g2/m checkpoint and programmed cell death in human T-lymphotropic virus type 1-transformed cells. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infantino, S.; Benz, B.; Waldmann, T.; Jung, M.; Schneider, R.; Reth, M. Arginine methylation of the B cell antigen receptor promotes differentiation. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellis, O.; Arbabian, A.; Brouland, J.P.; Kovàcs, T.; Rowe, M.; Chomienne, C.; Joab, I.; Papp, B. Modulation of B-cell endoplasmic reticulum calcium homeostasis by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1. Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enouf, J.; Lawrence, F.; Tempete, C.; Robert-Gero, M.; Lederer, E. Relationship between inhibition of protein methylase I and inhibition of Rous sarcoma virus-induced cell transformation. Cancer Res. 1979, 39, 4497–4502. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, B.; Zheng, Y.G. Discovery and mechanistic study of a class of protein arginine methylation inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 6028–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissinger, E.M.; Heinke, R.; Spannhoff, A.; Eberlin, A.; Metzger, E.; Cura, V.; Hassenboehler, P.; Cavarelli, J.; Schüle, R.; Bedford, M.T.; et al. Acyl derivatives of p-aminosulfonamides and dapsone as new inhibitors of the arginine methyltransferase hPRMT1. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 3717–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Influence of Histological Type: Comparison of Immunohistochemical Staining for PRMT1, CARM1 and PRMT5 in Nodular Sclerosis (NS, n = 40) and Mixed Cellularity (MC, n = 37) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| intensity of nuclear staining | PRMT1 | CARM1 | PRMT5 | |||||
| NS | MC | NS | MC | NS | MC | |||
| strong | 21 | 22 | 15 | 17 | 2 | 2 | ||
| moderate | 17 | 15 | 13 | 13 | 7 | 5 | ||
| weak | 1 | 0 | 9 | 2 | 7 | 6 | ||
| negative | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 23 | 24 | ||
| X2 3df = 3.0; p = 0.39 | X2 3df = 5.5; p = 0.14 | X2 3df = 0.4; p = 0.94 | ||||||
| intensity of cytoplasmic staining | strong | 11 | 11 | 22 | 19 | 18 | 20 | |
| moderate | 17 | 18 | 12 | 12 | 19 | 17 | ||
| weak | 5 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | ||
| negative | 6 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||
| X2 3df = 1.3; p = 0.73 | X2 3df = 1.8; p = 0.62 | X2 3df = 3.1; p = 0.37 | ||||||
| Influence of Age of Diagnosis in: Comparison of Immunohistochemical Staining for PRMT1, CARM1 and PRMT5 in Paediatric (n = 17) and Adult (n = 60) Cases | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| intensity of nuclear staining | PRMT1 | CARM1 | PRMT5 | ||||
| adult | paediatric | adult | paediatric | adult | paediatric | ||
| 3 | 43 | 8 | 32 | 4 | 4 | 2 | |
| 2 | 32 | 8 | 26 | 9 | 12 | 5 | |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 11 | 4 | 13 | 2 | |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 47 | 7 | |
| X23df = 1.1; p = 0.79 | X23df = 4.0; p = 0.26 | X23df = 3.7; p = 0.3 | |||||
| intensity of cytoplasmic staining | 3 | 22 | 4 | 41 | 9 | 38 | 7 |
| 2 | 35 | 7 | 24 | 8 | 36 | 9 | |
| 1 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| 0 | 12 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| X23df = 4.5; p = 0.21 | X23df = 4.2; p = 0.24 | X23df = 1.1; p = 0.78 | |||||
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Leonard, S.; Gordon, N.; Smith, N.; Rowe, M.; Murray, P.G.; Woodman, C.B. Arginine Methyltransferases Are Regulated by Epstein-Barr Virus in B Cells and Are Differentially Expressed in Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Pathogens 2012, 1, 52-64. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens1010052
Leonard S, Gordon N, Smith N, Rowe M, Murray PG, Woodman CB. Arginine Methyltransferases Are Regulated by Epstein-Barr Virus in B Cells and Are Differentially Expressed in Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Pathogens. 2012; 1(1):52-64. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens1010052
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeonard, Sarah, Naheema Gordon, Nikki Smith, Martin Rowe, Paul G. Murray, and Ciarán B. Woodman. 2012. "Arginine Methyltransferases Are Regulated by Epstein-Barr Virus in B Cells and Are Differentially Expressed in Hodgkin’s Lymphoma" Pathogens 1, no. 1: 52-64. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens1010052
APA StyleLeonard, S., Gordon, N., Smith, N., Rowe, M., Murray, P. G., & Woodman, C. B. (2012). Arginine Methyltransferases Are Regulated by Epstein-Barr Virus in B Cells and Are Differentially Expressed in Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Pathogens, 1(1), 52-64. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens1010052




