Interaction of Phenol-Soluble Modulins with Phosphatidylcholine Vesicles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
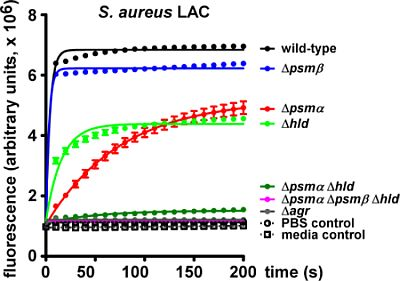
2.1. Lytic Activities of PSM Peptides

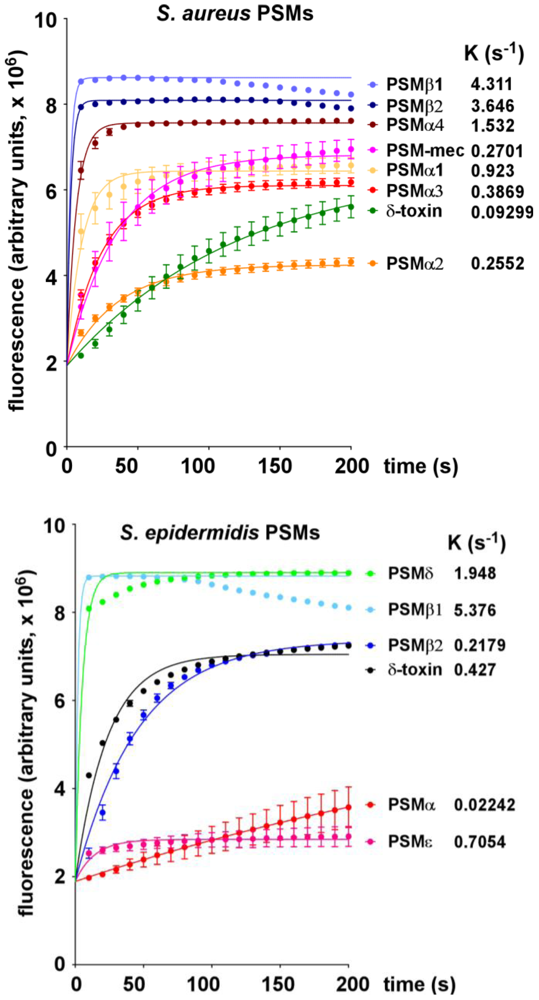
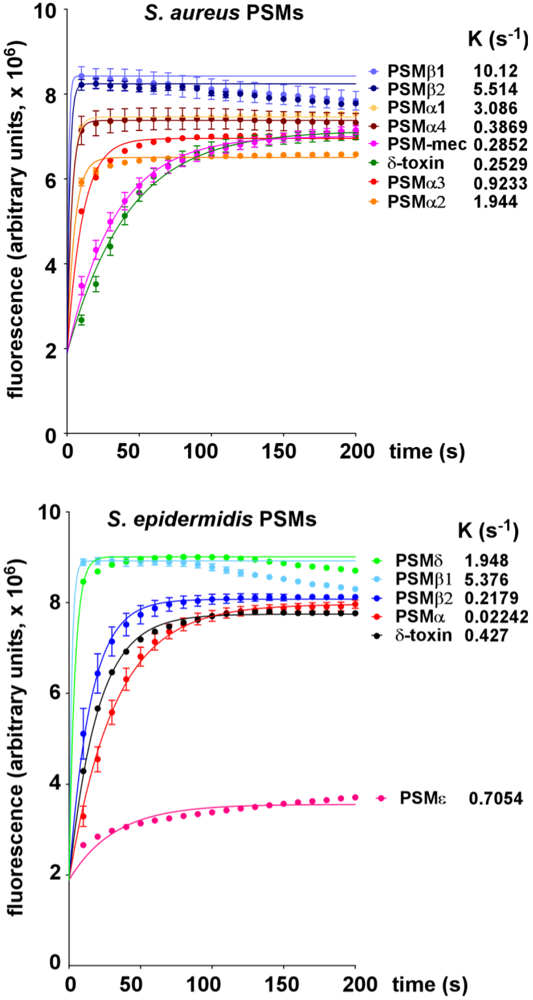
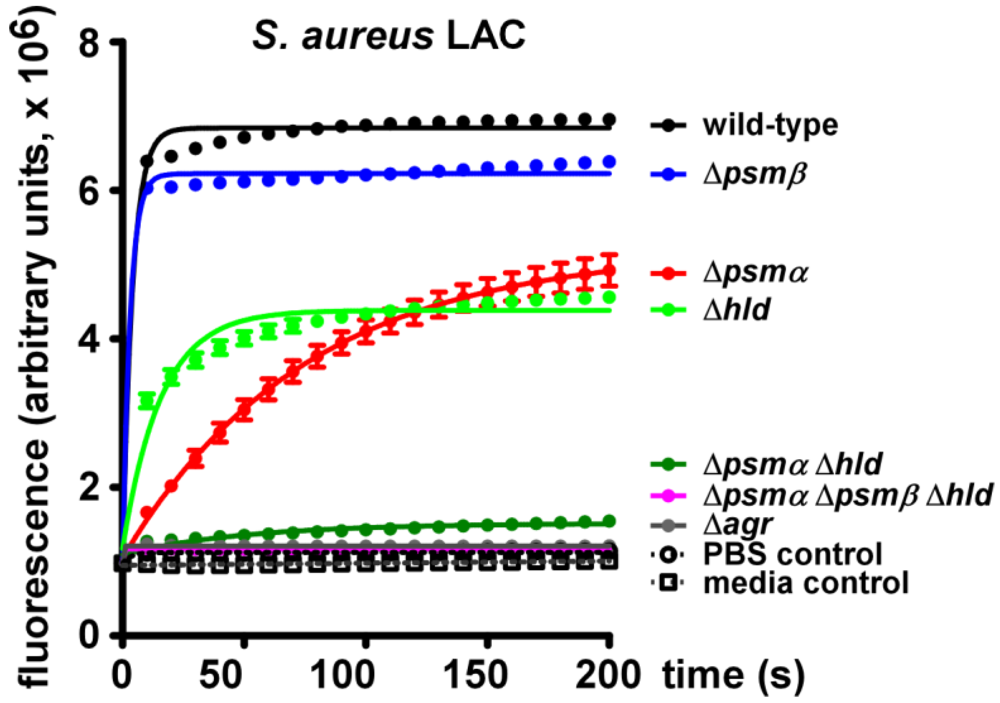
2.2. Lytic Activities of S. aureus Culture Filtrates
3. Experimental Section
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Lowy, F.D. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis - the ‘accidental’ pathogen. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Virulence factors of the coagulase-negative staphylococci. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 841–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Braughton, K.R.; Kretschmer, D.; Bach, T.H.; Queck, S.Y.; Li, M.; Kennedy, A.D.; Dorward, D.W.; Klebanoff, S.J.; Peschel, A.; et al. Identification of novel cytolytic peptides as key virulence determinants for community-associated MRSA. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1510–1514. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, S.D.; Malachowa, N.; Whitney, A.R.; Braughton, K.R.; Gardner, D.J.; Long, D.; Bubeck Wardenburg, J.; Schneewind, O.; Otto, M.; DeLeo, F.R. Comparative analysis of USA300 virulence determinants in a rabbit model of skin and soft tissue infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, 937–941. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Diep, B.A.; Villaruz, A.E.; Braughton, K.R.; Jiang, X.; DeLeo, F.R.; Chambers, H.F.; Lu, Y.; Otto, M. Evolution of virulence in epidemic community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5883–5888. [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer, D.; Gleske, A.K.; Rautenberg, M.; Wang, R.; Koberle, M.; Bohn, E.; Schoneberg, T.; Rabiet, M.J.; Boulay, F.; Klebanoff, S.J.; et al. Human formyl peptide receptor 2 senses highly pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 7, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periasamy, S.; Joo, H.S.; Duong, A.C.; Bach, T.H.; Tan, V.Y.; Chatterjee, S.S.; Cheung, G.Y.; Otto, M. How Staphylococcus aureus biofilms develop their characteristic structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Khan, B.A.; Cheung, G.Y.; Bach, T.H.; Jameson-Lee, M.; Kong, K.F.; Queck, S.Y.; Otto, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis surfactant peptides promote biofilm maturation and dissemination of biofilm-associated infection in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 238–248. [Google Scholar]
- Cogen, A.L.; Yamasaki, K.; Sanchez, K.M.; Dorschner, R.A.; Lai, Y.; MacLeod, D.T.; Torpey, J.W.; Otto, M.; Nizet, V.; Kim, J.E.; et al. Selective antimicrobial action is provided by phenol-soluble modulins derived from Staphylococcus epidermidis, a normal resident of the skin. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 192–200. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, H.S.; Cheung, G.Y.; Otto, M. Antimicrobial activity of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is caused by phenol-soluble modulin derivatives. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 8933–8940. [Google Scholar]
- Pokorny, A.; Birkbeck, T.H.; Almeida, P.F. Mechanism and kinetics of delta-lysin interaction with phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 11044–11056. [Google Scholar]
- Marinetti, G.V.; Cattieu, K. Composition and metabolism of phospholipids of human leukocytes. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1982, 31, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, J.S.; McIntyre, N. Erythrocyte lipid composition and sodium transport in human liver disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1978, 510, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, P.F.; Morris, R. Transmembrane asymmetry and lateral domains in biological membranes. Traffic 2004, 5, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Rigby, K.; Lai, Y.; Nair, V.; Peschel, A.; Schittek, B.; Otto, M. Staphylococcus aureus mutant screen reveals interaction of the human antimicrobial peptide dermcidin with membrane phospholipids. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 4200–4210. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, G.Y.; Rigby, K.; Wang, R.; Queck, S.Y.; Braughton, K.R.; Whitney, A.R.; Teintze, M.; DeLeo, F.R.; Otto, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis strategies to avoid killing by human neutrophils. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, C.; Durr, M.; Carmody, A.B.; Peschel, A.; Klebanoff, S.J.; Otto, M. Regulated expression of pathogen-associated molecular pattern molecules in Staphylococcus epidermidis: Quorum-sensing determines pro-inflammatory capacity and production of phenol-soluble modulins. Cell. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recsei, P.; Kreiswirth, B.; O’Reilly, M.; Schlievert, P.; Gruss, A.; Novick, R.P. Regulation of exoprotein gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus by agr. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1986, 202, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Vuong, C.; Kocianova, S.; Villaruz, A.E.; Lai, Y.; Sturdevant, D.E.; Otto, M. Characterization of the Staphylococcus epidermidis accessory-gene regulator response: Quorum-sensing regulation of resistance to human innate host defense. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 193, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, G.Y.; Wang, R.; Khan, B.A.; Sturdevant, D.E.; Otto, M. Role of the accessory gene regulator agr in community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis. Infect. Immunity 2011, 79, 1927–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Duong, A.C.; Cheung, G.Y.C.; Otto, M. Interaction of Phenol-Soluble Modulins with Phosphatidylcholine Vesicles. Pathogens 2012, 1, 3-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens1010003
Duong AC, Cheung GYC, Otto M. Interaction of Phenol-Soluble Modulins with Phosphatidylcholine Vesicles. Pathogens. 2012; 1(1):3-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens1010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuong, Anthony C., Gordon Y. C. Cheung, and Michael Otto. 2012. "Interaction of Phenol-Soluble Modulins with Phosphatidylcholine Vesicles" Pathogens 1, no. 1: 3-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens1010003
APA StyleDuong, A. C., Cheung, G. Y. C., & Otto, M. (2012). Interaction of Phenol-Soluble Modulins with Phosphatidylcholine Vesicles. Pathogens, 1(1), 3-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens1010003