Smallholder Telecoupling and Climate Governance in Jambi Province, Indonesia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Conceptual Framework
3. Methodology
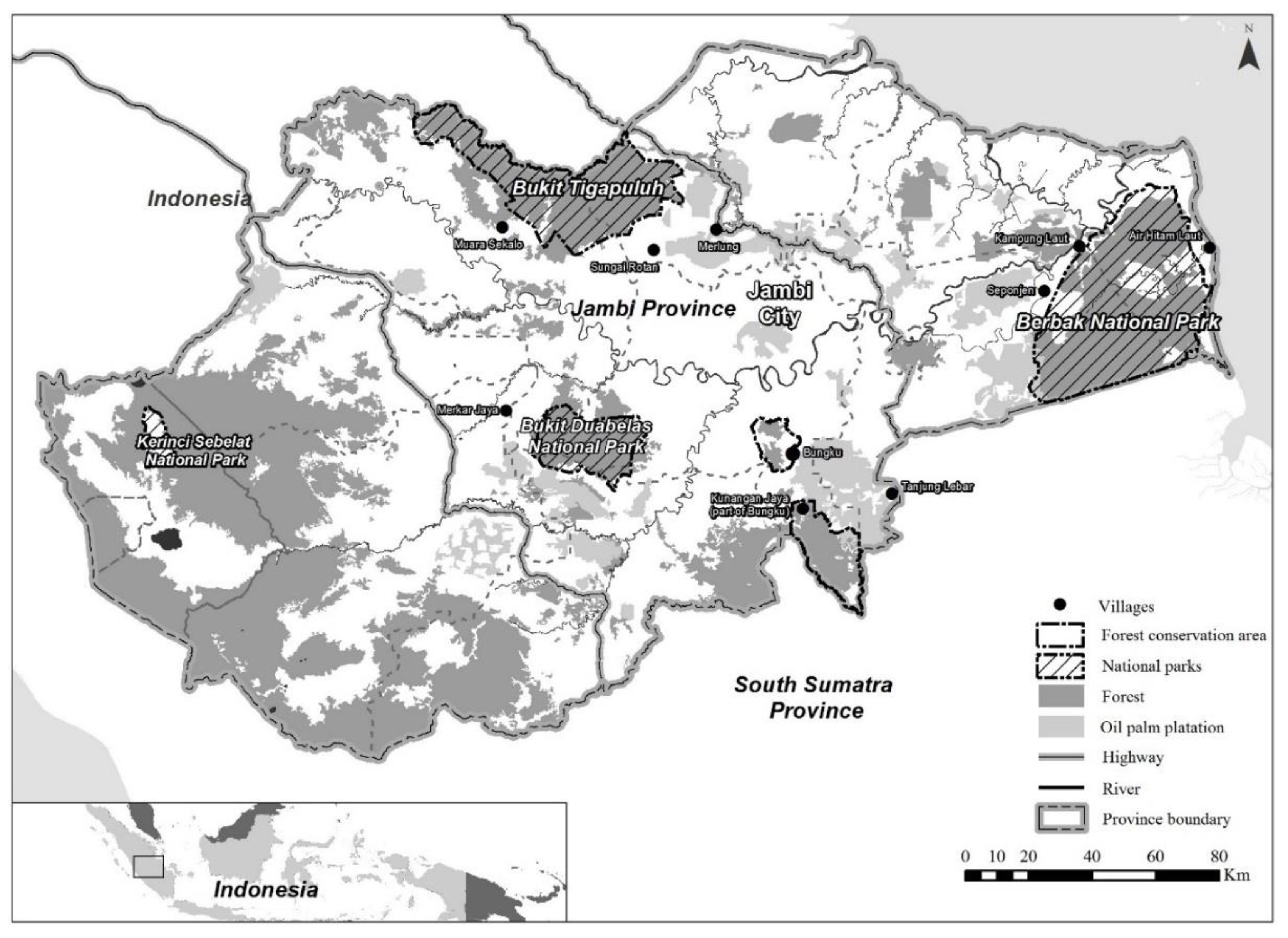
3.1. Study Sites
3.2. Multi-Stakeholder Initiatives at the Study Sites: RSPO and SNR-i
3.2.1. The Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO)
3.2.2. The Sustainable Natural Rubber Initiative (SNR-i)
3.3. Data Collection
4. Results
4.1. Smallholder Telecouplings under the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil
4.1.1. Telecoupled Systems—Demand for Sustainable Palm Oil
4.1.2. Smallholders’ Resource Use and Access to Land
4.1.3. National Institutions
4.1.4. Local Interactions
4.2. Smallholder Telecouplings under the Sustainable Natural Rubber Initiative (SNR-i)
4.2.1. Telecoupled Systems—Demand for Eco-Friendly Rubber
4.2.2. Smallholders’ Resource Use and Access to Land
4.2.3. National Institutions
4.2.4. Interactions between PT LAJ and the Local Community
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. SAFA Smallholders Survey
Basic Information
- 1.
- Name of assessor:
- 2.
- Assessing organization:
- 3.
- Date of assessment:
- 4.
- Name of person being interviewed:
- 5.
- Gender of the person being interviewed:
- ○
- Female
- ○
- Male
- 6.
- Is this person the farm owner?
- ○
- Yes
- ○
- No
- 7.
- Name of the farm:
- 8.
- The village of the farm:
- 9.
- Country of the farm:
- 10.
- Does the interview take place on or close to the farm?
- ○
- Yes
- ○
- No
- 11.
- If you do know the GPS coordinates of your farm, please type them here:
- 12.
- OR Collect the GPS coordinates of the interview (function in the app)
- 13.
- Phone number of interviewee:
- 14.
- E-Mail of interviewee (if any):
- 15.
- What are the main crops and products that you produce?
- Main product 1: Main product 6:
- Main product 2: Main product 7:
- Main product 3: Main product 8:
- Main product 4: Main product 9:
- Main product 5: Main product 10:
- 16.
- Which best describes your level of commercialization? (check all that apply)
- ○
- I am a subsistence farmer
- ○
- I sell mostly to local markets/customers
- ○
- I am a fully commercialized farmer (sell goods mostly for export)
- ○
- I am a contract farmer (with a company or a public-private partnership)
- 17.
- Do you produce any livestock on your farm?
- ○
- Yes
- ○
- No
- 18.
- What is the size of the farm (local units and preferably, in hectares)?
Mission Explicitness
- 1.
- Do you have a statement about the farm’s goals and values that you follow and that everyone on your farm understands? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- Partially (yellow)
- ○
- No (red)
Accountability
- 2.
- Do you keep accurate records of your production processes (e.g., planting and harvesting information, input use) so they can be made available to producer organizations, customers or suppliers when required? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Always or often (green)
- ○
- Sometimes (yellow)
- ○
- Never or rarely (red)
Participation
- 3.
- Do you belong to a producer organization (or another agriculturally focused organization)? [weight: 1]
- Yes (green)
- No (red)
- 4.
- How much value do you feel the farm receives from being a part of the organization? [weight: 1]
- Significant value (green)
- Some value (yellow)
- Little or no value (red)
Conflict Resolution
- 5.
- How often have you been able to peacefully and successfully resolve any problems or conflicts that you have experienced with your suppliers, workers, producer organization or buyers? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Always or often (green)
- ○
- Sometimes (yellow)
- ○
- Never or rarely (red)
- ○
- There have not been any problems or conflicts with other stakeholders (neutral)
Sustainability Management Plan
- 6.
- Do you have a farm management plan that provides for the success of your production in the long run? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- No (red)
- 7.
- How successful has this plan been? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Very successful (green)
- ○
- Somewhat successful (yellow)
- ○
- Not at all or limited success (red)
- 8.
- Which elements are part of your plan? [weight: 1] (green for 3 choices or more, yellow for 2 choices, red for 1 choice or less)
- □
- Finances
- □
- Soil fertility management
- □
- Environmental management
- □
- Expansion/Staff
- □
- Health and Safety
- □
- Marketing
- □
- Quality
- □
- Processing or adding value
- □
- Other
Profitability
- 9.
- Do you produce crops, animals, or agricultural products for sale or trade? [weight: 2]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- No (red)—no go
- 10.
- Do you know your farm revenue for the last production year? [weight: 2]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- No (red)
- 11.
- Do you know your paid labor costs for the last production year? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- No (red)
- ○
- Not applicable (neutral)
- 12.
- Do you know your fertilizer, pesticide, and seeds/plant material costs for the last production year? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- No (red)
- ○
- Not applicable (neutral)
- 13.
- Do you know your animal feed, veterinary care, and juvenile stock costs for the last production year? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- No (red)
- ○
- Not applicable (neutral)
- 14.
- During the last five years, how often were farm revenues greater than costs? [weight: 1]
- ○
- All or most of the time (green)
- ○
- Some of the time (yellow)
- ○
- Rarely/Never (red)—no go
- ○
- I don’t know (yellow)
Product Diversification
- 15.
- How many significant crops, products, or services are offered for sale? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Three or more significant crops, products, or services (green)
- ○
- Two significant crops, products, or services (yellow)
- ○
- One significant crop or product (red)
- 16.
- Do you do any processing or value adding in order to increase revenue from services or the sale price of your crops or agricultural products (e.g., tourism, butchered meat, drying coffee or fruit, processing jam)? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- No (yellow)
Stability of Market
- 17.
- How many buyers do you have for your significant crops or products? [weight: 1]
- ○
- I usually have multiple people or places to sell my product(s) to (green)
- ○
- I usually have one or two people or places to sell my product(s) to (yellow)
- ○
- I do not have a regular person or place to sell to (red)
- 18.
- How is your relationship with your most important buyer? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Very reliable and consistent (green)
- ○
- Somewhat reliable and consistent (yellow)
- ○
- Unreliable (red)—no go
- 19.
- Do you feel that you have a choice in where to sell your products? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- No (red)
Fair pricing and transparent contracts
- 20.
- Do you understand how buyer(s) calculate or establish prices paid? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Always or often (green)
- ○
- Sometimes (yellow)
- ○
- Never or rarely (red)
- 21.
- What type of market information did you know during the last production year? [weight: 1] Check all that apply (any of the first three answers gets a green score for the question):
- □
- Prices paid by different buyers throughout the region for the same product
- □
- Price my buyer received for the product
- □
- Retail price of the product
- □
- None (red)
Liquidity
- 22.
- Check the sources from which you could realistically get a loan if you needed one: [weight: 1] (two or more of the first four answers is green, one is red)
- □
- Informal sources, such as friends, relatives, or religious groups
- □
- Banks, government lending institutions
- □
- Directly from buyers (exporter, importer, roaster, trader)
- □
- NGOs, cooperatives, farmer associations, or microfinance group
- □
- My only option would be to ask a loan shark (red)—no go
- 23.
- If you requested a loan during the last year, how much did you receive compared to the amount that you requested? [weight: 1]
- ○
- All or most (green)
- ○
- Some (yellow)
- ○
- None (red)—no go
- ○
- I did not request a loan during the last year (neutral)
- 24.
- Have you set aside savings? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- No (red)
Safety Nets
- 25.
- Do you have crop-related insurance? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- No (red)
- ○
- It is not available (yellow)
- 26.
- Do you have a risk management plan that accounts for minimum costs or support in case of harvest loss (e.g., community supported schemes, agreements with cooperatives)? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- No (red)
- 27.
- Have you implemented on-farm measures to reduce risk from variability in natural conditions and inputs (e.g., building a water tank)? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- Some (yellow)
- ○
- No (red)
Food Quality
- 28.
- Do you take actions to maintain high-quality in your crops and products (e.g., hygienic processing, proper storing and packaging, grading)? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- No (red)
- 29.
- During the last two years, have you had a technical quality assessment of any of your main crops or products? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- No (red)
Certified Products
- 30.
- Do you produce any crops, animals, or products that meet, or are certified, to a standard? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- No (yellow)
- ○
- I had a certification, but it was rescinded/taken away (red)—no go
- 31.
- How much of your main products or crops are sold as certified? [weight: 1]
- ○
- All or most (more than 80%) (green)
- ○
- Some (40–80%) (yellow)
- ○
- Not much or none (less than 40%) (red)
Legitimacy
- 32.
- How do you ensure legal and regulatory compliance in general, including any standard, voluntarily entered into? [weight: 1]
- □
- (green for 2 choices, yellow for 1 choice, red no choice)
- □
- I use board agendas, other official records or notes of rights and compliances
- □
- I keep licenses and permits, if required by law
- □
- I regularly report on compliance to auditors
GHG Mitigation Practices
- 33.
- Which statement best describes the current area covered by trees on your farm? [weight: 1]
- ○
- About half or more of my farm is covered by trees (green)
- ○
- Less than half of my farm is covered by trees (yellow)
- ○
- I do not have any trees on my farm (red)
- 34./35.
- During the last production year, was there any change to the number of trees on your farm? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Increase (include planting new trees from cuttings or from seed) (green)
- ○
- Decrease (removing focus crop trees, shade trees, natural forest trees, or other crop trees) (yellow)
- ○
- No change (green)
- 36.
- What is your main tillage method? [weight: 1 for both GHG and Land]
- ○
- Conventional (red)
- ○
- Reduced (yellow)
- ○
- No-till (green)
- 37.
- Does your farm consist mostly of ruminant production (e.g., cattle, goats, sheep)? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (red)
- ○
- No (green)
- 38.
- What is the main type of manure management system used on the farm? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Open-air lagoon or discharged into water bodies (red)
- ○
- Compost or biodigestion (green)
- ○
- Direct use (collected and spread on cropping area, left on pasture) (yellow)
Air Pollution Prevention Practices
- 39.
- Do you use a smokeless fuel or chimney to vent smoke when cooking? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- No (red)
- 40.
- Do you ever burn your fields? [weight: 1 for both Air pollution and Species conservation]
- ○
- Yes (red)
- ○
- No (green)
Soil Improvement Practices
- 41.
- What is the main type of fertilizer used on the farm? [weight: 1 for GHG and Soil]
- ○
- Natural fertilizers applied according to crop and soil needs (green for GHG and Soil)
- ○
- Natural fertilizers applied without knowledge of crop or soil needs (yellow for GHG and green for Soil)
- ○
- A combination of natural and synthetic fertilizers (yellow for GHG and Soil)
- ○
- Synthetic fertilizers applied according to crop and soil needs (yellow for GHG and Soil)
- ○
- Synthetic fertilizers applied without knowledge of crop or soil needs (red for GHG and yellow for Soil)
- ○
- None (green for GHG and red for Soil)
- 42.
- Which of the following are used to improve soil fertility on the farm? [weight: 1] two or more of the first four answers is green, one is yellow
- □
- Cover crops
- □
- Nitrogen fixing annual or perennial plants
- □
- Intercropping
- □
- Crop rotation for maintaining soil health
- □
- None (red)
Nutrient Balance
- 43.
- How do you determine how much fertilizer (synthetic or natural) to apply to your crop(s)? [weight: 1]
- ○
- We apply fertilizer based on a careful assessment of our soil and crops (including farmer observation, professional tests, or analyses) (green)
- ○
- We apply fertilizer based on general advice for the region or for our crop(s) (yellow)
- ○
- We are not able to fertilize (red)
- ○
- We do not use enough fertilizer, but we apply as much as we can afford (yellow)
Land Conservation and Rehabilitation Practices
- 44.
- Which of the following are ways that you manage your soil? [weight: 1] (two or more of the first three answers are green, one is yellow)
- □
- Maintain a permanent soil cover through the mulch, planted soil cover, etc.
- □
- Terracing or contour planting on areas of significant slope
- □
- Hedgerows (e.g., trees and shrubs)
- □
- Soils are often bare between cropping cycles (red)
Hazardous Pesticides
- 45.
- Do you use any synthetic (chemical) pesticides on your farm? [weight: 1 for Pesticides and Water pollution]
- ○
- Yes (red)
- ○
- Only occasionally (yellow)
- ○
- No (green)
- 46.
- Do any of the synthetic pesticides used on your farm have a red band around the container or on the label? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (red)—no go
- ○
- No (neutral)
- 47.
- Do the pesticides used on your farm have labels that you understand? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes, they all have labels with instructions on dosage, safety, etc., that I understand (green)
- ○
- Some do not have readable labels (or are unlabeled) (red)—no go
- 48.
- Do you ever mix pesticides? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (red)—no go
- ○
- No (green)
Ecosystem Diversity
- 49.
- Did you convert any natural land (prairie, forest, or savannah) to production land during the last five years? [weight: 2 for Ecosystem diversity and weight: 1 for Land]
- ○
- Yes (red)
- ○
- No, there is no natural land on the farm (neutral)
- ○
- No, natural land on the farm was left as it is (green)
Species Conservation Practices
- 50.
- Do you have any of the following on your farm to preserve or restore natural species? [weight: 1] (two or more of the first three answers are green, one is yellow)
- □
- Permanent set-aside (land taken out of production to create a habitat for biodiversity)
- □
- Rehabilitated or restored natural areas
- □
- Hedgerows or buffer zones
- □
- None (red)
- 51.
- Check all of the pest and disease management practices used for the main crop(s) during the last production year: [weight: 1 for both Species conservation and Hazardous pesticides] (All four first choices should be marked for green, yellow if only some are marked)
- □
- Conduct regular visual examinations of plants to detect pests or disease
- □
- Use traps, repellents (including repellent species), and natural pesticides
- □
- Create or preserve places (including plant species) for beneficial predators of pests to live
- □
- Maintain written record of pest infestation, treatments, and results
- □
- I use synthetic pesticides specific to the crop and/or pest at the proper dosage and timing (yellow)
- □
- I apply synthetic pesticides preventatively (e.g., on a regular schedule regardless of whether a pest or disease threat currently exists) (red)
- 52.
- Which statement best describes the diversity of your farming system? [weight: 1]
- ○
- I produce multiple (4+) types of crops and/or livestock in the same area (green)
- ○
- I produce 2–3 types of crops and/or livestock in the same area (yellow)
- ○
- The majority of my farm is used to produce a single crop or one type of livestock (red)
Saving Seeds and Breeds
- 53.
- For the main crops and livestock produced on the farm, do you use any locally adapted varieties of seeds or breeds? [weight: 2]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- No (red)
- 54.
- What is the main source of your seeds or breeds? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Saved by the farmer, obtained from neighbors, or from a local seed bank (or breeding program for livestock) (green)
- ○
- A combination of local and non-local sources (yellow)
- ○
- Completely reliant on external non-local sources (red)
Water Conservation Practices
- 55.
- Do you use water conservation practices on the farm? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- No (red)
- ○
- Sometimes (yellow)
- 56.
- Do you irrigate your crops? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (neutral)
- ○
- No (green)
- 57.
- What form of irrigation do you use? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Manual irrigation (hand watering) (yellow)
- ○
- Surface irrigation (red)
- ○
- Drip irrigation (green)
Water Pollution Prevention Practices
- 58.
- Which of the following statements apply to your farm? [weight: 1]
- ○
- The land I use for cultivating crops and/or for pasturing animals is directly next to natural waterways (red)
- ○
- Pesticide application equipment is cleaned in natural water bodies (red)
- ○
- Untreated domestic or processing water is discharged into natural water bodies (red)
- ○
- None (green)
Renewable and Recycled Materials
- 59.
- How do you manage crop residues, processing residues, and organic matter? [weight: 2]
- ○
- Reused (e.g., through compost, as a soil cover, animal feed, biofuel, or other uses) (green)
- ○
- Burned or discharged into waterways (red)
- ○
- Left in piles or taken off farm (yellow)
- 60.
- Do you recycle or reuse metal, plastic containers or bags (with the exception of agrochemical containers), paper or cardboard? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- No (red)
- ○
- Not applicable (neutral)
Energy Use/Energy consumption/Renewable energy
- 61.
- If you use electricity, charcoal, wood, or fuel sources of energy, are you improving your efficiency? [weight: 1]
- ○
- I can demonstrate that I reduce energy use (e.g., through fuel-efficient stoves, solar drying, well-maintained machinery, switching from wood to gas) (green)
- ○
- I have made some efforts to reduce energy, but I have not applied them to most of my farm (yellow)
- ○
- I do not make any attempts to reduce energy (red)
- 62.
- If you used wood or charcoal for energy during the last production year, what was the main source? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Purchased, I don’t know (yellow)
- ○
- Managed natural forest with limited extraction (green)
- ○
- Unlimited forest use (red)
- ○
- Managed plantations or planted woodlots (green)
- ○
- Tree pruning (green)
- ○
- Not applicable, I do not use wood or charcoal energy (neutral)
- 63.
- Do you use any of the following renewable energy sources for a significant portion of your energy needs? [weight: 1] (any green answer gets green for the indicator)
- □
- Solar (green)
- □
- Hydropower or geothermal (green)
- □
- Wind (green)
- □
- Biofuel from the farm or household waste (green)
- □
- None of the above (yellow)
Food Loss and Waste Reduction
- 64.
- Which of the following best describes your pre- and post-harvest losses (i.e., the amount of crop lost during production, storage, and transport) during the last production year? [weight: 1]
- ○
- Minimal (less than 10%) (green)
- ○
- Some (10–30%) (yellow)
- ○
- Substantial (more than 30%) (red)
- 65.
- Do you take active steps to reduce pre- and post-harvest losses on your farm (through improving storage and transport methods, pest/disease management, harvesting at the appropriate time, etc.) [weight: 1]
- ○
- Yes (green)
- ○
- No (red)
Animal Health and Welfare
- 66.
- Do you have access to veterinary care for the livestock on your farm? [weight: 1]
- ○
- I do not have access (red)
- ○
- I have access, but it is problematic (unqualified personnel, too costly, too distant, or it is inhumane) (yellow)
- ○
- I have access to veterinary services that are of good quality, affordable, and nearby (green)
- 67.
- Which statement best describes the way livestock diseases are managed on the farm? [weight: 1]
- ○
- I give animals medication routinely to prevent them from becoming sick (red)
- ○
- I follow my veterinarian or a local expert’s recommendation for the treatment of diagnosed diseases (green)
- ○
- I do not consult professionals or experts about animal diseases (yellow)
- ○
- I do not provide my livestock with any veterinary care (red)
Legend
- ○
- Single choice
- □
- Multiple choice
References
- Ahrends, Antje, Peter M. Hollingsworth, Alan D. Ziegler, Jefferson M. Fox, Huafang Chen, Yufang Su, and Jianchu Xu. 2015. Current trends of rubber plantation expansion may threaten biodiversity and livelihoods. Global Environmental Change 34: 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, Badrul, Norzanalia Saadun, Chong L. Puan, Norizah Kamarudin, Najjib Aziz, Siti Nurhidayu, and Joern Fischer. 2015. Promoting landscape heterogeneity to improve the biodiversity benefits of certified palm oil production: Evidence from Peninsular Malaysia. Global Ecology and Conservation 3: 553–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badan Pusat Statistik Jambi. 2015. Jambi Dalam Angka 2015; Jambi: Badan Pusat Statistik Jambi.
- Badan Pusat Statistik Jambi. 2019. Luas, Penduduk, Tingkat Kepadatan, Rumah Tangga, Rata-rata Rumah Tangga, Kabupaten/Kota. 2000–2017. Available online: https://jambi.bps.go.id/dynamictable/2018/07/13/653/luas-penduduk-tingkat-kepadatan-rumah-tangga-rata-rata-rumah-tangga-kabupaten-kota-2000-2017.html (accessed on 29 January 2019).
- Barber, A. J., ed. 2005. Sumatra: Geology, Resources and Tectonic Evolution. Geological Society Memoirs 31. London: The Geological Society. [Google Scholar]
- Beckert, Barbara. 2016. A Post-Frontier in Transformation: Land Relations between Access, Exclusion and Resistance in Jambi Province, Indonesia. Ph.D. thesis, University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany. [Google Scholar]
- Brandi, Clara A. 2017. Sustainability Standards and Sustainable Development—Synergies and Trade-Offs of Transnational Governance. Sustainability Development 25: 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandi, Clara, Tobia Cabani, Christoph Hosang, Sonja Schirmbeck, Lotte Westermann, and Hannah Wiese. 2015. Sustainability Standards for Palm Oil. The Journal of Environment & Development 24: 292–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, Kimberly M., Robert Heilmayr, Holly K. Gibbs, Praveen Noojipady, David N. Burns, Douglas C. Morton, Nathalie F. Walker, Gary D. Paoli, and Claire Kremen. 2018. Effect of Oil Palm Sustainability Certification on Deforestation and Fire in Indonesia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 115: 121–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Sander, Robert Falkner, Matthew Goldberg, and Harro van Asselt. 2016. Effective and geographically balanced? An output-based assessment of non-state climate actions. Climate Policy 18: 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheyns, Emmanuelle. 2011. Multi-stakeholder initiatives for sustainable agriculture: limits of the ‘Inclusiveness’ paradigm. In Governing through Standards: Origins, Drivers and Limitations. Edited by Ponte Stefano, Gibbon Peter and Vestergaard Jakob. Londres: Palgrave Macmillan, pp. 210–35. [Google Scholar]
- Clay, Jason W. 2010. World Agriculture and the Environment: A Commodity-by-Commodity Guide to Impacts and Practices. Washington: Island Press. [Google Scholar]
- Climate Initiative Platform. 2019. Search Initiatives. Available online: http://climateinitiativesplatform.org/index.php/Special:RunQuery/QueryData (accessed on 11 February 2019).
- Cohn, Avery S., Peter Newton, Juliana D. B. Gil, Laura Kuhl, Leah Samberg, Vincent Ricciardi, Jessica R. Manly, and Sarah Northrop. 2017. Smallholder Agriculture and Climate Change. Annual Review of Environment and Resources 42: 347–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directorate General of State Crops. 2015. Tree Crop Estate Statistics of Indonesia 2015–2017 Rubber. Unpublished manuscript. Available online: http://ditjenbun.pertanian.go.id/tinymcpuk/gambar/file/statistik/2017/Karet-2015-2017.pdf (accessed on 6 February 2019).
- Drescher, Jochen, Katja Rembold, Kara Allen, Philip Beckschäfer, Damayanti Buchori, Yann Clough, Heiko Faust, Anas M. Fauzi, Dodo Gunawan, Dietrich Hertel, and et al. 2016. Ecological and Socio-Economic Functions Across Tropical Land Use Systems After Rainforest Conversion. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 371: 20150275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eakin, Hallie, Ruth DeFries, Suzi Kerr, Eric F. Lambin, Jianguo Liu, Peter J. Marcotullio, Peter Messerli, Anette Reenberg, Ximena Rueda, Simon R. Swaffield, and et al. 2014. Significance of Telecoupling for Exploration of Land-Use Change. In Rethinking Global Land Use in an Urban Era. Strüngmann Forum Reports. Edited by Karen C. Seto and Anette Reenberg. Cambridge: The MIT Press, pp. 141–61. [Google Scholar]
- Ekandinata, Andree, and Grègoire Vincent. 2011. Rubber Agroforests in a changing landscape: Analysis of land use/cover trajectories in Bungo district, Indonesia. Forests, Trees and Livelihoods 20: 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Sustainable Plam Oil. 2019. Choosing Sustainable Palm Oil: Progress Report on the Import and Use of Sustainable Palm Oil in Europe. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. 2012. Smallholders and Family Farmers. Available online: http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/nr/sustainability_pathways/docs/Factsheet_SMALLHOLDERS.pdf (accessed on 11 February 2019).
- FAOSTAT. 2019. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC (accessed on 18 February 2019).
- Feintrenie, Laurène, and Patrice Levang. 2009. Sumatra’s Rubber Agroforests: Advent, Rise and Fall of a Sustainable Cropping System. Small-Scale Forestry 8: 323–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fold, Niels, and Philip Hirsch. 2009. Re-thinking frontiers in Southeast Asia. Geographical Journal 175: 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friis, Cecilie, and Jonas Ø. Nielsen. 2017. Land-use change in a telecoupled world: The relevance and applicability of the telecoupling framework in the case of banana plantation expansion in Laos. E&S 22: 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, Derek. 2011. Land grabs, land control, and Southeast Asian crop booms. The Journal of Peasant Studies 38: 837–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, Jonas, and Yvonne Kunz. 2018. Adapting in a carbon pool? Politicising climate change at Sumatra’s oil palm frontier. In A Critical Approach to Climate Change Adaptation. Edited by S. Kleep and L. C. Rodríguez. Abingdon-on-Thames: Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Hidayat, Nia K., Astrid Offermans, and Pieter Glasbergen. 2018. Sustainable palm oil as a public responsibility? On the governance capacity of Indonesian Standard for Sustainable Palm Oil (ISPO). Agriculture and Human Values 35: 223–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Angel, Niklas Höhne, Takeshi Kuramochi, Mark Roelfsema, Amy Weinfurter, Yihao Xie, Katharina Lütkehermöller, Sander Chan, Jan Corfee-Morlot, Philip Drost, Pedro Faria, and et al. 2019. A research roadmap for quantifying non-state and subnational climate mitigation action. Nature Climate Change 9: 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indonesia Investments. 2017. Palm Oil. Available online: https://www.indonesia-investments.com/business/commodities/palm-oil/item166? (accessed on 18 February 2019).
- IPCC. 2014. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Geneva: IPCC. [Google Scholar]
- Jagers, Sverker C., and Johannes Stripple. 2003. Climate Governance beyond the State. Global Governance 9: 385–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelsma, Idsert, and George Christoffel Schoneveld. 2016. Towards More Sustainable and Productive Independent Oil Palm Smallholders in Indonesia: Insights from the Development of a Smallholder Typology. Bogor: Center for International Forestry Research (CIFOR). [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, Sharon, Peter Lacy, Rob Hayward, Edd McLEan, and Angela Jhanji. 2014. The Consumer Study: From Marketing to Mattering: The UN Global Compact-Accenture CEO Study on Sustainability. UN Global Compact Reports. Available online: http://www.fairtrade.travel/source/websites/fairtrade/documents/Accenture-Consumer-Study-Marketing-Mattering_2014.pdf (accessed on 11 February 2019).
- Kapsar, Kelly, Ciara Hovis, Ramon Bicudo da Silva, Erin Buchholtz, Andrew Carlson, Yue Dou, Yueyue Du, Paul R. Furumo, Yingjie Li, Aurora Torres, and et al. 2019. Telecoupling Research: The First Five Years. Sustainability 11: 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, Sean F., Beria Leimona, and Zhuang-Fang Yi. 2016. Making a green rubber stamp: Emerging dynamics of natural rubber eco-certification. International Journal of Biodiversity Science, Ecosystem Services & Management 13: 100–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney-Lazar, Miles, Grace Wong, Himlal Baral, and Aaron J. M. Russell. 2018. Greening rubber? Political ecologies of plantation sustainability in Laos and Myanmar. Geoforum 92: 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, Thomas, Zulkifli Alamsyah, Raja S. Fatricia, and Bernhard Brümmer. 2014a. Have Indonesian Rubber Processors Formed a Cartel? Analysis of Intertemporal Marketing Margin Manipulation. Ljubljana, Slovenia. August 26. Available online: http://ageconsearch.umn.edu/bitstream/182675/2/Kopp-Have_Indonesian_rubber_processors_formed_a_cartel_Analysis-142_a.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2019).
- Kopp, Thomas, Zulkifli Alamsyah, Raja Sharah Fatricia, and Bernhard Brümmer. 2014b. Have Indonesian rubber processors formed a cartel?: Analysis of intertemporal marketing margin manipulation. 2014 International Congress. European Association of Agricultural Economists. Ljubljana, Slovenia. August 26. Available online: http://ageconsearch.umn.edu/bitstream/182675/2/Kopp-Have_Indonesian_rubber_processors_formed_a_cartel_Analysis-142_a.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2019).
- Kunz, Yvonne, Jonas Hein, Rina Mardiana, and Heiko Faust. 2016. Mimicry of the Legal: Translating De Jure Land Formalization Processes into De Facto Local Action in Jambi Province, Sumatra. Journal of South-East Asian Studies 10: 47–64. [Google Scholar]
- Kunz, Yvonne, Stefanie Steinebach, Christoph Dittrich, Brigitta Hauser-Schäublin, Ir Rosyani, Endriatmo Soetarto, and Heiko Faust. 2017. ‘The fridge in the forest’: Historical trajectories of land tenure regulations fostering landscape transformation in Jambi Province, Sumatra, Indonesia. Forest Policy and Economics 81: 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laumonier, Yves, Yumiko Uryu, Michael Stüwe, Arif Budiman, Budi Setiabudi, and Oki Hadian. 2010. Eco-floristic sectors and deforestation threats in Sumatra: Identifying new conservation area network priorities for ecosystem-based land use planning. Biodiversity and Conservation 19: 1153–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Tania Muurray. 2015. Social Impacts of oil Palm in Indonesia: A Gendered Perspective from West Kalimantan. Bogor: Center for International Forestry Research (CIFOR). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Jianguo. 2014. Forest Sustainability in China and Implications for a Telecoupled World. Asia and the Pacific Policy Studies 1: 230–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelin. 2016. Sustainable Natural Rubber Policy: Reference Document 2016 Edition. Unpublished Work, Last Modified February 6, 2019. Available online: https://c402277.ssl.cf1.rackcdn.com/publications/1062/files/original/SUSTAINABLE_NATURAL_RUBBER_POLICY_VD.pdf?1495831479 (accessed on 11 February 2019).
- Michelin. 2017. Sustainable Natural Rubber Policy: Reference Document 2017 Edition. Unpublished manuscript, last modified February 6, 2019. Available online: https://purchasing.michelin.com/en/document-area/ (accessed on 11 February 2019).
- Morgans, Courtney L., Erik Meijaard, Truly Santika, Elizabeth Law, Sugeng Budiharta, Marc Ancrenaz, and Kerrie A. Wilson. 2018. Evaluating the effectiveness of palm oil certification in delivering multiple sustainability objectives. Environmental Research Letters 13: 64032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagiah, Claudine, and Reza Azmi. 2012. A Review of Smallholder Oil Palm Production: Challenges and Opportunities for Enhancing Sustainability—A Malaysian Perspective. Journal of Oil Palm and the Environment 3: 114–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, Pablo, Sophia Gnych, Ahmad Dermawan, Heru Komarudin, and Beni Okarda. 2017. The Palm Oil Global Value Chain: Implications for Economic Growth and Social and Environmental Sustainability. Bogor: Center for International Forestry Research (CIFOR). [Google Scholar]
- Peluso, Nancy L., and Christian Lund. 2011. New frontiers of land control: Introduction. The Journal of Peasant Studies 38: 667–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, Mattias B., and Christian Lund. 2017. Reconfiguring Frontier Spaces: The territorialization of resource control. World Development 101: 388–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribot, Jesse C., and Nancy L. Peluso. 2003. A Theory of Access. Rural Sociology 68: 153–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rival, Alain, Didier Montet, and Daniel Pioch. 2016. Certification, labelling and traceability of palm oil: Can we build confidence from trustworthy standards? OCL 23: D609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RSPO. 2010. National Interpretation RSPO Principles and Criteria for Sustainable Palm Oil Production: For Independent Smallholders Republic of Indonesia. Geneva: RSPO. [Google Scholar]
- RSPO. 2018. Impact Report 2018. Geneva: RSPO. Available online: https://rspo.org/key-documents/impact-reports (accessed on 11 February 2019).
- RSPO. 2019. How we Are. Available online: https://www.rspo.org/about#who-we-are (accessed on 25 February 2019).
- RSPO, and HCSA. 2018. RSPO and HCSA Collaborate to Implement No Deforestation in High Forest Cover Landscapes. News Release. 2018. Available online: http://highcarbonstock.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/Joint-RSPO-HCSA-Statement-on-NDJSG-final-211118.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2019).
- Ruysschaert, Denis, and Denis Salles. 2014. Towards global voluntary standards: Questioning the effectiveness in attaining conservation goals. Ecological Economics 107: 438–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffer, Eva, and Douglas Waale. 2008. Tracing Power and Influence in Networks: Net-Map as a Tool for Research and Strategic Network Planning. International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI), IFPRI discussion papers. [Google Scholar]
- SNR-i. 2017. SNR-i Update-Q3 2017. Available online: http://www.snr-i.org/news_details.php?nid=73 (accessed on 25 February 2019).
- Van der Ven, Hamish, Catherine Rothacker, and Benjamin Cashore. 2018. Do eco-labels prevent deforestation? Lessons from non-state market driven governance in the soy, palm oil, and cocoa sectors. Global Environmental Change 52: 141–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatn, Arild. 2015. Markets in environmental governance. From theory to practice. Ecological Economics 117: 225–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren-Thomas, Eleanor, Paul M. Dolman, and David P. Edwards. 2015a. Increasing Demand for Natural Rubber Necessitates a Robust Sustainability Initiative to Mitigate Impacts on Tropical Biodiversity. Conservation Letters 8: 230–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren-Thomas, Eleanor M., David P. Edwards, Daniel P. Bebber, Phourin Chhang, Alex N. Diment, Tom D. Evans, Frances H. Lambrick, James F. Maxwell, Menghor Nut, Hannah J. O’Kelly, and et al. 2018. Protecting Tropical Forests from the Rapid Expansion of Rubber Using Carbon Payments. Nature Communications 9: 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicke, Birka. 2014. Palm Oil as a Case Study of Distal Land Connections. In Rethinking Global Land Use in an Urban Era. Strüngmann Forum Reports. Edited by Karen C. Seto and Anette Reenberg. Cambridge: The MIT Press, pp. 163–80. [Google Scholar]
- WWF. 2016. WWF Statement on New Zero Deforestation Policy from Michelin. News Release. June 17. Available online: https://www.worldwildlife.org/press-releases/wwf-statement-on-new-zero-deforestation-policy-from-michelin (accessed on 19 February 2019).
- WWF. 2019. Sumatran Elephant: Elephas Maximus Sumatrensis. Available online: https://www.wwf.or.id/en/about_wwf/whatwedo/forest_species/species/sumatran_elephant/ (accessed on 26 February 2019).
- Zimmerer, Karl S., Eric F. Lambin, and Steven J. Vanek. 2018. Smallholder telecoupling and potential sustainability. E&S 23: 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulu, Leo C. 2009. Politics of scale and community-based forest management in southern Malawi. Geoforum 40: 686–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | Even though we know of one much appreciated article which explores palm oil production using the lens of telecoupling, but without focusing on smallholder production. For this article see (Wicke 2014). |
| 2 | For detailed information on Principles and Criteria see https://www.rspo.org/key-documents/certification/rspo-principles-and-criteria. |
| 3 | For the process of developing Principles and Criteria suitable for smallholder production (draft stage) see https://www.rspo.org/principles-and-criteria-review/public-consultation-rspo-smallholder-standard. |
| 4 | For detailed information http://snr-i.org/Voluntary%20Guidelines%20and%20Criteria%20Version%201_13_1.htm. |
| 5 | Amended by the authors. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kunz, Y.; Otten, F.; Mardiana, R.; Martens, K.; Roedel, I.; Faust, H. Smallholder Telecoupling and Climate Governance in Jambi Province, Indonesia. Soc. Sci. 2019, 8, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci8040115
Kunz Y, Otten F, Mardiana R, Martens K, Roedel I, Faust H. Smallholder Telecoupling and Climate Governance in Jambi Province, Indonesia. Social Sciences. 2019; 8(4):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci8040115
Chicago/Turabian StyleKunz, Yvonne, Fenna Otten, Rina Mardiana, Katrin Martens, Imke Roedel, and Heiko Faust. 2019. "Smallholder Telecoupling and Climate Governance in Jambi Province, Indonesia" Social Sciences 8, no. 4: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci8040115
APA StyleKunz, Y., Otten, F., Mardiana, R., Martens, K., Roedel, I., & Faust, H. (2019). Smallholder Telecoupling and Climate Governance in Jambi Province, Indonesia. Social Sciences, 8(4), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci8040115




