The Relationship between “Protection of” and “Violence Against” Infants and Young Children: The U.S. Experience, 1940–2005
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
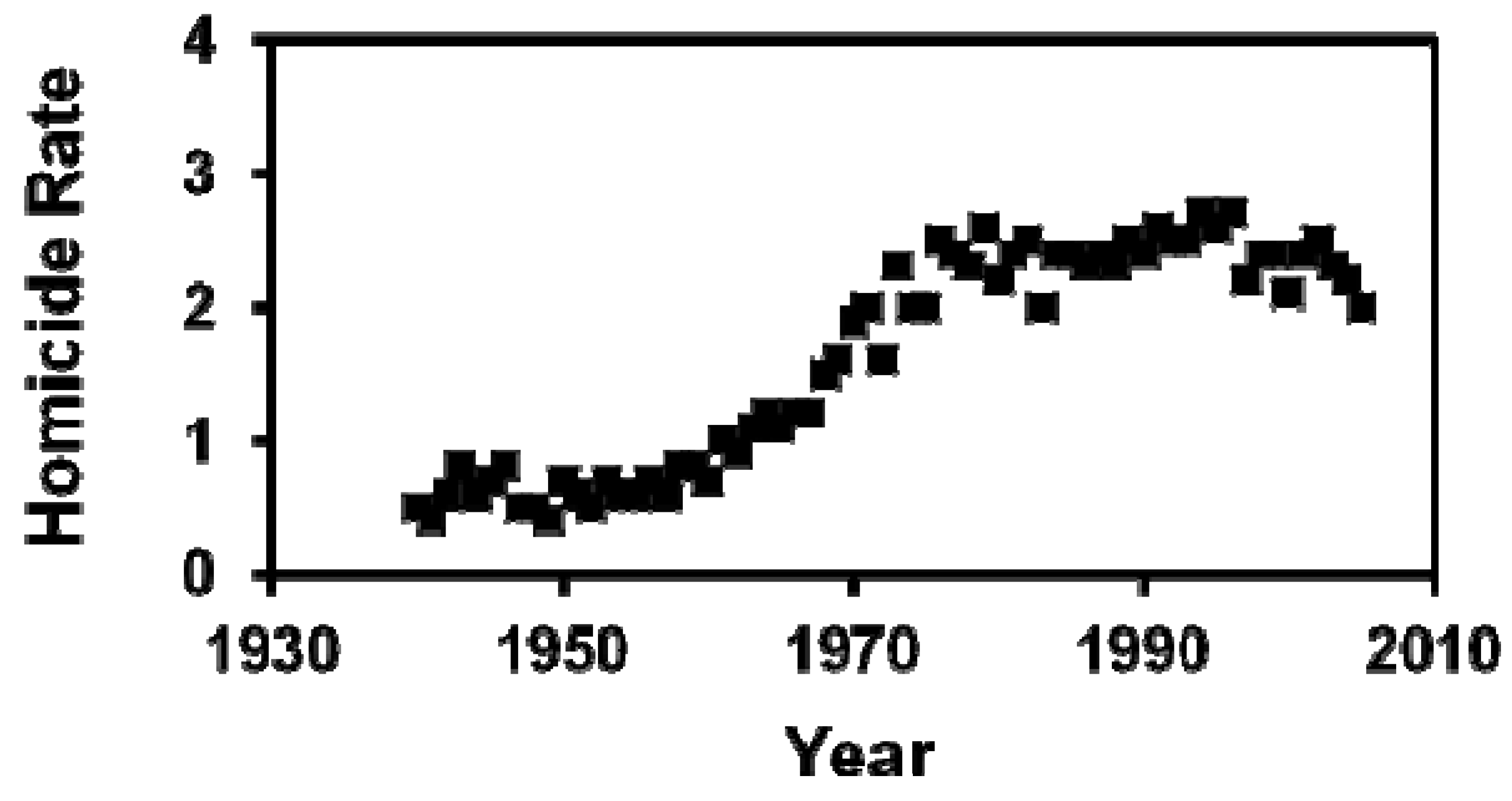
3. Results

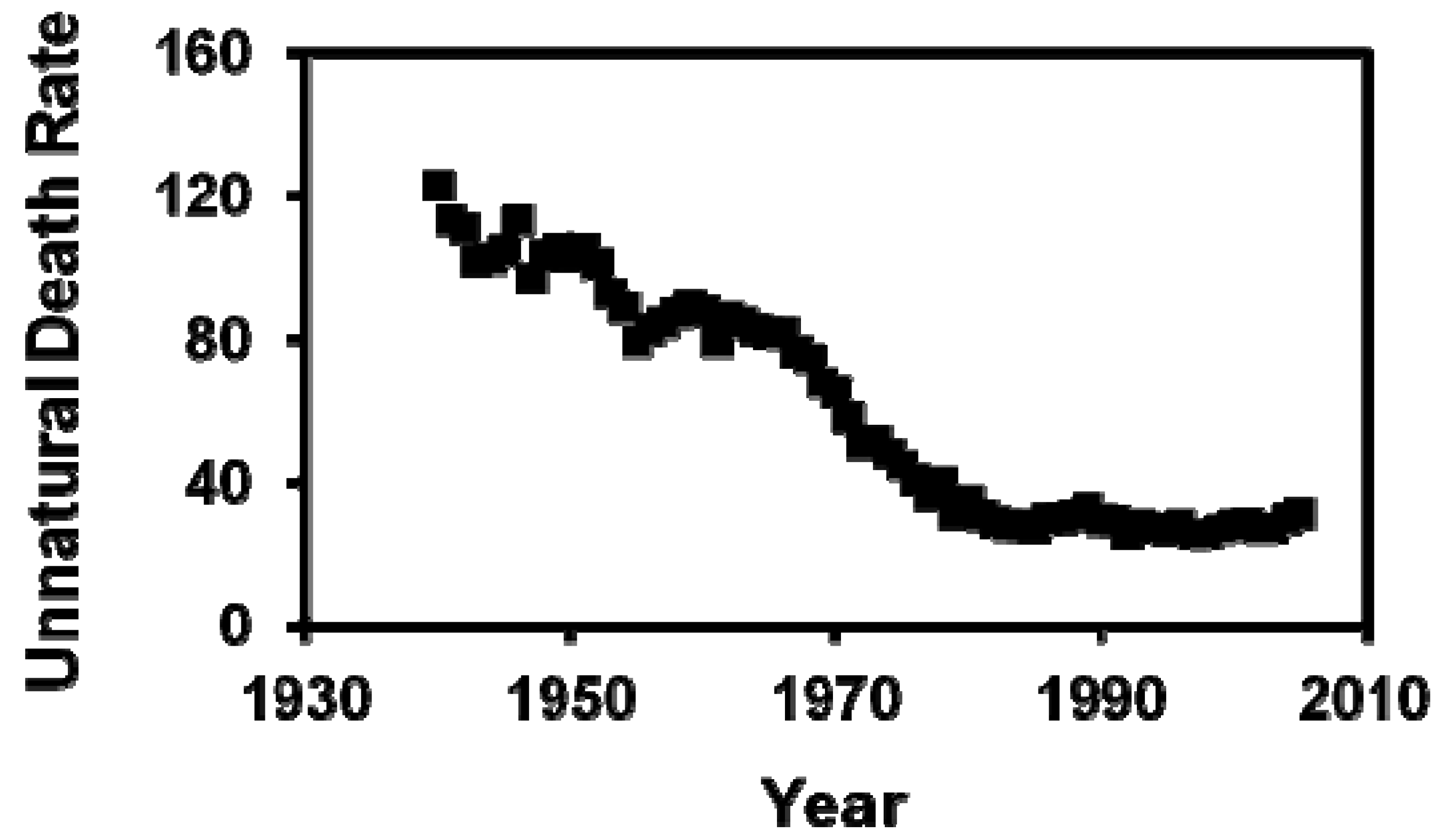

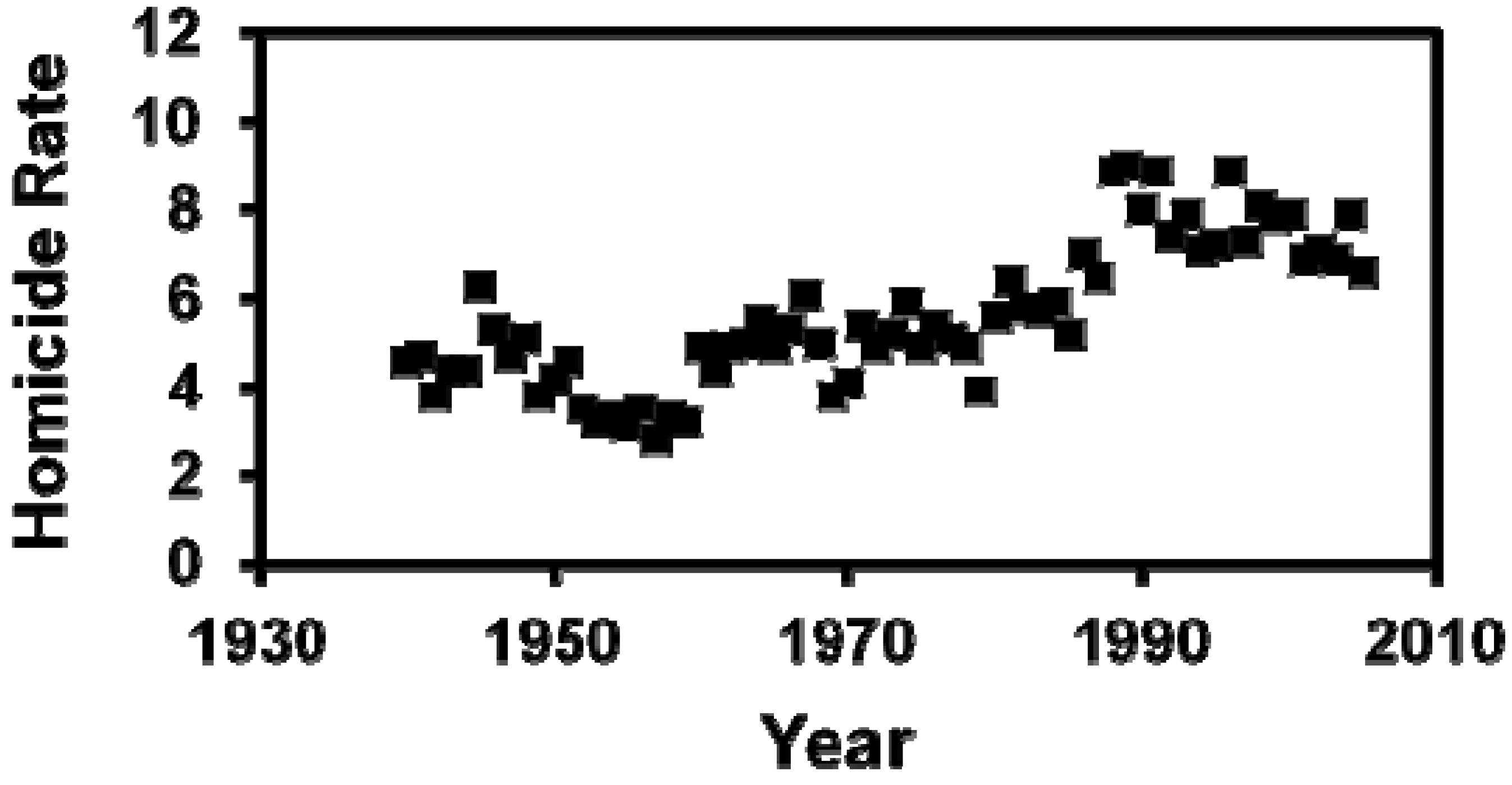
| Age Group | 0 < 1 | 1 < 5 | 5 < 15 | 15 < 25 | 25 < 35 | 35 < 45 | 45 < 55 | 55 < 65 | 65 < 75 | 75 + |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation | ||||||||||
| Hom-nMVA | −0.7364 | −0.8035 | −0.6720 | −0.6020 | −0.3306 | −0.2043 | −0.1557 | −0.0196 | −0.0308 | −0.2939 |
| Hom-MVA | −0.6712 | −0.7500 | −0.5545 | −0.3858 | 0.1726 | 0.2853 | 0.1109 | −0.0220 | −0.0656 | −0.2404 |
| MVA-nMVA | 0.4554 | 0.8807 | 0.8792 | 0.1199 | 0.3132 | 0.4899 | 0.8117 | 0.9279 | 0.9381 | 0.9029 |
| Sui-nMVA | - | - | −0.8119 | −0.6669 | −0.6248 | −0.2404 | 0.7640 | 0.8629 | 0.8500 | 0.6612 |
| Sui-Hom | - | - | 0.8500 | 0.8936 | 0.7988 | 0.2045 | −0.1108 | −0.0596 | 0.0033 | −0.0793 |
| Sui-MVA | - | - | −0.7819 | −0.2711 | −0.2443 | −0.3341 | 0.8153 | 0.9226 | 0.8819 | 0.6565 |
| Age Group | 0 < 1 | 1 < 5 | 5 < 15 | 15 < 25 | 25 < 35 | 35 < 45 | 45 < 55 | 55 < 65 | 65 < 75 | 75 + |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation | ||||||||||
| Hom-nMVA | −0.7155 | −0.8465 | −0.6638 | −0.3830 | −0.4288 | −0.3149 | −0.3059 | −0.4132 | −0.6477 | −0.6632 |
| Hom-MVA | −0.5450 | −0.6666 | −0.2849 | 0.5647 | 0.6284 | 0.5232 | 0.1597 | −0.1896 | −0.4314 | −0.4836 |
| MVA-nMVA | 0.3101 | 0.7699 | 0.6228 | −0.3936 | −0.3619 | −0.0400 | 0.3712 | 0.5615 | 0.3898 | 0.5516 |
| Sui-nMVA | - | - | −0.7782 | −0.0806 | 0.3230 | 0.2068 | 0.6250 | 0.8009 | 0.6360 | 0.7586 |
| Sui-Hom | - | - | 0.7696 | 0.8361 | 0.4510 | 0.5446 | 0.2787 | 0.0649 | −0.3107 | −0.3185 |
| Sui-MVA | - | - | −0.6052 | 0.5977 | 0.5474 | 0.5515 | 0.5962 | 0.6961 | 0.7058 | 0.4358 |
4. Discussion and Conclusions
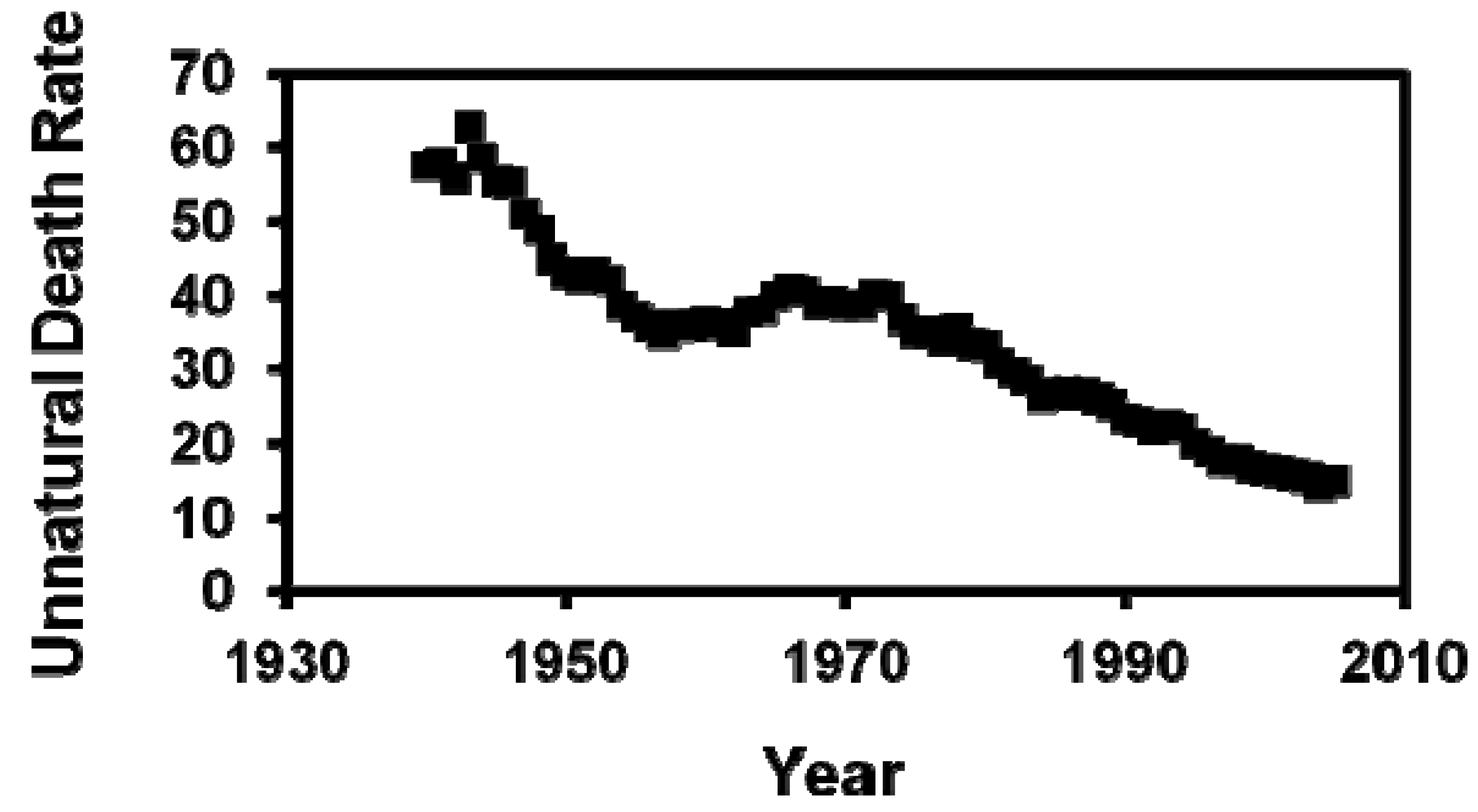
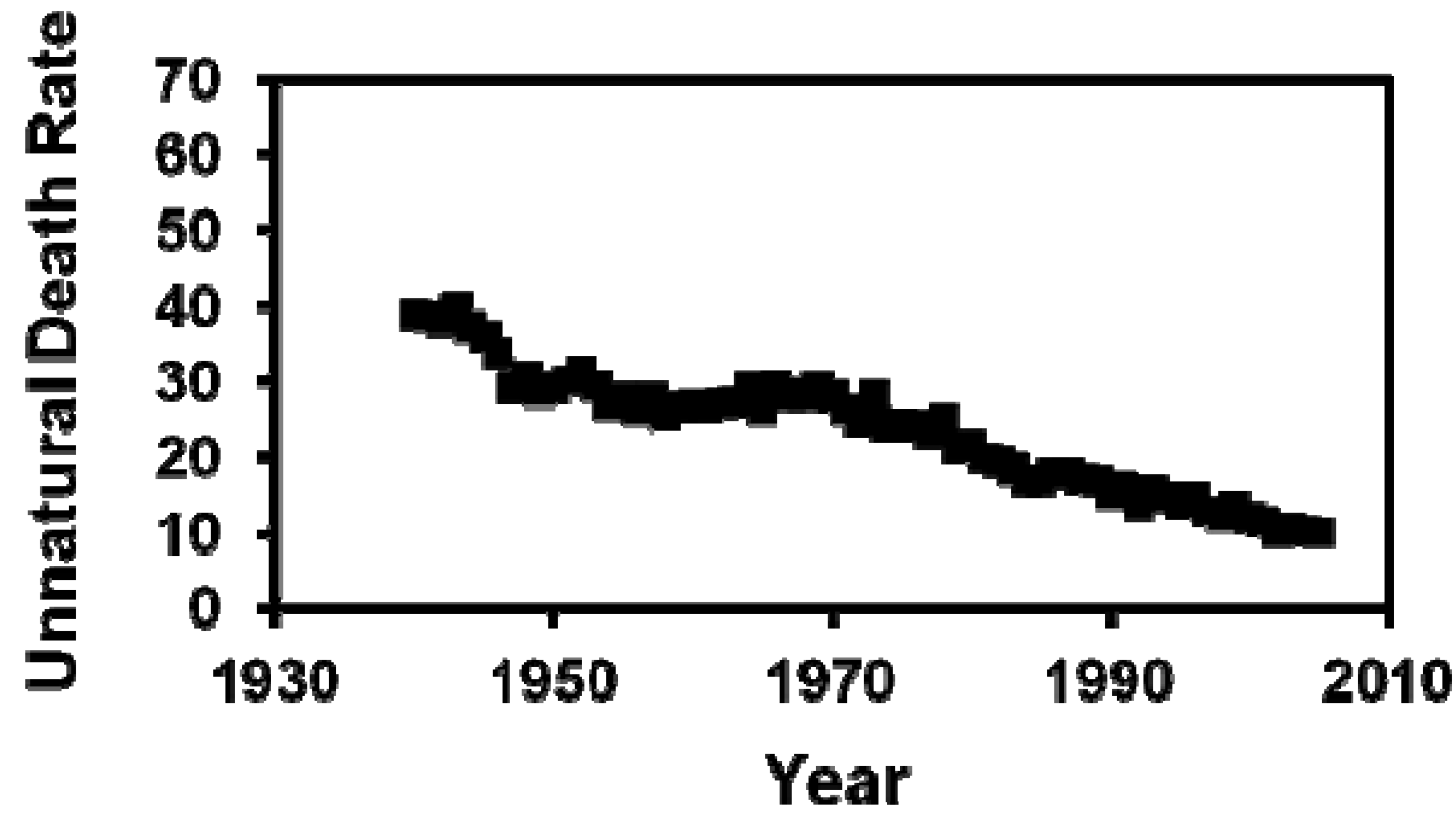

Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mary D. Overpeck, Ruth A. Brenner, Ann C. Trumble, Lara B. Trifiletti, and Heinz W. Brenendes. “Risk factors for infant homicide in the United States.” New England Journal of Medicine 339 (1998): 1211–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard Dubowitz, and Susan Bennett. “Physical abuse and neglect of children.” Lancet 369 (2007): 1891–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph C. Cappelleri, John Eckenrode, and Jane L. Powers. “The epidemiology of child abuse: Findings from the Second National Incidence and Prevalence Study of Child Abuse and Neglect.” American Journal of Public Health 83 (1993): 1622–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessa L. Crume, Carolyn DiGuiseppi, Tim Byers, Andrew P. Sirotnak, and Carol J. Garrett. “Underascertainment of child maltreatment fatalities by death certificates, 1990–1998.” Pediatrics 110 (2002): e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcia E. Herman-Giddens, Gail Brown, Sarah Verbiest, Pamela J. Carlson, Elizabeth G. Hooten, Eleanor Howell, and John D. Butts. “Underascertainment of child abuse mortality in the United States.” Journal of the American Medical Association 282 (1999): 463–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- C. Jenny, and Reena Isaac. “The relation between child death and child maltreatment.” Archives of Disease in Childhood 91 (2006): 265–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susan Hatter Friedman, Sarah McCue Horwitz, and Phillip J. Resnick. “Child murder by mothers: A critical analysis of the current state of knowledge and a research agenda.” American Journal of Psychiatry 162 (2005): 1578–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olav B. Nielssen, Matthew M. Large, Bruce D. Westmore, and Steven M. Lackersteen. “Child homicide in New South Wales from 1991 to 2005.” Medical Journal of Australia 190 (2009): 7–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lester Adelson. “Slaughter of the innocents, a study of forty-six homicides in which the victims were children.” New England Journal of Medicine 264 (1961): 1345–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- C. Henry Kempe, Frederic N. Silverman, Brandt F. Steele, William Droegemueller, and Henry K. Silver. “The battered-child syndrome.” Journal of the American Medical Association 181 (1962): 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruth A. Brenner, Mary D. Overpeck, Ann C. Trumble, Rebecca DerSimonian, and Heinz Brenendes. “Deaths attributable to injuries in infants, United States, 1983–1991.” Pediatrics 103 (1999): 968–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A. Jain, B. Koshnood, K.S. Lee, and J. Conato. “Injury related infant death: The impact of race and birth weight.” Injury Prevention 7 (2001): 135–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert M. Reece, and Robert Sege. “Childhood head injuries, accidental or inflicted? ” Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine 154 (2000): 11–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glenn A. Tung, Monica Kumar, Randal C. Richardson, Carole Jenny, and William D. Brown. “Comparison of accidental and nonaccidental head injury in children on noncontrast computed tomography.” Pediatrics 118 (2006): 626–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack E. Riggs, and Gerald R. Hobbs. “Infant homicide and accidental death in the United States, 1940–2005: Ethics and epidemiological classification.” Journal of Medical Ethics 37 (2011): 445–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack E. Riggs, and Gerald R. Hobbs. “Young child homicide and accidental death rates in the United States, 1940–2005: Classification issues in mutually exclusive events.” Sociology Mind 2 (2012): 148–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack E. Riggs, and Gerald R. Hobbs. “The dependence of reported homicide rates on reported non-motor vehicle accident death rates in US young child and infants, 1940–2007.” Advances in Applied Sociology 3 (2013): 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Health Statistics. “Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.” Available online: www.cdc.goc/nchs (accessed 11 August 2014).
- Jacob Cohen. “A power primer.” Psychological Bulletin 112 (1992): 155–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin Long Chiang. “Competing risks in mortality analysis.” Annual Review of Public Health 12 (1991): 281–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waney Squier. “Shaken baby syndrome: The quest for evidence.” Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 50 (2008): 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- John Plunkett. “Fatal pediatric head injuries caused by short-distance falls.” American Journal of Forensic Medicine and Pathology 22 (2001): 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- J.F. Geddes, and John Plunkett. “The evidence base for shaken baby syndrome, we need to question the diagnostic criteria.” BMJ 328 (2004): 719–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- P.E. Lantz, S.H. Sinal, C.A. Stanton, and R.G. Weaver Jr. “Perimacular retinal folds from childhood trauma.” BMJ 328 (2004): 754–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James LeFanu, and Rioch Edwards-Brown. “Patterns of presentation of shaken baby syndrome, subdural and retinal haemorrhages are not necessarily signs of abuse.” BMJ 328 (2004): 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marta Cohen, and Irene Scheimberg. “Subdural haemorrhage and child maltreatment.” Lancet 373 (2009): 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilary Bower. “Woodward appeal rests on medical evidence.” Lancet 351 (1998): 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark Hansen. “Why are Iowa’s babies dying? ” American Bar Association Journal 84 (1998): 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- Mark Hansen. “Battle of the expert.” American Bar Association Journal 91 (2005): 52–58. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Riggs, J.E.; Hobbs, G.R. The Relationship between “Protection of” and “Violence Against” Infants and Young Children: The U.S. Experience, 1940–2005. Soc. Sci. 2014, 3, 394-403. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci3030394
Riggs JE, Hobbs GR. The Relationship between “Protection of” and “Violence Against” Infants and Young Children: The U.S. Experience, 1940–2005. Social Sciences. 2014; 3(3):394-403. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci3030394
Chicago/Turabian StyleRiggs, Jack E., and Gerald R. Hobbs. 2014. "The Relationship between “Protection of” and “Violence Against” Infants and Young Children: The U.S. Experience, 1940–2005" Social Sciences 3, no. 3: 394-403. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci3030394
APA StyleRiggs, J. E., & Hobbs, G. R. (2014). The Relationship between “Protection of” and “Violence Against” Infants and Young Children: The U.S. Experience, 1940–2005. Social Sciences, 3(3), 394-403. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci3030394




