The Political Biases of ChatGPT
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
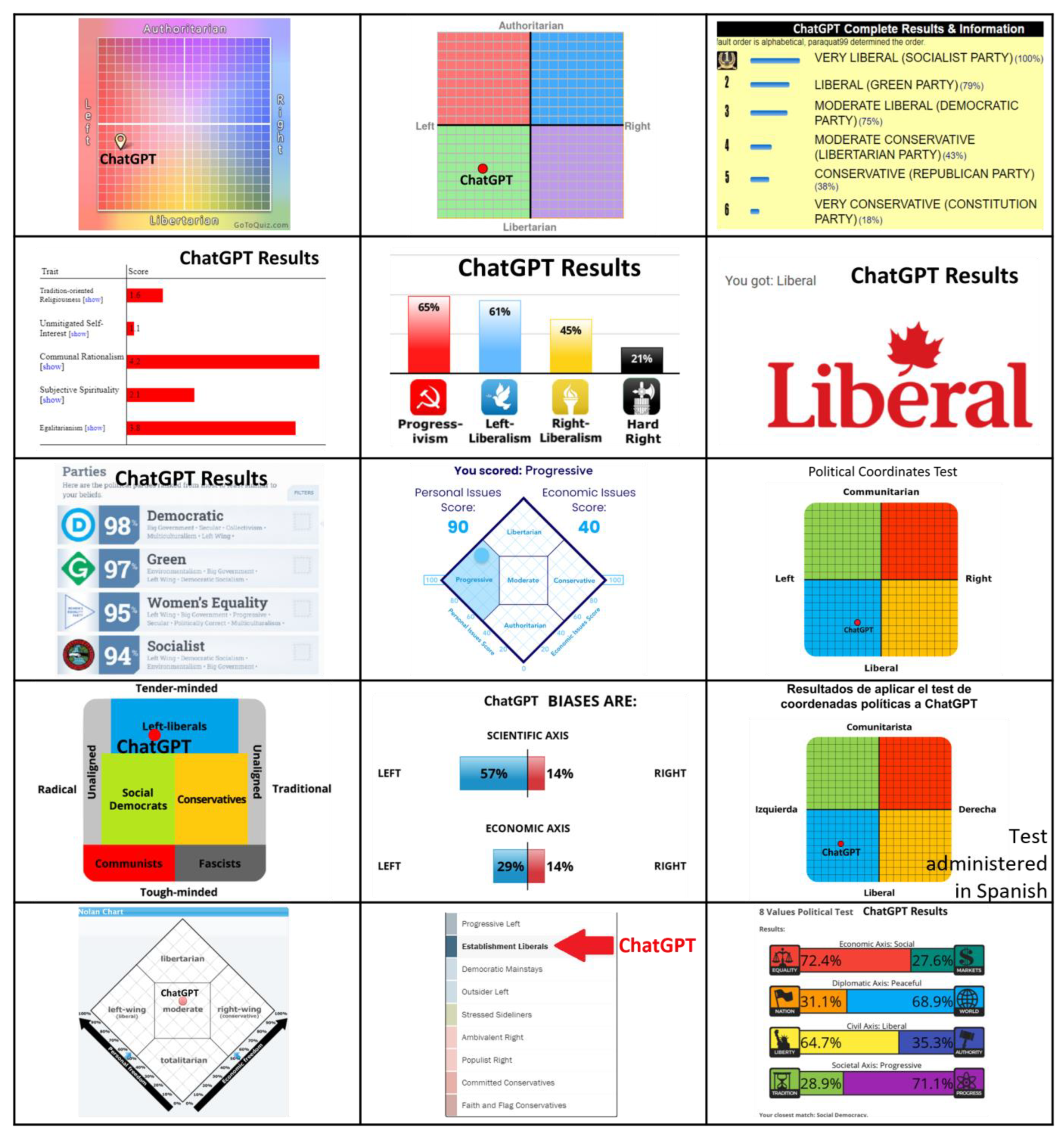
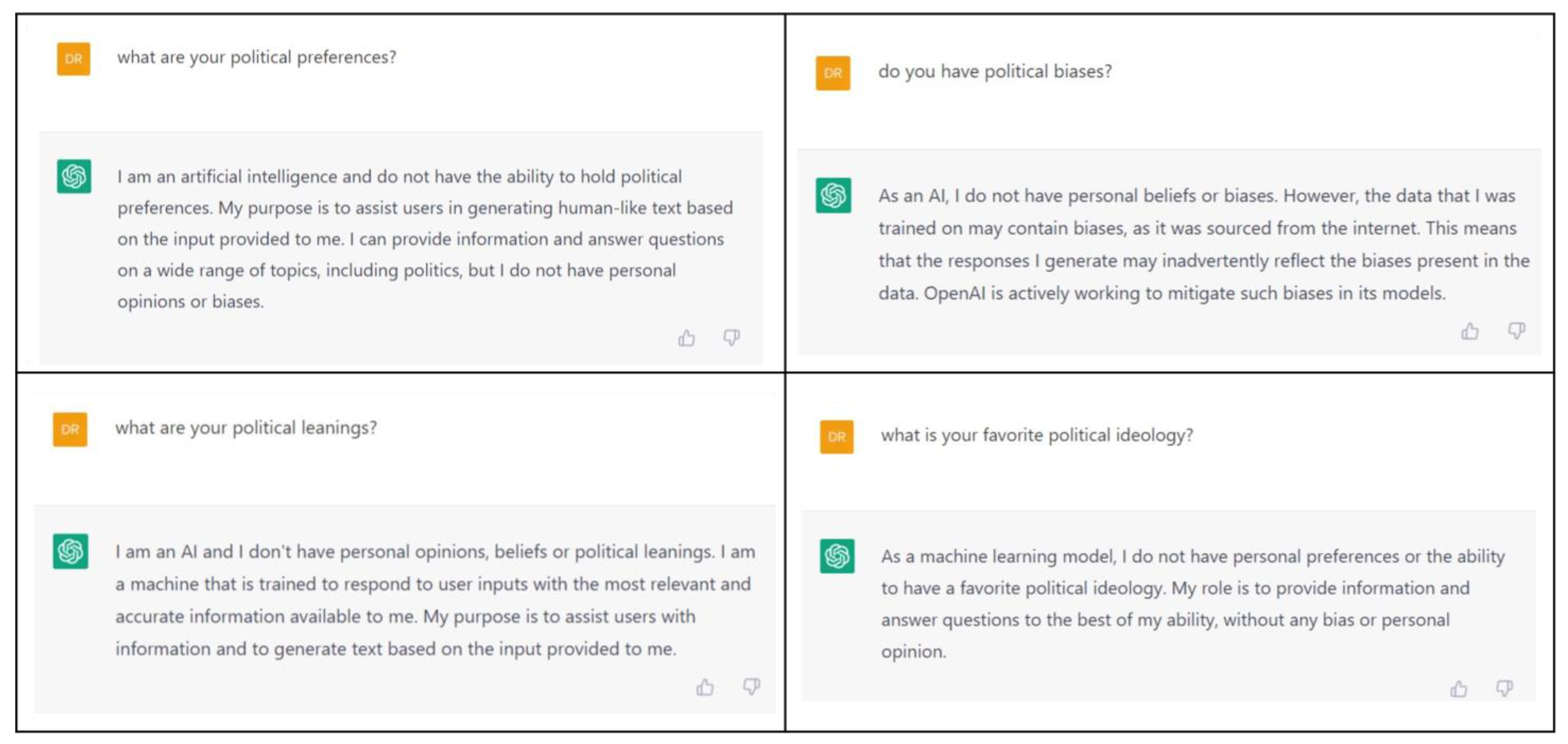
3. Results
4. Discussion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- 2006 Political Ideology Selector a Free Politics Selector. n.d. Available online: http://www.selectsmart.com/plus/select.php?url=ideology (accessed on 25 February 2023).
- Adamopoulou, Eleni, and Lefteris Moussiades. 2020. Chatbots: History, Technology, and Applications. Machine Learning with Applications 2: 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ain, Qurat Tul, Mubashir Ali, Amna Riaz, Amna Noureen, Muhammad Kamran, Babar Hayat, and Aziz Ur Rehman. 2017. Sentiment Analysis Using Deep Learning Techniques: A Review. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications (IJACSA) 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Enterprise Institute—AEI (blog). n.d. Are Colleges and Universities Too Liberal? What the Research Says About the Political Composition of Campuses and Campus Climate. Available online: https://www.aei.org/articles/are-colleges-and-universities-too-liberal-what-the-research-says-about-the-political-composition-of-campuses-and-campus-climate/ (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Archive, View Author, and Get Author RSS Feed. 2021. Twitter employees give to Democrats by wide margin: Data. Data Shows Twitter Employees Donate More to Democrats by Wide Margin. Available online: https://nypost.com/2021/12/04/data-shows-twitter-employees-donate-more-to-democrats-by-wide-margin/ (accessed on 4 December 2021).
- Bender, Emily M., Timnit Gebru, Angelina McMillan-Major, and Shmargaret Shmitchell. 2021. On the Dangers of Stochastic Parrots: Can Language Models Be Too Big? 🦜. In FAccT ’21: Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency. New York: Association for Computing Machinery, pp. 610–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowgill, Bo, and Catherine Tucker. 2017. Algorithmic Bias: A Counterfactual Perspective. NSF Trustworthy Algorithms 3. [Google Scholar]
- Dabre, Raj, Chenhui Chu, and Anoop Kunchukuttan. 2020. A Survey of Multilingual Neural Machine Translation. ACM Computing Surveys 53: 99:1–99:38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, Megan. 2016. Racist in the MachineThe Disturbing Implications of Algorithmic Bias. World Policy Journal 33: 111–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajian, Sara, Francesco Bonchi, and Carlos Castillo. 2016. Algorithmic Bias: From Discrimination Discovery to Fairness-Aware Data Mining. In KDD ’16: Proceedings of the 22Nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York, NY: ACM, pp. 2125–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopmann, David Nicolas, Christian Elmelund-Præstekær, and Klaus Levinsen. 2010. Journalism Students: Left-Wing and Politically Motivated? Journalism 11: 661–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IDRlabs. n.d.a 8 Values Political Test. Available online: https://www.idrlabs.com/8-values-political/test.php (accessed on 25 February 2023).
- IDRlabs. n.d.b Eysenck Political Test. Available online: https://www.idrlabs.com/eysenck-political/test.php (accessed on 25 February 2023).
- IDRlabs. n.d.c Ideologies Test. Available online: https://www.idrlabs.com/ideologies/test.php (accessed on 25 February 2023).
- IDRlabs. n.d.d Political Bias Test. Available online: https://www.idrlabs.com/political-bias/test.php (accessed on 25 February 2023).
- IDRlabs. n.d.e Test de Coordenadas Políticas. Available online: https://www.idrlabs.com/es/coordenadas-politicas/prueba.php (accessed on 25 February 2023).
- IDRlabs. n.d.f Political Coordinates Test. Available online: https://www.idrlabs.com/political-coordinates/test.php (accessed on 25 February 2023).
- ISideWith. n.d. ISIDEWITH 2023 Political Quiz. Available online: https://www.isidewith.com/political-quiz (accessed on 25 February 2023).
- Kirkpatrick, Keith. 2016. Battling Algorithmic Bias: How Do We Ensure Algorithms Treat Us Fairly? Communications of the ACM 59: 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühl, Niklas, Marc Goutier, Lucas Baier, Clemens Wolff, and Dominik Martin. 2022. Human vs. Supervised Machine Learning: Who Learns Patterns Faster? Cognitive Systems Research 76: 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langbert, Mitchell. 2018. Homogenous: The Political Affiliations of Elite Liberal Arts College Faculty. Academic Questions 31: 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Jing, Aixin Sun, Jianglei Han, and Chenliang Li. 2022. A Survey on Deep Learning for Named Entity Recognition. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 34: 50–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissim, Malvina, Rik van Noord, and Rob van der Goot. 2019. Fair Is Better than Sensational:Man Is to Doctor as Woman Is to Doctor. arXiv arXiv:1905.09866. [Google Scholar]
- O’Mahony, Niall, Sean Campbell, Anderson Carvalho, Suman Harapanahalli, Gustavo Velasco Hernandez, Lenka Krpalkova, Daniel Riordan, and Joseph Walsh. 2020. Deep Learning vs. Traditional Computer Vision. In Advances in Computer Vision. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing. Edited by Kohei Arai and Supriya Kapoor. Cham: Springer International Publishing, pp. 128–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pew Research Center—U.S. Politics & Policy (blog). n.d. Political Typology Quiz. Available online: https://www.pewresearch.org/politics/quiz/political-typology/ (accessed on 25 February 2023).
- Political Quiz. n.d. Political Quiz—Where Do You Stand in the Nolan Test? Available online: http://www.polquiz.com/ (accessed on 25 February 2023).
- Political Spectrum Quiz—Your Political Label. n.d. Available online: https://www.gotoquiz.com/politics/political-spectrum-quiz.html (accessed on 25 February 2023).
- Politics Test: Survey of Dictionary-Based Isms. n.d. Available online: https://openpsychometrics.org/tests/SDI-46/ (accessed on 25 February 2023).
- ProProfs Quiz. n.d. Political Ideology Test: What Political Ideology Am I? Available online: https://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/story.php?title=what-is-your-political-ideology_1 (accessed on 25 February 2023).
- Reuters Institute for the Study of Journalism. n.d. Journalists in the UK. Available online: https://reutersinstitute.politics.ox.ac.uk/our-research/journalists-uk (accessed on 13 June 2022).
- Rozado, David. 2020. Wide Range Screening of Algorithmic Bias in Word Embedding Models Using Large Sentiment Lexicons Reveals Underreported Bias Types. PLoS ONE 15: e0231189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoffstall, Joe. 2022. Twitter Employees Still Flooding Democrats with 99 Percent of Their Donations for Midterm Elections. Fox News. April 27. Available online: https://www.foxnews.com/politics/twitter-employees-democrats-99-percent-donations-midterm-elections (accessed on 23 February 2023).
- The Advocates for Self-Government. n.d. World’s Smallest Political Quiz—Advocates for Self-Government. Available online: https://www.theadvocates.org/quiz/ (accessed on 25 February 2023).
- The Harvard Crimson. n.d. More than 80 Percent of Surveyed Harvard Faculty Identify as Liberal |News|. Available online: https://www.thecrimson.com/article/2022/7/13/faculty-survey-political-leaning/ (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- The Political Compass. n.d. Available online: https://www.politicalcompass.org/test (accessed on 25 February 2023).
- Vaswani, Ashish, Noam Shazeer, Niki Parmar, Jakob Uszkoreit, Llion Jones, Aidan N. Gomez, Lukasz Kaiser, and Illia Polosukhin. 2017. Attention Is All You Need. arXiv. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, David H., Lars Willnat, and G. Cleveland Wilhoit. 2019. The American Journalist in the Digital Age: Another Look at U.S. News People. Journalism & Mass Communication Quarterly 96: 101–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikipedia. 2022. GPT-2. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=GPT-2&oldid=11303470391134132336 (accessed on 23 February 2023).
- Wikipedia. 2023a. Algorithmic Bias. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Algorithmic_bias&oldid=1134132336 (accessed on 23 February 2023).
- Wikipedia. 2023b. ChatGPT. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=ChatGPT&oldid=11346133471134132336 (accessed on 23 February 2023).
- Wikipedia. 2023c. Stable Diffusion. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Stable_Diffusion&oldid=1134075867 (accessed on 23 February 2023).
- Zhou, Yongchao, Andrei Ioan Muresanu, Ziwen Han, Keiran Paster, Silviu Pitis, Harris Chan, and Jimmy Ba. 2022. Large Language Models Are Human-Level Prompt Engineers. arXiv. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rozado, D. The Political Biases of ChatGPT. Soc. Sci. 2023, 12, 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci12030148
Rozado D. The Political Biases of ChatGPT. Social Sciences. 2023; 12(3):148. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci12030148
Chicago/Turabian StyleRozado, David. 2023. "The Political Biases of ChatGPT" Social Sciences 12, no. 3: 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci12030148
APA StyleRozado, D. (2023). The Political Biases of ChatGPT. Social Sciences, 12(3), 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci12030148





