Did the Characteristics of Kosovar Teachers Influence the Results of Students in TIMSS 2019? Findings from the Performance of Kosovar Students in TIMSS 2019
Abstract
:1. Introduction
“Effective professional development is continuous, includes training, practice, and feedback, and provides the right time and follow-up support. Successful programs involve teachers in learning activities that are similar to those they will use with their students and encourage the development of teacher-learning communities ”(OECD 2009).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Hypothesis
2.2. Research Methods
2.3. Respondents
2.4. Instruments
3. Results
3.1. The Performance of Kosovar Students in TIMSS 2019
3.2. How Much Influence Do the Teachers’ Characteristics Have on the Students’ Results?
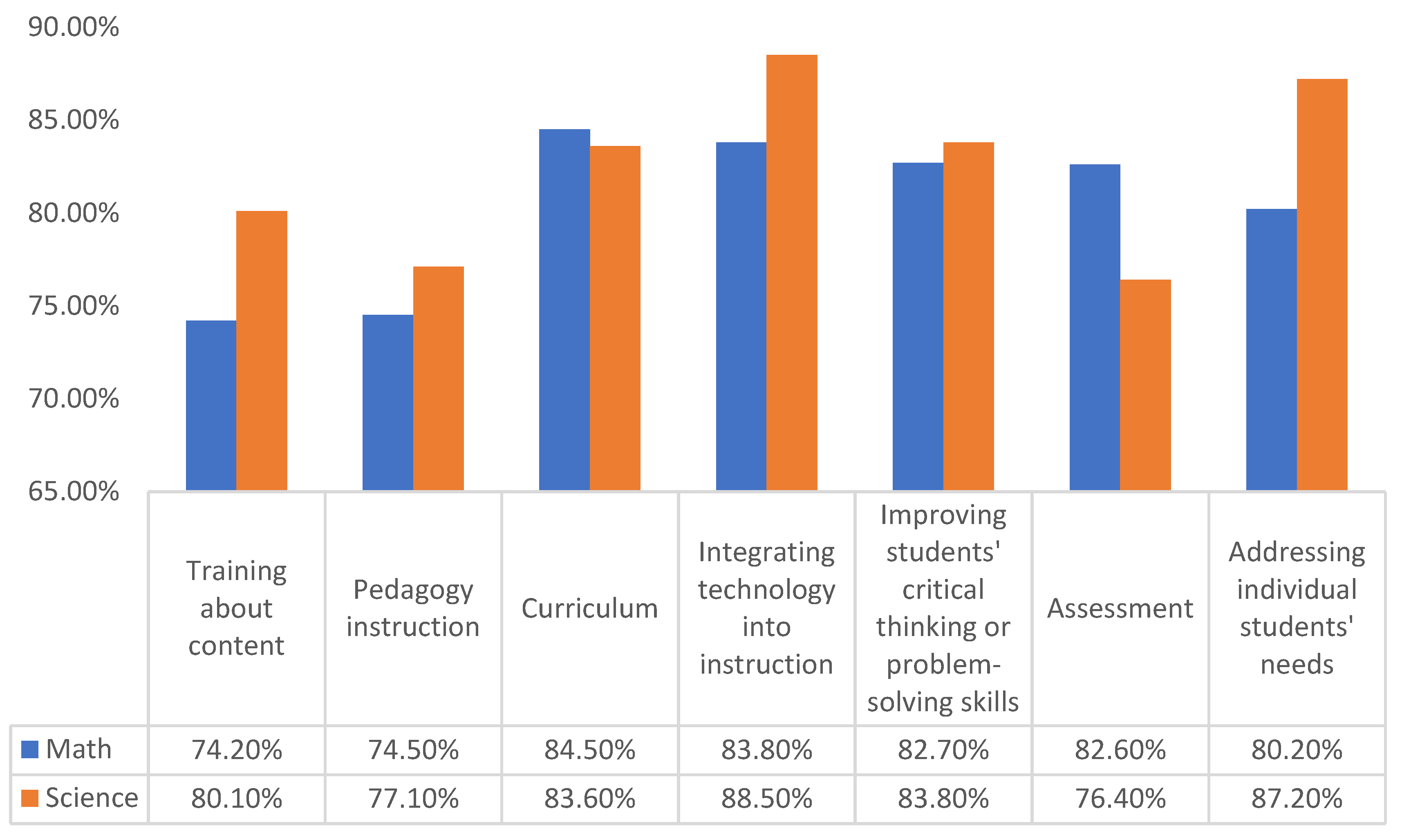
3.3. Professional Development of Teachers Compared with Average Scores of Students in Mathematics and Science
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baier, Franziska, Ana Theresia Decker, Thamar Voss, Thilo Kleickmann, Uta Klusmann, and Mareike Kunter. 2019. What makes a good teacher? The relative importance of mathematics teachers’ cognitive ability, personality, knowledge, beliefs, and motivation for instructional quality. British Journal of Educational Psychology 4: 767–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, E. Paul, and Richard J. Coley. 2009. Parsing the Achievement Gap II. Policy Information Report. Princeton: Educational Testing Service, Available online: https://www.ets.org/Media/Research/pdf/PICPARSINGII.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2021).
- Baumert, Jürgen, Mareike Kunter, Werner Blum, Martin Brunner, Thamar Voss, Alexander Jordan, Uta Klusmann, Stefan Krauss, Michael Neubrand, and Yi-Miau Tsai. 2010. Teachers’ Mathematical Knowledge, Cognitive Activation in the Classroom, and Student Progress. American Educational Research Journal 47: 133–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolyard, Johnna, and Courtney Baker. 2021. Examining the practice of elementary mathematics specialists through narratives: Implications for professional learning and development. Professional Development in Education 2021: 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borko, Hilda, Jennifer Jacobs, and Karen Koellner. 2010. Contemporary Approaches to Teacher Professional Development. International Encyclopedia of Education 7: 548–56. [Google Scholar]
- Burgess, Annete, Christine van Diggele, and Craig Mellis. 2016. Student teacher training: Participant motivation. The Clinical Teacher 13: 267–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clotfelter, T. Charles, Helen Ladd, and Jacob Vigdor. 2006. Teacher Student Matching and the Assessment of Teacher Effectiveness. Journal of Human Resources 41: 778–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, S. James, Ernest Q. Campbell, Carol J. Hobson, James McPartland, Alexander M. Mood, Frederic D. Weinfeld, and Robert L. York. 1966. Equality of Educational Opportunity; Reprinted from American Sociological Review 32: 1967. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office. Available online: https://www.ssc.wisc.edu/wlsresearch/publications/files/public/Sewell-Marascuilo-Pfautz_Review.Symposium.C.et.al.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Dam, Michiel, and Fred J. J. M. Janssen. 2021. Modularity in teacher professional development—Building blocks for bridging everyday teaching practices and reform ideals centered around whole tasks. Professional Development in Education 2021: 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearling, Linda Hammond. 2000. How Teacher Education Matters. Journal of Teacher Education 51: 166–73. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/249704714_How_Teacher_Education_Matters (accessed on 11 April 2020). [CrossRef]
- Didion, Lisa, Jessica R. Toste, and Marissa J. Filderman. 2020. Teacher professional development and student reading achievement: A meta-analytic review of the effects. Journal of Research on Educational Effectiveness 13: 29–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybowski, Christoph, Susanne Sehner, and Sigrid Harendza. 2017. Influence of motivation, self-efficacy and situational factors on the teaching quality of clinical educators. BMC Medical Education 17: 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, Christian, Barry Fishman, Chris Dede, Arthur Eisenkraft, Kim Frumin, Brandon Foster, Frances Lawrenze, Abigail Jurist Levy, and Ayna McCoy. 2018. Investigating relationships between school context, teacher professional development, teaching practices, and student achievement in response to a nationwide science reform. Teaching and Teacher Education 72: 107–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjelaj, Majlinda, Ema Rraci, and Kushtrim Bajrami. 2018. Preschool Education in Kosovo. Pristina. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Majlinda-Gjelaj/publication/334896051_PRE-SCHOOL_EDUCATION_IN_KOSOVO/links/5d4448bc92851cd0469a6722/PRE-SCHOOL-EDUCATION-IN-KOSOVO.pdf (accessed on 4 July 2022).
- Grajcevci, Albulena, and Arif Shala. 2021. A Review of Kosovo’s 2015 PISA Results: Analysing the Impact of Teacher Characteristics in Student Achievement. International Journal of Instruction 14: 489–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanushek, A. Eric. 1992. The Trade-off between Child Quantity and Quality. Journal of Political Economy 100: 84–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanushek, A. Eric. 2011. The economic value of higher teacher quality. Economics of Education Review 30: 466–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, Johana C. G., Scheltus J. van Luijk, Francisca Galindo-Garre, Arno M. M. Muijtjens, Cees P. M. van der Vleuten, Gerda Croiset, and Fedde Scheele. 2014. Five teacher profiles in student-centred curricula based on their conceptions of learning and teaching. BMC Medical Education 16: 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jepsen, Christopher. 2005. Teacher characteristics and student achievement: Evidence from teacher surveys. Journal of Urban Economics 57: 302–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jong, Mirabelle A Schaub-de, Johanna Schönrock-Adema, Hanke Dekker, Marian Verkerk, and Janke Cohen Schotanus. 2011. Development of a student rating scale to evaluate teachers’ competencies for facilitating reflective learning. Medical Education 45: 155–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, Heather R., Robert L. Mendro, and Dash Weersinghe. 1997. Teacher Effects on Longitudinal Student Achievement: A Preliminary Report on Research on Teacher Effectiveness. In Proceedings of the CREATE Annual Meeting, Indianapolis IN, USA, July 1997. Kalamazoo: CREATE, Western Michigan University, Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&q=Teacher+Effects+on+Longitudinal+Student+Achievement%3A+A+Report+on+Research+in+Progress (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Karlberg, Martin, and Christopher Bezzina. 2020. The professional development needs of beginning and experienced teachers in four municipalities in Sweden. Professional Development in Education 12: 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahler, Daniela, Jörg Großschedl, and Ute Harms. 2018. Does motivation matter?—The relationship between teachers’ self-efficacy and enthusiasm and students’ performance. PLoS ONE 21: e0207252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosteller, Frederick. 1995. The Tennessee Study of Class Size in the Early School Grades. The Future of Children 5: 113–27. Available online: https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/9781400851607.261/pdf (accessed on 11 April 2022). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mullis, Ina V. S., and Michael O. Martin. 2012. Using TIMSS and PIRLS to improve teaching and learning. Recherches en Éducation 14: 1–182. Available online: http://journals.openedition.org/ree/5835 (accessed on 1 February 2022). [CrossRef]
- Mullis, Inva V. S., Michael O. Martin, Pierre Foy, Dana L. Kelly, and Bethany Fishbein. 2020. TIMSS 2019 International Results in Mathematics and Science. Newton: Boston College. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. 2009. The Professional Development of Teachers. In Creating Effective Teaching and Learning Environments: First Results from TALIS. Paris: OECD Publishing, chp. 3. ISBN 978-92-64-05605-3. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. 2019. PISA 2018 Results (Volume I): What Students Know and Can Do. Paris: OECD Publishing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, Benjamin, Stephanie Simmons Zuilkowski, Margaret Dubeck, Evelyn Jepkemei, and Simon J. King. 2018. Identifying the essential ingredients to literacy and numeracy improvement: Teacher professional development and coaching, student textbooks, and structured teachers’ guides. World Development 106: 324–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponte, Petra. 2010. Action Research as a Tool for Teachers’ Professional Development. In International Encyclopedia of Education, 3rd ed. Utrecht: Hogeschool Utrecht, pp. 540–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, Cynthia. 2002. The Challenge of Attracting Good Teachers and Principals to Struggling Schools. American Association of School Administrators. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228951320_The_challenge_of_attracting_good_teachers_and_principals_to_struggling_schools (accessed on 13 March 2022).
- Quins University Charlote. n.d. The Importance of Professional Development for Educators. Available online: https://online.queens.edu/resources/article/professional-development-for-educators/ (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Ribers, Bjorn, Gitte Miller Balslev, and Christine Revsbech Jensen. 2021. Education, collaboration and pedagogical phronesis: Essential dimensions in professional learning and development. Professional Development in Education 2021: 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubie-Davies, Christine M. 2006. Teacher expectations and student self-perceptions: Exploring relationships. Psychology in the Schools 43: 537–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, L. William, and June C. Rivers. 1996. Cumulative and Residual Effects of Teachers on Future Student Academic Achievement. Knoxville: University of Tennessee Value-Added Research and Assessment Center. [Google Scholar]
- Sasson, Irit, and Shirley Miedijensky. 2020. Transfer skills in teacher training programs: The question of assessment. Professional Development in Education 2020: 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebruck, Ryan. 2015. Teacher quality and student achievement: A multilevel analysis of teacher credentialization and student test scores in California High Schools. McGill Sociological Review 5: 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sezer, Elif, and Mehtap Çakan. 2022. Role of Teacher Quality and Working Conditions in TIMSS 2019 Mathematics Achievement. Journal of Theoretical Educational Science 15: 395–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shala, Arif, Albulene Grajcevci, and Fadil Latifi. 2021a. Does Socioeconomic Status Influence Achievement? An analysis of the Performance of Kosovar Students on the 2015 and 2018 PISA Assessment. Journal of Elementary Education 14: 393–408. [Google Scholar]
- Shala, Arif, Albulene Grajcevci, and Fadil Latifi. 2021b. Do teacher characteristics matter? Findings from the PISA performance of Kosovar students. International Journal of Management in Education 15: 580–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, AiBin, Wen Ye Li, and Dawei Liu. 2022. The impact of teachers` professional development in science pedagogy on students’ achievement: Evidence from TIMSS 2019. Journal of Baltic Science Education 21: 258–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungar, Orit Avidov. 2020. The professional learning expectations of teachers in different professional development periods. Professional Development in Education, 1–12. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/19415257.2020.1763435 (accessed on 26 July 2021). [CrossRef]
- Zeggelaar, Albert, Marjan Vermeulen, and Wim M. G. Jochems. 2020. Evaluating effective professional development. Professional Development in Education 2020: 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Ling, Richard Allen Carter Jr., Jihong Zhang, Tiffany L. Hunt, Christopher R. Emerling, Sohyun Yang, and Fangjie Xu. 2021. Teacher perceptions of effective professional development: Insights for design. Professional Development in Education 2021: 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Teacher’s valid sample (N 192) | Male | Female |
| 23.5% | 76.5% | |
| Math (Average scores of students on the test) | 453.3 | 447.0 |
| Science (Average scores of students on the test) | 402.1 | 416.3 |
| Years of teaching (Mean) | 16.3 | |
| Years of teaching (Mode) | 10 | |
| Highest formal level of education completed by teachers | ||
| 1. No upper secondary | 0.0% | |
| 2. Upper secondary | 6.1% | |
| 3. Post-secondary, non-tertiary | 0.6% | |
| 4. Short-cycle tertiary | 9.0% | |
| 5. Bachelor’s or equivalent | 76.6% | |
| 6. Master’s or equivalent | 7.6% | |
| 7. Doctor or equivalent | 0.0% | |
| Age of Teachers | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Student scores on TIMSS 2019 | Under 25 (6.4%) | 25–29 (11.8%) | 30–39 (28.0%) | 40–49 (24.4%) | 50–59 (15.5%) | 60 or more (13.9%) |
| Students’ scores in mathematics (average) | 426.4 | 439.3 | 452.5 | 451.2 | 451.6 | 424.2 |
| Students’ scores in science (average) | 394.2 | 406.8 | 420.0 | 423.7 | 421.6 | 388.4 |
| How Would You Characterize Each of the Following within Your School? | Students’ Scores in Math and Science (TIMSS 2019) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Math | Science | ||
| My degree of success in implementing the school’s curriculum | Very high | 450.7 | 418.0 |
| High | 441.2 | 409.8 | |
| Medium | 444.1 | 414.8 | |
| Low | 416.4 | 383.6 | |
| Very low | - | - | |
| I understand the curricular goals of the school | Very high | 450.5 | 418.4 |
| High | 440.3 | 408.0 | |
| Medium | 445.7 | 416.9 | |
| Low | 416.4 | 383.6 | |
| Very low | - | - | |
| My expectations for student achievement | Very high | 437.6 | 403.2 |
| High | 447.2 | 416.4 | |
| Medium | 446.1 | 418.1 | |
| Low | - | - | |
| Very low | - | - | |
| How Would You Characterize Each of the Following within Your School? | Students’ Scores in Math and Science (TIMSS 2019) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Math | Science | ||
| I inspire my students to learn | Very high | 442.2 | 408.8 |
| High | 446.9 | 417.2 | |
| Medium | 451.4 | 428.2 | |
| Low | 450.6 | 426.9 | |
| Very low | - | - | |
| I am content with my profession as a teacher | Very high | 444.5 | 419.2 |
| High | 442.2 | 412.5 | |
| Medium | - | - | |
| Low | - | - | |
| Very low | - | - | |
| I am enthusiastic about my job | Very high | 446.3 | 432.0 |
| High | 415.5 | 397.5 | |
| Medium | - | - | |
| Low | - | - | |
| Very low | |||
| My work inspires me | Very high | 445.2 | 414.4 |
| High | 434.1 | 400.8 | |
| Medium | - | - | |
| Low | - | - | |
| Very low | - | - | |
| Teachers’ Declarations about Professional Development | During the Past Two Years, Have You Participated in Any Professional Development (PD) Training in Math? | |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | |
| Mathematics content | Student scores in TIMSS 2019 compared to teachers’ statements about PD | |
| 447.5 | 443.7 | |
| Mathematics/pedagogy instruction | 452.9 | 442.8 |
| Mathematics curriculum | 445.6 | 444.4 |
| Integrating technology into mathematics instruction | 441.7 | 445.5 |
| Improving students’ critical thinking or problem-solving skills | 447.2 | 443.1 |
| Mathematics assessment | 446.0 | 444.0 |
| Addressing individual students’ needs | 448.4 | 443.2 |
| Teachers’ Declarations about Professional Development | During the Past Two Years, Have You Participated in Any Professional Development (PD) Training in Science? | |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | |
| Science content | Student scores in TIMSS 2019 compared to teachers’ statements about PD | |
| 418.8 | 413.5 | |
| Science/pedagogy instruction | 414.2 | 412.6 |
| Science curriculum | 419.3 | 413.9 |
| Integrating technology into mathematics instruction | 415.6 | 413.3 |
| Improving students’ critical thinking or problem-solving skills | 419.3 | 415.1 |
| Science assessment | 415.7 | 413.4 |
| Addressing individual students’ needs | 415.3 | 413.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Latifi, F.; Latifi, E. Did the Characteristics of Kosovar Teachers Influence the Results of Students in TIMSS 2019? Findings from the Performance of Kosovar Students in TIMSS 2019. Soc. Sci. 2022, 11, 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci11080344
Latifi F, Latifi E. Did the Characteristics of Kosovar Teachers Influence the Results of Students in TIMSS 2019? Findings from the Performance of Kosovar Students in TIMSS 2019. Social Sciences. 2022; 11(8):344. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci11080344
Chicago/Turabian StyleLatifi, Fadil, and Endrit Latifi. 2022. "Did the Characteristics of Kosovar Teachers Influence the Results of Students in TIMSS 2019? Findings from the Performance of Kosovar Students in TIMSS 2019" Social Sciences 11, no. 8: 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci11080344
APA StyleLatifi, F., & Latifi, E. (2022). Did the Characteristics of Kosovar Teachers Influence the Results of Students in TIMSS 2019? Findings from the Performance of Kosovar Students in TIMSS 2019. Social Sciences, 11(8), 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci11080344







