Multi-Track Friction Stir Lap Welding of 2024 Aluminum Alloy: Processing, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
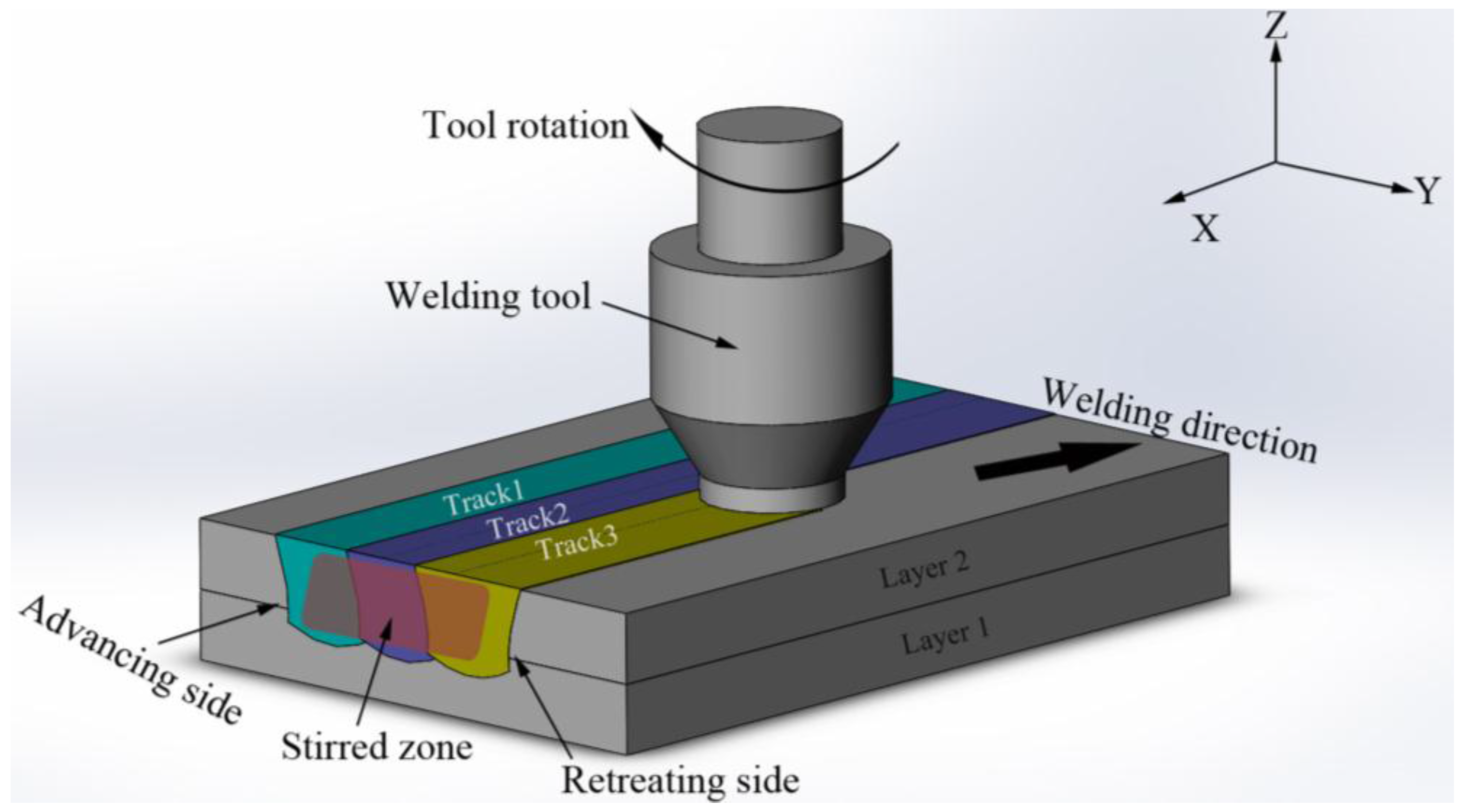
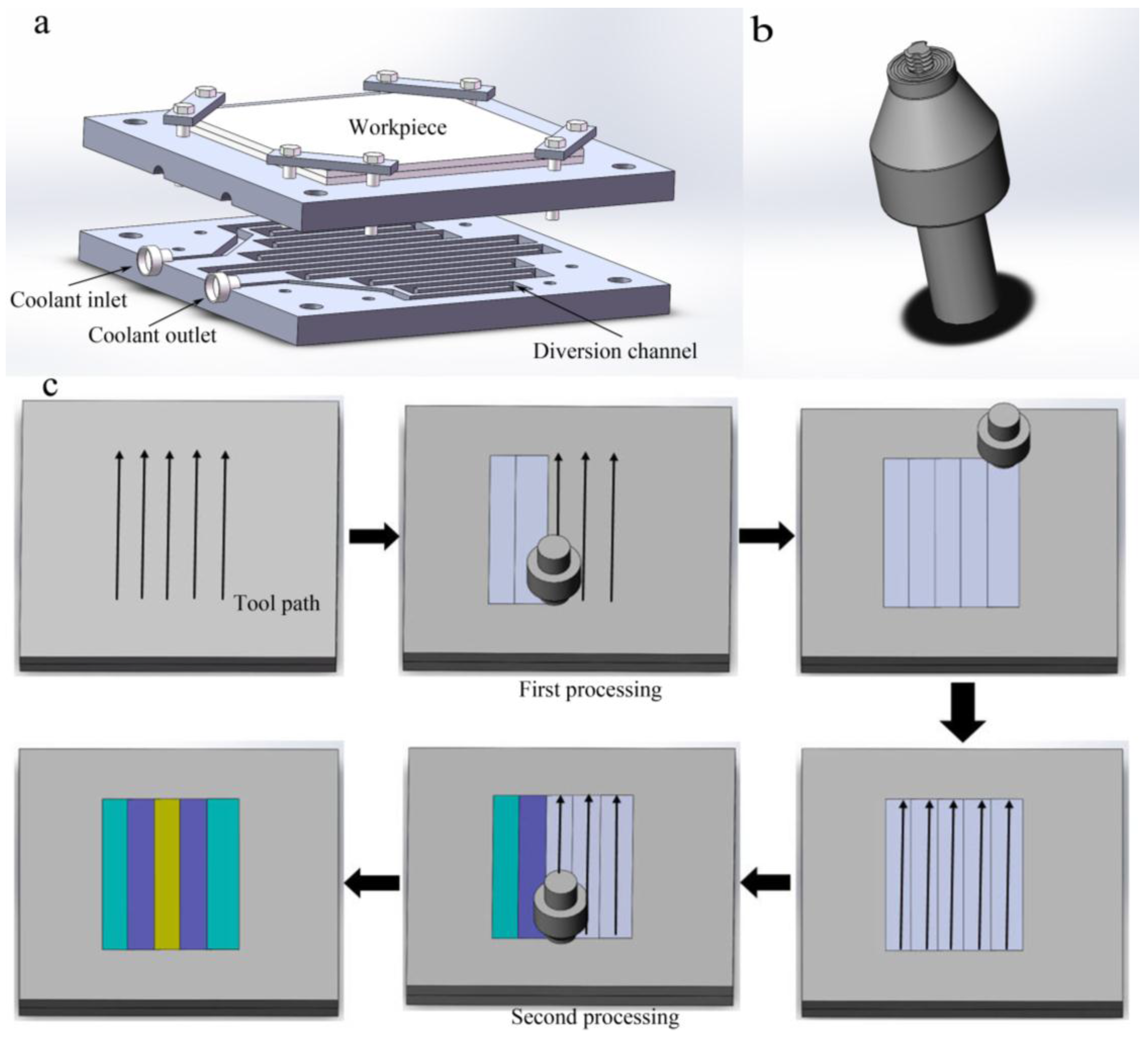
2.1. Experimental Setup and Manufacturing Process
2.2. Microstructural Characterization and Mechanical Testing
3. Results and Discussion
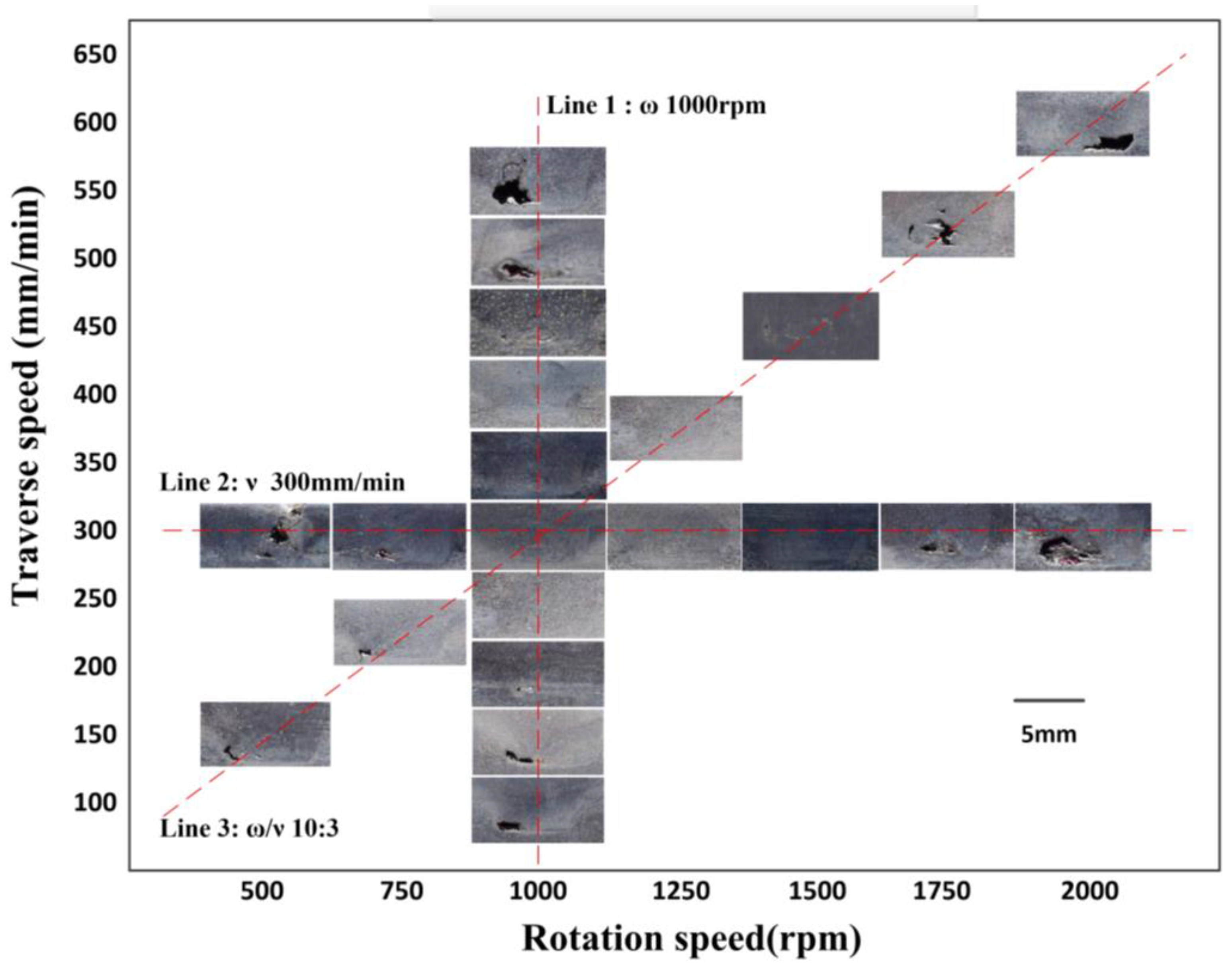
3.1. Single-Track Friction Stir Lap Welding
3.1.1. Single-Track FSLW with One-Pass Processing
3.1.2. Single-Track FSLW with Two-Pass Processing
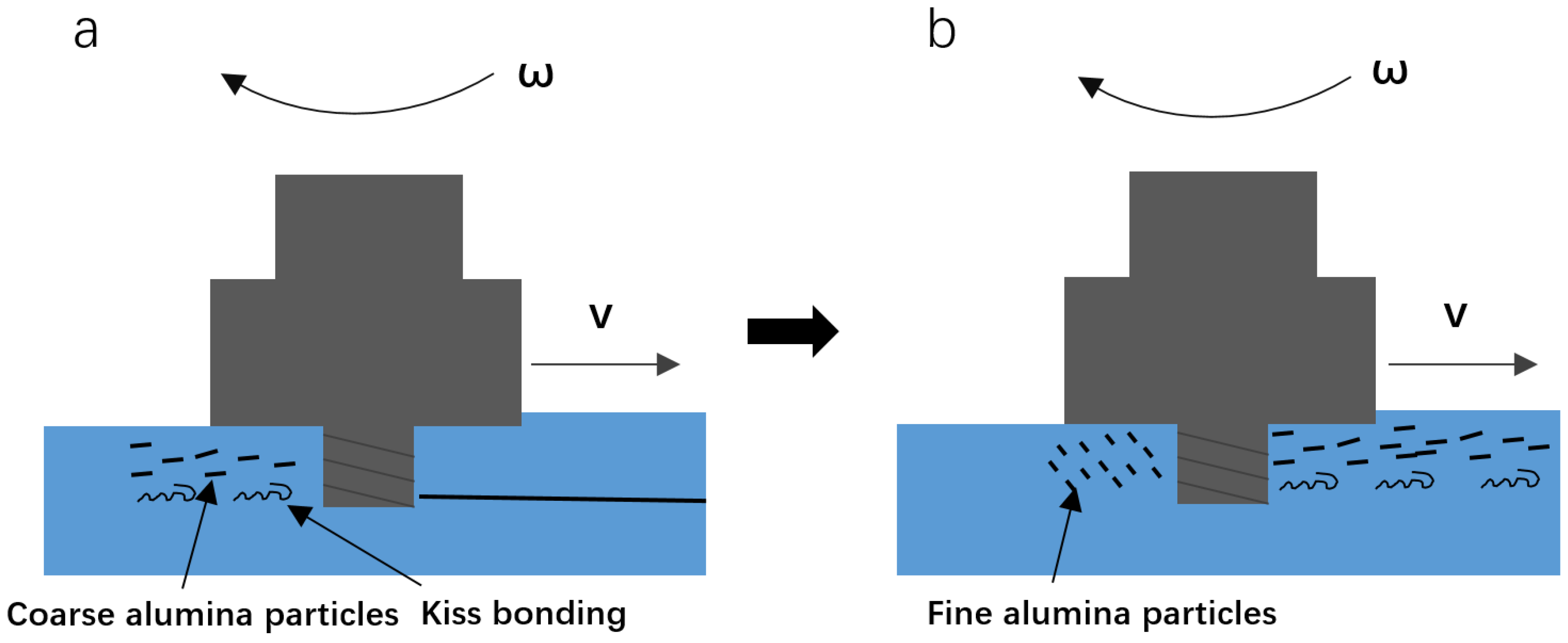
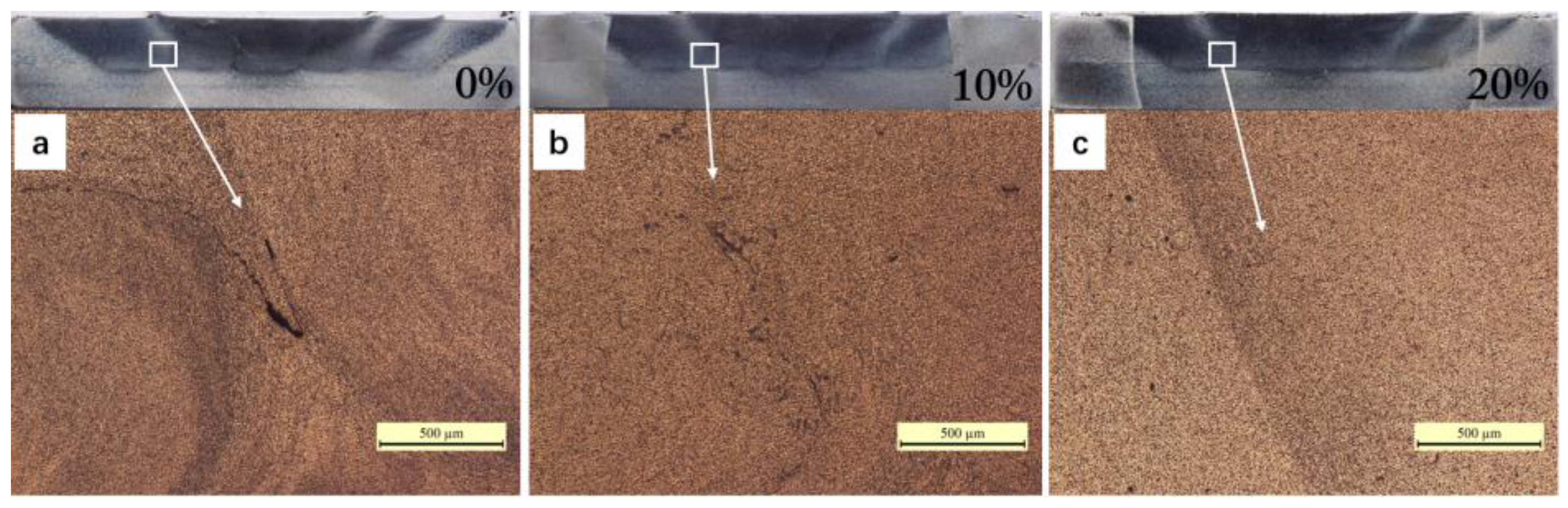
3.2. Multi-Track Friction Stir Lap Welding
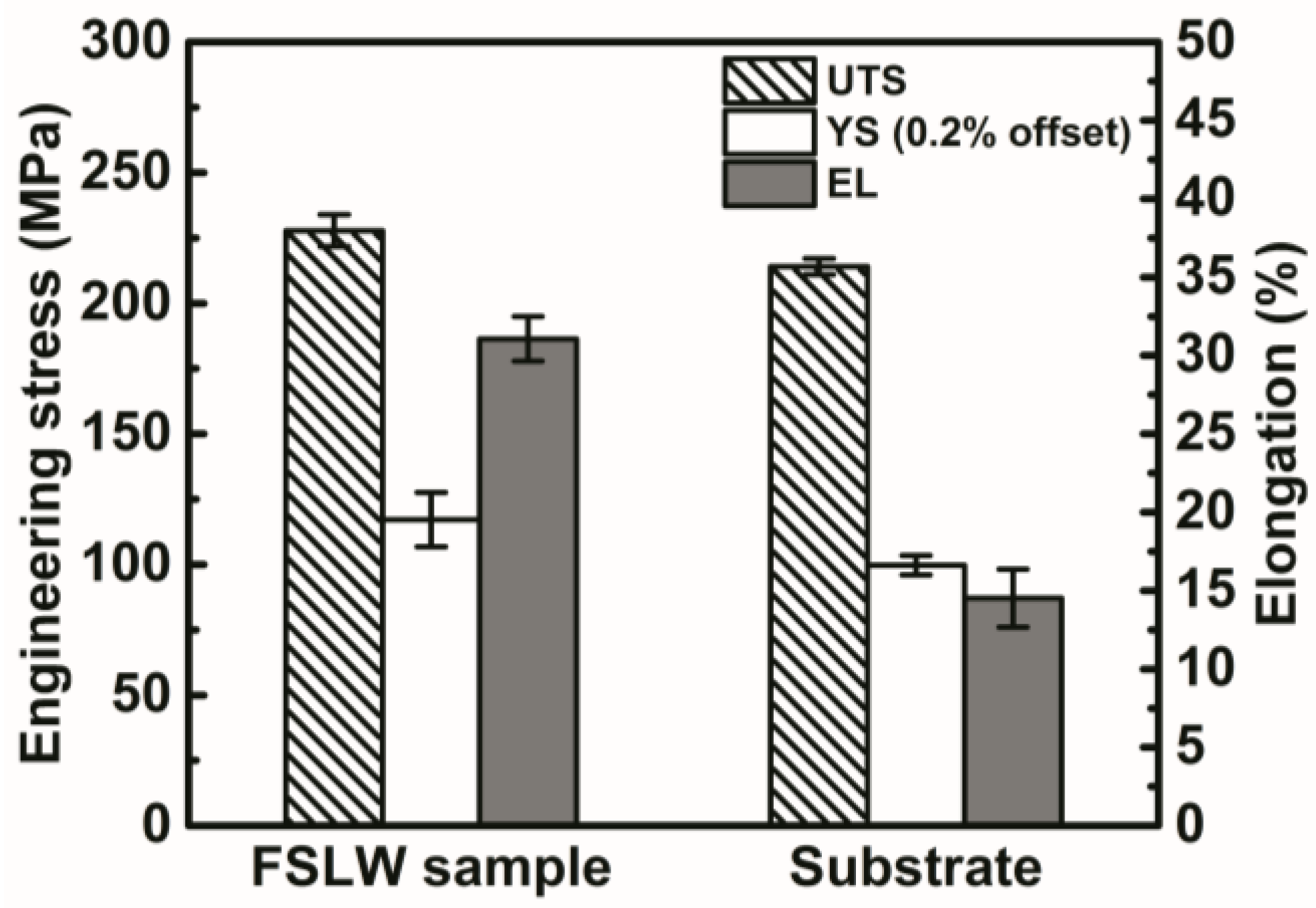
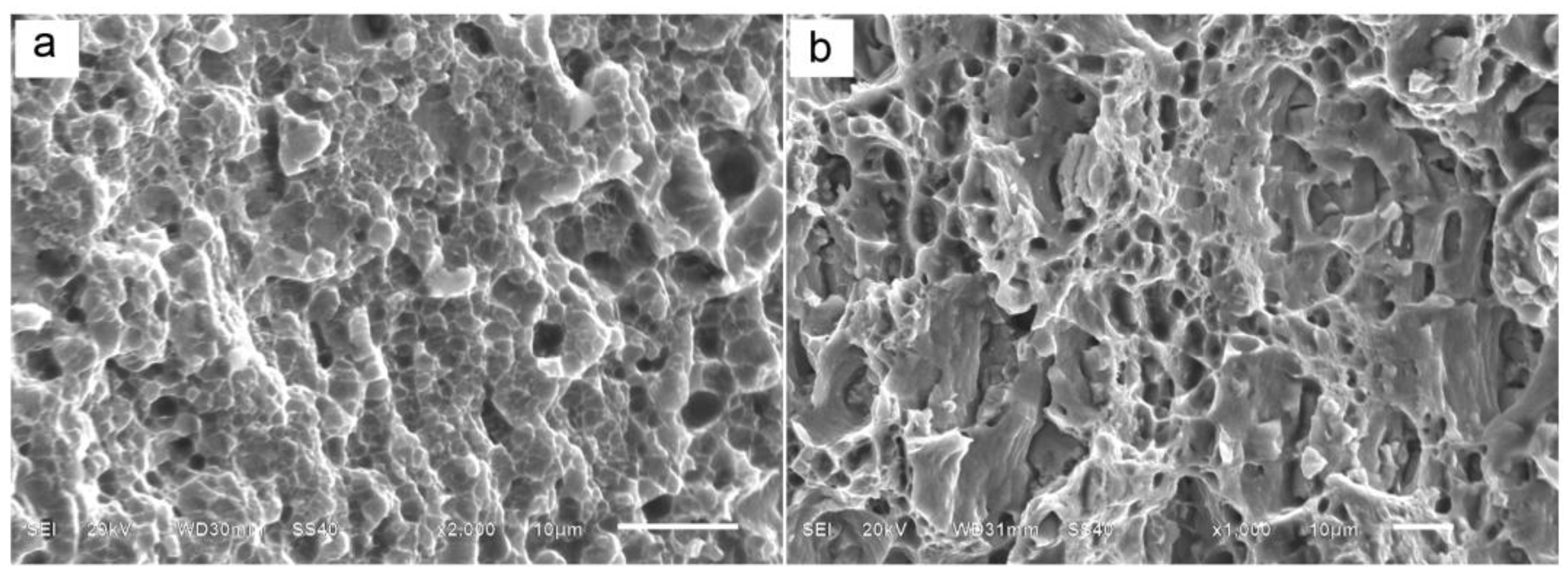
3.3. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Defects generated during FSLW are very sensitive to the variation of parameters. Systematic studies were carried out to determine the suitable processing parameters. The rotational speed and traverse speed are found to play an important role in hole generation.
- (2)
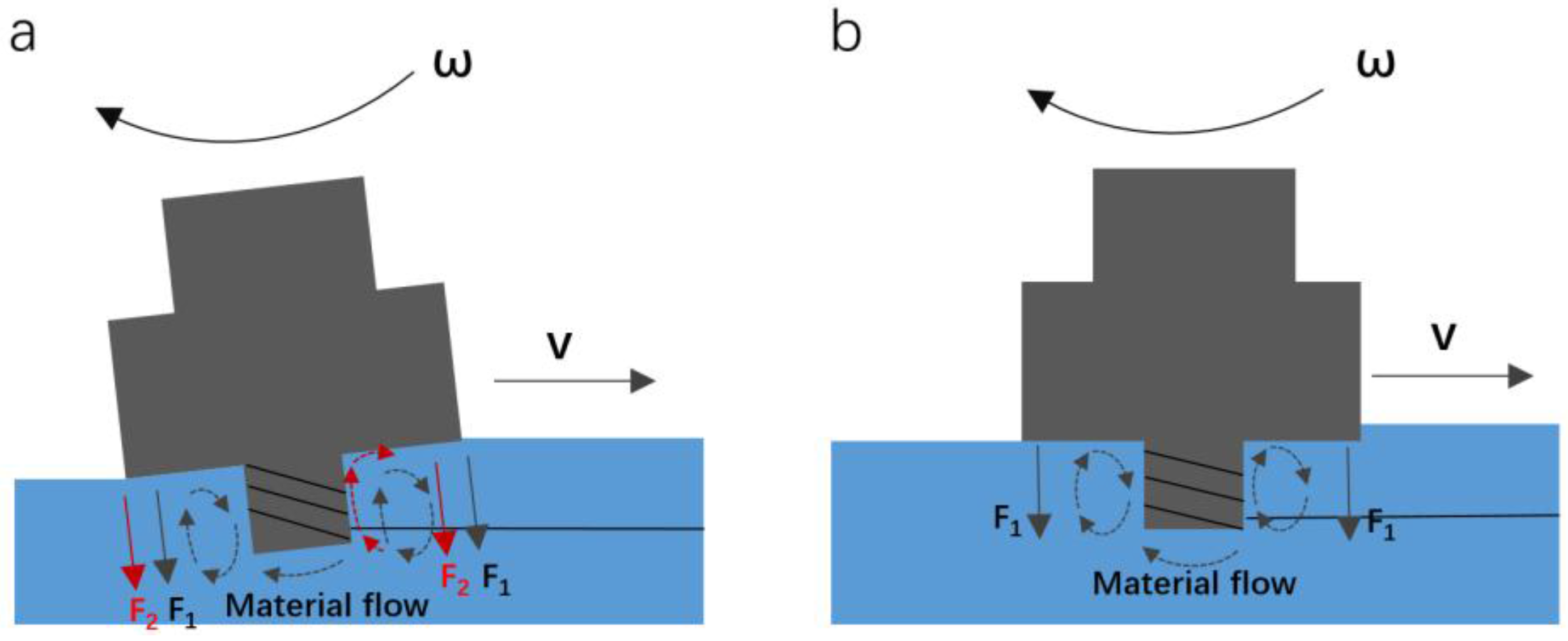
- Tilt angle has a certain positive effect on defect elimination, but significantly increases equipment cost. Alternatively, two-pass processing is found to be able to replace the tilt angle and ensure defect-free forming. Under two-pass processing with welding speed 300 mm/min, rotation rate 1000 rpm and plunge depth 0.2 mm, defect-free samples were successfully fabricated.
- (3)
- Hook-shaped defects are an inherent feature of FSLW, which combine to become crack-like unbonded defects in the overlapping zone during multi-track processing. The overlapping rate of 20% is found to be enough to eliminate these unbonded defects, and obtain full density multi-track samples.
- (4)
- Ultrafine equiaxed grains with the diameter about 9.4 μm are obtained in FSLW samples, because of the dynamic recrystallization during FSLW. Accordingly, the strength of the multi-track FSLW samples is much higher than that of the rolled 2024-O substrate. Meanwhile, it exhibits a high ductility of the elongation about 31.05%, which is about two times that of the rolled 2024-O substrate.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, Z.; Yuan, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, G.; Huang, Y. Effect of post-weld heat treatment on the microstructure and plastic deformation behavior of friction stir welded 2024. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 5055–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, E.; Heckenberger, U.; Holzinger, V.; Buchbinder, D. Additive manufactured AlSi10Mg samples using selective laser melting (SLM): Microstructure, high cycle fatigue, and fracture behavior. Mater. Des. 2012, 34, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.W.; Kang, M.S.; Yoon, S.O.; Kwon, Y.J.; Hong, S.T.; Kim, D.I.; Lee, K.H.; Seo, J.D.; Moon, J.S.; Han, K.S. Influence of tool plunge depth and welding distance on friction stir lap welding of AA5454-O aluminum alloy plates with different thicknesses. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. Chin. 2012, 22, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.S.; Ma, Z.Y. Friction stir welding and processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2005, 50, 13–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, S.; Cakir, R. Effect of friction stir welding parameters on the mechanical and microstructure properties of the Al-Cu butt joint. Metals 2016, 6, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, P.M.G.P.; Figueiredo, M.A.V.D.; Castro, P.M.S.T.D. Fatigue behaviour of fsw and mig weldments for two aluminium alloys. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2007, 48, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.W.; Yazdanian, S. Friction stir lap welding: Material flow, joint structure and strength. J. Achieve Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2012, 55, 629–637. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, T.; Yang, G. Effect of welding speed on defect features and mechanical performance of friction stir lap welded 7b04 aluminum alloy. Metals 2016, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Kumar, K.; Mishra, R.S. Friction stir lap welded advanced high strength steels: Microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 8111–8119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Ke, L.; Huang, C.; Liu, F.; Liu, Q. Formation characteristic, microstructure, and mechanical performances of aluminum-based components by friction stir additive manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 83, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar]
- Palanivel, S.; Sidhar, H.; Mishra, R.S. Friction stir additive manufacturing: Route to high structural performance. JOM 2015, 67, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivel, S.; Nelaturu, P.; Glass, B.; Mishra, R.S. Friction stir additive manufacturing for high structural performance through microstructural control in an mg based WE43 alloy. Mater. Des. 2015, 65, 934–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, H.A.D.; Roslee, A.A. Study the role of friction stir welding tilt angle on microstructure and hardness. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 799–800, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badheka, V.J. Effects of tilt angle on properties of dissimilar friction stir welding copper to aluminum. Adv. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2016, 31, 255–263. [Google Scholar]
- Latif, A.; Fadhil, M. Friction Stir Welding (FSW): The Effect of Tilting Angle; Universiti Teknologi Petronas: Seri lskandar, Malaysia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, C.; Li, X.; Song, D.; Zhou, N.; Li, Y.; Qi, W. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of friction stir welded dissimilar joints of Mg–Zn–Gd and Mg–Al–Zn alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 664, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, E.; Jahazi, M.; Khodabandeh, A.; Ghasemi-Nanesa, H. Influence of tool geometry and rotational speed on mechanical properties and defect formation in friction stir lap welded 5456 aluminum alloy sheets. Mater. Des. 2014, 58, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yang, X.; Cui, L.; Hou, X.; Shen, Z.; Xu, Y. Defect features and mechanical properties of friction stir lap welded dissimilar AA2024–AA7075 aluminum alloy sheets. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbegast, W.J. A flow-partitioned deformation zone model for defect formation during friction stir welding. Scr. Mater. 2008, 58, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colligan, K.J.; Mishra, R.S. A conceptual model for the process variables related to heat generation in friction stir welding of aluminum. Scr. Mater. 2008, 58, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundararajan, V.; Yarrapareddy, E.; Kovacevic, R. Investigation of the friction stir lap welding of aluminum alloys AA 5182 and AA 6022. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2007, 37, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.G.; Fujii, H.; Tsumura, T.; Komazaki, T.; Nakata, K. Three defect types in friction stir welding of aluminum die casting alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 415, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.R.; Ma, Z.Y.; Chen, L.Q. Effect of welding parameters on tensile properties and fracture behavior of friction stir welded Al–Mg–Si alloy. Scr. Mater. 2007, 56, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radisavljevic, I.; Zivkovic, A.; Radovic, N.; Grabulov, V. Influence of FSW parameters on formation quality and mechanical properties of Al 2024-T351 butt welded joints. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. Chin. 2013, 23, 3525–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.J.; Kailas, S.V.; Srivatsan, T.S. Effect of tool angle on friction stir welding of aluminum alloy 5052: Role of sheet thickness. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 410, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, M.B.; Meran, C.; Canyurt, O.E. Effect of tool angle on friction stir weldability of AISI 430. Weld. J. 2013, 92, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Behmand, S.A.; Mirsalehi, S.E.; Omidvar, H.; Safarkhanian, M.A. Single- and double-pass fsw lap joining of AA5456 sheets with different thicknesses. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.S.; Mahoney, M.W. Friction Stir Welding and Processing II; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 13–58. [Google Scholar]
- El-Rayes, M.M.; El-Danaf, E.A. The influence of multi-pass friction stir processing on the microstructural and mechanical properties of aluminum alloy 6082. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktarer, S.M.; Sekban, D.M.; Saray, O.; Kucukomeroglu, T.; Ma, Z.Y.; Purcek, G. Effect of two-pass friction stir processing on the microstructure and mechanical properties of as-cast binary Al–12Si alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 636, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldanondo, E.; Arruti, E.; Alvarez, P.; Echeverria, A. Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Fsw Lap Joints; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.Z.; Wang, S.Z.; Li, B.L.; Yin, Z.M.; Wan, Q.; Liu, P. Grain growth and microstructure evolution based mechanical property predicted by a modified hall–petch equation in hot worked Ni76Cr19AlTiCo alloy. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, K.N.; Pradeep, S.; Pancholi, V. Multipass friction-stir processing and its effect on mechanical properties of aluminum alloy 5086. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 4311–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | No. | Welding Speed, ν (mm/min) | Rotation Speed, ω (rpm) | Plunge Depth, h (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant ν | a1 | 300 | 500 | 0.2 |
| a2 | 300 | 750 | 0.2 | |
| a3 | 300 | 1000 | 0.2 | |
| a4 | 300 | 1250 | 0.2 | |
| a5 | 300 | 1500 | 0.2 | |
| a6 | 300 | 1750 | 0.2 | |
| a7 | 300 | 2000 | 0.2 | |
| Constant ω | b1 | 100 | 1000 | 0.2 |
| b2 | 150 | 1000 | 0.2 | |
| b3 | 200 | 1000 | 0.2 | |
| b4 | 250 | 1000 | 0.2 | |
| b5 | 300 | 1000 | 0.3 | |
| b6 | 350 | 1000 | 0.2 | |
| b7 | 400 | 1000 | 0.2 | |
| b8 | 450 | 1000 | 0.2 | |
| b9 | 500 | 1000 | 0.2 | |
| b10 | 550 | 1000 | 0.2 | |
| Constant ω/ν | c1 | 150 | 500 | 0.2 |
| c2 | 225 | 750 | 0.2 | |
| c3 | 300 | 1000 | 0.4 | |
| c4 | 375 | 1250 | 0.2 | |
| c5 | 450 | 1500 | 0.2 | |
| c6 | 525 | 1750 | 0.2 | |
| c7 | 600 | 2000 | 0.2 |
| FSLW Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Rotation speed | 1000 rpm |
| Traverse speed | 300 mm/min |
| Plunge depth | 0.2 mm |
| Tilt angle | 0 |
| Overlapping rate | 20% |
| Tool path pattern | Same direction |
| Special process | Two-pass processing |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, S.; Ma, S.; Liu, C.; Chen, C.; Ma, L.; Lu, J.; Guo, J. Multi-Track Friction Stir Lap Welding of 2024 Aluminum Alloy: Processing, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. Metals 2017, 7, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7010001
Zou S, Ma S, Liu C, Chen C, Ma L, Lu J, Guo J. Multi-Track Friction Stir Lap Welding of 2024 Aluminum Alloy: Processing, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. Metals. 2017; 7(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Shengke, Shuyuan Ma, Changmeng Liu, Cheng Chen, Limin Ma, Jiping Lu, and Jing Guo. 2017. "Multi-Track Friction Stir Lap Welding of 2024 Aluminum Alloy: Processing, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties" Metals 7, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7010001
APA StyleZou, S., Ma, S., Liu, C., Chen, C., Ma, L., Lu, J., & Guo, J. (2017). Multi-Track Friction Stir Lap Welding of 2024 Aluminum Alloy: Processing, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. Metals, 7(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7010001







