Abstract
A deeper understanding of the mechanical behavior of ultra-fine (UF) and nanocrystalline (NC) grained metals is necessary with the growing interest in using UF and NC grained metals for structural applications. The cyclic deformation response and behavior of UF and NC grained metals is one aspect that has been gaining momentum as a major research topic for the past ten years. Severe Plastic Deformation (SPD) materials are often in the spotlight for cyclic deformation studies as they are usually in the form of bulk work pieces and have UF and NC grains. Some well known techniques in the category of SPD processing are High Pressure Torsion (HPT), Equal Channel Angular Pressing (ECAP), and Accumulative Roll-Bonding (ARB). In this report, the literature on the cyclic deformation response and behavior of SPDed metals will be reviewed. The cyclic response of such materials is found to range from cyclic hardening to cyclic softening depending on various factors. Specifically, for SPDed UF grained metals, their behavior has often been associated with the observation of grain coarsening during cycling. Consequently, the many factors that affect the cyclic deformation response of SPDed metals can be summarized into three major aspects: (1) the microstructure stability; (2) the limitation of the cyclic lifespan; and lastly (3) the imposed plastic strain amplitude.
1. Introduction
The small size grains in the ultra-fine (UF) and nanocrystalline (NC) grained metals and alloys provide a significant increase in mechanical strength compared to its conventional grain sized counterparts. At the same time, the small grain sizes in such materials lead to the deviation of its mechanical behavior from that described by conventional dislocation theories [1,2,3,4,5]. Such deviation from conventional dislocation theories has been attributed to the significant interactions of the stress fields surrounding dislocations with that surrounding the grain boundaries as a result of the small grain size [1]. In addition, the participation of other deformation mechanisms also play important role in such deviations [1,2,3,4,5]. As such, many new studies regarding the mechanical behavior of UF and NC grained metals have been emerging in literature.
There are many different processing techniques for producing UF and NC grained metals, and generally speaking each of them is with its own characteristics. One category of techniques is known as Severe Plastic Deformation (SPD). As the name suggests, these techniques involve large amount of plastic deformation imposed on to the work piece during processing. Many of the techniques within this category are capable of producing fully-dense products in bulk form. Equal Channel Angular Pressing (ECAP), first reported in [6], is often considered to be the most developed, and likely most popular, of the SPD techniques [7]. Another emerging technique that is also gathering interest is Accumulative Roll-Bonding (ARB), first reported in [8,9]. These techniques are known to be capable of producing products with dimensions large enough for standardized specimen designs, making them popular for mechanical behavior studies. Other SPD techniques include High Pressure Torsion (HPT) [10], Multi-Directional Forging (MDF) [11], Cyclic Extrusion and Compression (CEC) [12], and so on. The details of these SPD techniques are reviewed in various publications, e.g., [7,13,14,15,16,17], and will not be elaborated on here.
One aspect of interest is the cyclic deformation behavior of UF and NC grained metals. The small characteristic microstructural length scale, in this case grain size, has been reported to inhibit the formation of spatial patterns of dislocation configurations such as walls [18]. Consequently, many of the well known conventional dislocation mechanisms for cyclic strain accommodation, such as persistent slip bands, labyrinth structures, etc., are inhibited in UF and NC grained metals of high or medium-high stacking fault energy. Furthermore, other cyclic strain accommodation mechanisms, such as dislocation cells, are also inhibited due to the small grain size [5]. Thiele et al. [19] verified that dislocation—grain boundary interactions were the main activities during cyclic deformation of NC nickel material with conventional grain size, but when the grain size became smaller and in the range of 100 nm to 750 nm, grain boundary activity became an important part of the micro-activities during cycling. With the above considerations it is expected that new cyclic strain accommodation mechanisms, that are different from those of conventional grain size metals, would be in operation for UF and NC grained metals. The aim of this paper is to review the trends of the cyclic deformation behavior of SPD metals reported in literature and the factors that influence such cyclic deformation behavior.
2. Overview of the Cyclic Deformation Behavior of SPDed Metals
Many of the reports on the cyclic deformation behavior of SPDed metals have been based on metals processed by ECAP, e.g., for high purity copper [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38], technical purity copper [33,39,40,41,42,43,44], aluminium and aluminum alloys [45,46,47,48,49,50,51], commercial purity titanium [52], IF steel [53,54], and α-brass [55]. There are also reports, albeit fewer in quantity, based on products of different techniques, such as high purity copper processed by HPT [36], high purity copper processed by ARB [56,57], and aluminum and aluminum alloys processed by cryogenic rolling [58,59].
In the case of the high purity metals after SPD processing, cyclic softening of varying extent was revealed first in a systematic way by Agnew and Weertman [21] in ECAPed high purity copper in 1998, although Vinogradov et al. also presented data showing a minor cyclic softening response in 1997 [20]. In the latter case, however, the softening was detected after a period of minor cyclic hardening response in one of their high purity ECAPed copper samples, but they did not make any specific conclusion in that regard. Agnew and his co-workers [22] later in 1999 further confirmed such a phenomenon, i.e., cyclic softening response following cyclic hardening, reported in [20]. Later observations of various extent of cyclic softening were reported by a number of other researchers, i.e., reference [23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,35,36,37,38,56,58]. It should be noted that these reports are largely based on high purity copper. Interesting enough, this behavior follows an empirical relationship that annealed metals generally show cyclic hardening, whereas cold worked metals generally shows cyclic softening [60], although the underlying mechanisms seem to be largely different. In the case of SPDed metals, grain coarsening has been commonly observed to accompany the cyclic softening response in many of these reports [22,23,24,26,28,32,35,36,38,56,57]. A correlation between the extent of grain coarsening with the extent of cyclic softening was first shown by Höppel et al. in reference [24] for their ECAPed copper. In fact, this proportionate type relationship between the extent of grain coarsening and the extent of cyclic softening can also be shown in ARBed copper with the data from the previous published (i.e., [56,57]) and unpublished works [61] by the present authors, as consolidated in Figure 1. It should be noted that, in Figure 1, the extent of grain coarsening is represented by the relative change in area fraction of large grains at a specific location along the gauge length of each sample, whereas the extent of cyclic softening response is represented with the use of Cyclic Softening Ratio (CSR) as defined by Höppel et al. in [24]. It must be pointed out that grain coarsening may not be the sole cause of the observed cyclic softening, general dynamic recovery within the microstructure is also believed to contribute to the observed cyclic softening response [24].
It is reported that the cyclic deformation response of lower purity metals after SPD processing varies depending on the impurity content and the applied cyclic plastic strain level. A transition from cyclic hardening response to cyclic softening response with increasing applied plastic strain amplitudes or increasing cyclic stress amplitudes can be observed in many of the cases with technical purity copper [40,41,42], and that of aluminum alloys [45,46,47,49,50,51]. It is worth mentioning that Kunz et al. [44] have reported that cyclic softening is observed only in strain controlled tests, whereas load controlled tests generally yield cyclic hardening or cyclic saturation response. However, the cyclic plastic strain imposed on to the samples are lower in many of the reported stress controlled tests [40,41,42] compared to that of the strain controlled tests [44]. As such, the observation of cyclic softening only in the case of strain controlled tests and cyclic hardening/saturation in the load controlled tests reported in Reference [44] may be simply a manifestation of the same transition from cyclic hardening to cyclic softening described above. It should be noted that in some cases for aluminum alloys, the cyclic softening response is preceded by a cyclic hardening response [47,50]. At the same time, Canadinc et al. [48] have observed only cyclic hardening followed by cyclic saturation for their aluminum-magnesium alloys even when subjected to high levels of cyclic plastic strain. Similar observation of cyclic hardening followed by cyclic saturation has also been reported for technical purity copper [39], titanium [52], and α-brass [55]. Conversely, Niendorf et al. [53,54] have reported cyclic softening response in their studies on ECAPed IF steel. A lack of grain coarsening has been noted in many of the above reports, especially in those that have only noted a minor or insignificant cyclic softening response [40,41,42,47,48,52,59]. However, grain coarsening has been reported in some cases of lower purity SPDed metals, especially those that have exhibited some extent of cyclic softening [44,51,58]. Although the extent of coarsening is commonly reported to be much lower than the case of high purity SPDed metals.
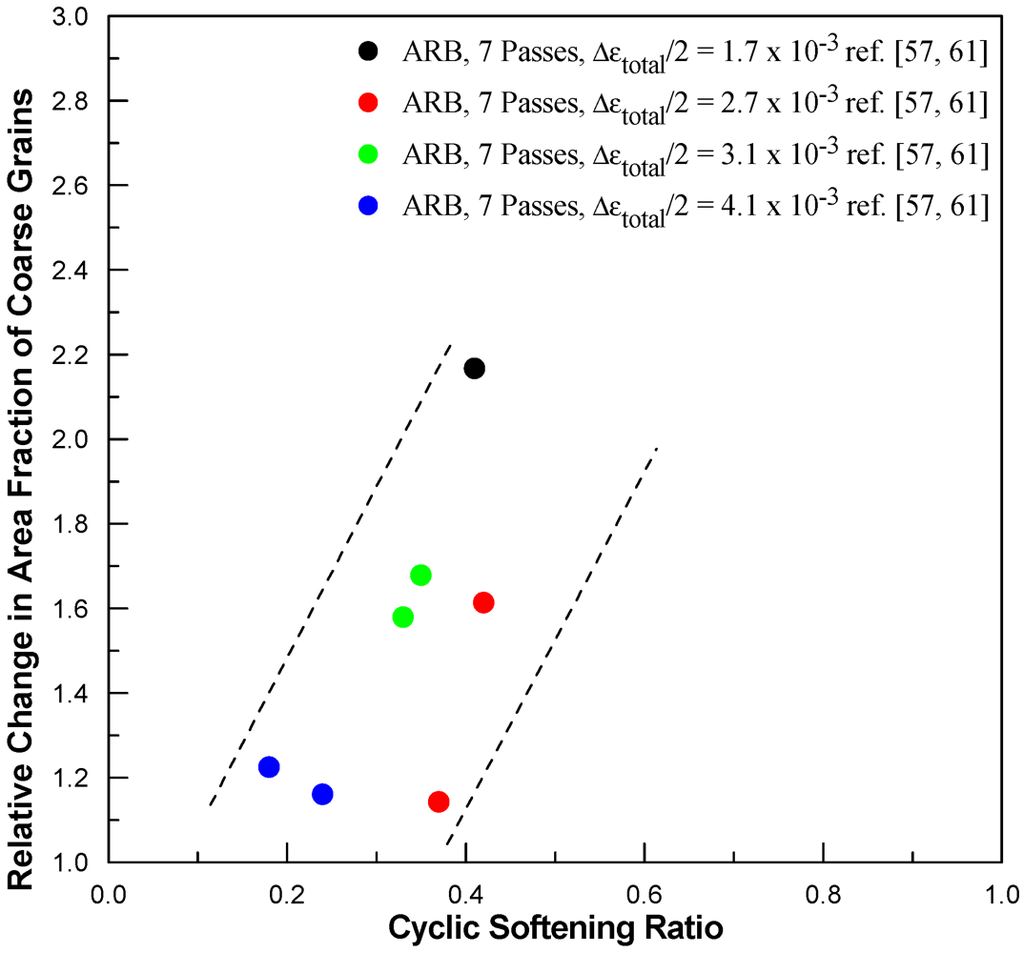
Figure 1.
A plot illustrating the correlation between the observed cyclic softening ratio according to [24] and the occurrence of grain coarsening upon cyclic loading of ARBed metals.
In addition to the observation of grain coarsening as a cyclic deformation mechanism, surface damages relating to shear banding have also been reported for SPDed metals in general [20,21,22,23,24,25,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,46,50,53,56,57,58,59]. The shear bands in the above listed reports are of a scale much larger than the grain size of the samples. In fact, early reports by Mughrabi and Höppel [62] and Höppel et al. [63] indicated the appearance of grain coarsening along the maximum shear stress direction in both commercially purified aluminum and high purity copper. Furukawa et al. [35] also reported similar observations of a band of coarsened grains along the plane of maximum shear stress in ECAPed high purity copper upon cyclic loading. Mughrabi and Höppel have suggested two possible mechanisms for the formation of large-scale shear bands with coarsened grains in their review [62]. One proposed mechanism in [62] is that a microstructure instability is created from the presence of a coarsened grain which then spreads out to form to observed band of coarsened grains. The second proposed mechanism in [62], catastrophic shear localization destroys the microstructure within the shear band due to a change in strain path, which is followed by the formation of coarsened grains within that region. In the case of high purity copper, the grain coarsening phenomenon discussed above has been specifically detected to be related to the shear bands, regardless of the fact that these bands were formed during material processing or during cyclic deformation, in ARBed pure copper [56,57].
In addition to all the aforementioned micro-activities on the materials’ response in cyclic deformation, as Mughrabi and Höppel further pointed out the purity of the metal, the cyclic loading mode, and the processing parameters all have clear effects on the resulting cyclic deformation responses [64]. A similar statement could be made from the current review, where the underlying factors that influence the cyclic deformation of SPDed metals will be discussed in the subsequent sections. Before these factors are presented and as a basis for analyzing them, the extent of the cyclic softening responses of selected UF grained metals after ECAP and ARB processing are first summarized and the results are given in Figure 2a,b, for the two types of materials respectively. Although UF grained copper of various compositions are used to illustrate the effect of composition, the applied plastic strain amplitudes, and the cyclic lifespan on the extent of cyclic softening in Figure 2, the trends shown can be extended to other SPDed metals. Each of the trends presented in Figure 2 will be systematically discussed in the following sections.
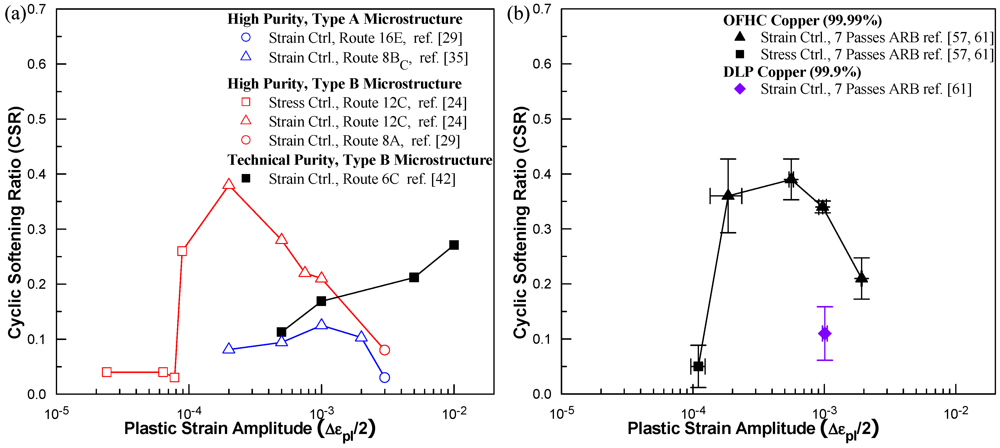
Figure 2.
The trend of cyclic ratio according to [24] with respect to the applied plastic strain amplitudes of: (a) ECAPed copper of different purity levels processed with various ECAP parameters; and (b) ARBed copper of different purity levels.
3. The Effect of Applied Cyclic Plastic Strain
The mechanism behind the phenomenon of grain coarsening upon cyclic deformation of SPDed metals is still unclear; however since the grain coarsening occurs upon cyclic deformation, it is likely that it is induced, or at least influenced, by the applied cyclic stress or strain. Consequently, the cyclic deformation response is expected to be influenced by the applied cyclic stress or strain, more importantly by the cyclic plastic strain. Such influence from the applied cyclic plastic strain is evidenced from the observed transition from cyclic hardening to cyclic softening with increasing applied cyclic plastic strain for SPDed technical purity copper samples upon cyclic deformation [40,41,42,44,45,46,47,49,50,51]. A similar dependence of the extent of cyclic softening response on the imposed cyclic plastic strain can be seen in Figure 2 for both ECAPed and ARBed high purity copper at low imposed plastic strain amplitudes (i.e., at εpl/2 < 2 × 10−4). Such a dependence of the cyclic softening response on the applied plastic strain amplitude has also been suggested in [24]. Considering the case of stress/strain induced grain coarsening, a large enough cyclic strain/stress must be applied in order to supply deformation energy high enough to overcome the activation energy needed for grain boundary motion. Following that, with increasing applied cyclic stress/strain the number of locations at which the above condition is satisfied increases thus increasing the total amount grain coarsening and hence the related cyclic softening as observed. On the other hand, this proportional relationship is reversed at high plastic strain amplitudes, and it has been first suggested that this reversal of trend is related to the kinetics of the grain coarsening phenomenon [24].
4. The Effect of Cyclic Lifespan
The trend of cyclic deformation behavior of SPDed metals, under a small applied cyclic plastic strain (i.e., at Δεpl/2 < 2 × 10−4), has been understood and attributed to the effect of the applied cyclic plastic strain above. However, the reversed trend of cyclic deformation behavior of SPDed metals under high plastic strain amplitudes (i.e., at Δεpl/2 > 2 × 10−4) remains to be discussed. This trend can be easily understood when a plot of CSRs versus the cyclic lifespan of each sample is employed, as shown in Figure 3. It is clear from Figure 3 that shorter cyclic lifespan is generally correlated to lower extent of cyclic softening, and vice versa. A similar statement could be made in the case of the extent of grain coarsening. The limited cyclic lifespan of the samples has clearly limited the extent of grain coarsening. The steeper trend of ARB copper compared to ECAPed copper in Figure 3 is due to the presence of a unique microstructural constituent, i.e., the large amount of pre-existing shear bands, see [56] for details. The presence of such constituent increases the quantity of strain localization sites and thus affects the extent of cyclic softening, as well it shortens the cyclic life span. As a matter of fact, grain coarsening phenomenon upon cyclic loading of SPDed metals is a manifestation of grain boundary migration processes. The operation of such process requires the satisfaction of the thermodynamic aspect, i.e., driving force and energy input to overcome the activation energy, and the kinetic aspect, i.e., given enough “time”. In the context of grain coarsening upon cyclic loading, “time” is equivalent to the number of cycles of cyclic loading, and the limited cyclic life span is equivalent to limiting the “time” for the process to occur. At the same time, shorter cyclic lifespan is generally found in the case of larger applied plastic strain amplitudes. As a result, the extent of cyclic softening response is reduced with increasing applied plastic strain amplitudes, or subdued by the short fatigue lifespan. This is believed to be the reason for the reversed trend at higher plastic strain amplitudes shown in Figure 2. A similar notion has been raised by Höppel et al. [24] to explain the reversing trend at higher plastic strain amplitudes as well.
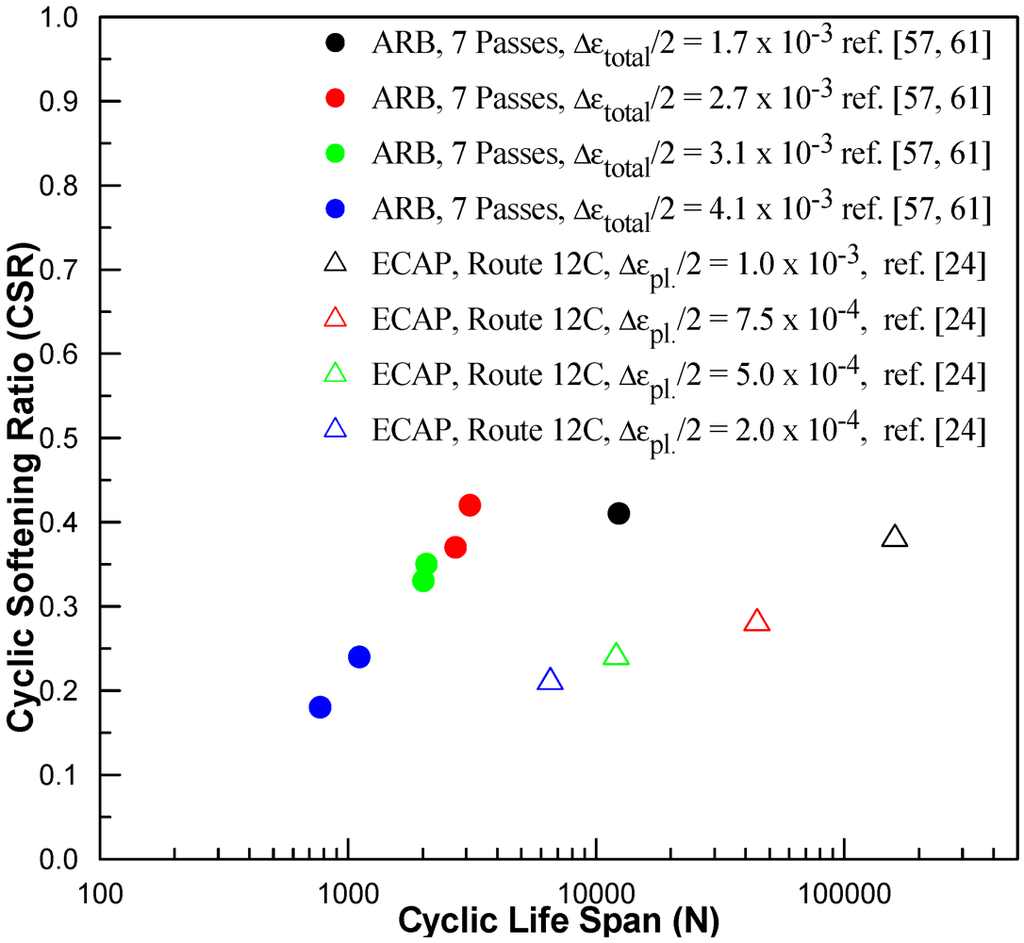
Figure 3.
A plot illustrating the correlation between the extent of the cyclic softening ratio according to [24] and the cyclic lifespan of ARBed and ECAPed OFHC copper.
To further elaborate the above analysis, the limitation imposed by short cyclic life span is demonstrated by comparing the extent of grain coarsening of fractured cyclic loading samples with that of samples with the cyclic lifespan extended by removing the surface damage at intervals of cyclic loading. Such comparison of overlays showing the coarse grain area fraction of two ARBed OFHC copper samples with similar initial microstructure cyclically strained at Δεtotal/2 = 1.7 × 10−3 is shown in Figure 4. However, the sample in Figure 4a has been cyclically strained until fracture, yet the sample in Figure 4b has had the surface damage removed periodically by ion milling, effectively extending the cyclic lifespan. Even under the same cyclic straining condition and with similar initial microstructure, the extent of grain coarsening upon cyclic loading is much higher for the sample shown in Figure 4b compared to that of Figure 4a. Although the thermodynamic aspect of the grain coarsening is clearly satisfied in both cases, the kinetic aspect is lacking due to the shorter cyclic lifespan for the sample shown in Figure 4a, i.e., no “time” for the further development of grain coarsening. Clearly, the cyclic lifespan has indeed limited the extent of grain coarsening and hence cyclic softening. Such relationship between the extent of grain coarsening and cyclic softening with regard to the cyclic lifespan can also be found for technical purity copper. In which case, massive grain coarsening could be found in the wake of the crack upon cyclic loading to 7 × 108 cycles [36], although this is not commonly reported in other reports on technical purity copper [45,46,47,48,49,50,51].
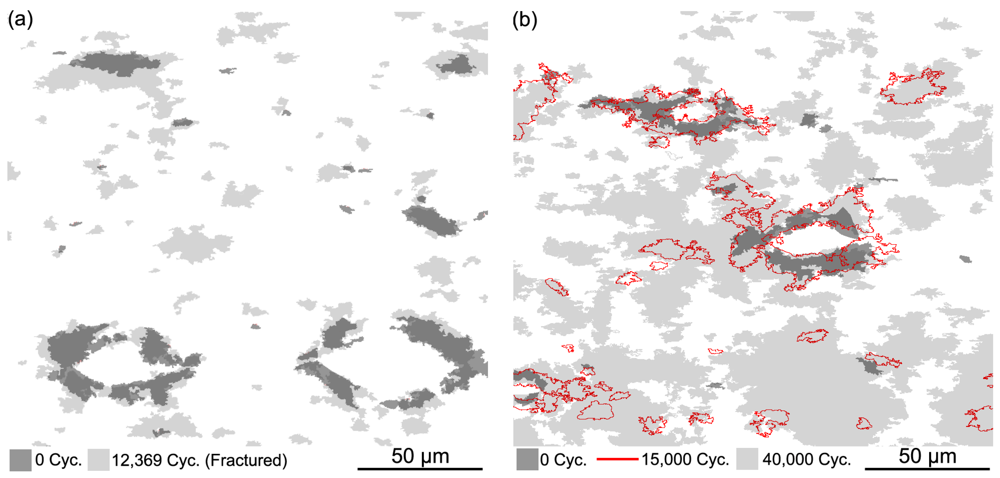
Figure 4.
Overlays of the development of the coarse grain constituent of two 7 passes ARBed copper samples with similar initial microstructure upon cyclic straining at Δεtotal/2 = 1.7 × 10−3. (a) Sample cyclically tested to fracture without any intervention; (b) Sample with surface damages removed by ion milling at various points along the cyclic lifespan such that the cyclic lifespan can be elongated significantly.
5. The Effect of Microstructure Stability
The UF and NC grained microstructure can be considered to be at a higher energy state compared to that of conventional large grain sized microstructure [65]. In addition, the severely deformed microstructure of SPDed metals may further increase the energy of the microstructure due to the further accrued deformation in the form of further increased dislocation density and more complicated dislocation structure. It is very likely that the high energy of the microstructure is one of the largest driving forces behind the grain coarsening phenomenon with the applied stress/strain providing the activation energy upon cyclic loading. Undoubtedly, the extent of grain coarsening is controlled by the stability of the microstructure. Following that, the microstructure stability will also affect the cyclic deformation response of the SPDed metals by affecting the extent of grain coarsening. Such a notion of cyclic stability has been contemplated in various reports on the cyclic deformation response of ECAPed metals, [37,48,49,52,55], and in ARBed metals [56,57].
In addition to the effect of processing technique, the stability of the microstructure is also highly dependent on the composition of the metals. The effect of composition on the microstructure stability and hence the cyclic response is clearly demonstrated by comparing the cyclic response of high purity copper and technical purity copper, as also demonstrated in Figure 2. The increased microstructure stability of technical purity copper as a result of the addition of trace elements has led to a lesser extent of grain coarsening upon cyclic loading at the same imposed plastic strain amplitudes. Consequently, the extent of the cyclic softening is also lowered in the case of the ECAPed technical purity copper shown in Figure 2a, and the same can be said for the ARBed DLP copper, as shown in Figure 2b. In some of the reports on technical copper, e.g., [38,39,40,41,43], the suppressed grain coarsening is often related to the observed cyclic saturation or even cyclic hardening response. Similar observation has been reported for SPDed aluminum alloy with 0.5% to 2% magnesium [48], commercial purity SPDed aluminum [50], and commercial purity SPDed titanium [52]. In fact, Höppel et al. [49] further reported a transition from cyclic softening to cyclic saturation with increasing magnesium content in aluminum from 0.5% to 2%. Furthermore, such a relationship between increasing additive concentrations and the decreasing of cyclic softening response is also clearly shown when comparing the CSRs of high purity copper, DLP copper, and technical purity copper, Figure 2. However, it must be mentioned that observation of cyclic softening has been reported also with alloys of higher alloying content, such as in the case of 5056 aluminum in [45], 6060 aluminum in [51], and the IF steel in [53,54], albeit softening response in these materials is seen to a lower extent than that of high purity SPDed metals. This trend is likely to be due to the different manner of incorporating the alloying addition into the matrix at the various concentrations as well as of the various different alloying elements, and its overall effectiveness of resisting grain boundary movement.
There are also other aspects of the microstructure that directly affect the stability of the microstructure. One of such is the geometry of the grains, which is a direct consequence of the processing parameters. Vinogradov and Hashimoto [65] have categorized the possible grain geometry from ECAP processing as type A and type B, for equiaxed grain geometry and elongated grain geometry, respectively. In combination with the observations by Iwahashi et al. [66] and Langdon [66,67,68], it is clear that routes Bc and E of the ECAP processing will yield a type A grain geometry whereas routes A and C will yield a type B grain geometry. Vinogradov and Hashimoto [65] have found that the different grain geometry has indeed affected the monotonic mechanical strength. Similarly, the different grain geometry is also expected to affect the stability of the microstructure during cyclic deformation. In fact, Agnew et al. [22] have presented calorimetry results showing the higher microstructure stability of type A grain geometry compared to that of type B grain geometry. Consequently, the extent of grain coarsening, hence cyclic softening, upon cyclic loading at the same imposed cyclic strain level is found to be lower for ECAPed high purity copper with type A grain geometry compared to that with type B grain geometry, also shown in Figure 2a. Furthermore, the influence from the difference in grain geometry is seemingly stronger than that resulting from the addition of trace amount of additives based on the CSRs plotted in Figure 2a. Although the present authors consider further studies will be needed to confirm the case of such observations, they may suggest that the trace quantity of additive is too low to have a significantly large influence on the microstructure stability.
The stage of development of the UF grain structure also plays a role in determining the stability of the microstructure. Such microstructure development includes the development of the grain boundaries upon SPD, i.e., the development of the initial low angle boundary network to a network that consists of mostly high angle grain boundaries with increasing SPD processing. This development process of the microstructure has been reported in [68] with increasing number of passes of ECAP, and in [69,70] with increasing number of passes of ARB. Indeed, Höppel et al. [49] have shown a transition from cyclic softening to cyclic saturation response upon cyclic loading of samples with increasing number of ECAP passes that further affects the development of the UF grain boundary structure. Finally, there are other mechanisms that may cause a decrease in the total energy of the microstructure, such as dynamic recovery or recrystallization process during processing, which may have a similar effect as the above case.
6. The Effects from Other Influencing Factors
Temperature: The cyclic deformation response has been reported to be influenced by the testing temperature as well [24,48]. The extent of cyclic softening is observed to increase when cyclic loading tests were performed at elevated temperatures [48]. On the other hand, the extent of cyclic softening is reported to lessen upon cyclic straining at −50 °C [24]. Alongside the lowered extent of cyclic softening response, the grain coarsening upon cyclic straining was reported to be much less pronounced in comparison to samples that were tested at room temperature as well [24]. Nevertheless, Höppel et al. [24] have noted that grain coarsening upon cyclic deformation also occurred even when testing at −50 °C. Clearly, grain coarsening in this case is indeed affected by the testing temperature but yet largely induced by the applied cyclic stress/strain. Such temperature dependence is likely the result of the dependence of the grain boundary mobility on the temperature. Consequently, such a temperature effect can be grouped with the influence of the microstructure stability.
Strain Rate: A minor dependence of the extent of cyclic softening on the cyclic strain rate was also reported [24,55]. The cyclic softening is reported to be less pronounced when cyclically deformed at higher strain rate [24]. Such effect is generally related to the enhanced strain rate sensitivity of UF grained metals as often reported [24,55,71,72]. Although no definitive trend could be concluded from these results, several speculations could be made. The enhanced strain rate sensitivity could affect the cyclic deformation response in two ways: Firstly, the sensitivity of the flow stress from the different strain rate could influence the cyclic plastic strain involved in each cycle; Secondly, the enhanced sensitivity could influence the cyclic life span of the samples due to the earlier occurrence of plastic instability within the sample.
7. Concluding Remarks
Up to date, the cyclic deformation responses of SPDed metals as available in the related literature are mixed, ranging from cyclic hardening to cyclic softening depending on various factors. These factors include the purity of the metal, the level of the imposed cyclic stress/strain, and the processing parameters. The effect from the above factors has been categorized into three fundamental influencing factors in this review.
The primary influencing factor is the microstructure stability of the initial microstructure. This includes the effects of the purity of the metals, the level of development of a UF grained microstructure, and the grain geometry of the final microstructure. The latter two are affected by the processing technique and the parameters used. In short, the above influence the cyclic deformation response by changing the driving force for the grain coarsening phenomenon.
The second influencing factor is the cyclic lifespan, which provides, or not, the satisfaction of the required kinetics for grain coarsening phenomenon. There are reports in which the thermodynamic driving force is in abundance but the short cycling time available limited the extent of grain coarsening, i.e., in the case of high applied plastic strain amplitudes for high purity copper.
Lastly, the applied cyclic plastic strain level is also an influencing factor. Such influence is based on changing the level of energy input for the grain coarsening phenomenon. The effects can be clearly seen from cyclic deformation of technical purity copper in which a transition from cyclic hardening to cyclic softening was reported with increasing imposed plastic strain. In the case of high purity metals, this effect is often overshadowed by the limitation by the cyclic life span of the sample and is only apparent at low imposed plastic strain amplitudes.
References
- Wang, N.; Wang, Z.; Aust, K.T.; Erb, U. Effect of grain size on mechanical properties of nanocrystalline materials. Acta Metall. Mater. 1995, 43, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, S. The Mechanism of the inverse hall-petch relation of nanocrystals. Scr. Mater. 2001, 44, 1483–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saada, G. Hall-Petch revisited. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 400–401, 146–149. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.T.; Langdon, T.G. Influence of grain size on deformation mechanisms: An extension to nanocrystalline materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 409, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, N.; Jung, K. Effects of grain size from millimeters to nanometers on the flow stress of metals and compounds. J. Electron. Mater. 2006, 35, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, V.M. Materials processing by simple shear. Mater. Sci. A 1995, 197, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Estrin, Y.; Horita, Z.; Langdon, T.G.; Zehetbauer, M.J.; Zhu, Y.T. Producing bulk ultrafine-grained materials by severe plastic deformation. JOM J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 2006, 58, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, Y.; Tsuji, N.; Utsunomiya, H.; Sakai, T.; Hong, R.G. Ultra-fine grained bulk aluminum produced by Accumulative Roll-Bonding (ARB) process. Scripta Mater. 1998, 39, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, Y.; Utsunomiya, H.; Tsuji, N.; Sakai, T. Novel ultra-high straining process for bulk materials—Development of the Accumulative Roll-Bonding (ARB) Process. Acta Mater. 1999, 47, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Karsilnikov, N.A.; Tsenev, N.K. Plastic deformation of alloys with submicron-grained structure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1991, 137, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Galeev, R.M.; Valiakhmetov, O.R.; Salishchev, G.A. Dynamic recrystallization of coarse-grained titanium alloy in the (α+β)-region. Russ. Metall. 1990, 4, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Korbel, A.; Richert, M. Formation of shear bands during cyclic deformation of aluminum. Acta Metall. 1985, 33, 1971–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Islamgaliev, R.K.; Alexandrov, I.V. Bulk nanostructured materials from severe plastic deformation. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2000, 45, 103–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, T.C.; Valiev, R.Z. The use of severe plastic deformation techniques in grain refinement. JOM J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 2004, 56, 64–77. [Google Scholar]
- Langdon, T.G. The processing of ultrafine-grained materials through the application of severe plastic deformation. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 3388–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, N.; Saito, Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Minamino, Y. ARB (Accumulative Roll-Bonding) and other new techniques to produce bulk ultrafine grained materials. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2003, 5, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azushima, A.; Kopp, R.; Korhonen, A.; Yang, D.Y.; Micari, F.; Lahoti, G.D.; Groche, P.; Yanagimoto, J.; Tsuji, N.; Rosochowski, A.; Yanagida, A. Severe Plastic Deformation (SPD) processes for metals. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2008, 57, 716–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazov, M.V.; Laird, C. Size effects of dislocation patterning in fatigued metals. Acta Metall. Mater. 1995, 43, 2849–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, E.; Klemm, R.; Hollag, L.; Holste, C.; Schell, N.; Natter, H.; Hempelmann, R. An approach to cyclic plasticity and deformation-induced structure changes of electrodeposited nickel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 390, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradov, A.; Kaneko, Y.; Kitagawa, K.; Hashimoto, S.; Stolyarov, V.; Valiev, R. Cyclic response of ultrafine-grained copper at constant plastic strain amplitude. Scr. Mater. 1997, 36, 1345–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnew, S.R.; Weertman, J.R. Cyclic softening of ultrafine grain copper. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 244, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Agnew, S.R.; Vinogradov, A.Yu.; Hashimoto, S.; Weertman, J. Overview of fatigue performance of Cu processed by severe plastic deformation. J. Electron. Mater. 1999, 28, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höppel, H.W.; Brunnbauer, M.; Mughrabi, H. Cyclic deformation behaviour of ultrafine grain size copper produced by equal channel angular extrusion. Munich, Germany, 25-28 September 2000; Werkstoffwoche-Partnerschaft GbR: Frankfurt, Germany, 2000; pp. 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Höppel, H.W.; Zhou, Z.M.; Mughrabi, H.; Valiev, R.Z. Microstructural study of the parameters governing coarsening and cyclic softening in fatigued ultrafine-grained copper. Philos. Mag. A 2002, 82, 1781–1794. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.D.; Wang, Z.G.; Jiang, C.B.; Li, G.Y.; Alexandrov, I.V.; Valiev, R.Z. The formation of PSB-like shear bands in cyclically deformed ultrafine grained copper processed by ECAP. Scr. Mater. 2003, 48, 1605–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.W.; Umakoshi, Y.; Wu, S.D.; Wang, Z.G.; Alexandrov, I.V.; Valiev, R.Z. Temperature effects on the fatigue behavior of ultrafine-grained copper produced by equal channel angular pressing. Phys. Stat. Sol. 2004, 201, R119–R122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.X.; Wang, S.C.; Wu, S.D.; Jiang, C.B.; Li, G.Y.; Li, S.X. On the stability of defects and grain size in ultrafine-grained copper during cyclic deformation and subsequent ageing at room temperature. Mater. Sci. Forum 2005, 475–479, 4055–4058. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.W.; Wu, S.D.; Wu, Y.; Yasuda, H.Y.; Umakoshi, Y. Temperature-dependent microstructures in fatigued ultrafine-grained copper produced by equal channel angular pressing. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2005, 7, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, H.J.; Gabor, P.; Gupta, N.; Karaman, I.; Haouaoui, M. Cyclic stress-strain response of ultrafine grained copper. Int. J. Fatigue 2006, 28, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, M.; Han, S.Z.; Yakushiji, T.; Lim, C.Y.; Kim, S.S. Formation process of shear bands and protrusions in ultrafine grained copper under cyclic stresses. Scr. Mater. 2006, 54, 2101–2106. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.Z.; Goto, M.; Lim, C.; Kim, C.J.; Kim, S. Fatigue behavior of nano-grained copper prepared by ECAP. J. Alloy. Comd. 2007, 434–435, 304–306. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.-W.; Jiang, Q.-W.; Ying, W.; Wang, Y.; Umakoshi, Y. Stress-amplitude-dependent deformation characteristics and microstructures of cyclically stressed ultrafine-grained copper. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, M.; Han, S.Z.; Yakushiji, T.; Kim, S.S.; Lim, C.Y. Fatigue strength and formation behavior of surface damage in ultrafine grained copper with different non-equilibrium microstructures. Int. J. Fatigue 2008, 30, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadinc, D.; Maier, H.J.; Haouaoui, M.; Karaman, I. On the cyclic stability of nanocrystalline copper obtained by powder consolidation at room temperature. Scr. Mater. 2008, 58, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, Y.; Fujii, T.; Onaka, S.; Kato, M. Cyclic deformation behaviour of ultra-fine grained copper produced by equal channel angular pressing. Mater. Trans. 2009, 50, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatibi, G.; Horky, J.; Weiss, B.; Zehetbauer, M.J. High cycle fatigue behavior of copper deformed by high pressure torsion. Int. J. Fatigue 2010, 32, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Du, Z.; Liu, X.; Kunz, L. Fatigue property and fatigue cracks of ultra-fine grained copper processed by equal-channel angular pressing. Mater. Sci. Forum 2011, 682, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadinc, D.; Niendorf, T.; Maier, H.J. A comprehensive evaluation of parameters governing the cyclic stability of ultrafine-grained FCC alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 6345–6355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradov, A.; Kaneko, Y.; Kitagawa, K.; Hashimoto, S.; Valiev, R. On the cyclic response of ultrafine-grained copper. Mater. Sci. Forum 1998, 269–272, 987–992. [Google Scholar]
- Kunz, L.; Lukáš, P.; Svoboda, M. Fatigue strength, microstructural stability and strain localization in ultrafine-grained copper. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 424, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukáš, P.; Kunz, L.; Svoboda, M. Effect of low temperature on fatigue life and cyclic stress-strain response of ultrafine-grained copper. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2007, 38A, 1910–1915. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.Z.; Wang, Q.J.; Zheng, M.S.; Li, J.D.; Huang, M.Q.; Jia, Q.M.; Zhu, J.W.; Kunz, L.; Buksa, M. Effect of low temperature on fatigue life and cyclic stress-strain response of ultrafine-grained copper. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 475, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, L.; Lukáš, P.; Pantelejev, L.; Man, O. Stability of microstructure of ultrafine-grained copper under fatigue and thermal exposition. Strain 2010, 47, 476–482. [Google Scholar]
- Kunz, L.; Lukáš, P.; Pantelejev, L.; Man, O. Stability of ultrafine-grained structure of copper under fatigue loading. Proc. Eng. 2011, 10, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patlan, V.; Higashi, K.; Kitagawa, K.; Vinogradov, A.; Kawazoe, M. Cyclic response of fine grain 5056 Al-Mg alloy processed by equal-channel angular pressing. Cyclic response of fine grain 5056 Al-Mg alloy processed by equal-channel angular pressing 2001, 319–321, 587–591. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Wu, S.D.; Li, Y.J.; Liu, S.M.; Wang, Z.G. Cyclic deformation and fatigue properties of Al-0.7 wt.% Cu alloy produced by equal channel angular pressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 412, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.K.; Kao, W.P.; Lui, J.T.; Chang, C.P.; Kao, P.W. Cyclic deformation of ultrafine-grained aluminum. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 715–725. [Google Scholar]
- Canadinc, D.; Maier, H.J.; Gabor, P.; May, J. On the cyclic deformation response of ultrafine-grained Al-Mg alloys at elevated temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 496, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höppel, H.W.; May, J.; Göken, M. Cyclic deformation behavior and fatigue lives of ultrafine-grained Aluminum-Magnesium alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum 2008, 584–586, 840–845. [Google Scholar]
- May, J.; Amberger, D.; Dinkel, M.; Höppel, H.W. Monotonic and cyclic deformation behavior of ultrafine-grained aluminum. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 483–484, 481–484. [Google Scholar]
- Hockauf, K.; Niendorf, T.; Wagner, S.; Halle, S.; Meyer, L.W. Cyclic behavior and microstructural stability of ultrafine-grained AA6060 under strain-controlled fatigue. Proc. Eng. 2010, 2, 2199–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradov, A.Yu.; Stolyarov, V.V.; Hashimoto, S.; Valiev, R.Z. Cyclic behavior of ultrafine-grain titanium produced by severe plastic deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 318, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niendorf, T.; Canadinc, D.; Maier, H.J.; Karaman, I. On the microstructural stability of ultrafine-grained interstitial-free steel under cyclic loading. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2007, 38A, 1946–1955. [Google Scholar]
- Niendorf, T.; Maier, H.J.; Canadinc, D.; Karaman, I. On the cyclic stability and fatigue performance of ultrafine-grained interstitial-free steel under mean stress. Key Eng. Mater. 2008, 378–379, 39–52. [Google Scholar]
- Höppel, H.W. Mechanical Properites of ultrafine grained metals under cyclic and monotonic loads: An overview. Mater. Sci. Forum 2006, 503–504, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, C.C.F.; Wang, Z. Cyclic deformation behavior of ultra-fine grained copper processed by accumulative roll-bonding. Proc. Eng. 2010, 2, 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Kwan, C.C.F.; Wang, Z. A composite nature of cyclic strain accommodation mechanisms of accumulative roll bonding (ARB) processed Cu sheet materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 2042–2048. [Google Scholar]
- Malekjani, S.; Hodgson, P.D.; Cizek, P.; Hilditch, T.B. Cyclic deformation response of ultrafine pure Al. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 5358–5367. [Google Scholar]
- Malekjani, S.; Hodgson, P.D.; Cizek, P.; Sabirov, I.; Hilditch, T.B. Cyclic deformation response of UFG 2024 Al alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 2011, 33, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S. Fatigue of Materials; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kwan, C.C.F.; Wang, Z. ARBed copper data. University of Toronto: Toronto, Canada, 2011; Unpublished work. [Google Scholar]
- Mughrabi, H.; Höppel, H.W. Cyclic deformation and fatigue properties of ultrafine grain size materials: current status and some criteria for improvement of the fatigue resistance. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 2001, 634, B2.1.1–B2.1.12. [Google Scholar]
- Höppel, H.W.; Xu, C.; Kautz, M.; Barta-Shreiba, N.; Langdon, T.G.; Mughrabi, H. Cyclic deformation behaviour and possibilities for enhancing the fatigue properties of ultrafine-grained metals. Vienna, Austria, 9–13 December; Zehetbauer, M.J., Valiev, R.Z., Eds.; Weinheim/Wiley VCG: New York, NY, USA; pp. 667–683.
- Mughrabi, H.; Höppel, H.W. Cyclic deformation and fatigue properties of very fine-grained metals and alloys. Int. J. Fatigue 2010, 32, 1413–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradov, A.; Hashimoto, S. Multiscale phenomena in fatigue of ultra-fine grain materials—An Overview. Mater. Trans. 2001, 42, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwahashi, Y.; Horita, Z.; Nemoto, M.; Langdon, T.G. The process of grain refinement in equal-channel angular pressing. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 3317–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langdon, T.G. The processing of ultrafine-grained materials through the application of severe plastic deformation. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 3388–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langdon, T.G. The principles of grain refinement in equal-channel angular pressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 462, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Lee, T.-O.; Shin, D.H. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of ultrafine grained commercially pure 1100 aluminum alloy processed by accumulative roll-bonding (ARB). Mater. Sci. Forum 2004, 449–452, 625–628. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Tsuji, N.; Hansen, N.; Minamino, Y. Microstructual evolution during accumulative roll-bonding of commercial purity aluminum. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 340, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; Ma, E. Strain hardening, strain rate sensitivity, and ductility of nanostructured metals. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Höppel, H.W; May, J.; Göken, M. Enhanced strength and ductility in ultrafine-grained aluminum produced by accumulative roll bonding. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).