Heterogenous Grain Nucleation in Al-Si Alloys: Types of Nucleant Inoculation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Determining the effect of different master alloys (Al-10%Ti, Al-5%Ti-1%B, and Al-4%B) on the grain size and on the morphology of the α-Al phase by varying the holding times before casting (30 min, 60 min, and 90 min).
- Studying the consequences of the addition of grain refiners (Al-10%Ti, Al-5%Ti-1%B, and Al-%B) in small quantities on grain refining using the A390.1 alloy.
- Identifying the effect of the interaction between the Sr modifier and the grain refiner (Al-10Ti, Al-5Ti-1B, and Al-4B), the interaction between silicon and titanium, and their competition in affecting the morphology of the eutectic silicon, on the grain size, and on the shape of the α-Al dendritic phase.
- Investigating the Si poisoning phenomenon.
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Results
3.1.1. Thermal Analysis
3.1.2. Ti-Si Interaction
3.1.3. Influence of Combined Sr and Grain Refiner Treatment on Grain Size
4. Discussion
4.1. Silicon Poisoning Phenomenon
4.2. Mechanism for Improving Dendrite Growth Rate
4.3. Ternary Aluminide Mechanism
4.4. Surface Tension Mechanism
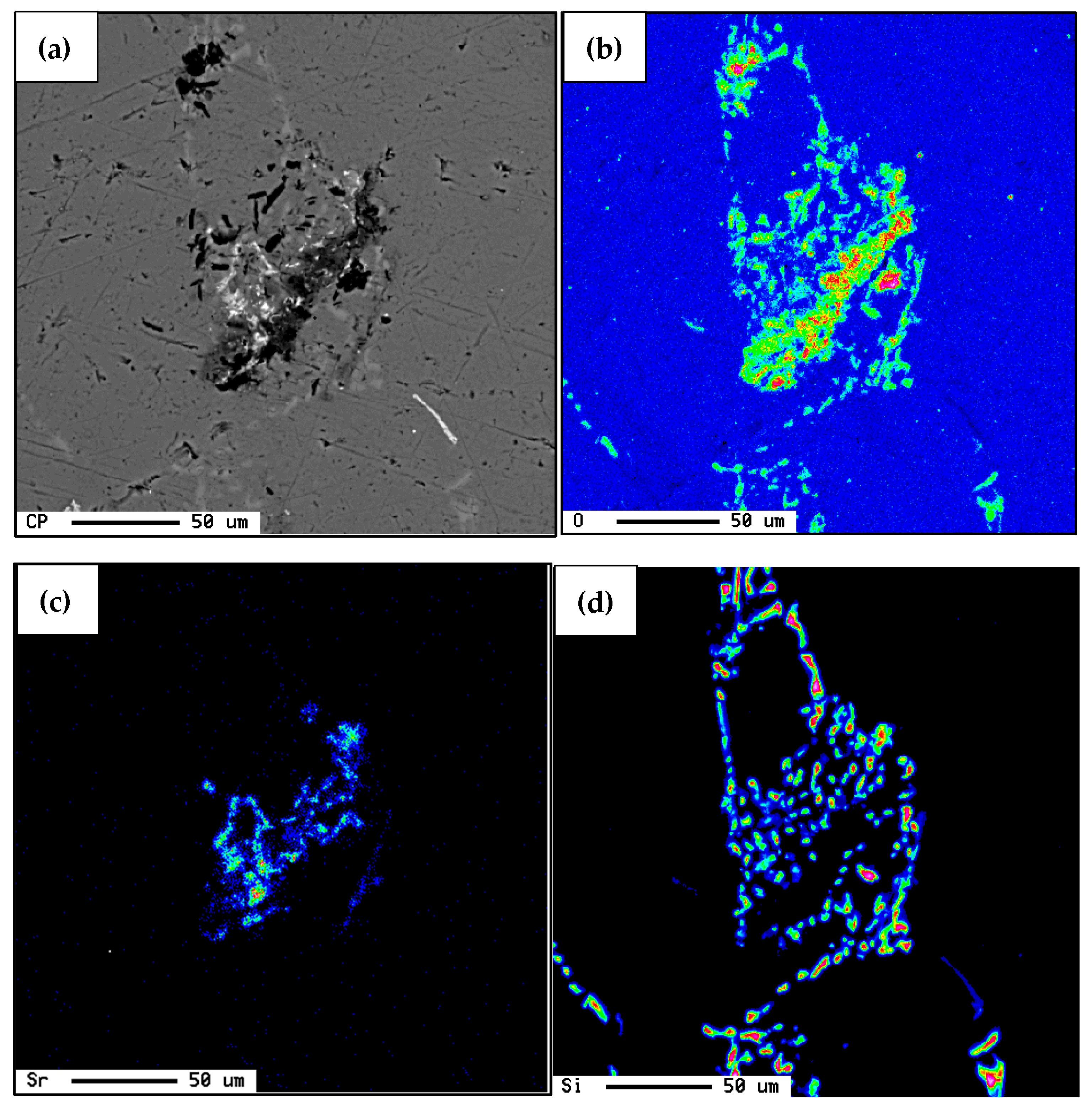
4.5. Mechanism of Silicide Segregation
5. Conclusions
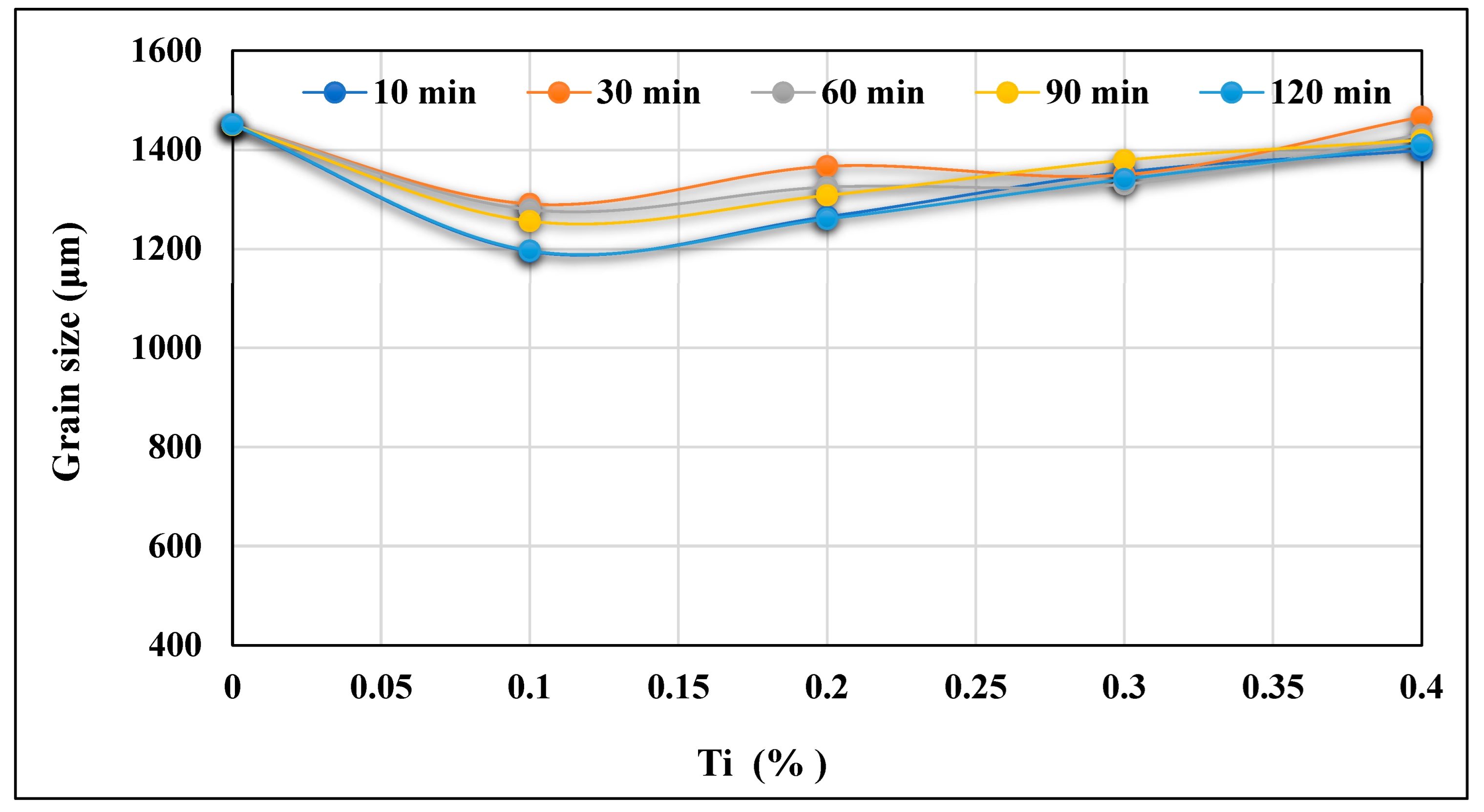
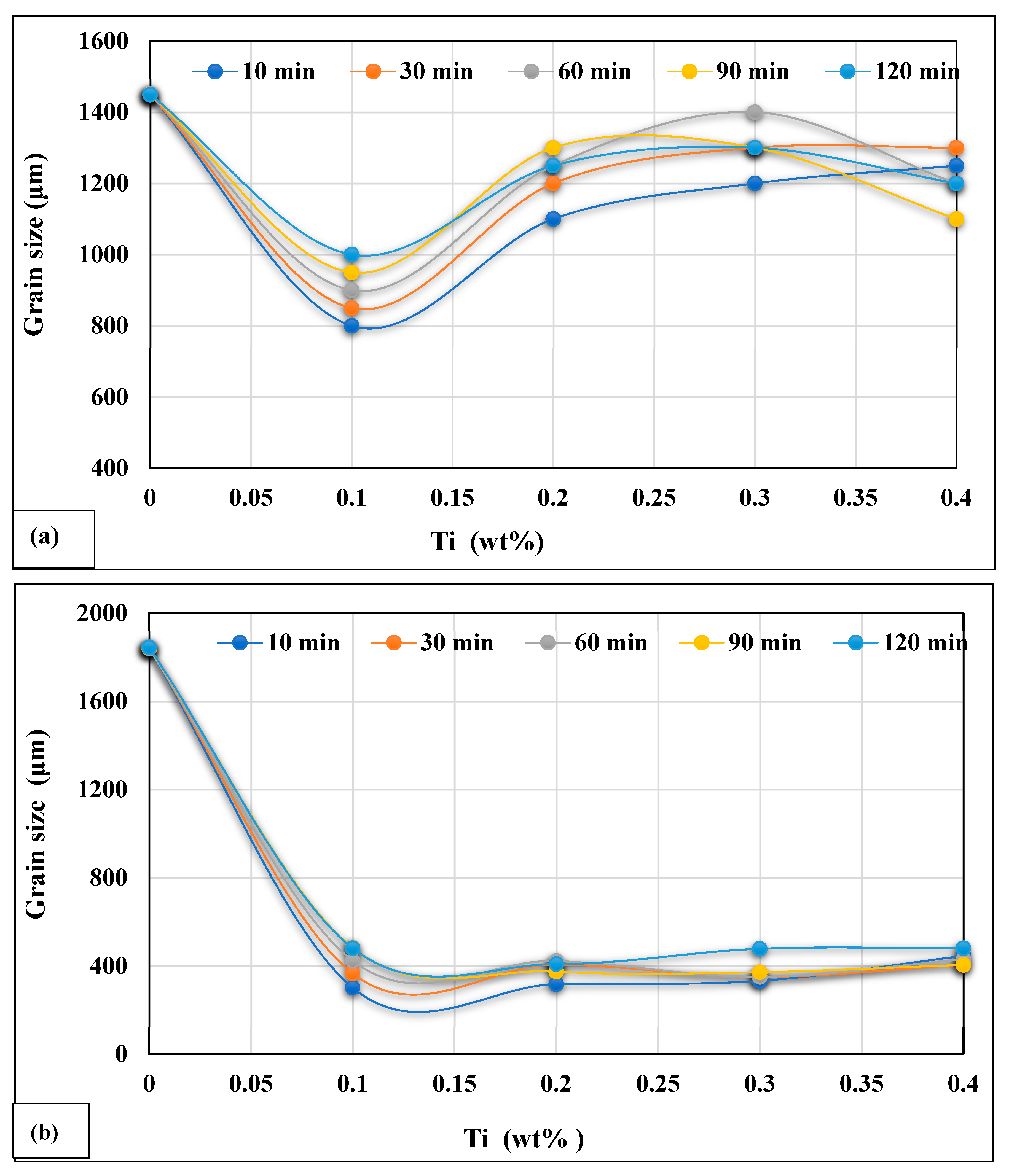
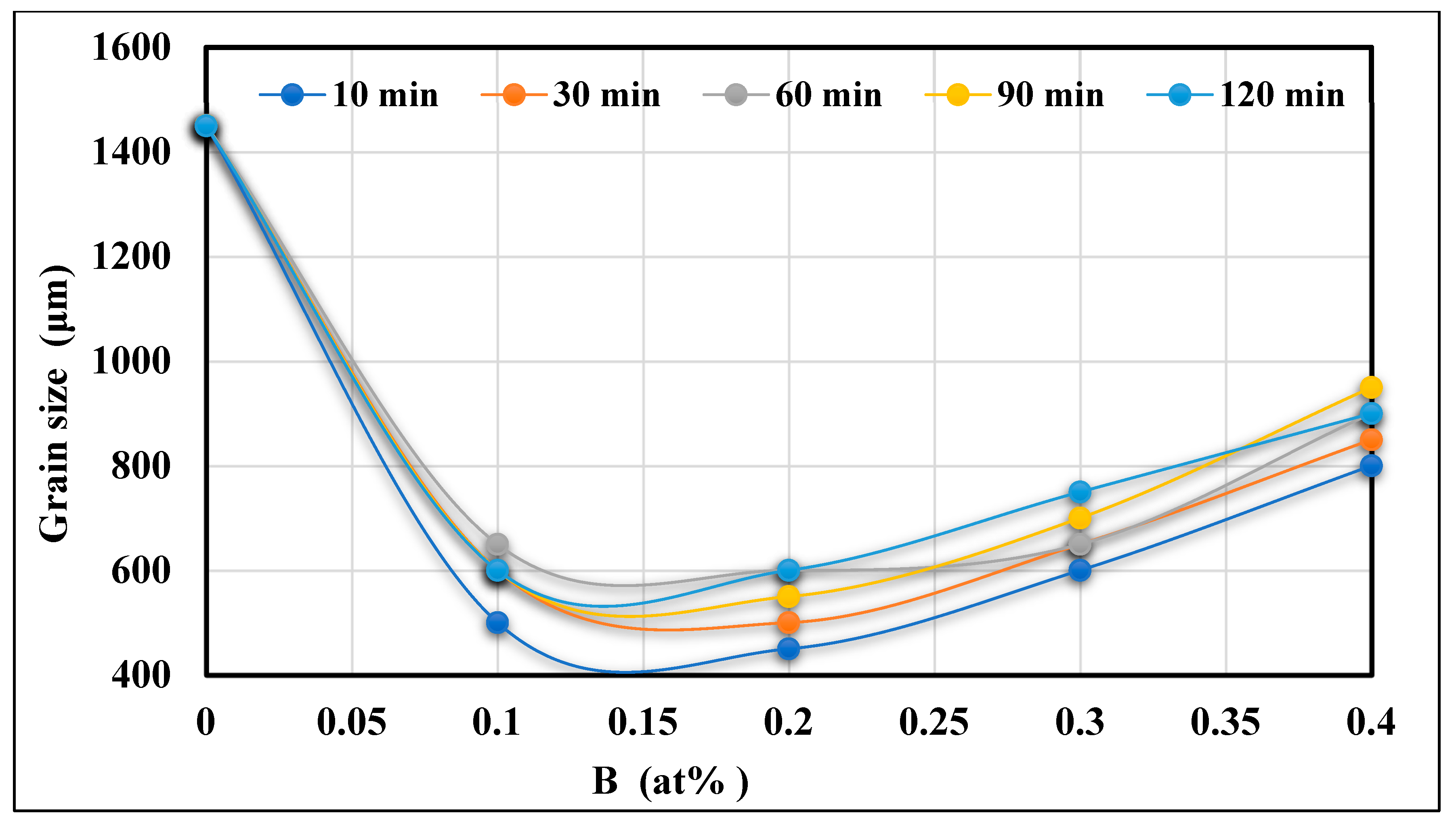
- The same addition of Ti in the hypereutectic alloy A390.1, cast after 10 min, reduces its initial grain size (varying from 1450 to 1600 µm) to approximately 1150 µm, equivalent to a percentage reduction of almost 20% to 30%. This reduction is followed by a slight increase depending on the progressive additions of Ti and the time the liquid bath is maintained.
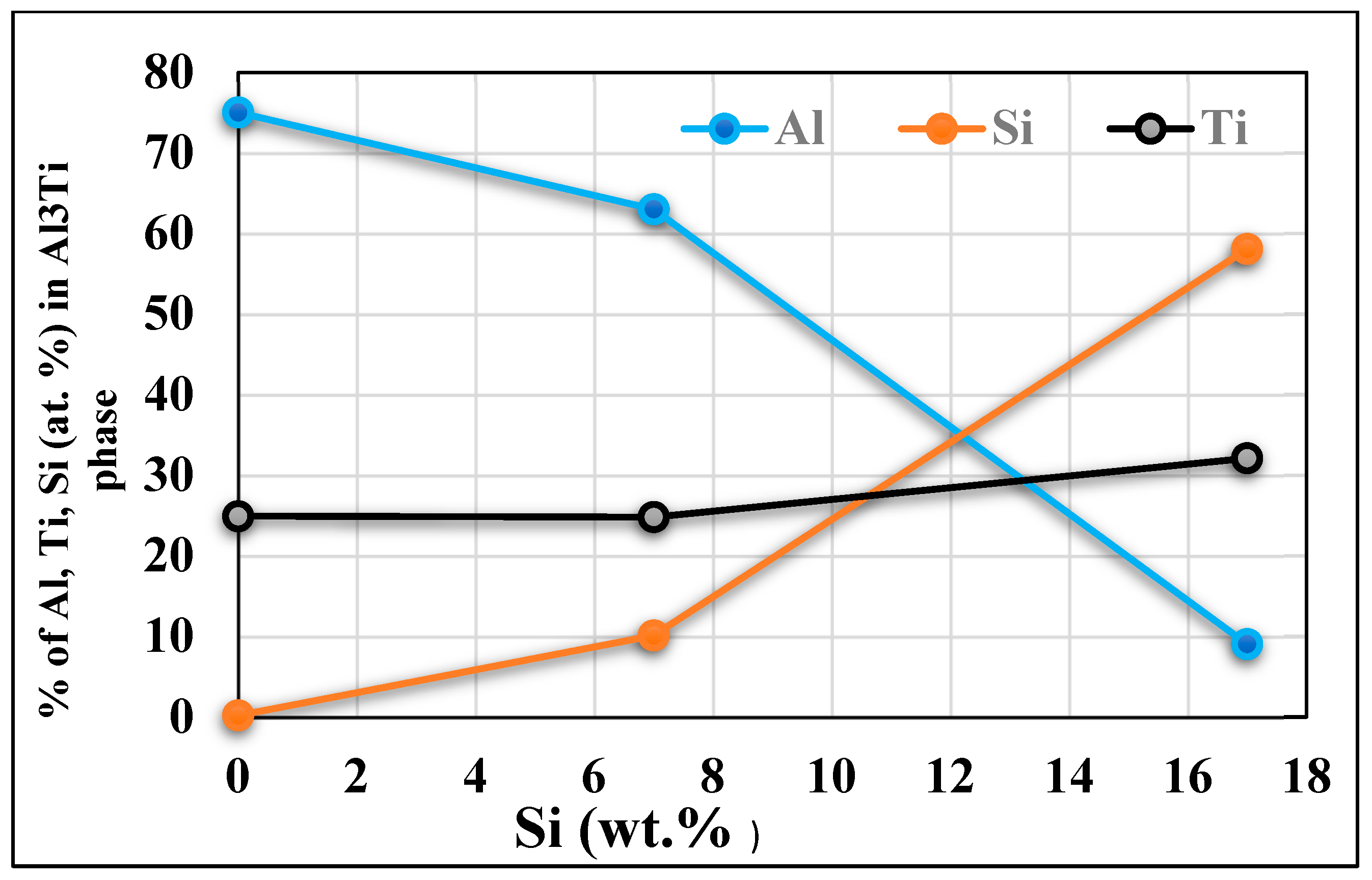
- Titinum addition to hypereutectic alloys results in the conversion of a good percentage of Al3Ti intermetallics into an (Al,Si)2Ti type form containing only 9 at% Al.
- The new phase (Al,Si)2Ti influences the degree of nucleation of the dendritic phase and therefore decreases the degree of grain refinement. This phase of titanium and aluminum disilicide tends to form more when the liquid metal is maintained for long periods since its surface fraction increases remarkably as a function of the holding time of the liquid bath.
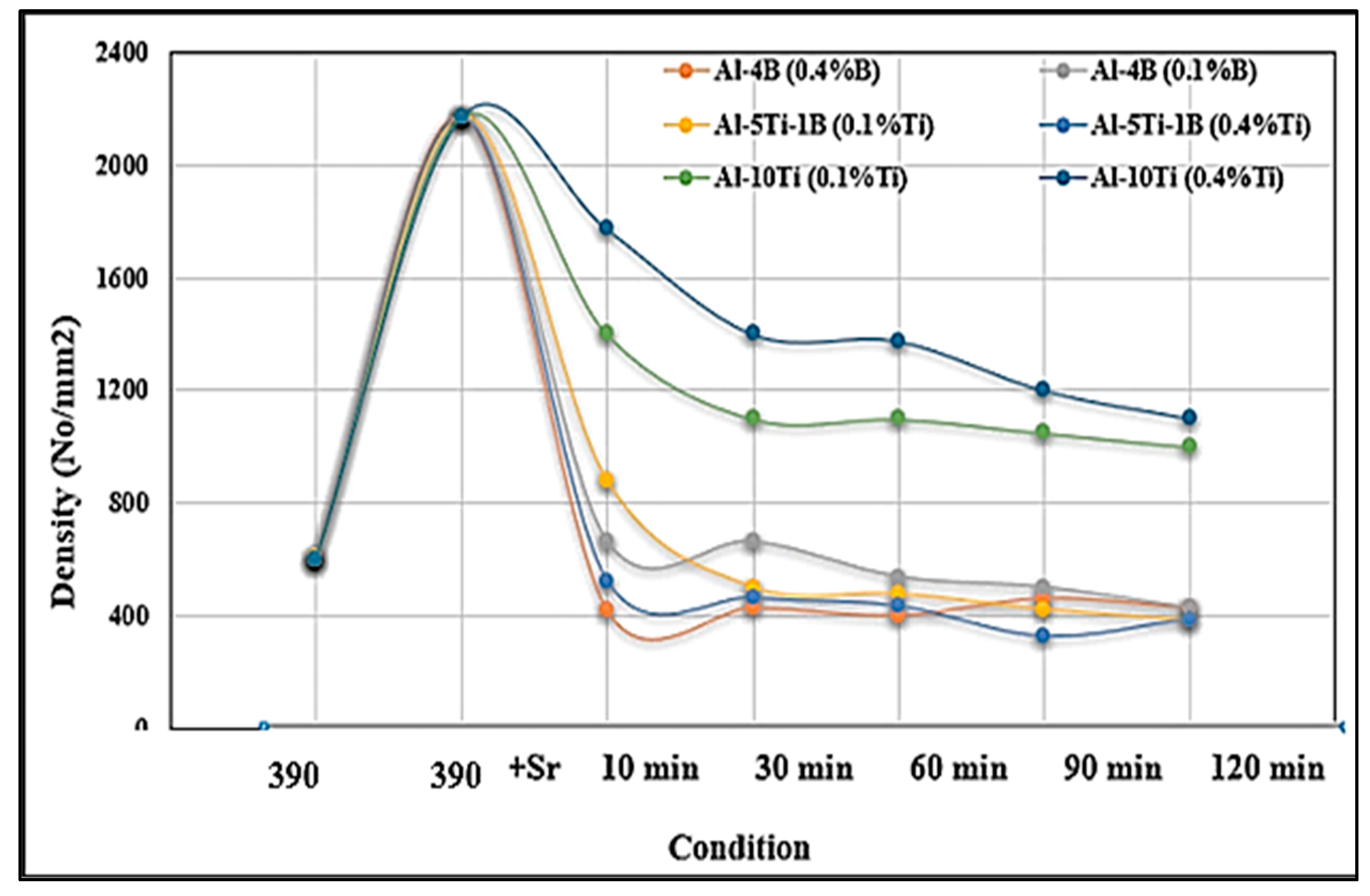
- The affinity between titanium and boron is stronger than the affinity between boron and strontium. All borides (AlB2, SrB6, and TiB2) have been found to be strong grain refiners leading to about an 80% reduction in the size of the original grains.
- The formation of SrB6 results in the degradation of the Si-modification process.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Majumder, A.; Chatterjee, D.; Nandy, S. On the primary silicon precipitation during the eutectic solidification of Al-Si alloys. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 31, 075004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wenner, S.; Yang, B.; Milkereit, B.; Broer, J.; Springer, A.; Schick, C.; Keßler, O. Rapid solidification of Al-Si alloys using differential fast scanning calorimetry. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 965, 171346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noga, P.; Skrzekut, T.; Wędrychowicz, M. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al-Si Alloys Produced by Rapid Solidification and Hot Extrusion. Materials 2023, 16, 5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulin, I.; Donik, C.; Cvahte, P.; Godec, M. Bimodal Microstructure Obtained by Rapid Solidification to Improve the Mechanical and Corrosion Properties of Aluminum Alloys at Elevated Temperature. Metals 2021, 11, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Park, Y.; Lee, Y. A Novel Approach to Investigate the Superheating Grain Refinement Process of Aluminum-Bearing Magnesium Alloys Using Rapid Solidification Process. Materials 2023, 16, 4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Xiang, Z.; Ma, X.; Huang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Shi, G.; Chen, Z. Investigation of Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Ultra-High Strength Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy Prepared by Rapid Solidification and Hot Extrusion. Metals 2023, 13, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaieb, O.; Olufayo, O.A.; Songmene, V.; Jahazi, M. Investigation on Surface Quality of a Rapidly Solidified Al–50%Si Alloy Component for Deep-Space Applications. Materials 2022, 13, 3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okugawa, M.; Furushiro, Y.; Koizumi, Y. Effect of Rapid Heating and Cooling Conditions on Microstructure Formation in Powder Bed Fusion of Al-Si Hypoeutectic Alloy: A Phase-Field Study. Materials 2022, 15, 6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Yang, B.; Milkereit, B.; Liu, D.; Spronger, A.; Rettenmayr, M.; Schick, C.; Keßler, O. Nucleation Behavior of a Single Al-20Si Particle Rapidly Solidified in a Fast Scanning Calorimeter. Materials 2021, 14, 2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerland, S.; Raatz, A. Adhesive Bonding of an Aluminum Alloy with and without an Oxide Layer in Atmospheres with Different Oxygen Contents. Appl. Sci. 2022, 13, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzoni, L.; Babu, N.H. Engineering the heterogeneous nuclei in Al-Si alloys for solidification control. Appl. Mater. Today 2016, 5, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzoni, L.; Hari Babu, N. Efficacy of Borides in Grain Refining Al-Si Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2019, 50, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, I.; Hellawell, A. A Simple Model for Grain Refinement During Solidification. Acta Metall. 1975, 23, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunitha, K.; Gurusami, K. Study of Al-Si alloys grain refinement by inoculation. Mater. Today 2021, 43, 1825–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Luo, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Li, Q. Enhanced grain refinement of Al-Si alloys by novel Al-V-B refiners. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 94, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumley, R. Fundamentals of Aluminium Metallurgy: Production, Processing, and Applications; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, C.M.; Zhou, L.; Hashimoto, T.; Zhou, X.; Ramasse, Q.M.; Fan, Z. Mechanism for Zr poisoning of Al-Ti-B based grain refiners. Acta Mater. 2019, 164, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perepezko, J.E.; LeBeau, S.L. Nucleation of Al During Solidification. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium “Al-Transformation Technology and Applications”, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 24–24 August 1981; pp. 309–346. [Google Scholar]
- Guzowski, M.M.; Sigworth, G.K.; Sentner, D.A. The role of boron in the grain refinement of aluminum with titanium. Metall. Trans. A 1987, 18, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, M.; StJohn, D.H. Grain refinement of aluminum alloys: Part I. The nucleant and solute paradigms—A review of the literature. Metall. Mater.Trans. A 1999, 30, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.P.; Pearson, J. Factors affecting grain refinement of aluminium using Ti and B Additives. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1976, 7, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StJohn, D.H.; Hogan, L.M. Al3Ti and the grain refinement of aluminum. J. Aust. Inst. Metals 1977, 22, 160–166. [Google Scholar]
- Easton, M.; StJohn, D. An analysis of the relationship between grain size, solute content, and the potency and number density of nucleant particles. Metall. Trans. A 2005, 36, 1911–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.L.; Cooper, P.S.; Meredith, M.W.; Schneider, W.; Schumacher, P.; Spittle, J.A.; Tronche, A. Grain refinement of aluminium alloys by inoculation. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2003, 5, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, M.E.J.; Fisher, P. Aluminum Technology; The Institute of Metals: London, UK, 1986; p. 117. [Google Scholar]
- Greer, A.L.; Bunn, A.M.; Tronche, A.; Evans, P.V.; Bristow, D.J. Modelling of inoculation of metallic melts: Application to grain refinement of aluminium by Al–Ti–B. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 2823–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quested, T.E.; Greer, A.L. The effect of the size distribution of inoculant particles on as-cast grain size in aluminium alloys. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 3859–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, B.S.; Kori, S.A.; Chakraborty, M. Grain refinement of aluminium and its alloys by heterogeneous nucleation and alloying. Int. Mater. Rev. 2002, 47, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.S.; Wang, C.; You, J.; Qiu, D.; Gao, Y.; Xu, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, H.Y. Substantial grain refinement of Al-Mn-Si alloys mediated by collaborative effect of Al-5Ti-1B refiner and sub-rapid solidification. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 187, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, N.; van Dijk, N.H.; Hansen, T.; Katgerman, L.; Kearley, G.J. The role of solute titanium and TiB2 particles in the liquid—Solid phase transformation of aluminum alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 386, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, E.; Tahiri, H.; Samuel, A.M.; Songmene, V.; Samuel, F.H. A Review on Fundamentals of Grain Refining of Al-Si Cast Alloys. Recent Advancements in Aluminum Alloys; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahiri, H.; Samuel, A.M.; Doty, H.W.; Valtierra, S.; Samuel, F.H. Effect of Sr–Grain Refiner–Si Interactions on the Microstructure Characteristics of Al–Si Hypereutectic Alloys. Int. J. Met. 2018, 12, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafisi, S.; Ghomashchi, R. Grain refining of conventional and semi-solid A356 Al–Si alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2006, 174, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Ji, S. Si poisoning and promotion on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al–Si–Mg cast alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 7778–7792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, M.A.; StJohn, D.H. A model of grain refinement incorporating alloy constitution and potency of heterogeneous nucleant particles. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 1867–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; Cao, P.; Easton, M.A.; McDonald, S.D.; StJohn, D.H. An analytical model for constitutional supercooling-driven grain formation and grain size prediction. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 3262–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, H.; Fan, Z. Effects of solute content on grain refinement in an isothermal melt. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 2704–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StJohn, D.H.; Qian, M.; Easton, M.A.; Cao, P. The Interdependence Theory: The relationship between grain formation and nucleant selection. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 4907–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, P.S.; Samuel, F.H.; Gruzleski, J.E. Experimental study on pore nucleation by inclusions in aluminum castings. Am. Foundrymen’s Soc. 1995, 99, 555–564. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Ye, C.Y.; Shen, Y.P.; Chang, W.; StJohn, D.H.; Wang, G.; Zhai, Q.J. Grain refinement of hypoeutectic Al-7wt.%Si alloy induced by an Al–V–B master alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 812, 152022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadendla, H.B.; Nowak, M.; Bolzoni, L. Grain Refiner for Al-Si Alloys. In Light Metals 2013; The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series; Sadler, B.A., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, B.; Li, Q. Novel Al-Ti-Nb-B grain refiners with superior efficiency for Al-Si alloys. Scr. Mater. 2020, 187, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafisi, S.; Ghomashchi, R. Boron-based refiners: Implications in conventional casting of Al–Si alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 452, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Okumura, A. Effects of TiC, TaC, WC, TaC-WC, NbC and VC on Grain Refining of Pure Aluminum and Its Alloys. J. Jpn. Inst. Light Met. 1970, 20, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, I.G.; Dennis, J.M.; Hellawell, A. The Nucleation of Aluminum Grains in Alloys of Aluminum with Titanium and Boron. Metall. Trans. 1970, 1, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.L.; Cantor, B. The Effect of Dopants on the Heterogeneous Nucleation of the Solidification of Cd and Pb Particles Embedded in an Al Matrix. Acta Metall. Mater. 1992, 40, 2951–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glicksman, M.E.; Childs, W.J. Nucleation Catalysis in Supercooled Liquid Tin. Acta Metall. 1962, 10, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, D.A.; Easterling, E. Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1992; pp. 192–197. [Google Scholar]
- Tøndel, P.A.; Arnberg, L. Grain refinement of an Al-10%Si alloy by Ti-additions. In Proceedings of the The 3rd International Conference on Aluminium Alloys, Yokohama, Japan, 5–9 September 2010; pp. 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Birol, Y. The effect of holding conditions in the conventional halide salt process on the performance of Al–Ti–B grain refiner alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 427, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Luo, W. Effects of grain refinement on the rheological behaviors of semisolid hypoeutectic Al–Si alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2007, 104, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Zhao, X.; Gao, A.; Li, R.; Chen, W.; Gao, M.; Liang, S.; Li, H. Effect of Si Content on the Morphology Evolution of the Si Primary Dendrites in Al-Si Alloy Solvent Refining Process. Silicon 2022, 14, 4501–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Du, Q.; Wu, G.; Dan, W.; Hu, W.; Zhang, J. The role of Ti and Si in the nucleation of α-Al during hot dip coating of steel with Al–43.4wt.%Zn–1.6wt.%Si alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 299, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondolfo, L.F.; Barlock, J.G. Effect of superheating on structure of some aluminum alloys. Metall. Trans. B Décembre 1975, 6B, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.A.; Wang, H.; StJohn, D.H.; Bainbridge, I.F. Anomalous grain coarsening behaviour in grain-refined aluminium alloys cast using low superheat. In Light Metals; Angier, J., Ed.; TMS: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2001; pp. 935–941. [Google Scholar]
- Bäckerud, L.; Chai, G.; Tamminen, J. Solidification Characteristics of Aluminium Alloys, Vol. 2: Foundry Alloys; AFS/Skanaluminium: Des Plaines, IL, USA, 1990; pp. 71–84. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Xue, C.; Wang, S. Boosting the grain refinement of commercial Al alloys by compound addition of Sc. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 1774–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spittle, J.A.; Keeble, J.M.; Meshhedani, A.L. The grain refinement of Al-Si foundry alloys. TMS Light Met. 1997, 1997, 795–800. [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth, G.K.; Guzowski, M.M. Grain refining of hypoeutectic Al-Si alloys. AFS Trans. 1985, 93, 907–912. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, P.; McKay, B. Solidification of Aluminum Alloys; Chu, G., Douglas, A., Granger, H.Q., Eds.; TMS: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Que, Z.; Hashimoto, T.; Zhou, X.; Fan, Z. Mechanism for Si Poisoning of Al-Ti-B Grain Refiners in Al Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 5743–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kori, S.A.; Murty, B.S.; Chakraborty, M. Development of an efficient grain refiner for Al-7Si alloy and its modification with strontium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 283, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, P.; Hardman, A.; Boot, D.; Burhop, E. Characterisation of a new generation of grain refiners for the foundry industry. In Light Metals; Crepeau, P.N., Ed.; TMS: San Diego, CA, USA, 2003; pp. 923–928. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.; Luo, Z.; An, X.; Liao, X.; Li, J.; Sha, G. Composition-dependent dynamic precipitation and grain refinement in Al-Si system under high-pressure torsion. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 68, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massalski, T.B.; Okamoto, H.; Subramanian, P.R.; Kacprzak, L. (Eds.) Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, 2nd ed.; ASM International: Almere, The Netherlands, 1990; p. 540. [Google Scholar]
- Gwalani, B.; Fu, W.; Olszta, M.; Silverstein, J.; Yadav, D.R.; Manimunda, P.; Guzman, A.; Xie, K.; Rohatgi, A.; Mathaudhu, S.; et al. Lattice misorientation evolution and grain refinement in Al-Si alloys under high-strain shear deformation. Materialia 2021, 18, 101146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Taylor, J.A.; Zhang, M.X.; Kelly, P.M. A mechanism for the poisoning effect of silicon on the grain refinement of Al–Si alloys. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Sun, Y.S.E.G. Effect of Al-5Ti-1B on the microstructure of near-eutectic Al-13%Si alloys modified with Sr. J. Mater. Sci. 2002, 37, 3489–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukow, C.A.; Nemanich, R.J. Morphology of TiSi2 and ZrSi2 on Si(100) and (111) surfaces. Mater. Res. Soc. 1994, 9, 1214–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, T.; Koma, M.; Ohwa, Y.; Shudo, K.; Tanaka, S.O.E.M. Observation of thermal growth of silicide on titanium-deposited silicon surfaces. Surf. Sci. 2007, 601, 4444–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njuguna, B.K.; Li, J.Y.; Tan, Y.; Sun, Q.Q.; Li, P.T. Grain refinement of primary silicon in hypereutectic Al-Si alloys by different P-containing compounds. China Foundry 2021, 18, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaislová, A.; Michna, Š.; Hren, I.; Vlach, T.; Michalcová, A.; Novák, P.; Stančeková, D. Microstructural Characteristics of Al-Ti-B Inoculation Wires and Their Addition to the AlSi7Mg0.3 Alloy. Materials 2022, 15, 7626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumalatha, C.; Rao, P.; Rao, V.; Deepak, M. Influence of Grain Refiner, Modifier and Graphene on the Dry Sliding Wear of Hypereutectic Al–Si Alloys. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2022, 11, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumalatha, C.; Rao, P.C.S.; Rao, V.; Deepak, M.S.K. Effect of grain refiner, modifier and graphene on the mechanical properties of hyper eutectic Al-Si alloys by experimental and numerical investigation. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsson, M. Grain refinement of aluminium studied by use of a thermal analytical technique. Thermochimica acta 1995, 256, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsson, M.; Backerud, L.; Sigworth, G.K. Study of the mechanism of grain refinement of aluminum after additions of Ti- and B-containing master alloys. Metall. Trans. A 1993, 24, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Aoyagi, K.; Zhao, Y.; Maeda, C.; Mouri, T.; Chiba, A. Microstructure refinement for superior ductility of Al–Si alloy by electron beam melting. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 32, 100982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, B.; Luo, Q.; Hu, B.; Li, Q. Understanding grain refining and anti Si-poisoning effect in Al-10Si/Al-5Nb-B system. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 65, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
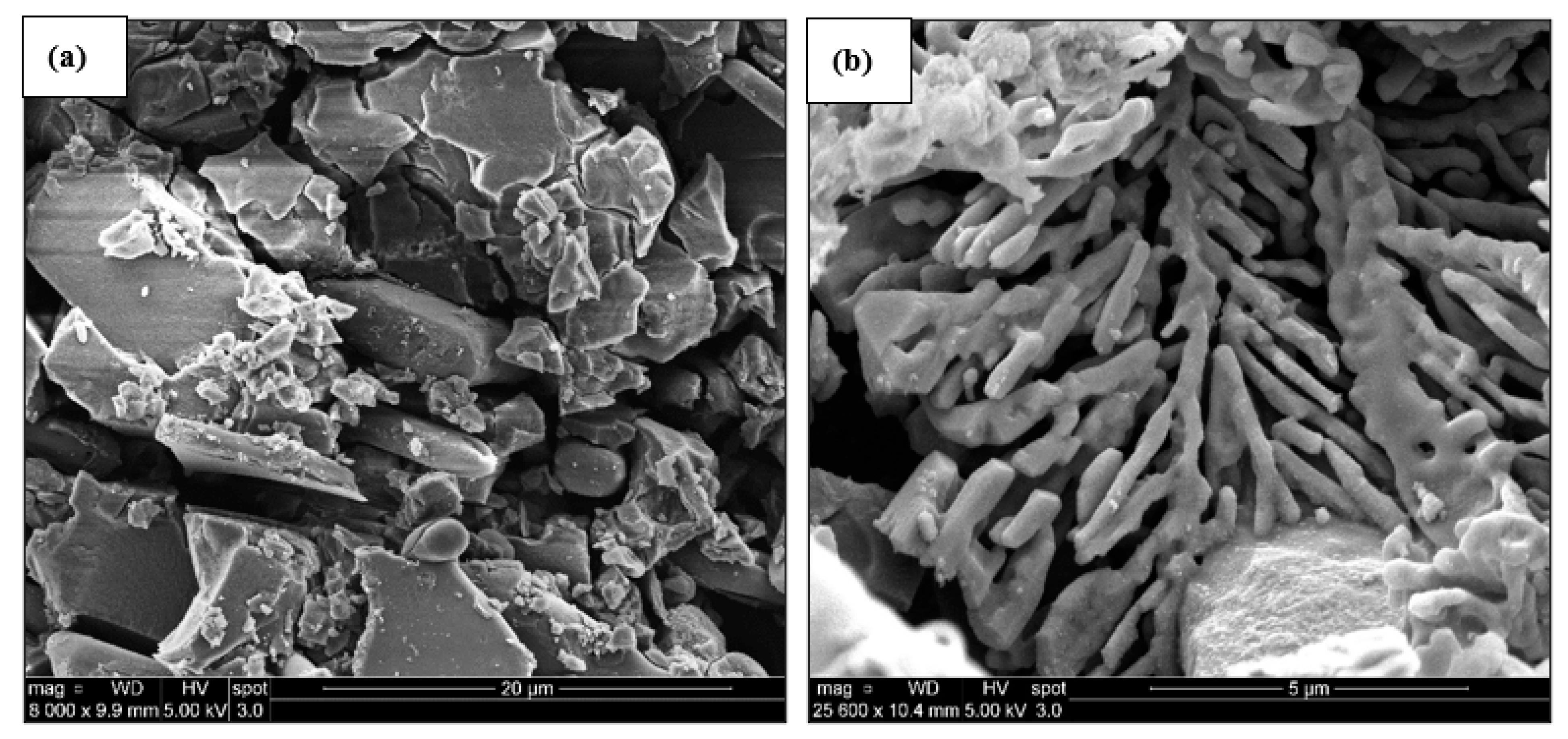
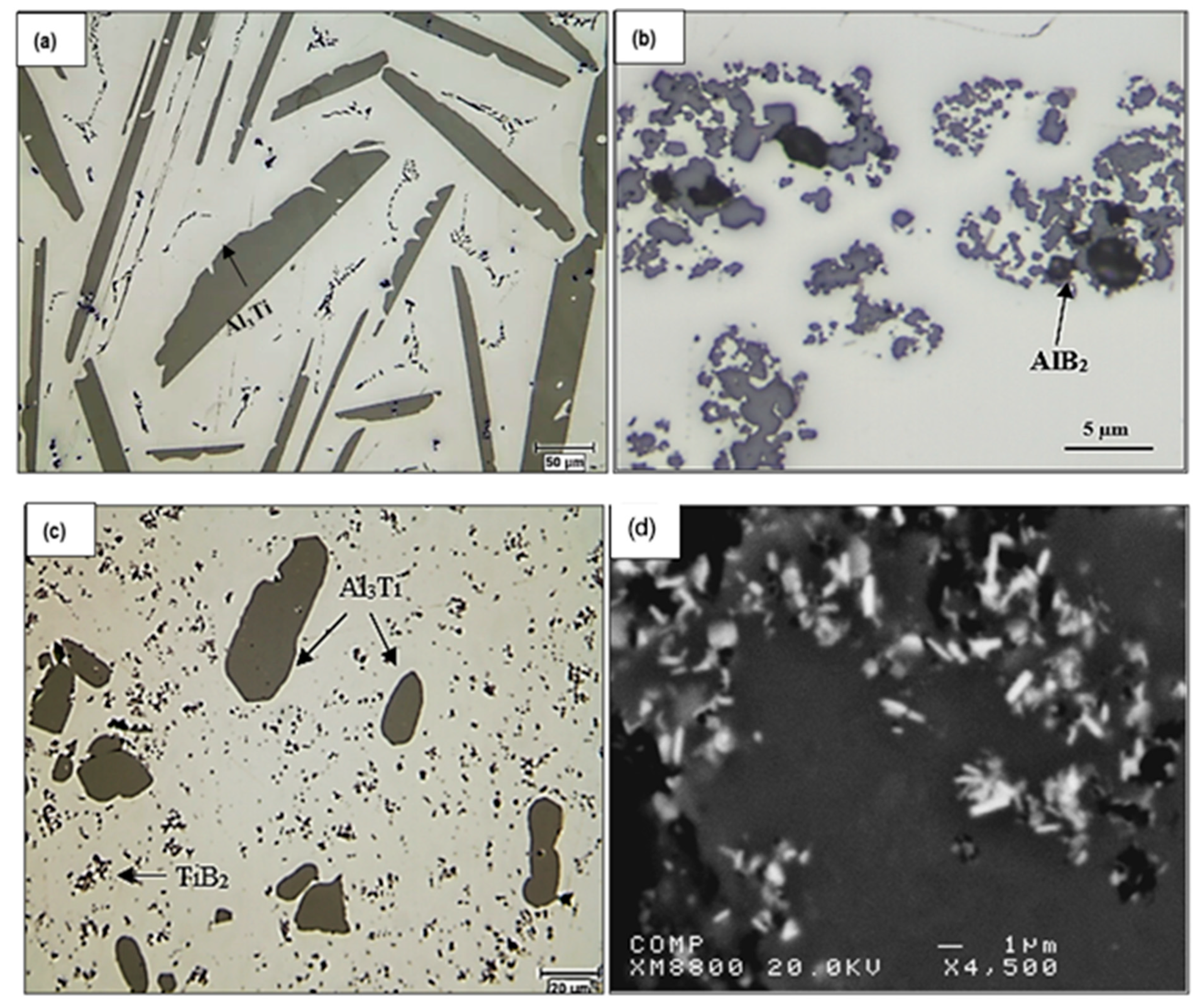
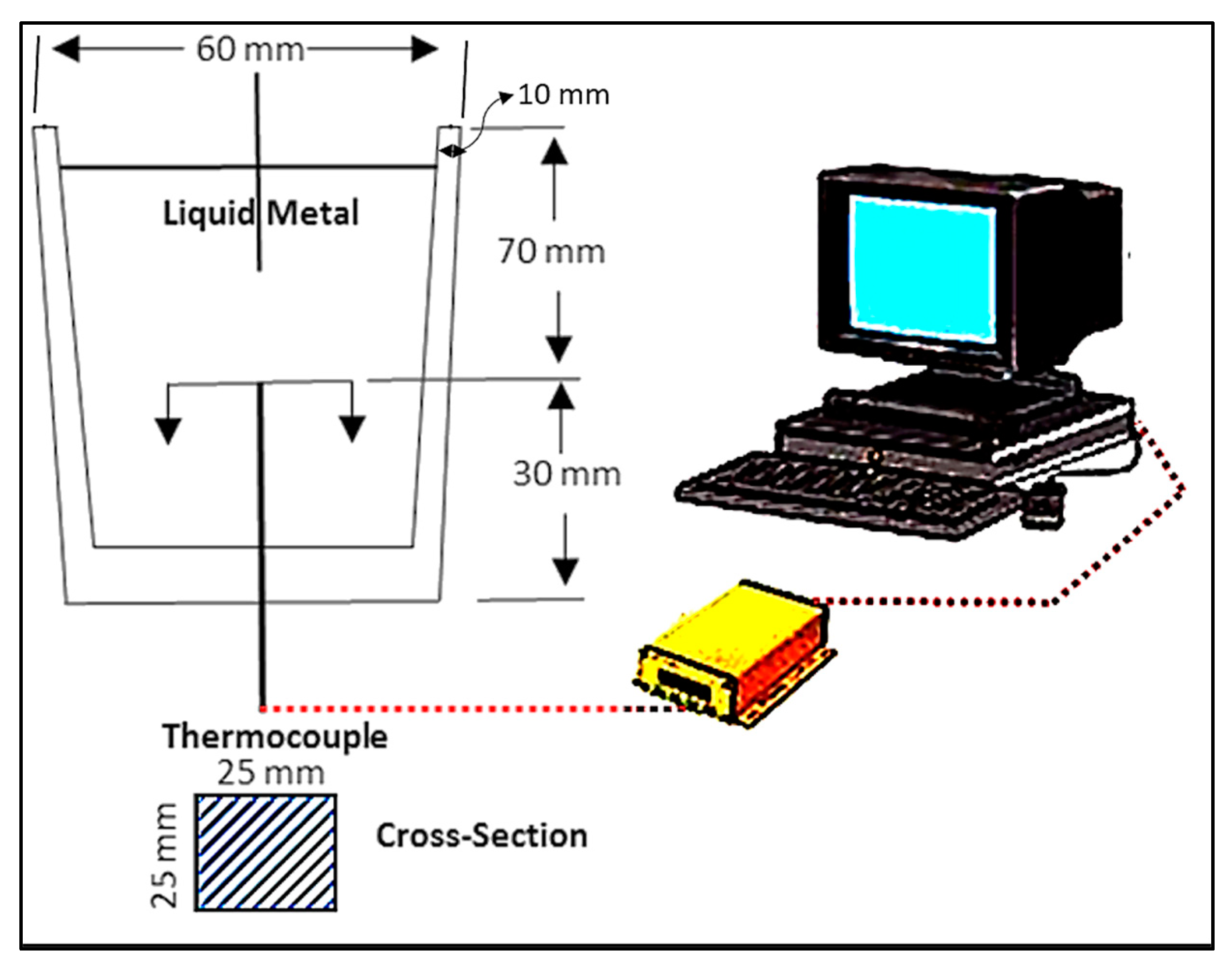
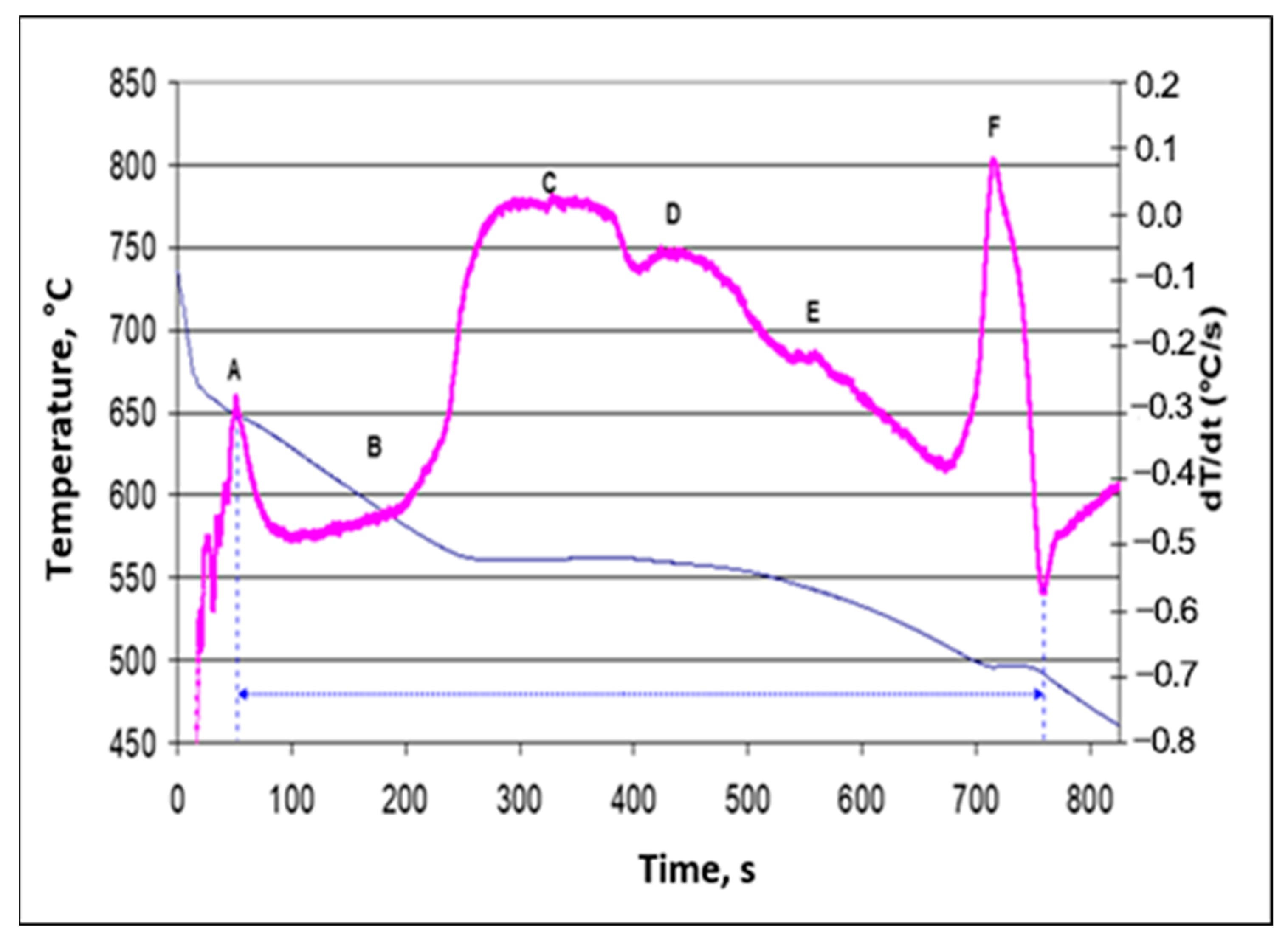

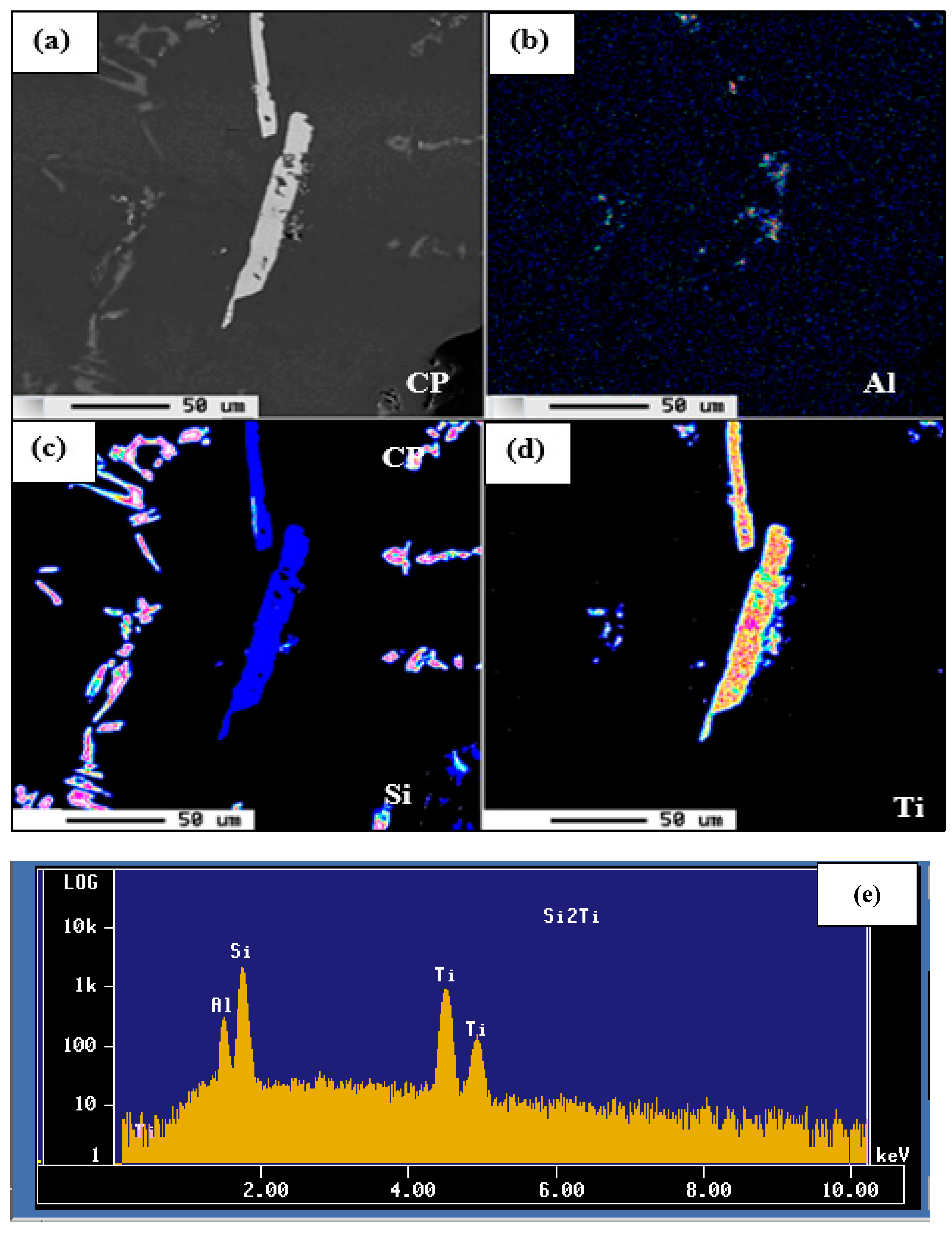
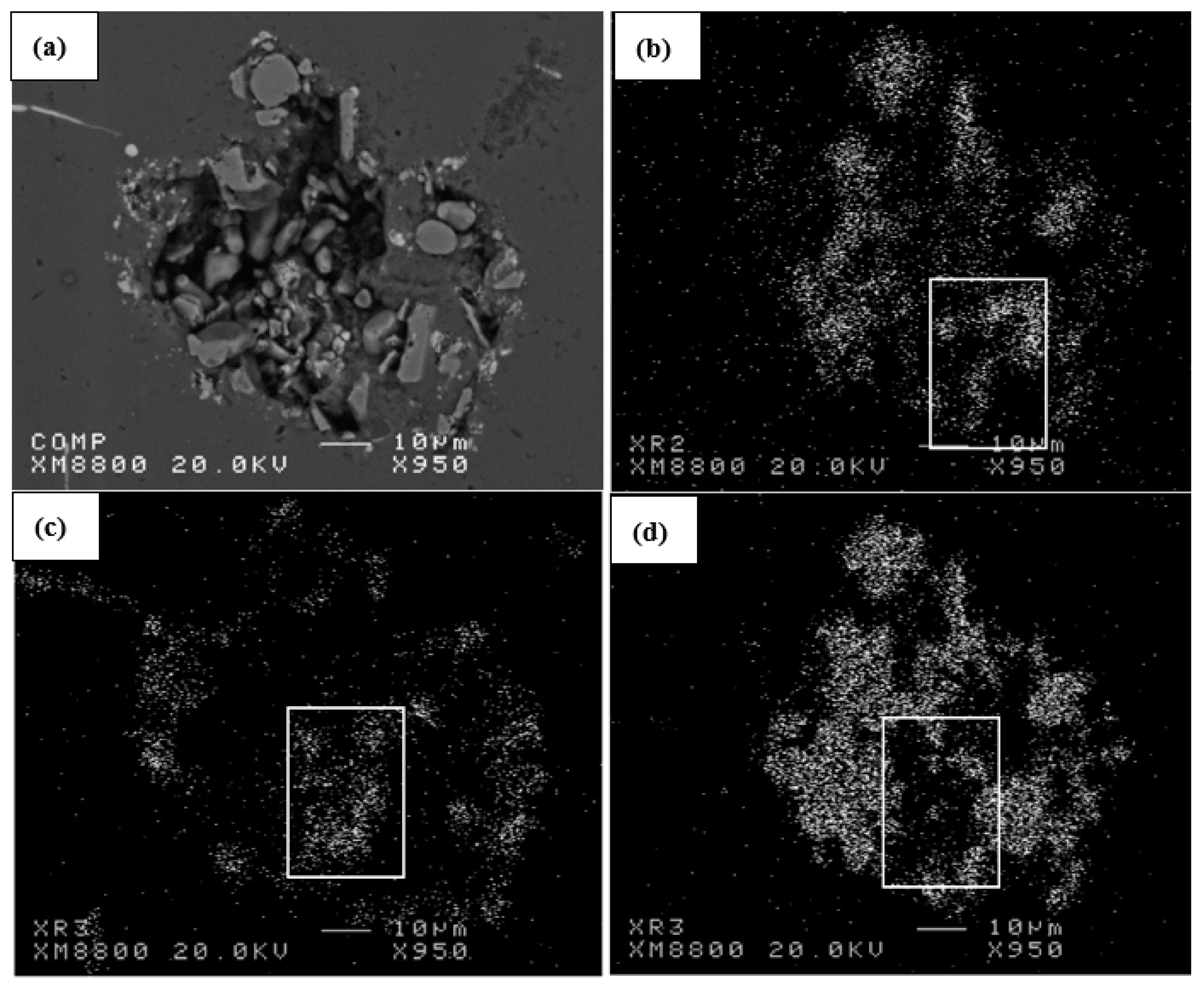
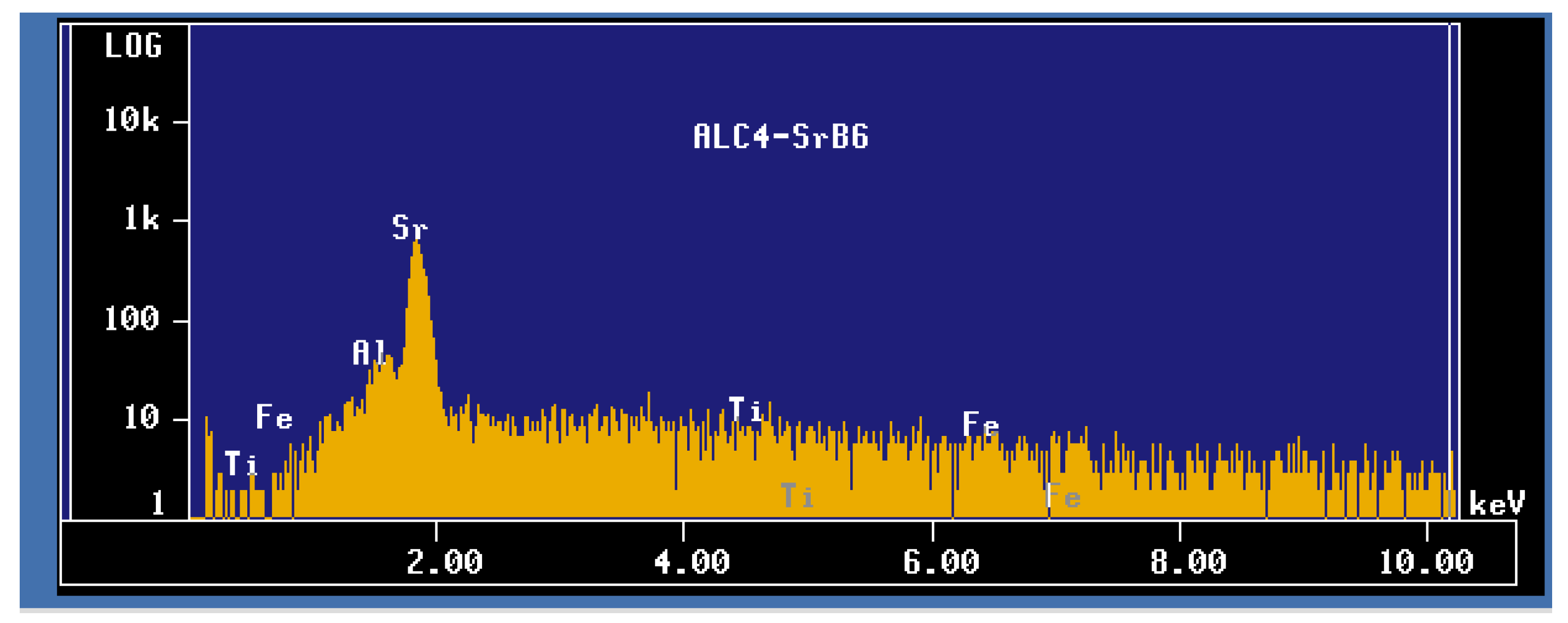
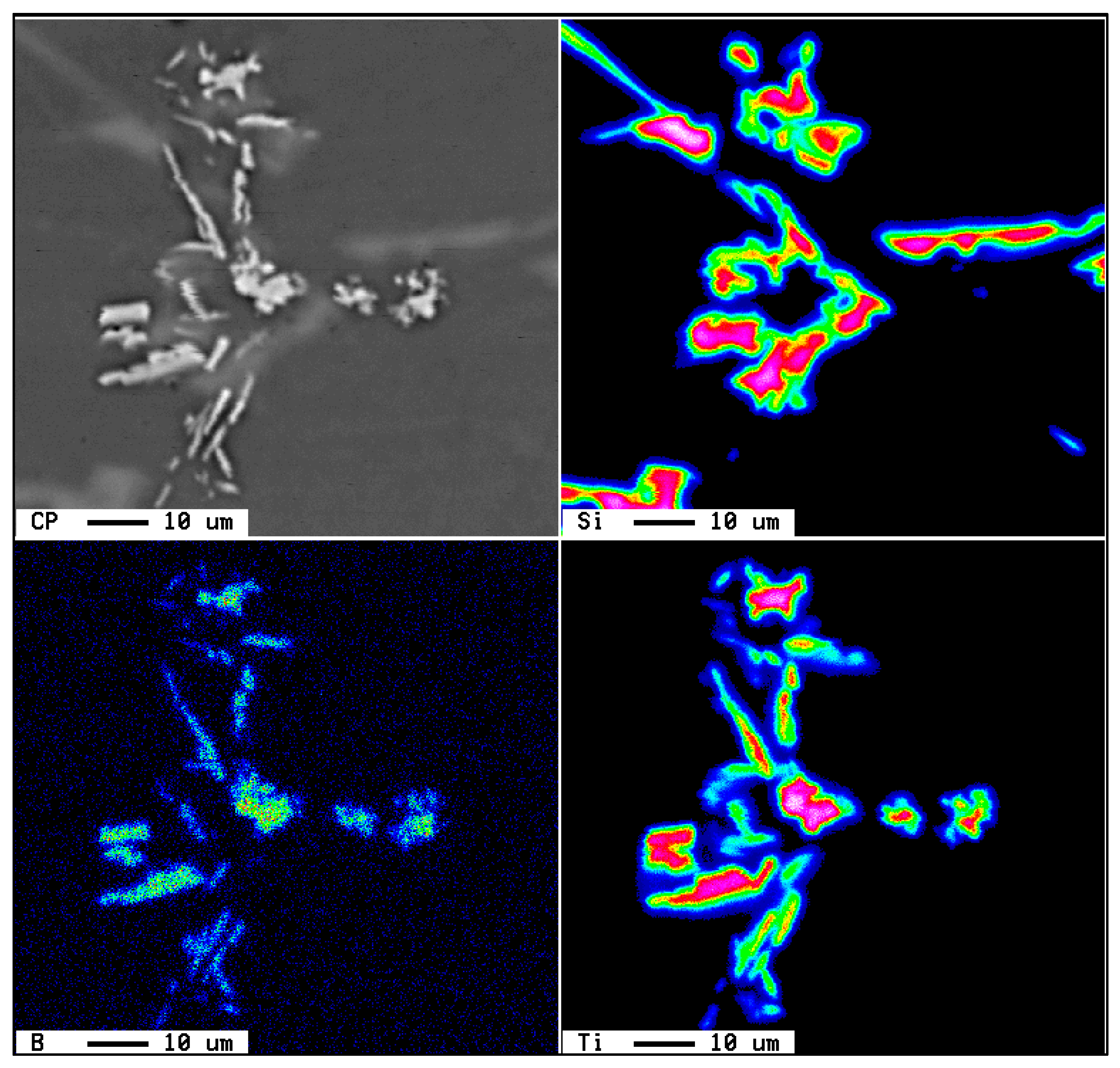

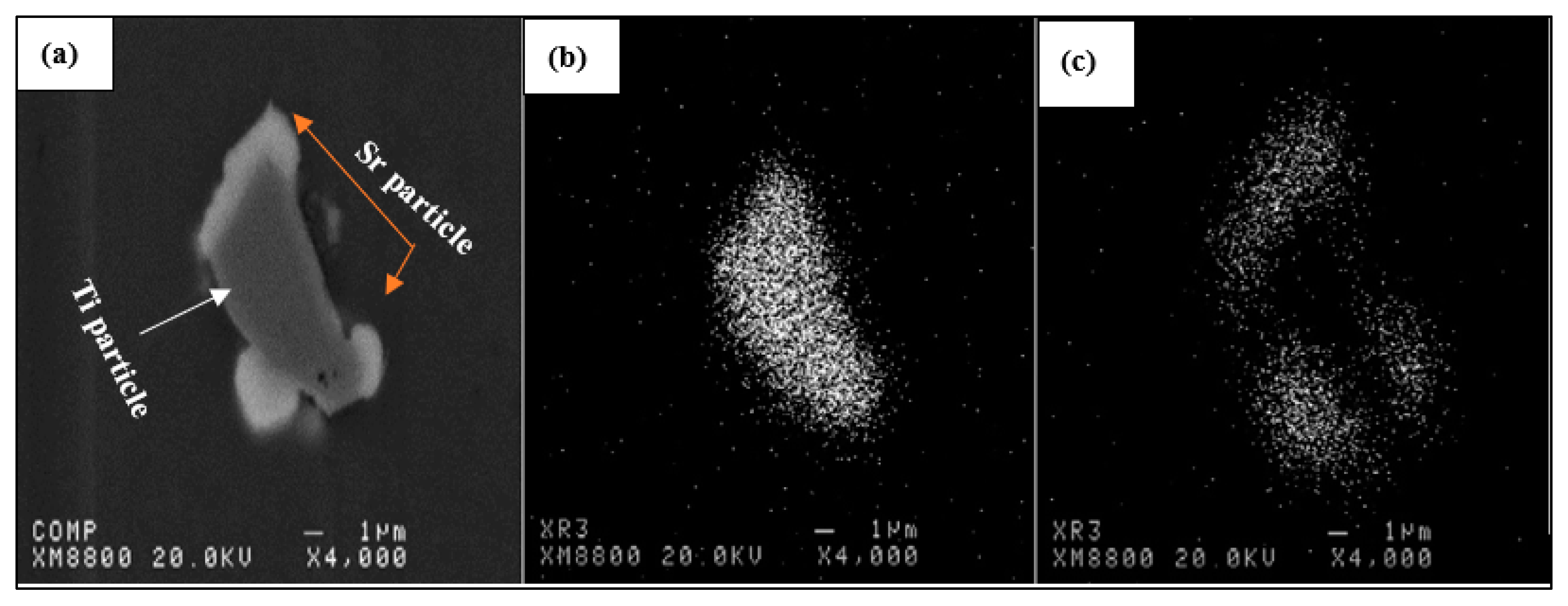
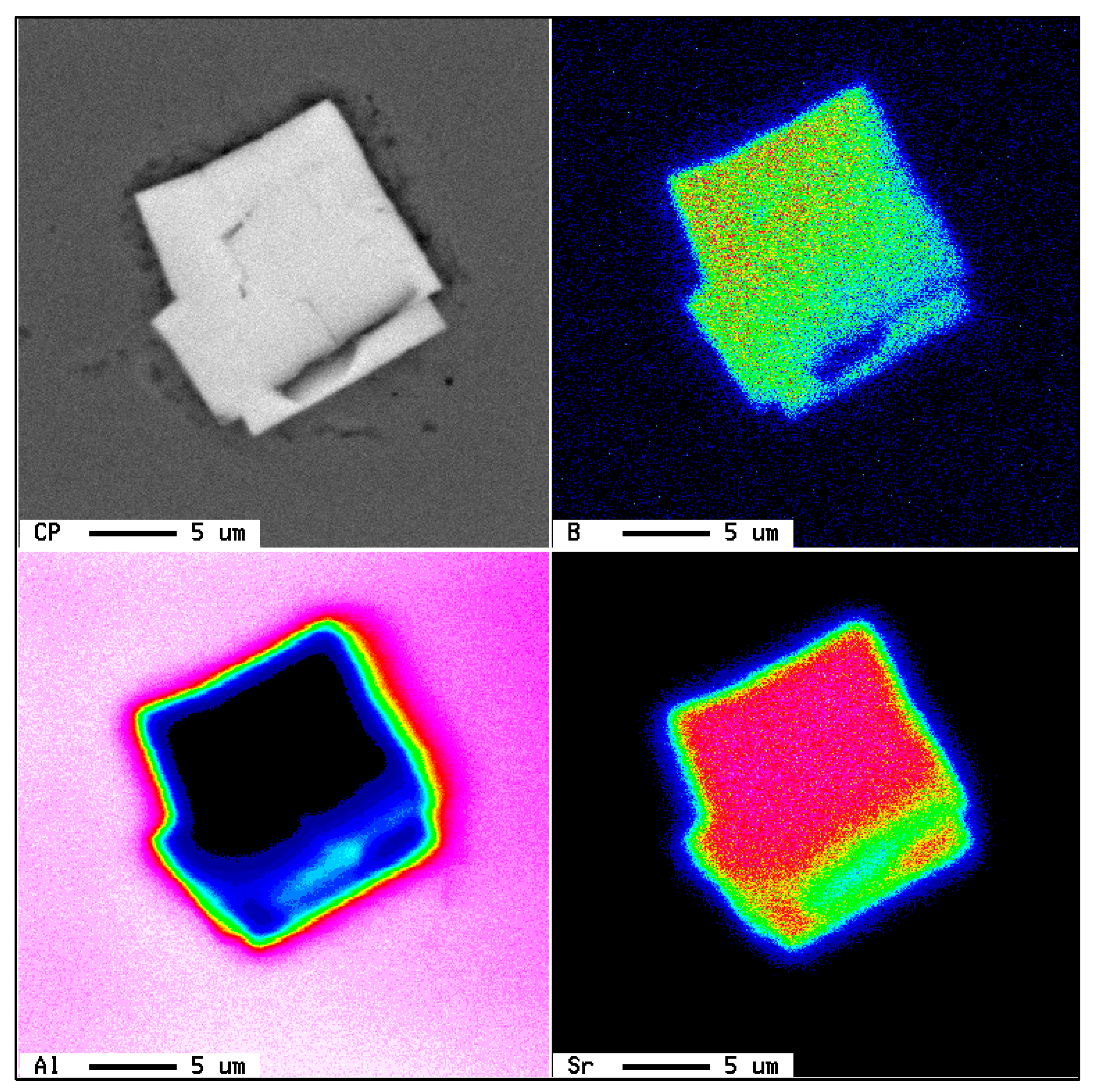

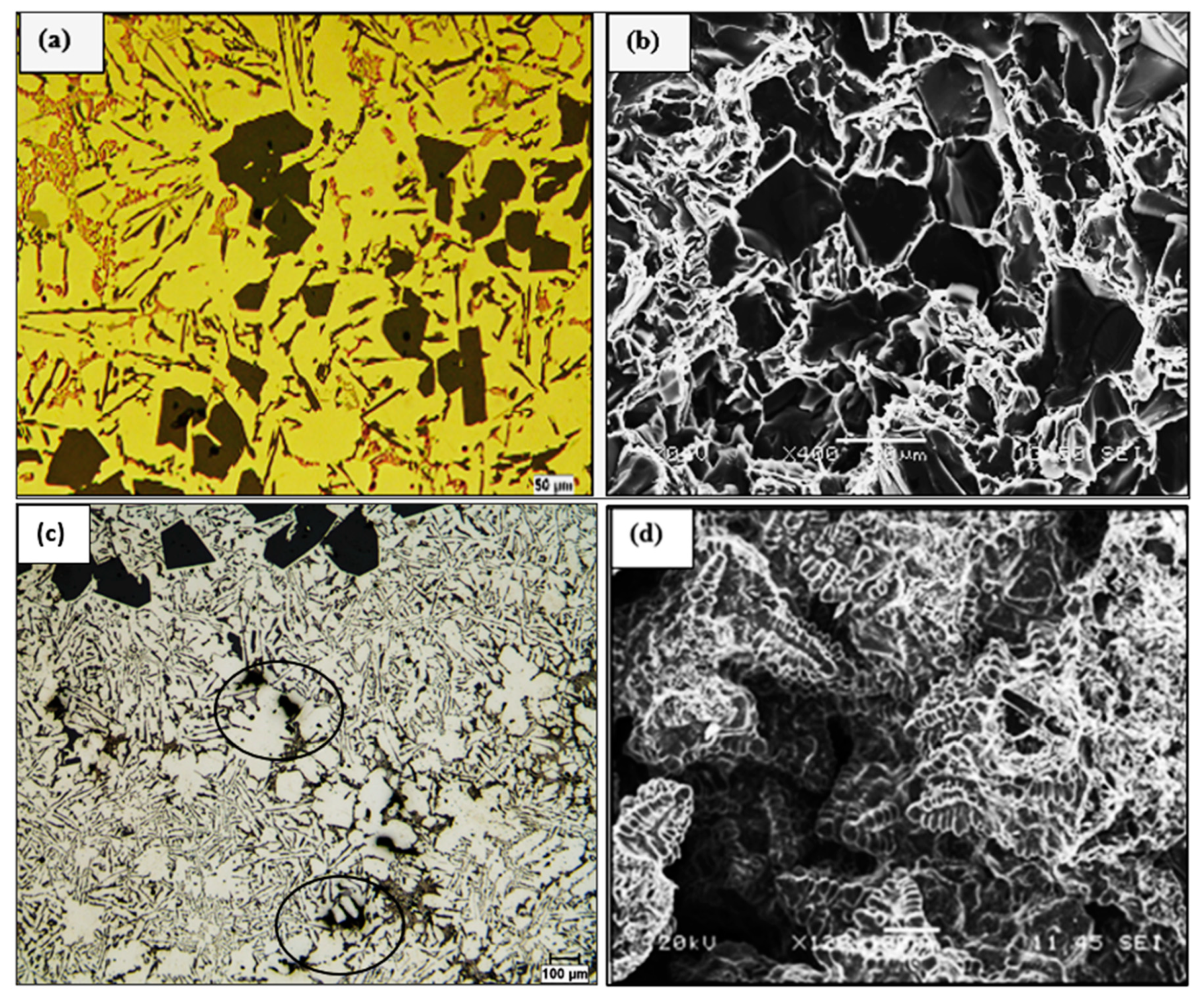

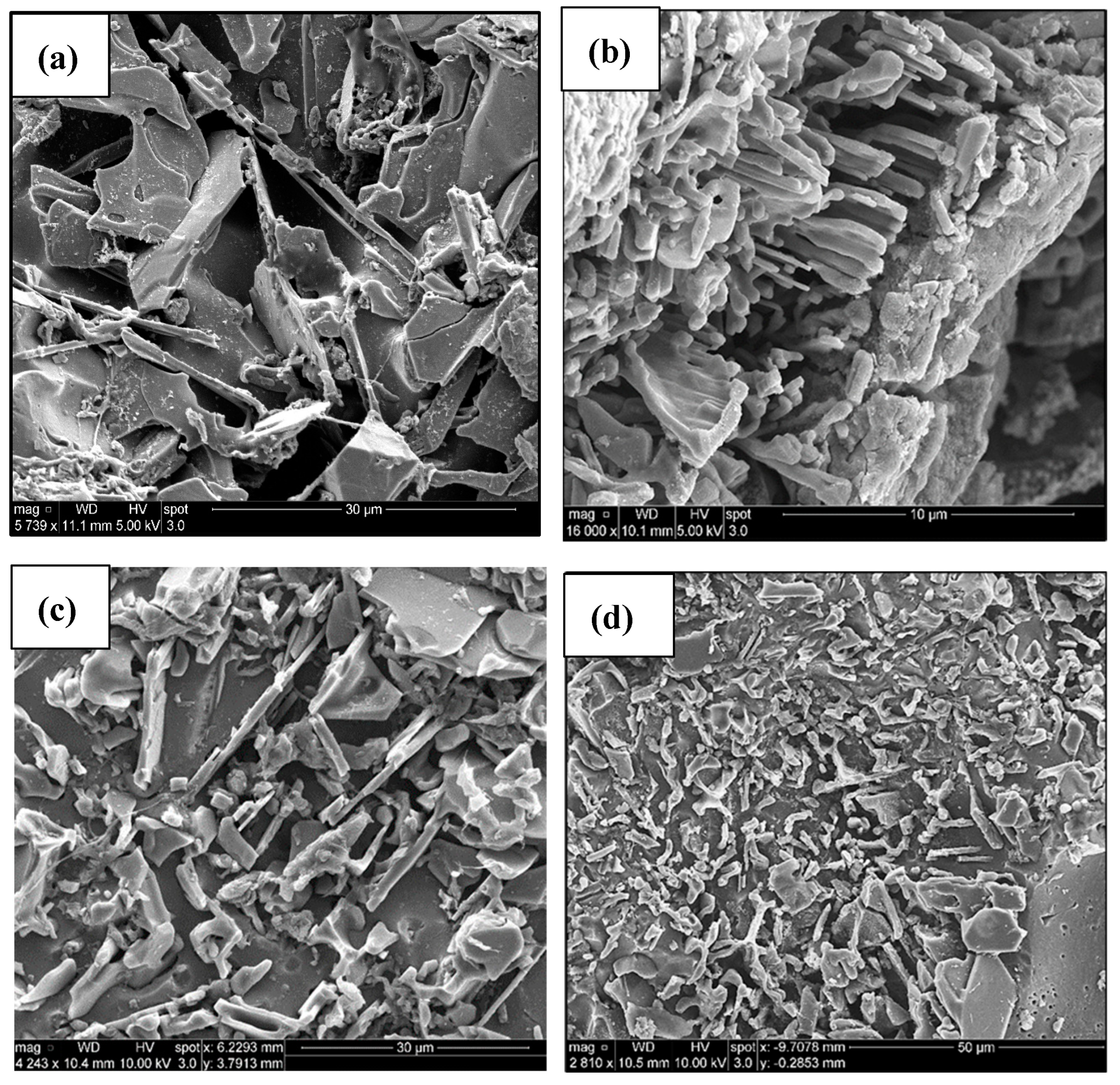
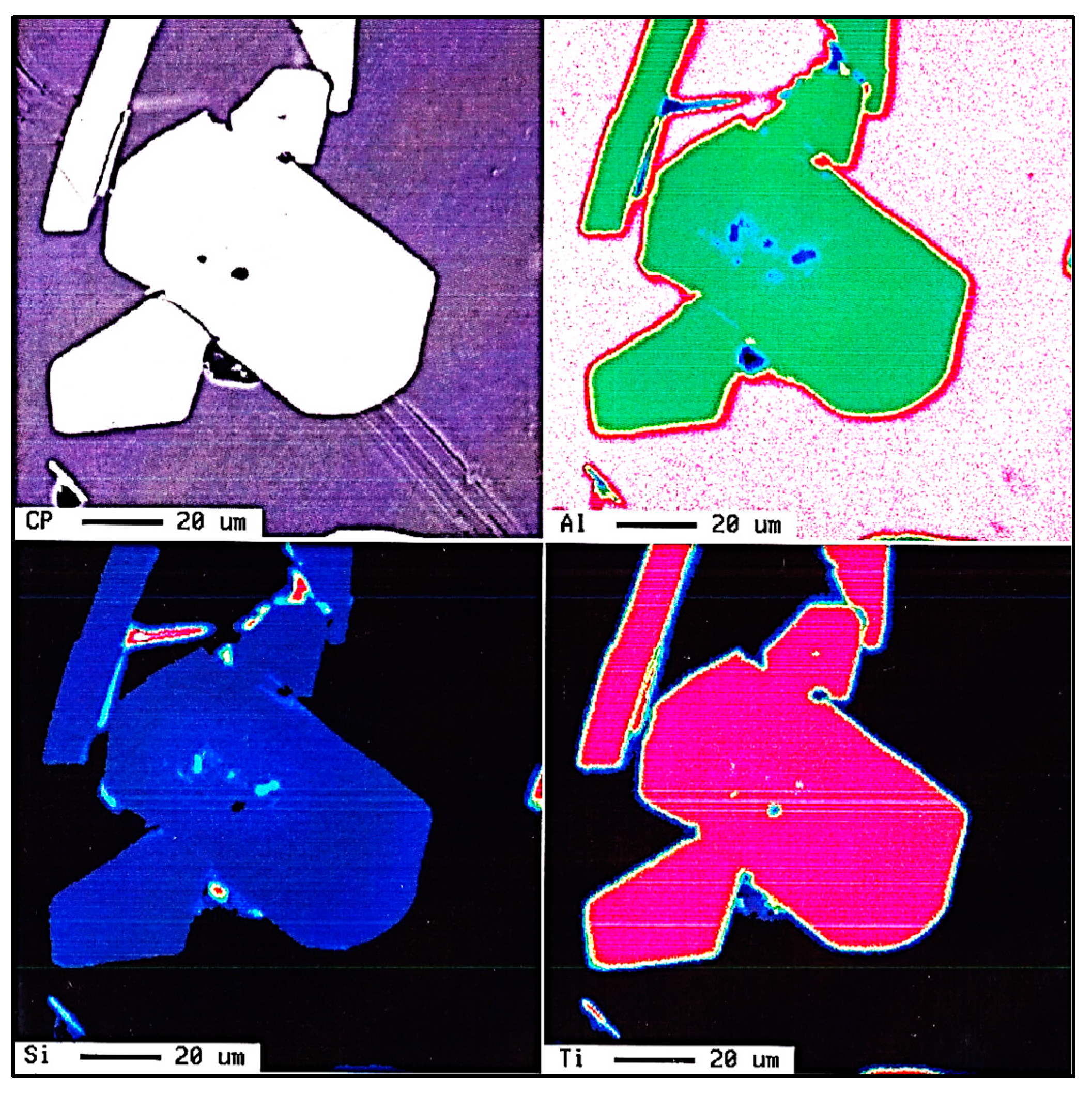
| Alloy | Al | Si | Cu | Mg | Fe | Mn | Zn | Ti | P (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A390.1 | bal. | 17.30 | 4.33 | 0.54 | 0.32 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 25 |
| Peak | Reactions | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| A | Primary Si | 670 |
| B | Development of a dendritic network | 561 |
| C | Liq. → Al + Si + Al5FeSi | 575 |
| D | Liq. → Al + Si + Mg2Si | 555 |
| E | Liq. + Mg2Si → Al + Si + Al2Cu + Al5Mg8Cu2Si6 | 512 |
| F | Liq. → Al + Al2Cu +Al5Mg8Cu2Si6 | 507 |
| Elements (at %) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Al | Ti | Si |
| 9.49 | 32.02 | 58.15 |
| 8.64 | 32.28 | 58.30 |
| 9.51 | 32.02 | 58.14 |
| ~8.95 | ~32.28 | ~58.30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samuel, E.; Tahiri, H.; Samuel, A.M.; Samuel, F.H. Heterogenous Grain Nucleation in Al-Si Alloys: Types of Nucleant Inoculation. Metals 2024, 14, 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14030271
Samuel E, Tahiri H, Samuel AM, Samuel FH. Heterogenous Grain Nucleation in Al-Si Alloys: Types of Nucleant Inoculation. Metals. 2024; 14(3):271. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14030271
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamuel, Ehab, Hicham Tahiri, Agnes M. Samuel, and Fawzy H. Samuel. 2024. "Heterogenous Grain Nucleation in Al-Si Alloys: Types of Nucleant Inoculation" Metals 14, no. 3: 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14030271
APA StyleSamuel, E., Tahiri, H., Samuel, A. M., & Samuel, F. H. (2024). Heterogenous Grain Nucleation in Al-Si Alloys: Types of Nucleant Inoculation. Metals, 14(3), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14030271







