Abstract
Abrasive waterjet technology is nowadays a well established non-conventional method with significant capabilities for material removal with high productivity and minimum environmental impact compared to other processes. However, in order to be in line with the green transition directives, further steps are required to ensure the sustainability of manufacturing processes and reduce the risk of material depletion by employing recyclable materials. For this purpose, an eco-friendly abrasive material such as walnut shell is employed for pocket machining of a titanium alloy workpiece. Due to the relatively low hardness of this material, compared to common abrasive materials such as garnet or alumina, it is required to determine the appropriate range of process parameters in order to obtain high-quality pockets with high productivity. Thus, in this work, a comprehensive experimental study is conducted in order to determine the effect of various process parameters on pocket depth, pocket width, material removal rate, flatness and parallelism error of produced pockets. The results prove the feasibility of using walnut shell as abrasive material for pocket milling, although MRR is almost an order of magnitude lower than the values commonly obtained for usual abrasives. Moreover, it is not recommended to use jet pressure values over 250 MPa so dimensional accuracy, flatness and parallelism error are maintained in acceptable values.
1. Introduction
The ever changing trends in manufacturing industry require that manufacturing processes should be flexible in order to be able to meet various requirements, such as high surface quality and integrity and high productivity in challenging conditions, e.g., machining of advanced alloys and other newly introduced materials. Furthermore, additional requirements, particularly those connected to process sustainability, are receiving greater attention these days. In fact, sustainability has three dimensions, economic, environmental and social, all of which should be considered during the production process [1].
Non-conventional machining processes have increased capabilities due to different mechanisms leading to material removal and thus can be considered superior to conventional ones in some cases, such as machining of hard-to-cut materials. The abrasive waterjet machining (AWJM) process is a non-conventional process which can be used for obtaining high material removal rates at affordable cost with minimal thermal impact [2,3]. Sustainability of AWJM process has been relatively less studied than other conventional and non-conventional machining processes, for which a large amount of studies have been conducted. Especially regarding the environmental dimension of sustainability of AWJM, the works conducted in the relevant literature can be distinguished into the following categories: studies relevant to the recycling/recharging of used abrasives, studies relevant to the recovery of abrasive material from various sources, studies relevant to the use of eco-friendly abrasives and studies relevant to more sustainable variants of AWJM. In fact, most studies are relevant to the first two categories, as it was already determined that there is a considerable potential for reuse of some types of abrasives. The activities described in the aforementioned categories are relevant to almost every category of the 6R concept (reduce, reuse, recycle, recovery, redesign and remanufacturing) and are also highly relevant to the principles of lean and green manufacturing, something that shows their great importance.
The reuse of abrasive materials is very important from economic point of view, as in most cases, the cost of abrasive constitutes over 50% of the machining cost in AWJ machining [4]. The stages of preparing the used abrasives for further use usually include collection of used abrasives, cleaning, removal of debris, sieving and sorting. Afterwards, the recycling potential and capabilities of machining with recycled abrasives are usually evaluated. Dong et al. [4] presented a method for on-line recycling of abrasive particles used during abrasive waterjet cleaning processes. Perec [5] studied the recycling capabilities of garnet and corundum based on the aspect of abrasive disintegration and showed that although corundum can have larger recyclability in some cases, it is related to excessive focusing tube wear. The same researcher also conducted other relevant studies [6,7] in which it was found that garnet has greater recyclability potential than olivine and ilmenite and that the use of recycled abrasives such as crushed glass has considerable potential for cutting. Kantha Babu and Krishnaiah Chetty [8] revealed that the disintegration degree is larger for fresh abrasives than recycled ones, due to their larger dimensions, leading to easier fragmentation. However, except from the first recycling time, the capabilities of abrasives change to a smaller degree after the next recycling times. Pi, Chau and Hung [9] found that the reusability of abrasives is dependent on the abrasive diameter, with smaller abrasives having greater potential for reuse. Finally, Kantha Babu and Krishnaiah Chetty [10] performed experiments with a mixture of fresh and used abrasives indifferent percentages and indicated that the use of a higher percentage of recycled abrasives results in lower depth of penetration but also less kerf taper and surface roughness.
Recycling in the context of AWJM is not limited to the recycling of abrasive materials; AWJM can also be used as means for recycling or remanufacturing of various industrial parts and devices, something that is very important for reducing e-waste and obtaining useful materials or preparing old parts to be used for other purposes. For example, Yang et al. [11] showed the potential of using AWJs for recycling electronic circuit boards and Dong et al. [4] used AWJs for the purpose of cleaning items to be remanufactured.
Apart from recycling, recovery of abrasive materials has a considerable potential, as evidenced by the increased interest in relevant studies during the last decade. There are several possibilities for obtaining abrasive materials through recovery procedures from different types of waste, thus providing some added value apart from reducing the amount of waste. Shinzato and Hypolito [12] noted that it is possible to recover abrasive oxides such as Al2O3, MgAl2O4 and SiO2 from the waste produced during aluminum recovery. However, for that purpose, the waste must have a specific composition. Moreover, Tsai [13] investigated the potential of recovering abrasive material, such alumina and SiC from sawing waste. Aydin, Kaya and Karakurt [14] explored the possibility of utilizing granite particles recovered from the machining of granite for the purpose of cutting marble. Their findings showed that granite abrasive particles can have performance comparable to garnet and are able to cut various hard-to-cut materials. In a similar study, Sarici and Ozdemir [15] also underlined the importance of recovering and reusing granite in order to reduce the amount of harmful waste and compared the performance of granite and alumina particles. Granite was proven efficient as abrasive medium, especially for reducing surface roughness. Sabarinathan, Annamalai and Rajkumar [16] presented a study relevant to the recovery of Al2O3 abrasive particles from grinding wheel waste. They found out that this material was able to provide superior cutting performance, both for ductile and brittle materials compared to garnet, especially for roughing operations, but also led to higher surface roughness. Muthukumaran et al. [17] performed a study on the recovery of abrasive particles from ceramic material found in sanitary equipment and compared its performance with Al2O3 particles.
Although the potential of copper slag to be used as abrasive material was underlined by Murari, Siddique and Jain [18], Barsukov, Zhuravieva and Kozhus [19] proposed a heat-treatment method for enhancing the properties of abrasive particles recovered by copper slag in order to be comparable to those of common abrasives, such as garnet, and achieved a notable increase in hardness. Kim et al. [20] investigated the appropriate techniques for the recovery of abrasive particles such as alumina from waste sludge and showed that these materials have comparable properties to those of raw abrasive particles. Palaniyappan et al. [21] produced abrasives particles by recovering them from electric insulator waste. The friability of these materials was comparable to that of garnet, as were the geometric parameters, and although MRR, obtained depth and surface quality were inferior to that achieved by garnet, slightly lower kerf width, significantly lower cost and sufficient recyclability was observed for the recovered abrasives. Sabarinathan and Annamalai [22] presented and optimized a method for recovering sol gel alumina abrasives from abrasive wheel waste. Fonseca [23] proposed the use of ferrous granules, produced during lead/zinc smelting operations for AWJ machining. The results showed that this abrasive had a similar cutting ability to garnet, but the surface quality achieved was inferior with several defects forming on the workpiece surface. Schuler, Day and Bergs [24] performed a comparison of many abrasive particle materials, including various materials such as coal slag, copper slag, steel slag, granite, gray-wacke and olivine. The best cutting performance was observed for the slag materials and olivine, but in general steel slag was more effective regarding MRR and coal slag regarding surface roughness. Perec [25] compared recovered crushed glass abrasives with conventional ones, such as garnet and olivine, and showed that crushed glass abrasives had the lowest efficiency between the three materials, but also the lowest nozzle wear. Zulkarnain et al. [26] also performed LCA for crushed glass abrasives and found out that it is related to negligible ecosystem damages.
During the last several decades, efforts towards creating sustainable variants of AWJM have emerged, with the most prominent one being abrasive ice jet machining. This process involves the use of ice particles instead of abrasives in order to achieve better quality of cut and avoid also the negative consequences of particle embedment on the surface. Moreover, other advantages include lower cost, negligible nozzle wear and waste elimination [27]. Ice jet machining is usually employed in surface cleaning or deburring operations, as the hardness of ice particles was estimated to be around 6 Mohs at most [27,28]. Although in general similar machine tools are employed for both waterjet and ice jet machining, various parts of the equipment and the basic principle of generating the jet exhibit differences [27]. More specifically, ice particles can be generated by two different methods, namely, by an apparatus used before they are introduced to the mixing chamber or during water jet formation through the use of cryogenic fluid [27,28]. However, the latter method is related to higher cost due to the use of liquid nitrogen [27]. Furthermore, according to Jerman, Orbanic and Valentincic [29], special studies need to be conducted in order to determine a feasible ice particle diameter which could be obtained and optimize the cutting head geometry in order to be able to efficiently use these particles. Apart from using ice particles as an abrasive, another possible alternative is to perform cryogenic-assisted AWJM by means of a liquid nitrogen jet. Lavorel et al. [30] compared the use of pure nitrogen and an abrasive nitrogen jet with garnet and walnut shell abrasives during cutting of bio-composites in order to avoid the development of intense thermal fields. Moreover, Natarajan et al. [31] compared the use of conventional AWJs to cryogenically assisted AWJM. In most cases, higher depth of cut and MRR, as well as lower kerf taper, surface roughness and particle embedment, were obtained by cryo-AWJM.
Finally, the use of eco-friendly abrasives, most usually obtained through natural or bio-based sources, is another interesting concept which can further enhance the sustainability of AWJM apart from the adoption of the aforementioned strategies [32,33]. In practice, various relevant materials such as plastic shot or organic materials such as corn cob, walnut shell, almond shell, coconut shell and apricot or plum stone were already employed for sandblasting purposes, but still nowadays the relevant literature on their use for abrasive waterjet machining remains scarce. As these materials have often much lower hardness than common abrasives, they are more suitable for lighter operations, as it would require much higher jet pressure and much lower traverse feed rate values for operations such as cutting in comparison to those used when garnet is selected as abrasive. However, under adequate circumstances, these abrasives can be considered as promising alternatives for common abrasives. Jiang et al. [34] employed sodium bicarbonate as an abrasive for desmearing of PCBs. They achieved surface quality comparable to industrial levels and found that this abrasive also has high recycling potential. Another uncommon abrasive type evaluated regarding its use as abrasive material was mussel shell, which can be available as by-product of the relevant canning industry [35]. It was proposed that mussel shell can be used for cleaning surfaces and its performance was compared to that of garnet. Based on the results, it was found that mussel shells were four times less friable than garnet and, given its moderate hardness, it was considered as a possible alternative material for cleaning surfaces. Awadh and Ali Khalid [36] investigated the use of river sediments as abrasives for polishing purposes and they revealed that this abrasive was suitable for polishing, as it reduced considerably the surface roughness of hard materials.
Based on the relevant literature, although various works have been conducted regarding sustainability in AWJM, the amount of works is still considerably lower than that of other process and many topics are not sufficiently explored. The present work aims to investigate the applicability of walnut shell abrasives for the purposes of pocket milling, a much more demanding operation than cleaning or polishing. Although a couple of studies mentioned the use of such abrasives, there is no work available on AWJ milling with a wide range of parameters and related to pocket milling. Thus, in this work, experiments under various process conditions are carried out and an analysis of their effect on pocket depth, width, material removal rate, flatness and parallelism error is conducted with a view to appropriately evaluate the potential of the chosen eco-friendly abrasive.
2. Materials and Methods
In this work, AWJ milling experiments were carried out, under varying process conditions, in order to investigate the applicability of using an ecological organic abrasive in this process. As this abrasive is considerably less hard than common abrasives, it is important to determine the range of process parameters that allows for the creation of the desired features on the workpiece as well as be able to optimize these conditions according to different requirements. Given that no similar study is yet reported in the relevant literature, the analysis conducted in this work includes not only the morphology of the pockets, but also their dimensional accuracy, as well as the productivity of this process. More specifically, at first, a series of experiments was conducted, designed by Taguchi L9 orthogonal array with three parameters, namely, stand-off distance (denoted as h), abrasive mass flow rate (denoted as ma) and jet pressure (P), varying at three levels each; then, an additional series of experiments was conducted based on interesting findings from the analysis of the results of the first series of experiments in order to further focus on the achievable pocket depth in respect to other parameters or a wider range of the existing parameters, as controlled-depth milling is very important to investigate in AWJM.
The levels of process parameters for the experimental design using Taguchi L9 orthogonal array are displayed in Table 1. The range of parameters selected for the first set of experiments is relevant to the machine tool capabilities, e.g., available range of jet pressure and abrasive mass flow rate, as well as being relevant to values which could provide meaningful results regarding pocket dimensions and accuracy and especially to provide a wide range of depths and surface quality in order to perform a comprehensive evaluation of the feasibility of using the walnut shell as an eco-friendly abrasive. Thus, after preliminary experiments were carried out, the specific parameter range was chosen.

Table 1.
Process parameters for the first series of experiments.
The parameters which remain constant throughout the experiments are the jet impingement angle of 90°, orifice diameter of 0.3 mm and nozzle diameter of 1.0 mm. As the abrasive was rather soft, the nozzle wear was negligible during the experiments. In every case, rectangular pockets were created with a zig-zag pattern for a width of 9.6 mm and horizontal length path of 35 mm, as can be seen in Figure 1. In order to avoid confusion, given that the dimension of the pocket in the direction of the workpiece width is larger, it is termed as pocket length, whereas the dimension in the direction of workpiece length is termed as pocket width. The length of each path was slightly longer than the width of workpiece (30 mm), because it was intended to eliminate the effect of acceleration and deceleration of the jet before creating the pockets, ensuring that material removal process could be uniform and any effect of acceleration or deceleration of the jet would be negligible, as it would occur outside the workpiece boundaries. Moreover, in the experiments conducted under the Taguchi L9 orthogonal array, traverse feed rate (denoted as vt) was 100 mm/min and stepover (denoted as SO) was 0.6 mm. In Figure 1, schematics depicting the process of pocket milling using AWJM and the used abrasive are presented. It is to be noted that the workpiece was fixed on the machine tool bed by two heavy steel pieces on both ends in order to avoid displacement during cutting and also eliminate possible interference of improper fixation of the workpiece on the obtained flatness and parallelism error [37]. The workpiece material was titanium grade 2, and its composition is displayed in Table 2.
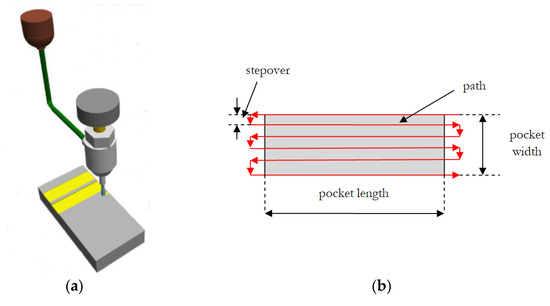
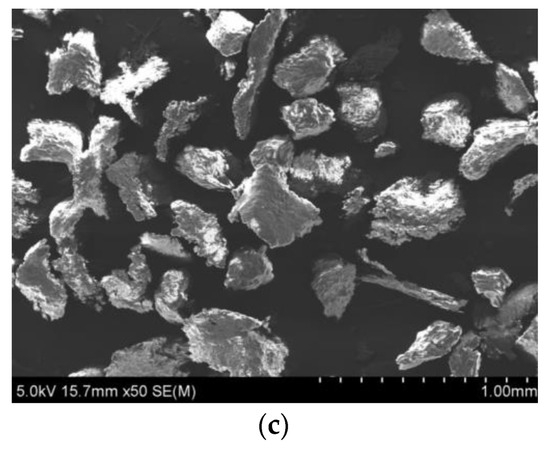
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic of the AWJ milling process for the creation of pockets, (b) basic geometric features of the pocket milling process, (c) SEM micrograph of the abrasive particles’ geometry.

Table 2.
Chemical composition of titanium grade 2.
The experiments were performed on a model HWE-1520 H.G. RIDDER Automatisierungs GmbH machine (H.G. RIDDER H., Hamm, Germany). This machine has the capability to adjust the pressure from 50 to 400 MPa and abrasive flow rate from 10 g/min to 600 g/min. The ecological abrasive which was used is actually walnut shell, acquired by HERUBIN company (HERUBIN, Dobra, Poland). The geometry of the abrasive particles can be seen in the SEM (Scanning Electron Microscope, SU-70, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) micrograph in Figure 1c, which is rather uncommon in comparison to the more usually used garnet abrasive which has an irregular but prismatic shape, or glass beads which have an almost perfect spherical shape. This abrasive is considered an appropriate medium for machining of soft metals, surface cleaning and especially coating removal. It is considered reusable and according to the manufacturer it contains 55–70% cellulose, 19–22% lignin and 22–27% hemicellulose. Its density is estimated around 1.28 g/cm3 and its hardness is rather low, around 2.5–3 Mohs.
The depth, flatness and parallelism error of the pockets were determined by the use of a Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM), namely the Mitutoyo CMM Crysta Plus M443 (Mitutoyo, Kawasaki, Japan). For each pocket, the appropriate procedure was used to estimate the average depth and the values of flatness and parallelism according to the relevant standard. Flatness and parallelism error are two responses of particular interest for practical reasons; however, only a limited number of authors have tried to analyze the influence of machining parameters. The flatness of surfaces has been mostly studied in the case of conventional end milling rather than non-conventional processes, e.g., in the works of Mikó and Rácz [38], Bustillo et al. [39], Tai, Stephenson and Shih [40], and Agarwal and Desai [41], where some conclusions on the effect of process parameters regarding flatness were discussed. Nevertheless, parallelism has been less studied in the field of manufacturing processes [42,43,44].
During the evaluation of the flatness of a surface, which is a form error, the surface should lie between two parallel planes and the tolerance value indicates the maximum distance of the two planes in length unit, whereas parallelism is an orientation error and is evaluated as the smallest possible distance between two theoretical parallel planes, which are also parallel to a reference surface (datum), such that all the measured points fall within this distance. In the present work, the flatness and perpendicularity were estimated based in measurements by the CMM machine on 12 points equally distributed on the pocket surface, a strategy which has also been employed in similar cases [39]. Especially for the parallelism error, the datum was chosen to be in the uncut surface of the workpiece which had low roughness in order to avoid interference with the measurement. Finally, for the determination of width, high-resolution images of the workpiece surface were analyzed by ImageJ software (version 15.3t, National Institute of Health and LOCI, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. First Series of Experiments
After the experiments were carried out and various measurements were performed on the workpiece regarding average depth (denoted as d) and width of pockets (denoted as w), flatness and parallelism deviation as well as MRR, the results presented in Table 3 were obtained. As multiple measurements were performed for d, w and MRR, the standard deviation values are also presented, denoted by σ. At first, the results pertinent to the first series of experiments, conducted based on the Taguchi L9 orthogonal array, will be analyzed using statistical methods and then discussed; afterwards, further investigations of additional parameters will be carried out in order to supplement the already-derived conclusions. It is worth noting that, in every graph containing surface plots, the color scale on the plots is relevant to the magnitude of the quantity presented in the z axis, with blue areas representing lower values and red areas higher values, in order to further emphasize its values and facilitate understanding by the readers.

Table 3.
Experimental results for the first series of experiments.
The depth of pockets in AWJ milling occur due to the superposition of adjacent grooves formed by the abrasive jet moving in a zig-zag pattern with alternating directions. Thus, the addition of new grooves produced close to the previous ones based on a constant stepover distance leads to much higher depth than the one obtained during slot milling under the same condition. Regarding pocket depth, it becomes obvious from the values presented in Table 3 that a considerable large variation of depth can be obtained under the selected range, mainly due to the very prominent effect of jet pressure on pocket depth. It is worth noting that the smaller pocket is barely distinguishable on the workpiece surface, having an average depth of only 14 μm and fairly flat morphology, whereas the largest one has a depth of over 1 mm, with a large amount of irregularities formed due to the intense impact of particles on the surface. This result is rather important, as it can prove that, under specific circumstances, the use of an uncommon, soft abrasive such as nut shell can produce pockets with dimensions comparable to those produced by common abrasives at the expense of high power and abrasive consumption. However, the results indicate that the use of this type of abrasive offers the capability of regulating the depth at very low values without the need of using very high speeds or very low pressure which could be beyond the capabilities of the machine tool if a harder abrasive such as garnet was used.
As can be seen in the main effects plot of Figure 2 and the surface plots of Figure 3, the jet pressure is definitely the most significant parameter regarding the pocket depth. When jet pressure increases, especially after 250 MPa, a tremendous increase in depth values occurs. This result indicates that the increase in particle velocity and the more intense interaction between the abrasives and workpiece surface can directly lead to increased material removal. Moreover, these findings are in accordance with the findings of previous works in the relevant literature, where it is underlined that jet pressure increases the momentum of the waterjet and subsequently the velocity of abrasive particles [45,46,47]. Thus, under higher jet pressure, it is easier to overcome the energy threshold for material removal [45]. It is also important to note that lower values of jet pressure have been reported to allow a more uniform erosion of the surface, whereas higher values of pressure can lead to lateral erosion as well, reducing the quality of the pockets and even creating a “speed bump” shape for the pockets [48]. However, as power consumption during AWJM is mainly dependent on jet pressure, using high values of jet pressure also increases the energy consumption and, apart from higher costs, contributes to a less sustainable process.
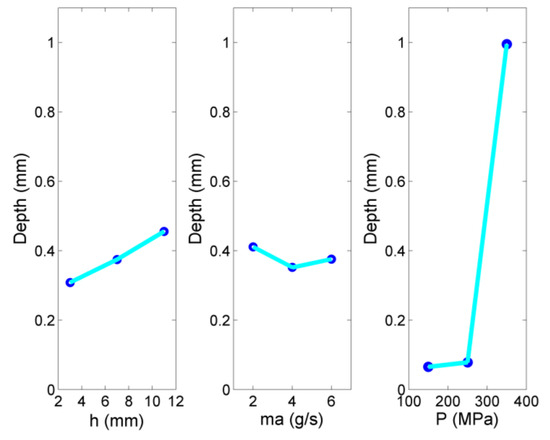
Figure 2.
Main effects plot of average pocket depth.
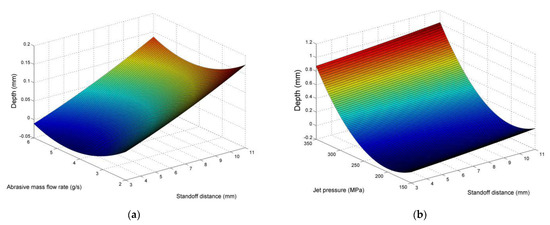
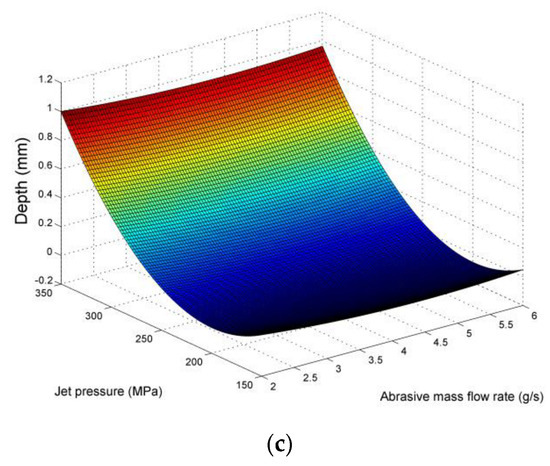
Figure 3.
Surface plots for average pocket depth in respect to (a) stand-off distance and abrasive mass flow rate, (b) stand-off distance and jet pressure, (c) abrasive mass flow rate and jet pressure.
On the other hand, the other two parameters are relatively less significant, with the increase in stand-off distance contributing to a slight increase in depth, and the increase in abrasive mass flow rate leading to a slight increase in depth. In the latter case, this behavior can probably be attributed to the higher level of fragmentation of the abrasive grains at high concentrations due the low hardness and inferior mechanical properties of the abrasive material, which lead to destruction of the sharp edges and size reduction, thus rendering them less effective and comparable to particles of a smaller size. These findings are also reported in the relevant literature on pocket milling using AWJM technology, as it was found that the impact of abrasive mass flow rate is relatively low in pocket milling compared to other parameters, being almost negligible in some cases [45,49]. Higher rate implies that more particles impact the workpiece per unit time, with the total kinetic energy increasing considerably [45]. However, above a certain value, the fracture of particles is more possible due to collisions between them, reducing the capabilities of material removal [45]. The stand-off distance was found to exhibit a non-linear relationship with pocket depth, as the increase in SOD up to a point is proven to be positively correlated with the depth, increasing the jet energy [45]. However, for higher values, the energy decreases due to lack of focus [45].
Consequently, given that the contribution of these two parameters is far smaller than that of jet pressure, these trends have only a minor importance regarding the regulation of pocket depth. Thus, apart from its contribution to energy consumption, jet pressure plays a significant role in achieving the desired pocket depth in a controlled-depth milling process.
The results regarding pocket depth will be also interesting to discuss alongside the results regarding the pocket width, as both results affect the material removal rate, which is a fundamental indicator regarding productivity of the process. As the length of the pocket, which coincides with the workpiece width, is constant, the estimation of removed volume of material requires the calculation of depth and width only.
Regarding the variation of pocket width, it can be also related to the superposition of adjacent grooves formed by the movement of the abrasive jet over the predefined path. Pocket width is more relevant to the kerf width, as it actually occurs as a summation of adjacent kerfs; thus, it is expected to be correlated with the process parameters to a different extent than the pocket depth. The values of pocket width, presented in Figure 4 and Figure 5, show that the variation of this quantity is much lower than the variation of average pocket depth, even in harsher conditions. The main effects plot of Figure 4 indicates that pocket width values increase mainly due to the increased jet pressure values, as the higher amount of material removed through the more intense interaction of abrasive particles and workpiece surface also leads to larger width of the pockets. The effect of stand-off distance is more complex, as it contributes to an increase in width up to a point, due to the larger dispersion of abrasive particles, but after the stand-off distance is higher than a certain value, due to several reasons such as the reduction of energy of the particles, the width is less affected. Finally, the increase in abrasive mass flow rate leads to a slight decrease in kerf width, possibly to the increase in particle fragmentation.
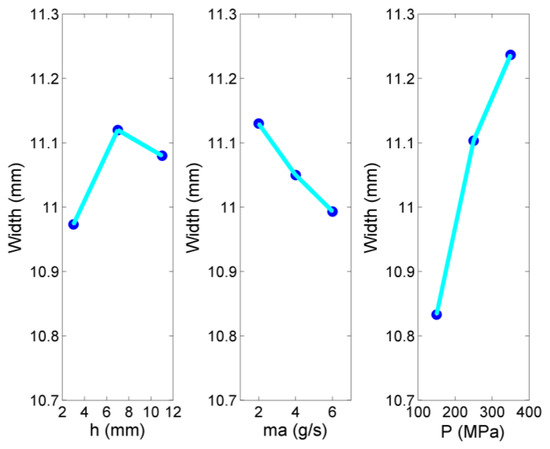
Figure 4.
Main effects plot of average pocket width.
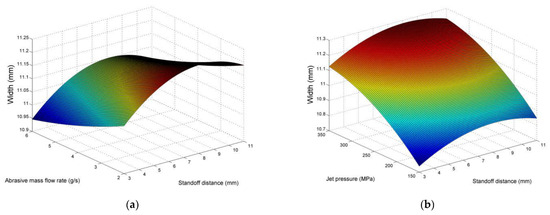
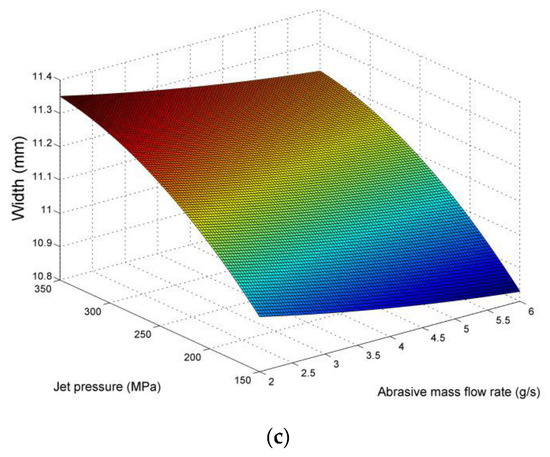
Figure 5.
Surface plots for average pocket width in respect to (a) stand-off distance and abrasive mass flow rate, (b) stand-off distance and jet pressure, (c) abrasive mass flow rate and jet pressure.
After having presented and discussed the results regarding depth and width of the produced pockets, the effect of process parameters on material removal rate will be discussed. In Figure 6, the main effects plot for MRR is presented. As it is expected, the material removal rate is highly correlated with the jet pressure which contributes to the enlargement of both pocket depth and width, something that was also observed in the relevant literature [48,49]. Taking into consideration that higher jet pressure also leads to higher energy consumption, it is necessary to perform a favorable compromise between two important targets, such as productivity and energy consumption, by regulating the values of jet pressure. On the other hand, the contribution of the two other parameters is rather minimal, as can be seen both in Figure 6 and Figure 7, with the increase in stand-off distance increasing the MRR due to the creation of wider pockets and the abrasive mass flow rate leading to a negligible decrease and subsequent increase in the MRR. Although these results were already anticipated based on the previous analysis of depth and width, it is worth noting that the magnitude of MRR is almost two orders of magnitude lower than the value obtained using other types of abrasives [46,49] in some cases, especially when jet pressure is minimal, rendering pockets with a depth of a few tens of micrometers; even at the highest pressure and abrasive mass flow rate values, it still remains under 100 mm3/min. The main reason for these observations is the considerably low hardness of the abrasive, being estimated around 2.5–3 Mohs, while garnet is usually reported to have a hardness of 7–7.5 Mohs. This result indicates that, although the use of softer abrasives even for cutting operations is justified under certain conditions, this organic ecological abrasive is not efficient for roughing but can used in conjunction with a harder abrasive in order to achieve both high productivity and better sustainability of the process.
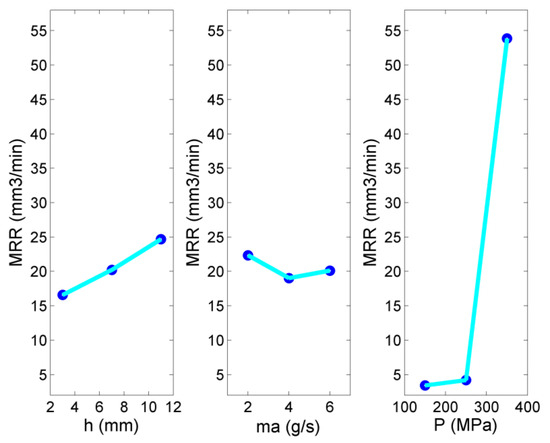
Figure 6.
Main effects plot of MRR.
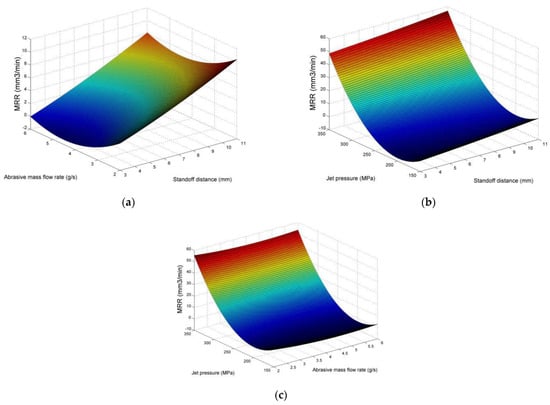
Figure 7.
Surface plots for MRR in respect to (a) stand-off distance and abrasive mass flow rate, (b) stand-off distance and jet pressure, (c) abrasive mass flow rate and jet pressure.
Flatness deviation is another important consideration in the manufacturing industry related to the geometry of the outer surfaces of produced parts. It is especially useful when it is required to connect two elements across a common surface in such a manner that air-tightness or liquid-tightness is achieved. In the context of geometric dimensioning and tolerancing, flatness is considered a geometric characteristic, relevant to form; according to the ASME Y14.5 standard, flatness is defined as a tolerance zone determined by two parallel planes, within which the surface must lie. The calculation of flatness does not require a datum and is often conducted by fitting of points using the least squares method or another relevant method. When flatness is perfect, all points of the surface should lie in the same plane. Flatness is a quantity which is very rarely studied in relevant works, especially in the field of AWJ machining, although it is a very important parameter in industrial practice. Flatness is significantly different to surface roughness as it is classified as being two levels higher beyond surface roughness and one level higher than waviness as a surface parameter. Thus, it is expected not to exhibit the same correlation as surface roughness in respect to process parameters or it is affected to a different degree by them.
In the present case, the results indicate again that there is a considerable variation of flatness values in the conducted experiments. These differences can be mainly attributed to the increase in jet pressure rather than the other two parameters, as can be seen in the main effects plot of Figure 8. In fact, jet pressure is a very effective parameter for the regulation of pocket flatness, as low pressure leads to almost perfectly flat surfaces, but in the case of moderate or higher jet pressure values, the deviations can be considerably large. Thus, it becomes obvious that jet pressure does not only alter the topography of the surface but its form as well, with observable deviations occurring at higher pressure values. Thus, it is important to note that the largest increase in flatness deviation occurs for jet pressure values over 250 MPa. On the other hand, stand-off distance and abrasive mass flow rate have a lower contribution to the deviation of flatness, as can be also seen in Figure 8 and Figure 9. In detail, the increase in stand-off distance leads to slightly higher flatness deviation values due to the large area of dispersion of the abrasive particles and less focusing of the jet, whereas the mass flow rate increase leads to slightly lower flatness error, as in the case of depth, probably to due to higher fragmentation of particles which smoothens their geometry, reduces their cutting ability and contributes to the achievement of better uniformity of the produced surface. Thus, in order to achieve flat surfaces during AWJM, jet pressure values should be carefully chosen within the acceptable range, whereas the other parameters can be adjusted with more flexibility, taking into consideration other process outcomes as well.
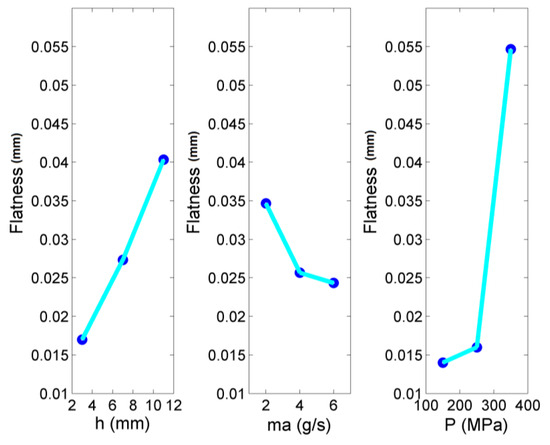
Figure 8.
Main effects plot of flatness.
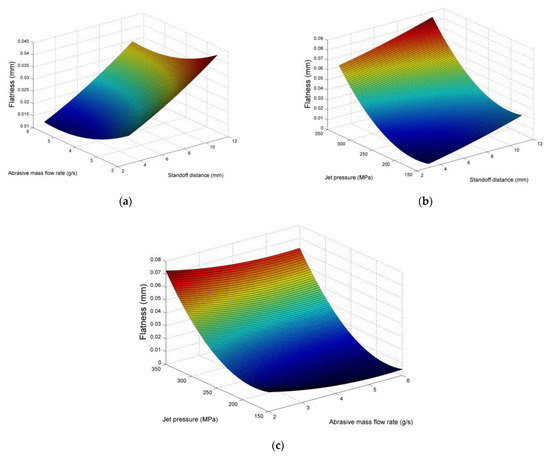
Figure 9.
Surface plots for flatness in respect to (a) stand-off distance and abrasive mass flow rate, (b) stand-off distance and jet pressure, (c) abrasive mass flow rate and jet pressure.
It is important to note that only a couple of studies exist in the relevant literature regarding flatness in AWJM. Srinivasu and Axinte [37] reported a flatness tolerance of 1.2 mm while creating pockets on a composite workpiece by the maskless procedure. Popan et al. [50] observed flatness values between 0.5–3 mm in their investigation. Kong et al. [51] obtained flatness error values below 0.33 mm at the bottom surfaces of pockets on a NiTi workpiece.
Parallelism or surface parallelism is another indicator relevant to the geometric characteristics of the surface, which is relevant to the comparison of two different surfaces which should be parallel between them within a suitable tolerance value. Contrary to flatness, the measurement of parallelism requires the definition of an appropriate datum. This parameter is rather useful when it is required to guarantee the contact between mating parts in an assembly which should be parallel and is not a form but orientation tolerance parameter. As in the case of flatness, parallelism is also is rarely studied as a parameter, although it has considerable importance in industrial applications.
From the results presented in Table 3, it can be observed that the variation of parallelism error is very high, with negligible values in some cases and much higher values in others. The main effects plot of Figure 10 and the surface plots of Figure 11 provide the necessary information in order to observe the trends regarding parallelism error in respect to the three process parameters. As it was expected, the jet pressure is a prominent parameter for affecting parallelism of pocket surfaces to a large extent. The indication that, in the present case, pressure values over 250 MPa have a detrimental effect on the outcome of the process is once more justified, given that the parallelism error deviates significantly when pressure is increased over 250 MPa. On the other hand, the results regarding the other two parameters are less conclusive, as, apart from the weaker correlation with parallelism error, stand-off distance seems to lead to a slight increase in the error, after which the error is decreased, probably due to the larger dispersion of particles positively affecting their impact on the surface, whereas an increased abrasive mass flow rate leads to deterioration of parallelism until it reaches a critical value. These results are not important given the considerably low contribution of these parameters to the total variation of parallelism. Thus, in order to achieve the required parallelism of pockets, low to moderate jet pressure values are recommended.
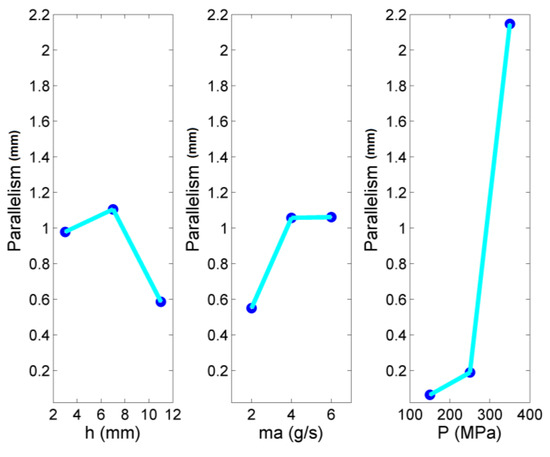
Figure 10.
Main effects plot of parallelism error.
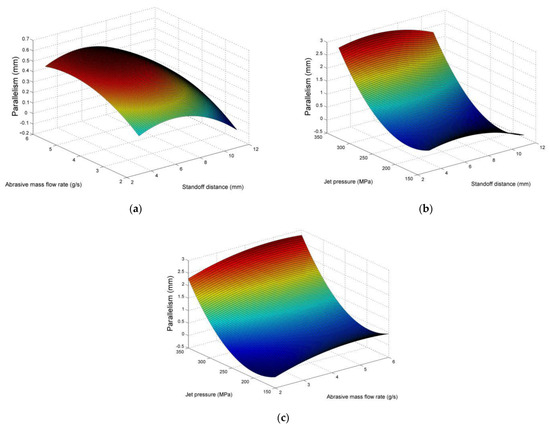
Figure 11.
Surface plots for parallelism error in respect to (a) stand-off distance and abrasive mass flow rate, (b) stand-off distance and jet pressure, (c) abrasive mass flow rate and jet pressure.
Nair and Kumanan [52] were among the few researchers to report findings on parallelism of pockets fabricated by AWJM. Although the results on parallelism were not separately analyzed, the range of values was found to be between 0.08 and 0.25 mm. Moreover, Babu and Chetty [8] mentioned that use of recycled abrasives can improve the parallelism error of cut surfaces.
3.2. Additional Series of Experiments
During the analysis of the experiments designed by the Taguchi L9 array, it seems that the most prominent parameter, which was related to all the outcome quantities, was jet pressure; for this parameter, an interesting observation was made, especially regarding the radical increase in depth, width and other quantities when jet pressure is increased in the range 250–350 MPa. So, in order to further investigate this phenomenon, especially in regards to the pocket depth, additional experiments were conducted. Emphasis was placed on the pocket depth, as the achievement of controlled-depth milling is fundamental in many non-conventional processes, such as AWJM. Moreover, in order to be able to further evaluate the possibilities offered by the ecological walnut shell abrasive for controlled-depth milling of pockets, it is important to determine the effect of other parameters such as traverse feed rate and stepover and their contribution to the results. Thus, the study was extended by additional experiments, with different traverse feed rate and stepover values, which are also important parameters of this process.
The results of the additional experiments regarding the effect of jet pressure are presented in Figure 12. These results are particularly useful in establishing the range of jet pressure values which is appropriate for efficient pocket milling and the jet pressure value which can be directly related to the onset of considerable deviation regarding surface quality. More specifically, in Figure 12a, the pocket depth values under different jet pressure values, with other parameters constant (stand-off distance 3 mm, abrasive mass flow rate 6 g/s, stepover 0.6 mm, traverse feed rate 100 mm/min) are depicted. These results extended the findings presented in Figure 2 and directly indicate that there is a non-linear correlation between depth and jet pressure. As was aforementioned, the high intensity of abrasive particle impact on the workpiece surface, even though walnut shell abrasive is rather soft, leads to excessive material removal and larger average depths. This additional investigation about the effect of jet pressure values is particularly important as this parameter is directly related to energy consumption during AWJ machining. Choosing the suitable jet pressure value is crucial in order to achieve the desired depth but also avoid higher energy consumption, deterioration of surface quality and distortion of its form, as was established in the previous subsection. In order to achieve all objectives, it is possible to use different strategies such as the multi-pass strategy by removing less material in each pass but avoiding the deterioration of the produced surface.
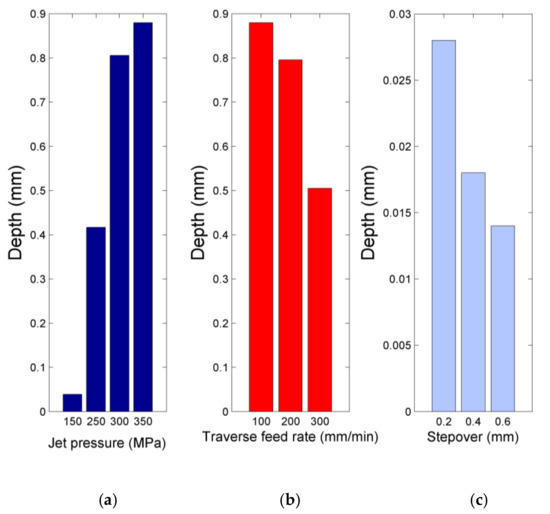
Figure 12.
Pocket depth variation in respect to (a) jet pressure, (b) traverse feed rate, (c) stepover values.
In Figure 12b, the correlation between pocket depth and traverse feed rate is depicted under the following conditions: stand-off distance of 3 mm, abrasive mass flow rate of 6 g/s, stepover of 0.6 mm and jet pressure 350 MPa. This investigation is necessary as the traverse feed rate has a direct implication in the productivity of the process and it is important to determine how much it can be increased for the specific combination of abrasive and workpiece material. In the previous series of experiments, traverse feed rate was not varied and it was kept constant at 100 mm/min, a value which was chosen by preliminary experiments as it was sufficient for material removal even at the lowest pressure value of 150 MPa and abrasive mass flow rate of 2 g/s. The findings of Figure 12b indicate the anticipated correlation between pocket depth and traverse feed rate, which is negative, as the reduction of exposure time of the jet at high traverse feed rates leads to a lower amount of removed material and more shallow depths. However, in comparison to the effect of jet pressure, the effect of traverse feed rate is rather low, as a threefold increase in traverse feed rate resulted in less than a twofold reduction of depth. This result is rather important for two reasons: at first, it can indicate the limit value of traverse feed rate which can be used (for the specific combinations) in order to remove a considerable amount of material, and on the other hand it is important as it shows that an increase in traverse feed rate does not decreases pocket depth proportionally, meaning that a twofold or threefold increase in traverse feed rate, which proportionally reduces the machining time, can be selected without having an adverse effects on productivity. Finally, the reason that traverse feed rate is not as important for the regulation of depth during pocket milling as during slot milling is that, in pocket milling, the depth is mainly regulated by the succession of adjacent slots; thus, stepover is expected to be more important, as well as jet pressure, which produces deeper grooves. The obtained results are in line with results from the relevant literature, which indicate that traverse feed rate is a significant parameter for pocket milling (although less significant than stepover or jet pressure), leading to a decrease in depth, as a faster speed is related to lower exposure time and a lower number of particles impacting the workpiece surface [45,46,48,49]. Moreover, an increase in traverse feed rate leads to a considerable decrease in MRR [48,49].
In Figure 12c, the variation of pocket depth in respect to the stepover values is plotted for experiments conducted under the following conditions: stand-off distance of 3 mm, abrasive mass flow rate of 2 g/s, traverse feed rate of 100 mm/min and jet pressure of 150 MPa. In the case of stepover, increased values of this parameter are related to higher distances between adjacent lateral grooves; thus, it is expected that the depth will decrease as the stepover is increased. The results directly reflect this anticipated trend, as the pocket depth decreases significantly for stepover values over 0.2 mm. In fact, a threefold increase in step over led to an almost twofold decrease in depth, indicating that variation in the stepover can affect the depth significantly, perhaps to a lesser degree than jet pressure, but to a higher degree than the other parameters. Moreover, as this parameter also affects machining time—given that, in order to machine a pocket of the same dimensions, a longer path is required when stepover is small—a favorable compromise between time and achievable depth is possible only for specific stepover values. These findings are similar to those reported in the relevant literature, as it is accepted that stepover is a considerably important parameter for pocket milling, as are jet pressure and traverse feed rate, with a clear decrease in pocket depth occurring when stepover increases due to lower overlap between subsequent traverse passes of the jet [46,49]. Furthermore, it is evident that it also can cause a large reduction of MRR when its values are increased [49].
4. Conclusions
In the present work, AWJ machining experiments were carried out with particles of an ecological organic abrasive material, namely, walnut shell. In order to determine the capabilities of such an abrasive type, at first a series of experiments conducted under a Taguchi L9 orthogonal array were carried out and a statistical analysis of pocket depth, width, material removal rate, flatness and parallelism error was performed. Afterwards, some additional experiments were carried out to further evaluate the capabilities of pocket milling with the selected abrasive and extended the investigation of the non-linear effect of jet pressure. The following conclusions were drawn from these investigations.
During the first series of experiments, it was revealed that, during pocket milling, jet pressure is the predominant parameter regarding various process outputs, including pocket depth, pocket width, material removal rate, flatness and parallelism error. For pressure values over 250 MPa, the pocket dimensions, material removal rate, form and orientation errors increase to a large extent, indicating that there should be a limit on the range of jet pressure in order to ensure the appropriate creation of pockets.
Regarding the other process parameters, namely, stand-off distance and abrasive mass flow rate, their relative contribution was found to be minimal for every process output.
The findings from the additional experiments showed that the traverse feed rate has an observable effect on pocket depth, although its relative contribution is much lower regarding pocket milling than slot milling. On the other hand, stepover is a considerable parameter of the AWJ milling process, perhaps second only to jet pressure, given that it can affect pocket depth significantly compared to the other parameters.
Finally, it was proven that soft abrasives, such as walnut shell, have the potential not only for cleaning or polishing operations but also for cutting operations under appropriate conditions. Although the cutting efficiency is rather low, these results are considered promising, especially regarding the potential use of soft abrasives in a mixture with harder ones in order to achieve both high productivity and better surface integrity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.E.K. and P.K.-O.; methodology, N.E.K. and P.K.-O.; software, N.E.K.; validation, N.E.K.; formal analysis, N.E.K.; investigation, N.E.K.; resources, P.K.-O.; data curation, N.E.K.; writing—original draft preparation, N.E.K. and P.K.-O.; writing—review and editing, N.E.K.; visualization, N.E.K.; supervision, N.E.K. and P.K.-O.; project administration, N.E.K. and P.K.-O.; funding acquisition, N.E.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Polish National Agency for Academic Exchange (NAWA, Agreement No. BPN/ULM/2022/1/00129/U/00001).
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Alvarez, M.E.P.; Barcena, M.M.; Gonzalez, F.A. On the sustainability of machining processes. Proposal for a unified framework through the triple bottom-line from an understanding review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 3890–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, Y.; Murugesan, P.K.; Mohan, M.; Khan, S.A.L.A. Abrasive water jet machining process: A state of art of review. J. Manuf. Process 2020, 49, 271–322. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Liang, Z.; Wen, G.; Yuan, X. Waterjet machining and research developments: A review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 102, 1257–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H. On-line recycling of abrasives in abrasive water jet cleaning. Procedia CIRP 2014, 15, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perec, A. Disintegration and recycling possibility of selected abrasives for water jet cutting. DYNA 2017, 84, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perec, A. Environmental aspects of abrasive water jet cutting. Annu. Set. Environ. Prot. 2018, 20, 258–274. [Google Scholar]
- Perec, A.; Radomska-Zalas, A.; Fajdek-Bieda, A.; Kawecka, E. Efficiency of tool steel cutting by water jet with recycled abrasive materials. Materials 2022, 15, 3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantha Babu, M.; Krishnaiah Chetty, O.V. A study on recycling of abrasives in abrasive water jet machining. Wear 2003, 254, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, V.N.; Chau, H.V.; Hung, T.Q. A study on recycling of supreme garnet in abrasive waterjet machining. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 248, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantha Babu, M.; Krishnaiah Chetty, O.V. Studies on recharging of abrasives in abrasive water jet machining. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2002, 19, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liu, H.; Ye, B.; Qian, W. Recycling of printed circuit boards by abrasive waterjet cutting. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 148, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinzato, M.C.; Hypolito, R. Solid waste from aluminum recycling process: Characterization and reuse of its economically valuable constituents. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, T.H. Silicon sawing waste treatment by electrophoresis and gravitational settling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 189, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, G.; Kaya, S.; Karakurt, I. Utilization of solid-cutting waste of granite as an alternative abrasive in abrasive waterjet cutting of marble. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 159, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarici, D.E.; Ozdemir, E. Utilization of granite waste as alternative abrasive material in marble grinding processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 201, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabarinathan, P.; Annamalai, V.E.; Rajkumar, K. Sustainable application of grinding wheel waste as abrasive for abrasive water jet machining process. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumaran, N.; Devaraj, P.; Arunkumar, P.; Sekar, T. Re-use of abandoned sanitary ware waste as abrasive particles for abrasive jet machine. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murari, K.; Siddique, R.; Jain, K.K. Use of waste copper slag, a sustainable material. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2015, 17, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsukov, G.; Zhuravleva, T.; Kozhus, O. Study of the effect of heat treatment of copper slag particles on abrasiveness for abrasive waterjet cutting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, S.B.; Park, H.H.; Cho, S.B. Effect of disagglomeration on the recovery of abrasives from waste sludge. Geosystem Eng. 2007, 10, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabarinathan, P.; Veiravan, A.; Kaliyamoorthy, R.; Kumar, V. Sustainable solution to low-cost alternative abrasive from electric ceramic insulator waste for use in abrasive water jet machining. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 5243–5257. [Google Scholar]
- Sabarinathan, P.; Annamalai, V.E. Removal of aluminosilicate bond and processs optimization on recovery of sol gel alumina abrasive grain from abrasive industry waste. Silicon 2021, 13, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, S.C.L. Characterization and Testing of Ferrous Granules as an Abrasive for Water Jet Cutting. Master’s Thesis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Schuler, M.; Day, R.; Bergs, T. Benchmark of abrasives for different applications. In Proceedings of the WJTA Conference & Expo 2022. Conference Proceedings, New Orleans, LA, USA, 1–3 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Perec, A. Experimental research into alternative abrasive material for the abrasive water-jet cutting of titanium. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkarnain, I.; Lai, L.S.; Syakir, M.I.; Rahman, A.A.; Yusuff, S.; Hanafiah, M.M. Life cycle assessment of crushed glass abrasive manufacturing from recycled glass. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 880, 12054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, A.; Bagal, D.K.; Pattanaik, A.K.; Panda, S.N.; Barua, A.; Barkey, R.K.; Jeet, S. Recent advancements in ice jet machining process as an alternative of AWJM. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 50, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerman, M.; Orbanic, H.; Junkar, M.; Lebar, A. Thermal aspects of ice abrasive water jet technology. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2015, 7, 1687814015597619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerman, M.; Orbanic, H.; Valentincic, J. CFD analysis of thermal fields for ice abrasive water jet. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 220, 107154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavorel, F.; El Mansori, M.; Chegdani, F.; Tazibt, A. Wear under brittle removal regime of an under-expanded cryogenic nitrogen jet machining of bio-composites. Wear 2021, 477, 203795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, Y.; Murugasen, P.K.; Sundarajan, L.R.; Arunachalam, R. Experimental investigation on cryogenic assisted abrasive waterjet machining of aluminium alloy. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2019, 6, 415–432. [Google Scholar]
- Kohli, R. Microabrasive technology for prediction cleaning and processing. In Developments in Surface Contamination and Cleaning, 2nd ed.; Kohli, R., Mittal, K.L., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; Volume 1, pp. 627–666. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.B.; Islam, M.; Islam, S.U. Facile fabrication of abrasive materials for sandpaper from waste materials. Clean. Waste Syst. 2023, 4, 100066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Cong, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, M. Application of sodium bicarbonate abrasive jet technology for PCB desmear process: Conditions and simulation. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 396, 136584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osa, J.L.; Mondragon, G.; Ortega, N.; Marzo, F.F.; Pena-Rodriguez, C. On the friability of mussel shells as abrasive. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 375, 134020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadh, S.M.; Ali Khalid, S. Tigris river sediments as abrasive for polishing marble. Nat. Resour. Res. 2019, 28, 1371–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasu, D.S.; Axinte, D.A. Maskless pocket milling of composites by abrasive waterjets: An experimental investigation. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2014, 136, 41005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikó, B.; Rácz, G. Investigation of Flatness and Angularity in Case of Ball-End Milling. In Proceedings of the International Symposium for Production Research 2018; Durakbasa, N., Gencyilmaz, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bustillo, A.; Pimenov, D.Y.; Mia, M.; Kapłonek, W. Machine-learning for automatic prediction of flatness deviation considering the wear of the face mill teeth. J. Intell. Manuf. 2021, 32, 895–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, B.L.; Shih, A.J.; Stephenson, D.A. Improvement of surface flatness in face milling by varying the tool cutting depth and feed rate. In Proceedings of the ASME 2009 International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference MSEC2009, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 4–7 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, A.; Desai, K.A. Tool and workpiece deflection induced flatness errors in milling of thin-walled components. Procedia CIRP 2020, 93, 1411–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazarika, M.; Dixit, U.S.; Deb, S. Effect of datum surface roughness on parallelism and perpendicularity tolerances in milling of prismatic parts. Proc. IMecheE Part. B J. Eng. Manuf. 2009, 224, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Ma, S.; Saifullah, S. New method of plane to plane parallelism error measurement based on flatness plane. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 941–944, 2209–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y. A strategy to evaluate and minimize parallelism errors of a rotor system in a precision rotary table. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 106, 3641–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Chen, J.; Gao, H.; Wang, X. An investigation into the abrasive waterjet milling circular pocket on titanium alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 107, 4503–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopichand, G.; Sreenivasarao, M. Multi-response parametric optimisation of abrasive waterjet milling of Hastelloy C-276. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Palafox, G.A.; Gault, R.S.; Ridgway, K. Characterisation of abrasive water-jet process for pocket milling in Inconel 718. Procedia CIRP 2012, 1, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, Y.; Naresh Raj, K.L.; Tandon, P. Measurement and analysis of pocket milling features in abrasive waterjet machining of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Arch. Civil. Mech. Eng. 2023, 23, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutham, U.; Hasu, B.S.; Chakraverti, G.; Kanthababu, M. Experimental investigation of pocket milling on Inconel 825 using abrasive water jet machining. Int. J. Curr. Eng. Technol. 2016, 6, 295–302. [Google Scholar]
- Popan, A.; Balc, N.; Carean, A.; Luca, A.; Miron, A. Research on Abrasive Waterjet milling of the planar surfaces, slots and profiles. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 760, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.C.; Srinivasu, D.; Axinte, D.; Voice, W.; McGourlay, J.; Hon, B. On geometric accuracy and integrity of surfaces in multi-mode abrasive waterjet machining of NiTi shape memory alloys. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 62, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.; Kumanan, S. Multi performance optimization of abrasive waterjet machining of Inconel 617 using WPCA. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2016, 32, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).