Abstract
The recovery of valuable metals from jarosites is a topic of great relevance regarding the implementation of the circular economy; however, these materials also contain metals such as arsenic and lead, which are harmful to health and the environment. Considering these factors, it is important to monitor these metals at each stage of treatment used to recover the valuable metals. In the present work, the behavior of As and Pb was assessed during the pretreatment conducted on a jarositic residue using direct zinc leaching (DLR), as well as leaching in cyanide and cyanide media with glycine. It was found that when no DLR pretreatment was performed, As and Pb naturally dissolved in the cyanide-leaching medium at concentrations of 34.08 mg/L and 99.12 mg/L, respectively. When an alkaline treatment was conducted on the residue (DLR-AH), it was found that there was no presence of As and Pb in the cyanidation solution, while in the case of the cyanide solution with glycine, we observed 83.35 mg/L of As and 213.63 mg/L of Pb. During the oxidizing alkaline hydrothermal treatment (DLR-AHO), 27.5 mg/L of As and 106.78 mg/L of Pb were detected in the cyanide solution. In the cyanide solution with glycine, there was less dissolution of As and Pb (11.68 and 66.75 mg/L), respectively. Finally, when desulfurization of the DLR was conducted prior to the DLR-AHO treatment, the dissolution of As and Pb increased due to the elemental sulfur covering the arsenopyrite and galena particles, so that, when removed, these were more susceptible to pretreatment and cyanidation.
1. Introduction
According to Wang et al. [1], jarosites, which are a residue of the hydrometallurgical process used to obtain zinc, contain valuable metals such as gold and silver that can be recovered. However, they also immobilize metals such as arsenic and lead within their crystalline structure, which could be released in the processes used to recover the valuable metals.
Trace element behavior during mineral processing is an area of growing concern for the mining industry because metal extraction processes tend to concentrate trace elements at levels that may pose risks to both human health and the environment [2]. According to Shamsollahni and Partovinia [3], some metals are pollutants that are harmful to the environment and health and are present in some types of water such as drinking water and wastewater, where their values may be above the permissible limits. The World Health Organization and the Environmental Protection Agency have determined the maximum permissible concentrations of the metals in drinking water; for copper, lead, nickel, arsenic, cadmium, and chromium, these values are 1.5, 0.05, 0.1, 0.01, 0.005, and 0.1 mg/L, respectively. Therefore, the current restrictions for maximum concentrations of metals introduced into the environment have led to the search for effective methods for their elimination, such as the adsorption method and precipitation processes with NaOH and chelating agents such as diethyldithiocarbamate and diphenyldithiocarbamate [4,5,6,7,8].
Traditionally, these trace elements have been investigated in mineral processing as impurities in raw materials, as well as base metals and concentrates. However, more recently, this research has been directed at increasing employee safety and complying with environmental regulations [2].
One of the processes of greatest interest in the mining industry is the extraction of gold and silver, where the predominant hydrometallurgical method for leaching gold and silver is the cyanidation process because cyanide remains the most efficient complexing agent compared to others such as thiocyanate and thiosulfate [9,10,11,12]. The dissolution chemistry of gold and silver in alkaline cyanide solutions has been the subject of considerable research since the first practical applications because, under oxidizing conditions, Au and Ag can be complexed and dissolved in alkaline cyanide solutions [13]. Ag, together with Au, exists in significant quantities; therefore, the behavior of cyanide solutions is particularly important [14].
Secondly, due to its high affinity for gold and silver, cyanide is capable of selectively leaching other metals from minerals [11]; in this sense, the presence of metals such as lead and arsenic in wastewater from gold and silver extraction processes can be significant [2,15,16,17]. On the other hand, the extraction of metals such as gold and silver is difficult in the presence of jarositic materials, therefore it is necessary to subject this type of material to treatment prior to cyanidation to release the gold and silver, which, in turn, can release other metals such as lead and arsenic contained in jarositic materials. The lead and arsenic contained in these wastewaters are classified as being of major importance for public health due to their high toxicity [18].
In addition to being a metal that is harmful to the environment and health, according to Parga et al. [19], the presence of lead decreases the leaching rates of gold and silver and consumes an excessive amount of cyanide, and lead ions affect the subsequent precipitation of gold, which is carried out through the Merrill–Crowe process, in which zinc powders are used because lead and copper precipitate together with gold and silver, causing a greater consumption of zinc powders and fluxes during the smelting of the precipitate [19].
Arsenic is a known carcinogenic element that is also associated with alterations in the cardiovascular, immune, and endocrine systems and even in the genetic material. Arsenic sulfides, i.e., iron, manganese, silver, lead, copper, nickel, and antimony sulfides, are the most typical inorganic arsenic compounds. Among them, arsenopyrite is the predominant arsenic-containing ore, which has been studied in gold processing, particularly the precipitation and disposal of solubilized arsenic waste. Based on the above, recent research has focused on studying the behavior of arsenic specifically in tailing discharges to determine the stability of these residues and thus reduce risks to health and the environment [20,21,22,23].
In previous studies, the behavior of insolubles from sphalerite and chalcopyrite leaching (which contain valuable gold and silver) during cyanidation was evaluated; however, due to the composition of these insolubles (elemental sulfur and jarosite), different pretreatments were evaluated [24,25]. The present work exposes the behavior of arsenic and lead during the cyanidation of the aforementioned insolubles, as well as the interaction they have with other elements such as iron and elemental sulfur.
2. Materials and Methods
In this work, the dissolution of arsenic in each of the stages of the treatment was studied for the recovery of gold and silver from a residue using a direct leaching process of sphalerite and the precipitation of iron in one stage (DLR). This process was conducted in a 200 L or 316 L stainless steel reactor, which can operate at 0.15 MPa. The residue was characterized by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry, and the MLA (Mineral Liberation Analyzer) system was used, which was adapted to an FEI Quanta 600 scanning electron microscope to determine the association and chemical composition of the DLR particles. The solid products obtained in each treatment were analyzed to conduct the balances of the chemical elements of interest.
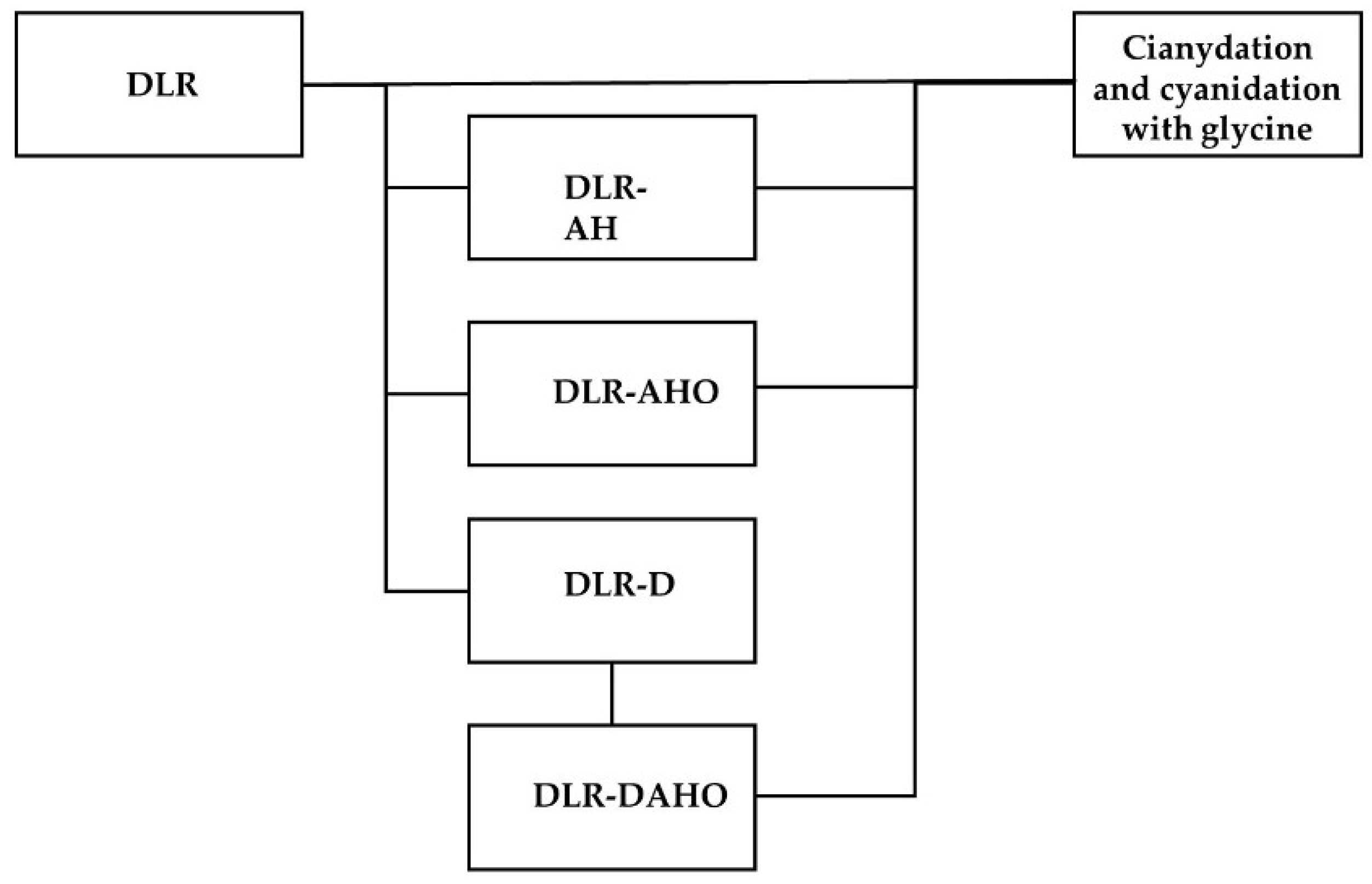
It is worth mentioning that the experimental methodology presented below was carried out in a previous study, where the authors of the present work analyzed the effect of the main components of the residue (jarosite and elemental sulfur) in the extraction of gold and silver [25]. The DLR was subjected to the treatments described in Table 1. It is worth mentioning that the DLR pretreatments were carried out in batches in 1 L beakers. In each pretreatment, the beaker was placed on a magnetic stirring rack at 350 RPM for a certain period of time.

Table 1.
Experimental conditions of the treatments applied to the DLR.
Finally, chemical analysis was performed using a Perkin Elmer ICP optical emission spectrometer. Figure 1 shows a diagram that shows the sequence of tests that was followed during the experimental stage.
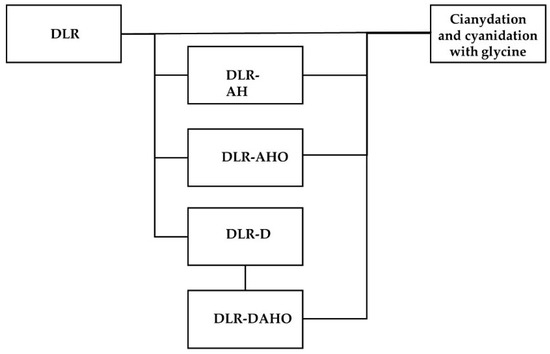
Figure 1.
Experimental test sequence.
3. Results
Table 2 shows the main species determined by MLA, where the DLR is constituted mainly as natrojarosite and elemental sulfur. Arsenic is present in the residue as arsenopyrite and lead as galena.

Table 2.
Results of the analysis of association and chemical composition of the DLR by the SEM-MLA system.
Table 3 shows the chemical analysis of the DLR with and without pretreatments, which was determined via inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry in a Perkin Elmer ICP optical emission spectrometer.

Table 3.
Chemical analysis of DLR.
Table 4 shows the behavior of As, Pb, Fe, and S during conventional cyanidation (DLR-CN) and glycine-assisted cyanidation (DLR-CN-GLY).

Table 4.
Concentration of As, Pb, Fe, and S of the liquid samples obtained from the conventional and glycine-assisted cyanidation of the DLR without pretreatments.
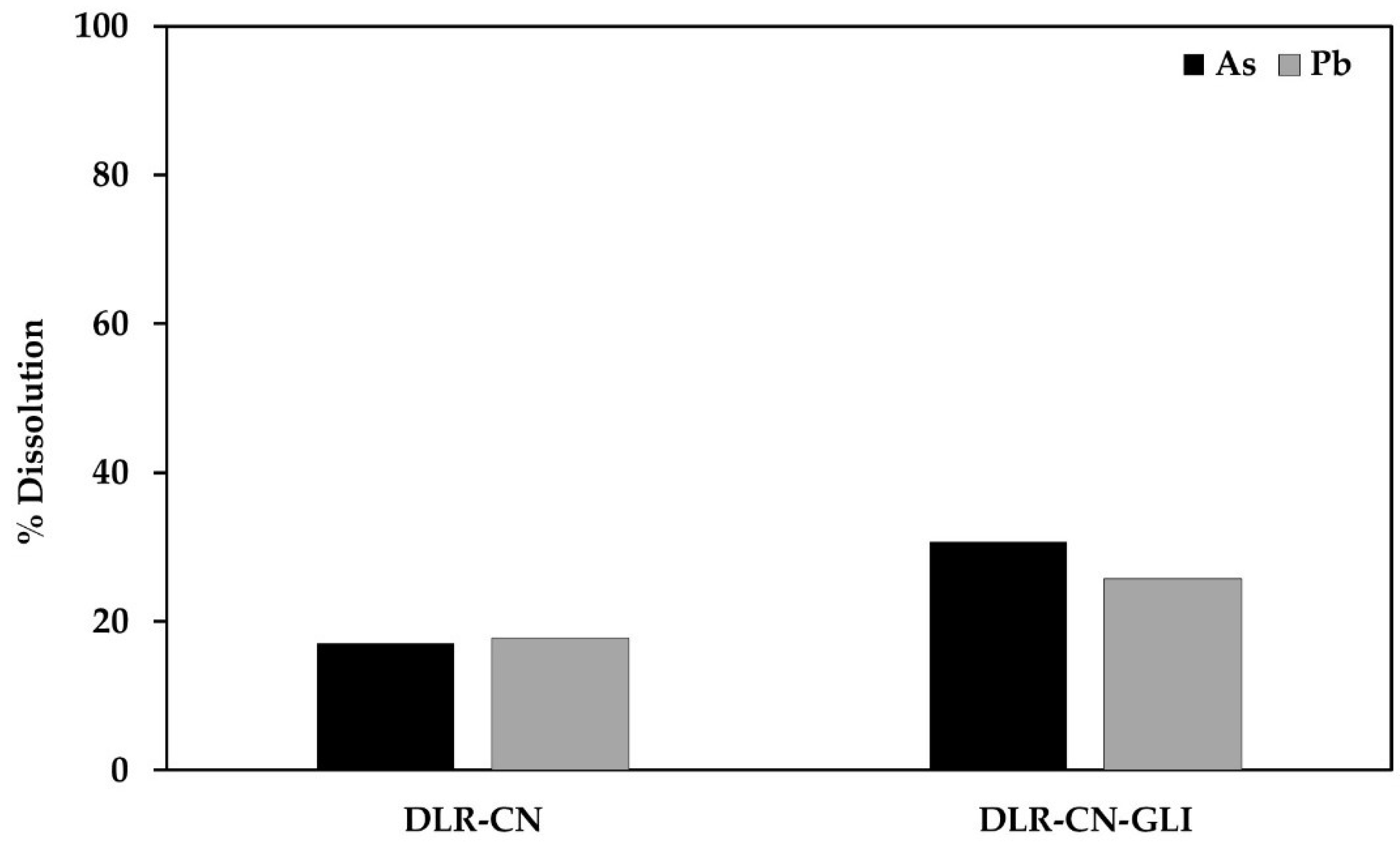
As can be seen in the table above, arsenic and lead can be dissolved in the cyanide and cyanide medium with glycine, remaining in the solutions above the established permissible limits. Figure 2 shows the % dissolution of As and Pb during conventional and glycine-assisted cyanidation of the DLR without pretreatments.
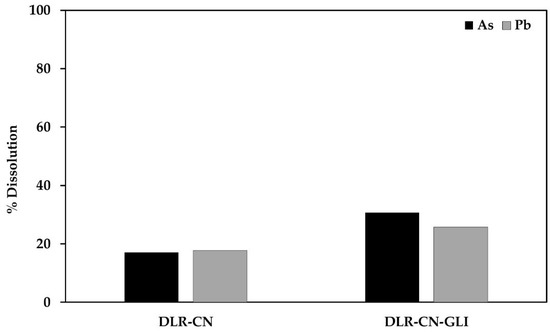
Figure 2.
% Dissolution of As and Pb during conventional and glycine-assisted cyanidation of the DLR without pretreatments.
Table 5 shows the concentration of As, Pb, Fe, and S of the solutions obtained after DLR-AH pretreatment and conventional and glycine-assisted cyanidation.

Table 5.
Concentration of As, Pb, Fe, and S of the liquid samples obtained during the DLR-AH pretreatment and the conventional and glycine-assisted cyanidation.
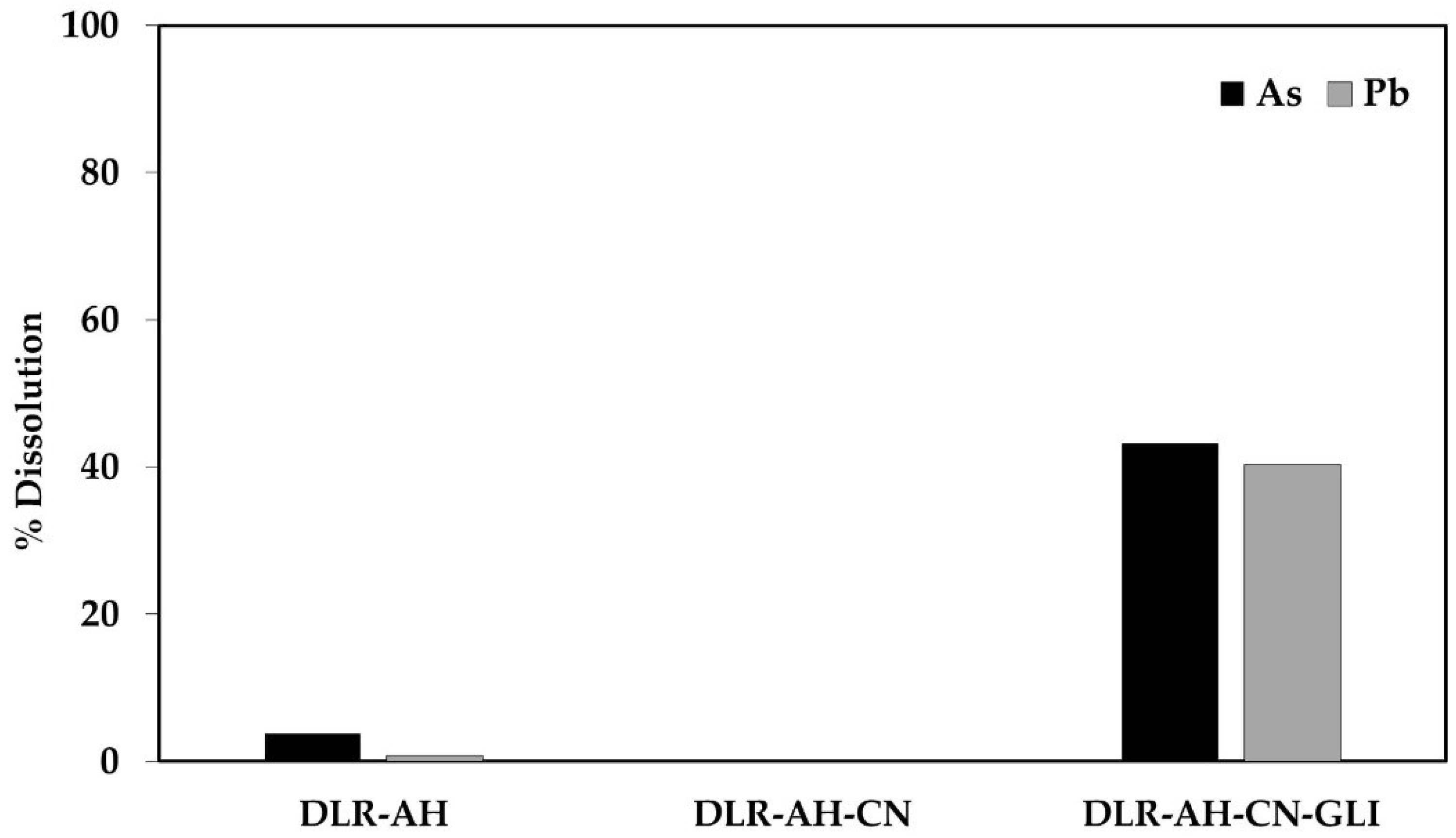
As can be seen in Figure 2, when the residue was subjected to the alkaline hydrothermal treatment, it is observed that there is an increase in the dissolution of iron and sulfur during pretreatment, as well as the leaching media. Figure 3 shows the % dissolution of As and Pb during conventional and glycine-assisted cyanidation of DLR-AH.
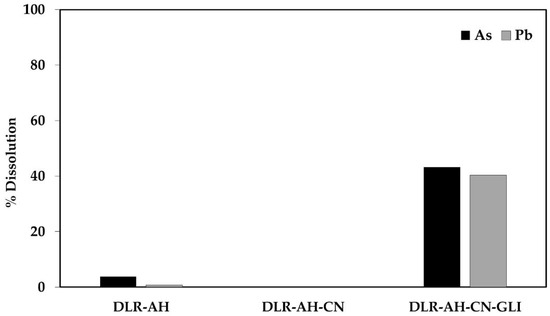
Figure 3.
% Dissolution of As and Pb during conventional and glycine-assisted cyanidation of DLR-AH.
Table 6 shows that when the DLR-AHO treatment was conducted, the presence of arsenic and lead increased during conventional cyanidation, unlike the DLR-AH treatment, where the presence of arsenic and lead was not detected.

Table 6.
Concentration of As, Pb, Fe, and S of the liquid samples obtained during the DLR-AHO pretreatment and the conventional and glycine-assisted cyanidation.
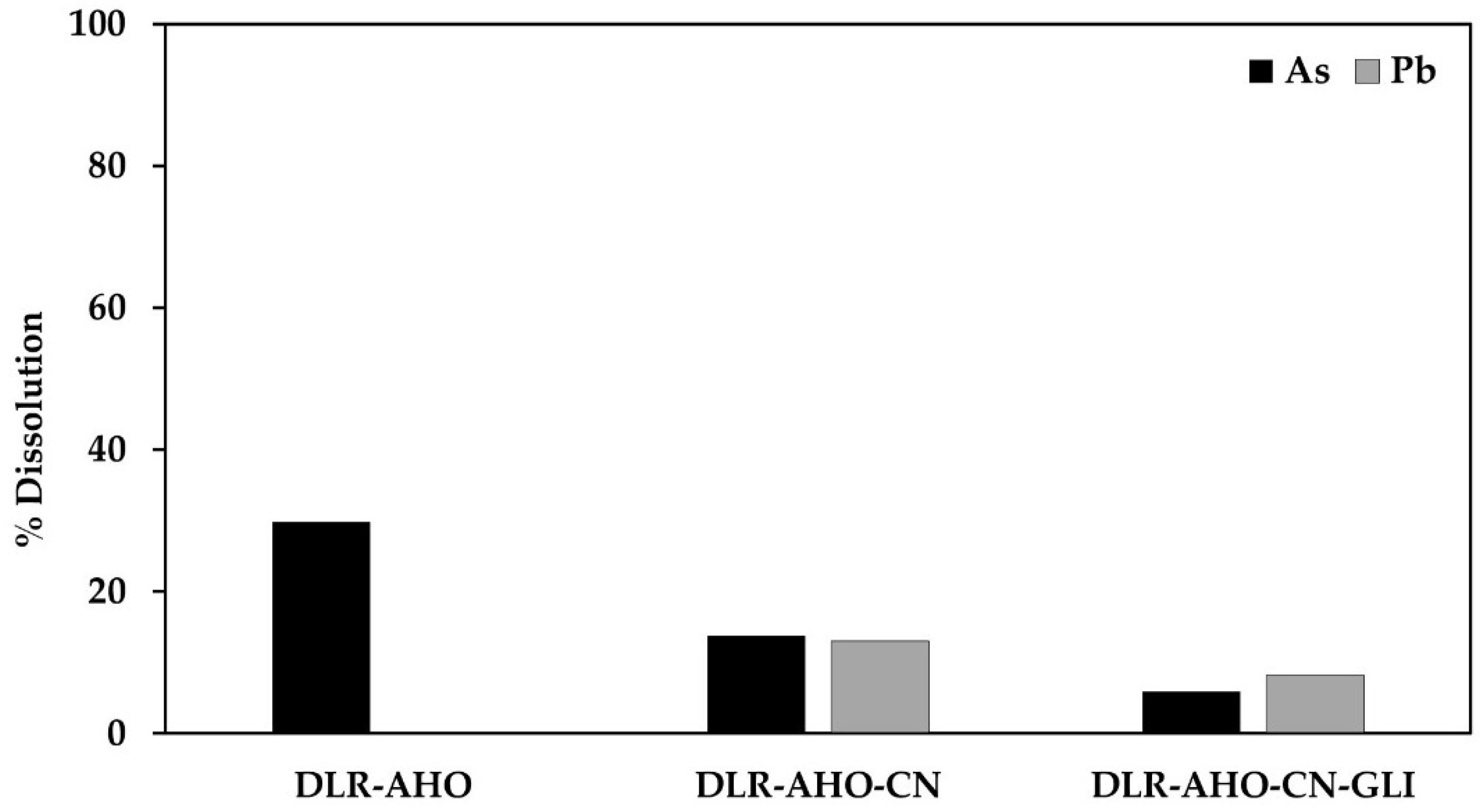
Figure 4 shows the % dissolution of As and Pb during conventional and glycine-assisted cyanidation of DLR-AH.
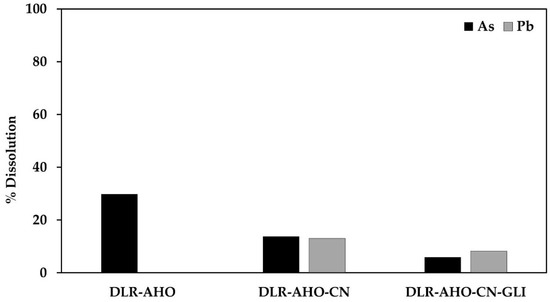
Figure 4.
% Dissolution of As and Pb during conventional and glycine-assisted cyanidation of DLR-AHO.
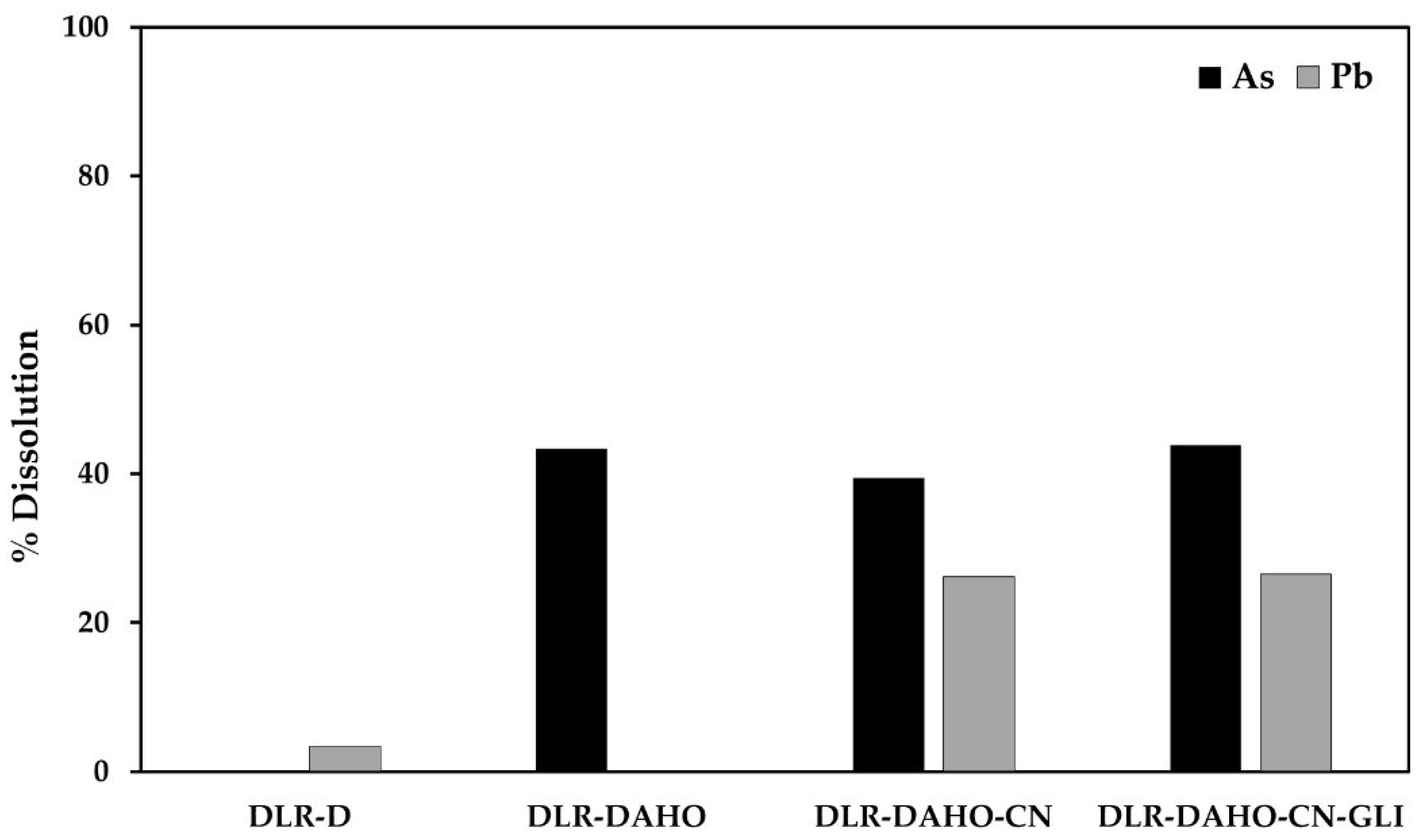
As mentioned previously, to perform the DLR-DAHO pretreatment, desulfurization of the residue jarositic was conducted prior and the treatment of hydrothermal alkaline oxidizing took place immediately. Table 7 shows the concentration of As, Pb, Fe, and S of the solutions obtained after DLR-DAHO pretreatment and conventional and glycine-assisted cyanidation.

Table 7.
Concentration of As, Pb, Fe and S of the liquid samples obtained during the DLR-DAHO pretreatment and the conventional and glycine-assisted cyanidation.
Figure 5 shows the % dissolution of As and Pb during conventional and glycine-assisted cyanidation of DLR-AH.
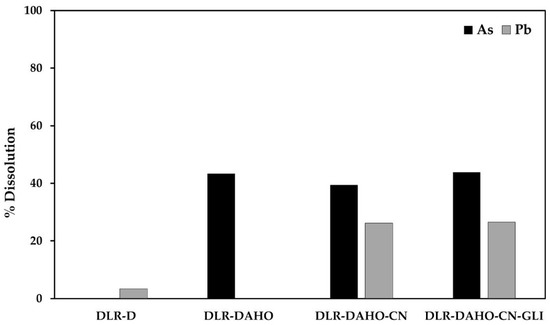
Figure 5.
% Dissolution of As and Pb during conventional and glycine-assisted cyanidation of DLR-DAHO.
4. Discussion
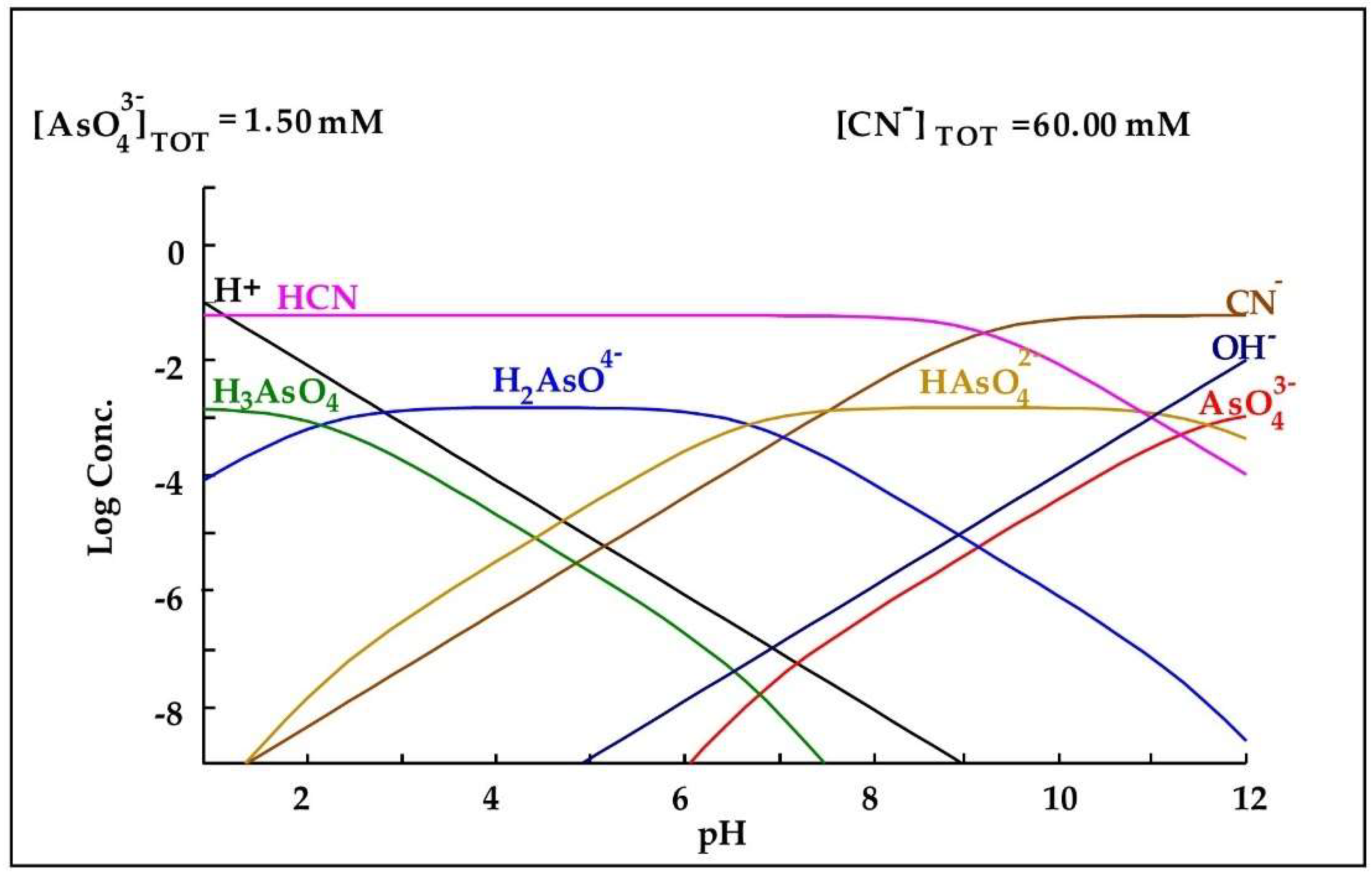
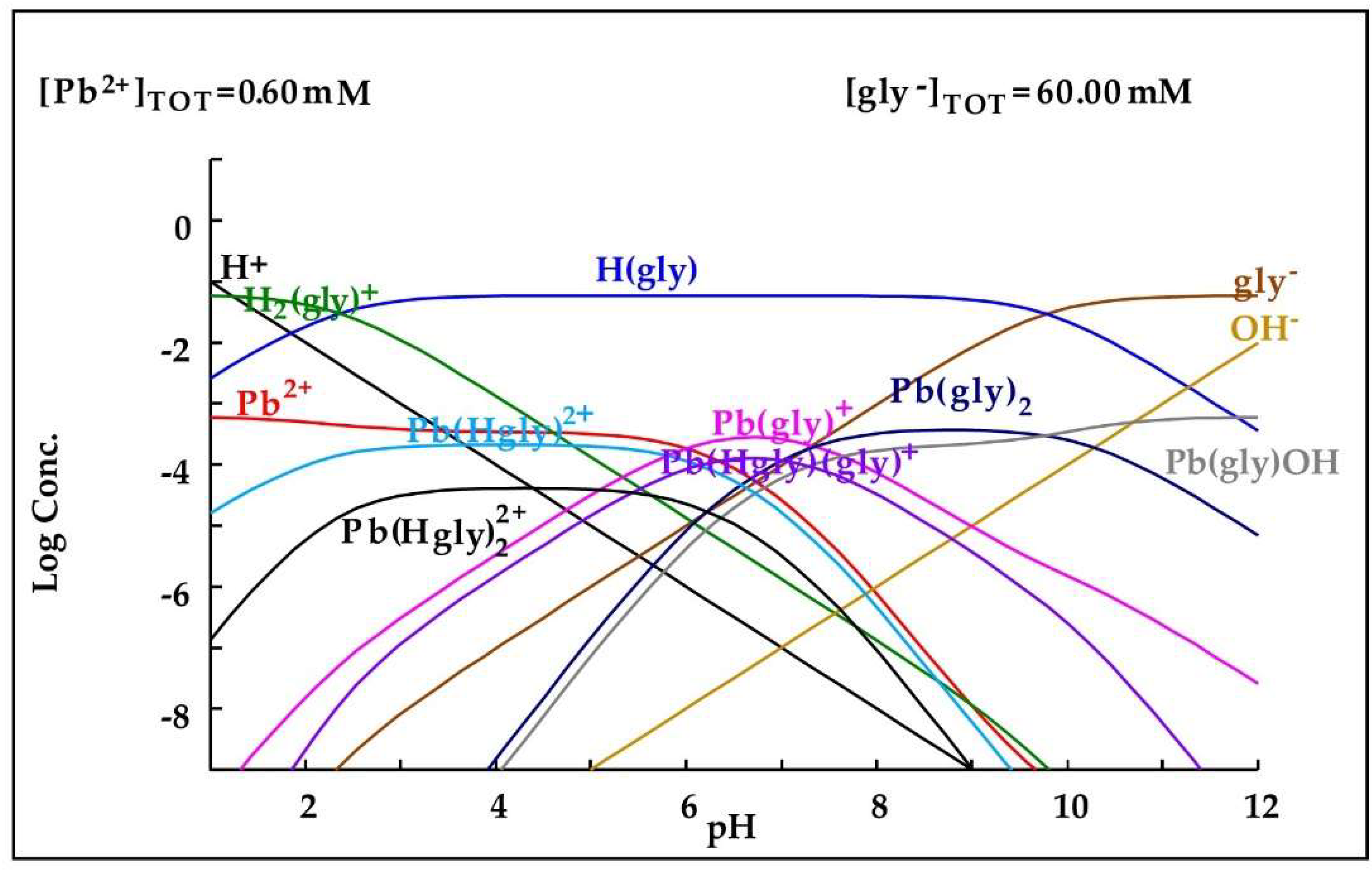
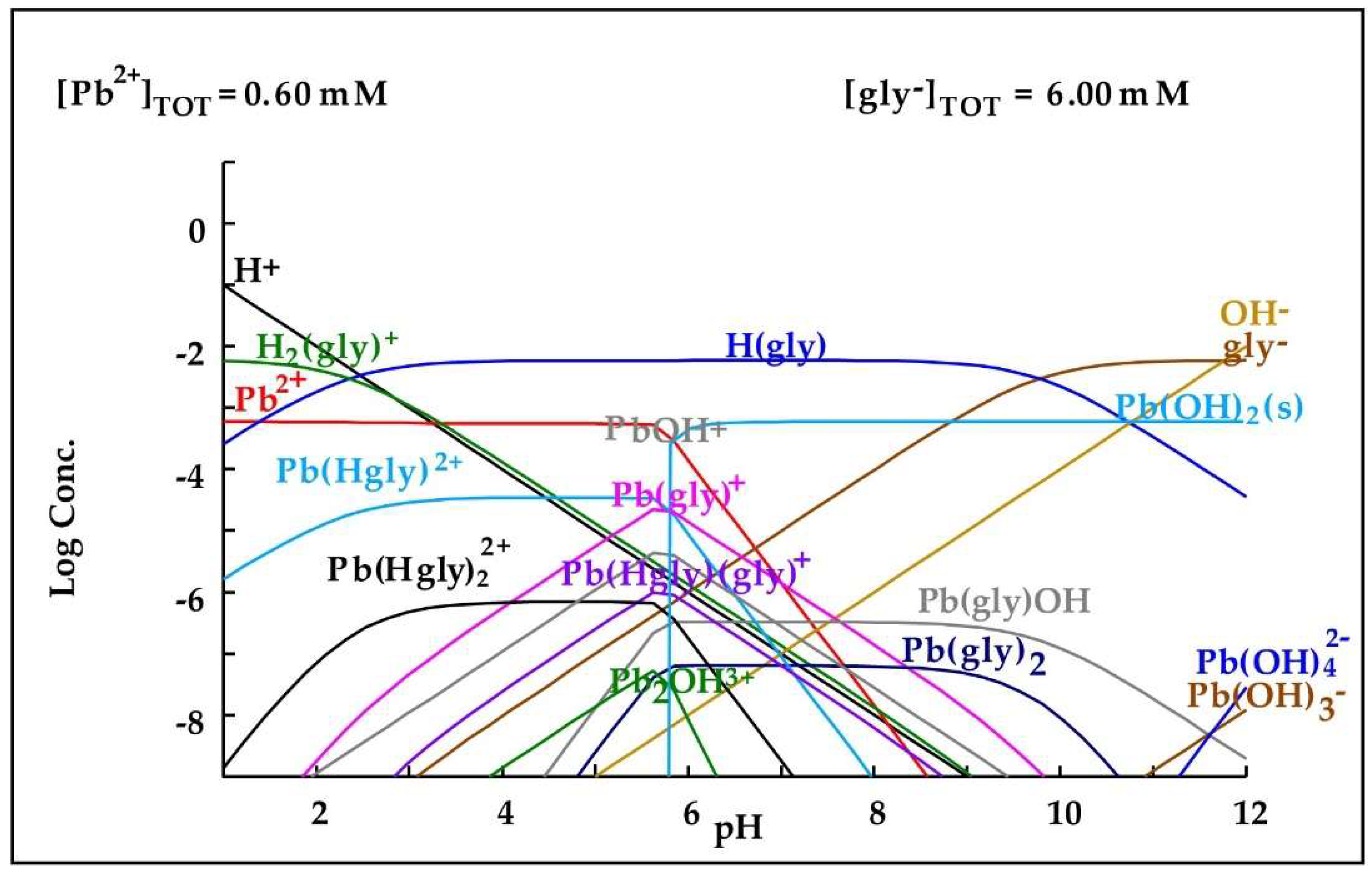
In relation to the behavior of As in the cyanidation process, Hamberg et al. [27] mention in their research work that arsenic does not form stable complexes with cyanide as gold and silver do, but tends to be released when the pH of the medium is alkaline. This can be seen in Figure 6, in which at an alkaline pH, no complexes of arsenic and cyanide are observed, rather only arsenic species such as and .
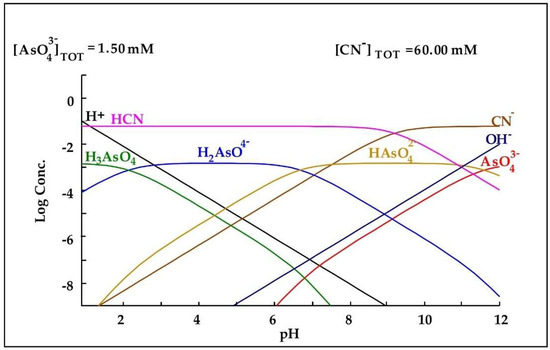
Figure 6.
Diagram of distribution of species of the -CN− system based on the concentrations present in the leaching medium. Diagram made by the authors in Medusa software version 2010.
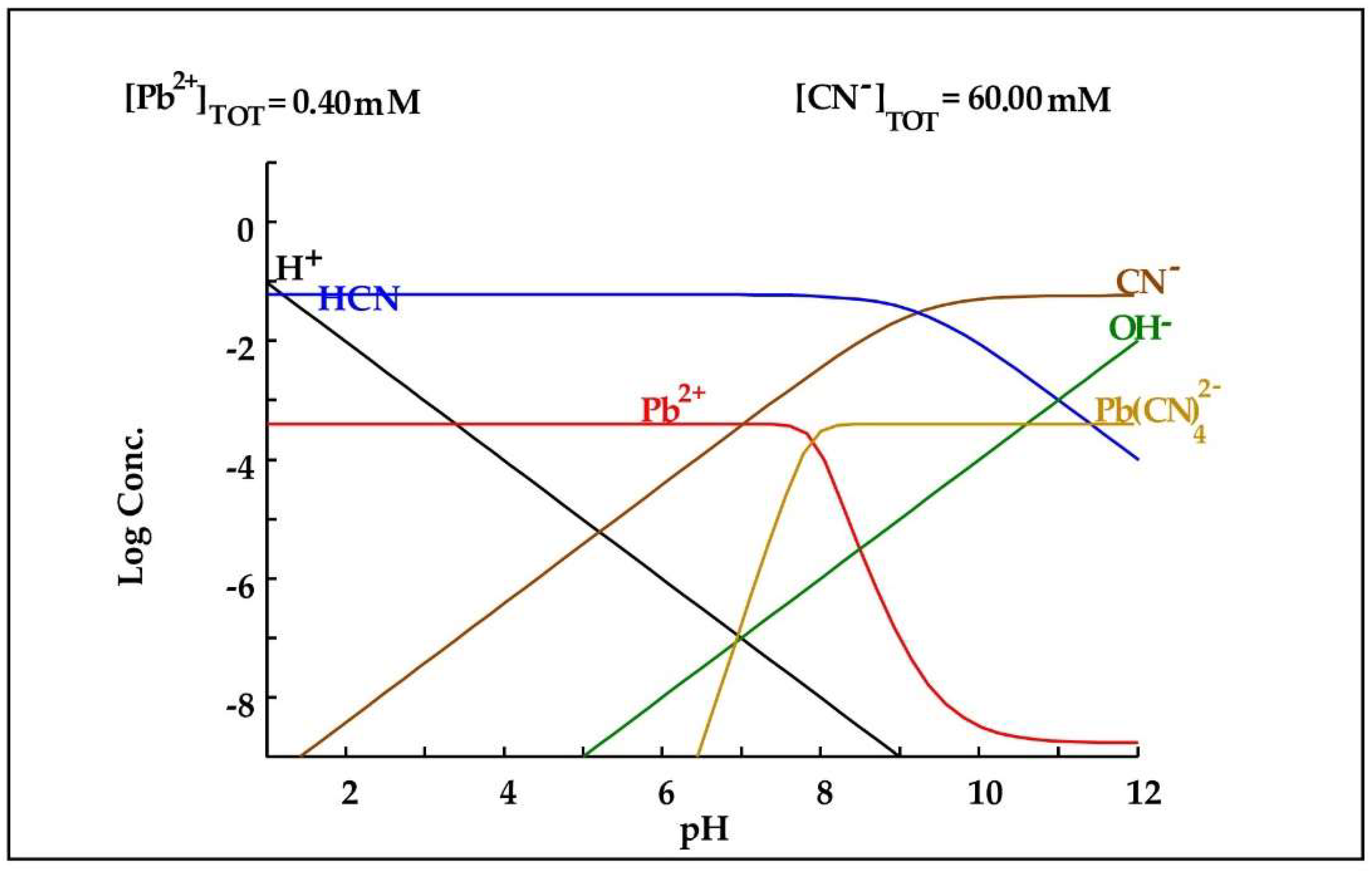
Therefore, during cyanidation, arsenic will be released into the leaching medium since the pH during this process must be alkaline to avoid the formation of hydrocyanic acid. In the case of lead, it can be seen in Table 1 that the DLR is composed of galena, and according to Parga et al. [19], this lead mineral can be easily dissolved in cyanide, since at alkaline pH, they oxidize and become sulfate. Subsequently, as shown in Figure 7, lead can form a complex with cyanide when it forms .
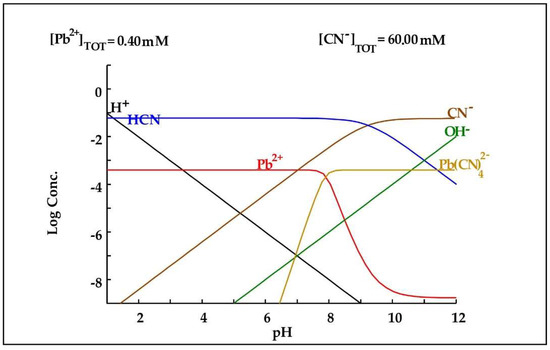
Figure 7.
Diagram of distribution of species of the Pb2+-CN− system based on the concentrations present in the leaching medium. Diagram made by the authors in Medusa software version 2010.
In the case of elemental sulfur, as mentioned in previous work [25], it is a consumer of cyanide; therefore, in the cyanidation medium, it dissolves and can possibly react with cyanide to form thiocyanate according to the following reaction:
On the other hand, part of the iron that is present in natrojarosite dissolves during cyanidation because it decomposes when it is present in an alkaline medium according to the following reaction:
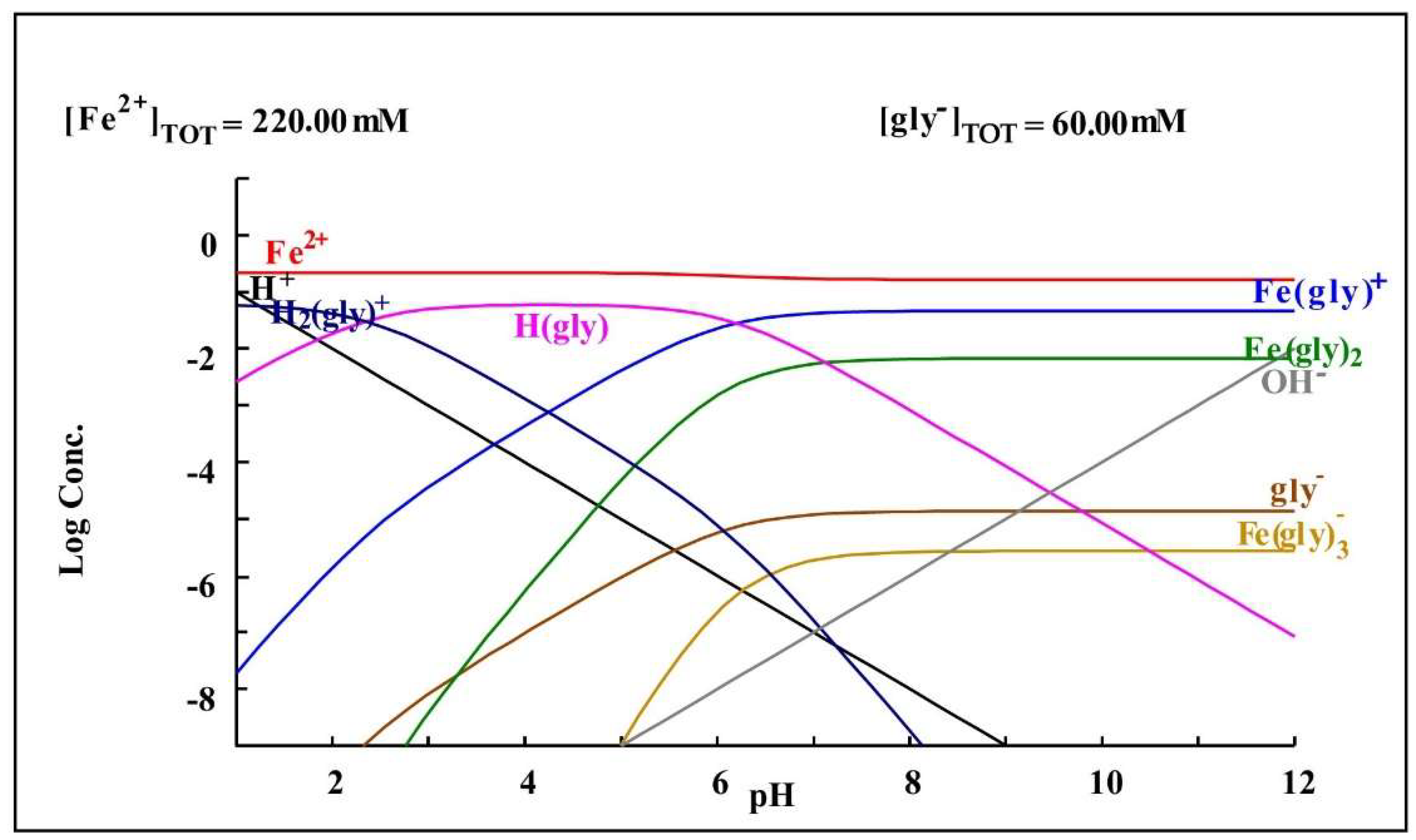
As can be observed in Table 4, the cyanide medium with glycine shows an increase in the dissolution of iron, which could be explained by the findings of Yin et al. [28], in which the iron and glycine tend to form a complex, which would increase their presence in the cyanide medium with glycine.
Figure 8 shows a species distribution diagram showing the formation of complexes of glycine and iron based on the concentrations present in the glycine cyanide-leaching medium.
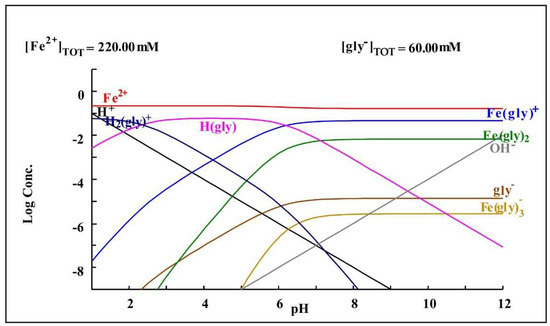
Figure 8.
Diagram of distribution of species of the Fe2+-glycine− system based on the concentrations present in the leaching medium. Diagram made by the authors in Medusa software version 2010.
The increase in arsenic in the cyanide-leaching medium with glycine is an effect of the increase in iron dissolution, which forms complexes with glycine and sulfur, which, when dissolved, release arsenic into the solution.
Regarding lead, as shown in Figure 9, the increase in its concentration in the cyanide medium with glycine can be explained by the fact that at alkaline pH, it tends to form complexes with glycine, which would increase its dissolution.
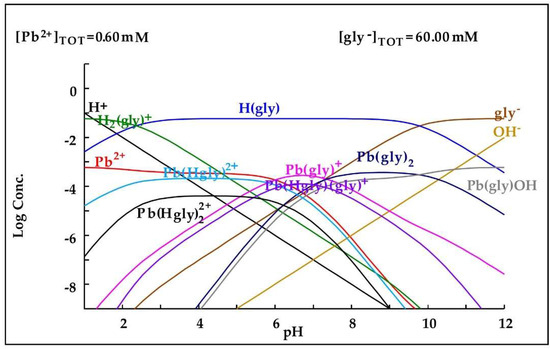
Figure 9.
Diagram of distribution of species of the Pb2+-glycine− system based on the concentrations present in the leaching medium. Diagram made by the authors in Medusa software version 2010.
On the other hand, as shown in Table 5, the concentrations of As and Pb found in the alkaline pretreatment solution were 18.86 and 10.04 mg/L, respectively. As stated in previous works [24,25], DLR is a refractory material due to its composition (jarosite and elemental sulfur), and these species tend to encapsulate their values as has been reported for arsenopyrite. Based on the above factors and according to what has been stated by certain researchers, carrying out pretreatments for this type of mineral can help break down the arsenopyrite, releasing the valuable metals encapsulated in them [26,29].
Regarding the conventional and glycine-assisted cyanidation solutions of DLR-AH, it was shown in Table 5 that during the first treatment, As and Pb did not dissolve, while in the second, the concentrations of As and Pb were 83.35 and 213.63 mg/L, respectively, which is equivalent to 43.24 and 40.38% dissolution of As and Pb.
Previously, Mesa and Lapidus [30] carried out pretreatments with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) with minerals where the gold was encapsulated in arsenopyrite, and observed that the hydroxyl ion releases it from the arsenopyrite matrix. These researchers explained that according to the work by Darban et al. [31], hydroxyl ions can be adsorbed on the surface sites of As and weaken the bond between arsenic with the generation of new chemical species such as ferric oxide, arsenate, and sulfates, which can be observed in Equation (4).
However, Zhao et al. [32] mention that a disadvantage of the process is the precipitation of iron, which could affect the subsequent gold recovery process since a layer is formed on the particles that passivate the process. This could explain the fact that, during cyanidation, the presence of arsenic and lead is not observed in conventional cyanidation, while a concentration of iron in the solution (83,770.03 mg/L) is observed, which could favor the precipitation of iron and the encapsulation of arsenopyrite and galena, and consequently their poor dissolution in the leaching medium.
In the case of the increase in arsenic and lead, as mentioned above, it is due to the formation of complexes of iron with glycine since, when the iron dissolves, it releases the arsenopyrite particles, increasing the dissolution of arsenic. On the other hand, the formation of complexes of lead and glycine promotes its dissolution in an alkaline medium.
As shown in Table 6, the presence of arsenic and lead increased during conventional cyanidation, unlike the DLR-AH treatment, where the presence of arsenic and lead was not detected.
According to Craw et al. [33] arsenopyrite is highly insoluble in reducing environments and becomes extremely soluble in oxidizing environments, which would explain the difference in arsenic dissolution between alkaline hydrothermal pretreatments with and without sodium persulfate. In addition, it could be inferred that when the oxidant is used, greater precipitation of iron occurs because there is a lower concentration of iron, which promotes the formation of a porous iron oxide layer, which would allow the arsenic to dissolve. Arsenopyrite would dissolve according to the following reaction:
Regarding lead, as shown in Table 6, there was no dissolution of it, which does occur. However, as shown in Reaction 7, it can dissolve and then precipitate as Pb(OH)2 due to strong oxidizing and alkaline conditions.
In the case of cyanide leaching of the residue subjected to this pretreatment, the presence of 27.57 mg/L of As and 106.78 mg/L of Pb can be observed in the cyanidation solution (13.78% and 13.02% dissolution) and 11.68 and 66.75 mg/L in the cyanide solution with glycine (5.84 and 8.14% solutions). This is because the use of an oxidant promotes the formation of a porous iron layer, facilitating the access of the leaching solution to the arsenopyrite and galena. In this case, unlike the previous treatments, less lead dissolution occurred during cyanidation with glycine, possibly due to the formation of Pb(OH)2 during this treatment, which decreases the complexation of lead and glycine, as shown in Figure 10.
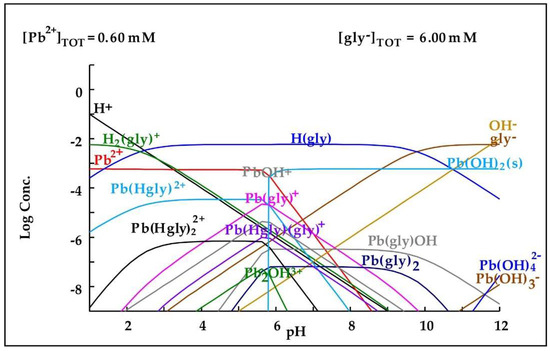
Figure 10.
Diagram of distribution of species of the Pb2+-glycine− system based on the concentrations present in the leaching medium. Diagram made by the authors in Medusa software version 2010.
It is important to note that when the elemental sulfur has been removed from the residue, and subsequently, the oxidizing alkaline hydrothermal treatment has been applied, a substantial increase in the dissolution of arsenic and lead is observed, unlike the previous treatments, as shown in Table 7 and Figure. During the DLR-DAHO treatment, 43.37% of As was dissolved, so a concentration of 138.8 mg/L was found in the solution. In this case, lead was not dissolved in the pretreatment, since it can dissolve and then precipitate as Pb(OH)2 under strongly oxidizing and alkaline conditions.
The concentrations detected were 266.66 mg/L of As and 308.8 mg/L of Pb in the conventional cyanidation solutions (equivalent to 39.5 and 26.16% dissolution) and 140.29 mg/L of As and 312.72 mg/L of Pb during cyanidation with glycine (equivalent to 43.84 and 26.5% solution). Based on the above, it could be inferred that both arsenopyrite and galena, in addition to being covered by a porous layer of iron (due to the use of oxidants), are also associated, or covered by elemental sulfur, so that once the DLR is desulfurized, the particles are released, making them more susceptible to the leaching medium.
5. Conclusions
In this research work, arsenic and lead were monitored during the pretreatments and cyanidation of a jarosite residue. It was found that under alkaline conditions, arsenic dissolves naturally, although it does not form complexes with cyanide; however, lead can form complexes with cyanide, thus facilitating its presence in these solutions. On the other hand, it was observed that iron and lead tend to form complexes with glycine, increasing the dissolution of arsenic and lead during the cyanide medium with glycine.
When the alkaline hydrothermal treatment was carried out, a decrease in the dissolution of As and Pb was observed during cyanidation, which was attributed to the possible formation of an iron layer on the particles, which, when repeating the pretreatment by adding an oxidant, it became a porous layer, facilitating the dissolution of As and Pb; however, in this case, there was less lead dissolution due to the fact that, under strongly alkaline and oxidizing conditions, it precipitates as Pb(OH)2.
In this research, it was determined that elemental sulfur plays an important role in the dissolution of As and Pb, and in the case of sulfur, it tends to cover the jarosite particles, so when it is eliminated, it allows the alkaline hydrothermal treatment to be more effective and facilitates contact between the particles with the leaching medium, increasing the dissolution of As and Pb in both conventional and glycine-assisted cyanidation.
Finally, according to the results obtained in this study, it was observed that the concentrations of arsenic and lead exceed the permissible limits, both in the pre-treatment solutions and in the cyanidation solutions. In this sense, it is important to consider that if the solutions obtained after cyanidation are recirculated within the process, there would be an accumulation of lead and arsenic each time it is reused, so the recommendation would be to treat it previously through some process of precipitation or ion metallic adsorption.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.G.P.-R. and F.R.C.-P.; methodology, N.G.P.-R.; formal analysis, N.G.P.-R., F.R.C.-P. and M.d.J.S.-A.; resources, M.F., F.R.C.-P. and I.A.-G.; visualization, F.R.C.-P. and M.d.J.S.-A.; supervision, J.C. and F.R.C.-P.; project administration, F.R.C.-P.; funding acquisition, M.F.; writing—original draft preparation, N.G.P.-R.; writing—review and editing, F.R.C.-P., I.A.-G. and J.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The Research and Development Center (CIDT-SEPSA) Peñoles supplied the samples, chemical analysis, DRX, and SEM characterization. N. Picazo appreciates the CONACYT scholarship for their PhD thesis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, G.; Kang, J.; Wang, C. Comprehensive recovery and recycle of jarosite residues from zinc hydrometallurgy. Adv. Chem. Eng. 2020, 3, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, J.; Breuer, P.; Bunney, K.; Pleysier, R.; May, P. Review of trace toxic elements (Pb, Cd, Hg, As, Sb, Bi, Se, Te) and their deportment in gold processing. Part 1: Mineralogy, aqueous chemistry, and toxicity. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 107, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsollahi, Z.; Partovinia, A. Recent advances on pollutants removal by rice husk as a bio-based adsorbent: A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabas, K. Removal of heavy metal ions from an electroplating effluent and the clarified water of the “Kowary” Tailing Pond (Jelenia Gora District, Lower Silesia). Ochr. Srodowiska 2009, 31, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Abu, R.; Zabin, S. Removal efficiency of Pb, Cd, Cu and Zn from polluted water using dithiocarbamate ligands. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2017, 11, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Astruc, D. Nanomaterials for removal of toxic elements from water. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 356, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, L.; Bashir, A.; Qureashi, A.; Pandith, A. Detection and removal of heavy metal ions: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1495–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, A. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water and Wastewaters by Sulfur-Containing Precipitation Agents. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsden, J.; House, I. The Chemistry of Gold Extraction, 2nd ed.; Society for Mining, Metallurgy, and Exploration Inc.: Englewood, CO, USA, 2005; pp. 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Kuyucak, N.; Akcil, A. Cyanide and removal options from effluents in gold mining and metallurgical processes. Miner. Eng. 2013, 50, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, P.; Ma, B.; Zeng, P.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q. Deep cleaning of a metallurgical zinc leaching residue and recovery of valuable metals. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2017, 24, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, I.; Patiño, F.; Flores, M.; Pandiyan, T.; Cruz, R.; Gutiérrez, E.; Reyes, M.; Flores, V. Dissolution rates of jarosite-type compounds in H2SO4 medium: A kinetic analysis and its importance on the recovery of metal values from hydrometallurgical wastes. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 167, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, C. Hydrometallurgy of precious metals recovery. Hydrometallurgy 1992, 30, 127–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calla, D.; Nava, F.; Fuentes, J. Acid decomposition and thiourea leaching of silver from hazardous jarosite residues: Effect of some cations on the stability of the thiourea system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 317, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, K.; Gupta, M.; Sharma, S. Process development for the removal of lead and chromium from aqueous solutions using red mud-an aluminum industry waste. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, P.; Abdollahi, H.; Amini, A.; Noaparast, M.; Shafaei, S.; Habashi, F. Cyanidation of gold ores containing copper, silver, lead, arsenic and antimony. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2010, 95, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheampong, M.; Meulepas, R.; Lens, P. Removal of heavy metals and cyanide from gold mine wastewater. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 590–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahoon, M.; Siddeeg, S.; Salsaiari, N.; Mnif, W.; Rebah, F. Effective Heavy Metals Removal from Water Using Nanomaterials: A Review. Processes 2020, 8, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parga, J.; Valdés, J.; Valenzuela, J.; Gonzalez, G.; Pérez, L.; Cepeda, T.F. New Approach for Lead, Zinc and Copper Ions Elimination in Cyanidation Process to Improve the Quality of the Precipitate. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2015, 6, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Leslie, M.; Moe, B.; Hongquan, Z.; Douglas, D.; Kneteman, N.; Le, C. Metabolism of a Phenylarsenical in Human Hepatic Cells and Identification of a New Arsenic Metabolite. Environ. Sci. 2018, 52, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, T.; Sun, D.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Z. Changes of RNA N6 methyladenosine in the hormesis effect induced by arsenite on human keratinocyte cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2019, 56, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, S.; Hamid, M.; Fiayyaz, A.; Saleem, U.; Hassan, M.; Rehman, K. Role of cadmium and arsenic as endocrine disruptors in the metabolism of carbohydrates: Inserting the association into perspectives. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 114, 108802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, M.; Santos, A.; Silva, C.; Chakmeng, J. Arsenic contamination assessment in Brazil—Past, present, and future concerns: A historical and critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 138217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza, M.; Carrillo, F.; Picazo, N.; Soria, M.; Almaguer, I.; Cháidez, J. Effects of pretreatment and leaching medium on the extraction efficiency of Au and Ag from a chalcopyrite leaching by-product. Dyna 2021, 88, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picazo, N.; Carrillo, F.; Luévanos, A.; Soria, M.; Almaguer, I. S° and jarosite behavior during recovery of values from the direct leaching residue of sphalerite using cyanide and glycine. J. Min. Metall. B Metall. 2021, 57, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haver, F.; Wong, M. Recovery of Copper, iron, and Sulfur from Chalcopyrite Goncentrate using a Ferric Chloride Leach. J. Met. 1971, 23, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg, R.; Alakangas, L.; Maurice, C. Release of arsenic from cyanidation tailings. Miner. Eng. 2016, 93, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Huang, L.; Pedersen, E.; Frandsen, C.; Hansen, H. Glycine buffered synthesis of layered iron (II)-iron (III) hydroxides (green rusts). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 497, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qin, W.; Jiao, F.; Yang, C.; Cui, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Song, H. Mineralogy and pretreatment of a refractory gold in Zambia. Minerals 2019, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesa, S.; Lapidus, G. Pretreatment of a refractory arsenopyritic gold ore using hydroxyl ion. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 153, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darban, A.; Aazami, M.; Meléndez, A.; Abdollahy, M.; Gonzalez, I. Electrochemical study of orpiment (As2S3) dissolution in a NaOH solution. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 105, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Abashina, T.; Vainshtein, M. Review on arsenic removal from sulfide minerals: An emphasis on enargite and arsenopyrite. Miner. Eng. 2021, 72, 107133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craw, D.; Falconer, D.; Younson, J. Environmental arsenopyrite stability and dissolution: Theory, experiment, and field observations. Chem. Geol. 2003, 199, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).