Investigating Alumina-Silicate Bauxite and Phenol-Formaldehyde Resin Embedded TiH2 as Foaming Agents for Producing A356 Foam
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
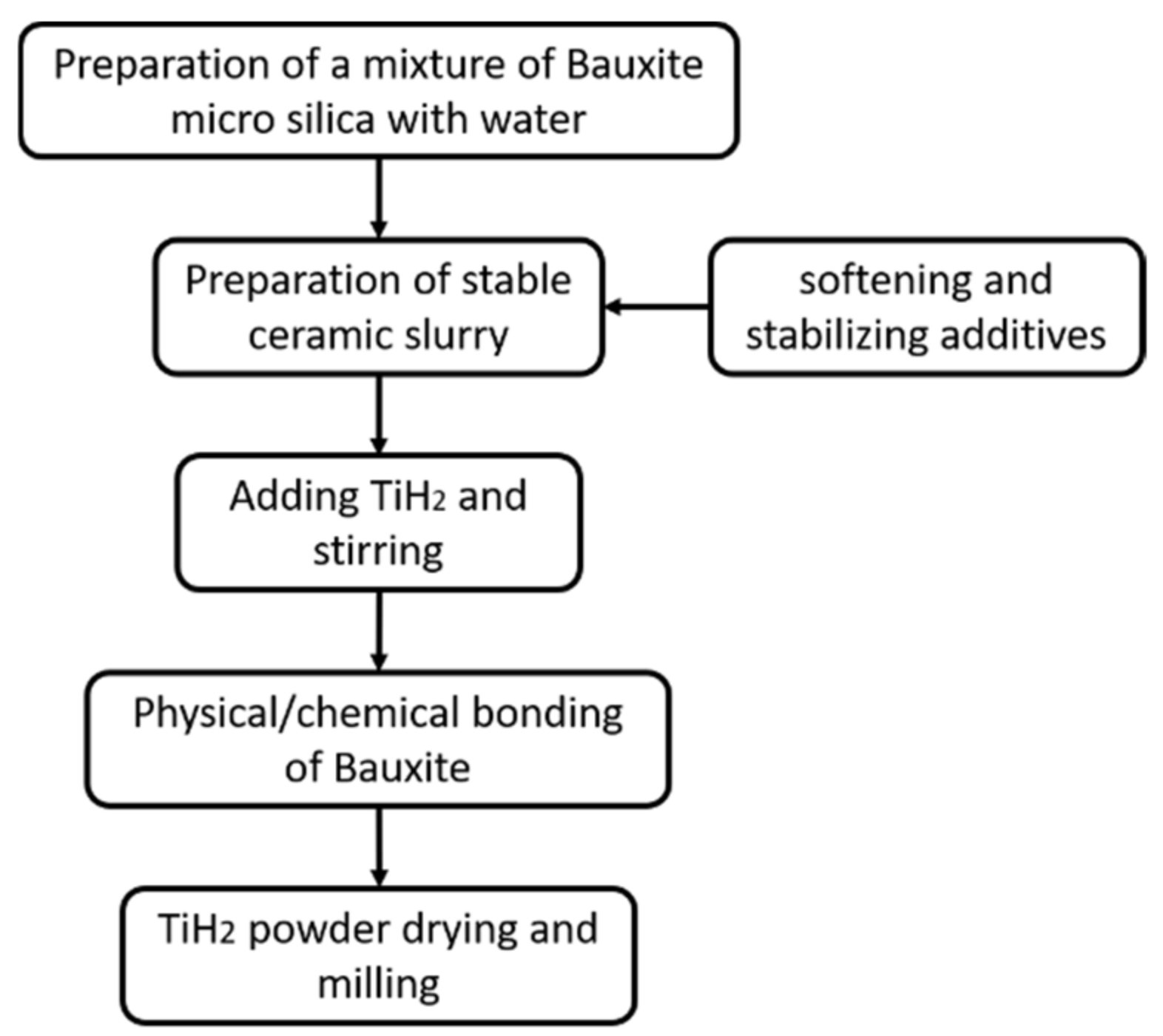
2.1. Modified Al2O3-TiH2 Preparation
2.2. Modified PFR-TiH2 Preparation
2.3. Al Foam Production
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Investigation of Bauxite Embedded TiH2
3.2. Investigation of Phenol-Formaldehyde Resin Embedded TiH2
3.3. Quantitive Investigation of Cells Sizes and Their Distribution
3.4. Mechanism for Delaying the Release of TiH2 Gas
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The EDX analysis and color map of bauxite-embedded TiH2 powders show the presence of Ti, Al, Si, O, and Ca elements, proving that Al2O3.SiO2 (bauxite) embeds TiH2 powders.
- (2)
- EDX analysis of PFR-embedded TiH2 powder was carried out from the three points, A, B, and C, indicated in the SEM micrograph. The results show a transition zone between TiH2 powder and the polymeric matrix (resin), proving TiH2 powders are embedded in the PFR matrix. According to the TGA results, this protective layer can delay the release of hydrogen and the decomposition of TiH2.
- (3)
- The heat-resistant protective layer is the mechanism of the delay in TiH2 decomposition in the presence of the Bauxite ceramic phase, silica gel formation, and a carbon layer due to the burning of resin.
- (4)
- The delay in the decomposition of H2 gas (120 s) gives the gas bubbles enough time to establish pores in the metallic matrix, making the pore sizes of produced foams by modified TiH2 small. Additionally, it makes more homogenous pores and size distribution in the produced foams by modified TiH2 compared with TiH2.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, T.J.; Xu, F.; Wen, T. Thermo-Fluid Behaviour of Periodic Cellular Metals; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- García-Moreno, F. Commercial applications of metal foams: Their properties and production. Materials 2016, 9, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, M.; Mirbagheri, S.; Ramiani, A.J. Efficient energy absorption of functionally-graded metallic foam-filled tubes under impact loading. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2021, 31, 92–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Dai, Z.; Xu, R.; Mao, R.; Song, B. The Preparation Methods and Application of Aluminum Foam. In Light Metals 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, S.; Sadighi, M.; Aghdam, M.; Mirbagheri, S. Micro–macro analysis of closed-cell aluminum foam with crushing behavior subjected to dynamic loadings. Mater. Today Commun. 2017, 13, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedi, N.; Mirbagheri, S. Comparison of the energy absorption of closed-cell aluminum foam produced by various foaming agents. Strength Mater. 2016, 48, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasa, C.; Shivakumar, K. A Review on Prodution of Aluminium Metal Foams. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Proceedings of 7th International Conference on Intelligent Textiles & Mass Customisation, Marrakech, Morocco, 13–15 November 2019; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; p. 012081. [Google Scholar]
- Banhart, J. Manufacture, characterisation and application of cellular metals and metal foams. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2001, 46, 559–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Ye, J.; An, X.; Ran, H. Multifunctional foaming agent to prepare aluminum foam with enhanced mechanical properties. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 036529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, H.; Liu, Y.; Ye, J.; An, X.; Li, X.; Yang, X. Al2O3 aerogel coating modified TiH2 to enhance the mechanical properties of aluminum foam. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 076543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wang, N. Optimizing Calcium Addition for Fabricating Aluminum Foams with Different Pore Sizes. Mater. Trans. 2018, 59, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, T.; Gnyloskurenko, S.V.; Sakamoto, K.; Byakova, A.V.; Ishikawa, R. Development of new foaming agent for metal foam. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, G.; Zhen, S. Metallic foams: Their production, properties and applications. J. Mater. Sci. 1983, 18, 1899–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, X. Development of AlMg35-TiH2 composite foaming agent and fabrication of small pore size aluminium foams. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 283, 116698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, C.; Dell’Era, A.; Pasquali, M. In situ activation with Mo of Ni–Co alloys for hydrogen evolution reaction. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 1932–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Romero, M.; Domínguez-Ríos, C.; Torres-Sánchez, R.; Aguilar-Elguezabal, A. Electroless Ni-B coating onto TiH2 powder: An approach for a simplified surface preparation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 315, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. Optimization of cellular structure of aluminum foams produced by powder metallurgy method. Mater. Lett. 2018, 216, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.; Lopez, V. The decomposition behavior of as-received and oxidized TiH2 foaming-agent powder. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 357, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matijasevic-Lux, B.; Banhart, J.; Fiechter, S.; Görke, O.; Wanderka, N. Modification of titanium hydride for improved aluminium foam manufacture. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 1887–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, J.; Ding, B.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, K.; Gu, C. The effect of SiO2 and Al2O3 coating on the surface of TiH2 powders on gas release. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 283, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proa-Flores, P.M.; Drew, R.A. Production of aluminum foams with Ni-coated TiH2 powder. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zuo, X.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, J. Preparation and gas release characteristic of TiH2 particles with composite layers of SiO2/TiOx. Thermochim. Acta 2016, 637, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solórzano, E.; Reglero, J.; Rodríguez-Pérez, M.; Lehmhus, D.; Wichmann, M.; De Saja, J. An experimental study on the thermal conductivity of aluminium foams by using the transient plane source method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2008, 51, 6259–6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, J.P.; Meador, M.A.B.; Jana, S.C. Tailoring mechanical properties of aerogels for aerospace applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baetens, R.; Jelle, B.P.; Gustavsen, A. Aerogel insulation for building applications: A state-of-the-art review. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, X.-Q.; Wang, Z.-H.; Zhao, L.-M.; Yang, G.-T. Effects of cell size on compressive properties of aluminum foam. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2006, 16, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieh, T.; Higashi, K.; Wadsworth, J. Effect of cell morphology on the compressive properties of open-cell aluminum foams. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 283, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Al2O3 | SiO2 | CaO | BaO | MgO | MnO | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | K2O | Na2O | P2O5 | SO3 | LOI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bauxite | 77.07 | 13.41 | 0.27 | <0.05 | 0.55 | <0.05 | 2.79 | 4.48 | 0.05 | 0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.27 |
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | C | Na2O | K2O | MgO | S | CaO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micro silica | 86–94 | 0.4–1.0 | 0.2–1.5 | 0.5–2.5 | 0.4–1.5 | 1.0–3.0 | 0.5–2.0 | 0.1–0.4 | 0.1–0.5 |
| Material | Purity (%) | Average Grain Size (μm) | Density (gm/cm3) | Decomposition Temperature (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiH2 | 99 | 45 | 3.7 | 400 |
| Al | Si | Mg | Cu | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bal. | 7.31 | 0.29 | 0.04 | 0.12 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasfpour, R.; Mirbagheri, S.M.H. Investigating Alumina-Silicate Bauxite and Phenol-Formaldehyde Resin Embedded TiH2 as Foaming Agents for Producing A356 Foam. Metals 2022, 12, 2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122105
Vasfpour R, Mirbagheri SMH. Investigating Alumina-Silicate Bauxite and Phenol-Formaldehyde Resin Embedded TiH2 as Foaming Agents for Producing A356 Foam. Metals. 2022; 12(12):2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122105
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasfpour, Ramin, and Seyed Mohammad H. Mirbagheri. 2022. "Investigating Alumina-Silicate Bauxite and Phenol-Formaldehyde Resin Embedded TiH2 as Foaming Agents for Producing A356 Foam" Metals 12, no. 12: 2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122105
APA StyleVasfpour, R., & Mirbagheri, S. M. H. (2022). Investigating Alumina-Silicate Bauxite and Phenol-Formaldehyde Resin Embedded TiH2 as Foaming Agents for Producing A356 Foam. Metals, 12(12), 2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122105





