Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the ((CoCrFeNi)95Nb5)100−xMox High-Entropy Alloy Coating Fabricated under Different Laser Power
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Powder Preparation
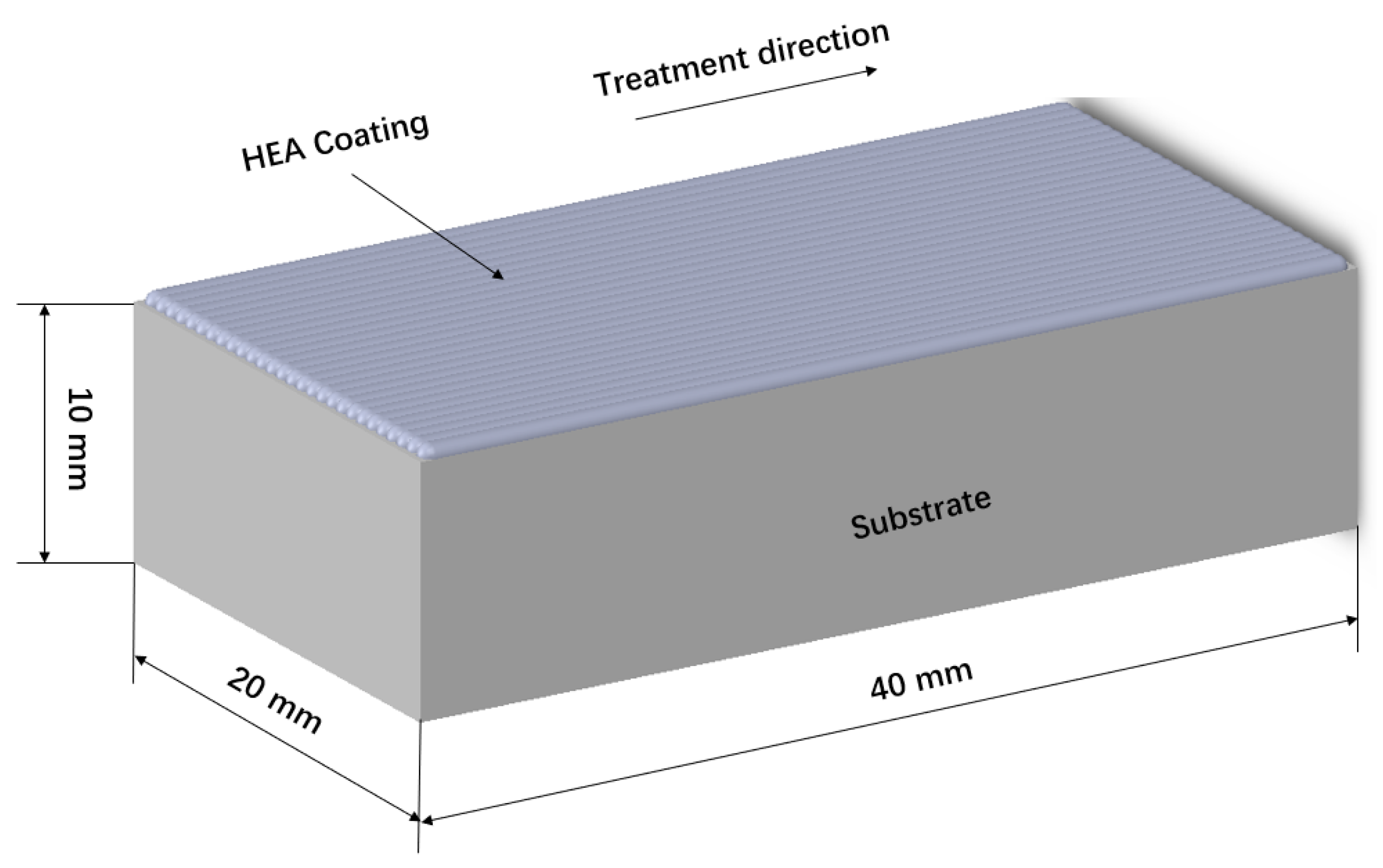
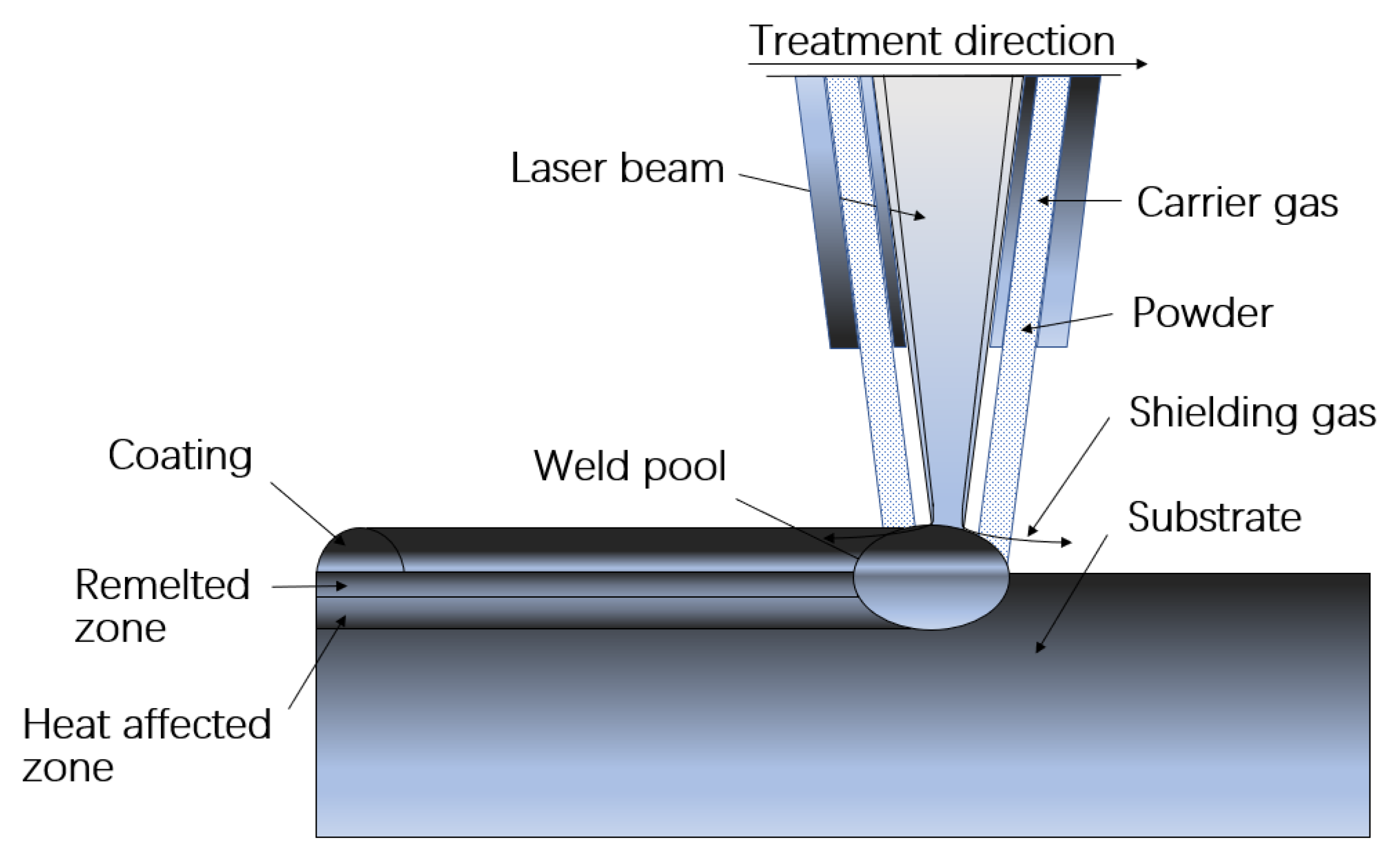
2.2. Coatings Preparation
2.3. Coating Characterization
2.4. Microhardness Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure of the ((CoCrFeNi)95Nb5)100−xMox Powder
3.2. The Effect of Mo Element Content on the Microstructure of the HEA Coating
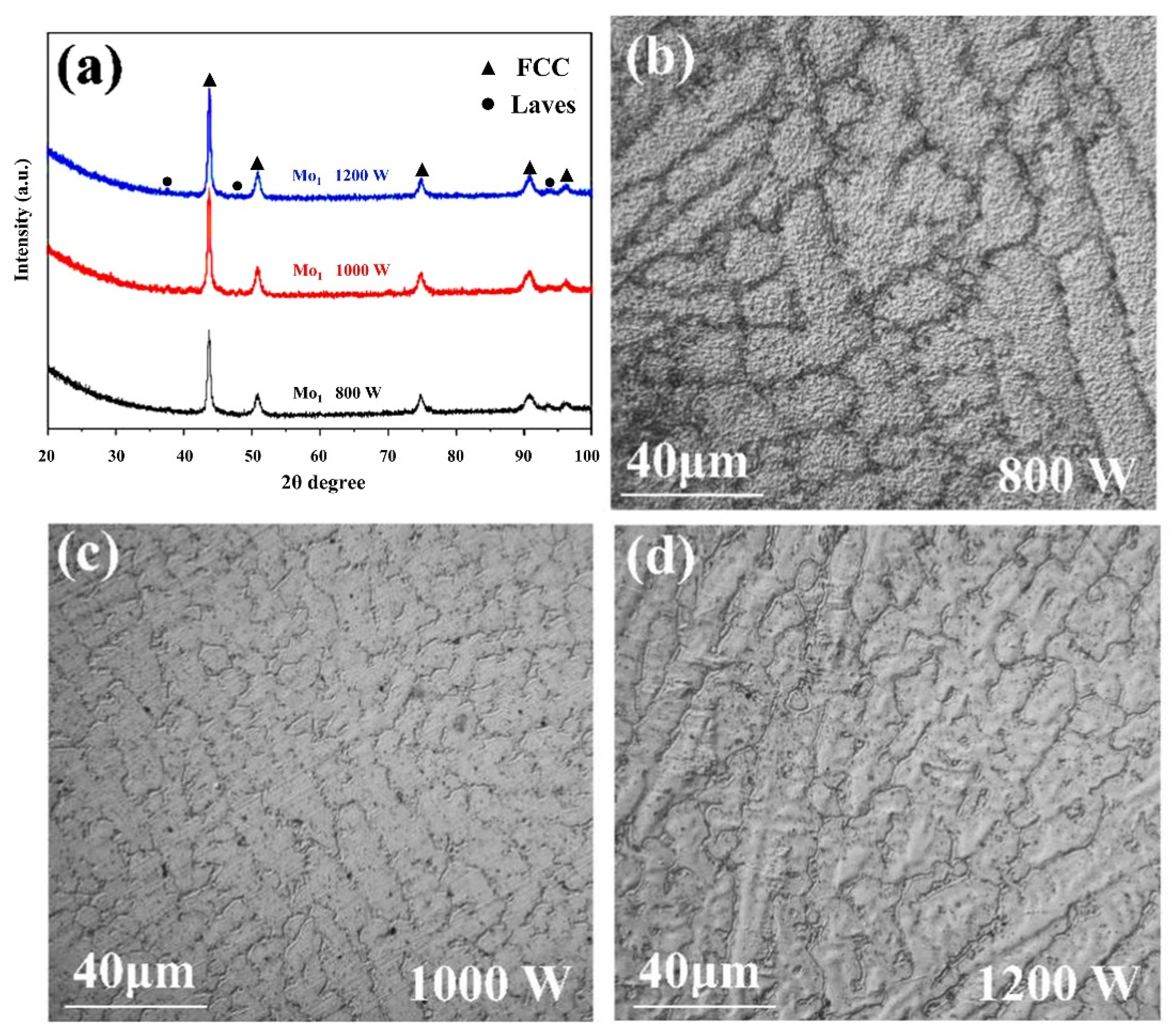
3.3. The Effect of Laser Beam Power on the Microstructure of the HEA Coating
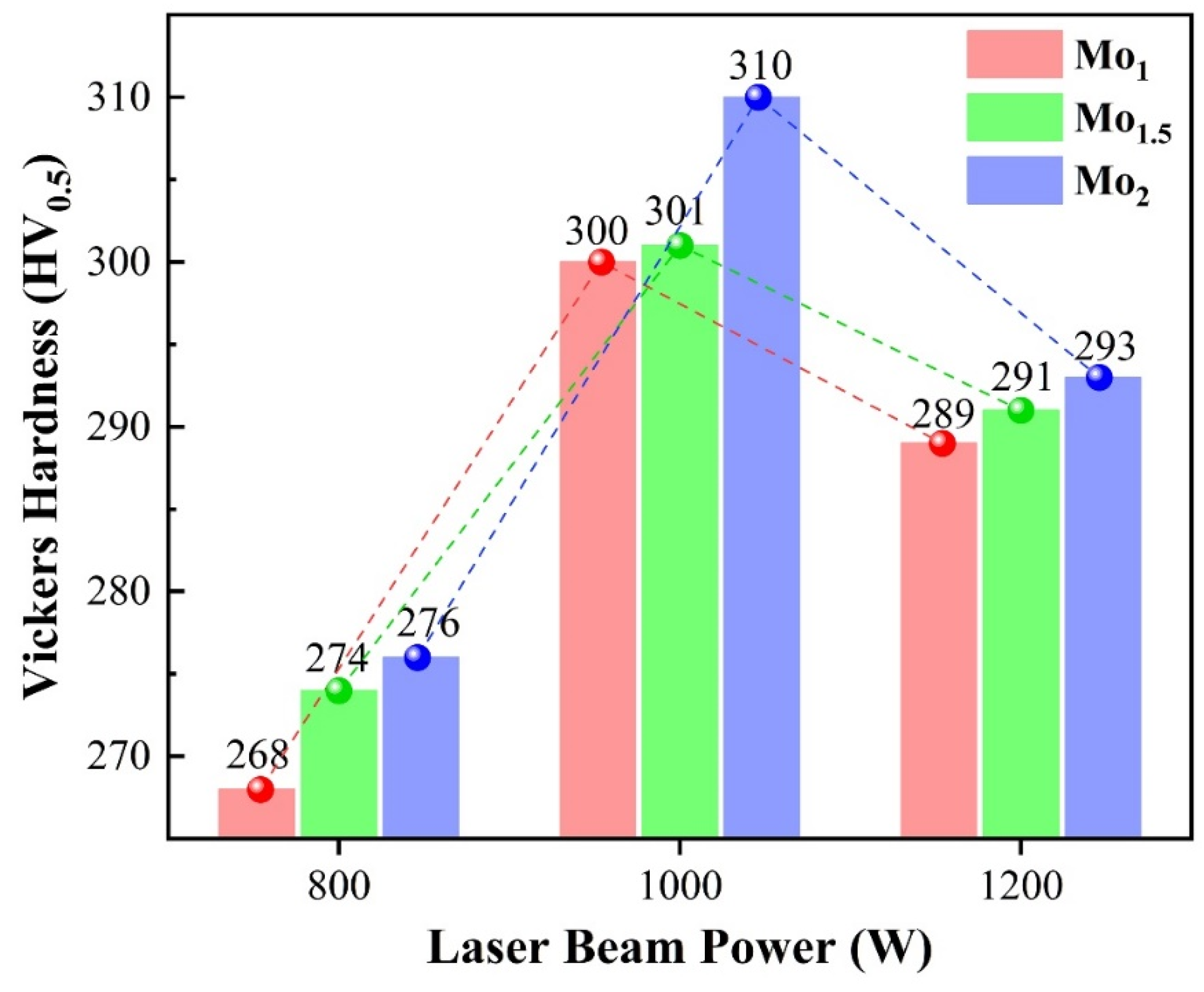
3.4. Mechanical Properties of the ((CoCrFeNi)95Nb5)100−xMox HEA Coating
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Results show that the HEA coatings consist of FCC phase and Laves phase. The porosity of the HEA coatings is low and the HEA coatings are combined with the substrate in a metallurgical way.
- (2)
- The HEA coatings exhibit a typical dendritic structure and the interdendritic phase enriches with Nb and Mo, which may be caused by the different melting points of the elements and the characteristics of the laser cladding process.
- (3)
- The grain size of the coating fabricated under the laser beam power of 800 W is coarse and irregular. After the laser beam power is increased to 1000 W, the grain size is refined. Under the laser beam power of 1200 W, the grain size becomes coarse again. The reason for this may be that the laser beam power determines the instantaneous energy input into the molten pool, and an appropriate increase in laser beam power can promote the non-spontaneous nucleation of the coating elements, so as to achieve the refinement of the microstructure. However, low laser beam power leads to low energy of the molten pool and insufficient energy absorbed by the HEA powder, which is not conducive to nucleation. In addition, a further increase in laser beam power may lead to high input energy, slow cooling rate of molten pool, prolonged grain growth time, and finally, larger grain size.
- (4)
- The microstructure of the coatings changed from a columnar dendritic structure to a cellular dendritic structure with the increase in molybdenum element content, the grain size was refined, and the degree of element segregation of the interdendritic phase decreased. The microhardness of the HEA coatings is much higher than that of the 45# steel substrate and greatly affected by laser beam power. With the increase in molybdenum element content, the microhardness of the HEA coatings also increased. The characteristics of the laser cladding process, the formation of Laves phase, and the fine grain strengthening lead to the high microhardness of the coatings.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.H.; Yang, T.; Liu, C.T. Precipitation hardening in CoCrFeNi-based high entropy alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 210, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiyamoorthi, P.; Basu, J.; Kashyap, S.; Pradeep, K.G.; Kottada, R.S. Thermal stability and grain boundary strengthening in ultrafine-grained CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy composite. Mater. Des. 2017, 134, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Fan, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, J. Deformation Behavior and Plastic Instabilities of Boronized Al0.25 CoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloys. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2020, 27, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salishchev, G.A.; Tikhonovsky, M.A.; Shaysultanov, D.G.; Stepanov, N.D.; Kuznetsov, A.V.; Kolodiy, I.V.; Tortika, A.S.; Senkov, O.N. Effect of Mn and V on structure and mechanical properties of high-entropy alloys based on CoCrFeNi system. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 591, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.T. Phase separation of metastable CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy at intermediate temperatures. Scr. Mater. 2017, 126, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Praveen, S.; Basu, J.; Kashyap, S.; Kottada, R.S. Exceptional resistance to grain growth in nanocrystalline CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy at high homologous temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 662, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, M.; Trubel, S.; Murty, B.S.; Wilde, G.; Divinski, S.V. Ni tracer diffusion in CoCrFeNi and CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 688, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Han, J.; Su, B.; Li, P.; Meng, J. Microstructure, mechanical properties and tribological performance of CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy matrix self-lubricating composite. Mater. Des. 2017, 114, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, C.; Axinte, E.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Li, P.; Du, J.; Qiao, P.; Wang, Y. CoCrFeNi(W1−xMox) high-entropy alloy coatings with excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance prepared by mechanical alloying and hot pressing sintering. Mater. Des. 2017, 117, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Q.; Guo, T.; Jarvis, T.; Wu, X.; Hodgson, P.; Fabijanic, D. Direct laser deposition cladding of AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys on a high-temperature stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 332, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.Q.; Li, J.; Juan, Y.F.; Lu, Z.J.; Jia, W.L. Evolution in microstructure and corrosion behavior of AlCoCrxFeNi high-entropy alloy coatings fabricated by laser cladding. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 775, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, T.; Xiao, M.; Shen, Y. Effect of process parameters on the microstructure and properties of laser-clad FeNiCoCrTi 0.5 high-entropy alloy coating. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2020, 27, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, C.L.; Yi, J.Z.; Zhang, C.H. Synthesis and characterization of FeCoCrAlCu high-entropy alloy coating by laser surface alloying. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 262, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, Y.-Z.; Pan, Y.; Guo, S. Thermally stable laser cladded CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy coating with low stacking fault energy. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 600, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Kong, D.; Song, R. Microstructures and Properties of Laser Cladding Al-TiC-CeO2 Composite Coatings. Materials 2018, 11, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, C.; Shi, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, G. Characterization of Al0.5FeCu0.7NiCoCr high-entropy alloy coating on aluminum alloy by laser cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 105, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Han, K.; Li, D.; Cao, Z. Synthesis and Characterization of AlCoCrFeNiNbx High-Entropy Alloy Coatings by Laser Cladding. Crystals 2019, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Pan, Y.; He, Y.-Z. Synthesis and characterization of FeCoNiCrCu high-entropy alloy coating by laser cladding. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.-J.; Chen, Y.-L.; Yeh, J.-W.; Lin, S.-J.; Chen, S.-K.; Shun, T.-T.; Tsau, C.-H.; Chang, S.-Y. Microstructure characterization of Alx CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multiprincipal elements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.S.; Wang, Y.P.; Ren, M.X.; Yang, C.; Fu, H.Z. Effects of Mn, Ti and V on the microstructure and properties of AlCrFeCoNiCu high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 498, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Delczeg, L.; Chen, N.; Varga, L.K.; Shen, J.; Vitos, L. Structural stability of NiCoFeCrAlx high-entropy alloy from ab initio theory. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 085128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, P.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Dang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.T. Designing eutectic high entropy alloys of CoCrFeNiNbx. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 656, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, D.; Nai, X. Microstructures and properties of CoCrCuFeNiMox high-entropy alloys fabricated by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Powder Metall. 2018, 61, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquelme, A.; Rodrigo, P.; Escalera-Rodríguez, M.D.; Rams, J. Analysis and optimization of process parameters in Al–SiCp laser cladding. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2016, 78, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, F.; Chen, C.; Yu, H. Research status of laser cladding on titanium and its alloys: A review. Mater. Des. 2014, 58, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocelík, V.; de Oliveira, U.; de Boer, M.; de Hosson, J.T.M. Thick Co-based coating on cast iron by side laser cladding: Analysis of processing conditions and coating properties. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Liu, F.; Miao, X.; Yang, F. Influence of laser cladding process on the magnetic properties of WC–FeNiCr metal–matrix composite coatings. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muvvala, G.; Karmakar, D.P.; Nath, A.K. Online monitoring of thermo-cycles and its correlation with microstructure in laser cladding of nickel based super alloy. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2017, 88, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, F.; Yu, H.; Chen, C.; Liu, J.; Zhao, L.; Dai, J.; Zhao, Z. Effect of process parameters on the microstructure evolution and wear property of the laser cladding coatings on Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 692, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Gong, Z.; Pang, X.; Xiong, S.M. Effect of laser scanning speed on microstructure and wear properties of T15M cladding coating fabricated by laser cladding technology. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2018, 110, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qi, W.; Xie, L.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of (CoCrFeNi)95Nb5 High-Entropy Alloy Coating Fabricated by Plasma Spraying. Materials 2019, 12, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Sun, Z.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Song, X.; Wen, X.; Xie, L.; Yang, X. Effect of Mo and aging temperature on corrosion behavior of (CoCrFeNi)100−xMox high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 812, 152139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.-D.; Zhao, T.-L.; Du, C.-W.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Zhang, D.-W. Effect of molybdenum content on the microstructure and corrosion behavior of FeCoCrNiMox high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 46, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.-L. Microstructure and Properties of Fecocroni-MX High Entropy Alloy Coating by Laser Murder; Jinan University: Guangzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.-X.; Niu, L.-Y.; Li, G.-Y.; Cao, H.-G.; Cao, Y.-L. Effects of laser power on the dilution rate and corrosion resistance of laser-clad coated CO based alloy coating of ball valve. Process 2014, 43, 112. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Ning, Y.-H.; Zhao, Y.-G.; Zhu, G.-B.; Xu, X.-F. Effect of Process Parameters on Tissue, Wear Resistance and Corrosion Resistance of Laser Cladding Ni - based Alloy Coatings of 304 Stainless Steel. Midament 2017, 31, 133. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.-B.; Hu, L.-W.; Liu, X.; Li, J.-F.; Zhang, J.; Le, G.-L.; Li, X.-Y. Influence of Laser Power on Microstructure and Properties of Fe-Si-B Laser Clay Coating. J. Mater. Heat Treat. 2018, 39, 113. [Google Scholar]





| Specimen | Laser Beam Parameters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Powder Feeding Rate (L/min) | Spot Diameter (mm) | Scanning Speed (mm/s) | Exposure Time of Laser Beam on Material (s) | Laser Beam Fluence (J/mm) | Laser Beam Power Density (W/mm2) | ||
| Laser beam power | Powder mixture composition | ||||||
| 800 W | Mo1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0.5 | 127 | 255 |
| Mo1.5 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0.5 | 127 | 255 | |
| Mo2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0.5 | 127 | 255 | |
| Powder mixture composition | Laser beam power | ||||||
| Mo1 | 800 W | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0.5 | 127 | 255 |
| 1000 W | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0.5 | 159 | 318 | |
| 1200 W | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0.5 | 191 | 382 | |
| Element | Area | Co | Cr | Fe | Ni | Nb | Mo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mo1 | Interdendrite | 19.18 | 20.22 | 19.92 | 19.11 | 20.34 | 1.23 |
| Dendrite | 22.97 | 24.13 | 25.87 | 24.56 | 2.42 | 0.05 | |
| Mo1.5 | Interdendrite | 22.05 | 20.13 | 20.98 | 20.82 | 14.13 | 1.89 |
| Dendrite | 22.13 | 22.95 | 27.12 | 24.09 | 3.02 | 0.69 | |
| Mo2 | Interdendrite | 22.13 | 21.14 | 24.56 | 20.04 | 9.79 | 2.34 |
| Dendrite | 23.32 | 22.87 | 29.29 | 22.87 | 1.02 | 0.63 |
| Element | Area | Co | Cr | Fe | Ni | Nb | Mo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800 W | Interdendrite | 19.18 | 20.22 | 19.92 | 19.11 | 20.34 | 1.23 |
| Dendrite | 22.97 | 24.13 | 25.87 | 24.56 | 2.42 | 0.05 | |
| 1000 W | Interdendrite | 22.37 | 18.32 | 19.18 | 20.13 | 18.42 | 1.58 |
| Dendrite | 22.56 | 24.08 | 27.38 | 22.83 | 2.52 | 0.63 | |
| 1200 W | Interdendrite | 20.24 | 19.01 | 23.22 | 19.36 | 17.23 | 0.94 |
| Dendrite | 21.37 | 20.29 | 34.82 | 21.42 | 1.73 | 0.37 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Sun, Q.; Wang, D.; Hou, J.; Qi, W.; Li, D.; Xie, L. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the ((CoCrFeNi)95Nb5)100−xMox High-Entropy Alloy Coating Fabricated under Different Laser Power. Metals 2021, 11, 1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11091477
Wang W, Sun Q, Wang D, Hou J, Qi W, Li D, Xie L. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the ((CoCrFeNi)95Nb5)100−xMox High-Entropy Alloy Coating Fabricated under Different Laser Power. Metals. 2021; 11(9):1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11091477
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wenrui, Qi Sun, Dingzhi Wang, Junsong Hou, Wu Qi, Dongyue Li, and Lu Xie. 2021. "Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the ((CoCrFeNi)95Nb5)100−xMox High-Entropy Alloy Coating Fabricated under Different Laser Power" Metals 11, no. 9: 1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11091477
APA StyleWang, W., Sun, Q., Wang, D., Hou, J., Qi, W., Li, D., & Xie, L. (2021). Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the ((CoCrFeNi)95Nb5)100−xMox High-Entropy Alloy Coating Fabricated under Different Laser Power. Metals, 11(9), 1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11091477







