Effects of Oxygen Precursor on Resistive Switching Properties of CMOS Compatible HfO2-Based RRAM
Abstract
1. Introduction
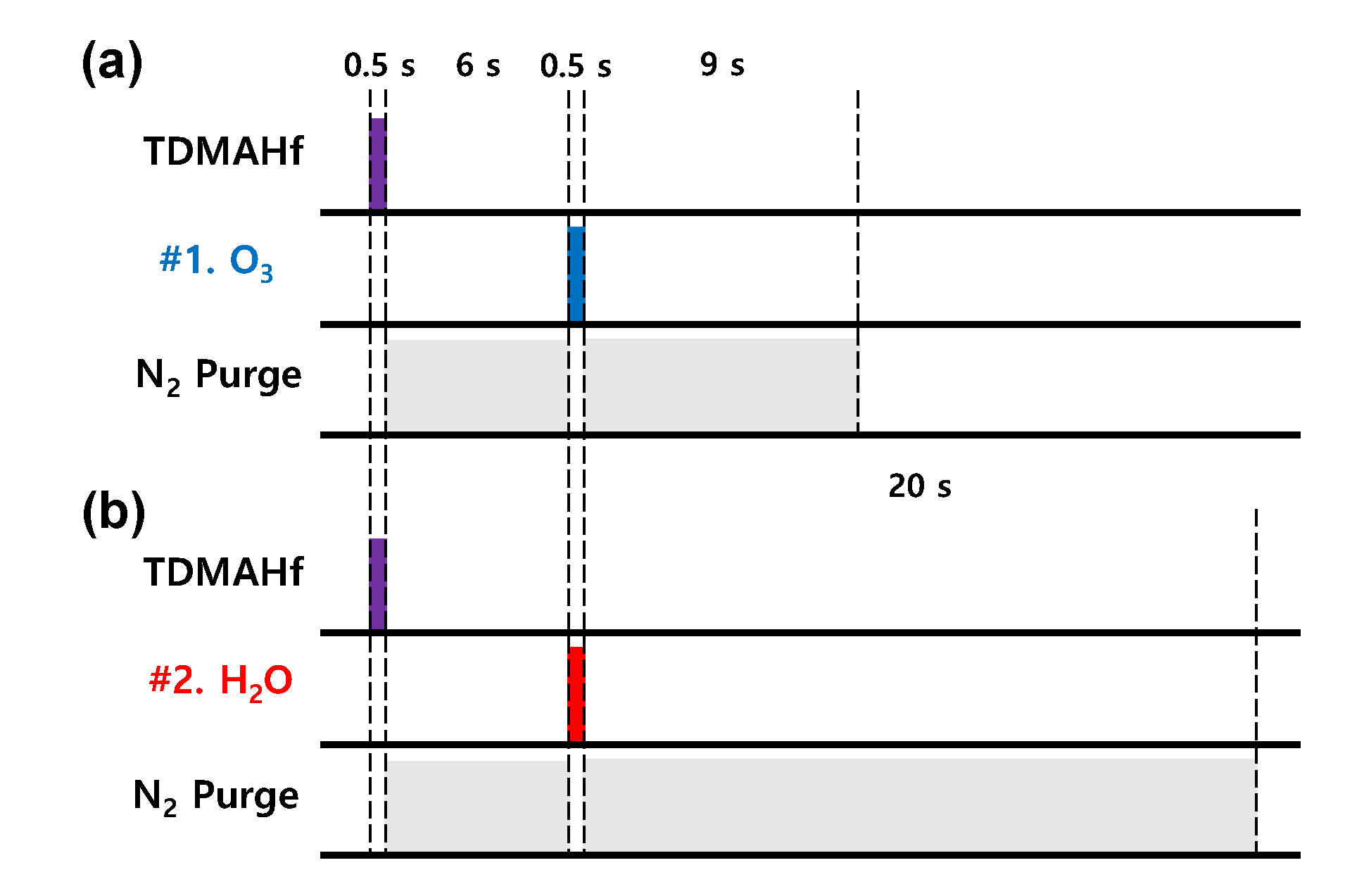
2. Materials and Methods
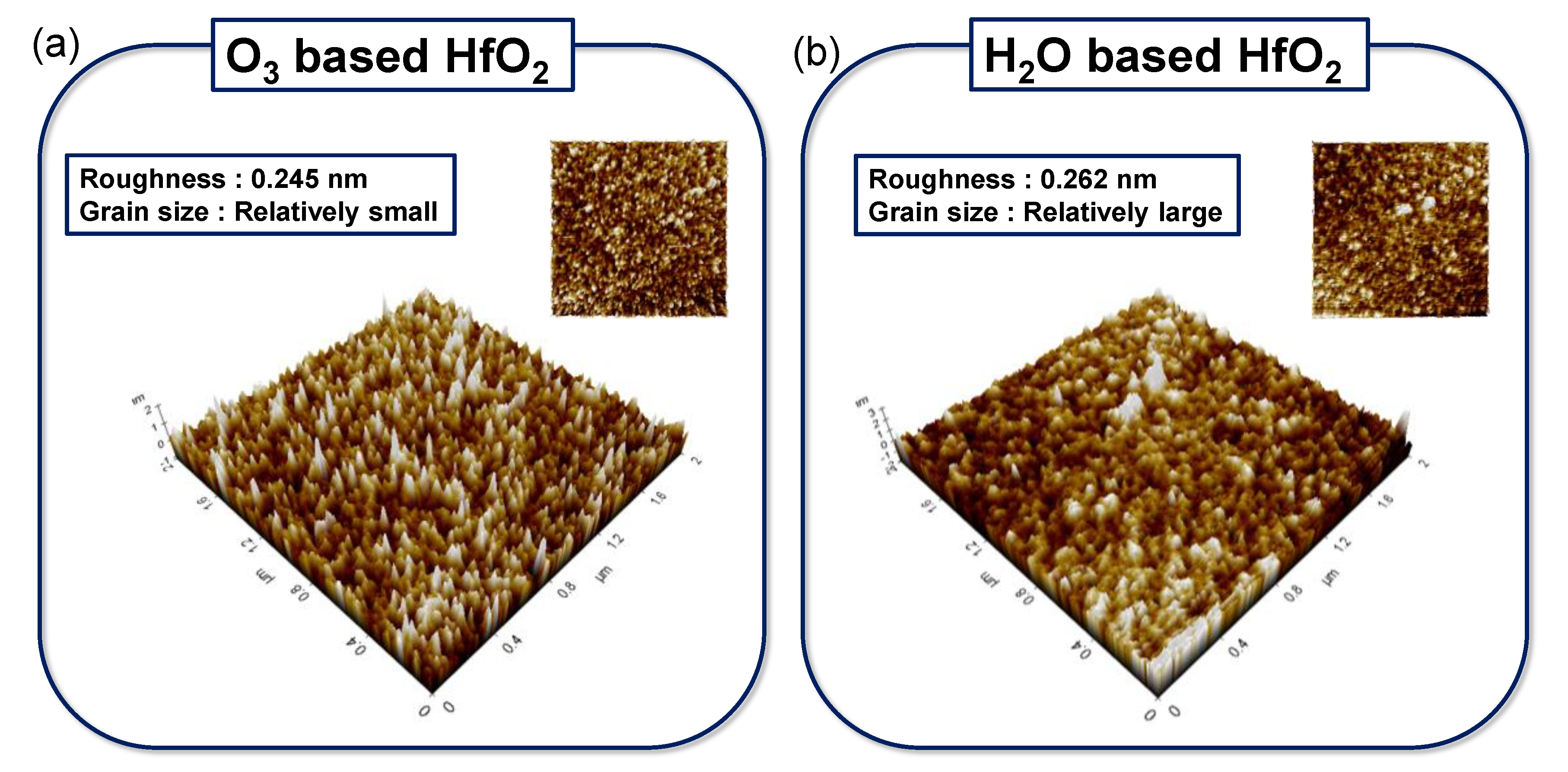
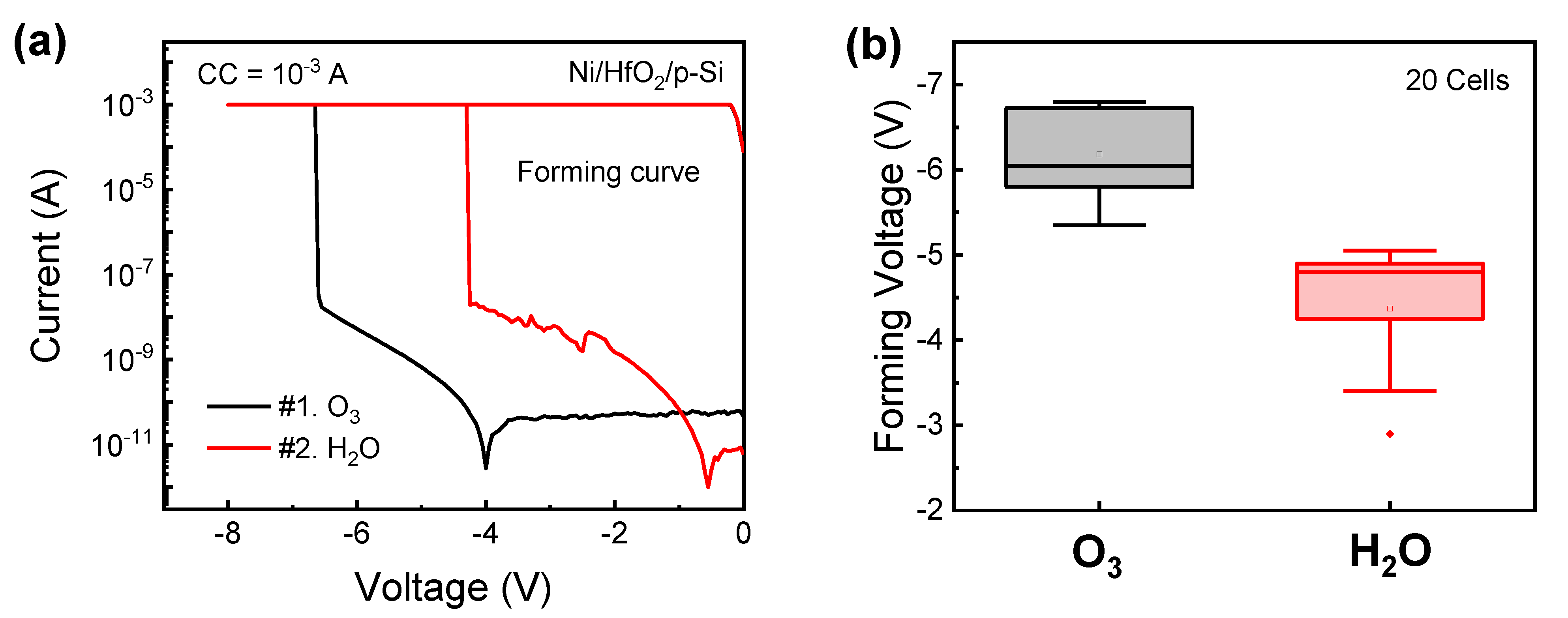
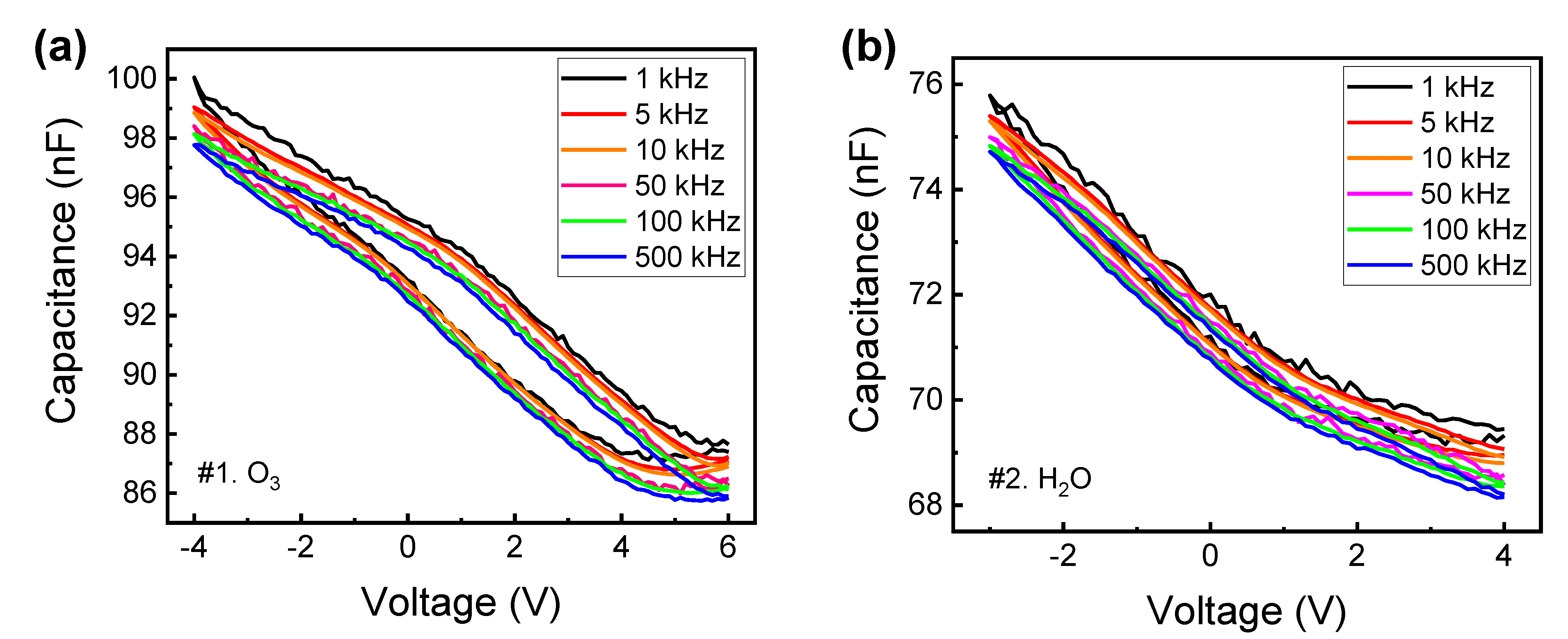
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lanza, M.; Wong, H.-S.P.; Pop, E.; Ielmini, D.; Strukov, D.; Regan, B.C.; Larcher, L.; Villena, M.A.; Yang, J.J.; Goux, L.; et al. Recommended Methods to Study Resistive Switching Devices. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2018, 5, 1800143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Gao, S.; Chen, C.; Song, C.; Zeng, F. Recent progress in resistive random access memories: Materials, switching mechanisms, and performance. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2014, 83, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waser, R.; Dittmann, R.; Staikov, G.; Szot, K. Redox-Based Resistive Switching Memories—Nanoionic Mechanisms, Prospects, and Challenges. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2632–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zhao, C.; Qi, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Mitrovic, I.Z.; Yang, L.; Zhao, C. Advances of RRAM Devices: Resistive Switching Mechanisms, Materials and Bionic Synaptic Application. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, S.W.; Neumann, C.M.; Wong, H.S.P. Phase-Change Memory—Towards a Storage-Class Memory. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2017, 64, 4374–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.S.; Zhang, Y.; Devolder, Y.; Klein, J.O.; Ravelosona, D.; Chappert, C.; Mazoyer, P. Failure and reliability analysis of STT-MRAM. Microelectron. Reliab. 2012, 52, 1848–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.C.; Lin, Y.-W.; Jang, W.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Tseng, T.-Y. Low-power and highly reliable multilevel operation in ZrO2 1T1R RRAM. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2011, 32, 1026–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.-H.; Lee, K.-J.; Wang, L.-W.; Chang, Y.-C.; Wang, Y.-H. Resistive Switching Behavior of Magnesium Zirconia Nickel Nanorods. Materials 2020, 13, 2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Irregular Resistive Switching Behaviors of Al2O3-Based Resistor with Cu Electrode. Metals 2021, 11, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Gradually Modified Conductance in the Self-Compliance Region of an Atomic-Layer-Deposited Pt/TiO2/HfAlOx/TiN RRAM Device. Metals 2021, 11, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maikap, S.; Banergee, W. In Quest of Nonfilamentary Switching: A Synergistic Approach of Dual Nanostructure Engineering to Improve the Variability and Reliability of Resistive Random-Access-Memory Devices. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2020, 6, 2000209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kim, S. Nonlinear Characteristics of Complementary Resistive Switching in HfAlOx-Based Memristor for High-Density Cross-Point Array Structure. Coatings 2020, 10, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, E.; Ossorio, Ó.G.; Dueñas, S.; Castán, H.; García, H.; Wenger, C. Programming Pulse Width Assessment for Reliable and Low-Energy Endurance Performance in Al:HfO2-Based RRAM Arrays. Electronics 2020, 9, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylov, A.; Belov, A.; Korolev, D.; Antonov, I.; Kotomina, V.; Kotina, A.; Gryaznov, E.; Sharapov, A.; Koryazhkina, M.; Kryukov, R.; et al. Multilayer Metal-Oxide Memristive Device with Stabilized Resistive Switching. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 1900607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Kim, S. Negative differential resistance effect and dual resistive switching properties in a transparent Ce-based devices with opposite forming polarity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 530, 147284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.S.; Chang, W.Y.; Lin, M.H.; Chen, W.S.; Chen, F.; Tsai, M.J. Polarity Reversion of the Operation Mode of HfO2-Based Resistive Random Access Memory Devices by Inserting Hf Metal Layer. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 1733–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Prakash, A.; Jana, D.; Maikap, S. TaOx-based resistive switching memories: Prospective and challenges. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Resistive and synaptic properties modulation by electroforming polarity in CMOS-compatible Cu/HfO2/Si device. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 145, 110783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Gradually Tunable Conductance in TiO2/Al2O3 Bilayer Resistors for Synaptic Device. Metals 2021, 11, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Self-Rectifying Resistive Switching and Short-Term Memory Characteristics in Pt/HfO2/TaOx/TiN Artificial Synaptic Device. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ielmini, D.; Wong, H.-S.P. In-memory computing with resistive switching devices. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.J.; Strukov, D.B.; Stewart, D.R. Memristive devices for computing. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.H.; Chang, T.; Ebong, I.; Bhadviya, B.B.; Mazumder, P.; Lu, W. Nanoscale memristor device as synapse in neuromorphic. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1297–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Kim, S. Short-Term Memory Dynamics of TiN/Ti/TiO2/SiOx/Si Resistive Random Access Memory. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Kim, S. Emulation of Biological Synapse Characteristics from Cu/AlN/TiN Conductive Bridge Random Access Memory. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhaylov, A.; Pimashkim, A.; Pigareva, Y.; Gerasimova, S.; Gryaznov, E.; Shchanikov, S.; Zuev, A.; Talanov, M.; Lavrov, I.; Demin, V.; et al. Neurohybrid memristive CMOS-integrated systems for biosensors and neuroprosthetics. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surazhevsky, I.A.; Demin, V.A.; IIlyasov, A.L.; Emelyanov, A.V.; Nikiruy, K.E.; Rylkov, V.V.; Shchanikov, S.; Bordanov, I.; Gerasimova, S.A.; Guseinov, D.; et al. Noise-assisted persistence and recovery of memory state in a memristive spiking neuromorphic network. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 146, 110890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Kim, S. Enhancing Short-Term Plasticity by Inserting a Thin TiO2 Layer in WOx-Based Resistive Switching Memory. Coatings 2020, 10, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Choi, J.; Kim, S. Voltage Amplitude-Controlled Synaptic Plasticity from Complementary Resistive Switching in Alloying HfOx with AlOx-Based RRAM. Metals 2020, 10, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Pseudo-Interface Switching of a Two-Terminal TaOx/HfO2 Synaptic Device for Neuromorphic Applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Nili, H.; Kim, M.H.; Min, K.K.; Park, B.G.; Kim, H. Reset-voltage-dependent precise tuning operation of TiOx/Al2O3 memristive crossbar array. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 117, 152103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Volatile Resistive Switching Characteristics of Pt/HfO2/TaOx/TiN Short-Term Memory Device. Metals 2021, 11, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Implementation of a reservoir computing system using the short-term effects of Pt/HfO2/TaOx/TiN memristors with self-rectification. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 150, 111223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, I.T.; Chang, C.C.; Chiu, L.W.; Chou, T.; Hou, T.H. 3D Ta/TaOx/TiO2/Ti synaptic array and linearity tuning of weight update for hardware neural network applications. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 365204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Nonideal resistive and synaptic characteristics in Ag/ZnO/TiN device for neuromorphic system. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.-G.; Woo, J.-U.; Lee, T.-H.; Park, S.M.; Lee, T.-G.; Lee, W.H.; Nahm, S. Synaptic plasticity and preliminary-spike-enhanced plasticity in a CMOS-compatible Ta2O5 memristor. Mater. Des. 2020, 187, 108400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovani, A.; Woo, J.; Hwang, H.; Larcher, L. Understanding and Optimization of Pulsed SET Operation in HfOx-Based RRAM Devices for Neuromorphic Computing Applications. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2018, 39, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, B.; Tang, J.; Li, X.; Wu, W.; Qian, H.; Wu, H. Analog-Type Resistive Switching Devices for Neuromorphic Computing. Phys. Status Solidi—Rapid Res. Lett. 2019, 13, 1900204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Gao, B.; Tang, J.; Qian, H.; Wu, H. Reliability of analog resistive switching memory for neuromorphic computing. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2020, 7, 011301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emelyanov, A.V.; Nikiruy, K.E.; Serenko, A.V.; Sitnikov, A.V.; Presnyakov, M.Y.; Rybka, R.B.; Sboev, A.G.; Rylkov, V.V.; Kashkarov, P.K.; Kovalchuk, M.V.; et al. Self-adaptive STDP-based learning of a spiking neuron with nanocomposite memristive weights. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 045201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Lee, C.B.; Lee, D.; Lee, S.R.; Chang, M.; Hur, J.H.; Kim, Y.-B.; Kim, C.-J.; Seo, D.H.; Chung, U.-I.; et al. A fast, high endurance and scalable non-volatile memory device made from asymmetric Ta2O5-x/TaO2-x bilayer structures. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Long, S.B.; Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.H.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Zuo, Q.; Yang, J.; et al. Investigation of resistive switching in Cu-doped HfO2 thin film for multilevel non-volatile memory applications. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 045202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; He, Z.-Y.; Wang, T.-Y.; Dai, Y.-W.; Zhu, H.; Sun, Q.-Q.; Zhang, D.W. CMOS Compatible Bio-Realistic Implementation with Ag/HfO2-Based Synaptic Nanoelectronics for Artificial Neuromorphic System. Electronics 2018, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, H. Multi-Level Switching of Al-Doped HfO2 RRAM with a Single Voltage Amplitude Set Pulse. Electronics 2021, 10, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Improved Pulse-Controlled Conductance Adjustment in Trilayer Resistors by Suppressing Current Overshoot. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-F.; Tang, X.-G.; Wang, L.-Q.; Tang, H.; Jiang, Y.-P.; Liu, Q.-X.; Li, W.-H.; Tang, Z.-H. Resistive Switching Characteristics of HfO2 Thin Films on Mica Substrates Prepared by Sol-Gel Process. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, S.M. Atomic Layer Deposition: An Overview. Chem. Rev. 2016, 110, 111–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Koide, Y. An Overview of High-k Oxides on Hydrogenated-Diamond for Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Capacitors and Field-Effect Transistors. Sensors 2018, 18, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kwon, O.; Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Improved Synaptic Device Properties of HfAlOx Dielectric on Highly Doped Silicon Substrate by Partial Reset Process. Metals 2021, 11, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahata, C.; Kim, S. Modified resistive switching performance by increasing Al concentration in HfO2 on transparent indium tin oxide electrode. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wu, H.; Wu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, N.; Yu, Z.; Qian, H. Study of Multi-level Characteristics for 3D Vertical Resistive Switching Memory. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapteva, M.; Beladiya, V.; Riese, S.; Hanke, P.; Otto, F.; Fritz, T.; Schmitt, P.; Stenzel, O.; Tünnermann, A.; Szeghalmi, A. Influence of temperature and plasma parameters on the properties of PEALD HfO2. Opt. Mater. Express 2021, 11, 1918–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, A.; Perez, E.; Zambelli, C.; Olivo, P.; Miranda, E.; Roelofs, R.; Woodruff, J.; Raisanen, P.; Li, W.; Givens, M.; et al. Impact of the precursor chemistry and process conditions on the cell-to-cell variability in 1T-1R based HfO2 RRAM devices. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zazpe, R.; Ungureanu, M.; Golmar, F.; Stoliar, P.; Llopis, R.; Casanova, F.; Pickip, D.; Rogero, C.; Hueso, L.E. Resistive switching dependence on atomic layer deposition parameters in HfO2-based memory devices. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 3204–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, A.S.; Jeon, Y.R.; Kim, S. Influence of oxygen vacancies in ALD HfO2-x thin films on non-volatile resistive switching phenomena with a Ti/HfO2-x/Pt structure. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 434, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, S.; Simanjuntak, F.M.; Saminatha, R.; Panda, D.; Tseng, T.Y. Improving linearity by introducing Al in HfO2 as a memristor synapse device. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 445205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, J.; Seo, H. Forming-less and Non-Volatile Resistive Switching in WOX by Oxygen Vacancy Control at Interfaces. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.L.; Chang, Y.L.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Lin, J.R. Comprehensive comparison of structural, electrical, and reliability characteristics of HfO2 gate dielectric with H2O or O3 oxidant. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2013, 31, 01A141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, J.H.; Yu, I.H.; Lee, J.H.; Hwang, C.S. Effects of O3 and H2O as oxygen sources on the atomic layer deposition of HfO2 gate dielectrics at different deposition temperatures. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachke, D.; Munnik, F.; Grenzer, J.; Rebohle, L.; Schmidt, H.; Zahn, P.; Gemming, S. A correlation study of layer growth rate, thickness uniformity, stoichiometry, and hydrogen impurity level in HfO2 thin films grown by ALD between 100 C and 350 C. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 506, 144188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.S.; Lee, J.; Yoon, S.; Chung, K.J.; Lee, S.; Park, J.; Kim, C.K.; Ahn, J. Oxidant Effect on Resistance Switching Characteristics of HfO2 film Grown Atomic Layer Deposition. ECS Trans. 2007, 11, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Effects of Oxygen Precursor on Resistive Switching Properties of CMOS Compatible HfO2-Based RRAM. Metals 2021, 11, 1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11091350
Ryu H, Kim S. Effects of Oxygen Precursor on Resistive Switching Properties of CMOS Compatible HfO2-Based RRAM. Metals. 2021; 11(9):1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11091350
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyu, Hojeong, and Sungjun Kim. 2021. "Effects of Oxygen Precursor on Resistive Switching Properties of CMOS Compatible HfO2-Based RRAM" Metals 11, no. 9: 1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11091350
APA StyleRyu, H., & Kim, S. (2021). Effects of Oxygen Precursor on Resistive Switching Properties of CMOS Compatible HfO2-Based RRAM. Metals, 11(9), 1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11091350




