Gradually Tunable Conductance in TiO2/Al2O3 Bilayer Resistors for Synaptic Device
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
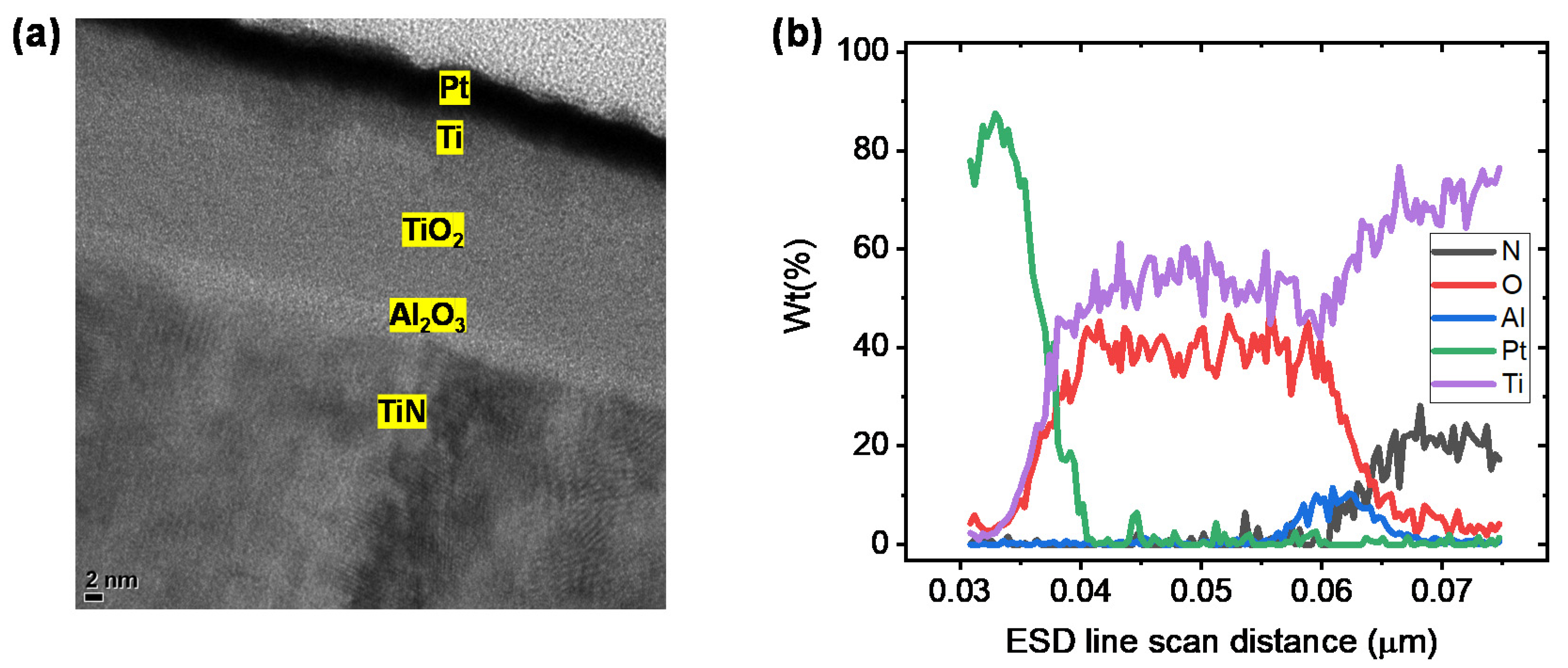
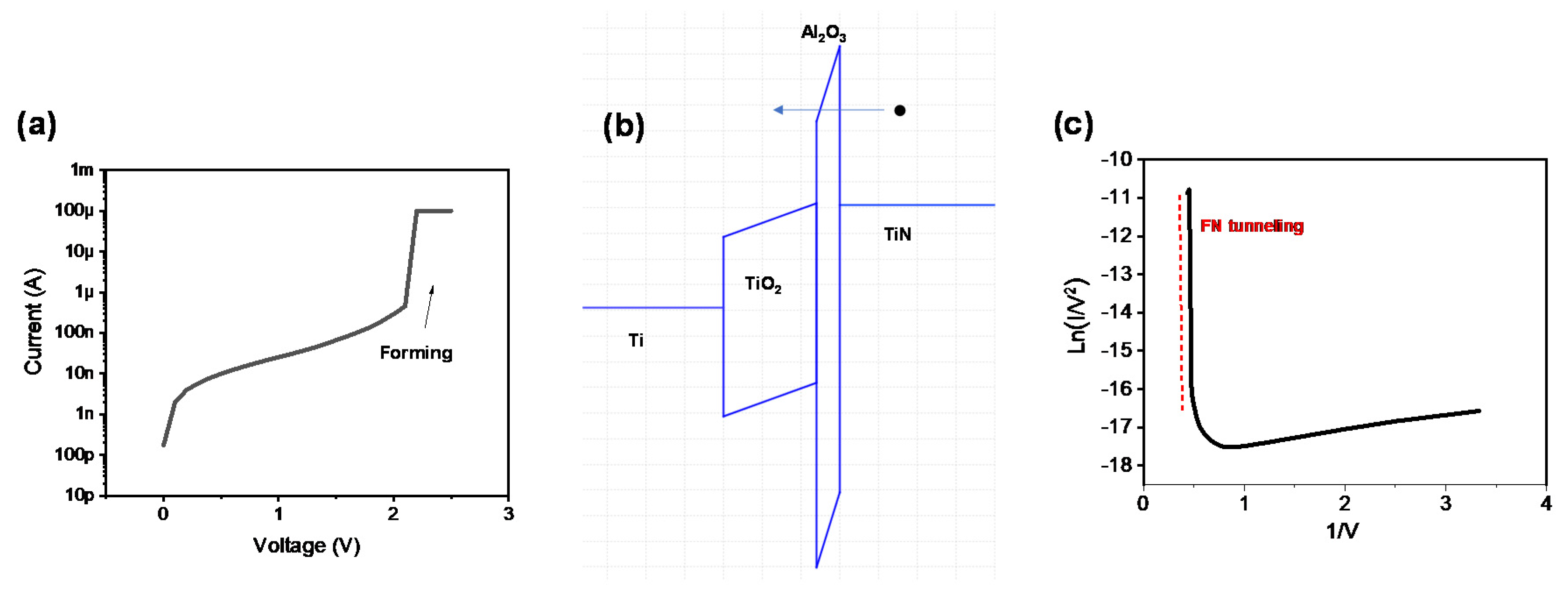
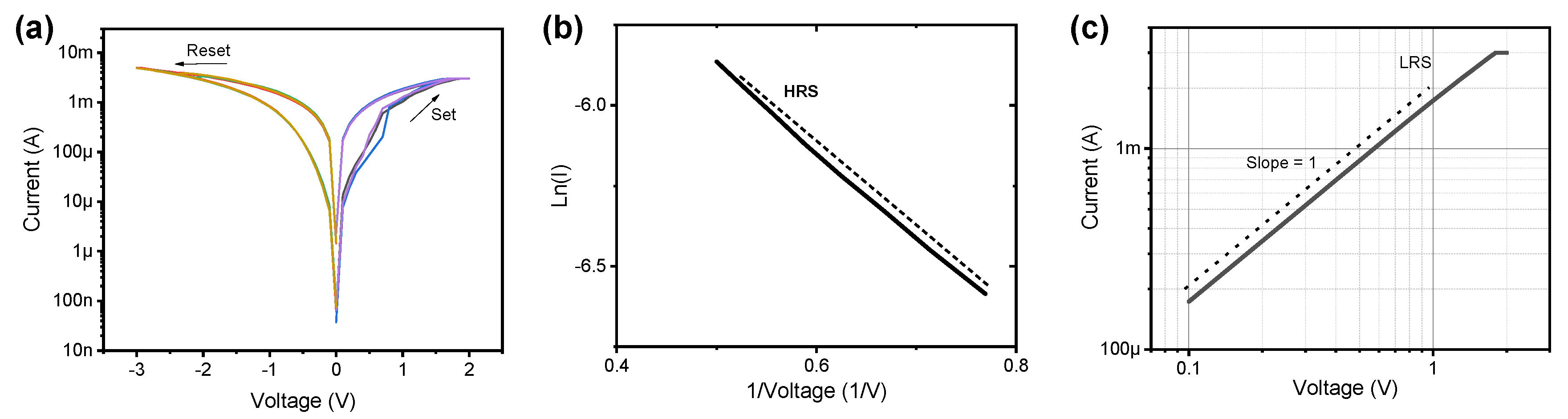
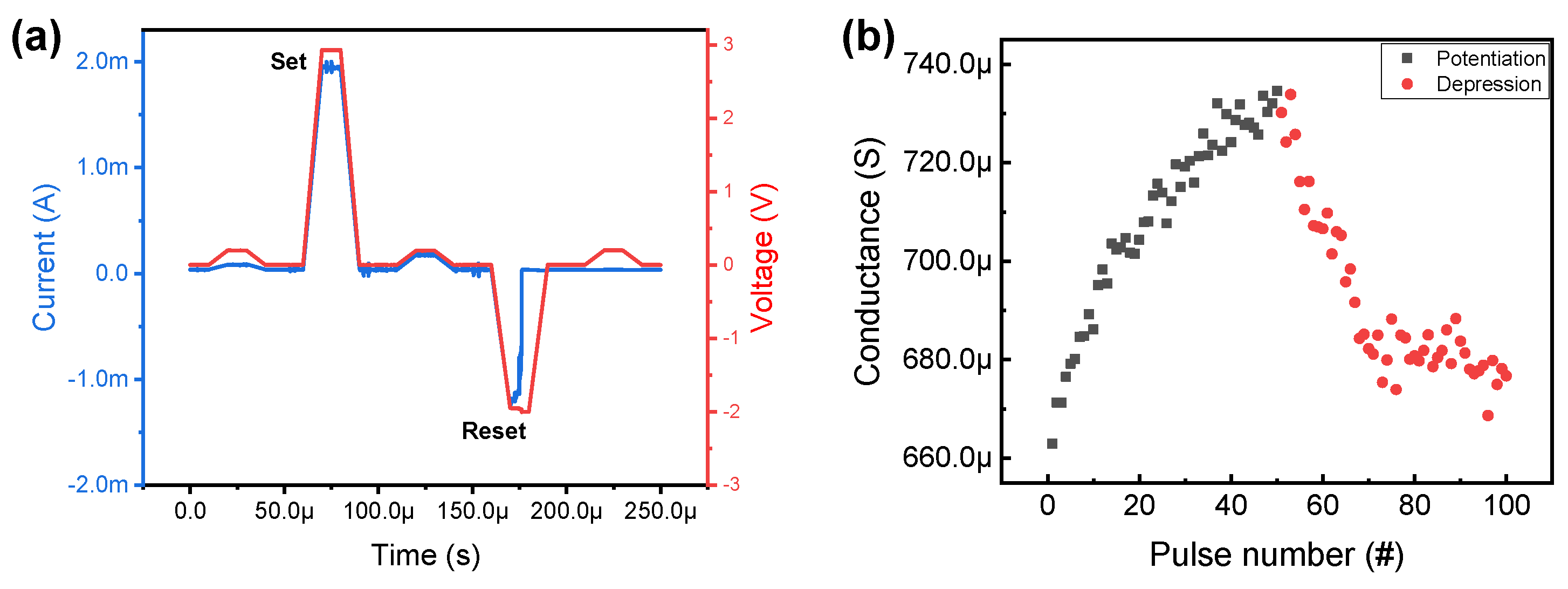
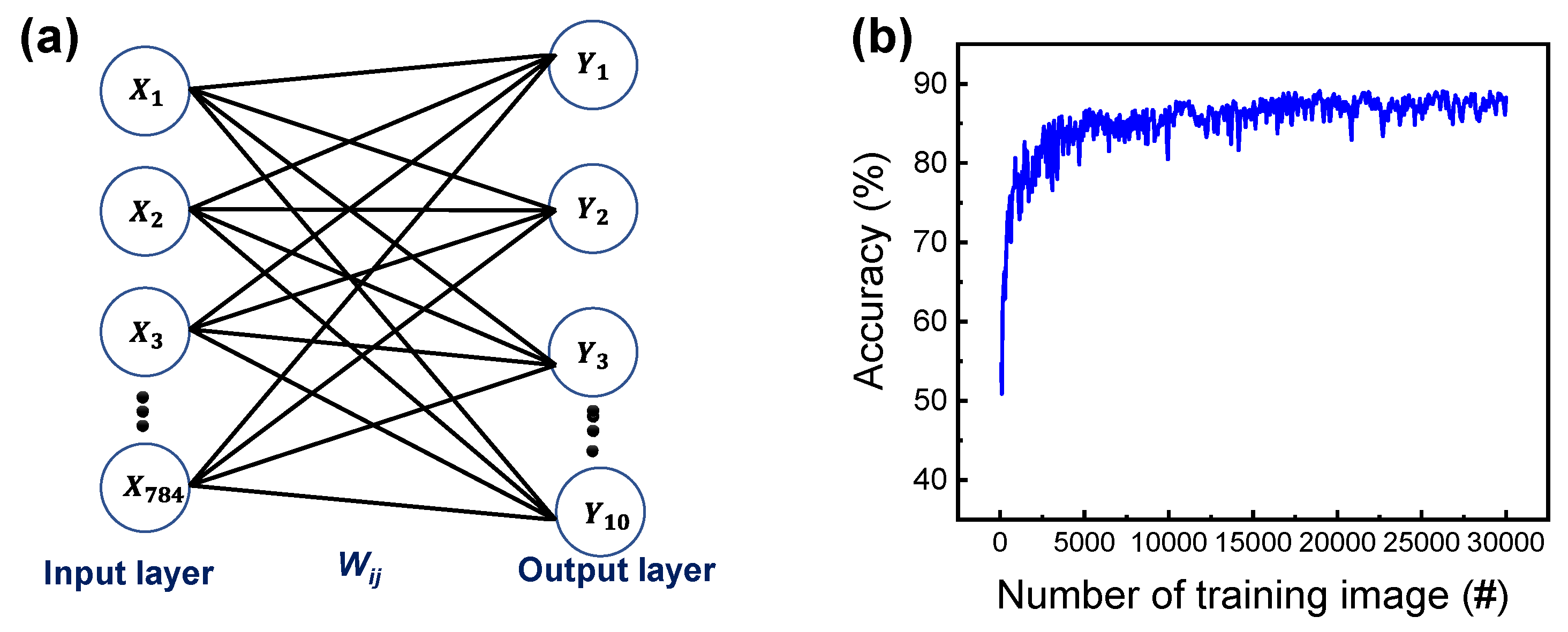
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chien, W.-C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Tsou, Y.-T.; Kuo, S.-Y.; Chang, C.-R. STT-DPSA: Digital PUF-Based Secure Authentication Using STT-MRAM for the Internet of Things. Micromachines 2020, 11, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J. Neuromorphic Computing Using Emerging Synaptic Devices: A Retrospective Summary and an Outlook. Electronics 2020, 9, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, M.; Wong, H.-S.P.; Pop, E.; Ielmini, D.; Strukov, D.; Regan, B.C.; Larcher, L.; Villena, M.A.; Yang, J.J.; Goux, L.; et al. Recommended Methods to Study Resistive Switching Devices. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2018, 5, 1800143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linn, E.; Rosezin, R.; Kügeler, C.; Waser, R. Complementary resistive switches for passive nanocrossbar memories. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Jung, S.; Kim, M.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chang, T.-C.; Ryoo, K.-C.; Cho, S.; Lee, J.-H.; Park, B.-G. Scaling Effect on Silicon Nitride Memristor with Highly Doped Si Substrate. Small 2018, 14, 1704062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Chang, Y.F.; Fowler, B.; Byun, K.; Lee, J.C. Stabilization of multiple resistance levels by current-sweep in SiOx-based resistive switching memory. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 063508. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, F.; Gao, S.; Chen, C.; Song, C.; Zeng, F. Recent progress in resistive random access memories: Materials, switching mechanisms, and performance. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2014, 83, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maikap, S.; Banergee, W. In Quest of Nonfilamentary Switching: A Synergistic Approach of Dual Nanostructure Engineering to Improve the Variability and Reliability of Resistive Random-Access-Memory Devices. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2020, 6, 2000209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Self-Rectifying Resistive Switching and Short-Term Memory Characteristics in Pt/HfO2/TaOx/TiN Artificial Synaptic Device. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Pseudo-Interface Switching of a Two-Terminal TaOx/HfO2 Synaptic Device for Neuromorphic Applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Synaptic Characteristics from Homogeneous Resistive Switching in Pt/Al2O3/TiN Stack. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kim, S. Nonlinear Characteristics of Complementary Resistive Switching in HfAlOx-Based Memristor for High-Density Cross-Point Array Structure. Coatings 2020, 10, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, D.; Qiao, R. Impacts of LaOx Doping on the Performance of ITO/Al2O3/ITO Transparent RRAM Devices. Electronics 2021, 10, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-C.; Chang, Y.-F. Post-Moore Memory Technology: Sneak Path Current (SPC) Phenomena on RRAM Crossbar Array and Solutions. Micromachines 2021, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, H.; Choi, J.; Kim, S. Voltage Amplitude-Controlled Synaptic Plasticity from Complementary Resistive Switching in Alloying HfOx with AlOx-Based RRAM. Metals 2020, 10, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Song, P.; Gai, H.; Li, Y.; Ai, C.; Wen, D. Li-Doping Effect on Characteristics of ZnO Thin Films Resistive Random Access Memory. Micromachines 2020, 11, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, E.; González Ossorio, Ó.; Dueñas, S.; Castán, H.; García, H.; Wenger, C. Programming Pulse Width Assessment for Reliable and Low-Energy Endurance Performance in Al:HfO2-Based RRAM Arrays. Electronics 2020, 9, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Kim, S. Emulation of Biological Synapse Characteristics from Cu/AlN/TiN Conductive Bridge Random Access Memory. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Jung, S.; Kim, M.H.; Lee, S.; Cho, S.; Park, B.G. Tuning resistive switching parameters in Si3N4-based RRAM for three-dimensional vertical resistive memory applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 663, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Bae, D.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.-D. Reduced Operation Current of Oxygen-Doped ZrN Based Resistive Switching Memory Devices Fabricated by the Radio Frequency Sputtering Method. Coatings 2021, 11, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, H.; Kim, H.; Rehman, S.; Kadam, K.D.; Aziz, J.; Khan, M.F.; Kim, D.-K. Stable and Multilevel Data Storage Resistive Switching of Organic Bulk Heterojunction. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Zhao, C.; Qi, Y.; Mitrovic, I.Z.; Yang, L.; Wen, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, P.; Zhao, C. Memristive Non-Volatile Memory Based on Graphene Materials. Micromachines 2020, 11, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.-C.; Kim, M.-H.; Kim, H.; Kwon, M.-W.; Hwang, S.; Ismail, M.; Li, Y.; Miao, X.-S.; et al. Neuronal dynamics in HfO x/AlO y-based homeothermic synaptic memristors with low-power and homogeneous resistive switching. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, W.; Xu, X.; Lv, H.; Liu, Q.; Long, S.; Liu, M. Variability Improvement of TiOx/Al2O3 Bilayer Nonvolatile Resistive Switching Devices by Interfacial Band Engineering with an Ultrathin Al2O3 Dielectric Material. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 6888–6895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chand, U.; Huang, K.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Tseng, T.Y. Mechanism of Nonlinear Switching in HfO2-Based Crossbar RRAM With Inserting Large Bandgap Tunneling Barrier Layer. IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 2015, 62, 3665–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylov, A.; Belov, A.; Korolev, D.; Antonov, I.; Kotomina, V.; Kotina, A.; Gryaznov, E.; Sharapov, A.; Koryazhkina, M.; Kryukov, R.; et al. Multilayer Metal-Oxide Memristive Device with Stabilized Resistive Switching. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 1900607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.S.; Schroeder, H.; Waser, R. Coexistence of Bipolar and Unipolar Resistive Switching Behaviors in a Pt/TiO2/Pt Stack. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 2007, 10, G51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylov, A.; Pimashkin, A.; Pigareva, Y.; Gerasimova, S.; Gryaznov, E.; Shchanikov, S.; Zuev, A.; Talanov, M.; Lavrov, I.; Demin, V.; et al. Neurohybrid Memristive CMOS-Integrated Systems for Biosensors and Neuroprosthetics. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzum, D.; Yu, S.; Wong, H.-S.P. Synaptic electronics: Materials, devices and applications. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 382001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, C.E.; Li, C.; Sheng, X.; Miller, D.; Ignowski, J.; Kiyama, L.; Strachan, J.P. In-Memory Computing with Memristor Content Addressable Memories for Pattern Matching. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2003437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Yang, J.J. Memristive crossbar arrays for brain-inspired computing. Nat. Mater. 2019, 18, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.H.; Mahata, C.; Kim, S. Long-term and short-term plasticity of Ta2O5/HfO2 memristor for hardware neuromorphic application. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 850, 156675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Nili, H.; Kim, M.H.; Min, K.K.; Park, B.G.; Kim, H. Reset-voltage-dependent precise tuning operation of TiOx/Al2O3 memristive crossbar array. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 117, 152103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Abbas, H.; Choi, C.; Kim, S. Controllable analog resistive switching and synaptic characteristics in ZrO2/ZTO bilayer memristive device for neuromorphic systems. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 529, 147107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.F.; Chen, P.Y.; Fowler, B.; Chen, Y.T.; Xue, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Lee, J.C. Intrinsic SiOx-based unipolar resistive switching memory. II. Thermal effects on charge transport and characterization of multilevel programing. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 043709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhou, Z.; Ding, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y. Superior resistive switching memory and biological synapse properties based on a simple TiN/SiO2/p-Si tunneling junction structure. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 2259–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Gradually Tunable Conductance in TiO2/Al2O3 Bilayer Resistors for Synaptic Device. Metals 2021, 11, 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11030440
Ryu H, Kim S. Gradually Tunable Conductance in TiO2/Al2O3 Bilayer Resistors for Synaptic Device. Metals. 2021; 11(3):440. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11030440
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyu, Hojeong, and Sungjun Kim. 2021. "Gradually Tunable Conductance in TiO2/Al2O3 Bilayer Resistors for Synaptic Device" Metals 11, no. 3: 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11030440
APA StyleRyu, H., & Kim, S. (2021). Gradually Tunable Conductance in TiO2/Al2O3 Bilayer Resistors for Synaptic Device. Metals, 11(3), 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11030440





