Influence of Coiling Temperature on Microstructure, Precipitation Behaviors and Mechanical Properties of a Low Carbon Ti Micro-Alloyed Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
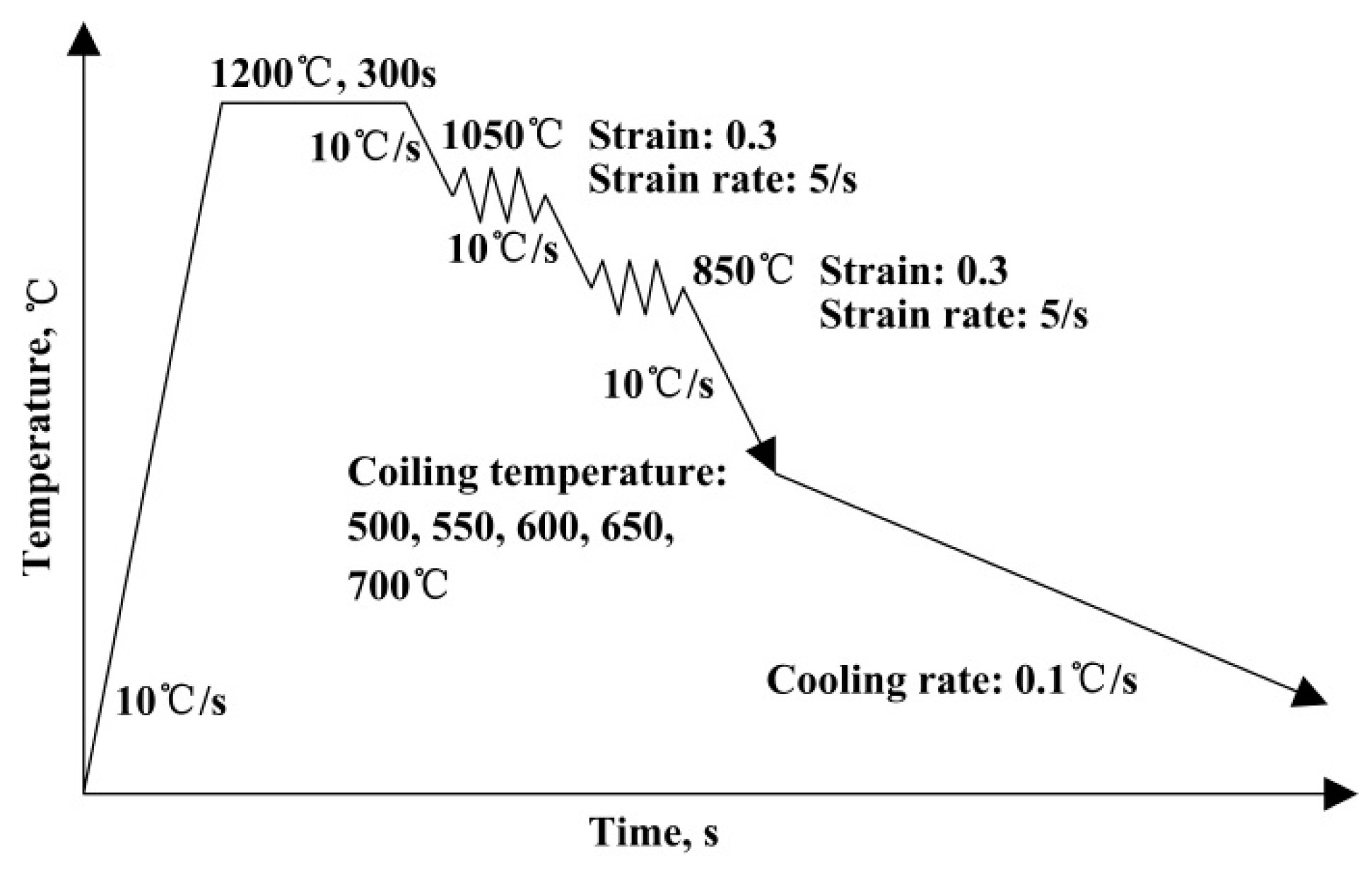
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optical Metallography
3.2. Vickers Hardness
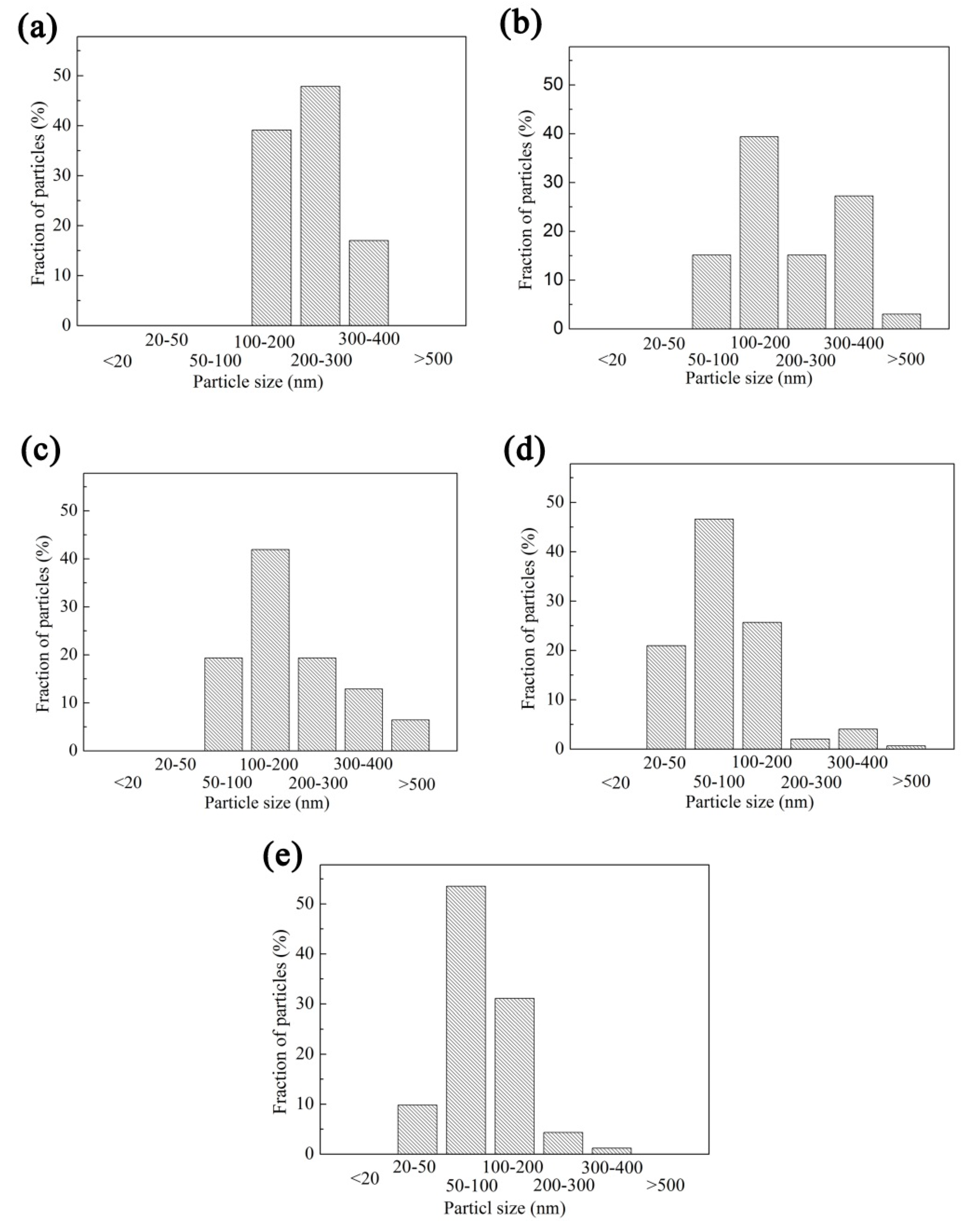
3.3. Precipitation Behavior
3.4. Rolling Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoshimasa, F.; Tsuyoshi, S. Development of high strength hot-rolled sheet steel consisting of ferrite and nanometer-sized carbides. ISIJ Int. 2004, 44, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.W.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, S.G.; Lee, C.S. Effects of rolling temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti–Mo microalloyed hot-rolled high strength steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 605, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.S.; Cheng, B.G.; Chen, Y.Y. Strengthening and toughening of a heavy plate steel for shipbuilding with yield strength of approximately 690 MPa. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 440–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Q.L.; Ma, M.T.; Wu, B.R. Microalloy Steel-the Physical and Mechanical Metallurgy; Machinery Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Senuma, T. Present status of future prospect s f or precipitation research in the steel industry. ISIJ Int. 2002, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, R.D.K.; Tennetis, K.K.; Weatherly, G.C.; Tither, G. Microstructure and texture of hot-rolled Cb-Ti and V-Cb microalloyed steels with differences in formability and toughness. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2001, 34, 2041–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, A.J.; He, K.; Garvie, L.A.J.; Baker, T.N. Complex heterogeneous precipitation in titanium-niobium microalloyed Al-killed HSLA steels-(Ti, Nb)(C, N)particles. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 3857–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Shi, J.; Xu, L.; Cao, W.Q.; Dong, H. TiC precipitation induced effect on microstructure and mechanical properties in low carbon medium manganese steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 530, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazuhiro, S.; Yoshimasa, F.; Shinjiro, K. Hot rolled high strength steels for suspension and chassis parts “NANOHITEN” and “BHT® steel”. JFE Technical. Rep. 2007, 10, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.F.; Cai, Q.W.; Wu, H.B.; Mao, H.Y.; Chen, H.Z. Effect of controlled rolling processing on nanometer-sized carbonitride of Ti-Mo ferrite matrix microalloyed steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 2012, 48, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.N.; Di, H.S.; Du, L.X. Effects of deformation and cooling rate on nano-scale precipitation in hot-rolled ultra-high strength steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 2012, 48, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.N.; Sun, M.X.; Yi, H.L.; Liu, Z.Y. The blocking effects of interphase precipitationon dislocations’ movement in Ti-bearing micro-alloyed steels. Mater. Lett. 2015, 139, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.X.; Wu, H.B.; Tang, Q.B. Effects of Coiling Temperature on microstructure and precipitation behavior in Nb–Ti microalloyed steels. ISIJ Int. 2018, 58, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, M.X.; Zhou, Y.L.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, G.D. Effect of Mo on nano-precipitation behavior and microscopic mechanical characteristics of ferrite. Steel Res. Int. 2015, 86, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, V.V.; Challa, V.S.A.; Misra, R.D.K. The determining impact of coiling temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a Titanium-Niobium ultrahigh strength microalloyed steel: Competing effects of precipitation and bainite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 665, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, M.X.; Yi, H.L.; Liu, Z.Y. Precipitation behavior of (Nb,Ti)C in coiling process and its effect on micro-mechanical characteristics of ferrite. Acta Metal. Sin. 2015, 51, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, X.L.; Yuan, Q.; Zhao, G.; Ma, H.W.; Liang, W.; Xue, Z.L.; Qiao, W.W.; Xu, G. Quantitative analysis of microstructures and strength of Nb-Ti microalloyed steel with different Ti additions. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 2084–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshio, M.; Hitoshi, H.; Goro, M.; Tadashi, F. Effects of ferrite growth rate on interphase boundary precipitation in V microalloyed steels. ISIJ Int. 2012, 52, 616–625. [Google Scholar]
- Jose, C.M.; Guillermo, E.; Estela, P.T. Characterization of microalloy precipitates in the austenitic range of high strength low alloy steels. Steel Res. 2002, 73, 340–345. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, H.W.; Chen, P.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Yang, J.R. Interphase precipitation of nanometer-sized carbides in a titanium-molybdenum-bearing low-carbon steel. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 6264–6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Heating Temperature °C | Cooling Rate °C/s | Coiling Temperature °C | Yield Strength MPa | Tensile Strength MPa | Elongation % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1200 | 20–30 | 630 | 682 ± 2.1 | 742 ± 4.9 | 24.2 ± 1.7 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, M.; Xu, Y.; Du, W. Influence of Coiling Temperature on Microstructure, Precipitation Behaviors and Mechanical Properties of a Low Carbon Ti Micro-Alloyed Steel. Metals 2020, 10, 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10091173
Sun M, Xu Y, Du W. Influence of Coiling Temperature on Microstructure, Precipitation Behaviors and Mechanical Properties of a Low Carbon Ti Micro-Alloyed Steel. Metals. 2020; 10(9):1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10091173
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Mingxue, Yang Xu, and Wenbo Du. 2020. "Influence of Coiling Temperature on Microstructure, Precipitation Behaviors and Mechanical Properties of a Low Carbon Ti Micro-Alloyed Steel" Metals 10, no. 9: 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10091173
APA StyleSun, M., Xu, Y., & Du, W. (2020). Influence of Coiling Temperature on Microstructure, Precipitation Behaviors and Mechanical Properties of a Low Carbon Ti Micro-Alloyed Steel. Metals, 10(9), 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10091173




