Abstract
In finite element (FE) simulations, the peak bone stresses were higher when loading with a cantilever extension (CE) than when loading without a CE by 33–49% in the cortical bone. In the in vitro experiments, the highest values of principal strain were all within the range of the minimum principal strain, and those peak bone strains were 40–58% greater when loading with a CE than when loading without a CE (p < 0.001). This study investigated how varying the implanted position and angulation of anterior implants in the All-on-Four treatment influenced the biomechanical environment in the alveolar bone around the dental implants. Ten numerical simulations of FE models and three in vitro samples of All-on-Four treatment of dental implants were created to investigate the effects of altering the implanted position and angulation type of anterior implants. A single load of 100 N was applied in the molar region in the presence or absence of a CE of the denture. The 3D FE simulations analyzed the von-Mises stresses in the surrounding cortical bone and trabecular bone. For the in vitro tests, the principal bone strains were recorded by rosette strain gauges and statistically evaluated using the Mann–Whitney U test and the Kruskal–Wallis test. Loading in the presence of a CE of the denture induced the highest bone stress and strain, which were 53–97% greater in the FE simulation and 68–140% in the in vitro experiments (p < 0.008) than when loading without a CE. The bone stresses in the FE models of various implanted positions and angulation types of anterior implants were similar to those in the model of a typical All-on-Four treatment. In vitro tests revealed that the bone strains were significantly higher in the samples with various angulation types of anterior implants (p < 0.008). In the All-on-Four treatment of dental implants, the bone stress and strain were higher when the load was applied to the CE of dentures. Altering the position or angulation of the anterior dental implant in the All-on-Four treatment has no benefit in relieving the stress and strain of the bone around the dental implant.
1. Introduction
Before dental implants became popular, patients with complete edentulism could only receive conventional removable complete dentures for oral reconstruction. Such dentures are easy to wear and enable the wearer to perform basic mastication through the absorption capability of his or her gums. However, some functional problems can be experienced by elderly patients [1], such as needing more time for chewing and experiencing pain when chewing [2]. These aspects result in such patients only being able to masticate soft food, which impairs the quality of their daily living in terms of diet. Additionally, patients who use conventional removable complete dentures are also subject to ulcerations and dissatisfied with the high vertical dimension of the dentures, which affects the chewing function [3].
Treatment with dental implants can overcome the problems mentioned above and improve the quality of life [2], and is nowadays the leading choice for edentulous patients. However, dental implantation is not always advantageous, especially in full-mouth reconstructions, since its high cost can result in many patients not receiving it. In 2003, Maló et al. developed a treatment concept called “All-on-Four” [4], which involves supporting full dentures with only four implants. Two of the four implants are planted in the incisor zone, and another two implants are embedded in the molar region at angles from 18° to 45° to avoid the maxillary sinus [5] or the inferior alveolar nerve [6], which is the small branch of the third trigeminal nerve below the posterior jawbone area. According to the statistical study of Babbush et al. [7], the All-on-Four treatment costs less, reduces the complexity of the treatment, and increases patient comfort relative to conventional implant treatment modalities.
While the All-on-Four treatment of dental implants seems to win favor with some patients, they often report biomechanical challenges related to the use of dentures with cantilever extension (CE) and tilted implants. Shortening the cantilever extension (CE) by applying tilted implants in the posterior molar region was reported to decrease the burden (both stress and strain) of the bone around the posterior implants [8,9,10,11]. However, this burden in the bone was still high [12], and the idea of using only four implants to support a complete denture still raises concern among some patients.
Surgical implant guidelines have made the placement of tilted implants easier in clinics. Using a tilted implant may also provide some biomechanical benefits [13], such as increasing the contact area with the cortical bone and thereby also the implant’s stability. Rearranging the position of implants supporting partial prostheses [14,15] and complete dentures [16] reportedly alters the stress and strain distribution in the bone around the implants and can improve their biomechanical performance.
In addition to the posterior tilted implants, altering the position or angle of anterior implants in the All-on-Four treatment might also change the biomechanical environment in the peri-implant bone; however, this has been investigated by only a few studies [11,16]. Therefore, the objective of the present study was to determine how changing the implanted position or angulation of anterior implants in the All-on-Four treatment influences the stress and strain in the bone around the implant. This study applied both the technologies of three-dimensional (3D) numerical simulation—finite element (FE) analysis and in vitro strain gauge experiment—to explore this topic.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Features of Bone Sample and Implantation Designs
A synthetic jawbone model (#8571, Synbone, Malans, Switzerland) with mild atrophy was employed (Figure 3) in this study. This bone model includes a dense outer layer that replicates the cortical shell and a softer inner content that imitates a cancellous bone. The use of this type of synthetic jawbone also helps to reduce the associated ethical issues [17].
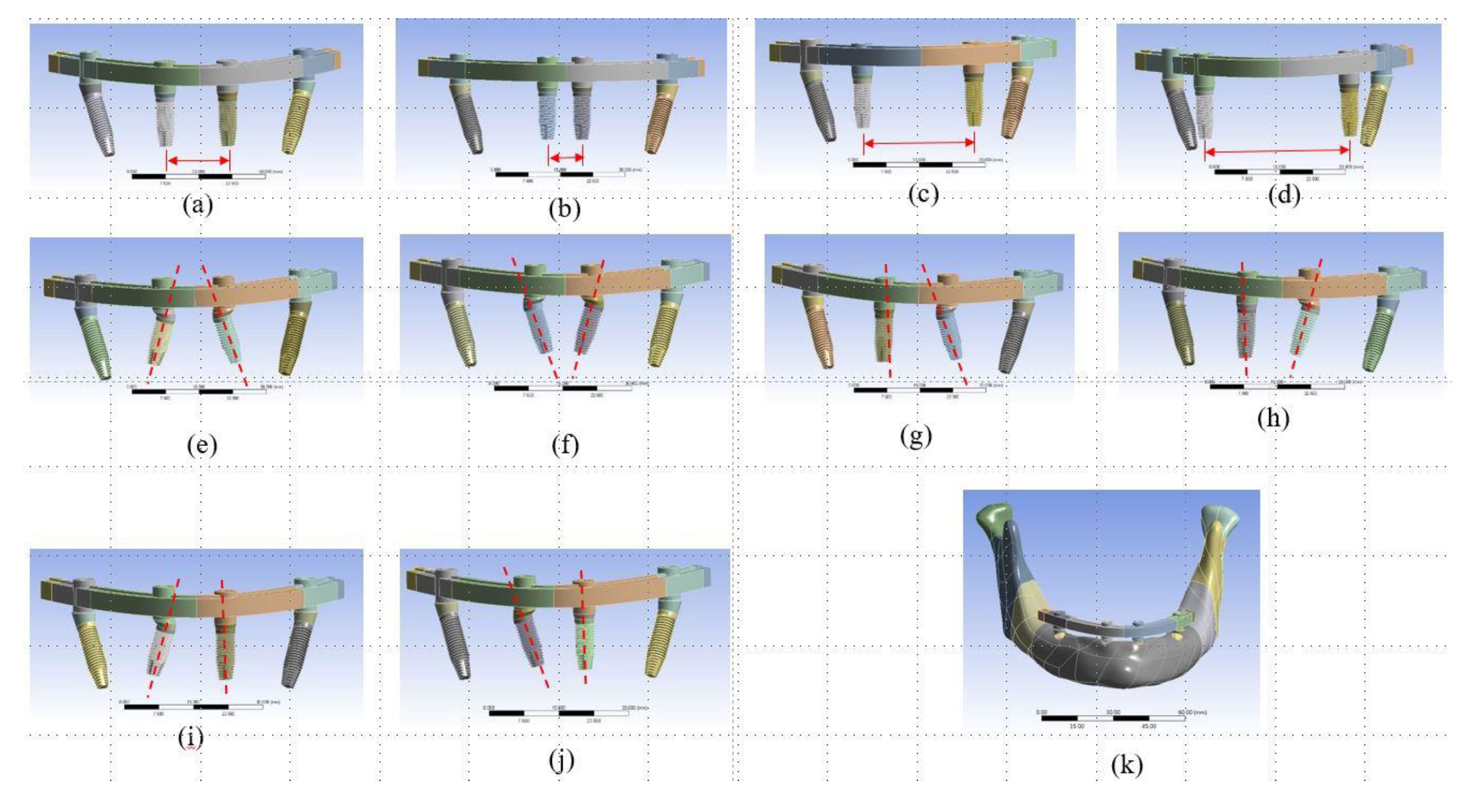
Implantation designs of anterior implants of All-on-Four treatment were classified into two groups: (1) alterations of the implanted position and (2) alterations of the angulation type of the implants. For the first group, there were four implanted positions designed in the models (Figure 1 a–d). Model Typical was the typical All-on-Four concept that included two vertical implants in the anterior incisor region and two implants tilted at 30° in the posterior molar region of the mandible. Model Position 1 (P1) was like Model Typical but with the two anterior implants implanted closer to the central incisor. Similarly, in Model Position 2 (P2) and Model Position 3 (P3) the anterior implants were moved to the molar area.
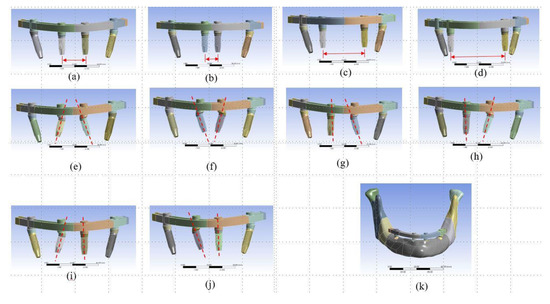
Figure 1.
The ten designs (test type, position of anterior implants, titled type of anterior implant), including (a) Model Typical (typical model, incisor region, vertical implantation), (b) Model P1 (implanted-position test, central incisor region, vertical implantation), (c) Model P2 (implanted-position test, incisor-canine region, vertical implantation), (d) Model P3 (implanted-position test, canine region, vertical implantation), (e) Model T1 (titled-type test, incisor region, 30°-tilted implants toward the distal direction), (f) Model T2 (titled-type test, incisor region, 30°-tilted implants toward the mesial direction), (g–j) Model T3–Model T6 (titled-type test, incisor region, one vertical implant and one 30°-tilted implants toward the mesial or distal direction), were investigated for All-on-Four implant treatment. (k) The 3D computer-aided design (CAD) model of Model Typical.
Six models with various angulation types of anterior implants were created for comparison with Model Typical, which was set as the control model. Models Tilted 1 (T1) and Tilted 2 (T2) had two pairs of 30°-tilted implants placed in the posterior molar region and in the anterior incisor region toward the mesial and distal directions, respectively (Figure 1e,f). The designs of Models Tilted 3 (T3), Tilted 4 (T4), Tilted 5 (T5), and Tilted 6 (T6) were based on Model Typical, Model T1, and Model T2, where there was one anterior vertical implant and one anterior tilted implant toward the mesial or distal direction (Figure 1g–j).
All of the ten analyzed models used an implant with a diameter of 4 mm and 11.5 mm long (NobelSpeedy™ Groovy, Nobel Biocare, Göteborg, Sweden), along with straight abutments (Multi-unit Abutment, Nobel Biocare) and 30°-angled abutments (30° Multi-unit Abutment, Nobel Biocare), as well as a customized titanium framework.
2.2. 3D FE Modeling
Based on a series of cone-beam computed tomography images of the synthetic jawbone model (#8571, Synbone), the 3D model of a mandible with mild atrophy was created in medical imaging software (Mimics version 15.0, Materialise, Leuven, Belgium). 3D models of the implants, the straight and angled abutments, and the customized frameworks were constructed using computer-aided design (CAD) software (SolidWorks 2017, SolidWorks Corporation, Concord, MA, USA). After the bone model was imported into the CAD software, Boolean operations were performed and all the 3D models were assembled for analysis (Figure 1k). The modeling complexity was also reduced by setting the abutment and implant as an integrated component. Once the 3D models had been constructed, they were exported to commercial FE software (ANSYS Workbench, Swanson Analysis, Huston, PA, USA).
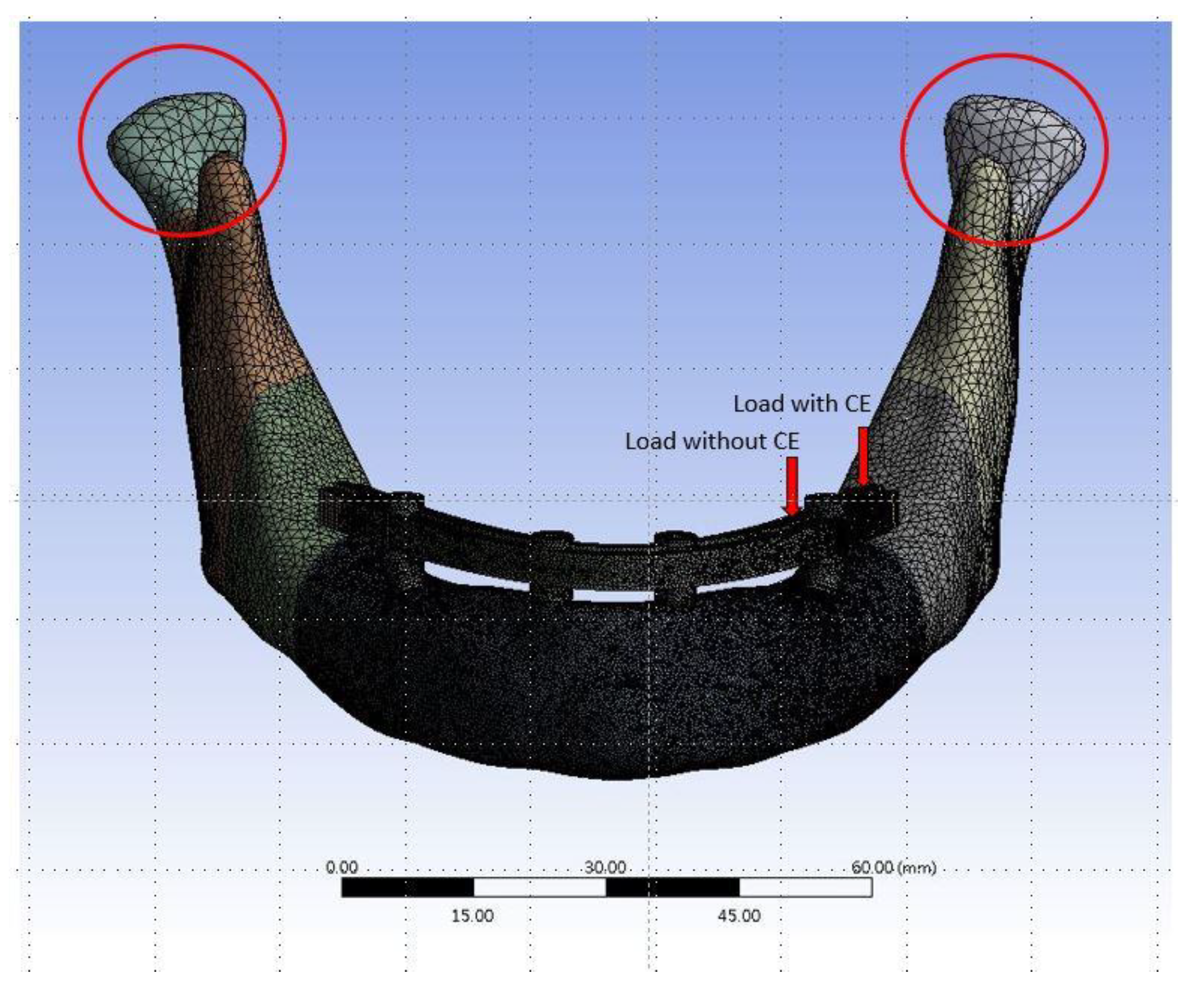
The thickness of the cortical bone in the 3D mandibular model is about 2 mm. Ten-node tetrahedral h-elements (ANSYS solid 187) were used to generate the FE model. In order to achieve the required accuracy for the results while reducing the solution time (computing resources), different element sizes were used in the FE models. For example, elements as small as 0.5 mm were used in the area of interest close to the peri-implant bone (Figure 2). The material properties of all components are listed in Table 1. [10,18,19]. The implants, abutment, framework, and bone were assigned to be homogeneous and have isotropic elastic properties. The interface between the bone and the implant was set as bonded based on the assumption of 100% osseointegration after the full healing time of the implant. The boundary condition of the FE models involved fixing the surface of the condyle to zero displacement in the x, y, and z directions (Figure 2). Two kinds of loading conditions were tested in this study. One was applied on the framework near the premolar position (without CE of denture), and another was added on the framework near the second or third molar (with CE of denture) (Figure 2). In both cases, a vertical load of 100 N was applied to the framework close to the posterior tilted implant. After the FE solution, the von-Mises stress of the cortical bone near the implants of each model was the focus of observation.
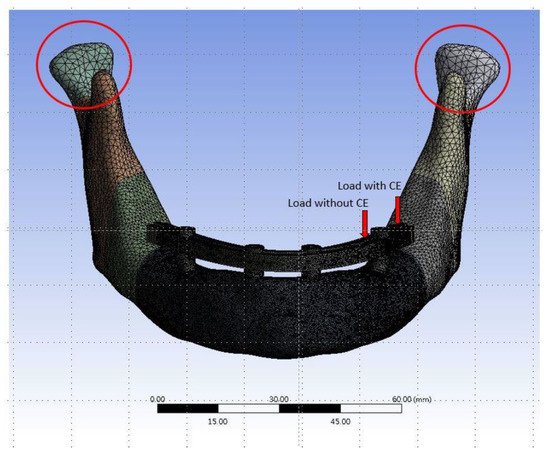
Figure 2.
The finite element (FE) mesh model of Model Typical. The red circles indicate the areas of boundary condition.

Table 1.
Material properties in the FE model. [10,18,19].
2.3. In Vitro Experimental Tests
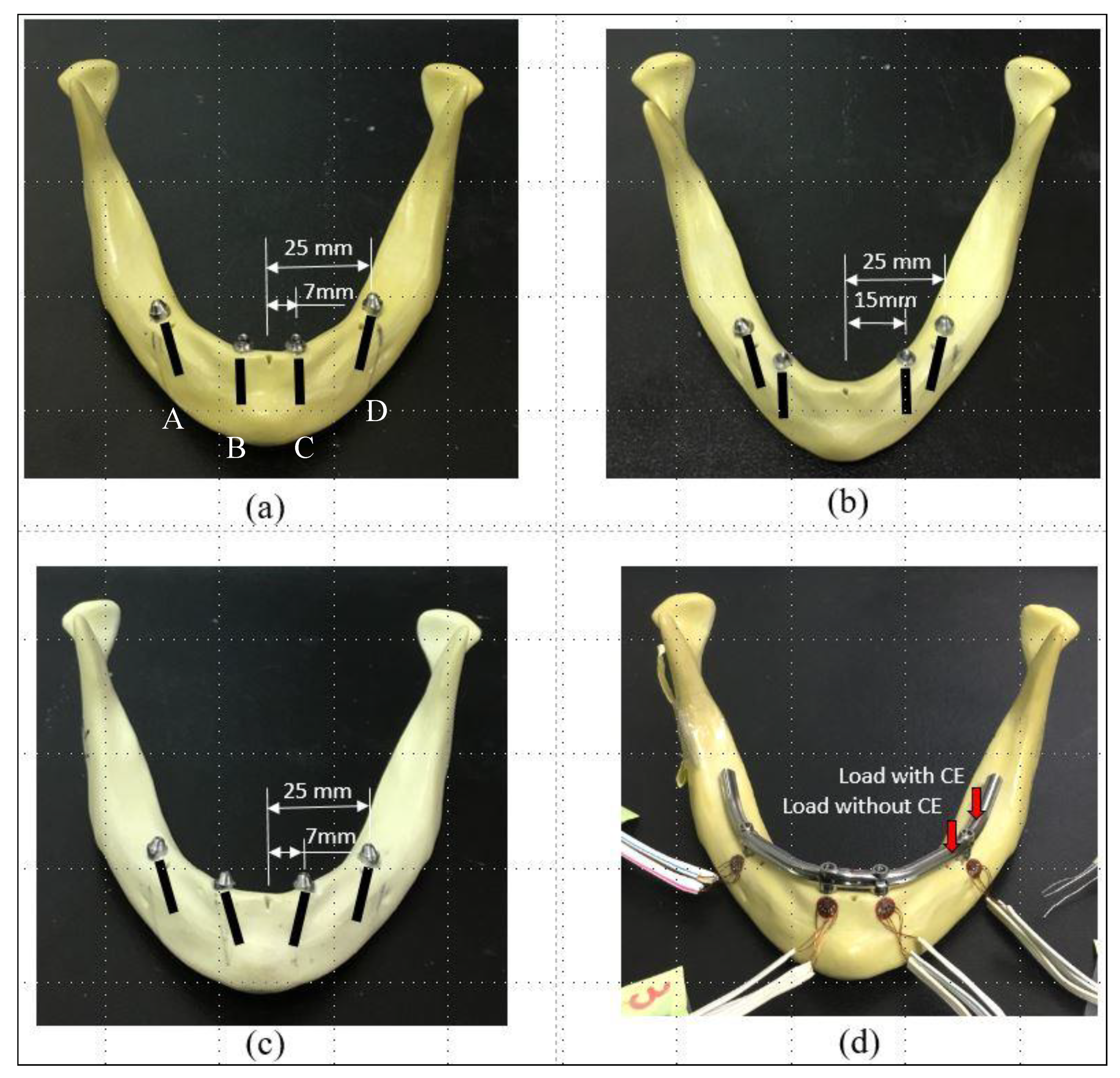
Three kinds of experimental samples were constructed for the in vitro tests: Sample Typical, Sample P2, and Sample T2, which related mainly to Model Typical, Model P2, and Model T2 in the FE simulations, respectively. For Sample Typical (Figure 3a), with the assistance of professional dentists, two NobelSpeedy implants (Nobel Biocare) with straight abutments (Multi-unit Abutment, Nobel Biocare) were placed upright and bilaterally in the incisor area of the synthetic jawbone model (#8571, Synbone). Two tilted implants with 30°-angled abutments (30° Multi-unit Abutment, Nobel Biocare) were placed about 30° relative to the occlusal plane into the posterior region of the mandible, bilaterally. For Sample P2 (Figure 3b), the anterior implants were located toward the molar area. For Sample T2 (Figure 3c), the anterior implants were angled 30° toward the mesial direction.
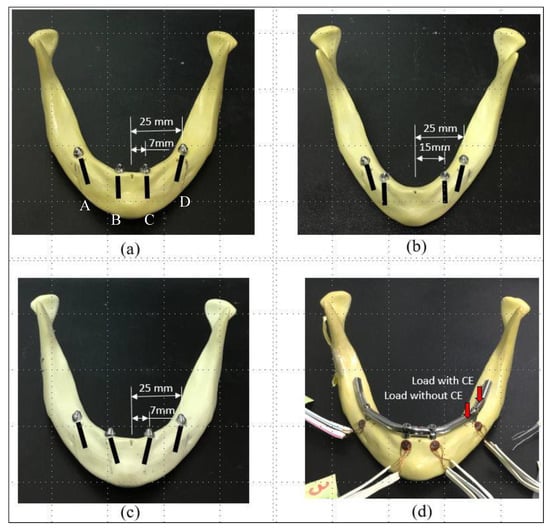
Figure 3.
Three samples involving (a) Sample Typical (typical model, incisor region, vertical implantation), (b) Sample P2 (implanted-position test, incisor-canine region, vertical implantation), and (c) Sample T2 (titled-type test, incisor region, 30°-tilted implants toward the mesial direction) were used in the in vitro tests. (d) Four strain gauges were attached to the buccal side of the alveolar bone around the four implants. Two kinds of loads were applied to the denture with and without a CE. A, B, C, and D refer to the location of each individual implant.
For all three experimental samples, the tilted implants were about 5 mm anterior to the foramina. A custom-made titanium framework was then joined to the abutment with titanium screws (Nobel Biocare). The CE was about 20 mm long. Rectangular rosette strain gauges (KFG-1-120-D17-11L3M3S, Kyowa, Tokyo, Japan) were attached to the buccal side of the crestal cortical bone around the implant using cyanoacrylate cement (CC-33A, Kyowa) (Figure 3d).
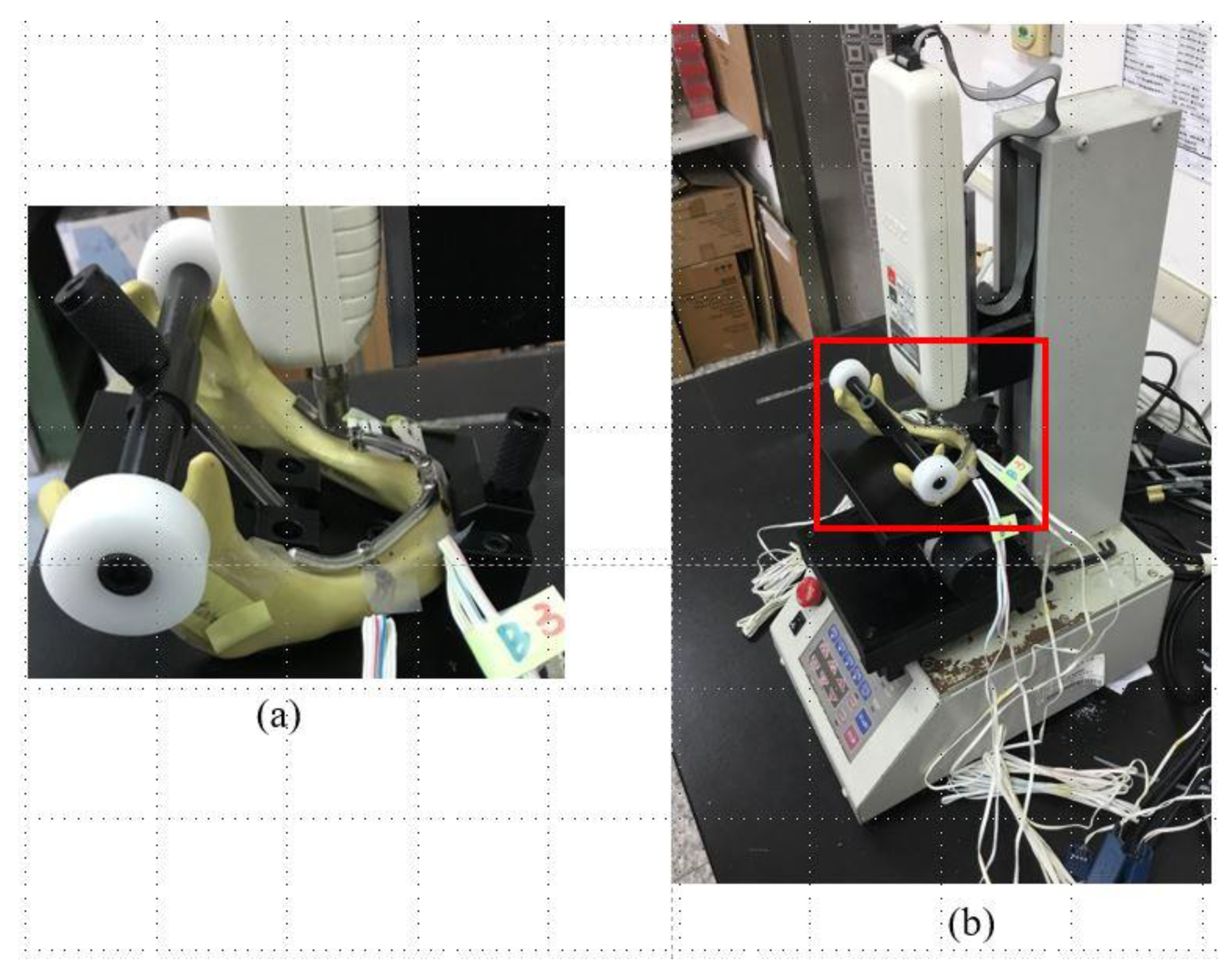
The loading conditions applied to the experimental samples were similar to those in the FE simulations (Figure 3d), with vertical loads applied to the framework close to the posterior tilted implant with and without a CE. For each type of loading, the maximum load was 100 N, and the head speed was 1 mm/min (Figure 4a). The full jawbone model was constrained on the testing platform of the loading machine (JSV-H1000, Japan Instrumentation System, Nara, Japan) by a self-developed jig (Figure 4b). This special jig meant that the regions between the condylar and coronoid processes, as well as the mental protuberance, were fixed. This jig included a rotational screwing device that could be adjusted to vary the direction of loading.
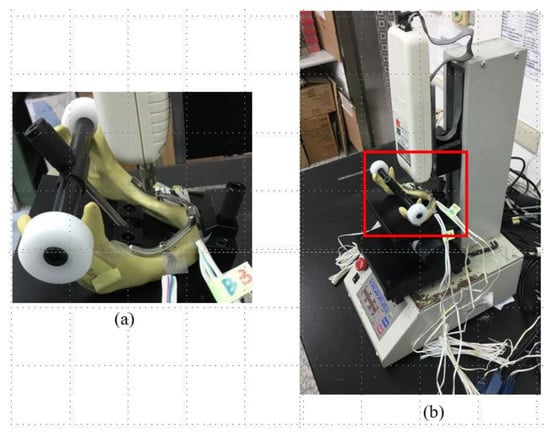
Figure 4.
(a) The loading machine. (b) The experimental sample in the All-on-Four treatment was fixed to the self-developed jig, which was then attached to the platform of the loading machine for applying a single occlusal force to the denture of the sample.
The signals corresponding to the three independent strains εa, εb, and εc on the rosette strain gauge were detected by a data acquisition system (NI CompackDAQ, National Instruments, Austin, TX, USA) and the associated software (LabVIEW SignalExpress 3.0, National Instruments) as each loading condition was applied (Figure 4b). After each measurement had been repeated five times for each sample, the maximum (εmax) and minimum (εmin) principal strains were obtained as follows:
εmax = 1/2 (εa + εc) + 1/2√[(εa − εc)2 + (2εb − εa – εc)2]
εmin = 1/2 (εa + εc) − 1/2√[(εa − εc)2 + (2εb − εa – εc)2]
The values of the maximum and minimum principal strains around the four implants under each loading condition were summarized as median and interquartile-range values. The Mann–Whitney U test was used to compare the difference in peak magnitudes of the principal strains of four implants between the two loading with and without CE The significance level was set at 0.05. In addition, the Kruskal–Wallis test was used to compare the difference in peak values of the principal strains of four implants among the three groups (sample typical, sample P2 and sample T2), and the significance level was also set at 0.05. Furthermore, the post hoc pairwise comparisons were conducted using the Mann–Whitney U test with the Bonferroni adjustment, and the significant difference was set at 0.0167 (0.05/3). All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS Version 19 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Loading with and without a CE
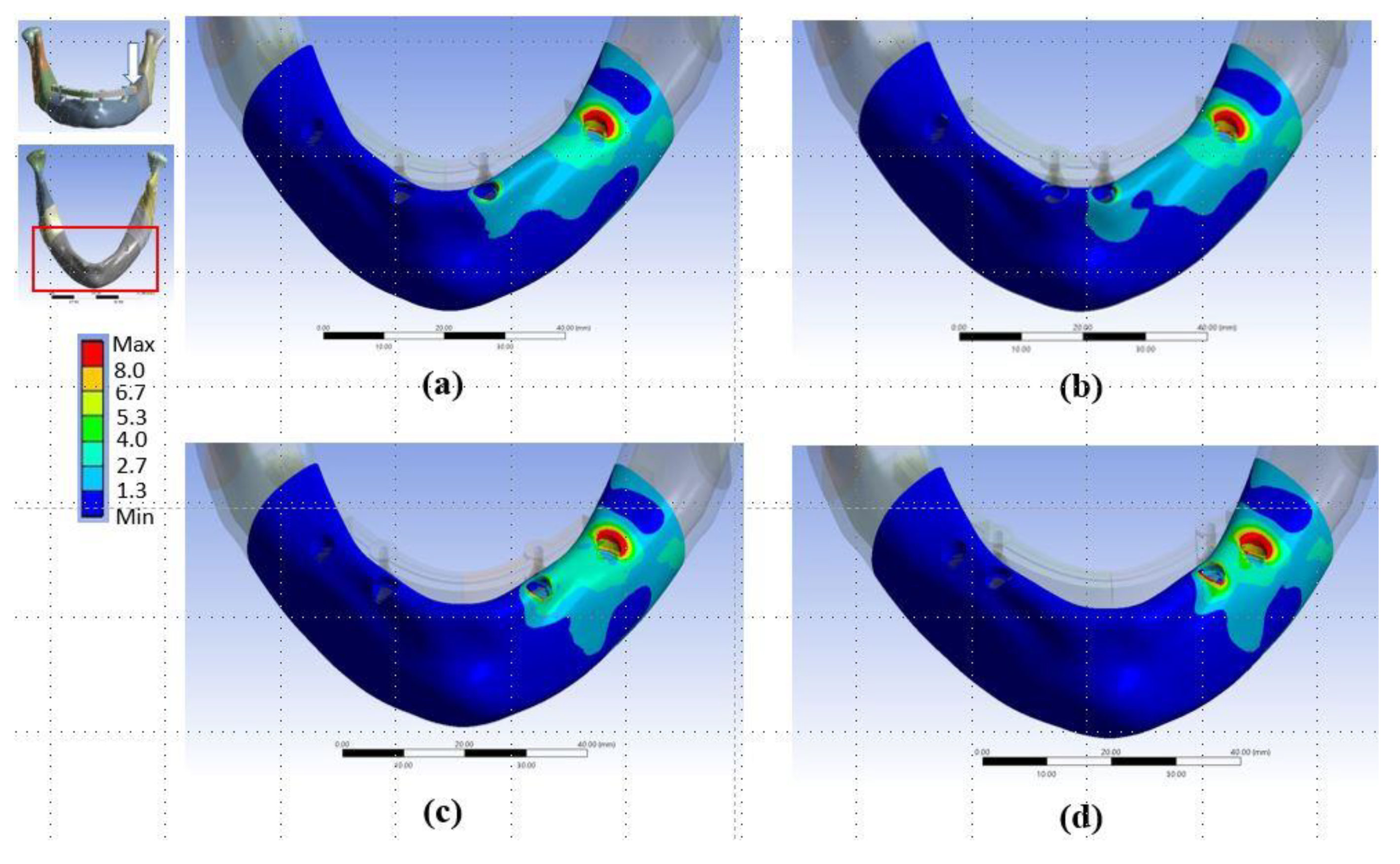
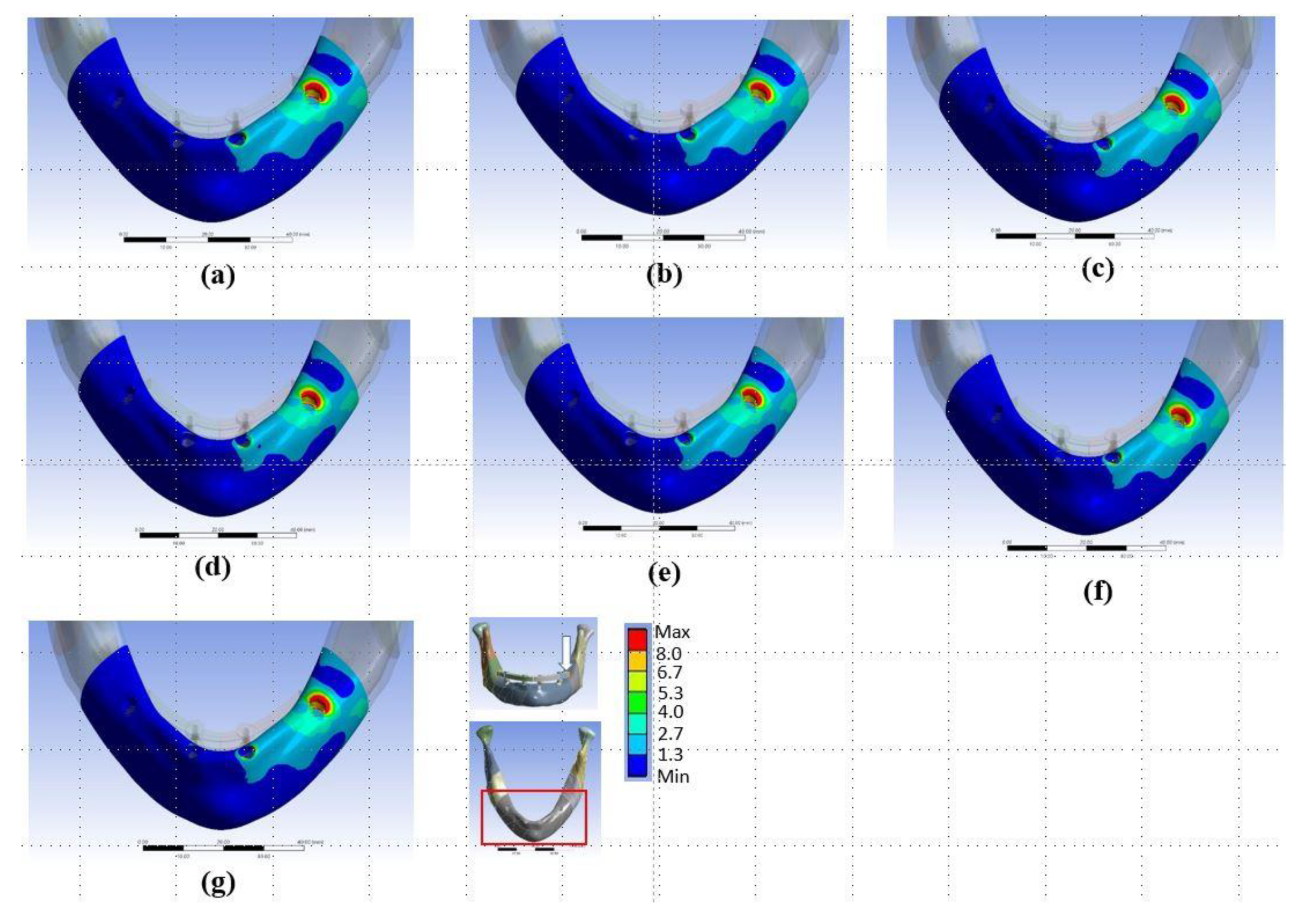
The stresses were always highest in the crestal cortical region of bone around the distal implant near the load, regardless of the implantation design (Figure 5 and Figure 6, and Table 2 and Table 3). In the FE simulations, the peak bone stresses were higher when loading with a CE than when loading without a CE by 53–97% in the cortical bone (Table 2 and Table 3). In the in vitro experiments, the highest values of the minimum principal strain (Table 4, Figure 7) and those peak bone strains were 89%, 140%, and 68% greater when loading with a CE than when loading without a CE (p < 0.001) in the Sample Typical, Sample P2, and Sample T2, respectively.
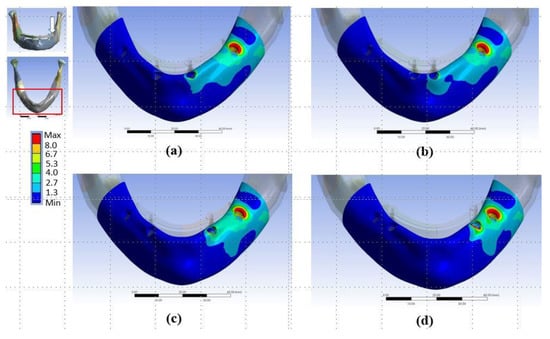
Figure 5.
Distributions of von-Mises stresses in cortical bone in (a) Model Typical, (b) Model P1, (c) Model P2, and (d) Model P3. The arrow shows where the load was applied.
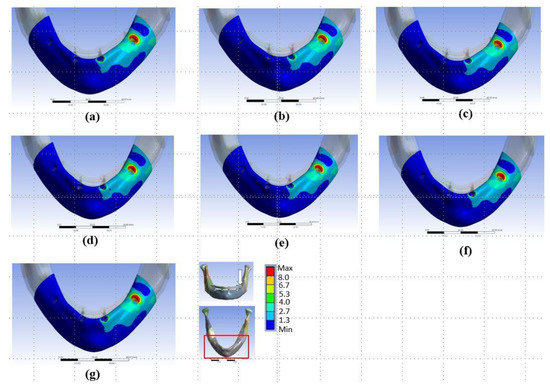
Figure 6.
Distributions of von-Mises stresses in cortical bone in (a) Model Typical, (b) Model T1, (c) Model T2, (d) Model T3, (e) Model T4, (f) Model T5, and (g) Model T6.

Table 2.
Peak values of von-Mises stresses of the cortical bone in models with anterior implants at different positions in the All-on-Four treatment.

Table 3.
Peak values of von-Mises stresses of the cortical bone in models with anterior implants at different angulations in the All-on-Four treatment.

Table 4.
Maximum principal strains (P_Max values) and minimum principal strains (P_Min values) in the bone near the buccal side of the implants in the All-on-Four treatment. A, B, C, and D indicate each implant in the All-on-Four treatment from right to left, respectively. IQR, interquartile range.
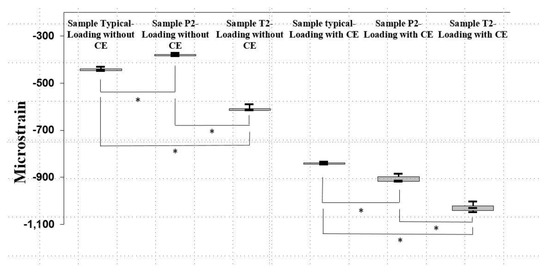
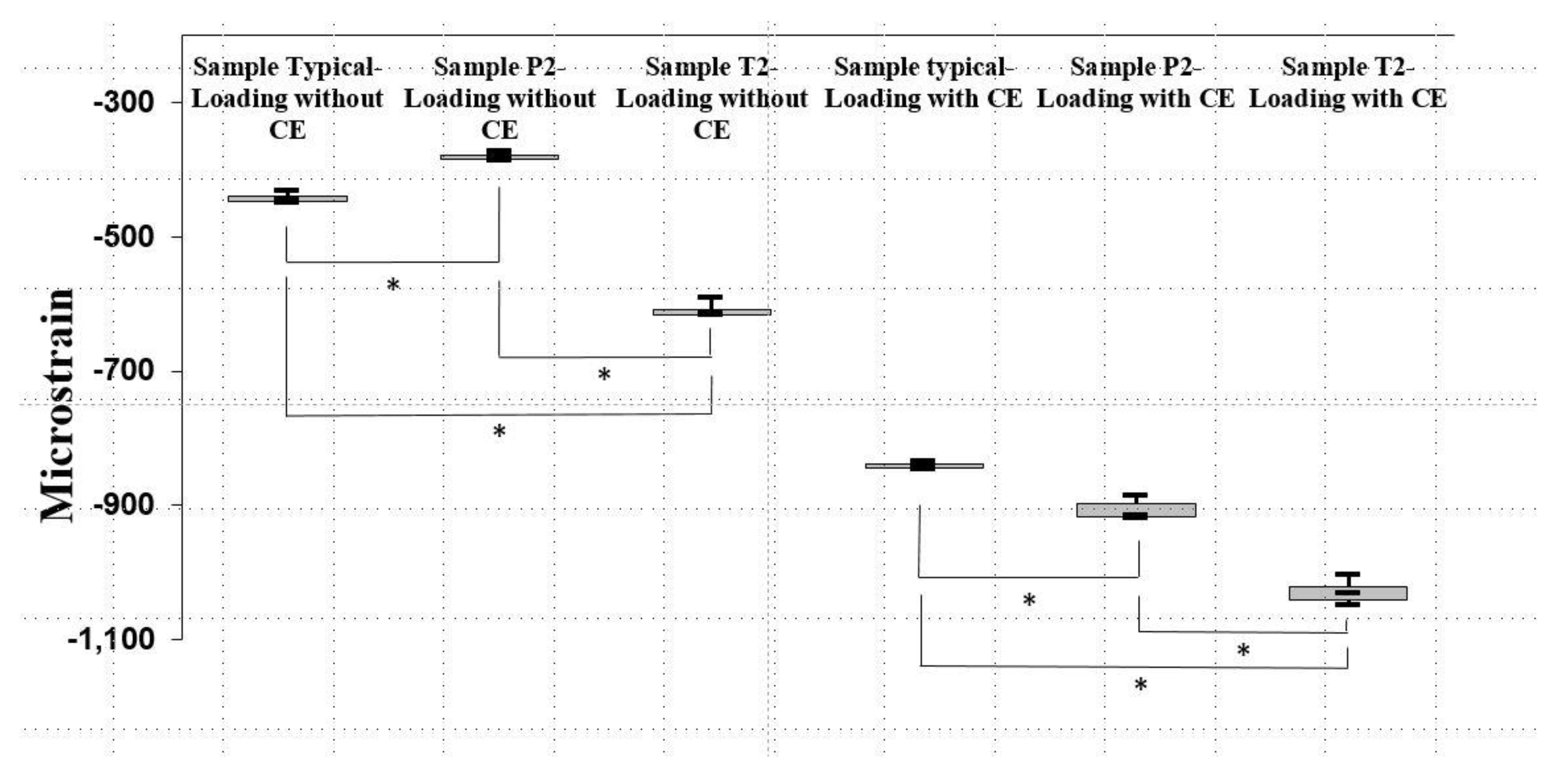
Figure 7.
Peak values of the minimum principal strain in (a) Sample Typical, (b) Sample P2, and (c) Sample T2 when loading with and without a CE. Data are median and interquartile-range values. An asterisk indicates a significant difference (p < 0.008).
3.2. Implanted Positions and Angulation Types of Anterior Implants
For the implanted positions of anterior implants, Models P1, P2, and P3 showed stresses of 23.7–25.2 MPa in the cortical bone when loading without a CE, which were similar to those in Model Typical (24.6 MPa) (Table 2) in the FE simulations. When loading with a CE, all of the models also exhibited comparable bone stresses of 36.5–38.7 MPa in the cortical bone, with the exception of Model P1, in which it was 48.9 MPa (Table 2).
For the angulation types of anterior implants, all of the models other than Model Typical showed similar stresses of 24.5–24.9 MPa in the cortical bone when loading without a CE (Table 3) in the FE results. When loading with a CE, the stresses in the cortical bone were 37.4–40.7 MPa in all models except Model T2, in which the stress value was 47.2 MPa (Table 3).
In the in vitro tests, the highest values of principal strain all occurred within the minimum principal strain (Table 4), and those peak bone strains differed significantly among the Sample Typical, Sample P2, and Sample T2 in the Kruskal-Wallis test results (p <0.002). On the samples of Loading without CE, those peak bone strains were significantly higher in Sample T2 (−613.5 με), followed by Sample Typical (−444.8 με), and the lowest were those of Sample P2 (−380.5 με) (Figure 7) (p <0.008). For the cases of Loading with CE, those peak bone strains were significantly greater in Sample T2 (–1030.6 με), followed by Sample P2 (−914.8 με), and the lowest were those of Sample Typical (−840.5 με) (Figure 7) (p <0.008).
4. Discussion
The concept of All-on-Four treatment of dental implants involves using only four implants to support a complete denture, and many researchers have used FE simulations [8,10,11,12,20,21,22] to investigate the related biomechanical issues. FE simulations make it easy to determine the peak values and the distribution of internal bone stresses and/or strains. However, only few studies used in vitro tests [9,23] to explore the biomechanical environment of the All-on-Four treatment of dental implants. While those experimental studies have produced some valuable results, such tests are also subject to limitations. For example, the bone models used in those previous studies [9,23] have neglected the differences between cortical bone and trabecular bone by using only one resin material to represent the entire bone structure. Moreover, the anatomical complexity of the jawbone makes it difficult to carry out experiments on a whole jawbone with implant-supported fixed full-arch dentures, given that constraining the full jawbone model in a loading machine using a standard procedure is particularly troublesome. The present study standardized the fixation process of each experimental model using a self-designed jig. Moreover, both structures of the cortical bone and trabecular bone were contained in the bone model in both the in vitro tests and the 3D FE simulations. These features of the investigations performed in this study should therefore facilitate the understanding of the biomechanical mechanisms that are especially relevant to the surrounding bone in the All-on-Four treatment of dental implants.
Excessive load and strain on the peri-implant bone may cause bone loss around the dental implant [24,25,26,27,28]. In the All-on-Four treatment, the biting force in the molar area may be located on the CE of the complete denture, and thereby induce a bending moment. The biomechanical influence of a bending moment has attracted the interest of many researchers [8,21,29,30,31]. The findings of the present study are consistent with those of previous studies [21,32], in that both the present FE simulations and in vitro tests indicate that applying a biting force in the region of the CE of a complete denture clearly increased the stress and strain in the peri-implant bone in the All-on-Four treatment [12]. Therefore, reducing the length of the CE or modifying the occlusal contact point so as to reduce the magnitude of the occlusal force applied to the CE of dentures might help to reduce the negative influence of the CE in clinical applications of the All-on-Four treatment of dental implants.
When loading without a CE, the present study showed that the bone stress and strain changed slightly in the All-on-Four treatment after the implanted position of anterior implants was moved to the central incisor or molar region. This result is similar to that found by Hussein and Rabie [16]. In their FE model, changing the implanted position of anterior implants from the incisor to the canine area reduced the peak stress in the peri-implant bone from 68.6 to 63.9 MPa. Additionally, when loading with a CE, the present study found that the stresses in the surrounding bone increased in some cases, such as Model P1. Because changing the implanted position of anterior implants does not relieve the stress in the surrounding bone and may actually worsen the biomechanical environment in the All-on-Four treatment, altering the implanted position of anterior implants does not appear to be beneficial from a biomechanical point of view in the All-on-Four treatment of dental implants.
One of the biomechanical advantages of using tilted implants is to engage more cortical bone [13], which might help to increase the implant’s stability [33]. In the present FE simulations, as compared with Model Typical, inclining the anterior implants did not reduce the bone stress in the All-on-Four treatment. Moreover, in some models (e.g., Model T2), when loading without a CE, inclining the anterior implants actually increased the bone stress. The results of the in vitro tests showed a similar trend, with the inclination of the anterior implants increasing the bone strain. The findings of this study are consistent with previous FE simulations [11,16] showing that inclining anterior implants did not cause significant changes in stress in the surrounding bone in the All-on-Four treatment. Therefore, inclining anterior implants does not seem to be a good choice for improving the biomechanical environment in the All-on-Four treatment of dental implants. However, some recent clinical studies found no difference in the survival rate between tilted and upright implants [34]. In addition, the results of marginal bone loss related to tilted implants are still controversial [13,35,36,37,38]. Therefore, the effects of inclining anterior implants in the All-on-Four treatment still need to be investigated in further long-term trials to confirm their clinical effects.
The main limitations of this study were the simplified loading and boundary conditions. The occlusal loads were reduced to a single force, and the boundary condition was set to be fixed at specific locations. Future research should include local multibite forces as loading conditions and add more muscle attachments as boundary conditions. Additionally, even though a rigorous process involving experienced dentists was used to prepare the samples in the in vitro tests, the sample was small due to the cost of each sample. Finally, the results of this study need to be validated in future clinical investigations.
5. Conclusions
Within the limitations of this study, FE simulations and in vitro experimental tests have revealed that the stress and strain in the bone around distal implants in the All-on-Four treatment both clearly increase as the occlusal load is moved to the denture’s CE. Changing the position of anterior implants has only a minor effect on the stress and strain in the surrounding bone. Similarly, inclining anterior implants might even increase the bone stress and strain in the All-on-Four treatment.
From a biomechanical point of view, this study has confirmed that varying the implanted position and angulation of anterior implants produces no benefits in terms of reducing the stress or strain in the surrounding bone in the All-on-Four treatment of dental implants.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.Y.-J.W. and H.-L.H.; formal analysis, J.-T.H. and H.-L.H.; funding acquisition, A.Y.-J.W. and H.-L.H.; investigation, A.Y.-J.W. and H.-L.H.; methodology, A.Y.-J.W. and H.-L.H.; project administration, A.Y.-J.W. and H.-L.H.; resources: L.-J.F. and J.-T.H.; software, L.-J.F.; validation, J.-T.H. and H.-L.H.; writing—original draft, H.-L.H.; writing—review and editing, A.Y.-J.W., J.-T.H., and H.-L.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the following government and academic organizations: Chang Gung Medical Foundation (grant no. CMRPG8E0302) and Ministry of Science and Technology (grant no. MOST 105–2628-E-039-001-MY2) in Taiwan.
Conflicts of Interest
None of the authors have a financial relationship with any of the private companies or organizations related to this study.
References
- Allen, P.; McMillan, A. A longitudinal study of quality of life outcomes in older adults requesting implant prostheses and complete removable dentures. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2003, 14, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkyilmaz, I.; Company, A.M.; McGlumphy, E.A. Should edentulous patients be constrained to removable complete dentures? The use of dental implants to improve the quality of life for edentulous patients. Gerodontology 2010, 27, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilhan, H.; Erdogan, O.; Ergin, S.; Celik, M.; Ates, G.; Geckili, O. Complication rates and patient satisfaction with removable dentures. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2012, 4, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malo, P.; Rangert, B.; Nobre, M. “All-on-Four” Immediate-Function Concept with Brånemark System® Implants for Completely Edentulous Mandibles: A Retrospective Clinical Study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2003, 5 (Suppl. 1), 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, O.T.; Adams, M.W.; Cottam, J.R.; Parel, S.M.; Phillips, W.R., III. The All-on-4 shelf: Maxilla. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 68, 2520–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, O.T.; Adams, M.W.; Cottam, J.R.; Parel, S.M.; Phillips, W.R., III. The all on 4 shelf: Mandible. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 69, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babbush, C.A.; Kanawati, A.; Kotsakis, G.A.; Hinrichs, J.E. Patient-related and financial outcomes analysis of conventional full-arch rehabilitation versus the All-on-4 concept: A cohort study. Implant. Dent. 2014, 23, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Shimamura, I.; Sakurai, K. Influence of number and inclination angle of implants on stress distribution in mandibular cortical bone with All-on-4 Concept. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2010, 54, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-S.; Kim, Y.-L.; Bae, J.-M.; Cho, H.-W. Biomechanical comparison of axial and tilted implants for mandibular full-arch fixed prostheses. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2011, 26, 976–984. [Google Scholar]
- Baggi, L.; Pastore, S.; Di Girolamo, M.; Vairo, G. Implant-bone load transfer mechanisms in complete-arch prostheses supported by four implants: A three-dimensional finite element approach. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2013, 109, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, H.E.; Camati, P.R.; Faot, F.; Sotto-Maior, B.S.; Martinez, E.F.; Peruzzo, D.C. Rehabilitation of the atrophic mandible with short implants in different positions: A finite elements study. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 80, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, A.; Postaire, M.; Lipinski, P. Biomechanical study of mandible bone supporting a four-implant retained bridge: Finite element analysis of the influence of bone anisotropy and foodstuff position. Med. Eng. Phys. 2009, 31, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Fabbro, M.; Ceresoli, V. The fate of marginal bone around axial vs. tilted implants: A systematic review. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2014, 7 (Suppl. 2), 171–189. [Google Scholar]
- De Souza Batista, V.E.; Junior, J.F.S.; De Faria Almeida, D.A.; De Toledo Piza Lopes, L.F.; Verri, F.R.; Pellizzer, E.P. The effect of offset implant configuration on bone stress distribution: A systematic review. J. Prosthodont. 2015, 24, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimura, Y.; Sato, Y.; Kitagawa, N.; Omori, M. Biomechanical effects of offset placement of dental implants in the edentulous posterior mandible. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2016, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.O.; Rabie, M.E. Three-dimensional nonlinear contact finite element analysis of mandibular All-on-4 design. J. Oral Implantol. 2015, 41, e12–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.; Tideman, H.; Merkx, M.; Jansen, J.; Goh, S.; Liao, K. Review of biomechanical models used in studying the biomechanics of reconstructed mandibles. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 40, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangan, V.; Raghuveer, H.; Rayapati, D.; Shobha, E.; Prashanth, N.; Sharma, R. The influence of stress distribution in four different fixation systems used in treatment of mandibular angle fractures—A three-dimensional finite element analysis. Oral Surg. 2013, 6, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-L.; Chang, C.-H.; Hsu, J.-T.; Faligatter, A.M.; Ko, C.-C. Comparison of implant body designs and threaded designs of dental implants: A 3-dimensional finite element analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2007, 22, 551–562. [Google Scholar]
- Naini, R.B.; Nokar, S.; Borghei, H.; Alikhasi, M. Tilted or parallel implant placement in the completely edentulous mandible? A three-dimensional finite element analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2011, 26, 776–781. [Google Scholar]
- Ozan, O.; Kurtulmus-Yilmaz, S. Biomechanical Comparison of Different Implant Inclinations and Cantilever Lengths in All-on-4 Treatment Concept by Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2018, 33, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gümrükçü, Z.; Korkmaz, Y.T. Influence of implant number, length, and tilting degree on stress distribution in atrophic maxilla: A finite element study. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2018, 56, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiossi, R.; Gomes, É.A.; Faria, A.C.L.; Rodrigues, R.C.S.; Ribeiro, R.F. Biomechanical behavior of titanium and zirconia frameworks for implant-supported full-arch fixed dental prosthesis. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2017, 19, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isidor, F. Influence of forces on peri-implant bone. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2006, 17, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, J.P.; Judge, R.B.; Palamara, J.E. In vitro bone strain analysis of implant following occlusal overload. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, e73–e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Araki, H.; Ohto, T.; Shin, K. The influence of controlled occlusal overload on peri-implant tissue. Part 3: A histologic study in monkeys. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2000, 15, 425–431. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.-H.; Hsu, Y.-T.; Wang, H.-L. Identifying occlusal overload and how to deal with it to avoid marginal bone loss around implants. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2012, 5, S91–S103. [Google Scholar]
- Kozlovsky, A.; Tal, H.; Laufer, B.Z.; Leshem, R.; Rohrer, M.D.; Weinreb, M.; Artzi, Z. Impact of implant overloading on the peri-implant bone in inflamed and non-inflamed peri-implant mucosa. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2007, 18, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, A.; Padmanabhan, T.; Mohamed, K.; Natarajan, S.; Elavia, U. Load transfer in tilted implants with varying cantilever lengths in an all-on-four situation. Aust. Dent. J. 2012, 57, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cao, Z.; Qiu, X.; Tang, Z.; Gong, L.; Wang, D. Does matching relation exist between the length and the tilting angle of terminal implants in the all-on-four protocol? stress distributions by 3D finite element analysis. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2015, 7, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gümrükçü, Z.; Korkmaz, Y.T.; Korkmaz, F.M. Biomechanical evaluation of implant-supported prosthesis with various tilting implant angles and bone types in atrophic maxilla: A finite element study. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 86, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horita, S.; Sugiura, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Murakami, K.; Imai, Y.; Kirita, T. Biomechanical analysis of immediately loaded implants according to the “All-on-Four” concept. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2017, 61, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, J.T.; Fuh, L.J.; Tu, M.G.; Li, Y.F.; Chen, K.T.; Huang, H.L. The effects of cortical bone thickness and trabecular bone strength on noninvasive measures of the implant primary stability using synthetic bone models. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2013, 15, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrcanovic, B.R.; Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A. Tilted versus axially placed dental implants: A meta-analysis. J. Dent. 2015, 43, 149–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monje, A.; Chan, H.-L.; Suarez, F.; Galindo-Moreno, P.; Wang, H.-L. Marginal bone loss around tilted implants in comparison to straight implants: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2012, 27, 1576–1583. [Google Scholar]
- Francetti, L.; Romeo, D.; Corbella, S.; Taschieri, S.; Del Fabbro, M. Bone level changes around axial and tilted implants in full-arch fixed immediate restorations. Interim results of a prospective study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat Res. 2012, 14, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnea, E.; Tal, H.; Nissan, J.; Tarrasch, R.; Peleg, M.; Kolerman, R. The use of tilted implant for posterior atrophic maxilla. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2016, 18, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutouzis, T.; Wennström, J.L. Bone level changes at axial-and non-axial-positioned implants supporting fixed partial dentures. A 5-year retrospective longitudinal study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2007, 18, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).