Prevalence and Impact of Hate Speech among Politicians in Switzerland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Procedure
2.2. Measures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characterization
3.2. Prevalence of Hate Speech and Risk Factors
3.3. Impact of Hate Speech Experiences
3.4. Characterization of Hate Speech Experiences
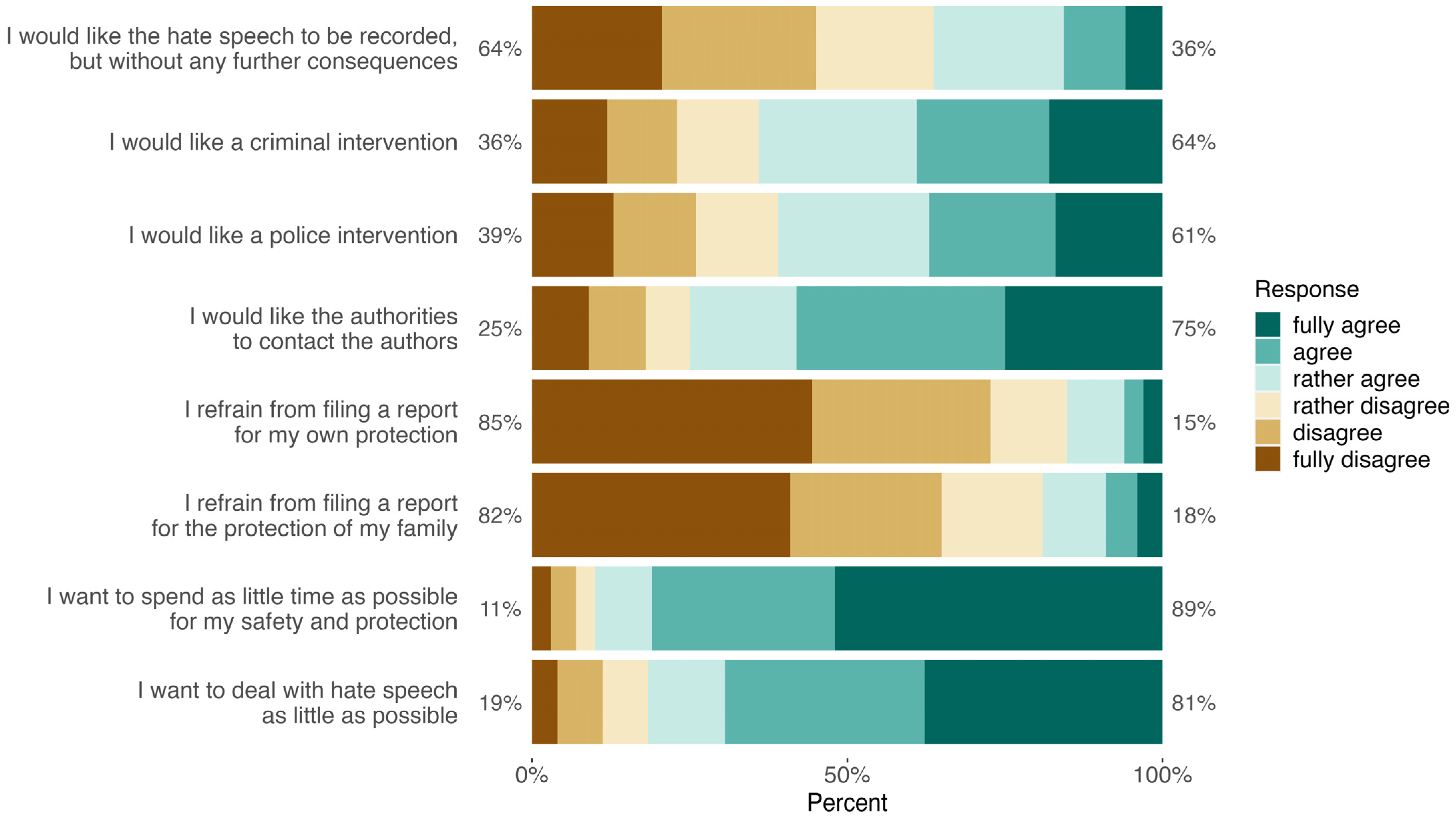
3.5. Potential Concerns Regarding the Handling of Hate Speech
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | Facebook, Instagram, Telegram, LinkedIn, TikTok, and X (Twitter). |
References
- Cervone, C.; Augoustinos, M.; Maass, A. The Language of Derogation and Hate: Functions, Consequences, and Reappropriation. J. Lang. Soc. Psychol. 2021, 40, 80–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreißigacker, A. Online Hate Speech Victimization: Consequences for Victims’ Feelings of Insecurity. Crime Sci. 2024, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leets, L. Experiencing Hate Speech: Perceptions and Responses to Anti-semitism and Antigay Speech. J. Soc. Issues 2002, 58, 341–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrell, G.; Bakir, M.E.; Roberts, I.; Greenwood, M.A.; Bontcheva, K. Which Politicians Receive Abuse? Four Factors Illuminated in the UK General Election 2019. EPJ Data Sci. 2020, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, M.A.; Montero-Díaz, J.; Moreno-Delgado, A. Hate Speech: A Systematized Review. SAGE Open 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetty, N.; Alathur, S. Hate Speech Review in the Context of Online Social Networks. Aggress. Violent Behav. 2018, 40, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hietanen, M.; Eddebo, J. Towards a Definition of Hate Speech—With a Focus on Online Contexts. J. Commun. Inq. 2023, 47, 440–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. United Nations Strategy and Plan of Action on Hate Speech: Detailed Guidance on Implementation for United Nations Field Presences; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Available online: https://www.un.org/en/genocideprevention/documents/UN%20Strategy%20and%20PoA%20on%20Hate%20Speech_Guidance%20on%20Addressing%20in%20field.pdf (accessed on 4 March 2024).
- Demaske, C. Free Speech and Hate Speech in the United States: The Limits of Toleration; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Ellithorpe, M.; Burt, S.A. Anonymity and Its Role in Digital Aggression: A Systematic Review. Aggress. Violent Behav. 2023, 72, 101856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansok-Dusche, J.; Ballaschk, C.; Krause, N.; Zeißig, A.; Seemann-Herz, L.; Wachs, S.; Bilz, L. A Systematic Review on Hate Speech among Children and Adolescents: Definitions, Prevalence, and Overlap with Related Phenomena. Trauma Violence Abus. 2023, 24, 2598–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahel, L.; Weingartner, S.; Lobinger, K.; Baier, D. Digitale Hassrede in der Schweiz: Ausmass und sozialstrukturelle Einflussfaktoren. Univ. Zür. 2022. Available online: https://www.zora.uzh.ch/id/eprint/260014/ (accessed on 4 March 2024). [CrossRef]
- Stahel, L.; Baier, D. Digital Hate Speech Experiences across Age Groups and Their Impact on Well-Being: A Nationally Representative Survey in Switzerland. Cyberpsychology Behav. Soc. Netw. 2023, 26, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauschke, R.; Jäckle, S. Hate Speech on Social Media against German Mayors: Extent of the Phenomenon, Reactions, and Implications. Policy Internet 2023, 15, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaño-Pulgarín, S.A.; Suárez-Betancur, N.; Vega, L.M.T.; López, H.M.H. Internet, Social Media and Online Hate Speech. Systematic Review. Aggress. Violent Behav. 2021, 58, 101608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamoros-Fernández, A.; Farkas, J. Racism, Hate Speech, and Social Media: A Systematic Review and Critique. Telev. New Media 2021, 22, 205–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.J.; Hazelwood, T.E.; Pitre, N.L.; Bedard, T.E.; Landry, S.D. Harassment of Members of Parliament and the Legislative Assemblies in Canada by Individuals Believed to Be Mentally Disordered. J. Forensic Psychiatry Psychol. 2009, 20, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erikson, J.; Håkansson, S.; Josefsson, C. Three Dimensions of Gendered Online Abuse: Analyzing Swedish MPs’ Experiences of Social Media. Perspect. Polit. 2023, 21, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjelland, H.F.; Bjørgo, T. Trusler Og Trusselhendelser Mot Politikere: En Spørreundersøkelse Blant Norske Stortingsrepresentanter Og Regjeringsmedlemme; Politihøgskolen: Oslo, Norway, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Every-Palmer, S.; Barry-Walsh, J.; Pathé, M. Harassment, Stalking, Threats and Attacks Targeting New Zealand Politicians: A Mental Health Issue. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2015, 49, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, D.V.; Farnham, F.R.; Sukhwal, S.; Jones, K.; Carlisle, J.; Henley, S. Aggressive/Intrusive Behaviours, Harassment and Stalking of Members of the United Kingdom Parliament: A Prevalence Study and Cross-National Comparison. J. Forensic Psychiatry Psychol. 2016, 27, 177–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathé, M.; Philips, J.; Perdacher, E.; Heffernan, E. The Harassment of Queensland Members of Parliament: A Mental Health Concern. Psychiatry Psychol. Law 2014, 21, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørgo, T.; Jupskås, A.R.; Thomassen, G.; Strype, J. Patterns and Consequences of Threats towards Politicians. Perspect. Terror. 2022, 16, 100–119. [Google Scholar]
- Bjørgo, T.; Silkoset, E. Threats and Threatening Approaches to Politicians: A Survey of Norwegian Parliamentarians and Cabinet Ministers; Politihøgskolen: Oslo, Norway, 2018; ISBN 978-82-7808-141-9. [Google Scholar]
- Solovev, K.; Pröllochs, N. Hate Speech in the Political Discourse on Social Media: Disparities across Parties, Gender, and Ethnicity. In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022, Lyon, France, 25 April 2022; pp. 3656–3661. [Google Scholar]
- van der Vegt, I. Gender Differences in Online Abuse: The Case of Dutch Politicians. Crime Sci. 2024, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistisches Amt (2020). Wandel im Zürcher Parteiensystem. Available online: https://www.zh.ch/de/news-uebersicht/mitteilungen/2020/politik-staat/statistik/wandel-im-zuercher-parteiensystem.html (accessed on 4 March 2024).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 4 March 2024).
| Measure | Question | Answer Options |
|---|---|---|
| All have been asked | ||
| Overall experience 1,2 | Have you experienced hate speech since you became a politician? | “yes”, “no” 3 |
| Twelve-months experience 1 | Have you experienced hate speech in the past 12 months as a politician? | “yes”, “no” 3 |
| Impact on being a politician | Do you feel affected in your role as a public official by hate speech? | “1-not at all affected” to “6-strongly affected” 3 |
| Concerns | I refrain from filing a report for the protection of my family. | “1-fully disagree” to “6-strongly agree” 3 |
| I refrain from filing a report for my own protection. | ||
| I would like the authorities to contact the authors. | ||
| I would like the hate speech to be recorded, but without any further consequences. | ||
| I want to deal with hate speech as little as possible. | ||
| I want to spend as little time as possible for my safety and protection. | ||
| I would like a criminal intervention. | ||
| I would like a police intervention. | ||
| Demographic characteristics | Gender | “female”, “male”, “non-binary”, “no answer” 3 |
| Age | “under 20 years”, “20–29 years”, “30–39 years”, “40–49 years”, “50–59 years”, and “60 years or older” 3 | |
| Political party affiliation | all popular parties in the Canton of Zurich as well as “independent” and “other” 3,4 | |
| Time in current political position | “less than 1 year”, “1–2 years”, “3–5 years”, “6–10 years”, and “11 years or longer” 3 | |
| Overall time as a politician | “less than 1 year”, “1–2 years”, “3–5 years”, “6–10 years”, and “11 years or longer” 3 | |
| Only those who had reported hate speech experience in the past 12 months have been asked | ||
| Impact on resigning | Did it ever occur to you to resign from your political position because of hate speech? | “yes, often”, “yes, sometimes” and “no” 3 |
| Characteristic(s) targeted | Which personal characteristic(s) were targeted by hate speech? | “gender/gender identity”, “sexual orientation”, “religious affiliation”, “ethnicity/origin/skin color”, “disability”, “physical appearance”, “education/income/profession”, “political position/party”, and “other” 5 |
| Channel | Through which channels have you experienced hate speech? | “personal”, “telephone”, “letter”, “email”, “SMS”, “messenger (e.g., WhatsApp)”, “Facebook”, “Instagram”, “Telegram”, “LinkedIn”, “TikTok”, “X (Twitter)”, and “other” 5 |
| Number of experienced (a) incidents and (a) reactions within the past 12 months 6 | ||
| Variable | % (n) |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Female | 31.6 (209) |
| Male | 57.9 (382) |
| Non-binary | 0.2 (1) |
| No answer | 10.3 (68) |
| Age group | |
| <20 years | 0.2 (1) |
| 20–39 years | 3.2 (21) |
| 30–39 years | 8.0 (53) |
| 40–49 years | 20.3 (134) |
| 50–59 years | 33.6 (222) |
| ≥60 years | 25.0 (165) |
| No answer | 9.7 (64) |
| Political party | |
| Left-leaning | 17.7 (117) |
| Centrist | 15.2 (100) |
| Right-leaning | 30.8 (203) |
| Independent | 24.5 (162) |
| No answer | 11.8 (78) |
| Length of time as a politician | |
| <1 year | 2.6 (17) |
| 1–2 years | 14.7 (97) |
| 3–5 years | 12.6 (83) |
| 6–10 years | 22.1 (146) |
| ≥11 years | 36.4 (240) |
| No answer | 11.7 (84) |
| Length of time in current position | |
| <1 year | 4.4 (29) |
| 1–2 years | 29.7 (196) |
| 3–5 years | 18.2 (120) |
| 6–10 years | 25.2 (166) |
| ≥11 years | 12.7 (84) |
| No answer | 9.8 (65) |
| Independent Variable | N | Odds Ratio [2.5%, 97.5%] * | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (reference: female) | 591 | ||
| Male | 0.78 [0.54, 1.23] | 0.19 | |
| Age group (reference: ≥60 years) | 596 | ||
| <30 years | 1.67 [0.63, 4.20] | 0.28 | |
| 30–39 years | 1.64 [0.84, 3.16] | 0.15 | |
| 40–49 years | 1.16 [0.69, 1.94] | 0.57 | |
| 50–59 years | 1.11 [0.70, 1.76] | 0.66 | |
| Political party (reference: independent) | 582 | ||
| Left-leaning | 3.90 [2.30, 6.75] | <0.001 | |
| Centrist | 1.17 [0.62, 2.17] | 0.62 | |
| Right-leaning | 1.76 [1.07, 2.93] | 0.03 | |
| Length of time as a politician (reference: ≥11 years) | 583 | ||
| ≤2 years | 0.41 [0.23, 0.72] | 0.002 | |
| 3–5 years | 0.65 [0.36, 1.15] | 0.15 | |
| 6–10 years | 1.25 [0.81, 1.93] | 0.31 |
| Variable | % (n) | |
|---|---|---|
| Characteristic targeted by hate speech | ||
| Political position/party | 86.0 (117) | |
| Education/income/profession | 22.1 (30) | |
| Gender/gender identity | 18.4 (25) | |
| Physical appearance | 11.0 (15) | |
| Sexual orientation | 6.6 (9) | |
| Religious affiliations | 3.7 (5) | |
| Ethnicity/origin/skin color | 3.7 (5) | |
| Disability | 0 (0) | |
| Other | 11.0 (15) | |
| No answer | 2.2 (3) | |
| Channel through with hate speech was received | ||
| 46.3 (63) | ||
| Personal | 44.1 (60) | |
| 27.9 (38) | ||
| X (formerly Twitter) | 24.3 (33) | |
| Letter | 21.3 (29) | |
| Telephone | 9.6 (13) | |
| 8.1 (11) | ||
| Messenger (e.g., WhatsApp) | 5.9 (8) | |
| SMS | 2.2 (3) | |
| Telegram | 1.5 (2) | |
| 0.7 (1) | ||
| TikTok | 0.7 (1) | |
| Other | 11.0 (15) | |
| No answer | 4.4 (6) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albrecht, J.N.; Endrass, J.; Dreifuss, M.S.; Schnyder, N.; Rossegger, A. Prevalence and Impact of Hate Speech among Politicians in Switzerland. Societies 2024, 14, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc14070098
Albrecht JN, Endrass J, Dreifuss MS, Schnyder N, Rossegger A. Prevalence and Impact of Hate Speech among Politicians in Switzerland. Societies. 2024; 14(7):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc14070098
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbrecht, Joëlle Ninon, Jérôme Endrass, Michal Sonja Dreifuss, Nina Schnyder, and Astrid Rossegger. 2024. "Prevalence and Impact of Hate Speech among Politicians in Switzerland" Societies 14, no. 7: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc14070098
APA StyleAlbrecht, J. N., Endrass, J., Dreifuss, M. S., Schnyder, N., & Rossegger, A. (2024). Prevalence and Impact of Hate Speech among Politicians in Switzerland. Societies, 14(7), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc14070098






