Abstract
The present study examines teachers’ perceptions, attitudes, and practices regarding the use of English as a lingua franca (ELF) to teach Greek as a second language (L2) in multicultural classrooms in Greece, a largely underexplored area in the field of applied linguistics. The research was based on self-reports collected through questionnaires, written accounts, metaphor elicitation, and semi-structured interviews provided by 20 teachers of young learners with a migrant background in public schools in Greece. The findings showed that the classroom discourse takes place mainly in the target language, i.e., Greek, and ELF was also reported to be used by both teachers and learners for specific functions, such as vocabulary translation, explanation of grammar rules, and checking for comprehension. As reported by the participants, both teachers and learners welcome the idea of ELF use because a sense of security and comfort is provided through its employment. The study suggests that ELF may allow a smooth transition into the new social reality of the host country and a better approach of L2 Greek for young learners with a migrant background in the context of multilingual and intercultural education.
1. Introduction
The rising number of refugees and migrants in Europe has transformed the Greek society into a multilingual and multicultural setting. Refugee and migrant children access the national education system under the same conditions as Greek students do. Teachers who teach in multilingual classrooms in Greek schools act as mediators and interpreters so as to meet the educational needs of culturally and linguistically diverse students. There has been, thus, an urgency for classroom-level policies and educational approaches to be adapted accordingly in order to manage the coexistence of different cultures and languages in today’s classrooms and meet students’ needs.
In the wider framework of globalization and migration, people with a refugee or a migrant background find themselves in various international interactions throughout their migration journeys. They need to communicate in the languages that they already know, which is where the worldwide spread of English becomes particularly relevant. The use of English as a lingua franca (ELF) indicates an international communicative framework in which speakers from linguistically and culturally diverse backgrounds use English to engage in communication [1,2,3]. Although the use of English has the potential to promote communication, using English may also be characterized as a form of power, under certain views, as it may function as a status indicator for the group that uses it; it forces other groups to conform linguistically and excludes from social processes those who do not use it see, e.g., [4,5].
Since it is difficult for the educators to learn and use the different languages of their bi-/multilingual students, ELF may act as a facilitative tool and have a positive impact on the teaching methods and strategies as it can be used as a medium of instruction in educational systems all over the world [6]. In the context of intercultural and second language (L2) education, it becomes highly important to explore the perceptions, attitudes, and practices of language teachers regarding integrating ELF as a means to teach the target language in multicultural classrooms. As there is lack of previous research studies on integrating ELF as a tool to teach Greek as an L2, the present study focuses on the Greek educational context and aims to explore teachers’ perceptions, attitudes, and practices related to the use of ELF in teaching L2 Greek in multicultural formal environments in Greece.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Migration in the European and the Greek Context
Patterns of migration from, toward, and within Europe have gone through important transformations and further diversifications throughout the years [7]. According to UNHCR (2023) [8], in 2015 more than one million migrants and refugees arrived at Europe’s borders, most of them heading for Greece, following the short voyage from Turkey to the Greek islands. Greece, in 2015, received almost 900,000 reported sea arrivals from Turkey without being ready to respond to such a high influx of people seeking asylum and international protection [9]. Currently, according to the UNHCR Greece Factsheet (2021) [10], more than 160,000 refugees and migrants continue to stay in the country and try to improve their lives in their new home. For these people, integration is the only way to ensure that they build successful lives in their new homes, including acquiring the host language.
Focusing on teaching and learning L2 Greek in public schools, the Greek government, since 2016, has released a series of legislative measures for the education of children with refugee and migrant backgrounds. However, with a view to creating an effective multicultural school environment for refugees and migrants, it is important for teachers to encourage inclusive behaviors in the classroom, including the use of students’ first language (L1) in the teaching and learning process, as will be discussed in the following section.
2.2. The Role of L1 in Teaching Students with a Refugee/Migrant Background
In multicultural classrooms that include students with a refugee/migrant background, the use of L1 not only serves a number of cognitive and social functions [11,12,13,14], but also supports L2 learning while promoting the implementation of intercultural education and a whole-child approach [15]. Having a strong L1 foundation and opportunities for L1 use, e.g., through translanguaging [16], leads to a much better understanding of the curriculum as well as a more positive stance toward school. This is in line with Hornberger (2014) [17], who suggests that the most significant point in teaching in multicultural and multilingual classrooms is to respect the minority languages and offer openness and acceptance to the students’ linguistic repertoires. Leveraging L1 in multicultural classrooms has also been rationalized by Cummins (2015) [15], who observes that, in the context of intercultural education, it generates respect and understanding across social groups and consequently promotes a more cohesive and equitable society.
However, while the Council of Europe has created a European model for the multicultural curriculum and has established a series of initiatives to promote the implementation of intercultural education [18], no substantial changes have been made so far in the way that the Greek educational system confronts diversity [19]. Migrant students’ bilingualism is not encouraged at school, as teachers fail to adopt classroom-level policies and practices that promote language diversity [19]. According to Mattheoudakis et al. (2017) [20], educators’ attitudes are not particularly encouraging toward students’ use of their L1 either at school or at home. Consequently, teachers tend to follow a monolingual approach with the target language (TL) as the only medium of instruction. However, today classrooms accept significant numbers of students from various linguistic backgrounds. In this context, the status of ELF may have an impact on educational approaches and strategies, as it can be used as a medium of instruction in multicultural classrooms around the world (e.g., [6]) and, more specifically, in the Greek educational context.
2.3. The English Language
English is used by around 1.5 billion people worldwide today [21], being an essential tool for communication, empowerment, and unification for people in the global community, regardless of nationality, cultural background, or race. It is considered to hold an unparalleled position in world history and to be one of the most important vehicles of multiculturalism [22,23]. In this context, English is also used in mediating second/foreign/additional language learning [24]. The use of English as a widely spoken lingua franca allows communication between teachers and students of different L1s and works as a bridge between their L1 and the TL. As Ife (2008) [24] and Turnbull (2018) [14] observe, ELF narrows the gap between the existing level of ability in the TL and the level required for successful communication. In addition to the development of cognitive skills, the support of ELF offers a cushion or scaffolding in socio-cultural terms, enabling learners to negotiate the demanding early phases of language learning and providing safety in addressing the psychological vulnerability of the new language learner [25].
In Kantzou and Vasileiadi’s (2021) [26] study on L2 Greek teachers’ views and practices regarding use of other languages in classrooms of adult students, it was shown that English was employed, noticeably more than other languages, for a variety of functions. These included teaching vocabulary, grammar, and pragmatics of language use, explaining instructions for classroom activities, as well as providing affective and interpersonal support. Although the teachers were generally positive toward using other languages in the L2 context, they also expressed reservations related to reduced opportunities for TL practice, hence protracted TL development.
The use of ELF, however, may contribute to creating an inclusive environment, as it allows learners to make meaning, to communicate their personalities, feelings, and thoughts, and to socialize with peers. This is in line with Turnbull (2018) [14], who suggests that for multilingual students, the employment of ELF may provide a sense of security and comfort in the known, bridging the gap between learners’ L1 and the gradual development of the TL. A prerequisite, of course, for leveraging ELF in the L2 classroom is the knowledge of the language, at least to some extent, by students and teachers. Based on all the above, the present study conceptualizes English as a third, intermediary functional language and places emphasis on the teachers’ reported perceptions, attitudes, and practices in using ELF as a tool to teach L2 Greek in multicultural settings in Greece.
3. Methodology
The aim of the current study is to explore Greek teachers’ reported perceptions, attitudes, and practices in the use of ELF as a mediator in Greek multilingual and multicultural educational settings focusing on the following research questions:
- What are teachers’ perceptions and attitudes toward the use of ELF in teaching L2 Greek in this context?
- What are teachers’ reported practices regarding the use of ELF to teach L2 Greek in multicultural classrooms in formal primary education in Greece?
3.1. Participants
The sample of the study consisted of twenty primary school teachers (N = 20) who teach Greek in classrooms that include learners with different linguistic and cultural backgrounds in formal environments in Greece. They reported that their students were mostly from Russia, Syria, Afghanistan, Iraq, Albania, Ukraine, and Congo. The teachers were upper intermediate to proficient users of English, at a B2 to C2 level according to the Common European Framework of Reference. They were mostly female (N = 17, 85%) given the under representation of male teachers in primary education. Most of them (N = 14) were aged between 20 and 30, five were aged from 30 to 40, and one participant was aged between 40 and 50. All participants were primary education teachers with teaching experience in multicultural settings in Greece. Regarding their teaching experience in such contexts, 19 out of 20 had 1 to 5 years of experience and only one had more than 6 years of experience. Among the participants, eight out of twenty teachers also took part in qualitative interviews. Three of them worked in specialized reception classes (the so-called ZEP classes), one worked in Reception Structures for Refugee Children Education (RRES), while the rest worked in mainstream classes with some students with a refugee and migrant background.
3.2. Data Collection Methods
The research was conducted by adopting an introspective approach relying on a combination of self-reported data, including questionnaires, metaphor elicitation, and written accounts, as well as oral semi-structured interviews. Triangulation of data was employed to strengthen the validity and reliability of the research findings. A questionnaire was designed and administered to the participants using Google forms so that they could easily access it online. The first part contained four questions on the participants’ demographic information: sex, age, English proficiency level, and number of years of teaching experience in multicultural settings. The second section consisted of ten 5-point Likert scale survey questions that aimed to examine teachers’ practices regarding the use of ELF in teaching Greek. The third section explored teachers’ perceptions and attitudes toward the matter. It included four 5-point Likert scale survey questions and a metaphor elicitation task [27]. Finally, in the fourth section, which involved reflective writing, the participants were requested to provide a written account to describe how ELF was used in their last class.
The interviews were semi-structured, took place in a quiet place, and lasted approximately 20 min. They were orthographically transcribed and submitted to qualitative analysis. Questions of the interview protocol included the following: (1) Do you use any English words in your teaching process? (2) For what reasons? (3) To what extent and how often? (4) Is this method helpful for your lessons? (5) Do students with refugee and migrant backgrounds seem to enjoy this technique? (6) Does this method have positive results? The questionnaire, the written accounts, and the interview data were examined using thematic analysis by focusing on key issues with an overall approach which was content-driven [28].
Metaphors involve comparisons between two dissimilar notions, where one is understood in terms of the other [29]. By combining cognitive and linguistic aspects, the use of a metaphor may capture ambivalent or discrepant perceptions on a particular matter through the creativity of language [30]. A wealth of studies have employed metaphor elicitation as an alternative method to explore perceptions in education e.g., [27,30,31]. According to Ellis (2008) [27], metaphor elicitation and analysis is an effective approach to perceptions since it provides an “indirect” means of accessing individuals’ belief systems. The participants of the current study were requested to use a metaphor to describe EFL in their L2 Greek classroom and then to explain it.
4. Findings
4.1. Questionnaire Findings Regarding Teachers’ Perceptions and Attitudes
The participants were first asked whether the use of English is helpful during their lessons. The majority of them (70%, N = 14) responded positively, namely that it was (very/extremely) helpful. Only one participant out of twenty (5%) indicated that it was not helpful at all. However, half of them (N = 10) reported that they did not use it frequently in the L2 Greek class (see Section 4.2).
The teachers were also asked if the use of ELF was expected to make bi-/multilingual students feel more secure and confident in order to enable them to participate in the lessons regardless of their progress in Greek. Fourteen of them (strongly) agreed with the idea that English can promote students’ self-confidence and security. None of the participants strongly disagreed with this view, four of them were undecided (20%), and only two (10%) disagreed.
The participants were also asked to what extent they agree with the statement that bi-/multilingual students seem to enjoy the use of English during the lessons. According to the results, 14 (70%) of the participants (strongly) agreed with this statement, none of them disagreed, while five of them (25%) were undecided.
Finally, participants were asked to what extent they agree with the statement that the use of ELF is expected to create an inclusive atmosphere and allow learners to express their personalities, feelings, and thoughts. The majority of them (N = 15, 75%) reported that they (strongly) agreed that ELF can create an inclusive atmosphere to bi-/multilingual students who learn Greek. Four of them reported that they disagreed, while only one was undecided.
In sum, the teachers’ perceptions and attitudes were concurring regarding the issue of using ELF in L2 Greek classes and revealed that teachers generally maintain positive attitudes toward ELF. The participants seemed to agree that ELF is useful and that it can promote an inclusive environment in which bi-/multilingual students feel secure and confident to participate in the lesson.
4.2. Questionnaire Findings Regarding Teachers’ Practices
The participants were asked how often they use English in their classrooms. Their responses covered almost all spectrums of the scale (Figure 1): five out of twenty (25%) participants reported that English was frequently employed in their classroom (i.e., 76–90% of the time) while four out of twenty (20%) declared that it was often employed (i.e., 51–75%). Only one participant (5%) stated that he/she always used English in the Greek class. The remaining ten (50%) reported a less frequent use while two participants (10%) stated that English was used rarely (between 1% and 15% of the time).
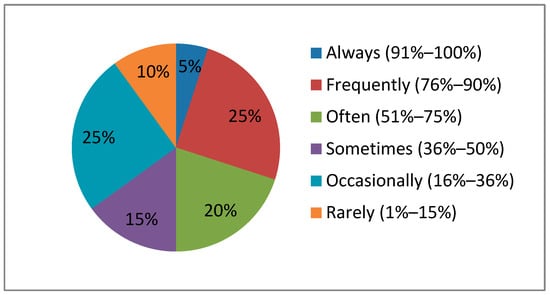
Figure 1.
Degree to which ELF is used by the teachers in L2 Greek classes.
The participants answered nine more Likert scale questions, which aimed at exploring their practices and purposes for using ELF in the lessons. Their responses were also broad but the greater agreement for which ELF was employed in L2 Greek classes was to explain and translate vocabulary. Twelve participants (60%) reported that it was (very) probable to use the ELF as a tool to explain/translate vocabulary in the class, while only one (5%) reported that this use was very improbable. Six participants (30%) were neutral regarding this function of English in their classrooms.
Regarding the use of ELF as a tool to explain grammar, the majority of the participants (60%, N = 12) indicated that it was (very) improbable to use English for such purpose, while six participants (30%) reported that it was (very) probable to use English to explain grammar in the L2 Greek class.
The participants were then asked how probable it was for them to use ELF to teach culture in class. Six of them (30%) reported that this use of English was (very) probable. Eleven of them (55%) reported that it was (very) improbable in their teaching procedure, while three (15%) were neutral regarding this use.
The participants were also asked how probable it was that they explain something in Greek and then repeat the explanation in English to ensure understanding on the part of the students or whether they do the opposite (i.e., first English and then Greek). The majority of participants (60%, N = 12) reported that it was (very) improbable to use first English and then Greek, while only a few teachers (20%, N = 4) reported that this was probable. It seems that it is slightly more likely to first use Greek and then English, as eight participants (35%, N = 8) reported that this was (very) probable. Eight more teachers (35%, N = 8) reported that it was (very) improbable to first explain something in Greek and then repeat the explanation in English. The remaining answers were neutral.
When participants were asked how probable it was for them to use English for classroom management (e.g., managing student behavior), eleven (55%) reported that it was (very) improbable to use English for this function, while seven (35%) answered that this was (very) probable. Two participants were neutral regarding this practice.
The participants also responded to three Likert scale questions on the use of ELF in the L2 Greek class for social interaction, i.e., chatting in class, giving instructions, and checking for comprehension. Regarding chatting during the lessons, less than half of the participants (35%, N = 7) indicated that it was (very) probable to use English for this function, while half of them (50%, N = 10) reported that this use was (very) improbable. The remaining answers were neutral. Focusing on giving instructions, six participants (30%) reported that this EFL use was (very) probable, while the double of them (N = 12, 60%) answered that it was (very) improbable. Finally, regarding ELF to check for comprehension, the participants were divided: eight teachers (40%) reported that it was (very) probable to use English for this purpose, nine (45%) reported that it was (very) improbable and three participants were neutral.
Considering the questionnaire results on teachers’ practices in relation to the use of English in the L2 Greek class, it was observed that there was no great agreement on the issues examined, contrary to teachers’ attitudes as revealed through the relevant questionnaire items, in which there was greater agreement among the participants’ answers. Therefore, the findings of the questionnaire alone disallow the possibility to draw strong conclusions.
4.3. Written Accounts Findings Regarding Teachers’ Practices
In the second set of data, the participants described instances of ELF use in their lessons. Most of them reported instances that refer to the use of English as a tool to explain or translate Greek vocabulary. For instance:
Sometimes I translate difficult words like ‘revolution’ or ‘slavery’ in order to make them understand historical events or the contexts.(T1)
Some participants also referred to the use of ELF as a tool to explain grammar in the L2 Greek class:
A typical example in one of the last lessons was related to the order of the words in the sentence (subject-verb-object). A student of mine who started learning Greek in October (8 years old) has difficulty in understanding this word order in simple sentences and I told her to have in mind the very simple and useful sentence ‘I LOVE YOU’. The same happens in Greek; the subject usually enters first, then the verb, and finally the object.(T4)
There were also instances describing use of ELF as a tool to elaborate on cultural elements:
One example that I remember was during the Carnival. I was explaining this day to my students and a boy from Syria mentioned the word ‘Halloween’. Based on that reference, we continued the discussion with more students and they mentioned words [in English] like costumes, pumpkins, and spiders.(T7)
The instances of ELF use described by the teachers indicated a contrastive presentation of Greek lexical items, grammatical phenomena, and cultural aspects in relation to students’ prior knowledge on language and culture.
4.4. Metaphor Elicitation Findings
The body of metaphors referring to the use of English in multicultural classrooms in Greek schools was divided into three categories: positive, negative, and neutral views regarding the use of ELF as a facilitator in Greek language teaching and learning. As shown in Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3, nine metaphors revealed a positive view on ELF, three metaphors indicated a negative view, while three more metaphors connoted a neutral view. The remaining five responses involved non-metaphoric answers given in the metaphor elicitation task, which all reported a positive view toward ELF.

Table 1.
Metaphors that reveal a positive stance of the use of English.

Table 2.
Metaphors that reveal negative stance of the use of English.

Table 3.
Metaphors that reveal neutral stance of the use of English.
Overall, the teachers’ metaphors and non-metaphoric statements in this set of data indicated a positive stance toward ELF in the L2 Greek context. The participants used mostly positive connotations (lifesaver, godsend, bridge, and ice cream) in their attempt to reveal their perceptions on the mediating function of English. The notions of disaster and open sea suggest negative attitudes that two teachers had toward ELF in teaching Greek in multicultural environments. These views were accounted for by the fact that the students had low or no proficiency in English, which is an important prerequisite for ELF use.
4.5. Interview Findings Regarding Teachers’ Perceptions and Attitudes
In the interviews, the participants were given more time and space to elaborate thoroughly on the topic and to provide examples of their classrooms’ reality. They were asked whether they think that using English is useful in teaching Greek in multicultural environments. All of them responded positively. These findings are consistent with the questionnaire data on teachers’ attitudes, according to which most of them agreed that ELF is (extremely) helpful in the L2 Greek context. In the interviews, the participants also had the opportunity to elaborate on their views, as shown in the following excerpt:
It definitely makes it easier and I feel better, otherwise there could be no lesson. I don’t speak Russian; they don’t speak Greek at a good level, so there could not be a lesson. Therefore, English is very useful and, as I see it, the children are happy with English as they seem to understand. Otherwise, they would not understand.(T1)
As for the question on whether the participants perceive English as a means to enhance students’ self-confidence and a sense of security, the interviewees answered mostly positively:
Yes, of course, they feel more secure. They feel that they can confront this difficult situation. Sometimes they make connections directly between the English and the Greek language.(T4)
Positive comments were also reported in relation to the refugee and migrant pupils’ feelings when using English, as in the questionnaire, in which most participants (strongly) agreed with the fact that students seem to enjoy the use of English in class while none of them disagreed with this statement.
They are proud of it. They keep telling me that they are good at using English and they feel happy.(T2)
They are happy because they see it [speaking English] as a game.(T5)
Despite the positive comments toward the use of ELF as a facilitator in the L2 Greek class, teachers’ interview answers also indicated some concerns and limitations regarding this issue:
It helps but not in learning Greek terminology but in communication. […] It helps a lot in some cases in which students already speak English well.(T7)
Interrupting the lesson to explain something to five students in English interrupts the flow of the lesson and this is time consuming.(T4)
Overall, the interview findings again revealed a mostly positive stance regarding the use of ELF in L2 Greek classrooms from the teachers’ viewpoint. There were relatively few comments that also revealed some hesitancy toward the use of ELF, which was related to time constraints and some students’ unfamiliarity with English.
4.6. Interview Findings Regarding Teachers’ Practices
In the question concerning the languages that these teachers use to communicate with their pupils, they mostly referred to Greek, but also to some instances of students L1 use, and to use of ELF. According to these reports:
These children come to school without speaking Greek. Therefore, the first approach is always in English, but unfortunately, many children do not understand this language. […] I am talking specifically about refugees because it is very difficult to communicate with them. For example, I learned some Russian to communicate with the immigrants from the Soviet Union. On the contrary, I cannot do the same with the refugees because they speak too many different languages and dialects. In these cases, English is the key to communicate with them, with the refugees.(T2)
Focusing particularly on ELF, participants were asked to give examples regarding the use of English during their L2 Greek lessons. The majority of them gave examples in which English is used to explain/translate vocabulary. These findings are consistent with the questionnaire data, according to which most participants supported the view that it was (very) probable to use the English language as a tool to explain or translate vocabulary in class. For example:
If I want to explain something, I will say the word or the phrase first in English and then I will translate these phrases into Greek. For example, when I want to teach children about food, I will say this word in English ‘Food’ so as to be sure that my learners understand the meaning. I also use simpler vocabulary that is frequently used. For example: ‘let’s go’. Therefore, I translate vocabulary, especially during my students’ first days at school.(T5)
One of them (T4) gave an interesting example in which ELF was employed as a tool to explain a grammatical phenomenon in relation to teaching history, revealing a cross-curricular use of ELF:
We very often use the English language to teach Greek but it is also useful in history. For example, when I want to teach the tenses in Greek, during the history lesson I sometimes use the past tenses of English in order to make them understand this grammatical phenomenon.(T4)
One participant answered this question by reporting that she uses the ELF in order to raise students’ phonological awareness:
We also use English to raise phonological awareness. When I try to teach them the sound/d/in Greek, I tell them the word ‘dog’ and they understand the phonological rules.(T2)
5. Discussion
5.1. ELF as a Facilitator and Promoter of Self-Confidence and Inclusion
The first research question aimed to investigate teachers’ perceptions and attitudes toward the use of ELF as a facilitator in the L2 Greek teaching and learning process in multicultural settings. Overall, triangulation of data showed that L2 Greek language teachers hold an attitude toward ELF which could generally be regarded as positive. The majority of participants reported that the lack of a common linguistic code among refugees and migrant students makes them resort to the use of English. This is in line with Nunan (2012) [6], who suggests that the status of ELF has an important influence on educational methods and strategies, as it can be used as a medium of instruction in multicultural classrooms around the world. These views are also similar to those attested in Ife’s (2008) [24], Wang’s (2013) [32], Turnbull’s (2018) [14], and Kantzou and Vasileiadi’s (2021) [26] studies, which reveal that even though the amount of EFL use varies among the targeted educational environments, it is an important part of the learning and teaching process, as it bridges the gap between learners’ L1 and the TL. Elaborating more on the teachers’ attitudes, it was revealed that ELF use was perceived as a means to improve the development of learners’ cognitive skills and works as a facilitator in learning and meaning making. Additionally, it was also perceived as promoting students’ sense of self-confidence and inclusion, crucial aspects in the context of intercultural education. This is in line with Turnbull (2018) [14], who suggests that for multilingual students, a sense of security and comfort in the known is formed through the employment of ELF, easing the gap between learners’ native language and their development in the TL.
5.2. Teachers’ Reported Practices Involving ELF
The second research question aimed to explore teachers’ practices involving use of ELF in the L2 Greek teaching and learning process in formal primary education in Greece through their self-reports. The results showed that ELF was indeed used in multilingual and multicultural classrooms in Greek schools in the everyday teaching and learning practice, according to the participants’ reports. This is in line with recent accounts that refer to English as a multilingua franca, according to which English can be seen as a vehicle of multilingual communication, i.e., functioning as a contact language of choice, which makes links to other languages and facilitates translanguaging [3,33]. More specifically, even though the dominant classroom discourse was in the TL, ELF was used by both teachers and students, non-native speakers of English, for specific purposes and in specific situations, which assisted teaching and learning, similarly to Kantzou and Vasileiadi’s (2021) [26] findings. According to the teachers’ reports, the most common function for which ELF was employed in the L2 Greek classroom was for explanation or translation of vocabulary. Apart from this general agreement in the participants’ responses, various other functions of ELF were also reported, such as use of ELF to explain grammar, to introduce cultural elements, to give instructions, to check for comprehension, and to teach phonological awareness, among other functions see also [26]. As in Ife’s (2008) study [24], these results cannot show the full extent to which learners use ELF in the L2 context.
5.3. Pedagogical Implications
The study aimed to provide an insightful understanding of teachers’ views regarding ELF in multilingual settings in teaching L2 Greek to learners with a refugee and migrant background. The current approaches to L2 teaching and learning question the monolingual approaches and methods adopted by language teachers. Exposure to the target language should not be viewed as a priority to the detriment of learners’ L1s or other linguistic repertoires that are available and could assist the learning process. The monolingual teaching methods have led to the banishing of L1 from L2 classes and to L2 educators being hesitant to admit any use of L1 [12]. However, judicious use of L1 has been highlighted by many scholars as an important tool in L2 teaching and learning e.g., [11,13,16,26,34]. What has been explored in the present study is the fact that ELF fulfills several of the functions visualized for the use of L1 in learning a second language. Since L1 use is rarely a classroom option in multilingual environments in Greek classrooms, as teachers do not normally have access to learners’ L1s, they may resort to the use of ELF to help students develop their linguistic, cognitive, and social skills and create an emotionally safe space.
Another significant implication of this study is the importance of examining teachers’ attitudes, as they affect students in many ways and shape their learning experiences and academic success [35]. Teachers’ attitudes toward the use of ELF as a facilitator in learning L2 Greek influences the cognitive and social development as well as the school performance of students with a refugee and migrant background. As most participants reported, teachers’ strategies to use ELF not only helps learners acquire Greek but also promotes self-confidence and a sense of security and comfort. These findings may contribute to support and improve teachers’ training in L2 teaching within the context of intercultural education.
6. Conclusions
The present study showed that Greek language teachers hold a generally positive attitude toward the use of ELF in the Greek educational context, as it can be used as a medium of L2 instruction with culturally and linguistically diverse students. English was perceived as a facilitator and promoter of students’ self-confidence and inclusion according to teachers’ views. As per the reported practices, although the dominant classroom discourse was aimed to be in the TL, ELF was in fact used by both teachers and learners for various functions. The findings further highlight the need for educators to challenge the previously monolingual teaching methods and to propose a strategic use of L1 or other additional languages, such as ELF, as they may play a highly beneficial role in L2 learning. As teachers normally do not speak their students’ L1s in multilingual environments in Greece, they may resort to English, which is a dominant global language extensively used as a lingua franca.
Future research could draw on the present findings and investigate further the topic from the perspective of a larger number of participants, including students, and through classroom observations, which would enable the comparison between attitudes, reported practices, and observed practices. It is crucial to continue exploring ELF viewed as a tool and as a means through which bi-/multilingual students may work to develop new practices in their attempt to learn the TL. Further research is also needed to explore the impact that language teachers’ specific training in intercultural education may have on teaching methods and approaches that they choose in different L2 contexts. Teachers’ training and education could also be informed by related research with a view to promoting the idea of making the most of students’ linguistic repertoires and prior knowledge while embracing their identities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.G. and K.K.; methodology, A.G. and K.K.; software, A.G. and K.K.; validation, A.G. and K.K.; formal analysis, A.G. and K.K.; investigation, A.G. and K.K.; resources, A.G. and K.K.; data curation, A.G. and K.K.; writing—original draft preparation, A.G. and K.K.; writing—review and editing, A.G.; visualization, A.G. and K.K.; supervision, A.G.; project administration, A.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of the Hellenic Open University (512705, 1 July 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
Part of the data reported in this study were used in the second author’s research for her MA thesis conducted in the Open Hellenic University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ferguson, G. The Practice of ELF. J. Engl. A Ling. Fr. 2012, 1, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifakis, N.C.; Fay, R. Integrating an ELF pedagogy in a changing world: The case of Greek state schooling. In Latest Trends in ELF Research; Archibald, A., Cogo, A., Jenkins, J., Eds.; Cambridge Scholars: London, UK, 2011; pp. 285–298. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, J. Repositioning English and Multilingualism in English as a Lingua Franca. Englishes Pract. 2015, 2, 49–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostoulas, A. Ιδεολογικοί μηχανισμοί προτυποποίησης στα διδακτικά εγχειρίδια αγγλικής γλώσσας [Ideological standardisation processes in ELT coursebooks]. In Ιδεολογίες, γλωσσική επικοινωνία και εκπαίδευση [Ideologies, Linguistic Communication and Education]; Motsiou, E.V., Gana, E., Kostoulas, A., Eds.; Gutenberg: Athens, Greece, 2021; pp. 162–189. [Google Scholar]
- Siqueira, S. Critical perspectives of Brazilian teachers on English as a lingua franca. In Social Justice, Decoloniality, and Southern Epistemologies within Language Education; Routledge: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Nunan, D. The impact of English as a global language on educational policies and practices in the Asia-Pacific region. In Learner-Centered English Language Education; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 164–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Mol, C.; De Valk, H. Migration and immigrants in Europe: A historical and demographic perspective. In Integration Processes and Policies in Europe; Garcés-Mascareñas, B., Penninx, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham Switzerland, 2016; pp. 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNHCR. Situation Mediterranean Situation. 2023. Available online: https://data2.unhcr.org/en/situations/mediterranean (accessed on 2 August 2023).
- Sakellis, Y.; Spyropoulou, N.; Ziomas, D. The Refugee Crisis in Greece in the Aftermath of the 20 March 2016 EU-Turkey Agreement; European Social Policy Network: Brussels, Belgium, 2016; p. 64. [Google Scholar]
- UNHCR. Greece Factsheet—September 2021 [EN/EL]—Greece. 2021. Available online: https://reliefweb.int/report/greece/unhcr-greece-factsheet-september-2021-enel (accessed on 10 November 2022).
- Atkinson, D. The Mother Tongue in the Classroom: A Neglected Resource? ELT J. 1987, 41, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, V. Using the First Language in the Classroom. Can. Mod. Lang. Rev. 2001, 57, 402–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. L1 Use in L2 Vocabulary Learning: Facilitator or Barrier. Int. Educ. Stud. 2008, 1, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, B. The Use of English as a Lingua Franca in the Japanese Second Language Classroom. J. Engl. A Ling. Fr. 2018, 7, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, J. Intercultural Education and Academic Achievement: A Framework for School-Based Policies in Multilingual Schools. Intercult. Educ. 2015, 26, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, O.; Kleyn, T. Translanguaging with Multilingual Students: Learning from Classroom Moments; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hornberger, N.H. The Continua of Biliteracy and the Bilingual Educator: Educational Linguistics in Practice. Int. J. Biling. Educ. Biling. 2004, 7, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurydice Report. In Integrating Students from Migrant Backgrounds into Schools in Europe: National Policies and Measure; Education, Audiovisual and Culture Executive Agency (EACEA), Education and Youth Policy Analysis, Cop: Brussels, Belgium, 2019.
- Manoli, P.; Mouti, A.; Kantzou, V. Children with a Refugee and Migrant Background in the Greek Formal Education: A Study of Language Support Classes. Multiling. Acad. J. Educ. Soc. Sci. 2021, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Mattheoudakis, M.; Chatzidaki, A.; Maligkoudi, C. Greek teachers’ views on linguistic and cultural diversity. Sel. Pap. ISTAL 2017, 22, 358–371. [Google Scholar]
- Statista. The Most Spoken Languages Worldwide in 2023. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/266808/the-most-spoken-languages-worldwide/#statisticContainer (accessed on 2 August 2023).
- Kachru, B.B.; Nelson, C.L. World Englishes. In Sociolinguistics and Language Education; McKay, S., Hornberger, N., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996; pp. 71–102. [Google Scholar]
- Kachru, B.B. World Englishes and Culture Wars; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ife, A. A role for English as Lingua Franca in the foreign language classroom? In Intercultural Language Use and Language Learning; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 79–100. [Google Scholar]
- Antón, M.; DiCamilla, F. Socio-Cognitive Functions of L1 Collaborative Interaction in the L2 Classroom. Can. Mod. Lang. Rev. 1998, 54, 314–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantzou, V.; Vasileiadi, D.M. On Using Languages Other Than the Target One in L2 Adult Language Education: Teachers’ Views and Practices in Modern Greek Classrooms. J. Lang. Educ. 2021, 7, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R. The Study of Second Language Acquisition; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Charmaz, K. Grounded Theory in Global Perspective. Qual. Inq. 2014, 20, 1074–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R.; Barkhuizen, G. Analyzing Learner Language; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kramsch, C. Metaphor and the subjective construction of beliefs. In Beliefs about SLA: New Research Approaches; Kalaja, P., Barcelos, A.M.F., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 109–128. [Google Scholar]
- Kalaja, P.; Barcelos, A.M.; Aro, M.; Ruohotie-Lyhty, M. Beliefs, Agency and Identity in Foreign Language Learning and Teaching; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D. The use of English as a lingua franca in teaching Chinese as a foreign language: A case study of native Chinese teachers in Beijing. In Language Alternation, Language Choice and Language Encounter in International Tertiary Education; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 161–177. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, T. English as a Multilingua Franca and ‘Trans-’ Theories. Englishes Pract. 2022, 5, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, H. The role of native language in the teaching of the FL grammar. J. Educ. 2012, 1, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Ulug, M.; Ozden, M.S.; Eryilmaz, A. The Effects of Teachers’ Attitudes on Students’ Personality and Performance. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2011, 30, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).