An Analysis of the Factors Influencing Public Attitudes toward Implementing Basic Income (BI) from an Individual Perspective: A Case Study of Hokuriku Region, Japan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theorizing the Public Attitudes toward BI
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Area and Sample Size
3.2. BI Proposal for the Case Study Area
3.3. Hypothesis
3.4. Measurement of Model Variables
3.5. Empirical Model
4. Result and Discussion
4.1. Descriptive Analysis
4.2. Factors Affecting Public Attitudes on Basic Income
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Statement
References
- Van Parijs, P. Basic income: A simple and powerful idea for the twenty-first century. Polit. Soc. 2004, 32, 7–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, B. The Low Road to Basic Income? Tax-Benefit Integration in the UK. J. Soc. Policy 2012, 41, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opielka, M. The likelihood of a basic income in Germany. Int. Soc. Secur. Rev. 2008, 61, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koistinen, P.; Perkiö, J. Good and bad times of social innovations: The case of Universal basic income in Finland. Basic Income Stud. 2014, 9, 25–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkiö, J. Basic Income Proposals in Finland, Germany and Spain. 2013. Available online: https://www.transform-network.net/fileadmin/_migrated/news_uploads/paper__2_13.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- Federal Chancellery of Switzerland. Homepage of the Federal Chancellery of Switzerland. Available online: https://www.bk.admin.ch/ch/d/pore/va/20160605/det601.html (accessed on 19 March 2020).
- Lee, S. Attitudes toward universal basic income and welfare state in Europe: A research note. Basic Income Stud. 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roosma, F.; van Oorschot, W. Public opinion on basic income: Mapping European support for a radical alternative for welfare provision. J. Eur. Soc. Policy 2020, 30, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.O.; Kangas, O. Popular support for basic income in Sweden and Finland. In Proceedings of the Basic Income European Network 9th International Congress, Geneva, Switzerland, 12–14 September 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bay, A.H.; Pedersen, A.W. The limits of social solidarity: Basic income, immigration and the legitimacy of the universal welfare state. Acta. Sociol. 2006, 49, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R. Introduction: Financing approahes to basic income. In Financing Basic Income: Addressing the Cost Objection, 1st ed.; Pereira, R., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Pierson, P. The New Politics of the Welfare State. World Politics 1996, 48, 143–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumeier, S. Why do Social Innovations in Rural Development Matter and Should They be Considered More Seriously in Rural Development Research?–Proposal for a Stronger Focus on Social Innovations in Rural Development Research. Sociol. Ruralis 2012, 52, 48–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooteboom, B. Basic income as a basis for small business. Int. Small Bus. J. 1987, 5, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standing, G. Income security: Why unions should campaign for a basic income. Transfer 2004, 10, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jens-Eberhard, J. A basic income for rural areas? A proposal for a strategic realignment of agricultural, social and structural policy within the EU. In Proceedings of the Basic Income Earth Network Congress 2012, Munich, Germany, 14–16 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Forget, E.L.; Peden, A.; Strobel, S. Cash transfers, basic income and community building. J. Soc. Incl. 2013, 1, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, A. Universal basic income as development solution? Glob. Soc. Policy 2017, 17, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krozer, A. A regional basic income: Towards the eradication of extreme poverty in Central America. Available online: https://repositorio.cepal.org/bitstream/handle/11362/25938/lcmexl998.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- Altman, J.; Klein, E. Lessons from a basic income programme for Indigenous Australians. Oxf. Dev. Stud. 2018, 46, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.M.; Chou, K.L. Public Attitudes towards Income Redistribution: Evidence from Hong Kong. Soc. Policy Adm. 2017, 51, 738–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linos, K.; West, M. Self-interest, Social Beliefs, and Attitudes to Redistribution. Re-addressing the Issue of Cross-national Variation. Eur. Sociol. Rev. 2003, 19, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svallfors, S. Contested Welfare States: Welfare Attitudes in Europe and Beyond, 1st ed.; Stanford University Press: Redwood City, CA, USA, 2012; p. 226. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Barrett, N. Understanding public attitudes towards Social Security. Int. J. Soc. Welf. 2006, 15, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, E.M. Diffusion of Innovations, 4th ed.; Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 22–23. [Google Scholar]
- Statistics Bureau of Japan. National Census 2015. Statistics of Prefecture and Municiaplity Population. Available online: https://www.e-stat.go.jp/stat-search/files?page=1&layout=datalist&toukei=00200521&tstat=000001049104&cycle=0&tclass1=000001049105&stat_infid=000031594311 (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- Statistic Bureau of Japan. 2015 Population Census of Japan: Overview of Population and Household in Japan. Available online: https://www.stat.go.jp/data/kokusei/2015/pdf/wagakuni.pdf (accessed on 28 June 2020).
- Statistics Bureau of Japan. Summary of the Result of Population Estimation in Japan (As of October 1st). Available online: http://www.stat.go.jp/data/jinsui/2018np/index.html (accessed on 29 April 2020).
- Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan. Basic Survey on Wage Structure 2018. Available online: https://www.e-stat.go.jp/stat-search/files?page=1&layout=datalist&toukei=00450091&tstat=000001011429&cycle=0&tclass1=000001113395&tclass2=000001113397&tclass3=000001113406 (accessed on 13 November 2019).
- National Tax Agency of Japan. Statistical survey of actual status for salary in the private sector 2017. 2018. Available online: https://www.nta.go.jp/publication/statistics/kokuzeicho/minkan2017/pdf/000.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2019).
- Basic income Earth Network (BIEN). Home page of BIEN. Available online: https://basicincome.org/ (accessed on 10 May 2019).
- Parlevliet, J. What drives public acceptance of reforms? Longitudinal evidence from a Dutch pension reform. Public Choice 2017, 173, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, A. Japan as a Prototype of the ‘Degreeocracy’ Society? Educ. Rev. 2001, 53, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgarte, J.M. Basic income and the gendered division of labour. Basic Income Stud. 2008, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J. All things considered, should feminists embrace basic income? Basic Income Stud. 2008, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, W.A. Basic income and the right to work: A Keynesian approach. J. Post Keynes. Econ. 1999, 21, 639–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E.O. Basic income, stakeholder grants, and class analysis. Polit. Soc. 2004, 32, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widerquist, K. Perspectives on the Guaranteed Income, part I. J. Econ. Issues 2001, 35, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan Trade Union Confederation. Survey about Working Time. 2015. Available online: https://www.jtuc-rengo.or.jp/info/chousa/data/20150116.pdf (accessed on 24 December 2019).
- Jackson, A. Basic income: A social democratic perspective. Glob. Soc. Policy 2017, 17, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelleke, A. Feminist political theory and the argument for an unconditional basic income. Policy Polit. 2011, 39, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, S. Should surfers be ostracized? Basic income, liberal neutrality, and the work ethos. Polit. Philos. Econ. 2011, 10, 396–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskivker, J. An alternative reply to the free-rider objection against unconditional citizenship grants. In Public Policy: Why Ethics Matters, 1st ed.; ANU Press: Canberra, Australia, 2010; pp. 257–276. [Google Scholar]
- Hasenfeld, Y.; Rafferty, J.A. The determinants of public attitudes toward the welfare state. Soc. Forces 1989, 67, 1027–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, F.L.; Barrett, E.J. Public support for social security. J. Aging Stud. 1988, 2, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangas, O.E. Attitudes on Means-Tested Social Benefits in Finland. Acta. Sociol. 1995, 38, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ida, M. Nihon Jin No Seiji Syakaikan Ni Kansuru Kousatsu Jiko Sekinin to Fukushikokka Ni Tsuite (Consideration on the views of Japanese on politics and society: Own responsibility and welfare state). Rev. Econ. Political Sci. 2000, 69, 213–253. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Takenaka, Y. The impact of age on De-ideologization of Japanese Voters. Jpn. Elect. Stud. 2014, 30, 5–18. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Calnitsky, D.; Latner, J.P. Basic Income in a Small Town: Understanding the Elusive Effects on Work. Soc. Probl. 2017, 64, 373–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, B.A.; Alstott, A.; Van Parijs, P.; Wright, E.O. Redesigning Distribution: Basic Income and Stakeholder Grants as Alternative Cornerstones for a More Egalitarian Capitalism; Verso Books: Brooklyn, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 5, pp. 150–157. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, M.W. Basic income, liberal neutrality, socialism, and work. Rev. Soc. Econ. 2005, 63, 613–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.M.; Kavanagh, C. Basic income, inequality, and unemployment: Rethinking the linkage between work and welfare. J. Econ. Issues 1996, 30, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, A.C.; Trivedi, P.K. Microeconometrics: Methods and Applications; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 465–466. [Google Scholar]
- Lemessa, S.D.; Yismaw, M.A.; Watabaji, M.D. Risk induced farmers’ participation in agricultural innovations: Evidence from a field experiment in eastern Ethiopia. Dev. Stud. Res. 2019, 6, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velandia, M.; Rejesus, R.M.; Knight, T.O.; Sherrick, B.J. Factors Affecting Farmers’ Utilization of Agricultural Risk Management Tools: The Case of Crop Insurance, Forward Contracting, and Spreading Sales. J. Agric. Appl. Econ. 2015, 41, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan. Annual Report on Welfare Pension and National Pension. 2017. Available online: https://www.e-stat.go.jp/stat-search/files?page=1&layout=datalist&toukei=00450463&tstat=000001064713&cycle=8&month=0&tclass1=000001129735&cycle_facet=cycle (accessed on 30 November 2019).
- Cabinet office of the Japanese Government. Questions and Answers on the Nursery Allowance. Available online: https://www8.cao.go.jp/shoushi/jidouteate/ippan.html (accessed on 26 June 2020).
- Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan. Situation of Expenditure on Medical Treatement of Children Hesei 27. 2015. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/file/05-Shingikai-12401000-Hokenkyoku-Soumuka/0000096264.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2020).
- National Tax Agency of Japan. Exemption of Individual Income Tax for Handicapped Person. Available online: https://www.nta.go.jp/taxes/shiraberu/taxanswer/shotoku/1160.htm (accessed on 26 June 2020).
- Niigata Prefecture Government. Individual Prefectural Resident Tax. Available online: https://www.pref.niigata.lg.jp/sec/zeimu/kkenmin.html (accessed on 26 June 2020).
- Statistics Bureau of Japan. National Survey of Family Income and Expenditure 2014. Available online: https://www.e-stat.go.jp/stat-search/files?page=1&toukei=00200564&tstat=000001073908&cycle=0&tclass1=000001073965&cycle_facet=tclass1%3Acycle (accessed on 26 December 2019).
- Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan. Public Assistance Act. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/web/t_doc?dataId=82048000&dataType=0&pageNo=1 (accessed on 16 July 2020).
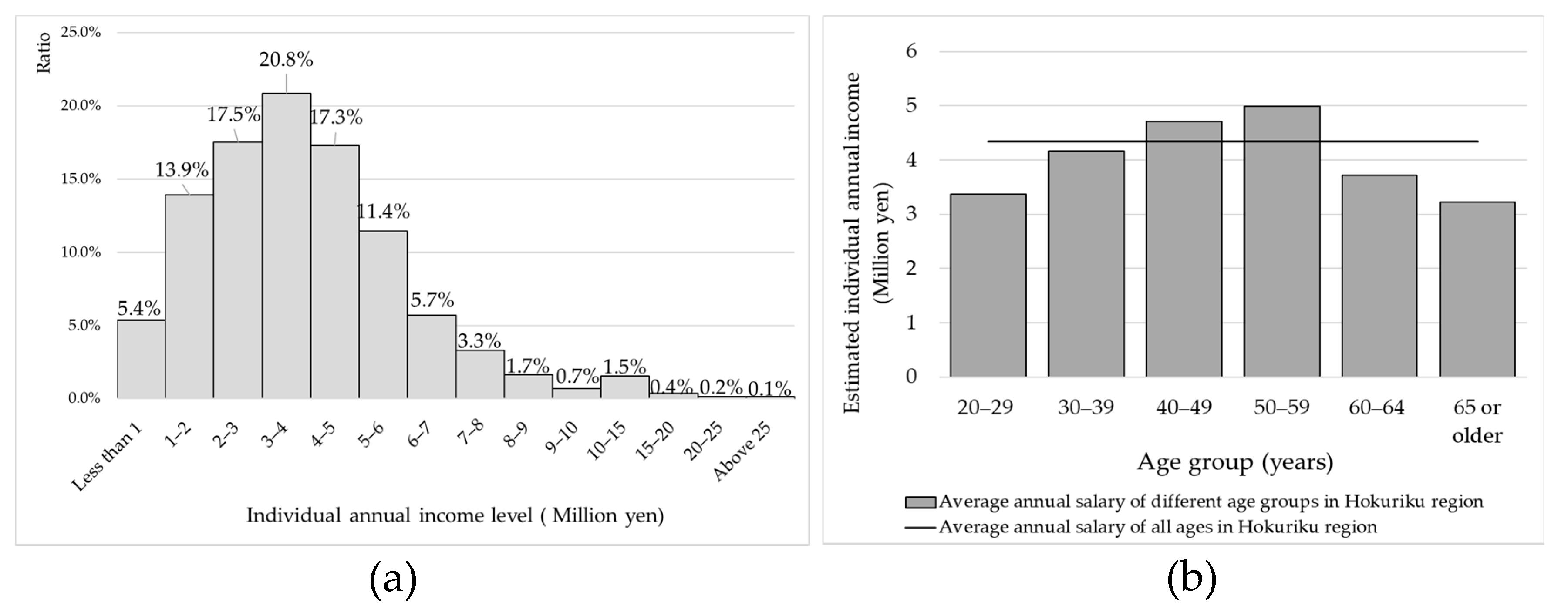
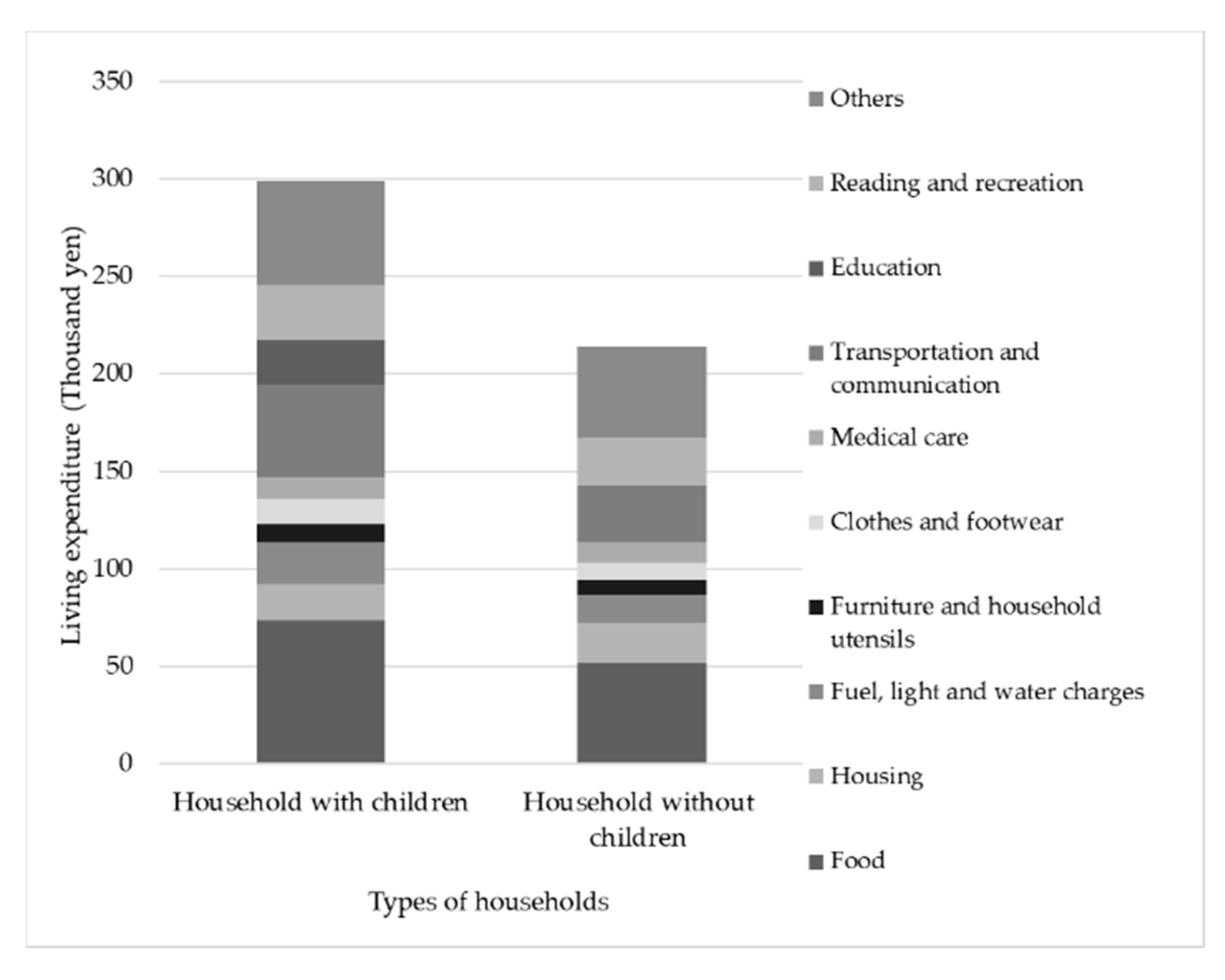
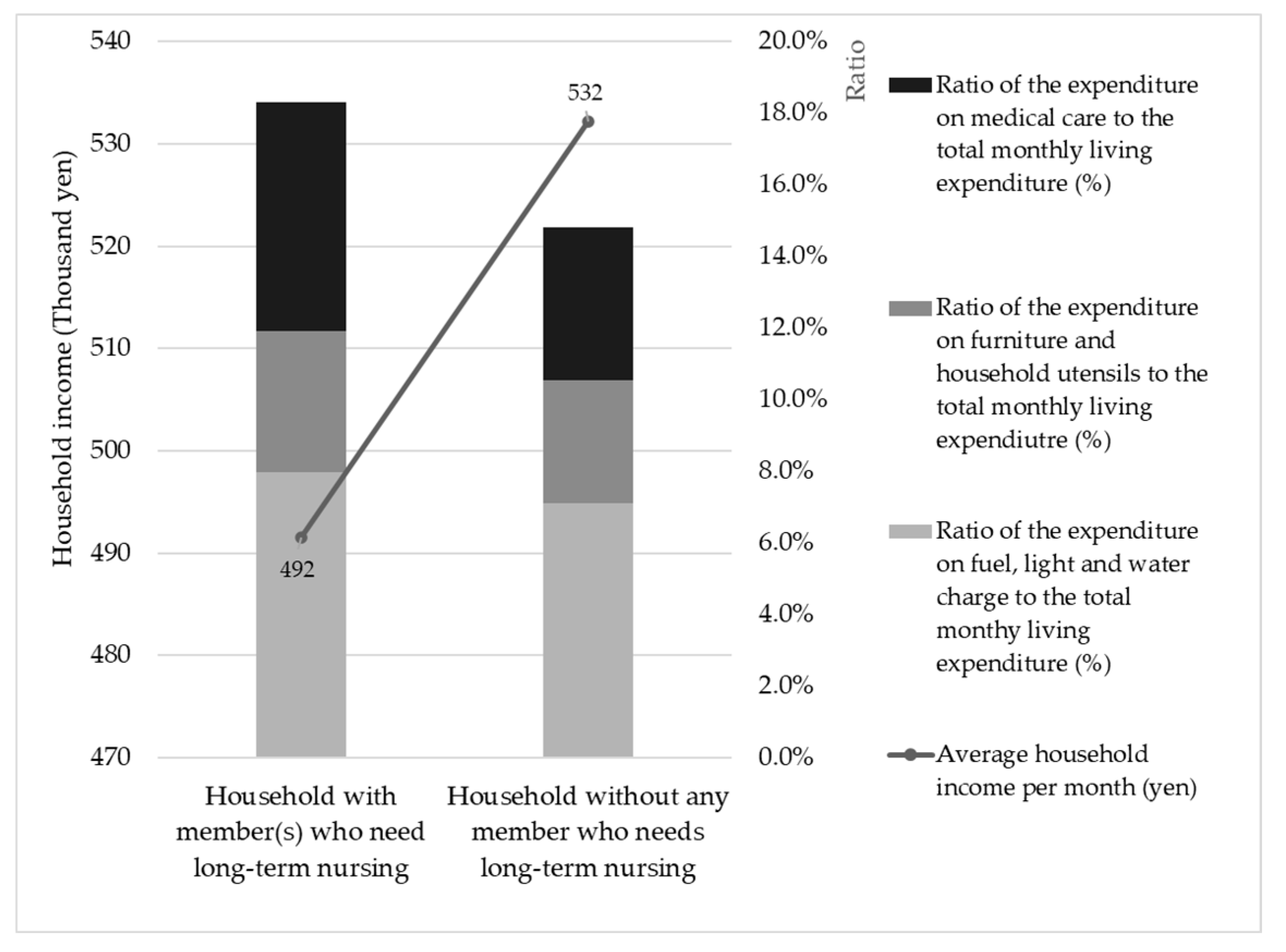
| Proposed BI Amount per Capita per Month | Policies Considered to be Abolished due to the Implementation of BI |
|---|---|
| Adult (Above 20 years old): 100,000 yen/month/capita Minor (0–19 years old): 25,000 yen/month/capita | Welfare policies:
|
Adjustment on the tax system
|
| Attitudes toward BI | Agree with the BI Proposal | Do Not Agree with the BI Proposal |
|---|---|---|
| Number of respondents | 503 | 525 |
| Variable | Description | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Attitude towards BI | Dummy = 1 if the respondent agrees with BI proposal, 0 otherwise | 0.489 | 0.500 |
| Gender | Dummy = 1 if the respondent is Male, 0 otherwise | 0.541 | 0.499 |
| Age | Age of respondent in years | 46.223 | 13.011 |
| Economically independent | Dummy = 1 if the respondent is economically independent, 0 otherwise | 0.407 | 0.491 |
| Neither economically dependent nor independent | Dummy = 1 if the respondent is neither economically dependent nor independent, 0 otherwise | 0.290 | 0.454 |
| Economically dependent | Dummy = 1 if the respondent is economically dependent, 0 otherwise | 0.304 | 0.460 |
| Less than 3 million yen | Dummy = 1 if the annual individual income level of the respondent is less than 3 million yen, 0 otherwise | 0.638 | 0.481 |
| 3–6 million yen | Dummy = 1 if the annual individual income level of the respondent is between 3 to 6 million yen, 0 otherwise | 0.274 | 0.446 |
| 6–9 million yen | Dummy = 1 if the annual individual income level of the respondent is between 6 to 9 million yen, 0 otherwise | 0.064 | 0.245 |
| More than 9 million | Dummy = 1 if the annual individual income level of the respondent is more than 9 million yen | 0.023 | 0.151 |
| Below or equal to high school | Dummy = 1 if the educational background of the respondents equal to or below high school, 0 otherwise | 0.545 | 0.498 |
| Vocational school | Dummy = 1 if the educational background of the respondent is a vocational school, 0 otherwise | 0.122 | 0.327 |
| Above or equal to undergraduate | Dummy = 1 if the educational background of the respondent is above or equal to undergraduate school, 0 otherwise | 0.334 | 0.472 |
| Permanent employment | Dummy = 1 if the respondent is a permanent employee, 0 otherwise | 0.469 | 0.499 |
| Non-permanent employment | Dummy = 1 if the respondent is a non-permanent employee, 0 otherwise | 0.252 | 0.434 |
| Others | Dummy = 1 if the respondent is doing agriculture, a family business, or freelance, or the respondents is a full-time household/ husband or student, 0 otherwise. | 0.169 | 0.375 |
| Unemployment | Dummy = 1 if the respondent is unemployed, 0 otherwise | 0.110 | 0.313 |
| Presence of children | Dummy = 1 if the respondent has children need to be raised in the household | 0.363 | 0.481 |
| Long-term nursing | Dummy = 1 if the respondent has children need to be raised in the household | 0.159 | 0.365 |
| Interest in participating in non-market activities | Dummy = 1 if the respondent has an interest in participating in non-market activities, 0 otherwise | 0.541 | 0.499 |
| Acceptable | Dummy = 1 if the respondent feels the future vision of a community with BI is acceptable, 0 otherwise | 0.111 | 0.314 |
| Somehow acceptable | Dummy = 1 if the respondent feels the future vision of a community with BI is somehow acceptable, 0 otherwise | 0.219 | 0.414 |
| Neither acceptable nor unacceptable | Dummy = 1 if the respondent feels the future vision of a community with BI is neither acceptable nor unacceptable | 0.410 | 0.492 |
| Somehow unacceptable | Dummy = 1 if the respondent feels the future vision of a community with BI is somehow unacceptable | 0.170 | 0.376 |
| Unacceptable | Dummy = 1 if the respondent feels the future vision of a community with BI is unacceptable | 0.090 | 0.287 |
| Dependent Variable: Attitude toward BI | Odds Ratio | Standard Error |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | 1.599 *** | 0.283 |
| Age | 0.981 *** | 0.006 |
| Economic independence (Reference group: Economically independent) | ||
| Neither economically dependent nor independent | 0.927 | 0.170 |
| Economically dependent | 1.143 | 0.220 |
| Individual income (Reference group: Less than 3 million yen) | ||
| 3-6 million yen | 0.793 | 0.161 |
| 6-9 million yen | 1.036 | 0.345 |
| More than 9 million yen | 0.247 ** | 0.140 |
| Educational background (Reference group: Below or equal to high school) | ||
| Vocational school | 1.802 ** | 0.410 |
| Above or equal to undergraduate | 1.148 | 0.183 |
| Status of employment (Reference group: Others) | ||
| Permanent employment | 1.255 | 0.273 |
| Non-permanent employment | 0.851 | 0.191 |
| Unemployed | 0.873 | 0.252 |
| Presence of children | 1.290 * | 0.196 |
| Long-term nursing | 1.458 * | 0.285 |
| Interest in participating in non-market activities | 1.683 *** | 0.245 |
| Perception of the future vision of a society with BI (Reference group: Somehow acceptable) | ||
| Acceptable | 1.252 | 0.365 |
| Neither acceptable nor unacceptable | 0.239 ** | 0.046 |
| Somehow unacceptable | 0.145 *** | 0.034 |
| Unacceptable | 0.075 *** | 0.024 |
| Constant | 3.312 *** | 1.292 |
| LR chi2(19) | 243.09 | |
| Pseudo R2 | 0.1706 |
| Dependent Variable: Attitude toward BI | dy/dx | Standard Error |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.092 *** | 0.034 |
| Age | −0.004 *** | 0.001 |
| Economic independence (Reference group: Economically independent) | ||
| Neither economically dependent nor independent | −0.015 | 0.036 |
| Economically dependent | 0.026 | 0.038 |
| Individual income (Reference group: Less than 3 million yen) | ||
| 3–6 million yen | −0.045 | 0.040 |
| 6–9 million yen | 0.007 | 0.065 |
| More than 9 million yen | −0.274 ** | 0.110 |
| Educational background (Reference group: Below or equal to high school) | ||
| Vocational school | 0.115 *** | 0.044 |
| Above or equal to undergraduate | 0.027 | 0.031 |
| Status of employment (Reference group: Others) | ||
| Permanent employment | 0.044 | 0.042 |
| Non-permanent employment | −0.031 | 0.044 |
| Unemployed | −0.027 | 0.056 |
| Presence of children | 0.050 * | 0.030 |
| Long-term nursing | 0.074 * | 0.038 |
| Interest in participating in non-market activities | 0.102 *** | 0.028 |
| Perception of the future vision of a society with BI (Reference group: Somehow acceptable) | ||
| Acceptable | 0.044 | 0.057 |
| Neither acceptable nor unacceptable | −0.279 *** | 0.034 |
| Somehow unacceptable | −0.377 *** | 0.040 |
| Unacceptable | −0.506 *** | 0.056 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Mohan, G.; Fukushi, K. An Analysis of the Factors Influencing Public Attitudes toward Implementing Basic Income (BI) from an Individual Perspective: A Case Study of Hokuriku Region, Japan. Societies 2020, 10, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc10030052
Yang J, Mohan G, Fukushi K. An Analysis of the Factors Influencing Public Attitudes toward Implementing Basic Income (BI) from an Individual Perspective: A Case Study of Hokuriku Region, Japan. Societies. 2020; 10(3):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc10030052
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jiaqi, Geetha Mohan, and Kensuke Fukushi. 2020. "An Analysis of the Factors Influencing Public Attitudes toward Implementing Basic Income (BI) from an Individual Perspective: A Case Study of Hokuriku Region, Japan" Societies 10, no. 3: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc10030052
APA StyleYang, J., Mohan, G., & Fukushi, K. (2020). An Analysis of the Factors Influencing Public Attitudes toward Implementing Basic Income (BI) from an Individual Perspective: A Case Study of Hokuriku Region, Japan. Societies, 10(3), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc10030052




