Annual Baseline King-Devick Oculomotor Function Testing Is Needed Due to Scores Varying by Age
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. King-Devick Test
2.3. Data Collection Procedures
2.4. Procedures
2.5. Statistical Analyses
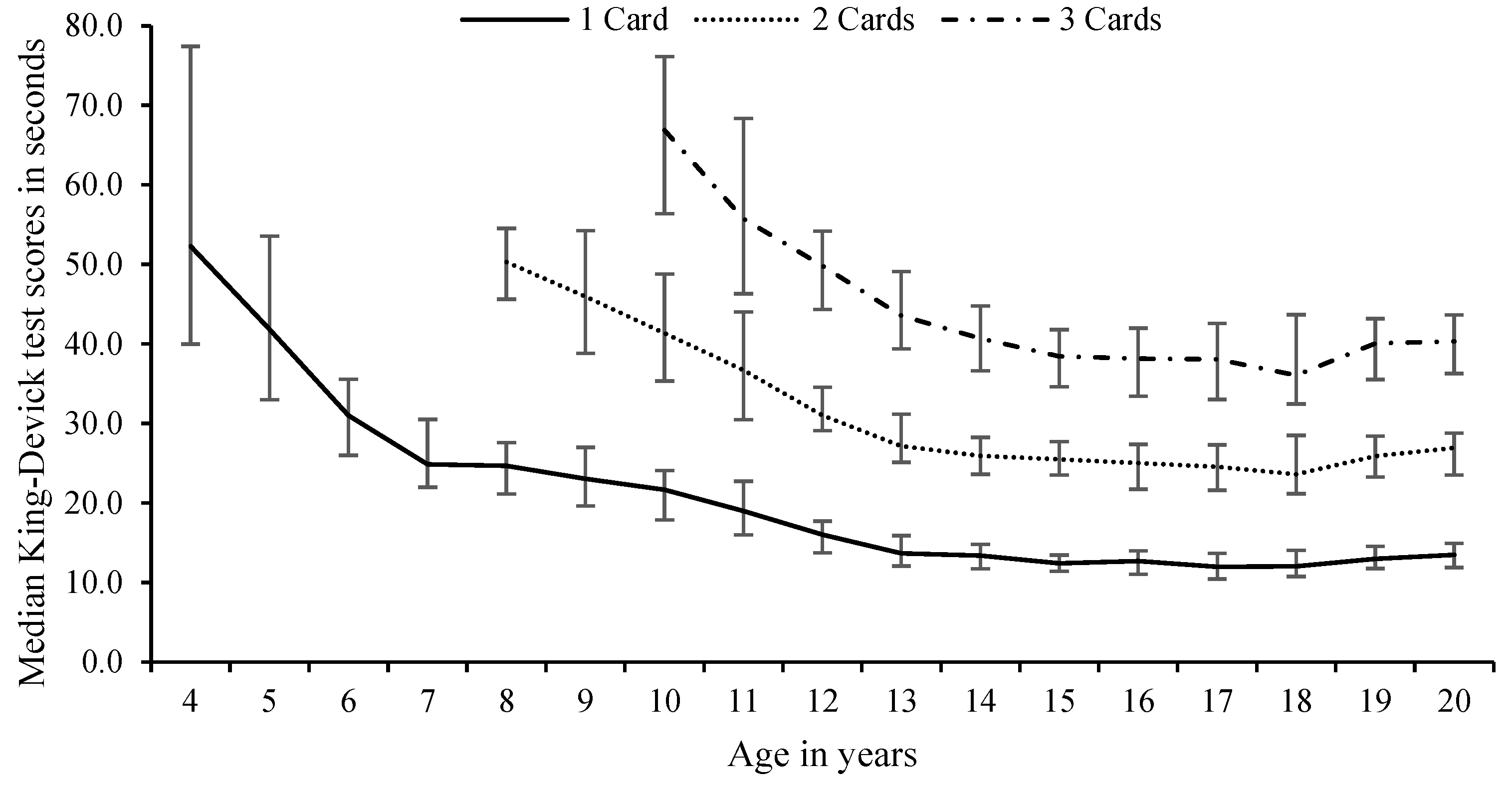
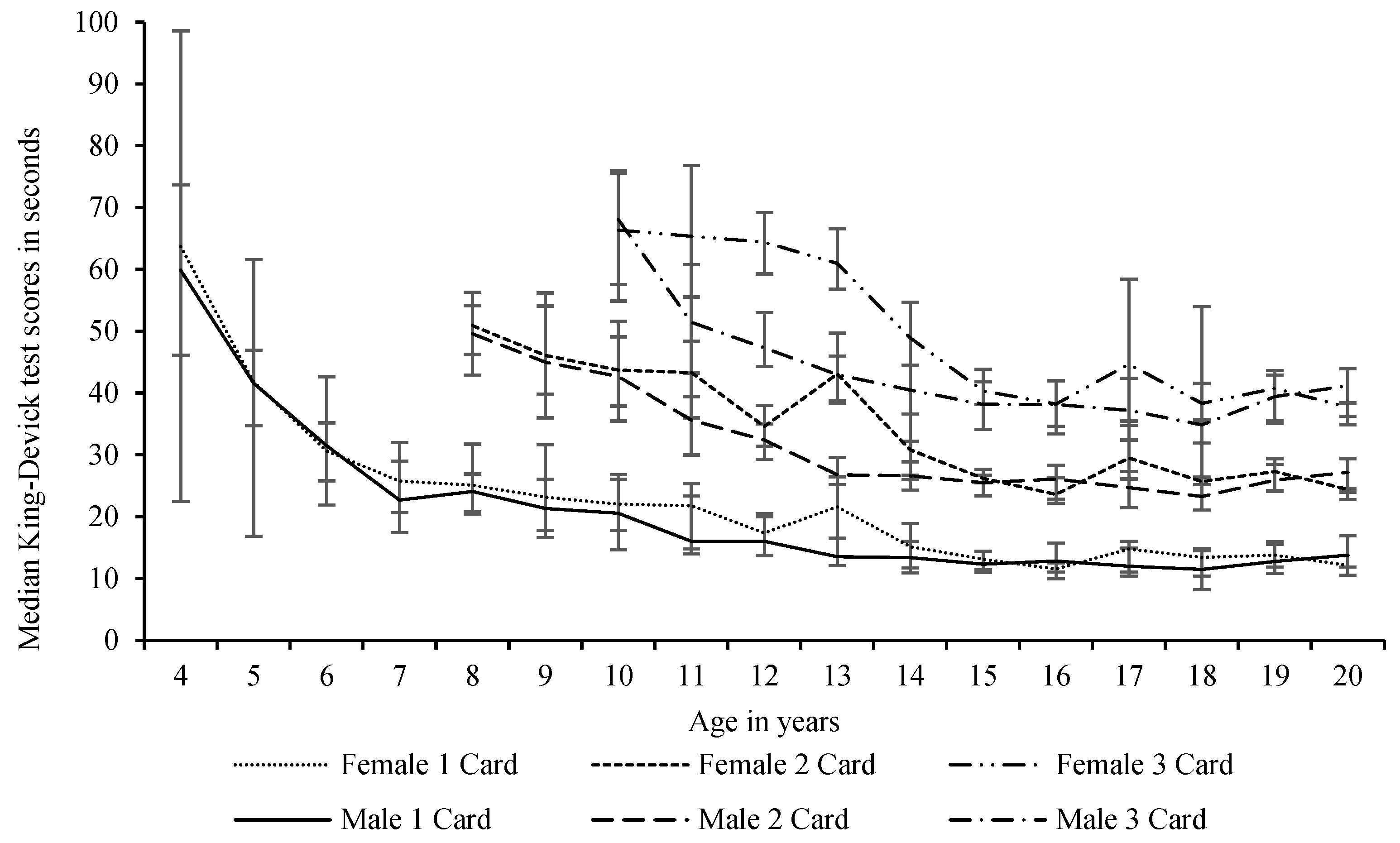
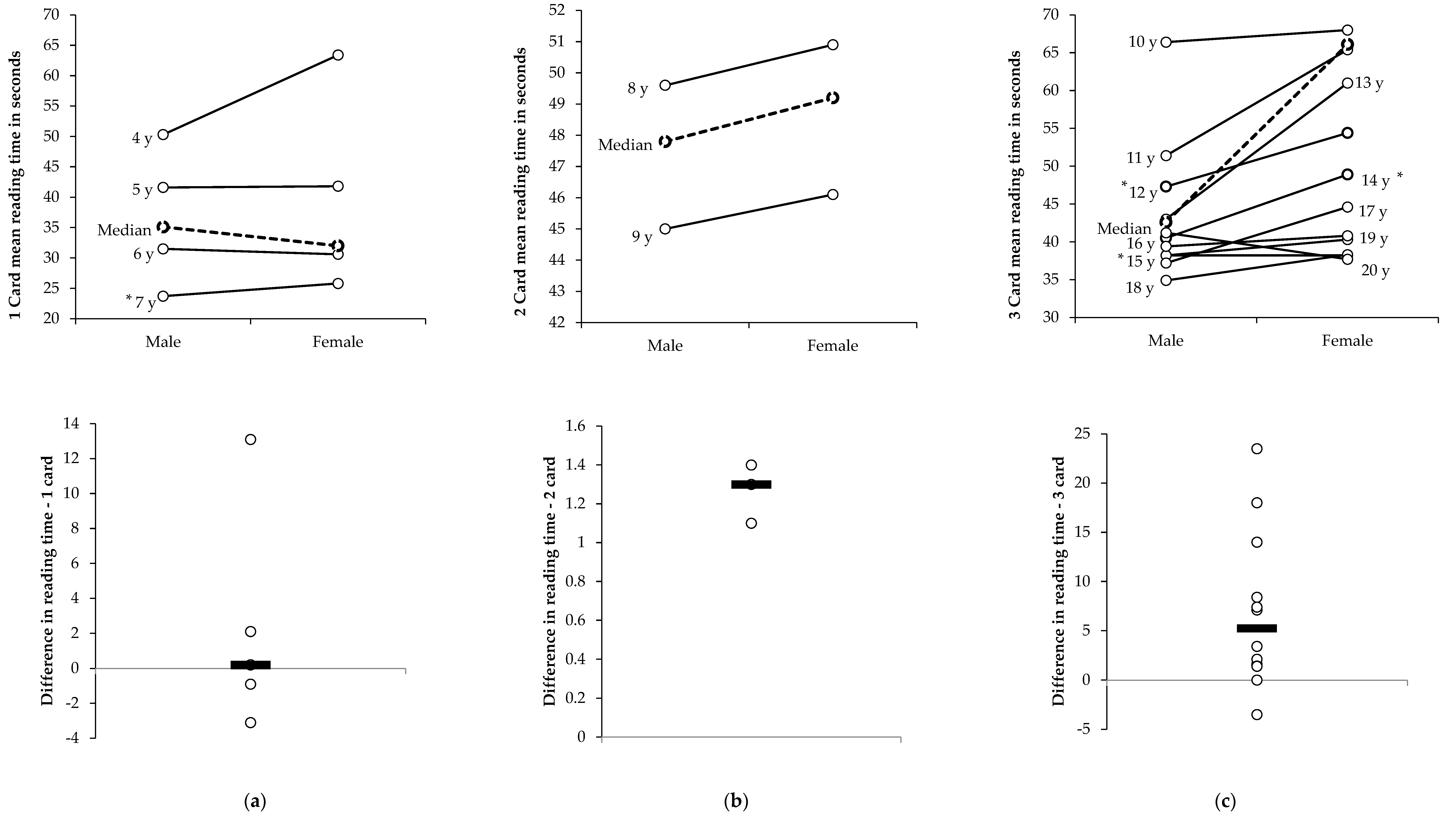
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khurana, V.G.; Kaye, A.H. An overview of concussion in sport. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2012, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, D.; Brughelli, M.; Hume, P.; Gissane, C. Assessment, Management and Knowledge of Sport-Related Concussion: Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 449–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, G.; Purcell, L. The evaluation and management of acute concussion differs in young children. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 48, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrory, P.; Meeuwisse, W.; Dvořák, J.; Aubry, M.; Bailes, J.; Broglio, S.; Cantu, R.C.; Cassidy, D.; Echemendia, R.J.; Castellani, R.J.; et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport—The 5th international conference on concussion in sport held in Berlin, October 2016. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 838–847. [Google Scholar]
- Echemendia, R.J.; Meeuwisse, W.; McCrory, P.; Davis, G.A.; Putukian, M.; Leddy, J.; Makdissi, M.; Sullivan, S.J.; Broglio, S.P.; Raftery, M.; et al. The Sport Concussion Assessment Tool 5th Edition (SCAT5): Background and rationale. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 848–850. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davis, G.A.; Purcell, L.; Schneider, K.J.; Yeates, K.O.; Gioia, G.A.; Anderson, V.; Ellenbogen, R.G.; Echemendia, R.J.; Makdissi, M.; Sills, A.; et al. The Child Sport Concussion Assessment Tool 5th Edition (Child SCAT5): Background and rationale. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 859–861. [Google Scholar]
- Eckner, J.; Kutcher, J. Concussion symptoms scales and sideline assessment tools: A critical literature update. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2010, 9, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galetta, K.; Morganroth, J.; Moehringer, N.; Mueller, B.; Hasanaj, L.; Webb, N.; Civitano, C.; Cardone, D.A.; Silverio, A.; Galetta, S.L.; et al. Adding vision to concussion Testing: A prospective study of sideline testing in youth and collegiate athletes. J. Neuroophthalmol. 2015, 35, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinides, Z.; Galetta, K.M.; Andrews, C.N.; Wilson, J.A.; Herman, D.C.; Robinson, C.D.; Smith, M.S.; Bentley, B.C.; Galetta, S.L.; Balcer, L.J.; et al. Vision testing is additive to the sideline assessment of sports-related concussion. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2015, 5, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Echemendia, R.J.; Broglio, S.P.; Davis, G.A.; Guskiewicz, K.M.; Hayden, K.A.; Leddy, J.J.; Meehan, W.P.; Putukian, M.; Sullivan, S.J.; Schneider, K.; et al. What tests and measures should be added to the SCAT3 and related tests to improve their reliability, sensitivity and/or specificity in sideline concussion diagnosis? A systematic review. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talavage, T.M.; Nauman, E.A.; Breedlove, E.L.; Yoruk, U.; Dye, A.E.; Morigaki, K.E.; Feuer, H.; Leverenz, L.J. Functionally-Detected Cognitive Impairment in High School Football Players without Clinically-Diagnosed Concussion. J. Neurotrauma 2014, 31, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galetta, K.M.; Liu, M.; Leong, D.F.; Ventura, R.E.; Galetta, S.L.; Balcer, L.J. The King-Devick test of rapid number naming for concussion detection: Meta-analysis and systematic review of the literature. Concussion 2016, 1, CNC8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heitger, M.H.; Jones, R.; MacLeod, A.D.; Snell, D.L.; Frampton, C.M.; Anderson, T.J. Impaired eye movements in post-concussion syndrome indicate suboptimal brain function beyond the influence of depression, malingering or intellectual ability. Brain 2009, 132, 2850–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.; Hume, P.; Gissane, C.; Clark, T. Use of the King–Devick test for sideline concussion screening in junior rugby league. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 357, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galetta, K.M.; Barrett, J.; Allen, M.; Madda, F.; Delicata, D.; Tennant, A.T.; Branas, C.C.; Maguire, M.G.; Messner, L.V.; Devick, S.; et al. The King-Devick test as a determinant of head trauma and concussion in boxers and MMA fighters. Neurology 2011, 76, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tjarks, B.J.; Dorman, J.C.; Valentine, V.D.; Munce, T.A.; Thompson, P.A.; Kindt, S.L.; Bergeron, M.F. Comparison and utility of King-Devick and ImPACT® composite scores in adolescent concussion patients. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 334, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, D.F.; Balcer, L.J.; Galetta, S.L.; Liu, Z.; Master, C. The King-Devick test as a concussion screening tool administered by sports parents. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2014, 54, 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Chrisman, S.; Quitiquit, C.; Rivara, F.P. Qualitative Study of Barriers to Concussive Symptom Reporting in High School Athletics. J. Adolesc. Health 2013, 52, 330–335.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meehan, W., III; d’Hemecourt, P.; Collins, C.; Comstock, R. Assessment and management of sport-related concussions in United States high schools. Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 2304–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrory, P.; Meeuwisse, W.; Aubry, M.; Cantu, R.; Dvořák, J.; Echemendia, R.; Engebretsen, L.; Johnston, K.; Kutcher, J.S.; Raftery, M.; et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport: The 4th International Conference on Concussion in Sport held in Zurich, November 2012. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, D.; Gissane, C.; Hume, P.; Flaws, M. The King–Devick test was useful in management of concussion in amateur rugby union and rugby league in New Zealand. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 351, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsalaheen, B.; Haines, J.L.; Yorke, A.; Diebold, J. King-Devick Test reference values and associations with balance measures in high school American football players. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 26, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartiainen, M.V.; Holm, A.; Peltonen, K.; Luoto, T.; Iverson, G.; Hokkanen, L. King-Devick test normative reference values for professional male ice hockey players. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 25, e327–e330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oride, M.K.H.; Marutani, J.K.; Rouse, M.W.; Deland, P.N. Reliability study of the Pierce and King-Devick saccade tests. Am. J. Optom. Physiol. Optics. 1986, 63, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rist, B.; Cohen, A.; Pearce, A. King-Devick performance following moderate to high exercise intensity bouts. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2017, 10, 619–628. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioural Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, W.G.; Marshall, S.W.; Batterham, A.M.; Hanin, J. Progressive Statistics for Studies in Sports Medicine and Exercise Science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silverberg, N.D.; Luoto, T.; Ohman, J.; Iverson, G. Assessment of mild traumatic brain injury with the King-Devick Test® in an emergency department sample. Brain Inj. 2014, 28, 1590–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieberman, S.; Cohen, A.H.; Rubin, J. NYSOA K-D test. J. Am. Optom. Assoc. 1983, 54, 631–637. [Google Scholar]
- Konynenbelt, B.; Harris, P.; Pérez Robles, F. A comparison of performance on the NYSOA King-Devick Test between Mexican and American school-aged children. Optom Vis. Perform. 2016, 4, 221–224. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, H.D.; Biely, S.A. Baseline King–Devick scores for adults are not generalizable; however, age and education influence scores. Brain Inj. 2017, 31, 1813–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinton-Bayre, A.D. Normative Versus Baseline Paradigms for Detecting Neuropsychological Impairment Following Sports-Related Concussion. Brain Impair. 2015, 16, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.; Register-Mihalik, J.; Milhalik, J.; Kerr, Z.; Guskiewicz, K. Identifying impairments after concussion: Normative data versus individualized baselines. Med. Sci. Sport Exerc. 2012, 44, 1621–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valovich McLeod, T.; Bay, R.; Lam, K.; Chhabra, A. Representative baseline values on the Sport Concussion Assessment Tool 2 (SCAT2) in adolescent athletes vary by gender, grade, and concussion history. Am. J. Sports Med. 2012, 40, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echemendia, R.J.; Bruce, J.M.; Bailey, C.M.; Sanders, J.F.; Arnett, P.; Vargas, G. The Utility of Post-Concussion Neuropsychological Data in Identifying Cognitive Change Following Sports-Related MTBI in the Absence of Baseline Data. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2012, 26, 1077–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmon, K.G.; Drezner, J.A.; Gammons, M.; Guskiewicz, K.; Halstead, M.; Herring, S.A.; Kutcher, J.S.; Pana, A.; Putukian, M.; Roberts, W.O. American Medical Society for Sports Medicine position statement: Concussion in sport. Br. J. Sports Med. 2012, 47, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabinowitz, A.R.; Arnett, P.A. Reading Based IQ Estimates and Actual Premorbid Cognitive Performance: Discrepancies in a College Athlete Sample. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2012, 18, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaplan, G.A.; Turrell, G.; Lynch, J.W.; Everson, S.A.; Helkala, E.-L.; Salonen, J.T. Childhood socioeconomic position and cognitive function in adulthood. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 30, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kontos, A.P.; Elbin, R.J.; Covassin, T.; Larson, E. Exploring Differences in Computerized Neurocognitive Concussion Testing Between African American and White Athletes. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2010, 25, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Covassin, T.; Elbin, R.; Kontos, A.; Larson, E. Investigating baseline neurocognitive performance between male and female athletes with a history of multiple concussion. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2010, 81, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Covassin, T.; Elbin, R.; Bleecker, A.; Lipchik, A.; Kontos, A.P. Are There Differences in Neurocognitive Function and Symptoms Between Male and Female Soccer Players After Concussions? Am. J. Sports Med. 2013, 41, 2890–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, A.; Piecora, K.; Schuster, D.; Webbe, F. Sport and Team Differences on Baseline Measures of Sport-Related Concussion. J. Athl. Train. 2013, 48, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moran, R.; Covassin, T. Risk factors associated with baseline King-Devick performance. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 383, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynowska, J.; Hasanaj, L.; Zhang, I. Agreement of the spiral-bound and computerized tablet versions of the King-Devick test of rapid number naming for sports concussion. Ann. Sports Med. Res. 2015, 2 (Suppl. 16), 1051. [Google Scholar]
- Galetta, K.M.; Brandes, L.E.; Maki, K.; Dziemianowicz, M.S.; Laudano, E.; Allen, M.; Lawler, K.; Sennett, B.; Wiebe, D.; Devick, S.; et al. The King–Devick test and sports-related concussion: Study of a rapid visual screening tool in a collegiate cohort. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 309, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, D.; Brown, N.; Gissane, C. Reported concussion incidence in youth community Rugby Union and parental assessment of post head injury cognitive recovery using the King-Devick test. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 388, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Trial 1 (s) | Trial 2 (s) | Difference Trial 1 vs. Trial 2 (s) | Baseline/Fastest Times (s) | Slowest Times (s) | Difference Fastest vs. Slowest (s) | Test–retest and Cronbach’s α between Trial 1 and Trial 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n= | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | α= | ICC (95% CI) | ||
| 1 Card (4–7 years) | Male | 336 | 36.0 (27.4–51.3) bd | 38.6 (30.5–56.8) ad | 2.2 (−1.5–10.0) | 35.1 (26.0–48.6) df | 41.2 (31.4–61.2) de | −5.0 (−11.0–−2.0) | 0.946 | 0.940 (0.911–0.957) |
| Female | 290 | 33.1 (27.0–43.2) bc | 35.4 (29.1–50.0) ac | 2.8 (−1.4–7.0) | 32.0 (26.1–42.0) cf | 36.7 (30.3–50.8) ce | −4.4 (−8.6–−1.9) | 0.961 | 0.957 (0.938–0.969) | |
| Combined sexes | 626 | 34.0 (27.0–47.1) b | 37.1 (29.7–52.5) a | 2.4 (−1.4–8.4) | 33.1 (26.1–45.1) f | 38.6 (31.0–54.7) e | −4.5 (−10.0–−2.0) | 0.955 | 0.950 (0.929–0.963) | |
| 2 Cards (8 and 9 years) | Male | 130 | 48.6 (41.2–56.3) b | 54.3 (46.7–67.1) a | 6.2 (3.2–15.4) | 47.8 (41.2–56.0) f | 57.0 (47.2–67.1) e | −6.2 (−15.4–3.9) | 0.871 | 0.782 (0.218–0.908) |
| Female | 146 | 49.8 (43.9–54.8) b | 53.6 (48.4–58.6) a | 4.7 (1.0–8.4) | 49.2 (43.5–54.1) f | 54.5 (49.4–59.1) e | −4.9 (−8.4–−2.1) | 0.867 | 0.818 (0.549–0.907) | |
| Combined sexes | 276 | 49.4 (42.6–55.3) b | 54.1 (48.0–62.2) a | 5.4 (1.9–11.0) | 49.0 (42.1–54.4) f | 54.6 (48.4–62.3) e | −5.5 (−11.2–−2.7) | 0.864 | 0.796 (0.413–0.902) | |
| 3 Cards (10+ years) | Male | 834 | 44.4 (38.8–53.3) b | 40.6 (35.3–45.9) a | 1.3 (−0.5–3.2) | 42.9 (37.2–48.3) f | 42.7 (39.6–51.7) e | −2.1 (−3.7–−0.9) | 0.996 | 0.950 (0.921–0.966) |
| Female | 200 | 66.4 (51.2–79.2) b | 70.0 (65.5–74.2) a | 2.1 (0.2–4.1) | 66.1 (51.2–79.2) f | 72.2 (69.1–76.4) e | −2.6 (−4.6–−1.3) | 0.957 | 0.996 (0.995–0.997) | |
| Combined sexes | 1034 | 46.5 (39.7–58.1) b | 40.5 (36.0–45.7) a | −1.4 (−3.4–0.4) | 40.5 (35.6–45.7) f | 46.5 (39.7–58.1) e | −2.1 (−3.8–−0.9) | 0.955 | 0.948 (0.915–0.965) | |
| Total Score | Male | 1300 | 43.7 (36.3–53.3) | 41.5 (34.6–50.5) d | 0.0 (−2.7–3.7) | 42.0 (35.0–52.3) f | 43.8 (36.7–53.4) de | −3.0 (−6.2–−1.3) | 0.900 | 0.894 (0.881–0.907) |
| Female | 636 | 45.7 (33.6–62.0) b | 42.7 (33.0–54.7) ac | 2.6 (−1.4–7.0) | 45.0 (32.4–60.0) f | 44.0 (34.0–55.9) ce | −4.3 (−8.3–−2.0) | 0.953 | 0.951 (0.942–0.959) | |
| Combined sexes | 1966 | 44.0 (35.5–55.0) b | 41.9 (34.0–52.6) a | 0.6 (−2.2–5.3) | 42.6 (34.3–54.0) f | 43.6 (35.6–53.9) e | −3.3 (−7.0–−1.5) | 0.917 | 0.913 (0.904–0.921) | |
| No of Cards | Differences from | Range of Differences (s) | Differences | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Previous Age (s) | across Ages | ||||
| Median (IQR) | Min–Max | t= | p= | ||
| Female | 1 card | −1.6 (−4.8–−0.4) | −21.9–4.2 | −2.1 | 0.0535 |
| 2 card | −2.8 (−4.8–1.1) | −12.3–8.5 | −1.3 | 0.2069 | |
| 3 card | −2.6 (−6.9–−0.1) | −12.1–6.4 | −1.7 | 0.1208 | |
| All cards | −2.0 (−4.8–−0.3) | −21.9–8.5 | −3.0 | 0.0053 | |
| Male | 1 card | −0.8 (−4.1–0.4) | −18.3–1.4 | −2.2 | 0.0466 |
| 2 card | −1.4 (−4.2–0.4) | −7.1–2.6 | −2.3 | 0.0457 | |
| 3 card | −2.3 (−4.2–0.4) | −16.6–4.5 | −1.5 | 0.1632 | |
| All cards | −1.4 (−4.2–0.0) | −18.3–4.5 | −3.4 | 0.0016 | |
| Sexes Combined | 1 card | −1.2 (−2.9–−0.1) | −10.8–0.9 | −2.7 | 0.0176 |
| 2 card | −1.1 (−4.5–−0.4) | −5.7–2.3 | −2.6 | 0.0237 | |
| 3 card | −2.1(−6.0–0.0) | −11.2–4.0 | −2.0 | 0.0786 | |
| All cards | −1.4 (−4.5–−0.3) | −11.2–4.0 | −4.2 | 0.0001 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gallagher, D.; King, D.; Hume, P.; Clark, T.; Pearce, A.; Gissane, C. Annual Baseline King-Devick Oculomotor Function Testing Is Needed Due to Scores Varying by Age. Sports 2021, 9, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9120166
Gallagher D, King D, Hume P, Clark T, Pearce A, Gissane C. Annual Baseline King-Devick Oculomotor Function Testing Is Needed Due to Scores Varying by Age. Sports. 2021; 9(12):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9120166
Chicago/Turabian StyleGallagher, Dearbhla, Doug King, Patria Hume, Trevor Clark, Alan Pearce, and Conor Gissane. 2021. "Annual Baseline King-Devick Oculomotor Function Testing Is Needed Due to Scores Varying by Age" Sports 9, no. 12: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9120166
APA StyleGallagher, D., King, D., Hume, P., Clark, T., Pearce, A., & Gissane, C. (2021). Annual Baseline King-Devick Oculomotor Function Testing Is Needed Due to Scores Varying by Age. Sports, 9(12), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9120166







