Acute and Long-Term Effects of Attentional Focus Strategies on Muscular Strength: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Methodological Quality
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
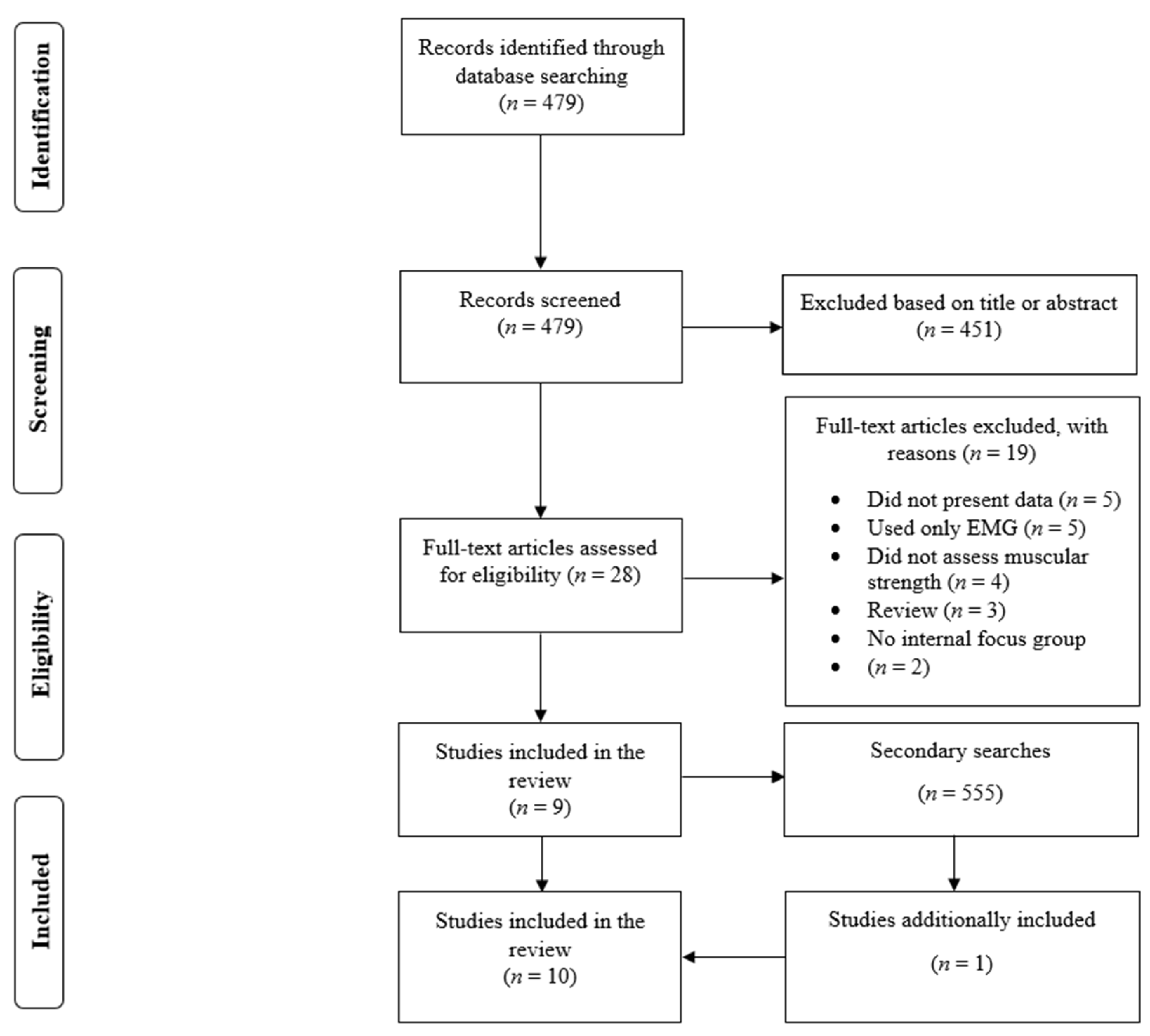
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Summary of Studies
3.3. Methodological Quality
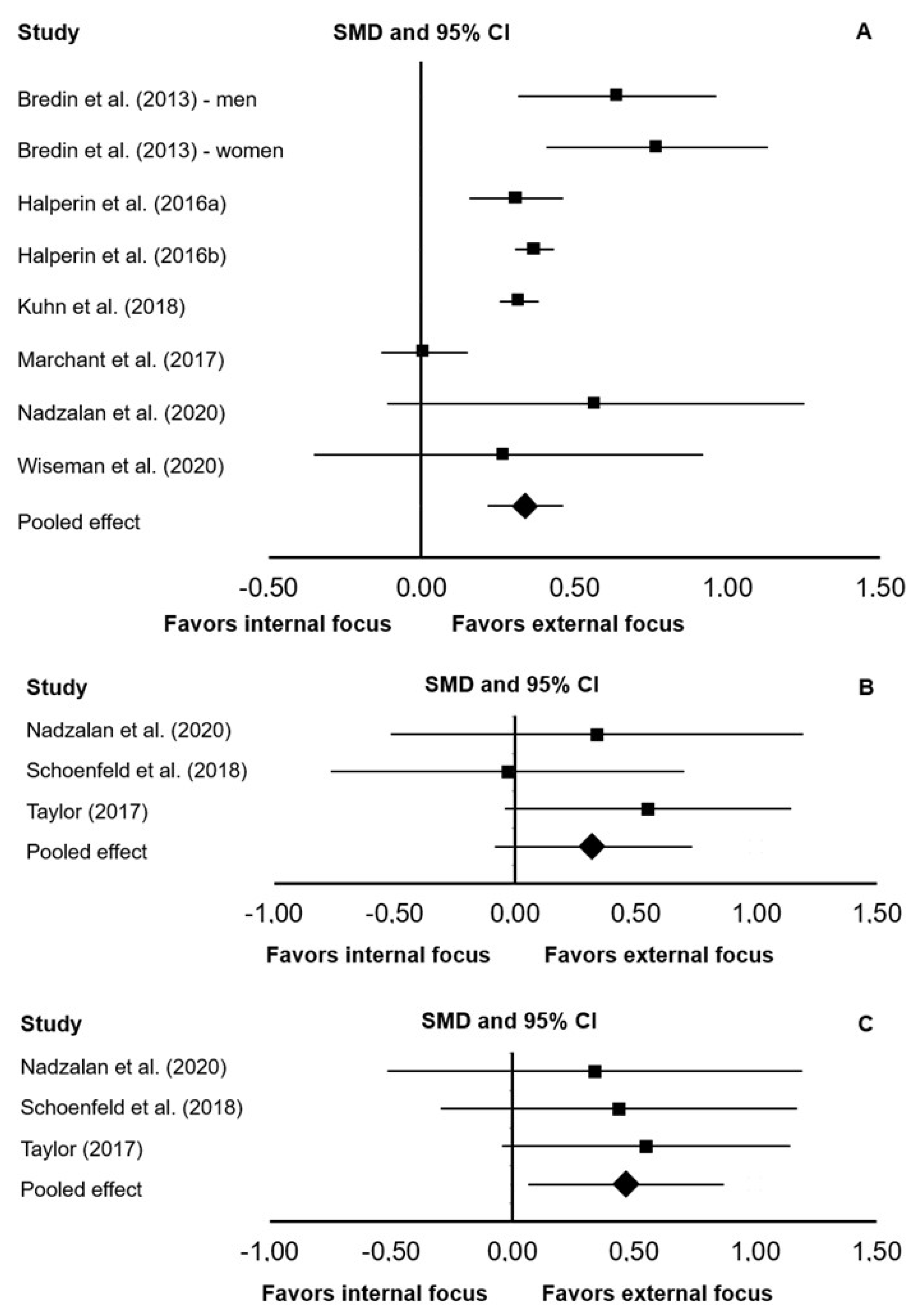
3.4. Meta-Analysis Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wulf, G. Attentional focus and motor learning: A review of 15 years. Int. Rev. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2013, 6, 77–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulf, G.; Höß, M.; Prinz, W. Instructions for motor learning: Differential effects of internal versus external focus of attention. J. Mot. Behav. 1998, 30, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, R.; Button, C. End-point focus of attention: Learning the catch in rowing. Int. J. Sport Psychol. 2009, 40, 616–635. [Google Scholar]
- Wulf, G.; Su, J. An external focus of attention enhances golf shot accuracy in beginners and experts. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2007, 78, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachry, T.; Wulf, G.; Mercer, J.; Bezodis, N. Increased movement accuracy and reduced EMG activity as the result of adopting an external focus of attention. Brain Res. Bull. 2005, 67, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, M.; Letafatkar, A.; Thomas, A.C.; Keyhani, S. Effects of a neuromuscular training program using external focus attention cues in male athletes with anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: A randomized clinical trial. BMC. Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhi, B.; Letafatkar, A.; Thomas, A.C.; Ford, K.R. Altered trunk and lower extremity movement coordination after neuromuscular training with and without external focus instruction: A randomized controlled trial. BMC. Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 13, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calatayud, J.; Vinstrup, J.; Jakobsen, M.D.; Sundstrup, E.; Brandt, M.; Jay, K.; Colado, J.C.; Andersen, L.L. Importance of mind-muscle connection during progressive resistance training. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 116, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, M.; Samani, A.; Vuillerme, N.; Madeleine, P.; Hansen, E.A. External and internal focus of attention increases muscular activation during bench press in resistance-trained participants. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 2442–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, D.C.; Greig, M.; Bullough, J.; Hitchen, D. Instructions to adopt an external focus enhance muscular endurance. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2011, 82, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, J.; Wulf, G.; Töllner, T.; McNevin, N.; Mercer, J. EMG activity as a function of the performer’s focus of attention. J. Mot. Behav. 2004, 36, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, A.; Mancin, L.; Saoncella, M.; Grigoletto, D.; Pacelli, F.Q.; Zamparo, P.; Schonefeld, B.J.; Marcolin, G. Mind-muscle connection: Effects of verbal instructions on muscle activity during bench press exercise. Eur. J. Transl. Myol. 2019, 29, 8250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halperin, I.; Williams, K.J.; Martin, D.T.; Chapman, D.W. The effects of attentional focusing instructions on force production during the isometric midthigh pull. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchant, D.C.; Greig, M. Attentional focusing instructions influence quadriceps activity characteristics but not force production during isokinetic knee extensions. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2017, 52, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadzalan, A.M.; Lee, J.L.F.; Azzfar, M.S.; Muhammad, N.S.; Shukri, E.W.M.C.; Mohamad, N.I. The effects of resistance training with different focus attention on muscular strength: Application to teaching methods in physical conditioning class. IJITEE 2019, 8, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Schoenfeld, B.J.; Vigotsky, A.; Contreras, B.; Golden, S.; Alto, A.; Larson, R.; Winkelman, N.; Paoli, A. Differential effects of attentional focus strategies during long-term resistance training. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2018, 18, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchomel, T.J.; Nimphius, S.; Stone, M.H. The importance of muscular strength in athletic performance. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 1419–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.X.M.; Yao, J.; Zirek, Y.; Reijnierse, E.M.; Maier, A.B. Muscle mass, strength, and physical performance predicting activities of daily living: A meta-analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maher, C.G.; Sherrington, C.; Herbert, R.D.; Moseley, A.M.; Elkins, M. Reliability of the PEDro scale for rating quality of randomized controlled trials. Phys. Ther. 2003, 83, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grgic, J.; Pickering, C. The effects of caffeine ingestion on isokinetic muscular strength: A meta-analysis. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2019, 22, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grgic, J.; Trexler, E.T.; Lazinica, B.; Pedisic, Z. Effects of caffeine intake on muscle strength and power: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2018, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G.; Higgins, J.P.; Green, S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0. In Chapter 16.1.3.2: Imputing Standard Deviations for Changes from Baseline; The Cochrane Collaboration: Chichester, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. A power primer. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 112, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredin, S.S.; Dickson, D.B.; Warburton, D.E. Effects of varying attentional focus on health-related physical fitness performance. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 38, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halperin, I.; Hughes, S.; Panchuk, D.; Abbiss, C.; Chapman, D.W. The effects of either a mirror, internal or external focus instructions on single and multi-joint tasks. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, Y.A.; Keller, M.; Lauber, B.; Taube, W. Surround inhibition can instantly be modulated by changing the attentional focus. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nadzalan, A.M.; Lee, J.L.F.; Mohamad, N.I.; Azzfar, M.S.; Abd Malek, N.F.; Waqqash, E. The effects of focus attention Instructions on the movement kinetics, muscle activation and performance during resistance exercise. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1529, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiseman, S.; Alizadeh, S.; Halperin, I.; Lahouti, B.; Snow, N.J.; Power, K.E.; Button, D.C. Neuromuscular mechanisms underlying changes in force production during an attentional focus task. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, L. The Impact of Attentional Focus Cueing within a Training Intervention on Back Squat and Deadlift Performance in Team Sport Athletes; St Mary’s University: Twickenham, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wulf, G.; McNevin, N.; Shea, C.H. The automaticity of complex motor skill learning as a function of attentional focus. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. Sect. A 2001, 54, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgic, J.; Lazinica, B.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Pedisic, Z. Test-retest reliability of the one-repetition maximum (1RM) strength assessment: A systematic review. Sports Med. Open 2020, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Sports Medicine. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Progression models in resistance training for healthy adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 687–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makaruk, H.; Porter, J.M.; Czaplicki, A.; Sadowski, J.; Sacewicz, T. The role of attentional focus in plyometric training. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2012, 52, 319–327. [Google Scholar]
- Diekfuss, J.A.; Rhea, C.K.; Schmitz, R.J.; Grooms, D.R.; Wilkins, R.W.; Slutsky, A.B.; Raisbeck, L.D. The influence of attentional focus on balance control over seven days of training. J. Mot. Behav. 2019, 51, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulf, G. Attentional focus and motor learning: A review of 10 years of research. Bewegung. Train. 2007, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
| Reference | Participants | External Focus Instructions | Internal Focus Instructions | Exercise Test | Training Intervention | Pedro Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bredin et al. (2013) [25] | 8 young men and 8 young women | Concentrate on the wall marker during the test | Concentrate specifically on the fingers | Handgrip strength | n/a | 6 |
| Halperin et al. (2016a) [13] | 18 trained athletes (10 men and 8 women) | “Focus on pushing the ground as hard and as fast as you possibly can.” | “Focus on contracting your leg muscles as hard and as fast as you possibly can.” | Isometric mid-thigh pull | n/a | 7 |
| Halperin et al. (2016b) [26] | 28 resistance-trained participants (14 men and 14 women) | “Attempt to produce as much force as you possibly can while focusing on pulling the strap as hard and as fast as you can.” | “Attempt to produce as much force as you possibly can while focusing on contracting your arm muscles as hard and as fast as you can.” | Elbow flexion MVC | n/a | 6 |
| Kuhn et al. (2018) [27] | 14 participants (11 men and 3 women) | “Exert pressure on the force transducer so that the moving line increases as fast as possible to the maximum after the tone.” | “Contract your finger flexor muscles so that the moving line increases as fast as possible to the maximum after the tone.” | Index finger flexion MVC | n/a | 6 |
| Marchant et al. (2017) [14] | 20 resistance-trained participants (16 men and 4 women) | “Try to exert maximal effort during the movement whilst focusing on pushing against the pad.” | “Contract the vastus medialis oblique whilst generating maximal effort.” | Isokinetic leg extension | n/a | 5 |
| Nadzalan et al. (2019) [15] | 20 resistance-trained men | Deadlift: “Focus your attention on pulling the bar up.” Squat: “Focus on moving and exerting force through and against the barbell.” | Deadlift: “Focus your attention on extending your knees and hips.” Squat: “Focus on moving and exerting force with your legs.” | Squat and deadlift 1RM | 6 weeks | 5 |
| Nadzalan et al. (2020) [28] | 30 resistance-trained men | Deadlift: “Focus your attention on pulling the bar up.” Squat: “Focus on moving and exerting force through and against the barbell.” | Deadlift: “Focus your attention on extending your knees and hips.” Squat: “Focus on moving and exerting force with your legs.” | Squat and deadlift 10RM | n/a | 5 |
| Schoenfeld et al. (2018) [16] | 27 untrained men | “Get the weight up!” | “Squeeze the muscle!” | Knee extension and elbow flexion MVC | 8 weeks | 6 |
| Taylor (2017) [30] | 44 male university team sport athletes | Squat: “Focus on driving the bar to the ceiling as explosively as possible.” Deadlift: “Focus on pushing the ground away as fast as possible.” | Squat: “Focus on extending at your knees as rapidly as possible.” Deadlift: “Focus on extending at your hips as rapidly as possible.” | Squat and deadlift 1RM | 12 weeks | 7 |
| Wiseman et al. (2020) [29] | 11 resistance-trained men | “Focus on pulling up on the handle as hard and as quickly as you possibly can.” | “Focus on contracting your biceps as hard and as quickly as you possibly can.” | Elbow flexion MVC | n/a | 6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grgic, J.; Mikulic, I.; Mikulic, P. Acute and Long-Term Effects of Attentional Focus Strategies on Muscular Strength: A Meta-Analysis. Sports 2021, 9, 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9110153
Grgic J, Mikulic I, Mikulic P. Acute and Long-Term Effects of Attentional Focus Strategies on Muscular Strength: A Meta-Analysis. Sports. 2021; 9(11):153. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9110153
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrgic, Jozo, Ivan Mikulic, and Pavle Mikulic. 2021. "Acute and Long-Term Effects of Attentional Focus Strategies on Muscular Strength: A Meta-Analysis" Sports 9, no. 11: 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9110153
APA StyleGrgic, J., Mikulic, I., & Mikulic, P. (2021). Acute and Long-Term Effects of Attentional Focus Strategies on Muscular Strength: A Meta-Analysis. Sports, 9(11), 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9110153






