Effects of Strength vs. Plyometric Training on Change of Direction Performance in Experienced Soccer Players
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Method
2.2. Participants
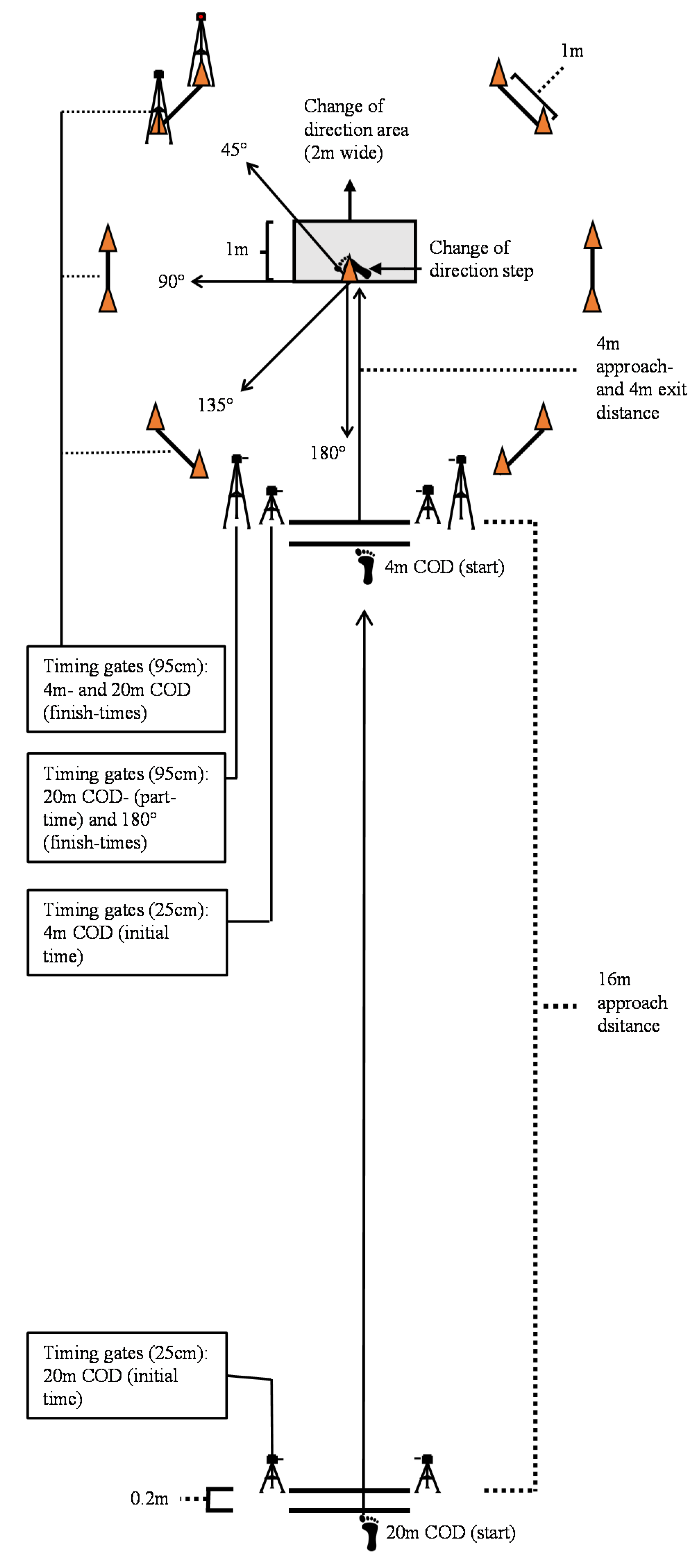
2.3. Procedures
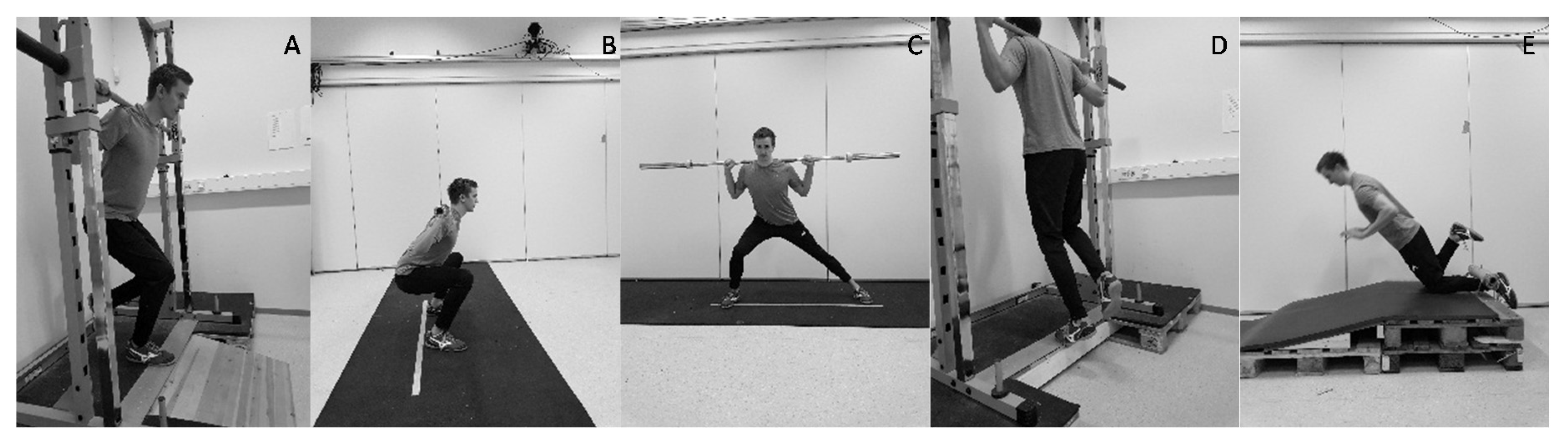
2.4. Strength Performances
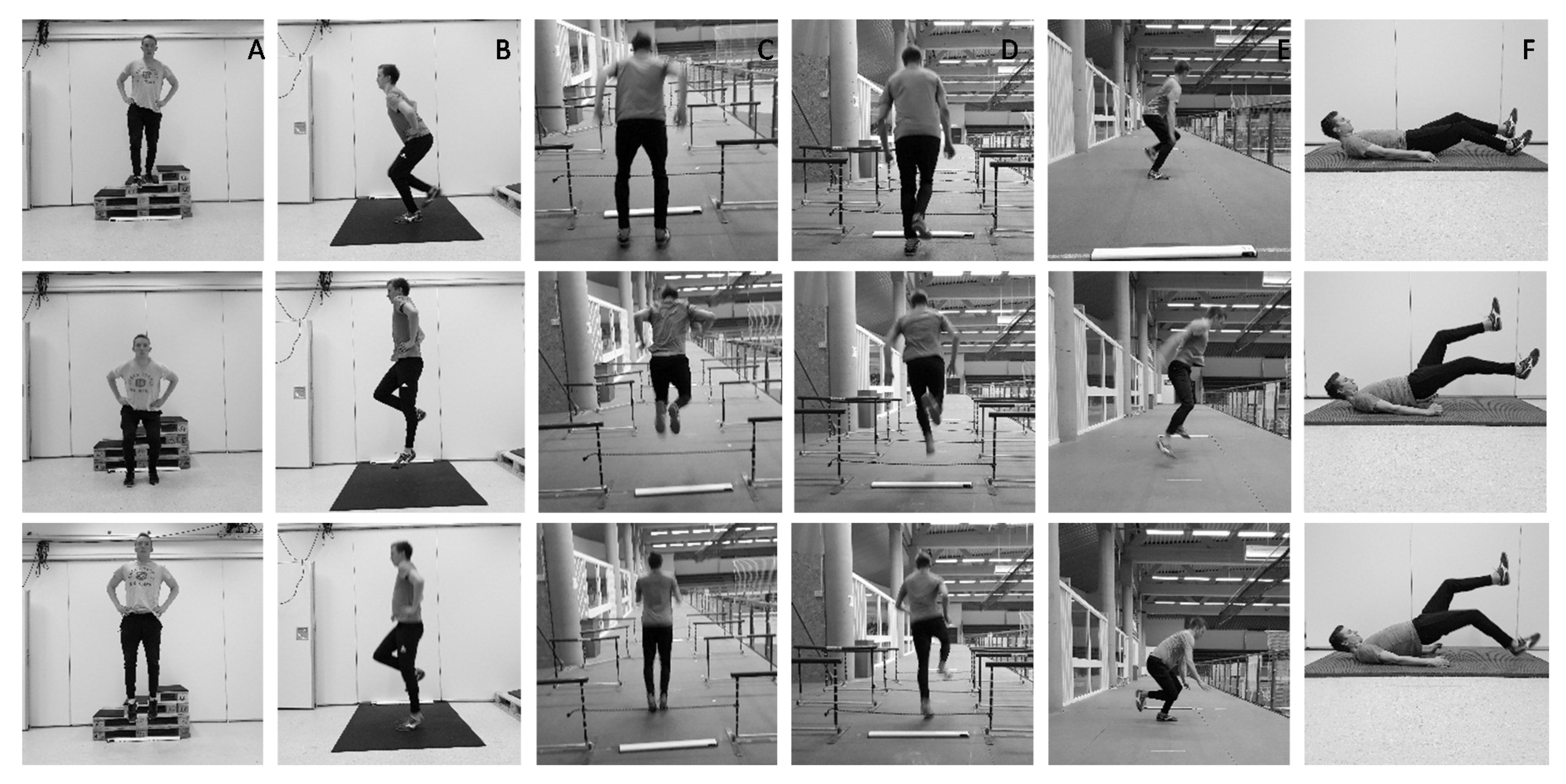
2.5. Plyometric Performances
2.6. Training
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reilly, T.; Williams, A.M.; Nevill, A.; Franks, A. A multidisciplinary approach to talent identification in soccer. J. Sports. Sci. 2000, 18, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangsbo, J. The physiology of soccer: With special reference to intense intermittent exercise. Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl. 1994, 619, 1–155. [Google Scholar]
- Dalen, T.; Ingebrigtsen, J.; Ettema, G.; Hjelde, G.H.; Wisløff, U. Player load, acceleration, and deceleration during forty-five competitive matches of elite soccer. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brughelli, M.; Cronin, J.; Levin, G.; Chaouachi, A. Understanding change of direction ability in sport. Sports Med. 2008, 38, 1045–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, J.M.; Young, W.B. Agility literature review: Classifications, training and testing. J. Sports Sci. 2006, 24, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trecroci, A.; Milanović, Z.; Frontini, M.; Iaia, F.M.; Alberti, G. Physical performance comparison between under 15 elite and sub-elite soccer players. J. Hum. Kinet. 2018, 61, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbett, T.J.; Kelly, J.N.; Sheppard, J.M. Speed, change of direction speed, and reactive agility of rugby league players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2008, 22, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockie, R.G.; Jeffriess, M.D.; McGann, T.S.; Callaghan, S.J.; Schultz, A.B. Planned and reactive agility performance in semiprofessional and amateur basketball players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisic, N.; Jelicic, M.; Pehar, M.; Spasic, M.; Sekulic, D. Agility performance in high-level junior basketball players: The predictive value of anthropometrics and power qualities. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 2016, 56, 884–893. [Google Scholar]
- Trecroci, A.; Longo, S.; Perri, E.; Iaia, F.M.; Alberti, G. Field-based physical performance of elite and sub-elite middle-adolescent soccer players. Res. Sports Med. 2019, 27, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, W.B.; Miller, I.R.; Talpey, S.W. Physical qualities predict change-of-direction speed but not defensive agility in Australian rules football. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadi, A.; Arazi, H.; Young, W.B.; de Villarreal, E.S. The effects of plyometric training on change-of-direction ability: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perf. 2016, 11, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois, F.; McGuigan, M.; Gill, N.; Gamble, G. Physical characteristics and performance in change of direction tasks: A brief review and training considerations. J. Austr. Strength Cond. 2017, 25, 104–117. [Google Scholar]
- Dos’Santos, T.; McBurnie, A.; Thomas, C.; Comfort, P.; Jones, P. Biomechanical comparison of cutting techniques: A review ans practical applications. Strength Cond. J. 2019, 41, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falch, H.N.; Rædergård, H.G.; van den Tillaar, R. Effect of different physical training forms on change of cirection ability: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2019, 5, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, D. A brief review on the role of maximal strength in change of direction speed. J. Austr. Strength Cond. 2015, 23, 100–108. [Google Scholar]
- Nimphius, S.; Callaghan, S.J.; Bezodis, N.E.; Lockie, R.G. Change of direction and agility tests: Challenging our current measures of performance. Strength Cond. J. 2018, 40, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos’Santos, T.; Thomas, C.; Comfort, P.; Jones, P.A. The effect of angle and velocity on change of direction biomechanics: An angle-velocity trade-off. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 2235–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, W.B.; James, R.; Montgomery, I. Is muscle power related to running speed with changes of direction? J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 2002, 42, 282–288. [Google Scholar]
- Nygaard Falch, H.; Guldteig Rædergård, H.; Van den Tillaar, R. Relationship of performance measures and muscle activity between a 180° change of direction task and different countermovement jumps. Sports 2020, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, G.; Mikulic, P. Neuro-musculoskeletal and performance adaptations to lower-extremity plyometric training. Sports Med. 2010, 40, 859–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Hoef, P.A.; Brauers, J.J.; van Smeden, M.; Backx, F.J.G.; Brink, M.S. The effects of lower-pxtremity Plyometric training on soccer-specific outcomes in adult male soccer players: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbalho, M.; Gentil, P.; Raiol, R.; Del Vecchio, F.B.; Ramirez-Campillo, R.; Coswig, V.S. Non-Linear Resistance Training Program Induced Power and Strength but Not Linear Sprint Velocity and Agility Gains in Young Soccer Players. Sports 2018, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coratella, G.; Beato, M.; Cè, E.; Scurati, R.; Milanese, C.; Schena, F.; Esposito, F. Effects of in-season enhanced negative work-based vs traditional weight training on change of direction and hamstrings-to-quadriceps ratio in soccer players. Biol. Sport 2019, 36, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Campillo, R.; Alvarez, C.; Gentil, P.; Loturco, I.; Sanchez-Sanchez, J.; Izquierdo, M.; Moran, J.; Nakamura, F.Y.; Chaabene, H.; Granacher, U. Sequencing effects of plyometric training applied before or after regular soccer raining on measures of physical fitness in young players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 1959–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.; Coratella, G.; Dello Iacono, A.; Beato, M. Comparative effects of single vs. double weekly plyometric training sessions on jump, sprint and change of directions abilities of elite youth football players. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 2019, 59, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMillan, K.; Helgerud, J.; Grant, S.J.; Newell, J.; Wilson, J.; Macdonald, R.; Hoff, J. Lactate threshold responses to a season of professional British youth soccer. Br. J. Sports Med. 2005, 39, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Villarreal, E.S.; González-Badillo, J.J.; Izquierdo, M. Low and moderate plyometric training frequency produces greater jumping and sprinting gains compared with high frequency. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2008, 22, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.R.; Nassis, G.P.; Rebelo, A. Strength training in soccer with a specific focus on highly trained players. Sports Med. Open 2015, 1, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.R.; McLeod, W.D.; Ward, T.; Howard, K. The cutting mechanism. Am. J. Sports Med. 1977, 5, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.; Bampouras, T.; Marrin, K. An investigation into the physical determinants of change of direction speed. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 2009, 49, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spiteri, T.; Nimphius, S.; Hart, N.H.; Specos, C.; Sheppard, J.M.; Newton, R.U. Contribution of strength characteristics to change of direction and agility performance in female basketball athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 2415–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettema, G.; Gløsen, T.; van den Tillaar, R. Effect of specific resistance training on overarm throwing performance. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perf. 2008, 3, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreurs, M.J.; Benjaminse, A.; Lemmink, K.A. Sharper angle, higher risk? The effect of cutting angle on knee mechanics in invasion sport athletes. J. Biomech. 2017, 63, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supej, M. 3D measurements of alpine skiing with an inertial sensor motion capture suit and GNSS RTK system. J. Sports Sci. 2010, 28, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Amri, M.; Nicholas, K.; Button, K.; Sparkes, V.; Sheeran, L.; Davies, J.L. Inertial measurement units for clinical movement analysis: Reliability and concurrent validity. Sensors 2018, 18, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, S.; Duthie, G.; Robertson, S.; Hopkins, W.; Ball, K. Concurrent validation of an inertial measurement system to quantify kicking biomechanics in four football codes. J. Biomech. 2018, 73, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, G.; O’Donoghue, P.; Nielson, P. Path changes and injury risk in English FA Premier League soccer. Int. J. Perf. Analys. Sport 2011, 11, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong-il, S.; Eonho, K.; Fahs, C.A.; Rossow, L.; Young, K.; Ferguson, S.L.; Thiebaud, R.; Sherk, V.D.; Loenneke, J.P.; Daeyeol, K.; et al. Reliability of the one-repetition maximum test based on muscle group and gender. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2012, 11, 221–225. [Google Scholar]
- Urquhart, B.G.; Moir, G.L.; Graham, S.M.; Connaboy, C. Reliability of 1RM split-squat performance and the efficacy of assessing both bilateral squat and split-squat 1RM in a single session for non-resistance trained recreationally active men. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 1991–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ribeiro, A.S.; do Nascimento, M.A.; Salvador, E.P.; Gurjão, A.L.D.; Avelar, A.; Ritti-Dias, R.M.; Mayhew, J.L.; Cyrino, E.S. Reliability of one-repetition maximum test in untrained young adult men and women. Isokin. Exerc. Sci. 2014, 22, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, B.J. Squatting kinematics and kinetics and their application to exercise performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 3497–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Campillo, R.; Alvarez, C.; García-Pinillos, F.; Sanchez-Sanchez, J.; Yanci, J.; Castillo, D.; Loturco, I.; Chaabene, H.; Moran, J.; Izquierdo, M. Optimal reactive strength index: Is tt an accurate variable to optimize plyometric training effects on measures of physical fitness in young soccer players? J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClymont, D. Use of the reactive strength index (RSI) as an indicator of plyometric training conditions. In Science and Football V: The proceedings of the fifth World Congress on Sports Science and Football; Taylor & Francis Group: Lisbon, Portugal, 2005; pp. 408–417. [Google Scholar]
- Markovic, G.; Jukic, I.; Milanovic, D.; Metikos, D. Effects of sprint and plyometric training on muscle function and athletic performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2007, 21, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Young, W. A simple method for evaluating the strength qualities of the leg extensor muscles and jumping ability. Strength Cond. Coach 1994, 2, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, K.; French, D.; Hayes, P.R. The effect of two plyometric training techniques on muscular power and agility in youth soccer players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappa, D.F.; Behm, D.G. Neuromuscular characteristics of drop and hurdle jumps with different types of landings. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 3011–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maulder, P.; Cronin, J. Horizontal and vertical jump assessment: Reliability, symmetry, discriminative and predictive ability. Phys. Ther. Sport 2005, 6, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.C.; Liberal, S.M.; Costa, A.M.; van den Tillaar, R.; Sánchez-Medina, L.; Martins, J.C.; Marinho, D.A. Effects of two different training programs with same workload on throwing velocity by experienced water polo players. Precept. Mot Skills 2012, 115, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Tillaar, R.; Marques, M.C. Effect of two different training programs with the same workload on soccer overhead throwing velocity. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perf. 2009, 4, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- van den Tillaar, R.; Marques, M.C. A comparison of three training programs with the same workload on overhead throwing velocity with different weighted balls. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 2316–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power for the Behavioural Sciences; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Loturco, I.; Kobal, R.; Kitamura, K.; Cal Abad, C.C.; Faust, B.; Almeida, L.; Pereira, L.A. Mixed training methods: Effects of combining resisted sprints or plyometrics with optimum power loads on sprint and agility performance in professional soccer players. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanci, J.; Los Arcos, A.; Camara, J.; Castillo, D.; García, A.; Castagna, C. Effects of horizontal plyometric training volume on soccer players’ performance. Res. Sports Med. 2016, 24, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiteri, T.; Cochrane, J.L.; Hart, N.H.; Haff, G.G.; Nimphius, S. Effect of strength on plant foot kinetics and kinematics during a change of direction task. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2013, 13, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havens, K.L.; Sigward, S.M. Whole body mechanics differ among running and cutting maneuvers in skilled athletes. Gait Posture 2015, 42, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos’ Santos, T.; Thomas, C.; Comfort, P.; Jones, P.A. Role of the penultimate foot contact during change of direction: Implications on performance and risk of injury. Strength Cond. J. 2019, 41, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havens, K.L.; Sigward, S.M. Cutting mechanics: Relation to performance and anterior cruciate ligament injury risk. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeWeese, B.; Nimphius, S. Program design and technique for speed and agility training. In Essentials of Strength Training and Conditioning; Human Kinetics Publishers: Champaign, IL, USA, 2016; pp. 521–558. [Google Scholar]
- Young, W.; Farrow, D. A review of agility: Practical applications for strength and conditioning. Strength Cond. J. 2006, 28, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhea, M.R.; Kenn, J.G.; Peterson, M.D.; Massey, D.; SimÃO, R.; Marin, P.J.; Favero, M.; Cardozo, D.; Krein, D. Joint-angle specific strength adaptations influence improvements in power in highly trained athletes. Hum. Mov. 2016, 17, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behm, D.; Sale, D. Velocity specificity of resistance training. Sports Med. 1993, 15, 374–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, J.; McNair, P.J.; Marshall, R.N. Developing explosive power: A comparison of technique and training. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2001, 4, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Reyes, P.; Samozino, P.; Brughelli, M.; Morin, J.-B. Effectiveness of an individualized training based on force-velocity profiling during jumping. Front. Physiol. 2017, 7, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loturco, I.; Pereira, L.A.; Reis, V.P.; Bishop, C.; Zanetti, V.; Alcaraz, P.E.; Freitas, T.T.; Mcguigan, M.R. Power training in elite young soccer players: Effects of using loads above or below the optimum power zone. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchomel, T.J.; Nimphius, S.; Stone, M.H. The importance of muscular strength in athletic performance. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 1419–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, B.M.; Franklyn-Miller, A.D.; King, E.A.; Moran, K.A.; Strike, S.C.; Falvey, É.C. Biomechanical factors associated with time to complete a change of direction cutting maneuver. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 2845–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Matched Exercises | Common Aspects | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Strength Training Group | Plyometric Training Group | Targeted Muscles from the Matched Exercises | Workload per Session |
| Parallel squat, Unilateral squat & Calf Raise | Drop Jump, Unilateral CMJ & Hurdle jumps | Hip, knee and ankle extensor muscles | ≈ 4250 Ns |
| Lateral squat | Skate jump | Hip abductor muscles | ≈ 1650 Ns |
| Unilateral Nordic hamstring | Laying kick | Hamstring muscles | Peak EMG activity ≈ 75% of MVC (van den Tillaar et al., 2017) |
| Week 1–3 (Session 1–6) | |||
| Day 1 | Intensity | Rest (s) | Series and Repetitions |
| Unilateral quarter squat | 85% of 1RM | 180> | 2 × 5 with each leg |
| Parallel squat | 85% of 1RM | 180> | 3 × 5 |
| Lateral squat | 75% of 1RM | 180> | 3 × 6 with each leg |
| Nordic hamstring | Max braking | 90> | 2 × 5 with each leg |
| Unilateral plantarflexion | 70% of 1RM | 90> | 3 × 8 with each leg |
| Day 2 | |||
| Unilateral quarter squat | 80% of 1RM | 180> | 2 × 6 with each leg |
| Parallel squat | 80% of 1RM | 180> | 3 × 8 |
| Lateral squat | 75% of 1RM | 180> | 3 × 8 with each leg |
| Nordic hamstring | Max braking | 90> | 2 × 5 with each leg |
| Unilateral plantarflexion | 70% of 1RM | 90> | 3 × 8 with each leg |
| Week 4–6 (Session 7–12) | |||
| Day 1 | Intensity | Rest (s) | Series and Repetitions |
| Lateral squat | 80% of 1RM | 240> | 4 × 4 with each leg |
| Unilateral quarter squat | 80% of 1RM | 240> | 2 × 6 with each leg |
| Parallel squat | 80% of 1RM | 240> | 3 × 6 |
| Nordic hamstring | Max braking | 90> | 2 × 8 with each leg |
| Unilateral plantarflexion | 75% of 1RM | 90> | 4 × 6 with each leg |
| Day 2 | |||
| Unilateral quarter squat | 88% of 1RM | 240> | 2 × 4 with each leg |
| Parallel squat | 85% of 1RM | 240> | 3 × 6 |
| Lateral squat | 70% of 1RM | 240> | 3 × 8 with each leg |
| Nordic hamstring | Max braking | 90> | 3 × 8 with each leg |
| Unilateral plantarflexion | 75% of 1RM | 90> | 4 × 6 with each leg |
| Week 1–3 (Session 1–6) | |||
| Day 1 | Main Focus | Rest (s) | Series and Repetitions |
| Unilateral CMJ | Height | 90 | 5 × 1 with each leg |
| Drop jump | Reactive strength | 60 | 10 × 1 |
| Unilateral hurdle jump | Contact time | 120 | 5 × 3 with each leg |
| Bilateral hurdle jump | Contact time | 90 | 4 × 3 |
| Skate jump | Reactive strength | 90 | 3 × 6 with each leg |
| Laying kick | Reactive strength | 90 | 2 × 5 with each leg |
| Day 2 | |||
| Drop Jump | Reactive strength | 20 | 4 × 3 |
| Unilateral CMJ | Height | 60 | 6 × 1 with each leg |
| Bilateral hurdle jump | Contact time | 60 | 6 × 3 |
| Unilateral hurdle jump | Contact time | 120 | 4 × 3 with each leg |
| Skate jump | Reactive strength | 90 | 3 × 6 with each leg |
| Laying kick | Reactive strength | 90 | 2 × 5 with each leg |
| Week 4–6 (Session 7–12) | |||
| Day 1 | Goal | Rest (s) | Series and Repetitions |
| Skate jump | Reactive strength | 90 | 4 × 4 with each leg |
| Bilateral hurdle jump | Contact time | 20 | 4 × 6 |
| Unilateral hurdle jump | Contact time | 120 | 4 × 3 with each leg |
| Drop jump | Reactive strength | 60 | 8 × 1 |
| Unilateral CMJ | Height | 90 | 6 × 6 with each leg |
| Laying kick | Reactive strength | 90 | 2 × 8 with each leg |
| Day 2 | |||
| Unilateral hurdle jump | Contact time | 90 | 4 × 3 with each leg |
| Bilateral hurdle jump | Contact time | 60 | 4 × 3 with each leg |
| Skate jump | Reactive strength | 120 | 3 × 8 with each leg |
| Unilateral CMJ | Height | 90 | 6 × 1 with each leg |
| Drop jump | Reactive strength | 60 | 8 × 1 |
| Laying kick | Reactive strength | 90 | 3 × 8 with each leg |
| Strength Training Group | Plyometric Training Group | ANOVA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exercise Variable | Pre | Post | Diff (%) | Pre | Post | Diff (%) | Effect: Group × Time (p) |
| Bilateral squat (kg) | 113.6 ± 22.5 | 127.8 ± 19.5 | 12.5 * | 130.0 ± 21.6 | 132.5 ± 13.0 | 1.9 | 0.021 |
| Unilateral squat (kg) | 88.3 ± 11.8 | 104.7 ± 11.3 | 18.6 * | 98.7 ± 10.7 | 103.4 ± 12.0 | 4.7 * | 0.023 * |
| Lateral squat (kg) | 90.6 ± 15.4 | 106.3 ± 16.0 | 17.2 * | 106.1 ± 15.4 | 104.3 ± 12.4 | −1.7 | 0.001 * |
| Bilateral squat (kg/BM·kg) | 1.47 ± 0.25 | 1.66 ± 0.22 | 12.7 * | 1.57 ± 0.28 | 1.60 ± 0.18 | 2.1 | 0.028 * |
| Unilateral squat (kg/BM·kg) | 1.15 ± 0.11 | 1.36 ± 0.08 | 18.2 * | 1.19 ± 0.16 | 1.25 ± 0.15 | 4.8 * | 0.019 * |
| Lateral squat (kg/BM·kg) | 1.16 ± 0.16 | 1.36 ± 0.19 | 17.5 * | 1.28 ± 0.21 | 1.26 ± 0.17 | −1.6 | 0.001 * |
| Drop jump (RSI) | 1.35 ± 0.27 | 1.31 ± 0.29 | −3.2 | 1.27 ± 0.31 | 1.48 ± 0.29 | 16.8 * | 0.015 * |
| Unilateral CMJ (m) | 0.173 ± 0.039 | 0.185 ± 0.041 | 6.8 | 0.165 ± 0.029 | 0.196 ± 0.024 | 19.0 * | 0.045 * |
| Bilateral hurdle jump (s) | 0.173 ± 0.018 | 0.152 ± 0.022 | −12.1 * | 0.168 ± 0.023 | 0.152 ± 0.012 | −9.5 * | 0.435 |
| Unilateral hurdle jump (s) | 0.193 ± 0.092 | 0.188 ± 0.019 | −2.7 | 0.197 ± 0.021 | 0.176 ± 0.017 | −10.6 * | 0.044 * |
| Skate-jump (m) | 2.02 ± 0.16 | 2.04 ± 0.16 | 1.4 | 1.92 ± 0.19 | 2.02 ± 0.20 | 5.4 * | 0.022 * |
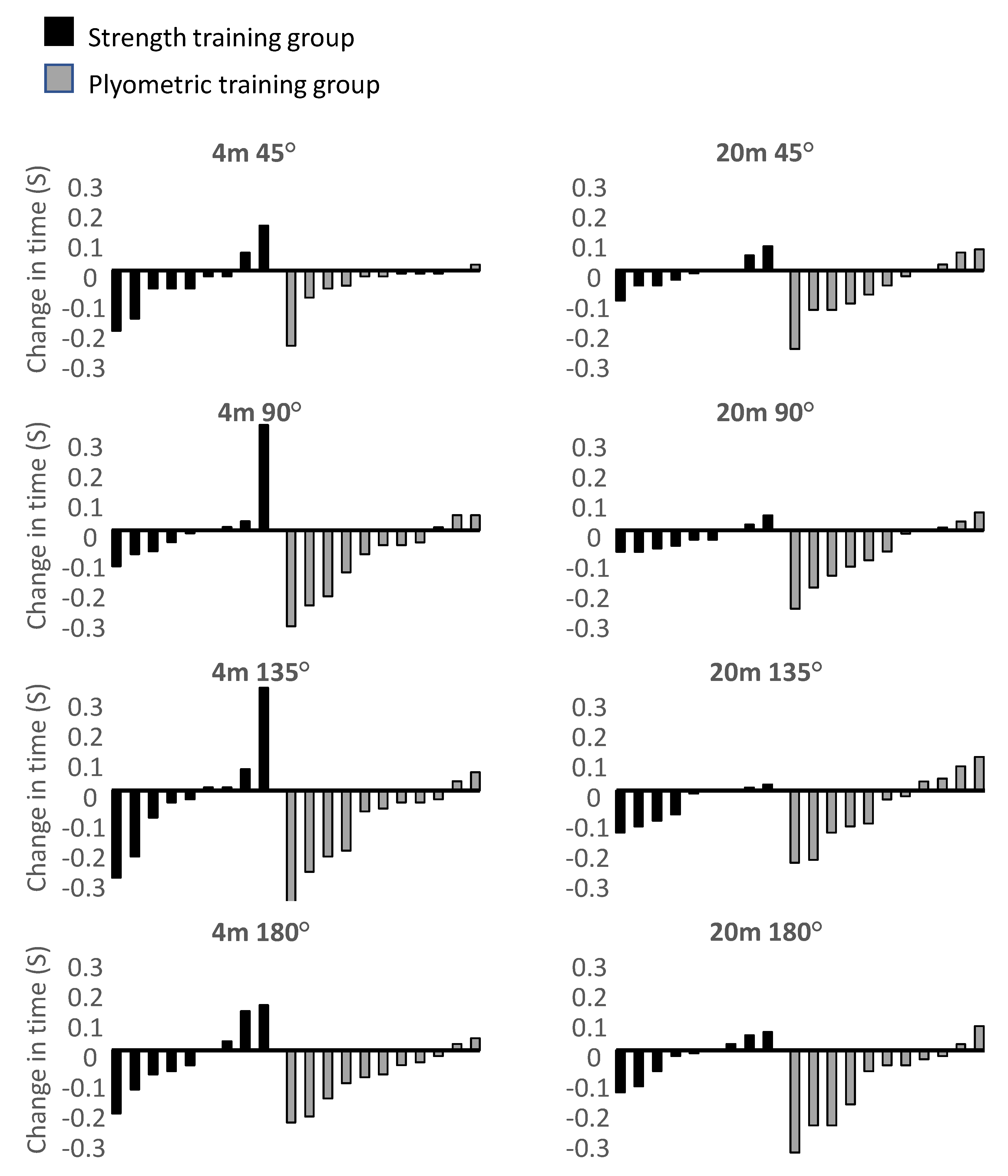
| Test | 4 m 45° | 4 m 90° | 4 m 135° | 4 m 180° | 20 m 45° | 20 m 90° | 20 m 135° | 20 m 180° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | ||||||||
| Pretest | 1.73 ± 0.15 | 2.06 ± 0.16 | 2.37 ± 0.17 | 2.48 ± 0.16 | 1.38 ± 0.11 | 1.84 ± 0.12 | 2.15 ± 0.14 | 2.30 ± 0.12 |
| Posttest | 1.69 ± 0.13 * | 2.01 ± 0.15 | 2.30 ± 0.14 | 2.42 ± 0.13 * | 1.36 ± 0.12 | 1.82 ± 0.09 | 2.11 ± 0.12 | 2.22 ± 0.11 * |
| Diff (%) | 2.31% | 2.43% | 2.95% | 2.42% | 1.45% | 1.09% | 1.86% | 3.48% |
| Strength training group | ||||||||
| Pretest | 1.71 ± 0.17 | 2.03 ± 0.19 | 2.37 ± 0.20 | 2.44 ± 0.18 | 1.38 ± 0.10 | 1.84 ± 0.13 | 2.17 ± 0.08 | 2.32 ± 0.07 |
| Posttest | 1.67 ± 0.15 | 2.04 ± 0.19 | 2.35 ± 0.15 | 2.41 ± 0.15 | 1.34 ± 0.13 | 1.83 ± 0.11 | 2.09 ± 0.9 | 2.25 ± 0.10 |
| Diff (%) | 2.34% | −0.49% | 0.84% | 1.23% | 2.90% | 0.54% | 3.69% | 3.02% |
| Plyometric training group | ||||||||
| Pretest | 1.74 ± 0.14 | 2.08 ± 0.13 | 2.37 ± 0.15 | 2.51 ± 0.15 | 1.38 ± 0.12 | 1.83 ± 0.11 | 2.13 ± 0.18 | 2.29 ± 0.15 |
| Posttest | 1.70 ± 0.12 | 1.99 ± 0.12 * | 2.26 ± 0.13 * | 2.43 ± 0.11 * | 1.38 ± 0.11 | 1.82 ± 0.08 | 2.12 ± 0.14 | 2.20 ± 0.12 * |
| Diff (%) | 2.30% | 4.33% | 4.64% | 3.19% | 0.00% | 0.55% | 0.47% | 3.93% |
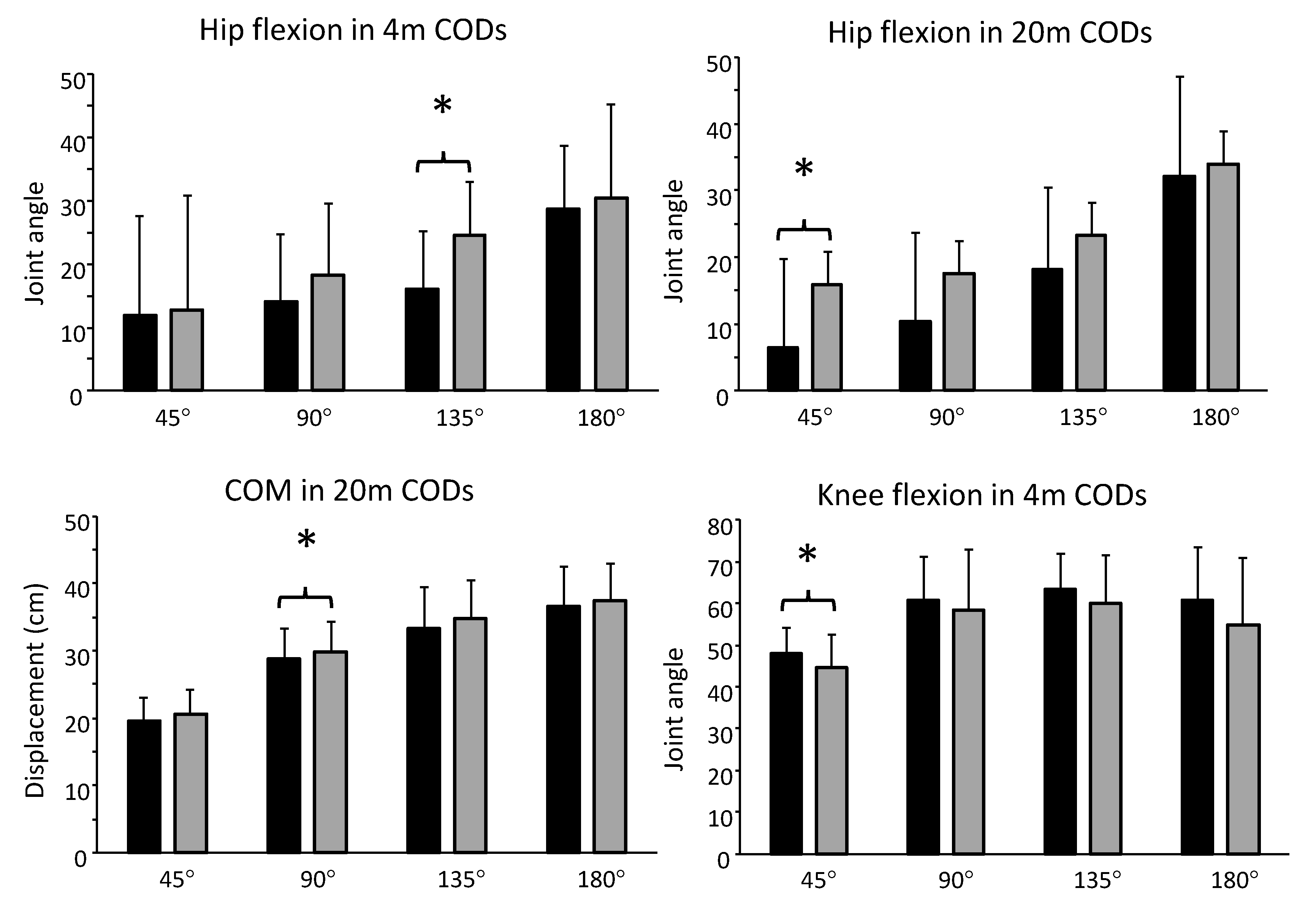
| 45° COD | 90° COD | 135° COD | 180° COD | ANOVA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | N | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Effect: Time (p) |
| 4 m | ||||||||||
| COM disp. (cm) | 17 | 17.7 ± 2.8 | 18.0 ± 4.3 | 25.4 ± 5.9 | 28.3 ± 5.3 | 31.2 ± 5.8 | 32.0 ± 6.9 | 34.5 ± 7.0 | 35.5 ± 9.5 | 0.200 |
| Contact time (ms) | 16 | 150 ± 23 | 160 ± 22 | 182 ± 37 | 204 ± 47 | 221 ± 42 | 238 ± 77 | 296 ± 82 | 304 ± 81 | 0.122 |
| Hip flexion (°) | 15 | 11.9 ± 15.8 | 12.8 ± 18.1 | 14.0 ± 10.8 | 18.3 ± 11.2 | 16.0 ± 9.2 | 24.6 ± 8.5 | 28.6 ± 10.2 | 30.4 ± 14.8 | 0.006 * |
| Hip abduction (°) | 14 | 7.4 ± 5.2 | 9.0 ± 4.9 | 10.5 ± 6.0 | 10.1 ± 6.2 | 7.9 ± 7.5 | 10.3 ± 6.5 | 13.5 ± 7.9 | 10.3 ± 10.2 | 0.834 |
| Knee flexion (°) | 15 | 48.0 ± 6.0 | 44.5 ± 7.9 | 60.8 ± 10.4 | 58.2 ± 14.6 | 63.2 ± 8.7 | 60.1 ± 11.3 | 60.7 ± 12.7 | 54.7 ± 16.3 | 0.032 * |
| Lean angle (°) | 11 | 28.1 ± 3.9 | 28.8 ± 4.9 | 38.0 ± 5.2 | 39.4 ± 2.3 | 43.1 ± 3.0 | 44.2 ± 4.3 | 47.1 ± 4.5 | 48.5 ± 3.7 | 0.279 |
| 20 m | ||||||||||
| COM disp. (cm) | 16 | 19.5 ± 3.5 | 20.5 ± 3.6 | 28.8 ± 4.6 | 29.8 ± 4.5 | 33.3 ± 6.1 | 34.6 ± 5.9 | 36.5 ± 5.9 | 37.3 ± 5.7 | 0.035 * |
| Contact time (ms) | 15 | 150 ± 23 | 145 ± 21 | 186 ± 35 | 198 ± 52 | 216 ± 71 | 241 ± 76 | 335 ± 114 | 318 ± 90 | 0.735 |
| Hip flexion (°) | 15 | 6.5 ± 13.2 | 15.9 ± 16.8 | 10.4 ± 13.2 | 17.5 ± 13.7 | 18.2 ± 12.4 | 23.3 ± 10.7 | 32.1 ± 15.2 | 34.0 ± 16.7 | 0.030 * |
| Hip abduction (°) | 14 | 9.8 ± 7.1 | 9.7 ± 4.9 | 10.0 ± 5.8 | 9.7 ± 6.0 | 11.7 ± 6.4 | 10.4 ± 8.0 | 16.7 ± 9.7 | 15.5 ± 7.0 | 0.562 |
| Knee flexion (°) | 15 | 49.0 ± 12.6 | 45.6 ± 12.2 | 59.6 ± 16.2 | 56.9 ± 15.7 | 61.4 ± 11.8 | 59.8 ± 14.8 | 60.2 ± 10.4 | 55.9 ± 17.0 | 0.185 |
| Lean angle (°) | 13 | 30.4 ± 5.6 | 32.7 ± 5.8 | 39.0 ± 4.7 | 40.1 ± 3.8 | 42.9 ± 3.7 | 44.4 ± 6.2 | 46.3 ± 6.6 | 48.2 ± 5.0 | 0.103 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rædergård, H.G.; Falch, H.N.; Tillaar, R.v.d. Effects of Strength vs. Plyometric Training on Change of Direction Performance in Experienced Soccer Players. Sports 2020, 8, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports8110144
Rædergård HG, Falch HN, Tillaar Rvd. Effects of Strength vs. Plyometric Training on Change of Direction Performance in Experienced Soccer Players. Sports. 2020; 8(11):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports8110144
Chicago/Turabian StyleRædergård, Håvard Guldteig, Hallvard Nygaard Falch, and Roland van den Tillaar. 2020. "Effects of Strength vs. Plyometric Training on Change of Direction Performance in Experienced Soccer Players" Sports 8, no. 11: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports8110144
APA StyleRædergård, H. G., Falch, H. N., & Tillaar, R. v. d. (2020). Effects of Strength vs. Plyometric Training on Change of Direction Performance in Experienced Soccer Players. Sports, 8(11), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports8110144






