The Bionomics of the Cocoa Mealybug, Exallomochlus hispidus (Morrison) (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae), on Mangosteen Fruit and Three Alternative Hosts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Preparation of Fruit Hosts and Rearing of Mealybug E. hispidus
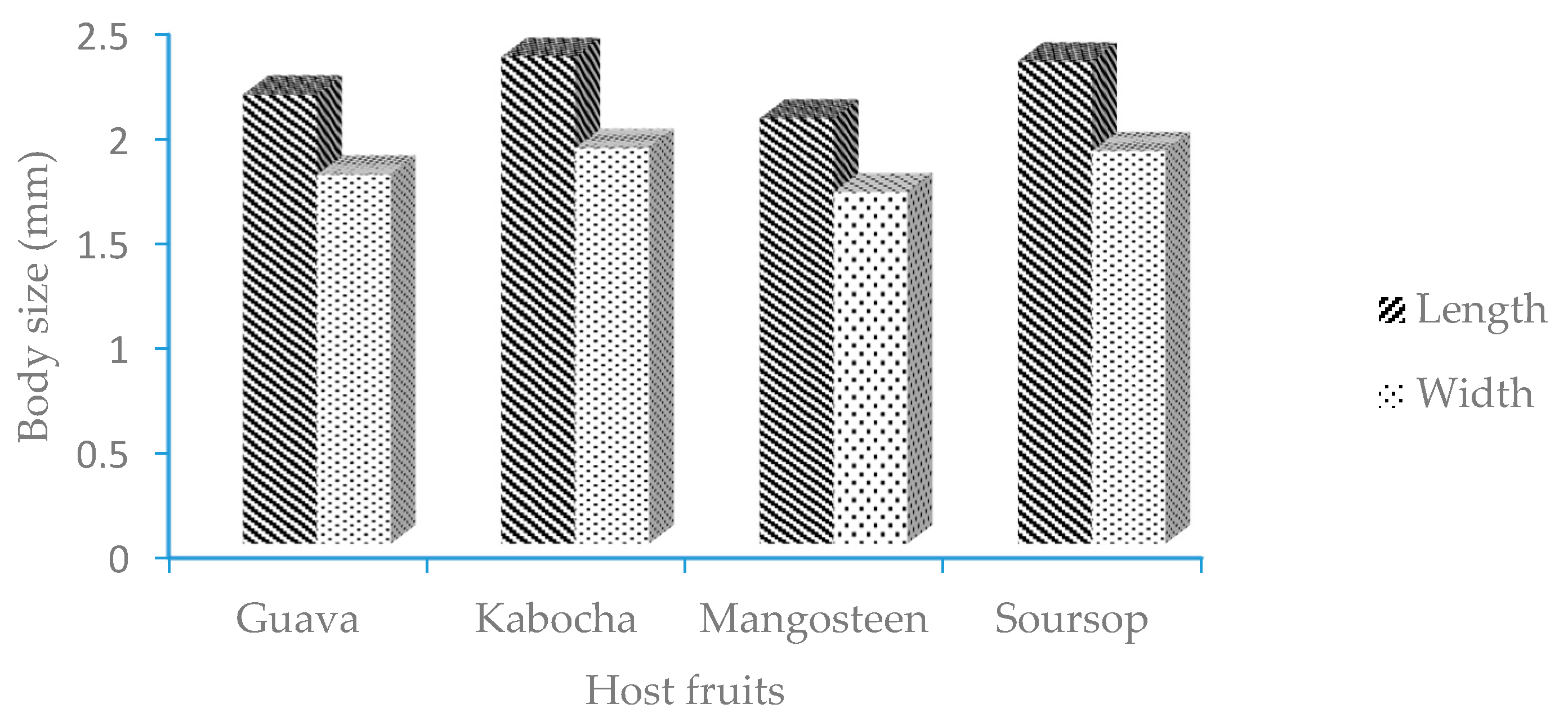
2.2. Morphometrics of Adult Female E. hispidus
2.3. Growth, Development, and Reproduction of E. hispidus
2.4. Water, Nitrogen, and Total Sugar Content of the Host Fruits
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Morphology of E. hispidus
3.2. The Bionomics of E. hispidus
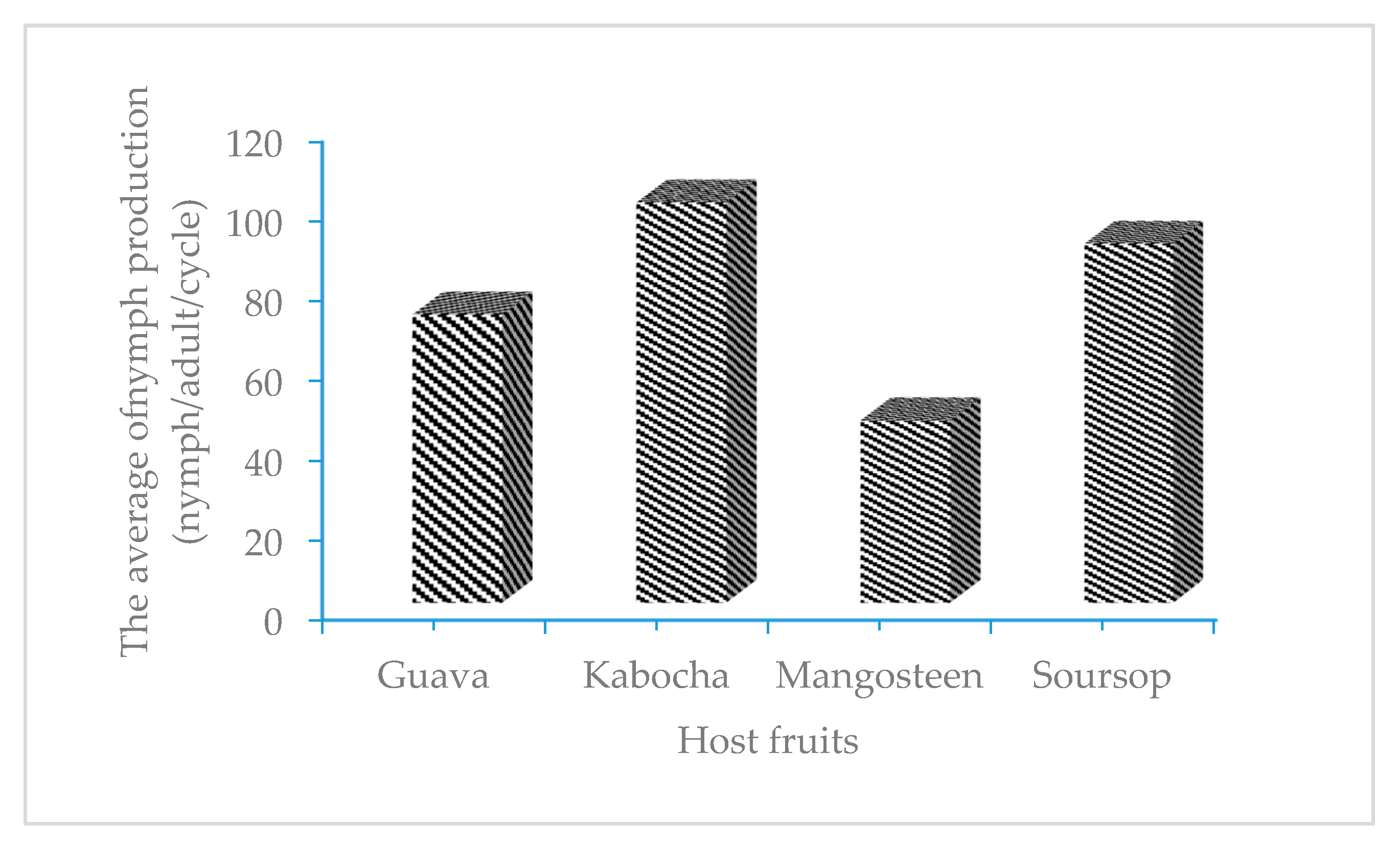
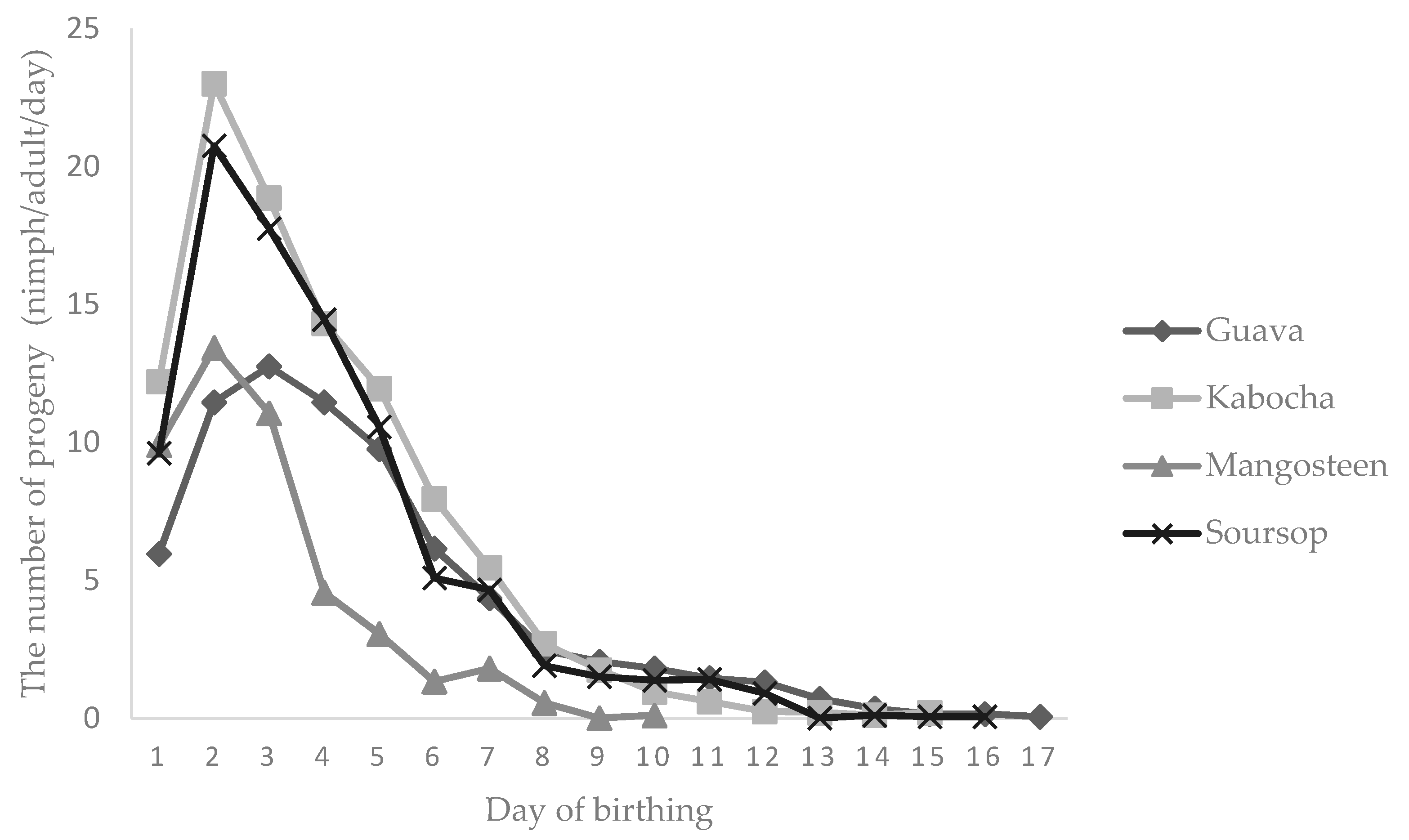
3.3. The Reproduction of E. hispidus
3.4. Water, Nitrogen, and Total Sugar Content in Host Fruits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, D.J. Mealybugs of Southern Asia; Southdene SDN. BHD.: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2004; pp. 9–250. [Google Scholar]
- ScaleNet. Scale Insects of the World. Available online: www.idtools.org/id/scales/factsheet.php?name=6973 (accessed on 22 October 2016).
- Ministry of Agriculture. Mangosteen Profile in Indonesia; Directorate of Fruit Cultivation, Directorate General of Horticulture, Ministry of Agriculture: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2007. (In Indonesian)
- Biosecurity Act Import Health Standard Fresh Fruit/Vegetables Mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana) from Indonesia. Ministry of Primary Industries: Wellington, New Zealand, 2014; pp. 1–9.
- Southampton Centre for Underutilised Crops (SCUC). Mangosteen, Garcinia mangostana. Field Manual for Extention Workers and Farmers; SCUC: Southampton, UK, 2006; pp. 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Tanga, C.M.; Ekesi, S.; Govender, P.; Mohamed, S.A. Effect of six host plant spesies on the life history and population growth parameters of Rastrococcus iceryoides (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae). Fla. Entomol. 2013, 96, 1030–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, A.; Bortoli, L.C.; Botton, M.; Parra, J.R.P. Host plant effects on the development, survival, and reproduction of Dysmicoccus brevipes (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) on grapevines. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2013, 106, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiedu, E.; Afun, J.V.K.; Kwoseh, C. Biology of Planococcus citri (Risso) (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) on five yam varieties in storage. Adv. Entomol. 2014, 2, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apriantono, A.; Fardiaz, D.; Puspitasari, N.L.; Sedarnawati; Budiyanto, S. Laboratory Instructions of Food Analysis; Faculty of Agricultural Technology, Bogor Agricultural University: Bogor, Indonesia, 1994. (In Indonesian) [Google Scholar]
- SAS INSTITUTE. SAS/STAT Users Guide: Statistic Version 9.1.3; Version 9.1.3; SAS Institute: Carry, NC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mau, R.F.L.; Kessing, J.L.M. Dysmicoccus brevipes (Cockerel) Pink Pineapple Mealybug. 2007. Available online: http://www.extento.hawaii.edu/Kbase/crop/Type/d_brevip.htm (accessed on 15 February 2014).
- Mamahit, J.M.E.; Manuwoto, S.; Hidayat, P.; Sobir. Biology of mealybug Dysmicoccus brevipes Cockerell (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) on pineapple and lesser galangale. Bul. Littro. 2008, XIX, 164–173. (In Indonesian) [Google Scholar]
- Kogan, M. Plant resistance in pest management. In Introduction to Insect Pest Management, 2nd ed.; Metcalf, R.L., Luckman, W.H., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 93–134. [Google Scholar]
- Maharani, Y.; Rauf, A.; Sartiami, D.; Anwar, R. Biology and life table of papaya mealybug Paracoccus marginatus (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae). J. HPT Tropika 2016, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Normark, B.B.; Kirkendall, R.L. Parthenogenesis in Insect and Mites. In Encyclopedia of Insects; Resh, V.H., Carde, R., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2009; pp. 688–756. [Google Scholar]
- Boavida, C.; Neuenschwander, P. Influence of host plant selection on the mango mealybug Rastrococcus invadens. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1995, 88, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Schoohoven, L.M.; van Loon, J.J.A.; Dicke, M. Insect—Plant Biology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, R.F. The Insect Structure and Function; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 69–90. [Google Scholar]
- Hogendorp, B.K.; Cloyd, R.A.S.; Expwiader, J.M. Effect of nitrogen fertility on reproduction and development of citrus mealybug Planococcus citri Risso (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) feeding on two colors of coleus, Solenostemon scutellarioides L. Codd. Environ. Entomol. 2006, 35, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janson, J.; Ekbom, B. The effect of different plant regimes on the aphid Macrosiphum euphorbiae growing on petunia. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2002, 104, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Average Number of Days per Developmental Stage (Days ± SE) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Instar | Second Instar | Third Instar | Life Cycle | |
| Host fruit | ||||
| Guava | 8.8 ± 0.7 a | 7.3 ± 0.4 a | 8.2 ± 0.4 a | 38.3 ± 1.8 a |
| Kabocha | 7.7 ± 0.5 b | 6.0 ± 0.6 b | 6.9 ± 0.5 b | 32.4 ± 1.3 c |
| Mangosteen | 9.1 ± 0.7 a | 7.3 ± 0.5 a | 8.4 ± 0.7 a | 38.2 ± 2.1 a |
| Soursop | 8.0 ± 0.7 b | 7.1 ± 0.5 a | 8.2 ± 0.8 a | 35.2 ± 2.5 b |
| F | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| df | 3,76 | 3,76 | 3,76 | 3,76 |
| p | 20.60 | 29.89 | 27.36 | 40.80 |
| Period (In Days) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prebirthing | Birthing | Postbirthing | Adult longevity | |
| Host | ||||
| Guava | 14.1 ± 0.8 a | 10.1 ± 3.4 a | 1.2 ± 0.8 ab | 25.3 ± 3.0 a |
| Kabocha | 11.8 ± 0.7 b | 8.9 ± 2.7 ab | 0.6 ± 0.7 b | 21.3 ± 2.2 b |
| Mangosteen | 13.5 ± 1.1 a | 6.2 ± 1.6 c | 1.1 ± 0.9 ab | 20.7 ± 1.7 b |
| Soursop | 12.0 ± 1.17 b | 7.4 ± 2.9 bc | 1.4 ± 0.8 a | 20.8 ± 2.5 b |
| F | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0146 | 0.0001 |
| df | 3,76 | 3,76 | 3,76 | 3,76 |
| p | 26.56 | 8.61 | 3.74 | 16.97 |
| Host Fruits | Water Content (%) | Nitrogen Content (%) | Total Sugar Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guava | 88.84 | 0.67 | 10.53 |
| Kabocha | 93.77 | 1.97 | 5.65 |
| Mangosteen | 64.52 | 0.41 | 1.98 |
| Soursop | 83.09 | 1.06 | 3.11 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Indarwatmi, M.; Dadang, D.; Ridwani, S.; Sri Ratna, E. The Bionomics of the Cocoa Mealybug, Exallomochlus hispidus (Morrison) (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae), on Mangosteen Fruit and Three Alternative Hosts. Insects 2017, 8, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects8030075
Indarwatmi M, Dadang D, Ridwani S, Sri Ratna E. The Bionomics of the Cocoa Mealybug, Exallomochlus hispidus (Morrison) (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae), on Mangosteen Fruit and Three Alternative Hosts. Insects. 2017; 8(3):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects8030075
Chicago/Turabian StyleIndarwatmi, Murni, Dadang Dadang, Sobir Ridwani, and Endang Sri Ratna. 2017. "The Bionomics of the Cocoa Mealybug, Exallomochlus hispidus (Morrison) (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae), on Mangosteen Fruit and Three Alternative Hosts" Insects 8, no. 3: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects8030075
APA StyleIndarwatmi, M., Dadang, D., Ridwani, S., & Sri Ratna, E. (2017). The Bionomics of the Cocoa Mealybug, Exallomochlus hispidus (Morrison) (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae), on Mangosteen Fruit and Three Alternative Hosts. Insects, 8(3), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects8030075





