Compatibility of Isaria fumosorosea (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae) Blastospores with Agricultural Chemicals Used for Management of the Asian Citrus Psyllid, Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Liviidae)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
| Product/Manufacturer | Type1 | Rate (% v/v) / acre | Use2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SuffOil-X™, BioWorks Inc. Victor, NY | P | 1–2 | I,M,F |
| Citrus Wrap™, Loveland Products, Inc., Greeley, CO | P | 1–5 quarts | A |
| Griffin 435 Oil™, Ben Hill Griffin, Inc., Frostproof, FL | P | 5–10 gals | I,M,F |
| PureSpray Green™, Whitmire Research Inc., St Louis, MO | P | 0.75–2 | I,M,F |
| Year-Round™, Summit, Baltimore, MD | P | 1–2.9 | I,M |
| Sylgard® 309, Wilbur-Ellis, Fresno, CA | S | 0.03–0.4 | A |
| Neem Oil, Dyna-Gro, Richmond, CA | B | 0.1 | I,M,F |
| OrocitTM (= Vintre™), Oro Agri Inc. Trophy Club, TX | B | 0.1–0.8 | A |
| OroboostTM, Oro Agri Inc. Trophy Club, TX | B | 0.2–0.8 | A |
| Prev-AmTM, Oro Agri Inc. Trophy Club, TX | R | 0.4–0.8 | I,M,F |
| Neemix® 4.5, Certis USA, Columbia, MD | B | 0.2 | I |
| Kocide® 3000, DuPontTM, Wilmington, DE | C | 3.2 lbs | F |
| Cuprofix® Ultra 40, United Phosphorus., King of Prussia, PA | C | 3.2 lbs | F |
| Copper-Count®-N, Mineral R&D, Charlotte, NC | C | 2 quarts | F |
| Champ® DP, NuFarm Americas Inc., Burr Ridge, IL | C | 4.0 lbs | F |
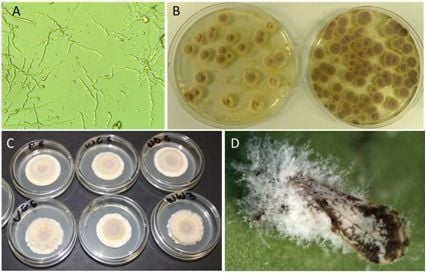
3. Results
3.1. Compatibility of I. fumosorosea with Spray Oils and Adjuvants In Vitro
| Oil/Adjuvant | % Germination | No. of CFU’s | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5% v/v | 2% v/v | 0.5% v/v | 2% v/v | |
| None | 100.0a | 100.0a | 100.0a | 100.0a |
| SuffOil-X | 51.2b | 29.2bcd | 62.3ab | 61.3ab |
| Citrus Wrap | 43.7bc | 25.9cde | 36.4b | 35.7bc |
| Griffin 435 | 31.0c | 28.8bcd | 35.7b | 45.3bc |
| PureSpray Green | 43.5bc | 38.0bc | 40.9b | 41.8bc |
| Year-Round | 36.2bc | 18.9def | 41.6b | 42.0bc |
| Sylgard 309 | 48.4b | 45.3b | 44.3b | 40.8bc |
| Neem Oil | 54.8b | 37.2bc | 61.1ab | 45.0bc |
| Orocit (=Vintre) | 36.7bc | 15.3ef | 55.0ab | 28.3bc |
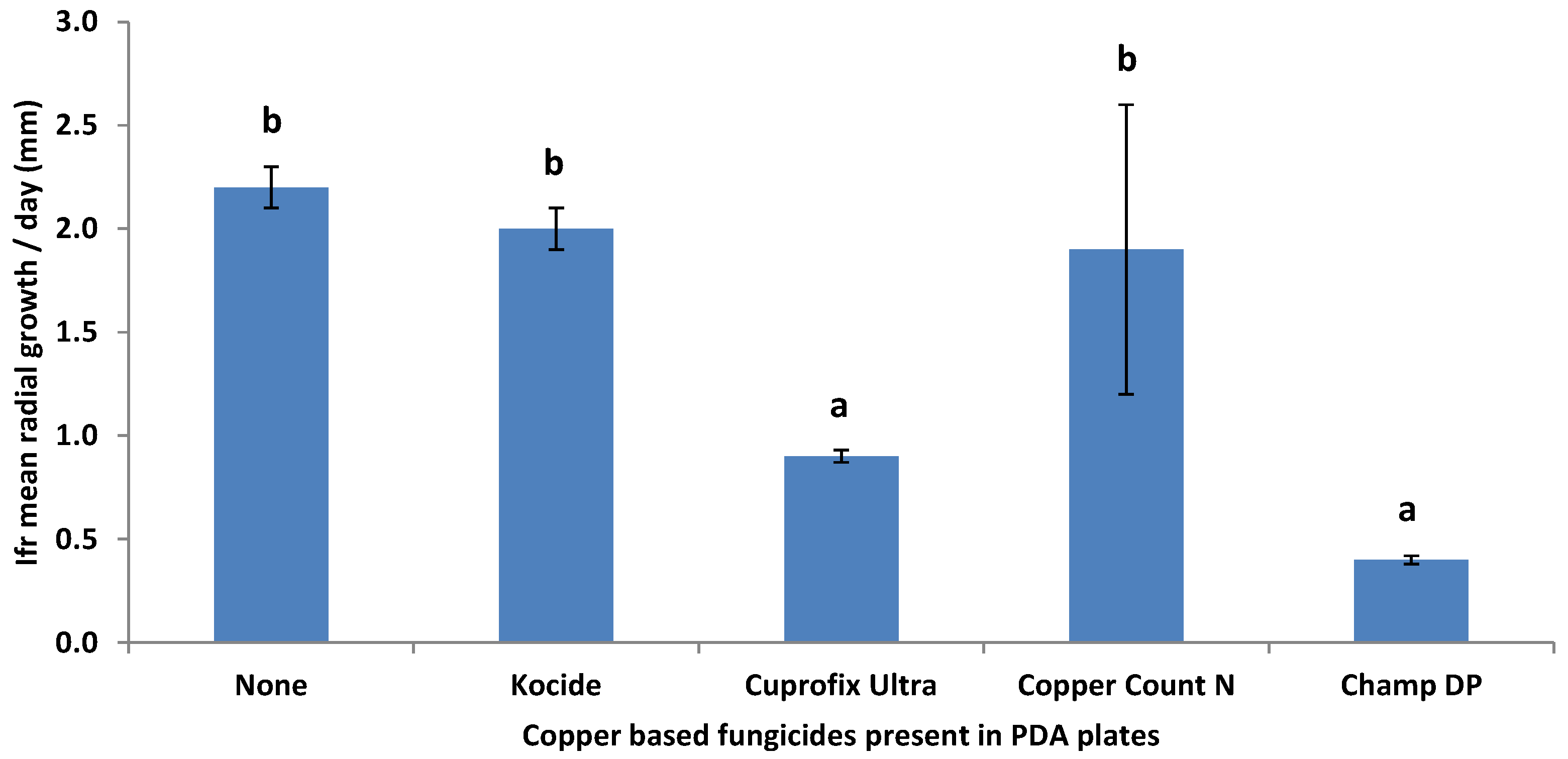
3.2. Compatibility of I. fumosorosea with Copper-Based Fungicides In Vitro

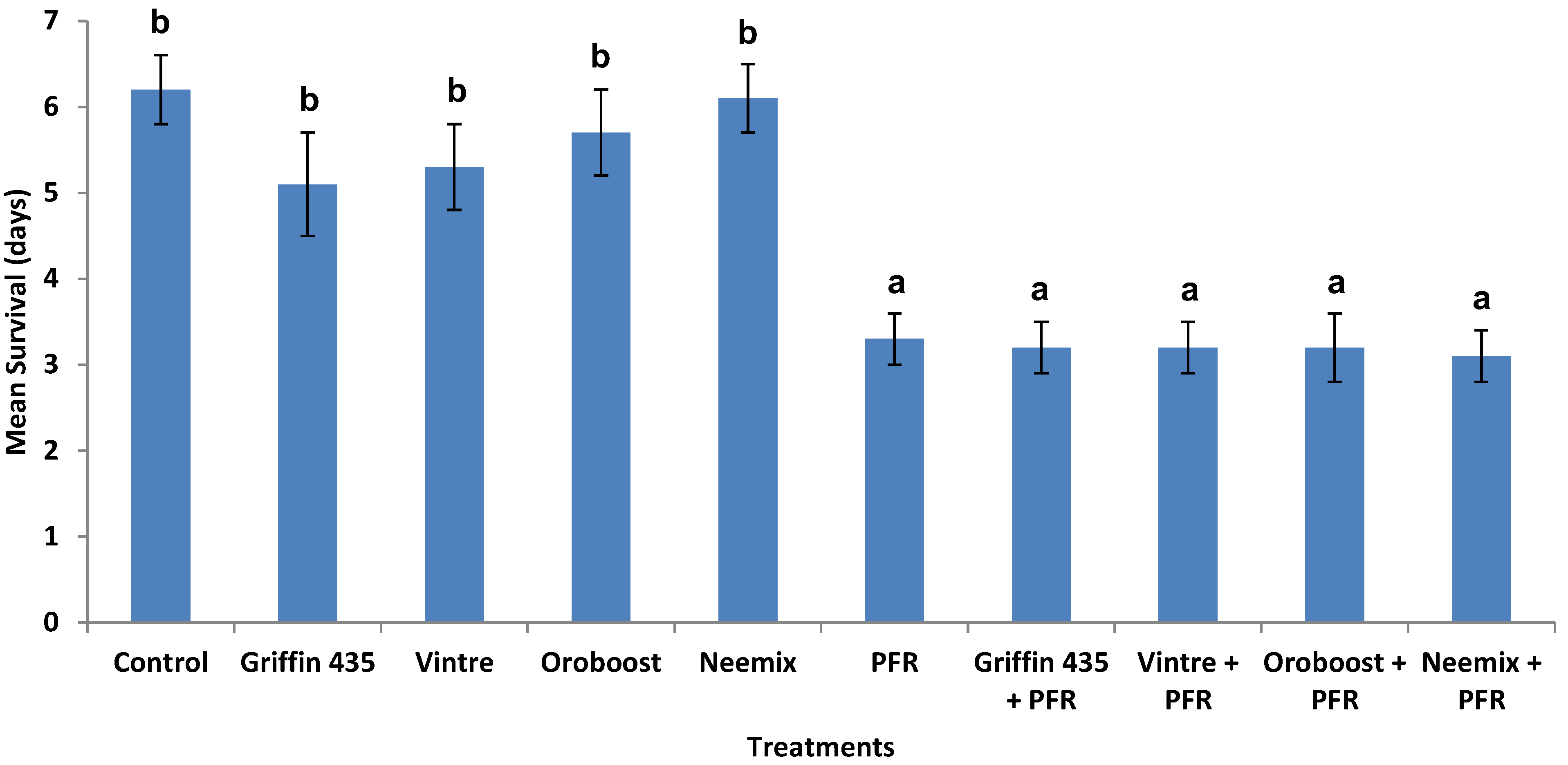
3.3. Compatibility of I. fumosorosea with Spray Oils In Vivo
3.4. Compatibility of I. fumosorosea with Copper-Based Fungicides in Vivo
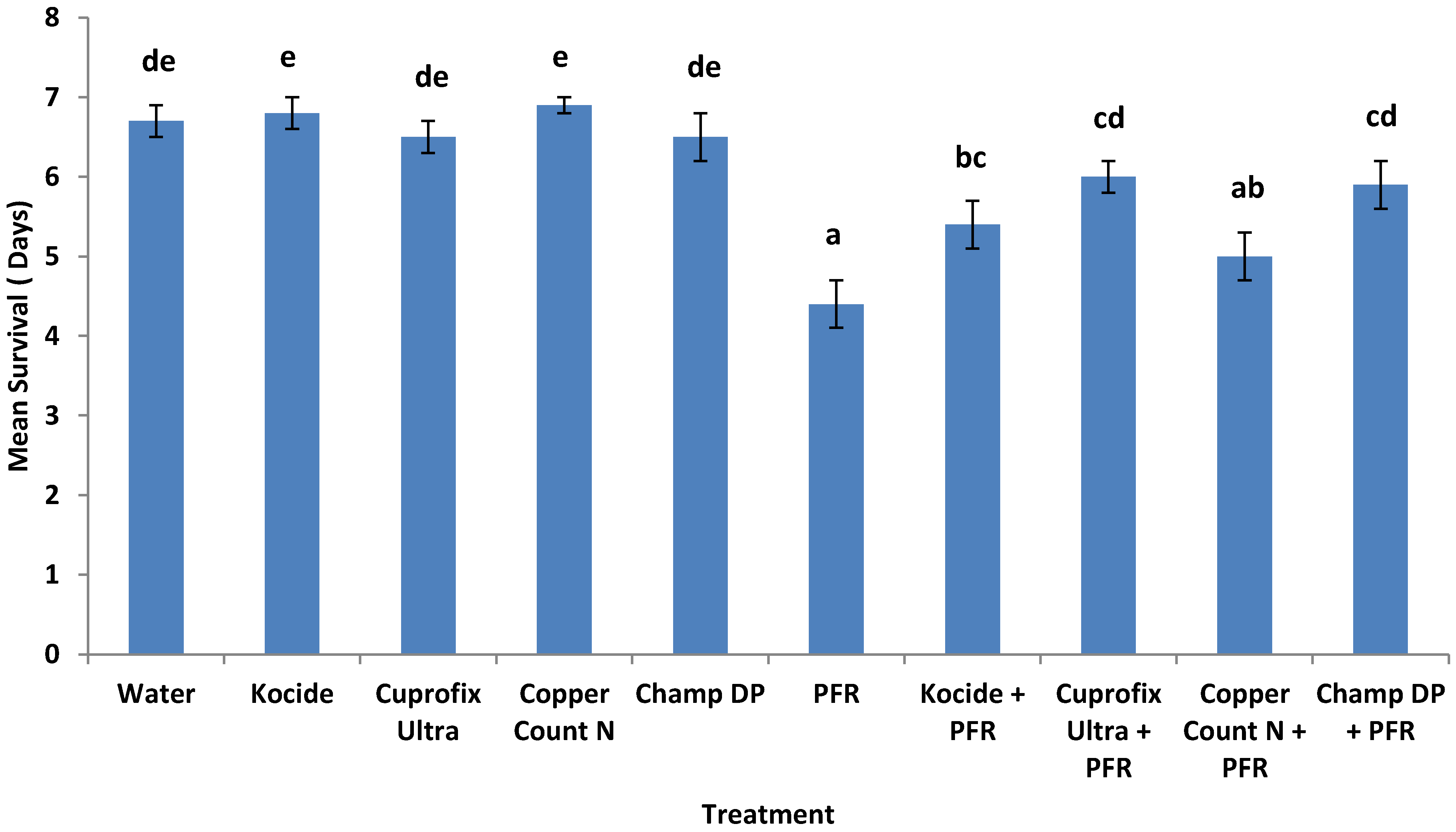
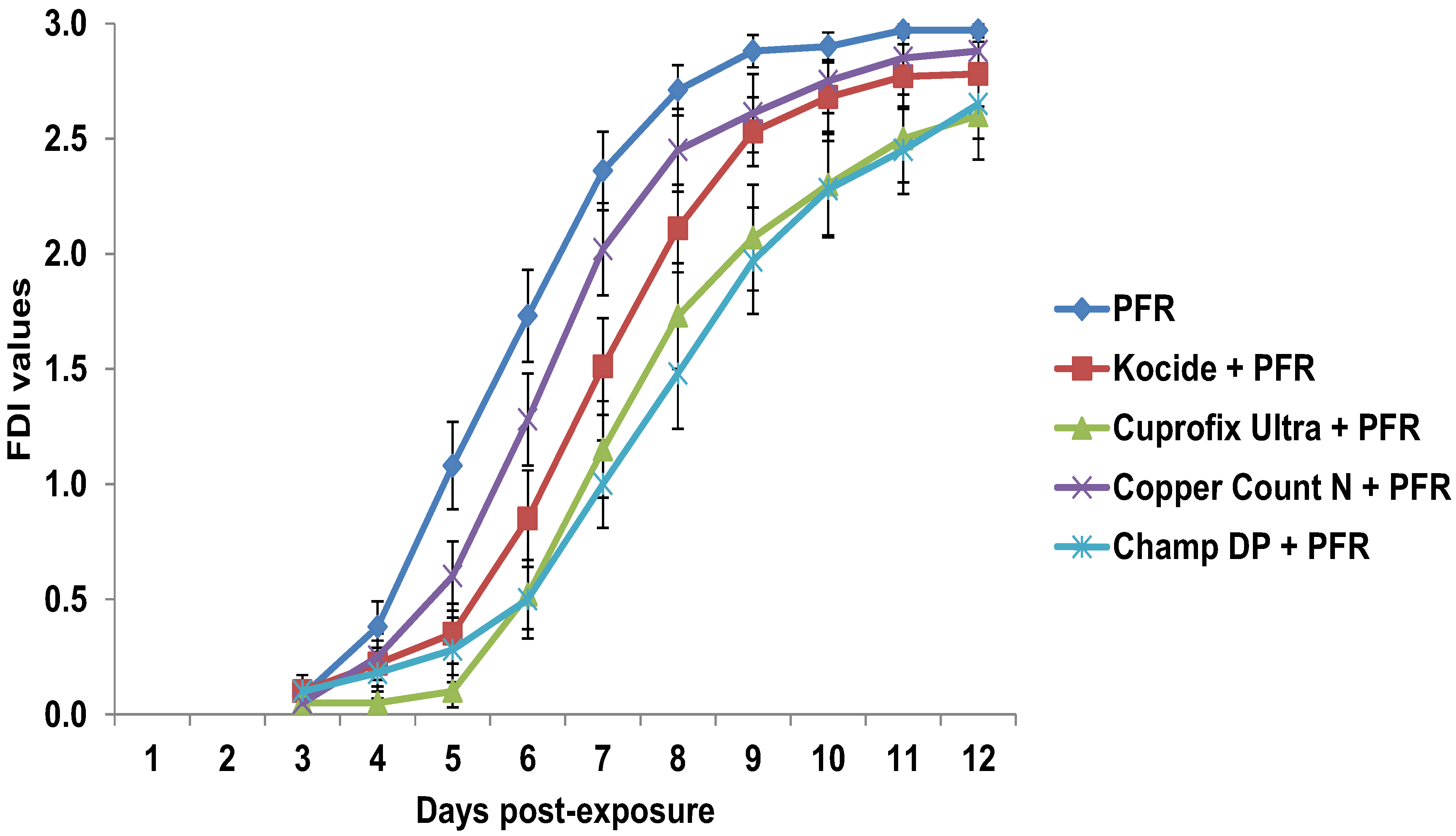
4. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Conflict of Interest
References and Notes
- Faria, M.R.; Wraight, S.P. Mycoinsecticides and mycoacaricides: A comprehensive list with worldwide coverage and international classification of formulation types. Biol. Control 2007, 43, 237–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambethgar, V. Potential of entomopathogenic fungi in insecticide resistance management (IRM): A review. J. Biopest. 2009, 2, 177–193. [Google Scholar]
- Arthurs, S.P.; Aristizábal, L.F.; Avery, P.B. Evaluation of entomopathogenic fungi against chilli thrips, Scirtothrips dorsalis. J. Insect Sci. 2013, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farenhorst, M.; Mouatcho, J.C.; Kikankie, C.K.; Brooke, B.D.; Hunt, R.H.; Thomas, M.B.; Koekemoer, L.L.; Knols, B.G.; Coetzee, M. Fungal infection counters insecticide resistance in African malaria mosquitoes. PNAS. 2009, 106, 17443–17447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Kim, J.J. Susceptibility of the tobacco whitefly, Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) biotype Q to entomopathogenic fungi. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2011, 21, 1471–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnley, A.K.; Collins, S.A. Entomopathogenic fungi and their role in pest control. In The Mycota IV, 2nd ed.; Kubicek, C.P., Druzhinina, I.S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 159–187. [Google Scholar]
- Lacey, L.A.; Frutos, R.; Kaya, H.K.; Vail, P. Insect pathogens as biological control agents: Do they have a future? Biol. Control 2001, 21, 230–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafton-Cardwell, E.E.; Stelinski, L.L.; Stansly, P.A. Biology and management of Asian citrus psyllid, vector of the huanglongbing pathogens. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 413–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.G.; Richardson, M.L.; El-Desouky, A.; Halbert, S.E. Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri, vector of citrus huanglongbing disease. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2013, 146, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belasque, J.J.; Bassanezi, R.B.; Yamamoto, P.T.; Ayres, A.J.; Tachibana, A.; Violante, A.R.; Tank, A., Jr.; Di Giorgi, F.; Tersi, F.E.A.; Menezes, G.M.; Dragone, J.; Jank, R.H., Jr.; Bové, J.M. Lessons from huanglongbing management in São Paulo state, Brazil. J. Plant Pathol. 2010, 92, 285–302. [Google Scholar]
- Stansly, P.; Arevalo, H.A.; Zekri, M. Area-wide psyllid sprays in southwest Florida: An update on the cooperative program aimed at controlling the HLB vector. Citrus Industry 2010, 91, 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, J.A.; Stansly, P.A. Rate, placement and timing of aldicarb applications to control Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri Kuwayama (Hemiptera: Psyllidae), in oranges. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottwald, T.R. Current epidemiological understanding of citrus huanglongbing. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2010, 48, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Mann, R.S.; Rogers, M.E.; Stelinski, L.L. Insecticide resistance in field populations of Asian citrus psyllid in Florida. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, S.; Stelinski, L.L.; Rogers, M.E. Biochemical basis of organophosphate and carbamate resistance in Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.G.; Nguyen, R. Toxicity of pesticides to Tamarixia radiata, a parasitoid of the Asian citrus psyllid. BioControl 2010, 55, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, J.P. Natural mortality of Asian citrus psyllid (Homoptera: Psyllidae) in central Florida. Biol. Control 2004, 29, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, B. Trioza erytreae Del Buercio and Diaphorina citri Kuwayama (Homoptera: Psylloidea), the two vectors of citrus greening disease: Biological aspects and possible control strategies. Fruits 1987, 42, 149–162. [Google Scholar]
- Casique-Valdes, R.; Reyes-Martinez, A.Y.; Sanchez-Peña, S.R.; Bidochka, M.J.; Lopez-Arroyo, J.I. Pathogenicity of Hirsutella citriformis (Ascomycota: Cordycipitaceae) to Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) and Bactericera cockerelli (Hemiptera: Triozidae). Fla. Entomol. 2011, 94, 703–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.M.; Hoy, M.A.; Boucias, D.G. Morphological and molecular characterization of a Hirsutella species infecting the Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri Kuwayama (Hemiptera: Psyllidae), in Florida. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2007, 95, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.M.; Hoy, M.A.; Boucias, D.G. Isolation and characterization of an Isaria fumosorosea isolate infecting the Asian citrus psyllid in Florida. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2008, 99, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero-Aragon, A.; Grillo-Ravelo, H. Natural enemies of Diaphorina citri Kuwayama (Homoptera: Psyllidae) in the central region of Cuba. Centro Agricola 2000, 27, 87–88. [Google Scholar]
- Samson, R.A. Paecilomyces and some allied hyphomycetes. In Studies in Mycology, 6th ed.; Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures: Baarn, The Netherlands, 1974; pp. 1–119. [Google Scholar]
- Subandiyah, S.; Nikoh, N.; Sato, H.; Wagiman, F.; Tsuyumyu, S.; Fukatsu, T. Isolation and characterization of two entomopathogenic fungi attacking Diaphorina citri (Homoptera, Psylloidea) in Indonesia. Mycoscience 2000, 41, 509–513. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, P.H.; Su, C.; Lin, Z.G. A preliminary study on an entomogenous fungus [Verticillium lecanii] of Diaphorina citri Kuwayama (Hom.: Psyllidae). Chin. J. Biol. Control 1988, 4, 92. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Q.; Chen, W.; Chen, D. Studies and application of entomogenous fungi of citrus pests. Zhejiang Citrus 1994, 4, 15–18. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Avery, P.B.; Hunter, W.B.; Hall, D.G.; Jackson, M.A.; Powell, C.A.; Rogers, M.E. Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) infection and dissemination of the entomopathogenic fungus Isaria fumosorosea (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae) under laboratory conditions. Fla. Entomol. 2009, 92, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, P.B.; Wekesa, V.W.; Hunter, W.B.; Hall, D.G.; McKenzie, C.L.; Osborne, L.S.; Powell, C.A.; Rogers, M.E. Effects of the fungus Isaria fumosorosea (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae) on reduced feeding and mortality of the Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Psyllidae). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2011, 21, 1065–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, M.; Singh, R.; Rogers, M.E. Evaluations of A novel isolate of Isaria fumosorosea for control of the Asian Citrus Psyllid, Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Psyllidae). Fla. Entomol. 2010, 93, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, W.B.; Avery, P.B.; Pick, D.; Powell, C.A. Broad spectrum potential of Isaria fumosorosea on insect pests of citrus. Fla. Entomol. 2011, 94, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, M.E.; Dewdney, M.M.; Futch, S.H. 2012 Florida Citrus Pest Management Guide: Pesticides Registered for Use on Florida Citrus. Available online: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/cg017 (accessed on 30 October 2013).
- Hall, D.G.; Lapointe, S.L.; Wenninger, E.J. Effects of a particle film on biology and behavior of Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) and its infestations in citrus. J. Econ. Entomol. 2007, 100, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.H.; Liu, Y.H. Biology of Diaphorina citri (Homoptera: Psyllidae) on four host plants. J. Econ. Entomol. 2000, 93, 1721–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauderman, K.; Avery, P.B.; Aristizábal, L.; Arthurs, S. Evaluation of Isaria fumosorosea (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae) for control of the Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Psyllidae). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2012, 22, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, R.P.; Carey, M.; Moore, D.; Prior, C. The enhanced infectivity of Metarhizium flavoviride in oil formulations to desert locusts at low humidities. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1993, 122, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burges, H.D. Formulation of mycoinsecticides. In Formulation of Microbial Biopesticides; Burges, H.D., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 131–185. [Google Scholar]
- Inglis, D.G.; Jaronski, S.T.; Wraight, S.P. Use of spray oils with entomopathogens. In Spray Oils Beyond 2000: Sustainable Pest and Disease Management; Beattie, G.A.C., Watson, D.M., Eds.; University of Western Sydney: Hawkesbury, Australia, 2002; pp. 302–312. [Google Scholar]
- Boucias, D.G.; Pendland, J.C. Attachment of mycopathogens to cuticle: The initial event of mycosis in arthropod hosts. In The Fungal Spore and Disease Initiation in Plants and Animals; Cole, G.T., Hoch, H.C., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 101–128. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, L.; Butt, T.M.; Beckett, A.; Clark, S.J. The germination of oil-formulated conidia of the insect pathogen Metarhizium anisopliae. Mycol. Res. 1991, 103, 901–907. [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap, C.A.; Biresaw, G.; Jackson, M.A. Hydrophobic and electrostatic cell surface properties of blastospores of the entomopathogenic fungus Paecilomyces fumosoroseus. Colloid. Surface. B 2005, 46, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holder, D.J.; Kirkland, B.H.; Lewis, M.W.; Keyhani, N.O. Surface characteristics of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria (Cordyceps) bassiana. Microbiology 2007, 153, 3448–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depieri, R.A.; Martinez, S.S.; Menezes, A.O. Compatibility of the fungus Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuill. (Deuteromycetes) with extracts of neem seeds and leaves and the emulsible oil. Neotrop. Entomol. 2005, 34, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, E.; Neves, P.M.O.; Zequi, J.A.C.; Martins, L.H.; Peralta, C.H.; Moino, A. Effect of biofertilizers and neem oil on the entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuill. and Metarhizium anisopliae (Metsch.) Sorok. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2001, 44, 419–423. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.T.; Olleka, A.; Ren, S. Influence of neem on susceptibility of Beauveria bassiana and investigation of their combined efficacy against sweetpotato whitefly, Bemisia tabaci on eggplant. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2010, 98, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa, Z.; Bohata, A. Compatibility of entomogenous fungus Paecilomyces fumosoroseus with natural insecticides based on azadirachtin and neem oil. Collect. Sci. Pap. Fac. Agric. Ces. Budejovice Ser. Crop Sci. 1999, 16, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Visalakshy, P.N.G.; Krishnamoorthy, A.; Kumar, A.M. Compatibility of plant oils and additives with Paecilomyces farinosus, a potential entomopathogenic fungus. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2006, 4, 333–335. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, M.C.; Narasimha, P.; Reddy, N.P.; Devi, U.K.; Kongara, R.; Sharma, H.C. Growth and insect assays of Beauveria bassiana with neem to test their compatibility and synergism. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2007, 17, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, J.; Rai, A.B.; Kodandaram, M.H. Compatibility of neem oil and different entomopathogens for the management of major vegetable sucking pests. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2013, 36, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroon, W.M.; Pages, C.; Vassal, J.M.; Abdalla, A.M.; Luong-Skovmand, M.H.; Lecoq, M. Laboratory and field investigation of a mixture of Metarhizium acridum and neem seed oil against the tree locust Anacridium melanorhodon melanorhodon (Orthoptera: Acrididae). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2011, 21, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, A.; Samih, M.A.; Khezri, M.; Riseh, R.S. Compatibility of Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuill. with several pesticides. Int. J. Agri. Biol. 2007, 9, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbertson, A.G.S.; Walters, K.F.A.; Deppe, C. Compatibility of the entomopathogenic fungus Lecanicillium muscarium and insecticides for eradication of sweetpotato whitefly, Bemisia tabaci. Mycopathologia 2005, 160, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, C.N.; Neves, P.M.; Kawazoe, L.S. Compatibility between the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana and insecticides used in coffee plantations. Sci. Agric. 2003, 60, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meitkiewski, R.; Gorski, R. Growth of selected entomopathogenic fungi species and isolates on media containing insecticides. Acta. Mycol. 1995, 30, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Wang, X.; Sheng, C. Impact of sixteen chemical pesticides on conidial germination of two entomophthoralean fungi: Conidiobolus thromboides and Pandora nouryi. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2004, 14, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa, Z.; Osborne, L.; Lopez, F.; Eyal, J. A bioassay for determining pathogenicity of entomogenous fungi on whiteflies. Biol. Control 1994, 4, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asi, M.R.; Bashir, M.H.; Afzal, M.; Ashfaq, M.; Sahi, S.T. Compatibility of entomopathogenic fungi, Metarhizium anisopliae and Paecilomyces fumosoroseus with selective insecticides. Pak. J. Bot. 2010, 42, 4207–4214. [Google Scholar]
- Demirci, F.; Mutu, M.; Kaydan, M.B.; Ülgentürk, S. Effects of some fungicides on Isaria farinosa, and in vitro growth and infection rate on Planococcus citri. Phytoparasitica 2011, 39, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbertson, A.G.S.; Blackburn, L.F.; Northing, P.; Luo, W.; Cannon, R.J.C.; Walters, K. Further compatibility tests of the entomopathogenic fungus Lecanicillium muscarium with conventional insecticide products for control of sweetpotato whitefly, Bemisia tabaci on poinsettia plants. Insect Sci. 2008, 15, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbertson, A.G.S.; Buxton, J.H.; Blackburn, L.F.; Mathers, J.J.; Robinson, K.K.; Powell, M.E.; Fleming, D.A.; Bell, H.A. Eradicating Bemisia tabaci Q biotype on poinsettia plants in the UK. Crop Prot. 2012, 42, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, R.B.; Pauli, G.; Mascarin, G.M.; Faria, M. Protection of entomopathogenic conidia against chemical fungicides afforded by an oil-based formulation. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2011, 21, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucias, D.G.; Stokes, C.; Storey, G.; Pendland, J.C. The effects of imidacloprid on the termite Reticulitermes flavipes and its interaction with the mycopathogen Beauveria bassiana. Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. Bayer 1996, 49, 103–144. [Google Scholar]
- Furlong, M.J.; Groden, E. Evaluation of synergistic interactions between the Colorado potato beetle (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) pathogen Beauveria bassiana and the insecticides, imidacloprid, and cyromazine. J. Econ. Entomol. 2001, 94, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwar, J.P.; Sachan, G.C. Synergistic effect of entomogenous fungi on some insecticides against Bihar hairy caterpillar Spilarctia oblique (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae). Microbiol. Res. 2006, 161, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintela, E.D.; McCoy, C.W. Synergistic effect of imidacloprid and two entomogenous fungi on behavior and survival of larvae of Diaprepes abbreviatus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in soil. J. Econ. Entomol. 1998, 91, 110–122. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, M.E.; Stansly, P.A.; Stelinski, L.L. Florida Citrus Pest Management Guide: Asian Citrus Psyllid and Citrus Leafminer; IFAS Extension Publication ENY-734; University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, P.J.; Patt, J.M.; Cabanillas, H.E.; Adamczyk, J.L.; Jackson, M.A.; Dunlap, C.A.; Hunter, W.B.; Avery, P.B. Localized autoinoculation and dissemination of Isaria fumosorosea for control of the Asian citrus psyllid in South Texas. Subtrop. Plant Sci. 2011, 63, 23–35. [Google Scholar]
- Martini, X.; Addison, T.; Fleming, B.; Jackson, I.; Pelz-Stelinski, K.; Stelinski, L.L. Occurrence of Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Liviidae) in an unexpected ecosystem: The Lake Kissimmee State Park Forest, Florida. Fla. Entomol. 2013, 96, 658–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bové, J.M. Huanglongbing: A destructive, newly-emerging, century-old disease of citrus. J. Plant Pathol. 2006, 88, 7–37. [Google Scholar]
- Kouassi, M.; Coderre, D.; Todorova, S.I. Effects of the timing of applications on the compatibility of three fungicides and one isolate of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) Vuillein (Deuteromycotina). J. Appl. Entomol. 2003, 127, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, C.P.; Padin, S.; Urrutia, M.I.; López Lastra, C.C. Interaction of fungicides with entomopathogenic fungus Isaria fumosorosea. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2011, 21, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Huang, Z.; Ren, S. Effect of fungicides on growth, germination and cuticle-degrading enzyme production by Lecanicillium muscarium. Bicontrol Sci. Technol. 2013, 6, 711–723. [Google Scholar]
- Avery, P.B.; Kumar, V.; Shareef, F.; Barbeau, E.; Nelson, P.; Landa, Z.; McKenzie, C.L.; Osborne, L.S.; Powell, C.A. Competitive capacity of Isaria fumosorosea with other fungal species present on the phylloplane of Ficus leaves for biocontrol of ficus whitefly. Fungal Ecol. 2013. in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Avery, P.B.; Faull, J.; Simmonds, M.S.J. Effects of Paecilomyces fumosoroseus and Encarsia formosa on the control of the greenhouse whitefly: Preliminary assessment of a compatibility study. BioControl 2008, 53, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pick, D.A.; Avery, P.B.; Hunter, W.B.; Powell, C.A.; Arthurs, S.P. Effect of Isaria fumosorosea (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae) and Lysiphlebus testaceipes (Hymenoptera: Aphidiinae) on the brown citrus aphid: Preliminary assessment of a compatibility study. Fla. Entomol. 2012, 95, 774–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterk, G.; Bolckmans, K.; de Jonghe, R.; de Wael, L.; Vermeulen, J. Side-effects of the microbial insecticide PreFeRal WG (Paecilomyces fumosoroseus, strain Apopka 97) on Bombus terrestris. Meded. Fac. Landbouww. Rijksuniv. 1995, 60, 713–717. [Google Scholar]
- Sterk, G.; Bolckmans, K.; van de Veire, M.; Sels, B.; Stepman, W. Side-effects of the microbial insecticide PreFeRal WG (Paecilomyces fumosoroseus, strain Apopka 97) on different species of beneficial arthropods. Meded. Fac. Landbouww. Rijksuniv. 1995, 60, 719–724. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.Q.; Weathersbee, A.A.; Mayer, R.T. Effect of neem seed extract on the brown citrus aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) and its parasitoid Lysiphlebus testaceipes (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae). Environ. Entomol. 2002, 31, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Avery, P.B.; Pick, D.A.; Aristizábal, L.F.; Kerrigan, J.; Powell, C.A.; Rogers, M.E.; Arthurs, S.P. Compatibility of Isaria fumosorosea (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae) Blastospores with Agricultural Chemicals Used for Management of the Asian Citrus Psyllid, Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Liviidae). Insects 2013, 4, 694-711. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects4040694
Avery PB, Pick DA, Aristizábal LF, Kerrigan J, Powell CA, Rogers ME, Arthurs SP. Compatibility of Isaria fumosorosea (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae) Blastospores with Agricultural Chemicals Used for Management of the Asian Citrus Psyllid, Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Liviidae). Insects. 2013; 4(4):694-711. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects4040694
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvery, Pasco B., David A. Pick, Luis F. Aristizábal, James Kerrigan, Charles A. Powell, Michael E. Rogers, and Steven P. Arthurs. 2013. "Compatibility of Isaria fumosorosea (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae) Blastospores with Agricultural Chemicals Used for Management of the Asian Citrus Psyllid, Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Liviidae)" Insects 4, no. 4: 694-711. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects4040694
APA StyleAvery, P. B., Pick, D. A., Aristizábal, L. F., Kerrigan, J., Powell, C. A., Rogers, M. E., & Arthurs, S. P. (2013). Compatibility of Isaria fumosorosea (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae) Blastospores with Agricultural Chemicals Used for Management of the Asian Citrus Psyllid, Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Liviidae). Insects, 4(4), 694-711. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects4040694