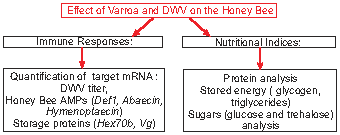
How Varroa Parasitism Affects the Immunological and Nutritional Status of the Honey Bee, Apis mellifera
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. The Insects and Sampling Procedure
2.2. Molecular Analysis
| Primer names and GenBank Accession [#] | Primers 5′→3′ |
|---|---|
| Deformed wing virus [AB605386] DWV_F DWV_R | GACAAAATGACGAGGAGATTGTT ACTACCTGTAATGTCGTCGTGTT |
| Defensin 1 [U15955] Def1_F Def1_R | GTTGAGGATGAATTCGAGCC TTAACCGAAACGTTTGTCCC |
| Abaecin [U159554] Abaecin_F Abaecin_R | GGTAGTGATATTTATCTTCGC TTGAGGCCATTTAATTTTCGG |
| Hymenoptaecin [U15956] Hymenoptaecin_F Hymenoptaecin_R | ATGGATTATATCCCGACTCG TCTAAATCCACCATTTATTCC |
| Hexamerin70b [NM_001011600] Hex70b_F Hex70b_R | CCGCTCTTCAAATGTGGTCTAC GATAGGTAAAAGGTTTGTGGTTC |
| Vitellogenin [NM_001011578] Vg_FVg_R | TGGCTCTGGACGGTGAAC CCCTCGCATTGGTTACTGAT |
| Actin [AB023025] Actin_F Actin_R | TGAAGTGCGATGTCGATATC GAGATCCACATCTGTTGGAA |
2.3. Nutritional Indices
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Abundance of Varroa in the Honey Bee Colonies
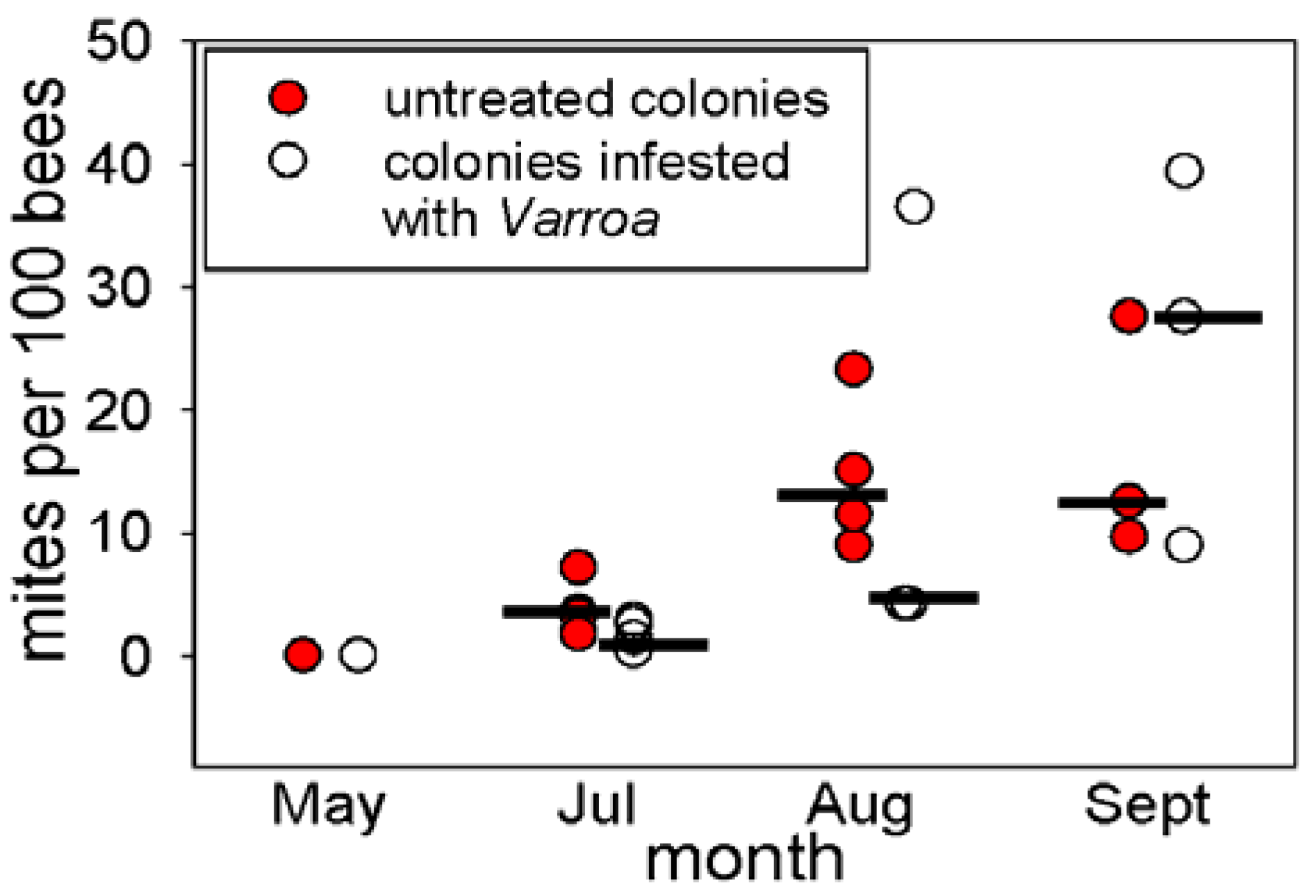
3.2. Effect of Varroa on DWV Titer and Immune-Related Indices of Bees

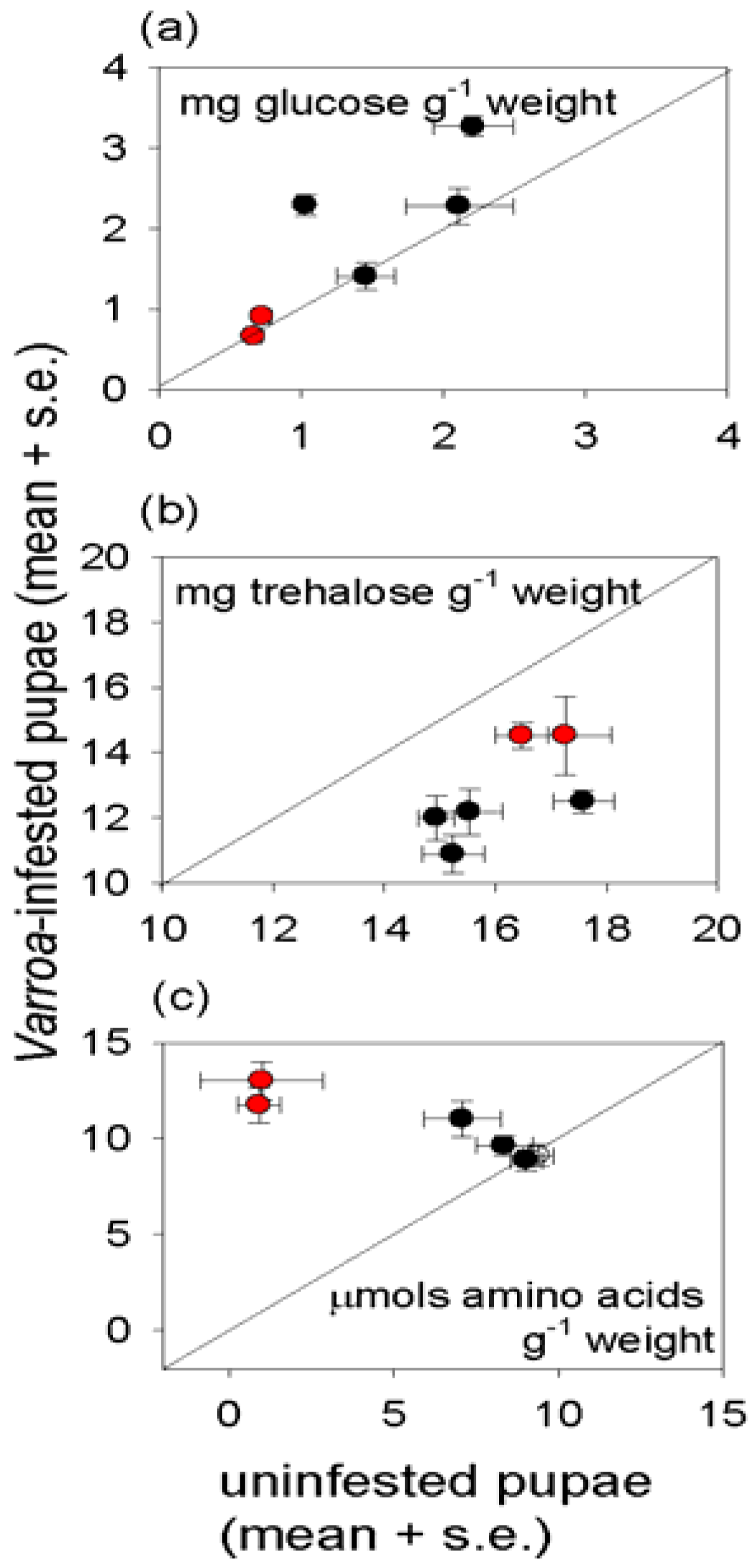
3.3. Effect of Varroa on Nutritional Status of Bees

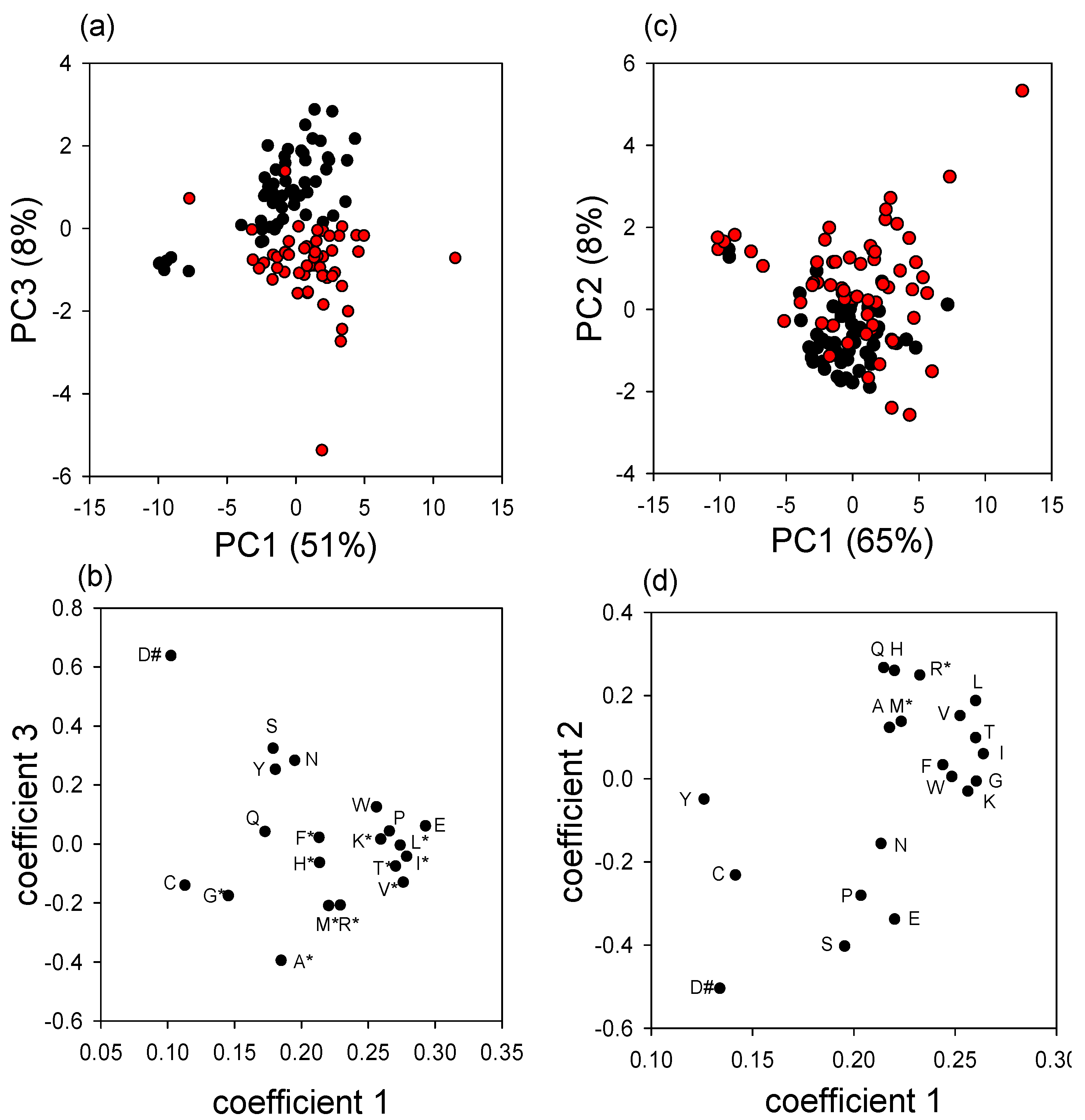
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
References
- Ponton, F.; Wilson, K.; Cotter, S.C.; Raubenheimer, D.; Simpson, S.J. Nutritional immunology: A multi-dimensional approach. PLoSPathog. 2011, 7, e1002223. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, D. Physiological Integration of Innate Immunity. In Insect Infection and Immunity; Rolff, J., Reynolds, S.E., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 106–116. [Google Scholar]
- Moret, Y.; Schmid-Hempel, P. Survival for immunity: The price of immune system activation for bumblebee workers. Science 2000, 290, 1166–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon, B.C.; Verhulst, S. Ecological immunology: Costly parasite defences and trade-offs in evolutionary ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1996, 11, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D.S.; Ayres, J.S. Two ways to survive infection: What resistance and tolerance can teach us about treating infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, S.S. Insulin/TOR signaling in growth and homeostasis: A view from the fly world. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.L.; Trueman, J.W.H. Varroa jacobsoni (Acari: Varroidae) is more than one species. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2000, 24, 165–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, J.; Dittmann, F.; Rosenkranz, P.; Engels, W. The first gonocycle of the parasitic mite (Varroa juobsoni) in relation to preimaginal development of its host, the honey bee (Apis mellifra carnicar). Invertebr.Reprod. Dev. 1994, 25, 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkranz, P.; Aumeier, P.; Ziegelmann, B. Biology and control of Varroa destructor. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2010, 103, S96–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.R.; Tarpy, D.R.; Engelsdorp, D.V.; Chauzat, M.-P.; Cox-Foster, D.L.; Delaplane, K.S.; Neumann, P.; Pettis, J.S.; Rogers, R.E.L.; Shutler, D. Colony collapse disorder in context. BioEssays 2010, 32, 845–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Engelsdorp, D.; Hayes, J., Jr.; Underwood, R.M.; Pettis, J.S. A survey of honey bee colony losses in the United States, fall 2008 to spring 2009. J. Apic. Res. 2010, 49, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.J. The role of Varroa and viral pathogens in the collapse of honeybee colonies: A modelling approach. J. Appl. Ecol. 2002, 38, 1082–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Cox-Foster, D.L. Impact of an ectoparasite on the immunity and pathology of an invertebrate: Evidence for host immunosuppression and viral amplification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 7470–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Cox-Foster, D.L. Effects of parasitization by Varroa destructor on survivorship and physiological traits of Apis mellifera in correlation with viral incidence and microbial challenge. Parasitology 2007, 134, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Pettis, J.S.; Feldlaufer, M.F. Detection of multiple viruses in queens of the honey bee Apis mellifera L. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2005, 90, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Siede, R. Honey bee viruses. Adv. Virus Res. 2007, 70, 33–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, J.R.D.; Genersch, E. Deformed wing virus. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2010, 103, S48–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronstein, K.; Saldivar, E. Characterization of a honey bee Toll related receptor gene Am18w and its potential involvement in antimicrobial immune defense. Apidologie 2005, 36, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.D.; Aronstein, K.; Chen, Y.P.; Hetru, C.; Imler, J.-L.; Jiang, H.; Kanost, M.; Thompson, G.J.; Zou, Z.; Hultmark, D. Immune pathways and defense mechanisms in honey bees Apis mellifera. Insect Mol. Biol. 2006, 15, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaplane, K.S.; Hood, W.M. Effects of delayed acaricide treatment in honey bee colonies parasitized by Varroa jacobsoni and a late season treatment threshold for the southeastern USA. J. Apic. Res. 1997, 36, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, T.C.; Delaplane, K.S. Mites of the Honey Bee; Dadant and Sons, Inc.: Hamilton, Illinois, 2001; p. 280. [Google Scholar]
- Scharlaken, B.; de Graaf, D.C.; Goossens, K.; Brunain, M.; Peelman, L.J.; Jacobs, F.J. Reference gene selection for insect expression studies using quantitative real-time PCR: The honeybee, Apis mellifera, head after a bacterial challenge. J. Insect Sci. 2008, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lourenco, A.P.; Mackert, A.; Cristino, A.S.; Simoes, Z.L.P. Validation of reference genes for gene expression studies in the honey bee, Apis mellifera, by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Apidologie 2008, 39, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, E45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, M.R.; Perry, J.H.; Houten, A.T. The effect of drifting honey bees on the spread of American foulbrood infections. J. Apic. Res. 1994, 33, 209–212. [Google Scholar]
- Delaplane, K.S. The managed pollinator CAP after Three Years: Highlights and emerging trends. Am. Bee J. 2012, January, 77. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, C.; Genersch, E. RT-PCR analysis of Deformed wing virus in honeybees (Apis mellifera) and mites (Varroa destructor). J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 3419–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navajas, M.; Migeon, A.; Alaux, C.; Martin-Magniette, M.L.; Robinson, G.E.; Evans, J.D.; Cros-Arteil, S.; Crauser, D.; Le Conte, Y. Differential gene expression of the honey bee Apis mellifera associated with Varroa destructor infection BMC. Genomics 2008, 9, 301. [Google Scholar]
- Panyasrivanit, M.; Khakpoor, A.; Wikan, N.; Smith, D.R. Co-localization of constituents of the dengue virus translation and replication machinery with amphisomes. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakpoor, A.; Panyasrivanit, M.; Wikan, N.; Smith, D.R. A role for autophagolysosomes in dengue virus 3 production in HepG2 cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisder, S.; Aumeier, P.; Genersch, E. Deformed wing virus: Replication and viral load in mites (Varroa destructor). J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.; Jironkin, A.; Chandler, D.; Burroughs, N.; Evans, D.J.; Ryabov, E.V. Recombinants between Deformed wing virus and Varroa destructor virus-1 may prevail in Varroa destructor-infested honeybee colonies. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zioni, N.; Soroker, V.; Chejanovsky, N. Replication of Varroa destructor virus 1 (VDV-1) and a Varroa destructor virus 1-deformed wing virus recombinant (VDV-1-DWV) in the head of the honey bee. Virology 2011, 417, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen-Walker, P.L.; Gunn, A. The effect of the ectoparasitic mite, Varroa destructor, on adult worker honey bee (Apis mellifera) emergence weights, water, protein, carbohydrate and lipid levels. Entomol. Exp. et Appl. 2001, 101, 207–217. [Google Scholar]
- Alaux, C.; Dantec, C.; Parrinello, H.; Le Conte, Y. Nutrigenomics in honey bees: Digital gene expression analysis of pollen's nutritive effects on healthy and varroa-parasitized bees. BMC Genomics 2011, 12, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodschneider, R.; Crailsheim, K. Nutrition and health in honey bees. Apidologie 2010, 41, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fefferman, N.H.; Traniello, J.F.A.; Rosengaus, R.B.; Calleri, D.V. Disease prevention and resistance in social insects: modeling the survival consequences of immunity, hygienic behavior, and colony organization. Behav.Ecol. Soc. 2007, 61, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, B.J.; Barribeau, S.M.; Laughton, A.M.; Roode, J.C.D.; Gerardo, N.M. Non-immunological defense in an evolutionary framework. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2011, 26, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Aronstein, K.A.; Saldivar, E.; Vega, R.; Westmiller, S.; Douglas, A.E. How Varroa Parasitism Affects the Immunological and Nutritional Status of the Honey Bee, Apis mellifera. Insects 2012, 3, 601-615. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects3030601
Aronstein KA, Saldivar E, Vega R, Westmiller S, Douglas AE. How Varroa Parasitism Affects the Immunological and Nutritional Status of the Honey Bee, Apis mellifera. Insects. 2012; 3(3):601-615. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects3030601
Chicago/Turabian StyleAronstein, Katherine A., Eduardo Saldivar, Rodrigo Vega, Stephanie Westmiller, and Angela E. Douglas. 2012. "How Varroa Parasitism Affects the Immunological and Nutritional Status of the Honey Bee, Apis mellifera" Insects 3, no. 3: 601-615. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects3030601
APA StyleAronstein, K. A., Saldivar, E., Vega, R., Westmiller, S., & Douglas, A. E. (2012). How Varroa Parasitism Affects the Immunological and Nutritional Status of the Honey Bee, Apis mellifera. Insects, 3(3), 601-615. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects3030601