Underground Inter-Nest Tunnels of Red Imported Fire Ants, Solenopsis invicta: Physical Features and Associations with Colony and Environmental Factors
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Locations, Habitats, and Nest Mounds
2.2. Nest Mounds
2.3. Excavation of Mounds and Recording of Habitat Features
2.3.1. Paired Mounds
2.3.2. Solitary Mounds
2.4. Relations of Tunnels to Nest Relocation
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
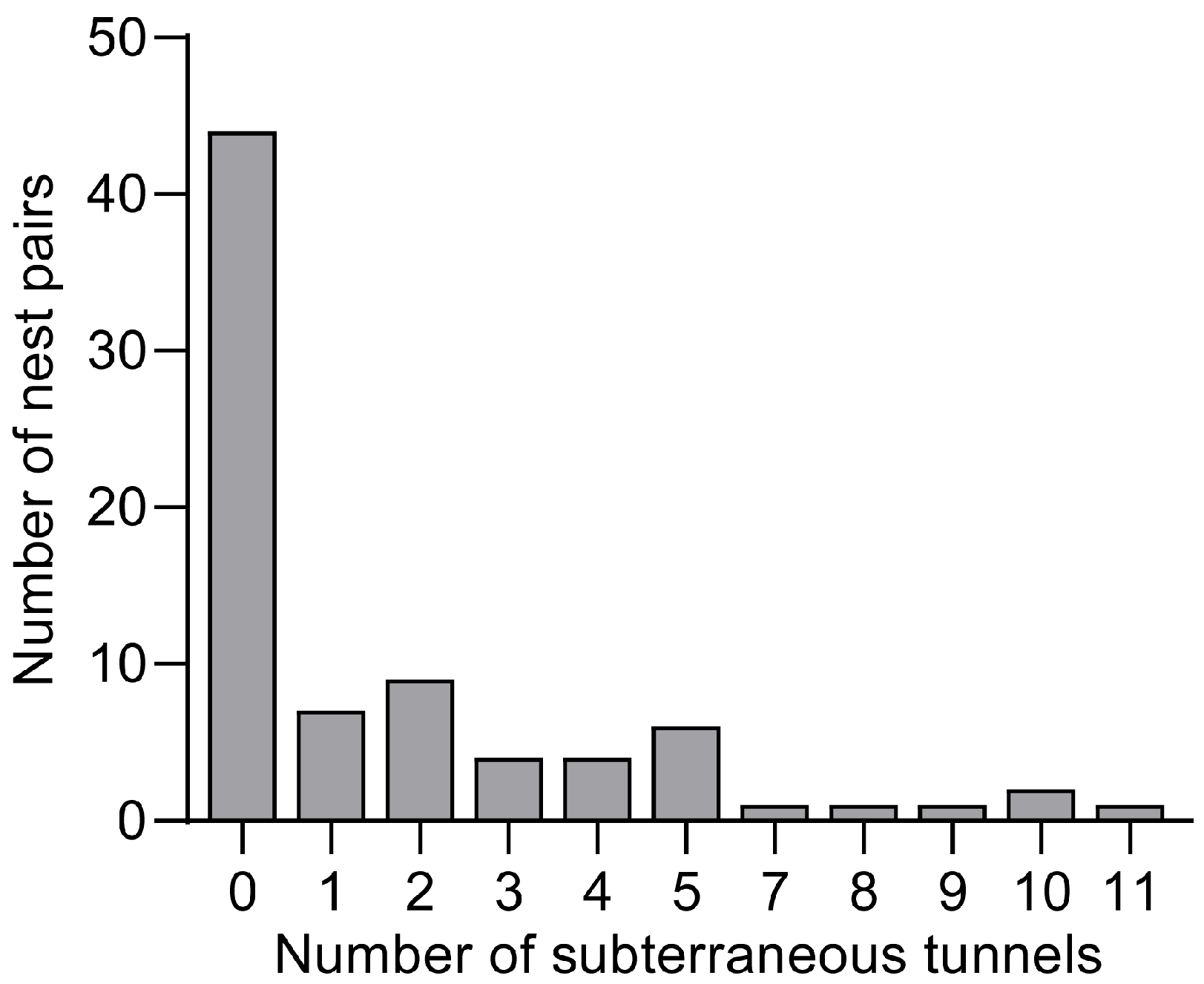
3.1. Features of the Tunnels Between Adjacent S. invicta Nests
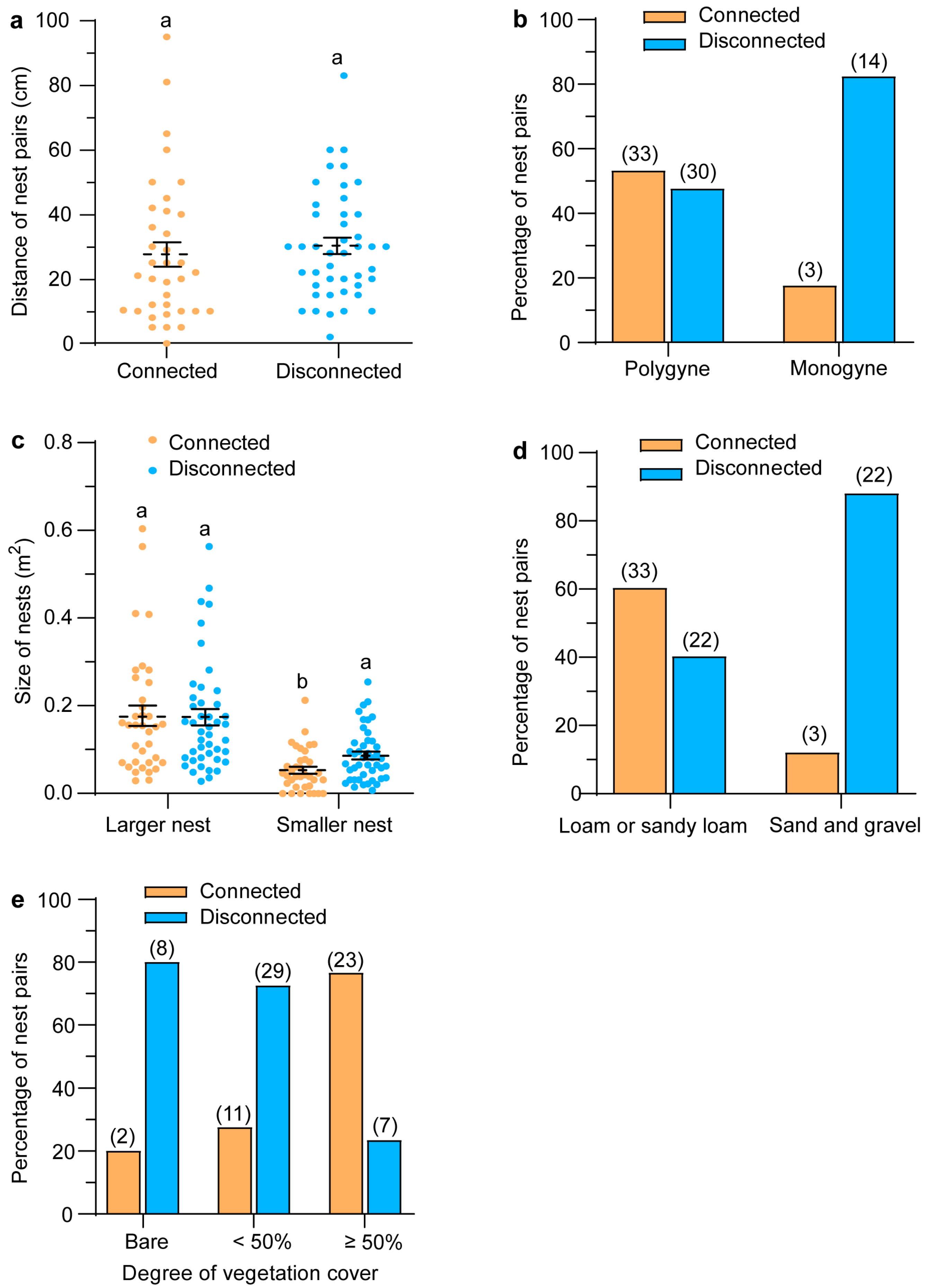
3.2. Associations of Inter-Nest Tunnels with Environmental Factors and Social Form
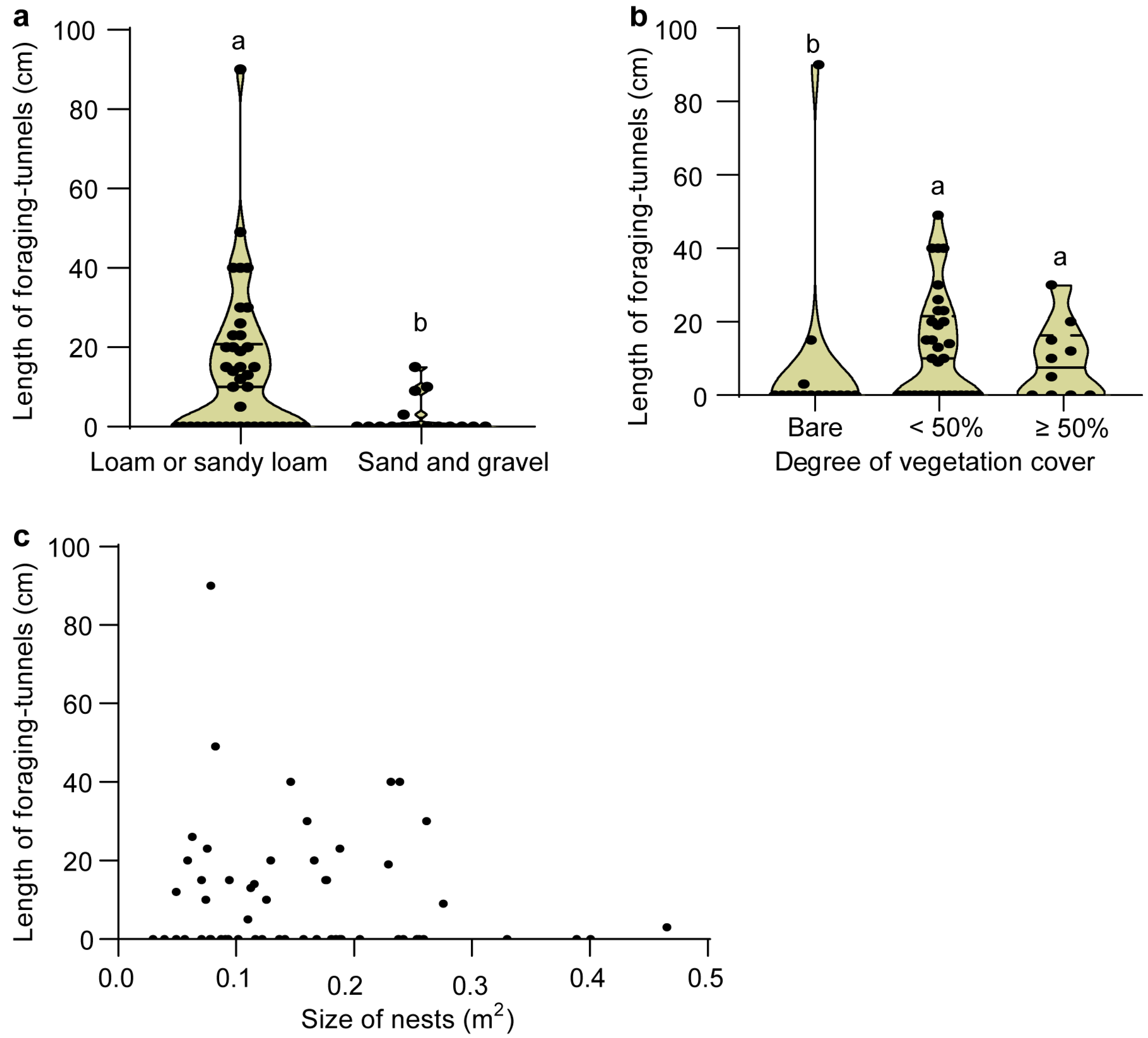
3.3. Comparisons of Inter-Nest Tunnels with the Foraging Tunnels
3.4. Contributions of Tunnels to Nest Relocation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tschinkel, W.R. The architecture of subterranean ant nests: Beauty and mystery underfoot. J. Bioeconomics 2015, 17, 271–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markin, G.P.; O’Neal, J.; Dillier, J. Foraging tunnels of the red imported fire ant, Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 1975, 48, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Cassill, D.; Tschinkel, W.R.; Vinson, S.B. Nest complexity, group size and brood rearing in the fire ant, Solenopsis invicta. Insectes Soc. 2002, 49, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüthgen, N.; Feldhaar, H. Food and Shelter: How Resources Influence Ant Ecology; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 115–136. [Google Scholar]
- Vandermeer, J.; Flores, J.; Longmeyer, J.; Perfecto, I. Spatiotemporal foraging dynamics of Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) and its potential effects on the spatial structure of interspecific competition. Environ. Entomol. 2022, 51, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byron, D.W.; Hays, S.B. Occurrence and significance of multiple mound utilization by colonies of the red imported fire ant (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 1986, 79, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, E.J.H. Polydomy: The organisation and adaptive function of complex nest systems in ants. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2014, 5, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.; McShea, D.W. Intermediate-level parts in insect societies: Adaptive structures that ants build away from the nest. Insectes Soc. 2001, 48, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, D.D.R.; Franks, D.W.; Parr, C.; Robinson, E.J.H. Ant colony nest networks adapt to resource disruption. J. Anim. Ecol. 2021, 90, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holway, D.A.; Lach, L.; Suarez, A.V.; Tsutsui, N.D.; Case, T.J. The causes and consequences of ant invasions. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2002, 33, 181–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, R.; Yang, C.C.S.; Tsuji, K. Invader at the gate: The status of red imported fire ant in Australia and Asia. Ecol. Res. 2020, 35, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchetti, M.; Schifani, E.; Alicata, A.; Cardador, L.; Sbrega, E.; Toro-Delgado, E.; Vila, R. The invasive ant Solenopsis invicta is established in Europe. Curr. Biol. 2023, 33, R896–R897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinson, S.B. Invasion of the red imported fire ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae): Spread, biology, and impact. Am. Entomol. 1997, 43, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, Y.J.; Zeng, L.; Lu, Y.Y. Impact of the red imported fire ant Solenopsis invicta Buren on biodiversity in South China: A review. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittman, S.E. Impacts of invasive ants on native ant communities (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecol. News 2014, 19, 111–123. [Google Scholar]
- Morel, L.; Meer, R.K.V.; Lofgren, C.S. Comparison of nestmate recognition between monogyne and polygyne populations of Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1990, 83, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinson, S.B.; Greenberg, L. The biology, physiology, and ecology of imported fire ants. In Economic Impact and Control of Social Insects; Vinson, S.B., Ed.; Praeger: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 193–226. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, S.D.; Tschinkel, W.R. Foraging in Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) effects of weather and season. Environ. Entomol. 1987, 16, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschinkel, W.R. The organization of foraging in the fire ant, Solenopsis invicta. J. Insect Sci. 2011, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.D.; Hudnall, W.H.; Reagan, T.E. Effects of soil types and cultural practices on the fire ant, Solenopsis invicta, in Sugarcane. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1986, 18, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farji-Brener, A.G.; Chinchilla, F.; Umaña, M.N.; Ocasio-Torres, M.E.; Chauta-Mellizo, A.; Acosta-Rojas, D.; Marinaro, S.; Curth, M.D.; Amador-Vargas, S. Branching angles reflect a trade-off between reducing trail maintenance costs or travel distances in leaf-cutting ants. Ecology 2015, 96, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, T.A.; Hastenreiter, I.N.; Almeida, N.G.; Lopes, J.F.S. Fast food delivery: Is there a way for foraging success in leaf-cutting ants? Sociobiology 2015, 62, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Self, S.R.; Nebeker, T.E. Imported fire ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) mound distribution relationships in connection to the heterogeneity of ten Christmas tree farm landscapes in Mississippi. Midsouth. Entomol. 2011, 4, 14–21. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Showler, A.T.; Reagan, T.E. Ecological interactions of the red imported fire ant in the southeastern United States. J. Entomol. Sci. Suppl. 1987, 1, 52–64. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Collins, H.L.; Callcott, A.M.A. Effectiveness of spot insecticide treatments for red imported fire ant (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) control. J. Entomol. Sci. 1995, 30, 489–496. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Qi, G.J.; Wang, G.; Shi, Q.X.; Lu, J.J.; Guan, Z.Y.; Chen, T.; Chen, J.; Waris, M.I.; Lu, L.H. Effects of contact insecticide dusts on the field population density and colony relocation of red imported fire ant Solenopsis invicta Buren. J. Plant Prot. 2023, 50, 1184–1192, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Qi, G.J.; Liu, J.; Chen, T.; Lu, L.H.; He, Y.R. Effect of drench insecticide dose on the nest movement of Solenopsis invicta Buren. Environ. Entomol. 2017, 39, 848–853, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Kjeldgaard, M.K.; Eyer, P.A.; McMichael, C.C.; Bockoven, A.A.; King, J.T.; Hyodo, A.; Boutton, T.W.; Vargo, E.L.; Eubanks, M.D. Distinct colony boundaries and larval discrimination in polygyne red imported fire ants (Solenopsis invicta). Mol. Ecol. 2022, 31, 1007–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valles, S.M.; Porter, S.D. Identification of polygyne and monogyne fire ant colonies (Solenopsis invicta) by multiplex PCR of Gp-9 alleles. Insectes Soc. 2003, 50, 199–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPSS. Base 25.0 Users Guide; SPSS: Chicago, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- GraphPad Software Inc. GraphPad Prism Version10.0.0 for Windows; GraphPad: Boston, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Helanterä, H. Supercolonies of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae): Ecological patterns, behavioural processes and their implications for social evolution. Myrmecol. News 2022, 32, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, T.H.; Leather, S.R.; Cook, J.M. Macroevolutionary patterns in the origin of mutualisms involving ants. J. Evol. Biol. 2008, 21, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, N.E.; Ingram, K.K.; Gordon, D.M. Nest connectivity and colony structure in unicolonial Argentine ants. Insectes Soc. 2008, 55, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschinkel, W.R. The Fire Ants; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; pp. 1–747. [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza, D.N.; Santamarina, J.C. Ant tunneling-a granular media perspective. Granul. Matter 2010, 12, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaenkova, D.; Gravish, N.; Rodriguez, G.; Kutner, R.; Goodisman, M.A.D.; Goldman, D. Behavioral and mechanical determinants of collective subsurface nest excavation. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Evidence of social facilitation and inhibition in digging behavior of red imported fire ants, Solenopsis invicta. Insect Sci. 2021, 28, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanan, M. Spatiotemporal resource distribution and foraging strategies of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecol. News 2014, 20, 53–70. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, S.A.; Thorvilson, H.G.; Phillips, S.A. Red imported fire ant Solenopsis invicta Buren (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) populations in Texas highway roadsides and rest areas. Southwest. Entomol. 2001, 26, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Lubertazzi, D.; Tschinkel, W.R. Ant community change across a ground vegetation gradient in north Florida’s longleaf pine flatwoods. J. Insect Sci. 2003, 3, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Nagatani, V.H.; Ramalho, M.O.; Alves, J.M.C.; Souza, R.F.; Kayano, D.Y.; Silva, N.S.; Silva, O.G.M.; Harakava, R.; Bueno, O.C.; Hilsdorf, A.W.S.; et al. Impact of native vegetation cover near crops on the occurrence and molecular diversity of fire ants. Agric. For. Entomol. 2022, 25, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, C.H.; King, J.R.; Boughton, E.H.; Jenkins, D. Distribution of the red imported fire ant Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in central Florida pastures. Environ. Entomol. 2020, 49, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankovitz, M.; Purcell, J. Ant nest architecture is shaped by local adaptation and plastic response to temperature. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargo, E.L.; Porter, S.D. Colony reproduction by budding in the polygyne form of Solenopsis-invicta (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1989, 82, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.H.; Yang, X.Y.; Zheng, Y.R.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, M.X. Discovering native ant species with the potential to suppress red imported fire ants. Insects 2024, 15, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerome, C.A.; McInnes, D.A.; Adams, E.S. Group defense by colony-founding queens in the fire ant Solenopsis invicta. Behav. Ecol. 1998, 9, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
| Sampling Locations | Coordinates | Habitat Type | No. of Sampled Nests |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wucheng, Zhejiang | 29.028~29.169° N, 119.592~119.738° E | Green belt and grassland | 31 paired nests and 9 isolated nests |
| Dongyang, Zhejiang | 29.095~29.116° N, 120.201~120.230° E | Roadside, grassland, and farmland | 42 paired nests and 49 isolated nests |
| Longyou, Zhejiang | 29.083~29.085° N, 119.264~119.265° E | Farmland | 7 paired nests |
| Factors | Values Produced from Tests | p-Value | df |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nest distance | −1.206 | 0.228 | 78 |
| Social form | 0.656 * | 0.011 | 1 |
| Larger nest size | −0.131 | 0.896 | 78 |
| Smaller nest size | 2.741 ** | 0.008 | 78 |
| Average nest size | 0.839 | 0.404 | 78 |
| Soil type | 16.000 ** | <0.001 | 1 |
| Vegetation cover | 19.630 ** | <0.001 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ni, M.; Lu, J.; Yang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, M. Underground Inter-Nest Tunnels of Red Imported Fire Ants, Solenopsis invicta: Physical Features and Associations with Colony and Environmental Factors. Insects 2025, 16, 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080835
Ni M, Lu J, Yang X, Zheng Y, Wang Y, Jiang M. Underground Inter-Nest Tunnels of Red Imported Fire Ants, Solenopsis invicta: Physical Features and Associations with Colony and Environmental Factors. Insects. 2025; 16(8):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080835
Chicago/Turabian StyleNi, Meihong, Juli Lu, Xinyi Yang, Yiran Zheng, Yuan Wang, and Mingxing Jiang. 2025. "Underground Inter-Nest Tunnels of Red Imported Fire Ants, Solenopsis invicta: Physical Features and Associations with Colony and Environmental Factors" Insects 16, no. 8: 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080835
APA StyleNi, M., Lu, J., Yang, X., Zheng, Y., Wang, Y., & Jiang, M. (2025). Underground Inter-Nest Tunnels of Red Imported Fire Ants, Solenopsis invicta: Physical Features and Associations with Colony and Environmental Factors. Insects, 16(8), 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080835





