Temporal miRNA Biomarkers for Pupal Age Estimation in Sarcophaga peregrina (Diptera: Sarcophagidae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Synchronization of Necrophagous Fly Samples
2.2. Observation and Documentation of Internal Pupal Morphology
2.3. miRNA Extraction, Library Construction, and Sequencing
2.4. Data Preprocessing and miRNA Expression Analysis
2.5. Differential Expression Analysis, Temporal Trend Identification, and Functional Enrichment
2.6. Selection of Candidate miRNAs and qRT-PCR Validation
2.7. Data Analysis and Model Construction
3. Results
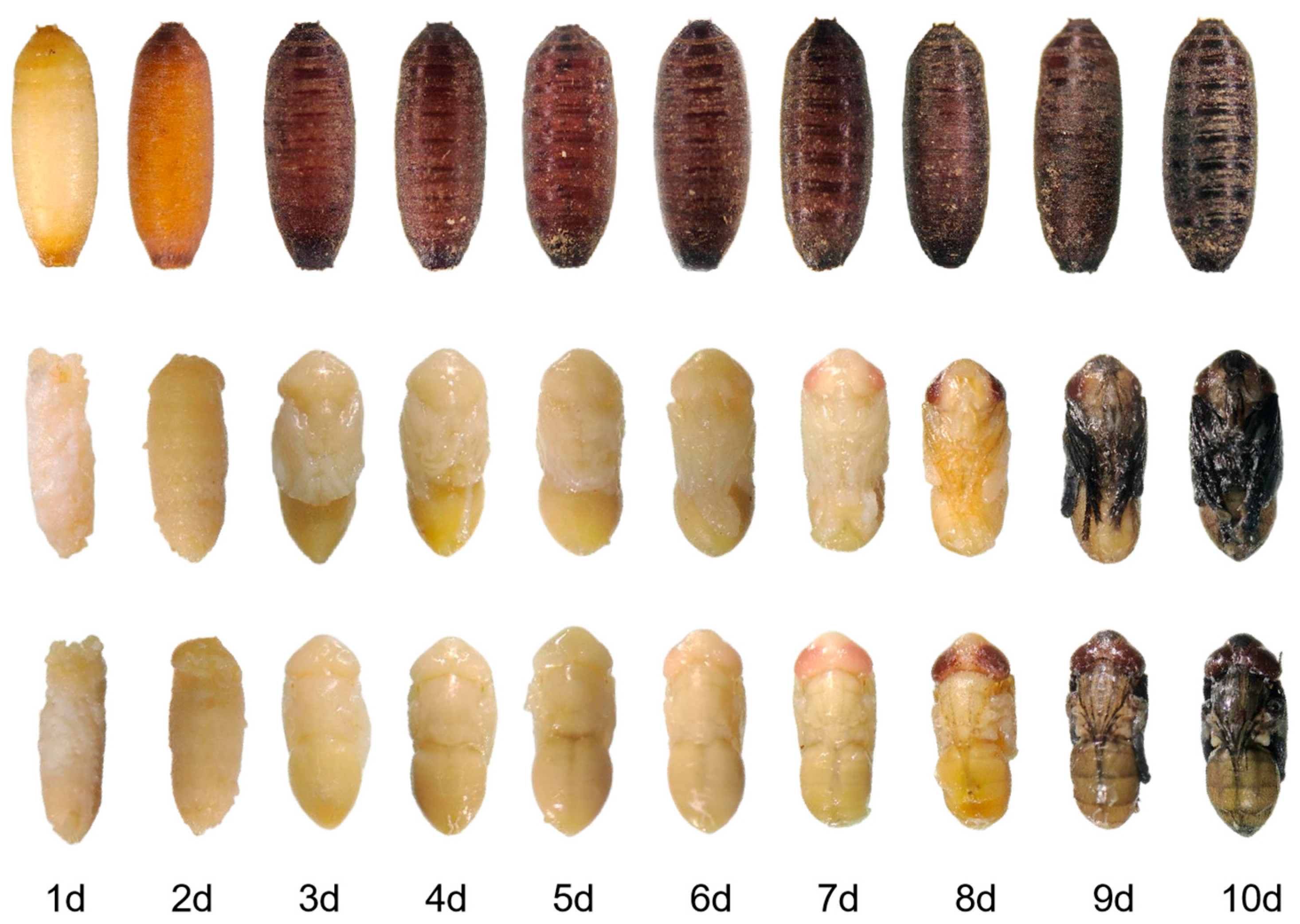
3.1. Stage-Specific Morphogenesis of Sarcophaga peregrina Pupae
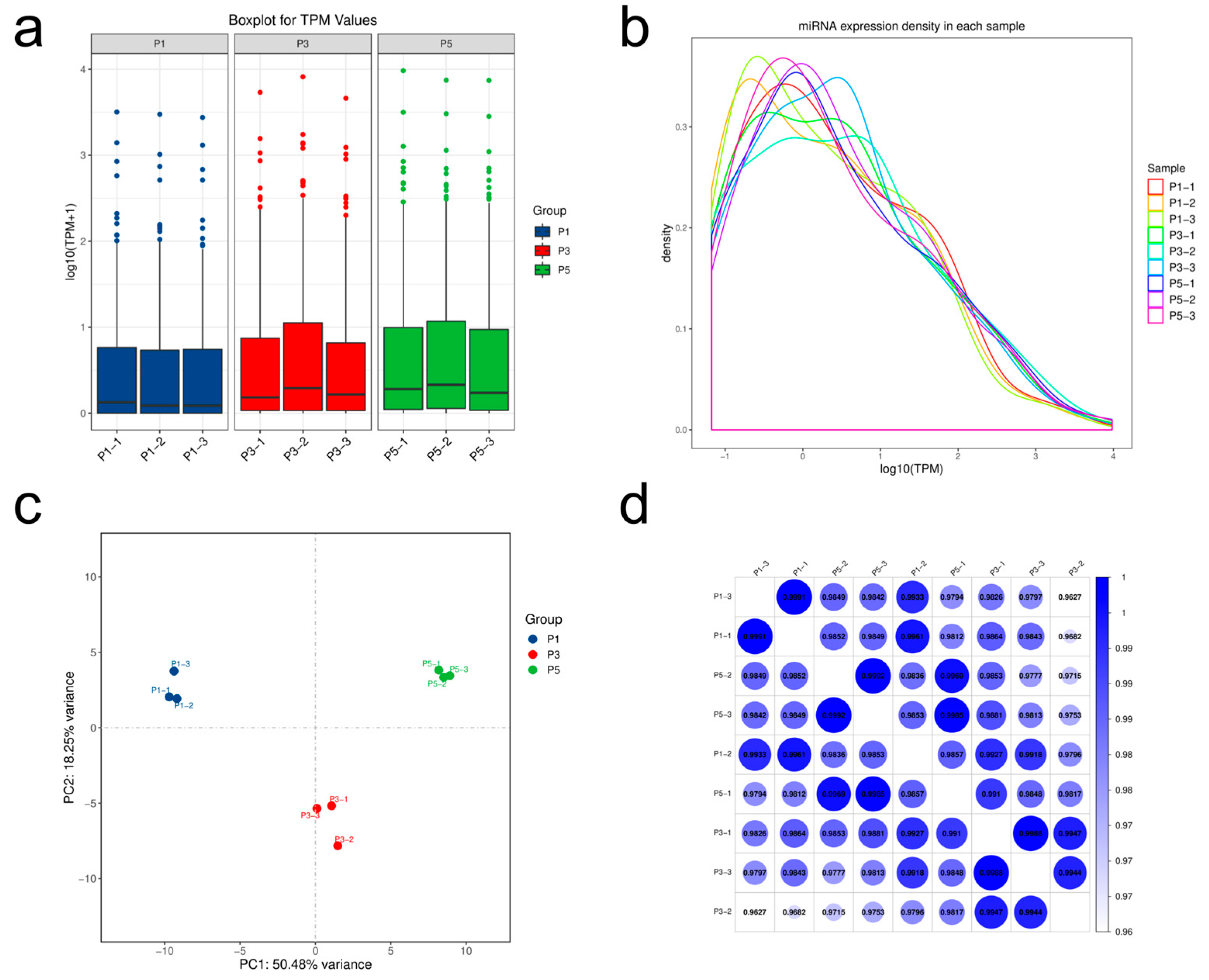
3.2. Quality Assessment of Small RNA Sequencing Data
3.3. Temporal Patterns of miRNA Expression Across Pupal Development
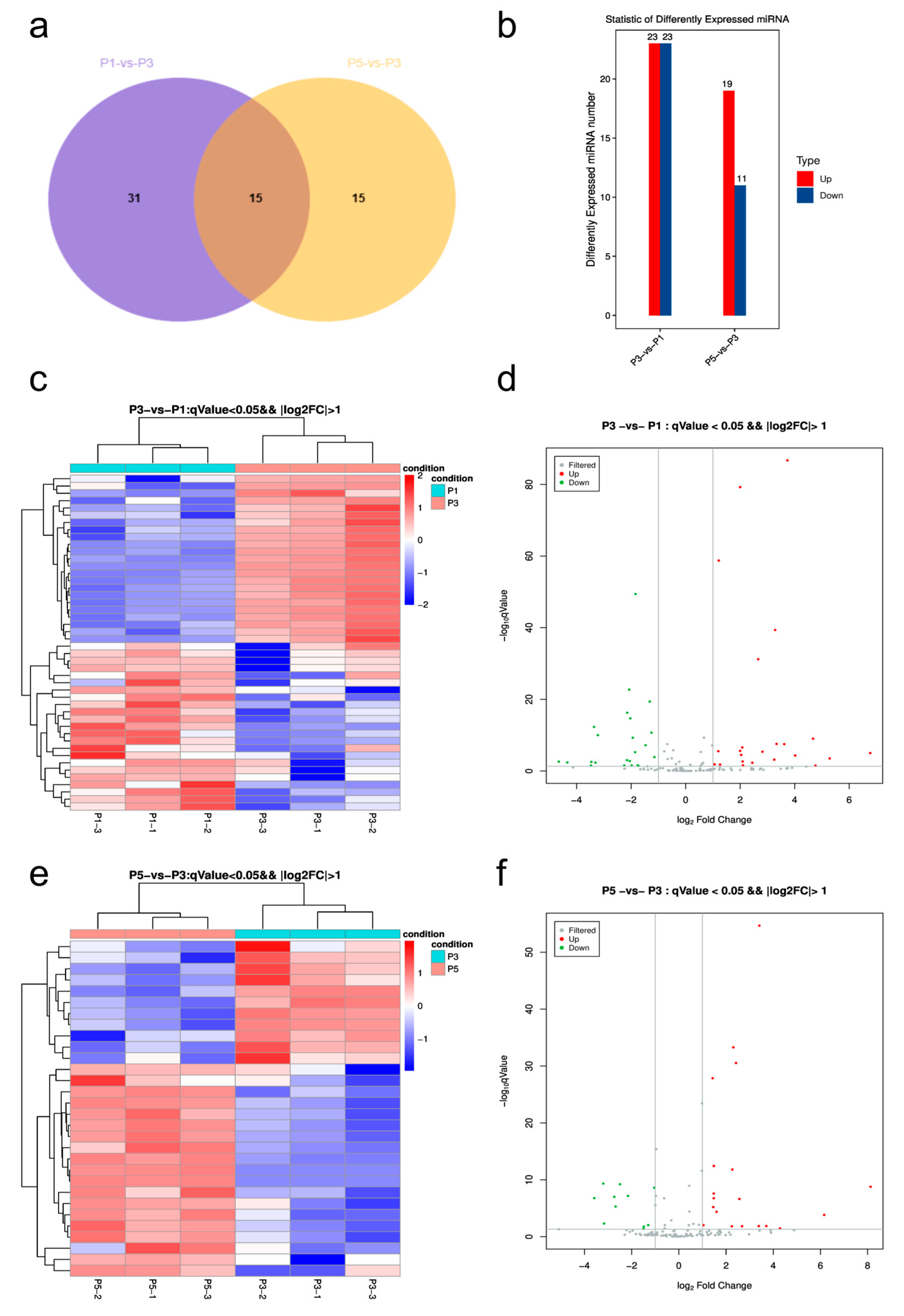
3.4. Differential Expression Analysis of miRNAs Across Developmental Stages
3.5. Target Prediction and Functional Enrichment of Differentially Expressed miRNAs
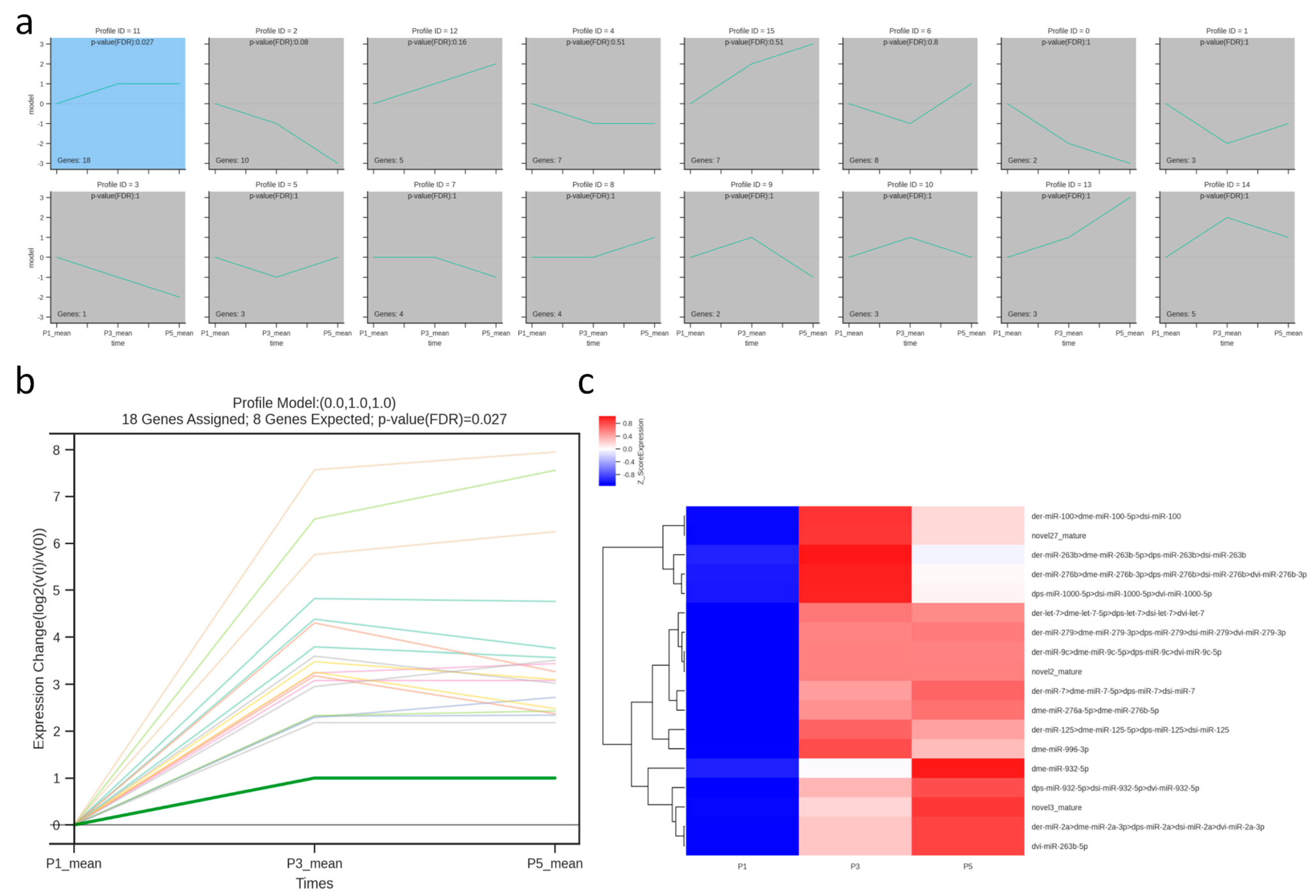
3.6. Temporal Trend Analysis of Differentially Expressed miRNAs
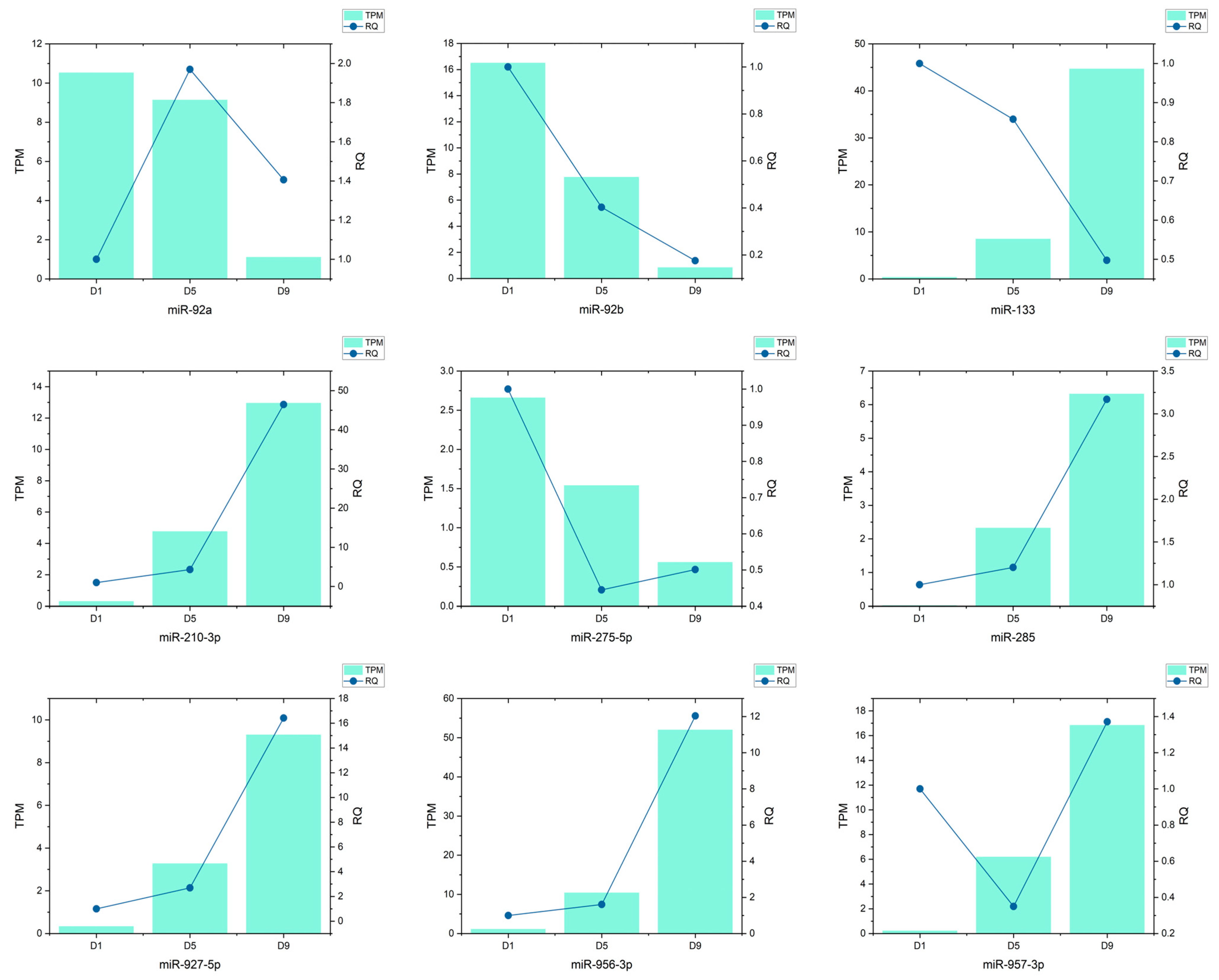
3.7. qRT-PCR Validation of Candidate miRNAs
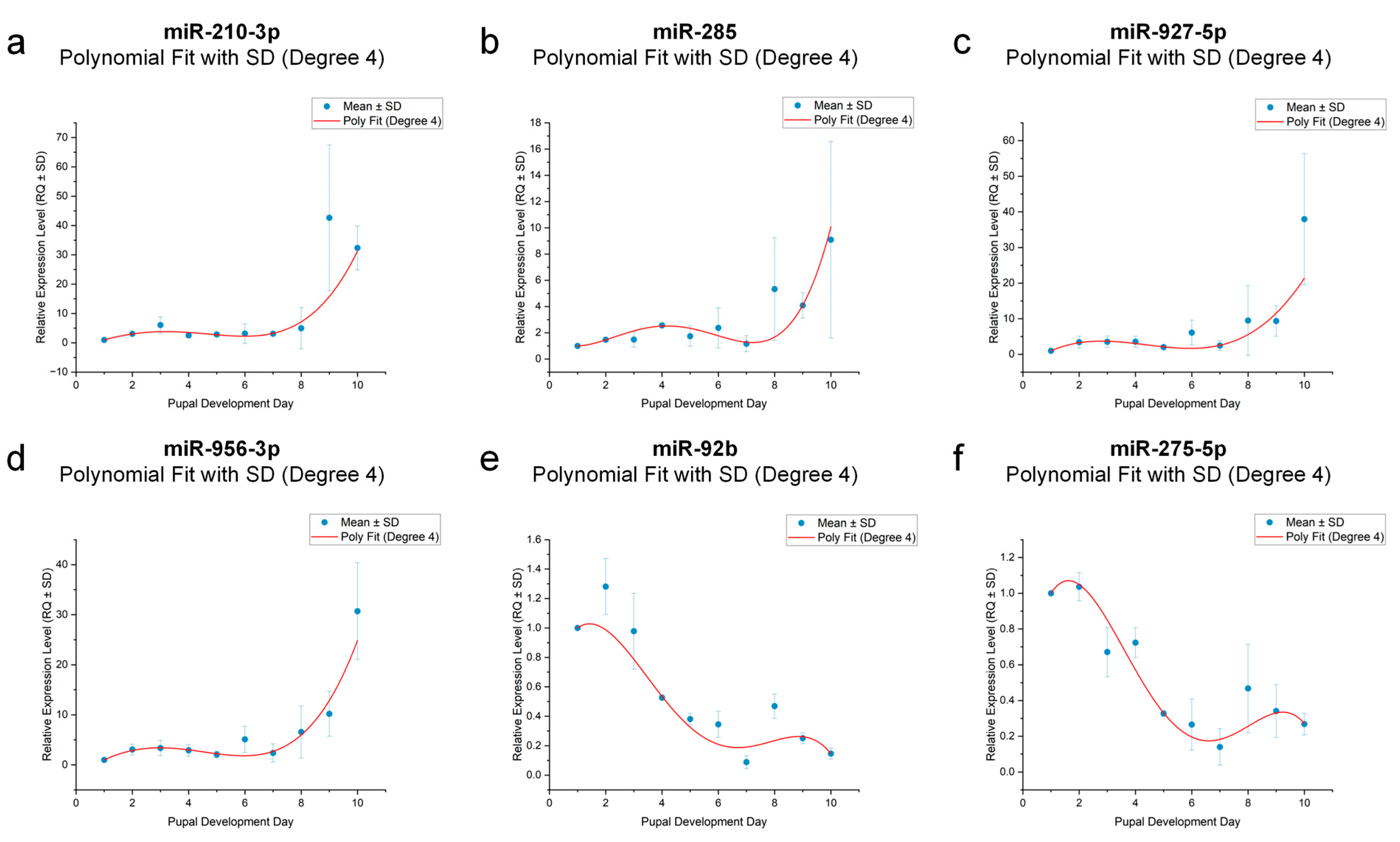
3.8. Dynamic Modeling of miRNA Expression Trends During Pupal Development
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rivers, D.B.; Dahlem, G.A. The Science of Forensic Entomology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, Y.; Ren, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Chen, W.; Dong, J.; Ma, H.; Qi, X.; Guo, Y. Differential Gene Expression for Age Estimation of Forensically Important Sarcophaga peregrina (Diptera: Sarcophagidae) Intrapuparial. J. Med. Entomol. 2020, 57, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reibe, S.; Doetinchem, P.V.; Madea, B. A new simulation-based model for calculating post-mortem intervals using developmental data for Lucilia sericata (Dipt.: Calliphoridae). Parasitol. Res. 2010, 107, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amendt, J.; Richards, C.S.; Campobasso, C.P.; Zehner, R.; Hall, M.J. Forensic entomology: Applications and limitations. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2011, 7, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarone, A.M.; Jennings, K.C.; Foran, D.R. Aging blow fly eggs using gene expression: A feasibility study. J. Forensic Sci. 2007, 52, 1350–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehme, P.; Spahn, P.; Amendt, J.; Zehner, R. Differential gene expression during metamorphosis: A promising approach for age estimation of forensically important Calliphora vicina pupae (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Int. J. Leg. Med. 2013, 127, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, K.; Herrmann, E.; Amendt, J.; Verhoff, M.A.; Zehner, R. Age-dependent gene expression of Calliphora vicina pupae (Diptera: Calliphoridae) at constant and fluctuating temperatures. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2021, 135, 2625–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Kang, L. Regulation of insect behavior by non-coding RNAs. Sci. China Life Sci. 2024, 67, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Ren, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Y. Genome-wide analysis of long noncoding RNAs and their association in regulating the metamorphosis of the Sarcophaga peregrina (Diptera: Sarcophagidae). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Tang, H.; Han, X.; Ngando, F.J.; Shang, Y.; Guo, Y. Identification of circular RNAs as biomarkers for pupal age estimation and postmortem interval in forensically important Sarcophaga peregrina (Diptera: Sarcophagidae). Int. J. Leg. Med. 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjelmen, C.E.; Yuan, Y.; Parrott, J.J.; McGuane, A.S.; Srivastav, S.P.; Purcell, A.C.; Pimsler, M.L.; Sze, S.H.; Tarone, A.M. Identification and Characterization of Small RNA Markers of Age in the Blow Fly Cochliomyia macellaria (Fabricius) (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Insects 2022, 13, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L. Corpse-Feeding Flies in China; Guizhou Science and Technology Press: Guiyang, China, 2013; p. 327. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Ren, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Y. Pupal Age Estimation of Sarcophaga peregrina (Diptera: Sarcophagidae) at Different Constant Temperatures Utilizing ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy and Cuticular Hydrocarbons. Insects 2023, 14, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Y.; Yang, F.; Ngando, F.J.; Zhang, X.; Feng, Y.; Ren, L.; Guo, Y. Development of Forensically Important Sarcophaga peregrina (Diptera: Sarcophagidae) and Intra-Puparial Age Estimation Utilizing Multiple Methods at Constant and Fluctuating Temperatures. Animals 2023, 13, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Y.; Amendt, J.; Wang, Y.; Ren, L.; Yang, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Y. Multimethod combination for age estimation of Sarcophaga peregrina (Diptera: Sarcophagidae) with implications for estimation of the postmortem interval. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2023, 137, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, N.; Tang, X.; Li, L.; Hu, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Estimating the Intra-Puparial Period of Chrysomya nigripes Aubertin Using Morphology and Attenuated Total Reflection Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR) Spectroscopy. Insects 2025, 16, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, N.; Li, L.; Guo, Y.; Hu, G.; Gao, Y.; Shao, S.; Gu, Z.; Wang, J.; et al. Development and age estimation of the intrapuparial period of Phormia regina (Diptera: Calliphoridae) for postmortem interval estimation. J. Med. Entomol. 2025, 62, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thümmel, L.; Tintner-Olifiers, J.; Amendt, J. A methodological approach to age estimation of the intra-puparial period of the forensically relevant blow fly Calliphora vicina via Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2025, 39, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.E.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, H.R.; Kang, J.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, J.H. MicroRNA-133 Targets Phosphodiesterase 1C in Drosophila and Human Oral Cancer Cells to Regulate Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 5296–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Pei, C.; Zhang, P.; Pan, L.; Xiao, J.; Meng, S.; Yuan, Z.; Bi, X. miR-285-Yki/Mask double-negative feedback loop mediates blood-brain barrier integrity in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E2365–E2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Rana, V.; Tridibes, A.; Sunil, S.; Bhatnagar, R.K. Dynamic expression of miRNAs across immature and adult stages of the malaria mosquito Anopheles stephensi. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegoraro, M.; Fishman, B.; Zonato, V.; Zouganelis, G.; Francis, A.; Kyriacou, C.P.; Tauber, E. Photoperiod-Dependent Expression of MicroRNA in Drosophila. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, J.; Freitas, F.C.P.; Cristino, A.S.; Moda, L.M.R.; Martins, J.R.; Bitondi, M.M.G.; Simões, Z.L.P.; Barchuk, A.R. miRNA-34 and miRNA-210 target hexamerin genes enhancing their differential expression during early brain development of honeybee (Apis mellifera) castes. Insect Mol. Biol. 2021, 30, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colaianni, D.; Virga, F.; Tisi, A.; Stefanelli, C.; Zaccagnini, G.; Cusumano, P.; Sales, G.; Preda, M.B.; Martelli, F.; Taverna, D.; et al. miR-210 is essential to retinal homeostasis in fruit flies and mice. Biol. Direct 2024, 19, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Nian, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y. miR-210 controls the evening phase of circadian locomotor rhythms through repression of Fasciclin 2. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1007655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Li, W.; Gao, L.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, M.; Zhou, S. miR-276 and miR-182013-5p modulate insect metamorphosis and reproduction via dually regulating juvenile hormone acid methyltransferase. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila-Bonilla, R.G.; Yocupicio-Monroy, M.; Marchat, L.A.; Pérez-Ishiwara, D.G.; Cerecedo-Mercado, D.A.; Del Ángel, R.M.; Salas-Benito, J.S. miR-927 has pro-viral effects during acute and persistent infection with dengue virus type 2 in C6/36 mosquito cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, W. MicroRNA miR-927 targets the juvenile hormone primary response gene Krüppel homolog1 to control Drosophila developmental growth. Insect Mol. Biol. 2020, 29, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Zhang, Y. Kr-h1, a Cornerstone Gene in Insect Life History. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 905441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Sun, B.; Gao, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, Y. miR-927 regulates insect wing development by targeting the Hippo pathway. Insect Sci. 2025, 32, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.L.; Li, J.M.; Chen, D.; Zhai, X.D.; Smagghe, G.; Jiang, H.; Wang, J.J.; Wei, D. Overexpression of miR-927-5p suppresses stalky expression and negatively reduces the spermatid production in Zeugodacus cucurbitae. Pest Manag. Sci. 2024, 80, 3412–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Calvi, B.R.; Hundley, H.A.; Sokol, N.S. MicroRNA mediated regulation of the onset of enteroblast differentiation in the Drosophila adult intestine. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, P.R.; Meng, A.; Moore, J.; Hobin, M.; Fulga, T.A.; Van Vactor, D.; Griffith, L.C. MicroRNAs Regulate Sleep and Sleep Homeostasis in Drosophila. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 3776–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iftikhar, H.; Johnson, N.L.; Marlatt, M.L.; Carney, G.E. The Role of miRNAs in Drosophila melanogaster Male Courtship Behavior. Genetics 2019, 211, 925–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Sheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Pang, L.; Dong, Z.; Wu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Communication between the stem cell niche and an adjacent differentiation niche through miRNA and EGFR signaling orchestrates exit from the stem cell state in the Drosophila ovary. PLoS Biol. 2024, 22, e3002515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, S.; Murat, S.; Almudi, I.; Nunes, M.D.; Bortolamiol-Becet, D.; McGregor, N.S.; Currie, J.M.; Hughes, H.; Ronshaugen, M.; Sucena, É.; et al. Evolution of mir-92a underlies natural morphological variation in Drosophila melanogaster. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuva-Aydemir, Y.; Xu, X.L.; Aydemir, O.; Gascon, E.; Sayin, S.; Zhou, W.; Hong, Y.; Gao, F.B. Downregulation of the Host Gene jigr1 by miR-92 Is Essential for Neuroblast Self-Renewal in Drosophila. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, D.; Kim, C.J.; Shin, B.H.; Lim, D.H. The Biological Roles of microRNAs in Drosophila Development. Insects 2024, 15, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guven-Ozkan, T.; Busto, G.U.; Jung, J.Y.; Drago, I.; Davis, R.L. miR-92a Suppresses Mushroom Body-Dependent Memory Consolidation in Drosophila. eNeuro 2020, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Rosbash, M. MicroRNA-92a is a circadian modulator of neuronal excitability in Drosophila. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.W.; Song, S.; Weng, R.; Verma, P.; Kugler, J.M.; Buescher, M.; Rouam, S.; Cohen, S.M. Systematic study of Drosophila microRNA functions using a collection of targeted knockout mutations. Dev. Cell 2014, 31, 784–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, A. Evolutionary genetics: Big effect of a small RNA. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, R247–R249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Liang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Han, Z. miR-92b regulates Mef2 levels through a negative-feedback circuit during Drosophila muscle development. Development 2012, 139, 3543–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wu, W.; Tang, J.; Feng, F.; Chen, P.; Li, B. Identification and Characterization of Development-Related microRNAs in the Red Flour Beetle, Tribolium castaneum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene Name | Primer Sequences (5′→3′) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference genes | U6 | Forward | GGAACGATACAGAGAAGATTAGC |
| Reverse | TGGAACGCTTCACGAATTTGCG | ||
| The DEmiRNAs * | miR-133 | Forward | AGCTGGTTGACATCGGGTCA |
| miR-285 | Forward | TAGCACCATTCGAAATCAGTGC | |
| miR-92a | Forward | ATTGCACTTGTCCCGGCCTA | |
| miR-92b | Forward | AATTGCACTAGTCCCGGCCT | |
| miR-210-3p | Forward | TTGTGCGTGTGACAGCGG | |
| miR-275-5p | Forward | CGCGCTAATCAGTGACCGG | |
| miR-927-5p | Forward | GGCTTTAGAATTCCTACGCTTTACC | |
| miR-956-3p | Forward | GGCTTTAGAATTCCTACGCTTTACC | |
| miR-957-3p | Forward | TGAAACCGTCCAAAACTGAGGC | |
| Gene | Simulation Equation | F | p | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-210-3p | y = −2.14053 + 3.5806x − 0.35337x2 − 0.1x3 + 0.0133x4 | 35.81396 | p < 0.001 | 0.96627 |
| miR-285 | y = 1.65554 − 1.59478x + 1.15842x2 − 0.23336x3 + 0.01419x4 | 46.49554 | p < 0.001 | 0.97382 |
| miR-927-5p | y = −3.81403 + 6.33601x − 1.64118x2 + 0.11845x3 + 0.00075x4 | 9.11545 | p < 0.05 | 0.87941 |
| miR-956-3p | y = −2.42511 + 4.23317x − 0.80865x2 − 0.00667x3 + 0.00725x4 | 13.90506 | p < 0.01 | 0.91752 |
| miR-92b | y = 0.64566 + 0.60861x − 0.29321x2 + 0.04075x3 − 0.0018x4 | 156.67715 | p < 0.001 | 0.99208 |
| miR-275-5p | y = 0.48393 + 0.83548x − 0.36654x2 + 0.04924x3 − 0.00212x4 | 410.45579 | p < 0.001 | 0.99696 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, Y.; Wu, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Shang, Y. Temporal miRNA Biomarkers for Pupal Age Estimation in Sarcophaga peregrina (Diptera: Sarcophagidae). Insects 2025, 16, 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080754
Xia Y, Wu H, Chen S, Wang Y, Sun J, Li Y, Guo Y, Shang Y. Temporal miRNA Biomarkers for Pupal Age Estimation in Sarcophaga peregrina (Diptera: Sarcophagidae). Insects. 2025; 16(8):754. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080754
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Yang, Hai Wu, Sile Chen, Yuanxing Wang, Jiasheng Sun, Yi Li, Yadong Guo, and Yanjie Shang. 2025. "Temporal miRNA Biomarkers for Pupal Age Estimation in Sarcophaga peregrina (Diptera: Sarcophagidae)" Insects 16, no. 8: 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080754
APA StyleXia, Y., Wu, H., Chen, S., Wang, Y., Sun, J., Li, Y., Guo, Y., & Shang, Y. (2025). Temporal miRNA Biomarkers for Pupal Age Estimation in Sarcophaga peregrina (Diptera: Sarcophagidae). Insects, 16(8), 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080754






