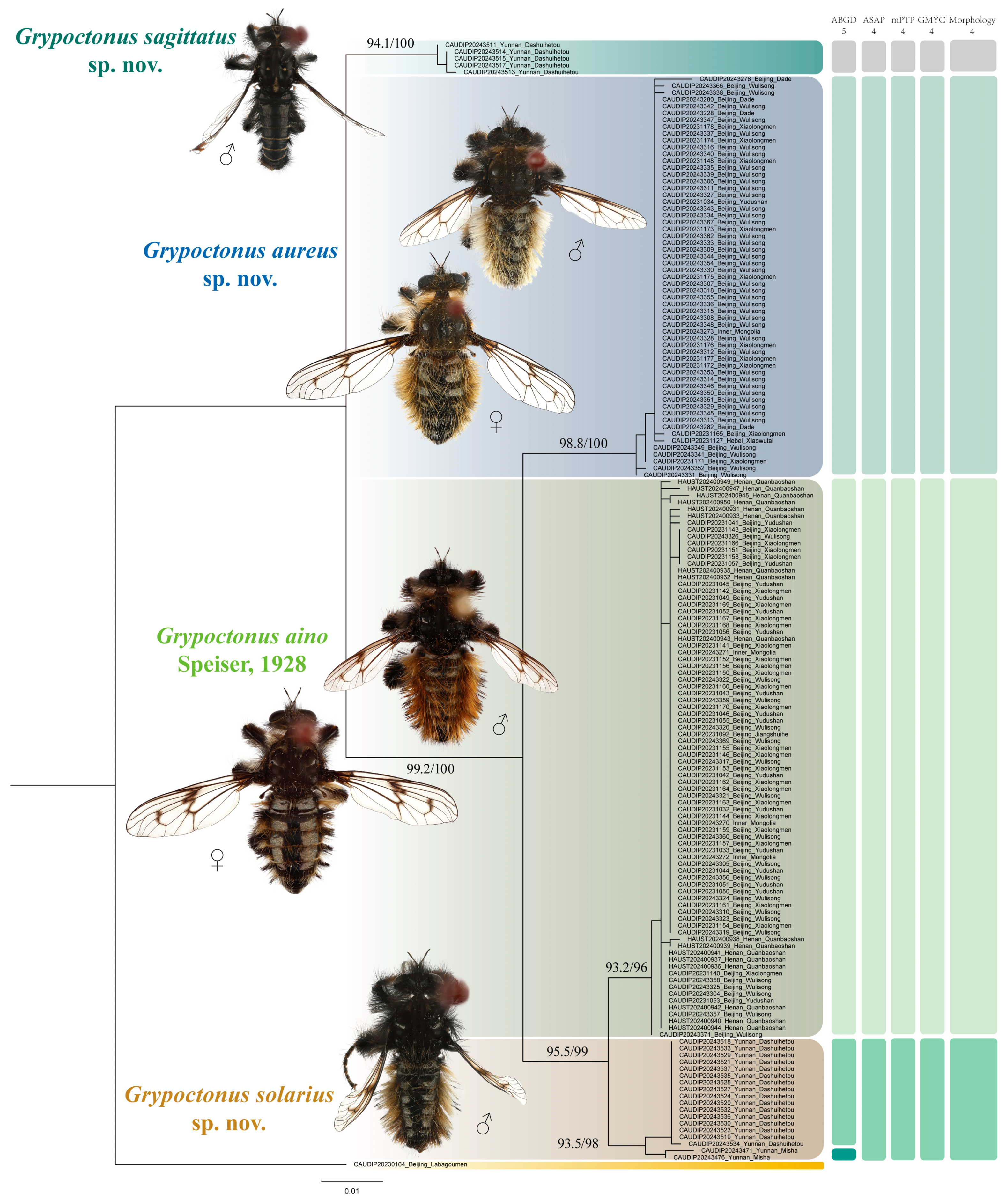
3.2.2. Species Description
Grypoctonus aino Speiser, 1928.
Chinese common name: 爱辅脉食虫虻 (following Yu & Wang [
42]).
Grypoctonus aino Speiser, 1928: 156. Type locality: Japan, Nagasaki; holotype in ZSM, 4 ♂.
Engel, 1930: 324 (key; description; wing) [
43]; Engel, 1934: 13 (specimen information; description;
Cyrtopogon) [
8]; Bromley, 1945: 93 (cat.;
Cyrtopogon) [
18]; Aoki, 1950: 1600 (drawing; description; distribution;
Cyrtopogon) [
17]; Hull, 1962: 184 (list) [
7]; Hisamatsu, 1965: 202 (description; distribution) [
9]; Hradský & Geller-Grimm, 1999: 100 (
stat. rev.; key; specimen information; genitalia; description) [
3]; Harusawa, 2002: 13 (distribution; biology) [
44]; Harusawa, 2004 (distribution; biology) [
45]; Young, 2005: 102 (key; description; male gentalia; distribution) [
46]; Zhang & Yang in Yang et al., 2018: 121 (cat.; distribution) [
12]; Tagawa, 2020 (photo) [
47]; Yu & Wang, 2023: 54 (photo; description; distribution) [
42]; Bock & Mengual, 2023: 80 (cat.; photo) [
48].
Materials examined. CHINA: BEIJING: 12 ♂♂ 7 ♀♀, Yanqing [延庆], Yudushan Scenic Area [玉渡山风景区], 40.55° N, 115.88° E, 887 m, 21.IX.2023, Xuankun Li, Yuezheng Tu, Haoyue Zhou (CAU) (CAUDIP20231032–CAUDIP20231033, CAUDIP20231041–CAUDIP20231057); 3 ♂♂ 27 ♀♀, Mentougou [门头沟], Xiaolongmen National Forest Park [小龙门国家森林公园], 39.96° N, 115.43° E, 1150 m, 24.X.2023, Xuankun Li, Yuezheng Tu, Haoyue Zhou, Yan Lai (CAU) (CAUDIP20231139–CAUDIP20231147, CAUDIP20231149–CAUDIP20231164, CAUDIP20231166–CAUDIP20231170); ♂, Mentougou [门头沟], Qingshui [清水镇], Jiangshuihe [江水河村], 40.04° N, 115.50° E, 1550 m, 4.X.2023, Yuezheng Tu (CAU) (CAUDIP20231092); 13 ♂♂ 10 ♀♀, Changping [昌平], Wulisong [五里松], 40.19° N, 115.88° E, 905 m, 11.X.2024, Haoyue Zhou, Zhanquan Ling, Hongna Guo, Dong Guo, Tianyu Zheng (CAU) (CAUDIP20243302, CAUDIP20243304–CAUDIP20243305, CAUDIP20243310, CAUDIP20243317, CAUDIP20243319–CAUDIP20243326, CAUDIP20243356–CAUDIP20243361, CAUDIP20243368–CAUDIP20243371); ♂, Fangshan [房山], Baihua Mt. [百花山], 1300 m, 21.IX.1984, Long Yang (NACRC, IOZ). HEBEI: 2 ♂♂ 4 ♀♀, Chengde [承德], Weichang [围场县], Saihanba National Forest Park [塞罕坝国家森林公园], 42.39° N, 117.30° E, 1599 m, 15.X.2024, Wei Xu, Tao Li (CAU). HENAN: 10 ♂♂ 12 ♀♀, Luoyang [洛阳], Luoning [洛宁县], Xiayu [下峪镇], Quanbao Mt. [全宝山], 34.12° N, 111.41° E, 1225 m, 6.XI.2024, Hongna Guo, Hao Liu, Xiaohan Ye, Bei Zhou, Yunzhu Huo (CAU) (HAUST202400930–HAUST202400951). INNER MONGOLIA: 1 ♂ 3 ♀♀, Ulanqab [乌兰察布], Xinghe [兴和县], Sumu Mt. [苏木山], 40.34° N, 113.46° E, 1830 m, 4.X.2024, Tianyu Zheng, Zhanquan Ling (CAU) (CAUDIP20243269–CAUDIP20243272, CAUDIP20243274–CAUDIP20243275). SICHUAN: 1 ♂ 1 ♀, Ngawa [阿坝], Jiuzhaigou [九寨沟], 2300 m, 6.IX.1983, Xuezhong Zhang (NACRC, IOZ).
Diagnosis. Male. Anterior and dorsal face of hind femora mostly with black hairs, but dorsal face admixed with several dark orange hairs. Anepisternum densely covered in long black hairs, hairs denser posteriorly and dorsally; Katatergite densely covered in long black hairs, admixed with long golden yellow hairs. Abdominal tergites with denser long black hairs posterolaterally and golden yellow hairs dorsally. Dorsal aedeagal sheath trifurcated, branches long, with the same length. Female. Anepisternum densely covered in long black hairs admixed with long pale hairs posteriorly. Scutum with sparse black hairs. Katatergite densely covered in long dark yellow hairs, admixed with black hairs; Tergites almost cover with black hairs and white hairs laterally.
Description. Male. Body length 9–12 mm, wing length 14–18 mm.
Head. Head about 1.5× wider than high (frontal view) (
Figure 5e) and 1.4× higher than long (lateral view, including face) (
Figure 5f), mostly black with light yellow pruinescence and covered in dense long black hairs with admixed long, white to light yellow hairs. Frons trapezoid with light yellow pruinescence, 1.1× length of ocellar tubercle, 2.9× as wide as ocellar tubercle, with black hairs (hairs relatively short and sparse compared to hairs on other parts of the head). Ocellar tubercle slightly raised, black with sparse light yellow pruinescence, with long black hairs. Face with thick light yellow pruinescence and admixed dense long black and yellow hairs (yellow hairs denser on dorsal half), except dorsolateral area with narrow, bare and shinning strip (
Figure 5e,f). Mystax not distinguishable from facial hairs. Gena narrow, with sparse light yellow pruinescence. Clypeus with thick light yellow pruinescence and otherwise bare. Occiput with thick light yellow pruinescence and dense long black hairs, ventral half with admixed dense long white to light yellow hairs, hairs denser in ventral half. Antenna black with sparse light yellow pruinescence, uniform from base to apex, scape and pedicel with dense long black hairs, flagellum bare (
Figure 5g). Scape 1.5× as long as wide, and 1.2× as long as pedicel; pedicel 1.2× as long as wide; flagellum 10.5× as long as wide, 2.0× as long as scape + pedicel, 3.6× as long as scape; stylus 0.3× as long as flagellum, two-segmented, with apical seta-like sensory article; apical segment 4.0× as long as basal segment. Palpus clavate, black with fine brownish to blackish hairs, two-segmented. Proboscis black, only slightly compressed laterally, basal 2/3 with sparse pruinescence and dense long light yellow hairs ventrally, apical 1/3 shinning, with short yellow hairs.
Thorax. Integumental color of scutum mostly brownish black with light yellow pruinescence, scutum with brown middle strip reaching posterior 4/5 of the scutum, anterolateral of transverse suture and inner-anterior of postalar callus with small, bare, and shinning spots (
Figure 5i). Antepronotum with admixed long light yellow and black hairs; postpronotum with long black hairs laterally; proepimeron densely covered in long white to pale yellow hairs. Lateral postpronotal lobe with shiny and dirty orange spot. Scutum covered with dense brown pruinescence and sparse long black hairs. Scutellum black with sparse brown pruinescence, covered with dense long golden yellow hairs admixed few black hairs, hairs in anterior margin strongly proclinate. Postalar callus with dense long black hairs. Pleura black with thick brown pruinescence; anepisternum densely covered in long black hairs, hairs denser posteriorly and dorsally; katepisternum with sparse black and light yellow hairs on dorsal margin; anepimeron, katepimeron, and meron bare. Metanepisternum covered in brown and pale yellow tomentums in middle area, posteroventral with sparse black hairs; metakatepisternum bare; katatergite densely covered in long black hairs, admixed with long golden yellow hairs; anatergite covered with dense light yellow pruinescence on dorsal margin.
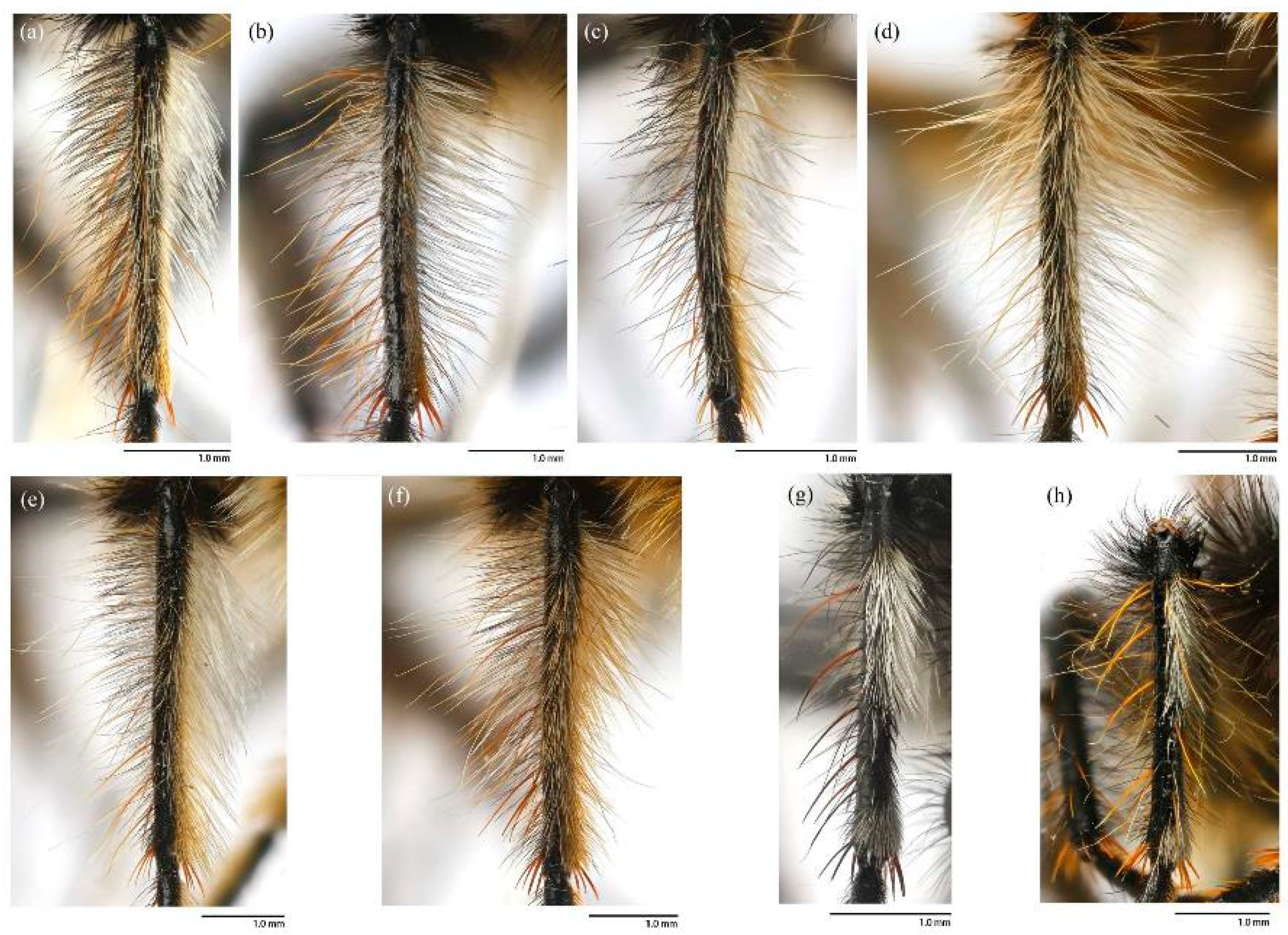
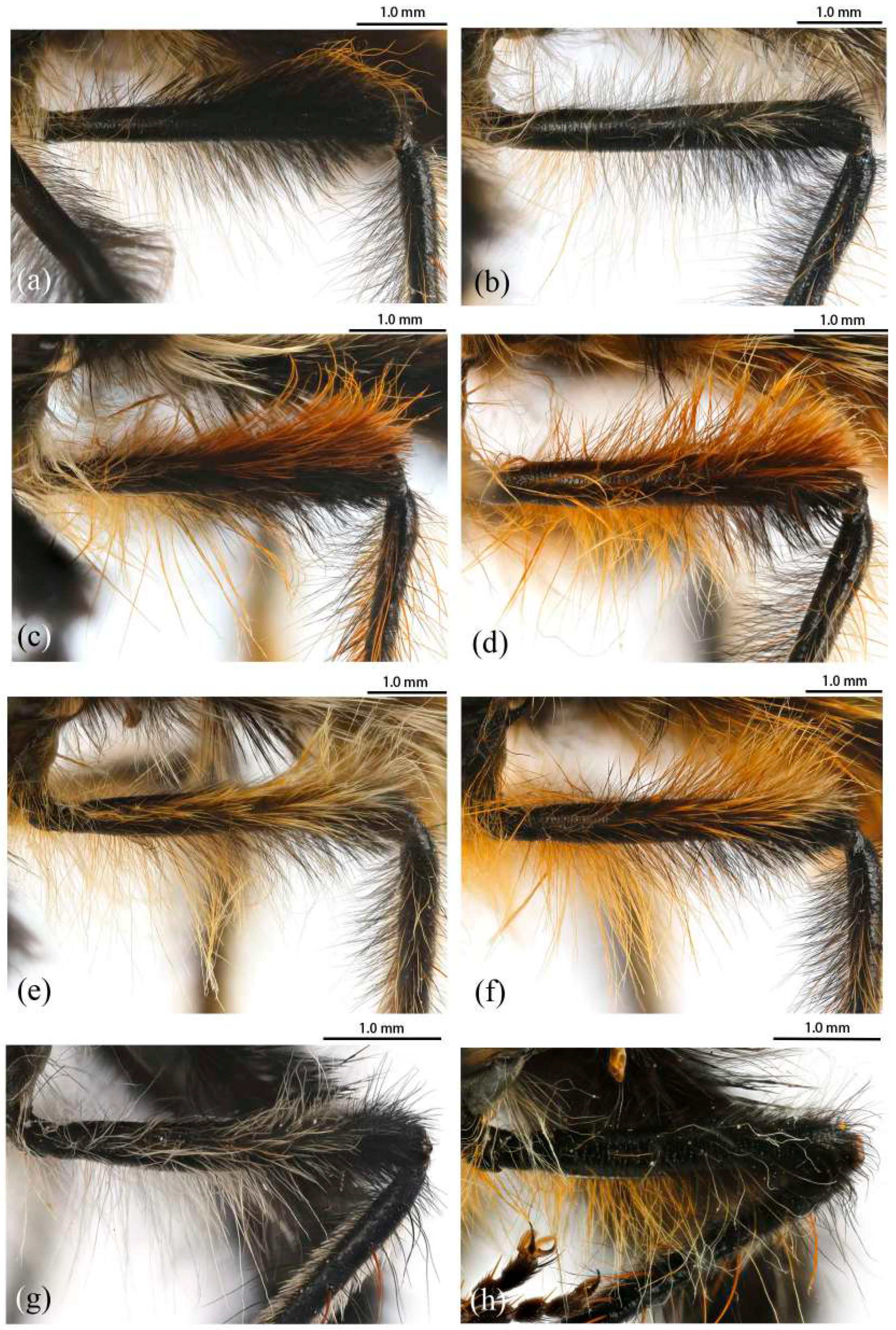
Legs. Legs black, coxae covered in dense light yellow and white hairs, femora mostly covered in dense long black hairs, ventral face admixed with dense long light yellow hairs. Dorsal half of mid and hind femora admixed with a few dark yellow hairs; ventral face of hind femora admixed with light yellow and white hairs (
Figure 4a). Fore tibiae mostly covered in dense long black hairs and strong long dark orange bristles, ventral face of fore tibia with dense short dark orange hairs on apical 4/5; dorsal face of mid tibia with black hairs, admixed with long yellow hairs and short white hairs; hind tibia posterior face with dense long white hairs on basal 4/5 and ventral face with dense short golden yellow hairs, admixed with long dark orange hairs (
Figure 3a). Ventral and a part of posterior face of tarsi with dense short dark orange or golden yellow hairs; tarsi with short, robust black hairs and with dark orangish bristles. Fore tibia 2.8× longer than fore basitarsus, mid tibia 3.1× longer than mid basitarsus, hind tibia 3.0× longer than hind basitarsus.
Wings. Wing membrane hyaline with infuscated wing base, anterior margin, apex and middle of cell
br, apex and posterior of cell
bm, and areas around crossveins
r-m1,
r-m2, and base of cell
m1. Haltere stem and knob black (
Figure 5h).
Abdomen. Integumental color of tergites black mostly with dark blue metallic and sparse light yellow pruinescence (
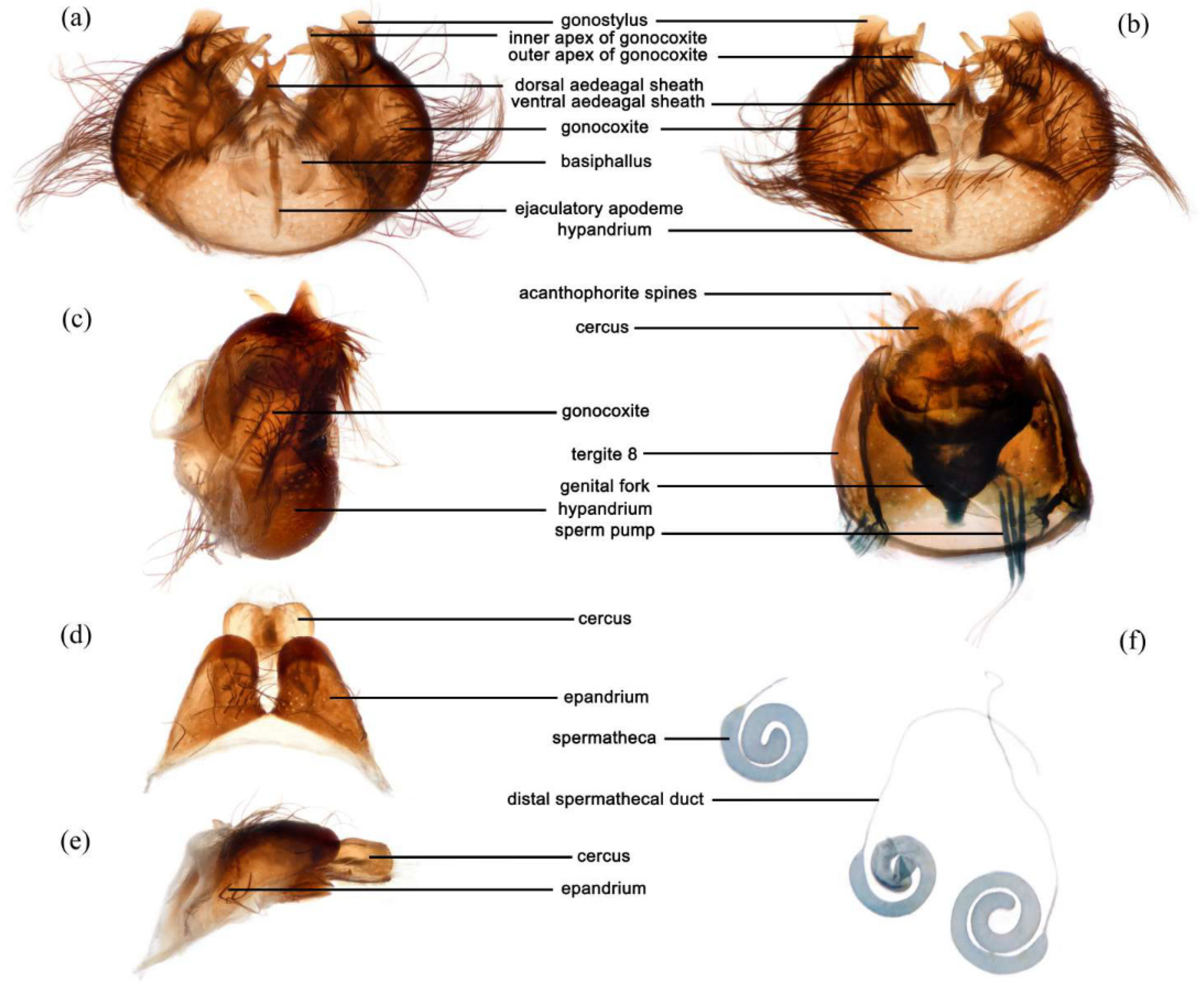
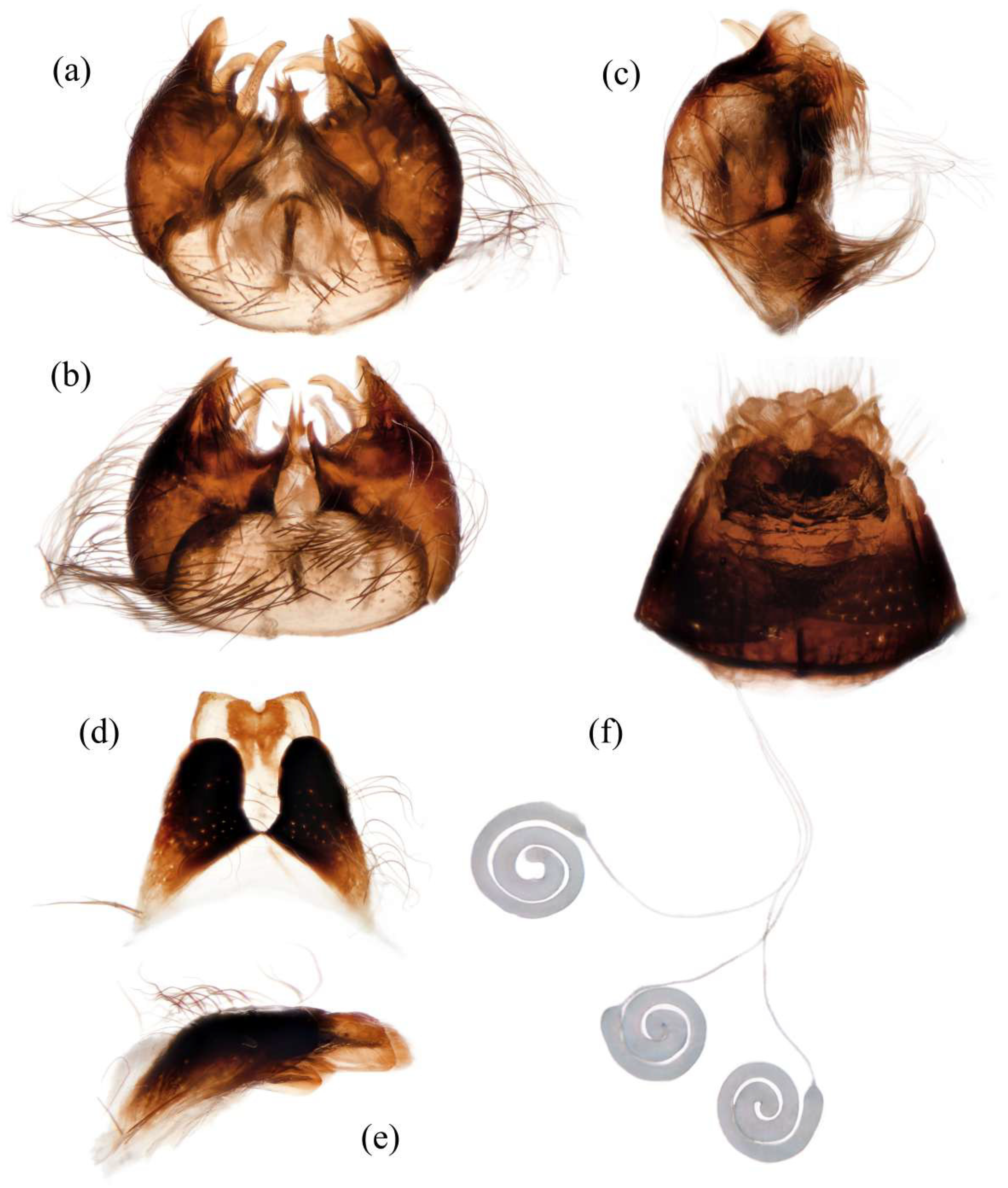
Figure 5d). Tergite 1 with dense long dark orange and golden yellow hairs, laterally admixed with more white hairs, and anterolaterally covered in dense short black hairs; tergites 2–6 with dense long dark orange and golden yellow hairs, laterally with dense long black hairs; tergites 7–8 with long black hairs, tergite 7 admixed with few dark yellow hairs. Sternites black with thick light yellow pruinescence, covered in long golden hairs admixed with some short black hairs; sternite 1 with yellow hairs, sternite 2 with black hairs, other sternites admixed with black and yellow hairs. Genitalia (
Figure 6a–e). Posterior margin of epandrium 1.2× longer than full length, the length between middle point of posterior and anterior margins 0.6× longer than full length. Basiphallus enlarged. Outer apex of gonocoxite long. Gonocoxite with large ventral extension on posterior half, bifid, blunt posteriorly, tapered innerly. Dorsal aedeagal sheath trifurcated, branches long, with the same length.
Female. Body length 8–14 mm, wing length 14–21 mm. Distinctly different from male. Overall hairs sparser and with more paler hairs than black hairs. Head. About 1.6× wider than high (frontal view) and 1.3× higher than long (lateral view, including face). Frons 1.1× higher than ocellar tubercle, 2.5× as wide as ocellar tubercle. Ocellar tubercle with long light yellow to white hairs. Face with thick light yellow pruinescence. Scape 1.7× as long as wide, and 1.6× as long as pedicel; pedicel 1.0× as long as wide; flagellum 11.7× as long as wide, 2.2× as long as scape + pedicel, 3.6× as long as scape; stylus 0.2× as long as flagellum; apical segment 1.6× as long as basal segment.
Thorax. Postpronotum with long black and pale hairs laterally; anepisternum densely covered in long black hairs dorsally and admixed long pale hairs posteriorly; postalar callus admixed with black and yellow hairs; katatergite densely covered in long dark yellow hairs, admixed with black hairs.
Legs. Femora mostly covered in dense long black hairs, admixed with light yellow and white hairs; posterior face of fore femora admixed with long black and white hairs, ventral face of fore femora with denser long light yellow hairs; anterior face and basal 4/5 of ventral face of mid and hind femora admixed with light yellow to white hairs (
Figure 4b). Dorsal face of mid and hind tibia with dense long white hairs admixed with dark orange hairs (
Figure 3b). Fore tibia 2.6× longer than fore basitarsus, mid tibia 3.5× longer than mid basitarsus, hind tibia 2.9× longer than hind basitarsus.
Wings. Anterior half of wing membrane less infuscated, especially in cells
c and
sc (
Figure 5j).
Abdomen. Tergites covered in sparse golden yellow hairs, admixed with short black and white hairs, laterally with dense, long black and white hairs. Tergite 1 with dense long yellow hairs and anterolaterally covered in dense short black hairs; tergites 2–6 laterally with dense long black and white hairs; tergites 7–8 with long yellow hairs, tergite 7 admixed with few black hairs (
Figure 5m). Genitalia. Acanthophorite spines located on plate above cerci with six spines on each side, on plate ventrolateral of cerci with four larger spines and several smaller spines (
Figure 6f).
Remarks. In some examined specimens, the apex of R4+5 was infuscated lightly; the female abdomen had denser yellow hairs.
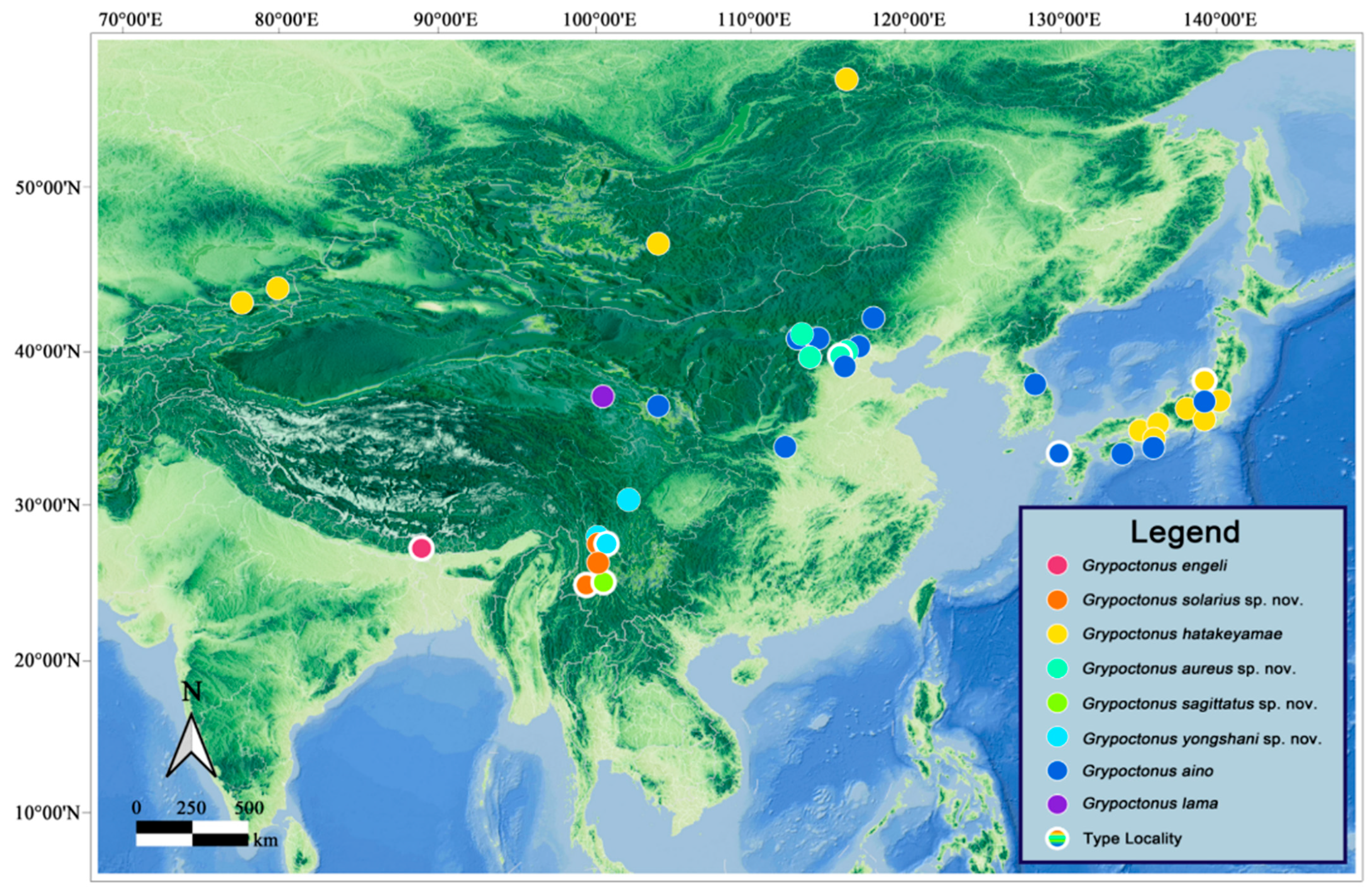
Distribution. China: Beijing (Yu & Wang, 2023 [
42]; this paper); Gansu (Engel, 1934 [
8]); Hebei (newly recorded); Henan (newly recorded); Inner Mongolia (newly recorded); Sichuan (newly recorded).
Japan: Honshu (Aoki, 1950 [
17]; Hisamatsu, 1965 [
9]); Hyogo (Harusawa, 2004 [
45]); Kyushu: Nagasaki (Speiser, 1928 [
1]); Nara (Harusawa, 2002 [
44]; Harusawa, 2004 [
45]); Shikoku (Hisamatsu, 1965 [
9]).
South Korea: Gangwon-do; Gyeongsangnam-do (Young [
46]).
Grypoctonus aureus Zhou & Li sp. nov.
Chinese common name: 错金辅脉食虫虻.
Type Materials. HOLOTYPE: ♂, CHINA: BEIJING: Changping [昌平], Wulisong [五里松], 40.19° N, 115.88° E, 905 m, 11.X.2024, Haoyue Zhou (CAU) (CAUDIP20243306). PARATYPES: CHINA: BEIJING: ♂, Yanqing [延庆], Yudushan Scenic Area [玉渡山风景区], 40.55° N, 115.88° E, 887 m, 21.IX.2023, Yuezheng Tu (CAU) (CAUDIP20231034); 4 ♂♂ 6 ♀♀, Mentougou [门头沟], Xiaolongmen National Forest Park [小龙门国家森林公园], 39.96° N, 115.43° E, 1150 m, 24.X.2023, Xuankun Li, Yuezheng Tu, Haoyue Zhou, Yan Lai (CAU) (CAUDIP20231148, CAUDIP20231165, CAUDIP20231171–CAUDIP20231178); ♂, Changping [昌平], Dade Temple [大德寺], 40.10° N, 115.54° E, 889 m, 23.IX.2024, Haoyue Zhou (CAU) (CAUDIP20243228); 4 ♂♂ 6 ♀♀, Changping [昌平], Dade Temple [大德寺], 40.10° N, 115.54° E, 889 m, 11.X.2024, Haoyue Zhou, Zhanquan Ling, Hongna Guo, Dong Guo, Tianyu Zheng (CAU) (CAUDIP20243276–CAUDIP20243285); 21 ♂♂ 27 ♀♀, Changping [昌平], Wulisong [五里松], 40.19° N, 115.88° E, 905 m, 11.X.2024, Haoyue Zhou, Zhanquan Ling, Hongna Guo, Dong Guo, Tianyu Zheng (CAU) (CAUDIP20243301, CAUDIP20243303, CAUDIP20243306–CAUDIP20243309, CAUDIP20243311–CAUDIP20243316, CAUDIP20243318, CAUDIP20243327–CAUDIP20243355, CAUDIP20243362–CAUDIP20243367). HEBEI: ♂, Yuxian [蔚县], Xiaowutai National Nature Reserve [小五台国家级自然保护区], 39.94° N, 114.94° E, 1123 m, 19.X.2023, Haoyang Xiong (CAU) (CAUDIP20231127). INNER MONGOLIA: 1 ♂ 1 ♀, Ulanqab [乌兰察布], Xinghe [兴和县], Sumu Mt. [苏木山], 40.34° N, 113.46° E, 1830 m, 4.X.2024, Zhanquan Ling (CAU) (CAUDIP20243273).
Other Materials. CHINA: BEIJING: ♀, Mentougou [门头沟], Huangta [黄塔], 28.IX.1984, Long Yang (NACRC, IOZ); ♂, Yanqing [延庆], Badaling [八达岭], 26.IX.1978, Yongshan Shi (NACRC, IOZ); 2 ♂♂, Yanqing [延庆], Badaling [八达岭], 5.X.1981, Zicheng Qin (NACRC, IOZ); 2 ♂♂, 2 ♀♀, Yanqing [延庆], Badaling [八达岭], 17.X.1985, Yiding Wang (NACRC, IOZ).
Diagnosis. Male. Medial occiput with pale yellow hairs. Pedicel with dense long black hairs and admixed with long yellow bristles. Scutum with blurry middle strip; anterolateral of transverse suture, inner-anterior of postalar callus, and the area between transverse suture and scutellum with small, bare, and shinning spots. Anterior and dorsal face of hind femora covered with yellow to pale yellow hairs and admixed with black hairs ventrally. Tergites with dense pale yellow hairs laterally. Dorsal aedeagal sheath trifurcated, branches short, with the same length. Female. Anepisternum densely covered with denser long yellow hairs posteriorly. Scutum with black and light yellow hairs. Anterior and dorsal face of hind femora covered with yellow hairs, ventral face of hind femora covered with black hairs on apical 1/5.
Description. Male. Body length 9–13 mm, wing length 16–19 mm.
Head. Head about 1.6× wider than high (frontal view) (
Figure 7e) and 1.3× higher than long (lateral view, including face) (
Figure 7f), mostly black with pale pruinescence and covered in dense long black and yellow hairs admixed with long white hairs. Frons trapezoid with light yellow pruinescence, 1.1× length of ocellar tubercle, 3.5× as wide as ocellar tubercle, with black hairs (hairs relatively short and sparse compared to hairs on other parts of the head). Ocellar tubercle slightly raised, black with sparse light yellow pruinescence and with long black hairs. Face with thick pale pruinescence and denser with long black and yellow hairs, yellow hairs longer than black hairs, without shinning strip (
Figure 7e,f). Mystax not distinguishable from facial hairs. Gena narrow, with sparse pale pruinescence. Clypeus with thick light yellow pruinescence and otherwise bare. Occiput with sparse pale pruinescence and dense long black hairs, hairs denser in ventral half, hairs near the gena and the compound eyes forward bend. Antenna black with sparse light yellow pruinescence, uniform from base to apex, scape with dense long black hairs, pedicel with dense long black hairs and admixed with long yellow bristles, flagellum bare (
Figure 7g). Scape 1.2× as long as wide, and 1.2× as long as pedicel; pedicel 1.1× as long as wide; flagellum 17.8× as long as wide, 2.8× as long as scape + pedicel, 5.2× as long as scape; stylus 0.3× as long as flagellum, two-segmented, with apical seta-like sensory article; apical segment 6.0× as long as basal segment. Palpus clavate, black with fine black hairs, two-segmented. Proboscis black, only slightly compressed laterally, basal 2/3 with sparse pruinescence and dense long black and light yellow hairs ventrally, apical 1/3 shinning, with short yellow hairs.
Thorax. Integumental color of scutum mostly black, brownish gray with dark yellow pruinescence; scutum with blurry middle strip; anterolateral of transverse suture, inner-anterior of postalar callus, and the area between transverse suture and scutellum with small, vertical, bare, and shinning spots (
Figure 7i). Antepronotum covered in long yellow to white hairs; postpronotum covered in long black admixed with light yellow hairs laterally; proepimeron densely covered in long light yellow hairs. Lateral postpronotal lobe with shiny and dirty orange spot. Scutum covered with black, brownish gray pruinescence and sparse long black hairs. Scutellum black with dark brownish yellow pruinescence, covered with dense long yellow hairs. Postalar callus with long black hairs. Pleura black with thick pale pruinescence; anepisternum densely covered in long black hairs, hairs denser posteriorly, dorsally, and ventrally; katepisternum with sparse black hairs gathered on the dorsal middle area; anepimeron, katepimeron, and meron bare. Metanepisternum covered in brown and pale yellow tomentums in middle area, admixed with sparse long black hairs; metakatepisternum bare; katatergite densely covered in long black hairs dorsally and admixed with long yellow hairs; anatergite covered with dense light yellow pruinescence on dorsal margin.
Legs. Legs black with sparse pale pruinescence, coxae covered in dense light yellow hairs, femora mostly covered in dense long black and yellow to white hairs, tarsi with short black hairs and admixed with dark orange bristles. Anterior face of fore femora with several robust hairs on apical 1/5, posterior face of fore femora with long black hairs admixed with light yellow to white hairs, ventral face of fore femora with light yellow hairs; mid femora with black hairs admixed with light yellow hairs on anterior and ventral face on basal 3/5; anterior face of hind femora mostly covered in golden yellow hairs admixed with short black hairs, ventral face of hind femora covered with yellow hairs on basal 3/5 (
Figure 4e). Fore tibiae mostly covered in dense long black hairs admixed strong long yellow bristles, ventral face of fore tibia with dense short golden yellow hairs on apical 8/9; mid tibia denser with long black hairs admixed with long dark yellow bristles; hind tibia admixed with long black and yellow hairs, posterior face on hind tibia with dense long white hairs on basal 2/5 and dense short golden yellow hairs on 3/5, admixed with long yellow hairs (
Figure 3e). Ventral face of tarsi with dense short pale yellow hairs. Fore tibia 2.7× longer than fore basitarsus, mid tibia 3.3× longer than mid basitarsus, hind tibia 3.2× longer than hind basitarsus.
Wings. Wing membrane hyaline with infuscated wing base, cell
br, areas around crossveins
r-m1,
r-m2, cell
bm, and a half of apex of cell
d. Haltere stem and knob brownish black (
Figure 7h).
Abdomen. Tergites with dark blue metallic, covered with long light yellow hairs dorsally and dense pale yellow to white hairs laterally, tergites 7–8 with black hairs, tergite 7 admixed with few dark yellow hairs (
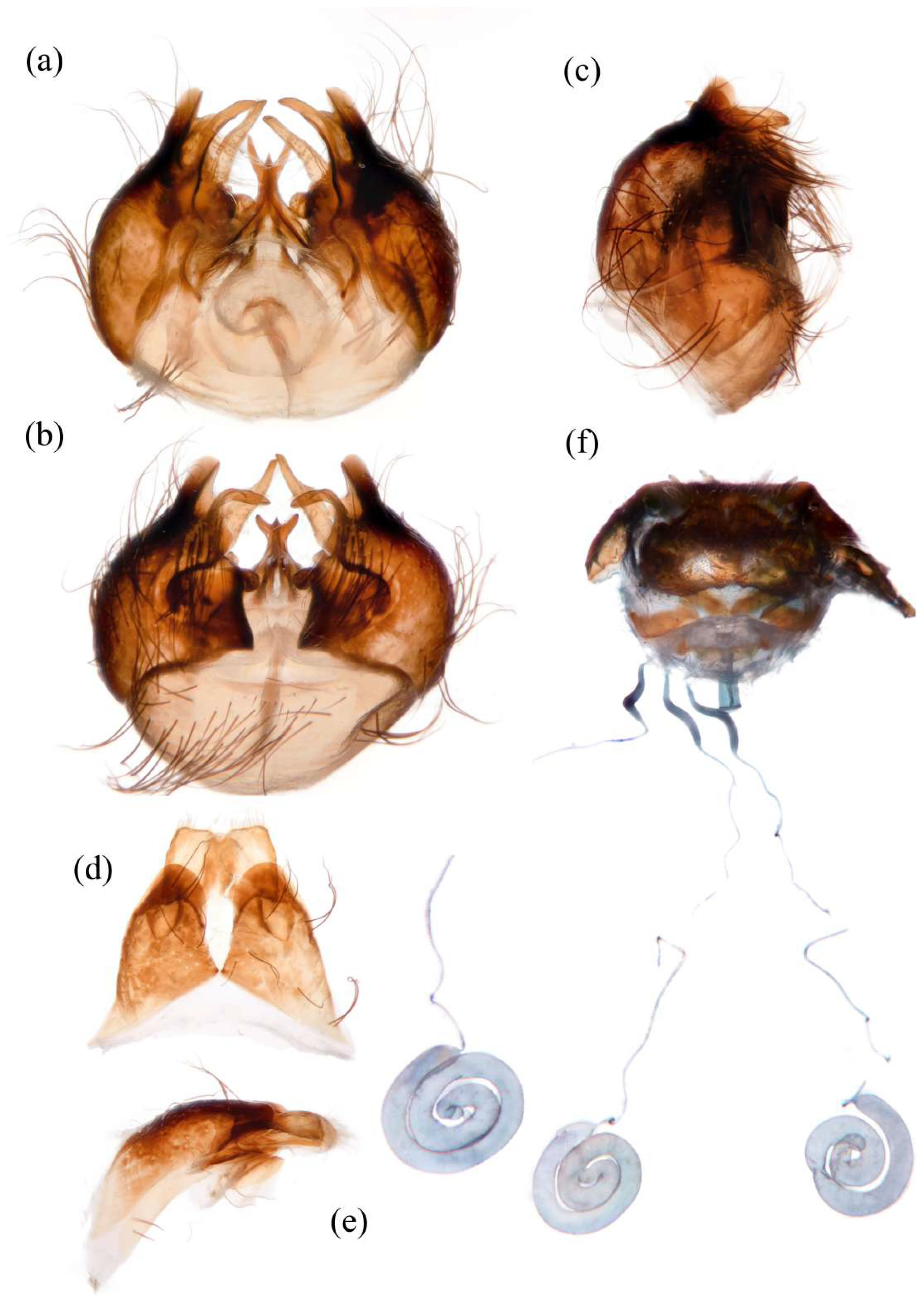
Figure 7d). Sternites black with sparse pale pruinescence, covered in long black hairs admixed with pale yellow hairs; sternites 1–2 covered in pale yellow hairs admixed with black hairs. Genitalia (
Figure 8a–e). Posterior margin of epandrium 1.2× longer than full length, the length between the middle point of posterior and anterior margins 0.48× longer than full length. Gonocoxite ventrally pointed on posterior margin. Basiphallus enlarged. Outer apex of gonocoxite long. Gonocoxite with large ventral extension on posterior half, trifurcated, blunt. Dorsal aedeagal sheath trifurcated, branch short, with the same length.
Female. Body length 11–15 mm, wing length 18–24 mm.
Head. Frons trapezoid with thick pale pruinescence, 3.3× as wide as ocellar tubercle. Ocellar tubercle with long light yellow hairs. Occiput with long black hairs admixed with light yellow hairs. Scape 1.6× as long as wide, and 1.3× as long as pedicel; pedicel 1.2× as long as wide; flagellum 16.4× as long as wide, 2.3× as long as scape + pedicel, 4.1× as long as scape; stylus apical segment 4.2× as long as basal segment.
Thorax. Scutum covered with brownish gray and dark yellow pruinescence and sparse long pale yellow hairs, admixed with short black hairs. Postalar callus with long yellow to white hairs, admixed with black hairs anteroventrally. Anepisternum densely covered in long black hairs, hairs denser dorsally and long yellow hairs posteriorly; katepisternum with sparse pale yellow hairs gathered on the dorsal middle area. Metanepisternum with several long pale yellow hairs ventrally; katatergite densely covered in long yellow hairs dorsally and admixed with black hairs anteriorly.
Legs. Posterior face of fore femora with yellow to white hairs, ventral face of fore femora with light yellow hairs (
Figure 4f). Mid tibia denser with long black hairs admixed with long dark yellow bristles and sparse white hairs; posterior face on hind tibia with dense long pale yellow hairs (
Figure 3f). Fore tibia 2.5× longer than fore basitarsus, mid tibia 4.1× longer than mid basitarsus.
Wings. Wing membrane hyaline with light infuscated wing base, apex of cell
br, crossveins
r-m1,
r-m2, apex of cell
d (
Figure 7j).
Abdomen. Tergites 1–6 with black hairs antrolaterally. Sternites covered in golden yellow hairs (
Figure 7m). Acanthophorite spines located on plate above cerci with 6–7 spines on each side, on plate ventrolateral of cerci with four larger spines and several smaller spines (
Figure 8f).
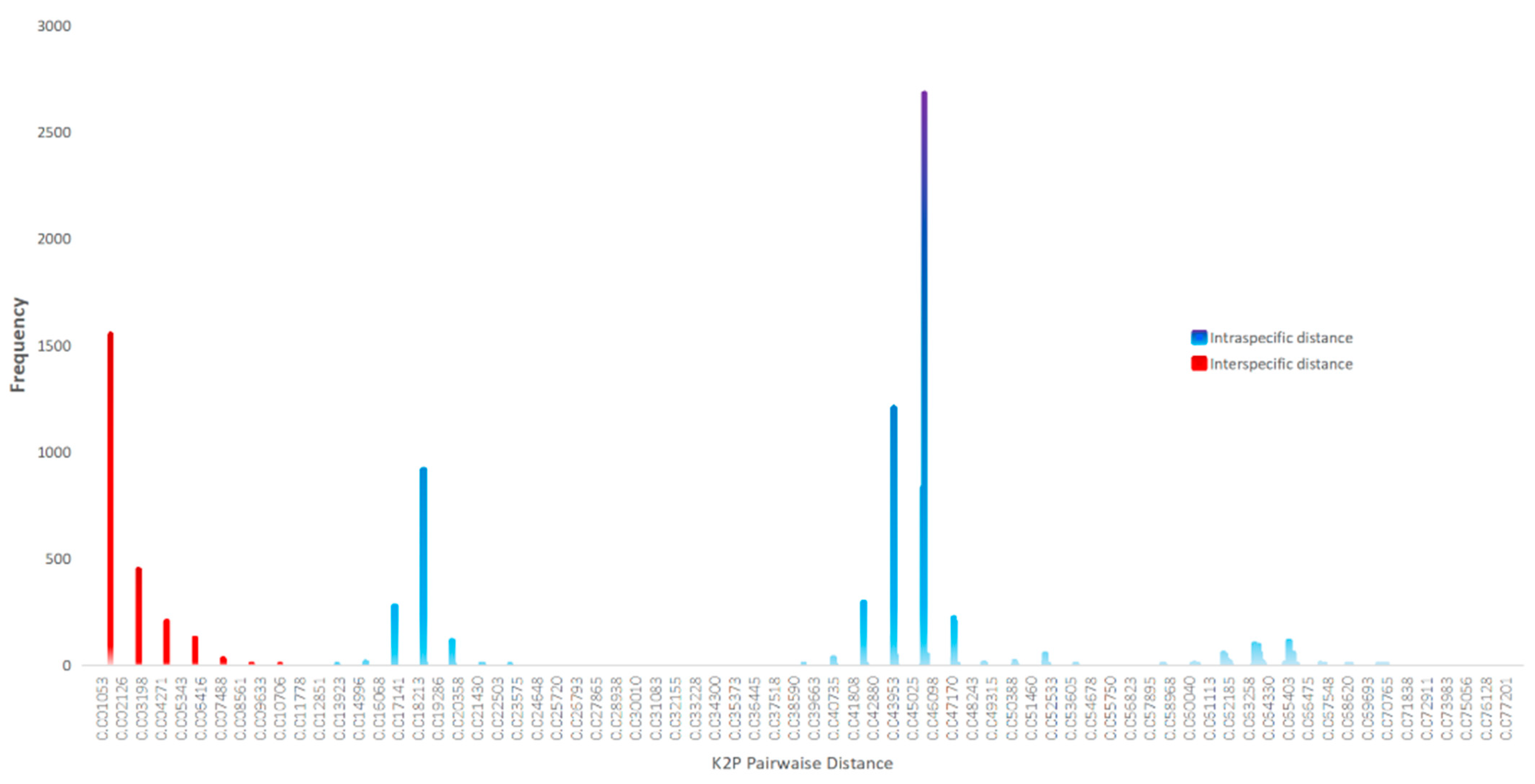
Remarks. Some males have more orange hairs on tergites and legs, to the extent that they appear to belong to a different species. However, DNA barcoding confirms they are the same species, with increased orange hair being the only variation.
G. aureus sp. nov. is similar to G. hatakeyamae, especially the body hairs of female, but differs as follows: wing not entirely infuscated; body hairs lighter; posterior face of hind tibia with white hairs in males and pale yellow in females.
G. aureus sp. nov. is also similar to
G. lama based on the original description. However, the type specimen of
G. lama is lost, and its original description lacks sufficient diagnostic details. Given that
G. lama was recorded from Qinghai, whereas
G. aureus sp. nov. specimens were collected from eastern Inner Mongolia and Beijing, we propose this as a new species to accommodate the current specimens. This species was previously recorded in Beijing by Yu and Wang [
42], but it was misidentified as
G. hatakeyamae.
Etymology. The specific epithet “aureus” (Latin for “of gold” or “golden”) refers to the golden yellow to light yellow hairs, dark body, and metallic abdomen. The body coloration resembles the appearance of “Gold inlaying” (错金), an ancient Chinese bronze decoration technique and intangible cultural heritage. The name also alludes to the aureus, a gold coin of ancient Rome.
Grypoctonus engeli Hradský & Geller-Grimm, 1999
Grypoctonus engeli Hradský & Geller-Grimm, 1999: 104 [
3]. Type locality: India, West Bengal, Darjeeling. Holotype in ZSM, ♂.
Yatoo et al., 2024: 61 (cat.) [
49].
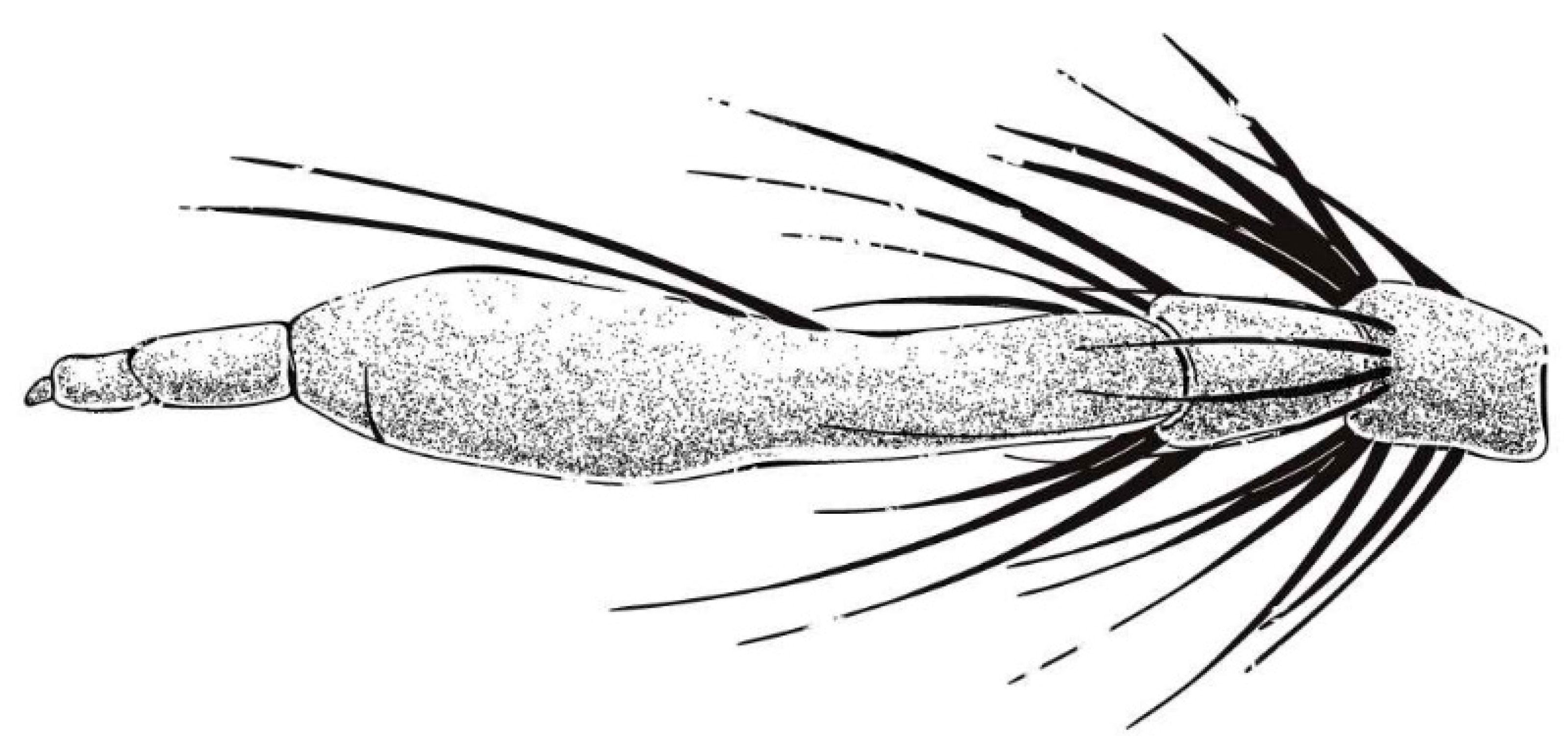
Diagnosis. (Modified from Hradský & Geller-Grimm, 1999 [
3].) Postpedicel expanded enlarged with two black bristles (
Figure 9). Scutum with light brown stripe and pale pruinescence, mesopleuron with black and white hairs. Wing membrane hyaline with infuscated anterior margin and most of crossveins. Posterior of tibia is red and anterior of tibia is black. The posterior margin of tergites 1–5 with white dense pruinescence on posterior margin and triangular in laterally. Tergite 6 with a disconnected dense pruinescence on posterior margin.
Distribution. India: Darjeeling (Hradský & Geller-Grimm, 1999 [
3]).
Grypoctonus hatakeyamae (Matsumura, 1916).
Chinese common name: 畠山辅脉食虫虻
Grypoctonus hatakeyamae (Matsumura, 1916): 296 (
Pycnopogon) [
2]. Type locality: Japan, Niigata [Honshu, Echigo]. Holotype ♂, paratypes 2 ♂ in EIHU.
Matsumura, 1931 (description; drawing;
Pycnopogon) [
50]; Aoki, 1950: 1600 (drawing; description; distribution;
Cyrtopogon) [
17]; Lehr, 1988: 239 (cat.; distribution) [
5]; Hradský & Geller-Grimm, 1999: 105 (key; specimen information; description) [
3]; Harusawa, 2002: 13 (distribution; biology) [
44]; Harusawa, 2004: 67 (distribution; biology) [
45]; Harusawa, 2006a: 45 (distribution; biology) [
51]; Harusawa, 2006b: 51 (distribution; biology) [
52]; Zhang & Yang in Yang et al., 2018: 122 (cat.) [
12]; Yu & Wang, 2023: 54 (misidentification) [
42].
Grypoctonus daimyo Speiser, 1928: 157 [
1]. Type locality: Japan, Tochigi, Nikko. Syntypes in MWNH, 2 ♂ 2 ♀.
Engel, 1930: 326 (key; description) [
43]; Hull, 1962: 184 (list) [
7]; Lehr, 1962: 363 (photos; biology;
Cyrtopogon) [
4]; Lehr, 1964: 214 (photo; biology;
Cyrtopogon) [
19]; Lehr, 1966: 99 (distribution; biology; specimens information) [
53]; Lehr, 1979: 68 (distribution; specimens information) [
10]; Hradský & Geller-Grimm, 1999: 106 (as synonym of
G. hatakeyamae; genitalia; distribution) [
3]; Zhang & Yang in Yang et al., 2018: 122 (cat.; distribution) [
12]; Shi, 1993: 1081 (misidentification) [
11].
Diagnosis. Most hairs dark brown and brownish dirty yellow; wing infuscated entirely; posterior face of hind tibia covered with dark to golden yellow hairs (
Figure 10).
Distribution.
Japan: Gunma (Hradský & Geller-Grimm, 1999 [
3]); Hyogo (Hradský & Geller-Grimm, 1999 [
3]; Harusawa, 2004 [
45]); Kyoto (Hradský & Geller-Grimm, 1999 [
3]); Nagano (Hradský & Geller-Grimm, 1999 [
3]); Niigata (Hradský & Geller-Grimm, 1999 [
3]); Nikko (Engel, 1930 [
43]; Hradský & Geller-Grimm, 1999 [
3]); Osaka (Harusawa, 2004 [
45]; Harusawa, 2006a [
51]; Harusawa, 2006b [
52]);
Kazakhstan: Almaty (Lehr, 1966 [
53]; Lehr, 1988 [
5]);
Kyrgyzstan (Lehr, 1966 [
53]; Lehr, 1988 [
5]);
Mongolia (Lehr, 1966 [
53]);
Russia? (Lehr, 1988 [
5]).
China (questionable).
Remarks. Specimens of G. hatakeyamae were not examined in the present study; therefore, diagnosis was based on published descriptions and type photos.
There are three published records of
G. hatakeyamae from China, but after revising these records, we consider its distribution in China to be highly questionable. Lehr (1966) [
53] recorded
G. hatakeyamae from Gansu, China, without diagnostic figures or detailed description. Considering Lehr used to treat
G. aino as a junior synonym of
G. hatakeyamae (Lehr, 1979) [
10] and
G. aino is known from Gansu, this record might be incorrect. Shi (1993) [
11] recorded
G. hatakeyamae from Yunnan, China. We examined the specimens and confirmed that it is an undescribed species instead of
G. daimyo and named it
G. yongshani sp. nov. (see details below). Yu & Wang [
42] published a field image of
G. aureus sp. nov. from Beijing but misidentified it as
G. hatakeyamae.
Grypoctonus lama Speiser, 1928.
Chinese common name: 薄辅脉食虫虻.
Grypoctonus lama Speiser, 1928: 156 [
1]. Type locality: China, Qinghai, Qinghai Lake [Kuku-noor]. Holotype in Museum Hamburg, ♂, destroyed.
Engel, 1930: 328 (description; distribution) [
43]; Hull, 1962: 184 (list) [
7]; Lehr, 1988: 240 (cat.; distribution) [
5]; Hradský & Geller-Grimm, 1999: 110 (key; specimen information; description) [
3]; Zhang & Yang in Yang et al., 2018: 122 (cat.; distribution) [
12].
Diagnosis. Wing hyaline, most hairs are pale, head and thorax with grayish yellow pruinescence. Most mystax yellow, only black on upper face. Abdomen entirely covered with light grayish yellow hairs, only on posterior tergite with black hairs. Hairs on the legs are lighter than G. aino, hind tibia with off-white hairs.
Remarks. The type specimen of
G. lama is lost, leaving only the original description by Speiser [
1] and a more detailed redescription by Engel [
43] as references. Hradský and Geller-Grimm [
3] speculated that Speiser’s specimens may have been transferred to Engel prior to the species’ description, raising doubts over whether the redescription truly represents
G. lama or a different species. However,
G. lama could potentially be the senior synonym of
G. aureus sp. nov., a hypothesis that could be tested if future collections from Qinghai yield specimens matching the original description.
Distribution. China: Qinghai (Speiser, 1928).
Grypoctonus sagittatus Zhou & Li sp. nov.
Chinese common name: 羿箭辅脉食虫虻
Type Materials. HOLOTYPE: ♂, CHINA: YUNNAN: Baoshan [保山], Shidian [施甸], Dashuihetou Mt. [大水河头山], 24.75° N, 99.28° E, 2817 m, 14.XI.2024, Wei He (CAU) (CAUDIP20243513). PARATYPES: CHINA: YUNNAN: 8 ♂♂ 3 ♀♀, Baoshan [保山], Shidian [施甸], Dashuihetou Mt. [大水河头山], 24.75° N, 99.28° E, 2817 m, 14.XI.2024, Wei He (CAU) (CAUDIP20243511–CAUDIP20243512, CAUDIP20243514–CAUDIP20243517).
Diagnosis. Small-sized. Male. Apical half of postpedicel expanded. Posterior margin of scutum with inverted “T” shape pale yellow pruinescence. Scutellum with an inverted triangle pale yellow pruinescence. Hind leg with black and white hairs. Abdominal tergites 2–6 with denser white pruinescence on posterior margin. Basiphallus not enlarged. Outer apex of gonocoxite short. Dorsal aedeagal sheath trifurcated, middle branch extremely short. Female. Postalar callus with long black hairs and pale pruinescence. Hind femora with sparse black and pale hairs.
Description. Male. Body length 9–11 mm, wing length 9–15 mm.
Head. Head about 1.6× wider than high (frontal view) (
Figure 11e) and 1.4× higher than long (lateral view, including face) (
Figure 11f), mostly black with yellow and golden yellow pruinescence and covered in dense long black hairs with admixed long white hairs. Frons trapezoid with yellow pruinescence, 1.5× length of ocellar tubercle, 2.9× as wide as ocellar tubercle, with black hairs (hairs relatively short and sparse compared to hairs on other parts of the head). Ocellar tubercle slightly raised, black with sparse yellow pruinescence, with long black hairs. Face with thick golden yellow pruinescence and denser with long black hairs (
Figure 11e,f). Mystax not distinguishable from facial hairs. Gena narrow, with sparse pale pruinescence. Clypeus with thick light yellow pruinescence and otherwise bare. Occiput with thick pale pruinescence and dense long black hairs, hairs denser in ventral half, hairs near the gena and the compound eyes forward bend. Antenna black with sparse light yellow pruinescence, uniform from base to apex, scape and pedicel with dense long black hairs, flagellum bare, anterior postpedicel expanded, apex of apical segment of stylus with short black hairs (
Figure 11g). Scape 1.2× as long as wide, and 1.1× as long as pedicel; pedicel 1.4× as long as wide; flagellum 10.0× as long as wide, 2.3× as long as scape + pedicel, 4.5× as long as scape; stylus 0.3× as long as flagellum, two-segmented, with apical seta-like sensory article; apical segment 5.0× as long as basal segment. Palpus clavate, black with fine black hairs, two-segmented. Proboscis black, only slightly compressed laterally, basal 2/3 with sparse pruinescence and dense long black and light yellow hairs ventrally, apical 1/3 shinning, with short yellow hairs.
Thorax. Integumental color of scutum mostly black, brownish gray with pale yellow pruinescence; scutum with black middle strip reaching posterior 4/5 of the scutum; anterior edge of transverse suture, near the middle of scutum with round pale yellow pruinescence, surrounding it with rectangular depression; posterior margin of scutum with inverted “T” shape pale yellow pruinescence; scutellum with an inverted triangle pale yellow pruinescence (
Figure 11i). Antepronotum admixed with long black and white hairs; postpronotum covered in long black admixed with white hairs laterally; proepimeron with thick pruinescence and densely covered in long white hairs. Lateral postpronotal lobe with shiny and dirty orange spot. Scutum covered with black, brownish gray with pale yellow pruinescence and sparse long black hairs. Scutellum black with sparse black and dense pale yellow pruinescence, covered with dense long black hairs. Postalar callus with long black hairs. Pleura black with thick pale pruinescence; anepisternum densely covered in long black hairs, hairs denser posteriorly and dorsally, admixed with a few white hairs; katepisternum with sparse white hairs gathered on the dorsal middle area; anepimeron, katepimeron, and meron bare. Metanepisternum densely covered in pale yellow tomentums and brownish black hairs in middle area; metakatepisternum bare; katatergite densely covered in long black hairs dorsally and long white hairs ventrally; anatergite covered with dense light yellow pruinescence on dorsal margin.
Legs. Legs black with sparse gray pruinescence, coxae covered in dense white hairs, femora mostly covered in dense long black and white hairs, ventral face covered in dense white hairs on basal 4/5 and black hairs on apical 1/5, apex of tibia with strong long dark orange bristles. Dorsal face of fore femora with long black hairs and mid femora with short black hairs, anterior face of fore and mid femora with several strong dark orangish to yellow bristles on middle area, all face of hind femora covered in white hairs on basal 4/5 and black hairs on apical 1/5 (
Figure 3g). Fore tibiae mostly covered in dense long black hairs admixed strong long dark orange bristles, ventral face of fore tibia with dense short dark orange hairs on apical 8/9, anterior face of fore tibia with long black hairs with short dark orange bristles; mid tibia denser with long black hairs admixed with long dark orange bristles, posterior face of hind tibia with dense pale hairs on basal 2/6 to 3/6 and apical 1/6, ventral face of hind tibia with white hairs admixed with black hairs (
Figure 4g). Fore tibia 2.9× longer than fore basitarsus, mid tibia 3.6× longer than mid basitarsus, hind tibia 3.1× longer than hind basitarsus.
Wings. Wing membrane hyaline with infuscated wing base, apex of cell
br, posterior of cell
m4, and crossveins
r-m1,
r-m2, and apex of cell
d, posterior of R
4+5. Haltere stem brownish black and knob orange (
Figure 11h).
Abdomen. Integumental color of tergites mostly black with dark blue metallic, covered with sparse long black hairs dorsally and dense long black hairs laterally. Tergites 2–6 with white dense pruinescence on posterior margin and triangular in laterally (
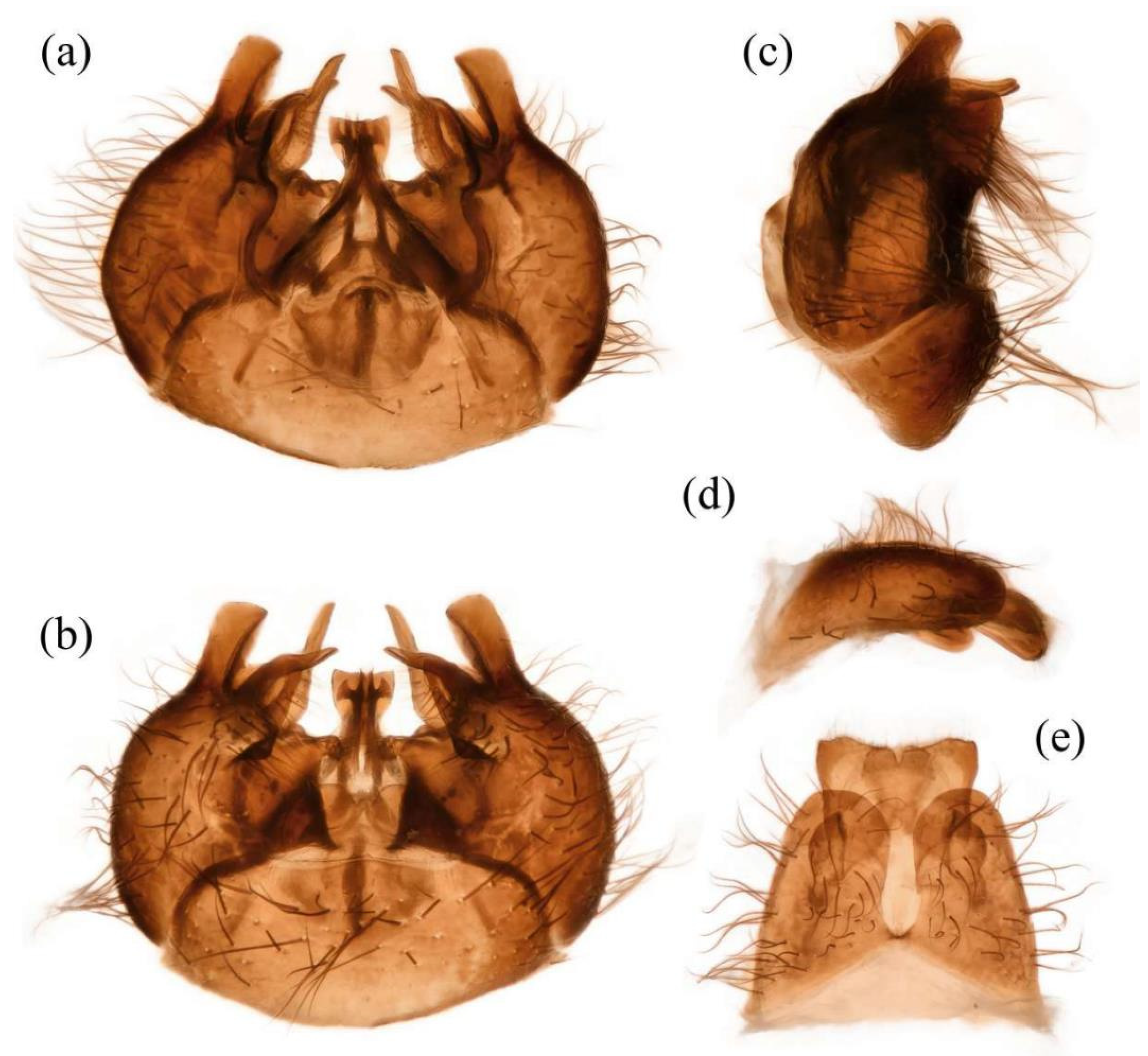
Figure 11d). Sternites black with sparse pale pruinescence, covered in long black hairs admixed with some white hairs; sternites 1–2 covered in white hairs admixed with black hairs. Genitalia (
Figure 12a–e). Posterior margin of epandrium 1.0× longer than full length, the length between middle point of posterior and anterior margins 0.64× longer than full length. Basiphallus normal, not enlarged. Gonocoxite with large ventral extension on posterior half, bifid, blunt posteriorly, inner tapered. Outer apex of gonocoxite relatively short. Dorsal aedeagal sheath trifurcated, but the middle fork extremely short.
Female. Body length 8–9 mm, wing length 9–15 mm.
Head. Frons 1.6× length of ocellar tubercle, 2.3× as wide as ocellar tubercle. Scape 1.3× as long as pedicel; pedicel 0.7× as long as wide; flagellum 6.4× as long as wide, 2.6× as long as scape + pedicel, 4.6× as long as scape; stylus apical segment 3.0× as long as basal segment.
Thorax. Posterior margin of scutum with inverted “T” shape pale yellow pruinescence, extending to anterior margin of scutum and tapering gradually; proepimeron with thick white pruinescence. Postalar callus with long black hairs and with a round pale pruinescence. anepisternum densely covered in long white hairs posteriorly and admixed with long black hairs; katepisternum with thick white pruinescence dorsally.
Legs. Ventral face of hind tibia without white hairs. Fore tibia 2.9× longer than fore basitarsus, mid tibia 2.7× longer than mid basitarsus, hind tibia 2.9× longer than hind basitarsus.
Wings. Anterior and base of wing membrane more hyaline.
Abdomen. Tergites 1–6 with white dense pruinescence on posterior margin, with black hairs admixed with white hairs on posterolateral face (
Figure 11m). Sternites 1–2 with covered in pale yellow to white hairs admixed with black hairs. Acanthophorite spines located on plate above cerci with six spines on each side, on ventrolateral plate of cerci with four larger spines and several smaller spines (
Figure 12f).
Remarks. Tergites 2–6 of the male sometimes do not have dense white pruinescence on the posterior margin or lateral area, and such cases are usually found in the anterior and/or posterior tergites, especially tergite 2, without dense white pruinescence entirely.
G. sagittatus sp. nov. is similar to G. engeli but differs from it as follows: flagellum bare; dorsal face of tibia without reddish stripe.
Etymology. This species was named for the distinctive pattern on its scutum and scutellum, which resembles an arrow in flight accompanied by two circular markings reminiscent of celestial bodies. This imagery evokes the Chinese legend of the archer Yi, who saved the Earth by shooting down nine of ten suns. The specific epithet “sagittatus” derives from Latin “sagitta” (arrow) and the suffix “-atus” (possessing), collectively meaning “arrow-shaped”.
Grypoctonus solarius Zhou & Li sp. nov.
Chinese common name: 秋光辅脉食虫虻
Type Materials. HOLOTYPE: ♂, CHINA: YUNNAN: Baoshan [保山], Shidian [施甸], Dashuihetou Mt. [大水河头山], 24.75° N, 99.28° E, 2817 m, 14.XI.2024, Wei He (CAU), (CAUDIP20243522). PARATYPES: 1 ♂ 5 ♀♀, CHINA: YUNNAN: Dali [大理], Jianchuan [剑川], Misha [弥沙乡], 26.27° N, 99.6° E, 3165 m, 26.X.2024, He Zhang (CAU) (CAUDIP20243471–CAUDIP20243476); 9 ♂♂ 37 ♀♀, Baoshan [保山], Shidian [施甸], Dashuihetou Mt. [大水河头山], 24.75° N, 99.28° E, 2817 m, 14.XI.2024, Wei He (CAU) (CAUDIP20243518–CAUDIP20243521, CAUDIP20243523–CAUDIP20243537).
Other Materials. CHINA: YUNAN: 2 ♂♂, Diqing [迪庆], Deqen [德钦], Baimang Snow Mt. [白芒雪山], 3300 m, 28.VIII.1981, Xuezhong Zhang (NACRC, IOZ).
Diagnosis. Male. Anterior face of hind femora covered with dark orange hairs in the top half and with black hairs in the lower half, dorsal face of hind femora with dark orange hairs, posterior face of hind tibia with dense short golden yellow hairs. Tergites with denser long black hairs ventrally. Dorsal aedeagal sheath trifurcated, middle branch short. Female. Anepisternum densely covered white hairs, denser posteriorly. Scutum with black and pale hairs. Anterior face of hind femora mostly covered with dark yellow hairs admixed with black hairs ventrally.
Description. Male. Body length 8–11 mm, wing length 13–15 mm.
Head. Head about 1.5× wider than high (frontal view) (
Figure 13e) and 1.4× higher than long (lateral view, including face) (
Figure 13f), mostly black with pale or light yellow pruinescence and covered in dense long black hairs with admixed long, white to light yellow hairs. Frons trapezoid with light yellow pruinescence, 1.3× length of ocellar tubercle, 3.2× as wide as ocellar tubercle, with black hairs (hairs relatively short and sparse compared to hairs on other parts of the head). Ocellar tubercle slightly raised, black with sparse light yellow pruinescence, with long black hairs. Face with thick pale pruinescence and admixed dense long black and a few pale hairs, except dorsolateral area with narrow, bare, and shinning strip (
Figure 13e,f). Gena narrow, with sparse light yellow pruinescence. Clypeus with thick light yellow pruinescence and otherwise bare. Mystax not distinguishable from facial hairs. Occiput with thick light yellow pruinescence and dense long black hairs ventral half with admixed dense long white to light yellow hairs, light yellow hairs denser in ventral half. Antenna black with sparse light yellow pruinescence, scape, and pedicel with dense long black hairs, flagellum bare (
Figure 13g). Scape 1.5× as long as wide, and 1.0× as long as pedicel; pedicel 1.4× as long as wide; flagellum 12.5× as long as wide, 2.1× as long as scape + pedicel, 4.2× as long as scape; stylus 0.2× as long as flagellum, two-segmented, with apical seta-like sensory article, apical segment 2.6× as long as basal segment. Palpus clavate, black with fine brownish to blackish hairs, two-segmented. Proboscis black, only slightly compressed laterally, basal 2/3 with sparse pruinescence and dense long pale yellow hairs ventrally, apical 1/3 shinning, with short brown to yellow hairs.
Thorax. Integumental color of scutum mostly brownish black with gray and light yellow pruinescence. Scutum with two brown middle strips reaching posterior 4/5 of the scutum; anterolateral of transverse suture and inner-anterior of postalar callus with small, bare, and shinning spots (
Figure 13i). Antepronotum with admixed long light yellow and black hairs; postpronotum with long black hairs laterally; proepimeron densely covered in black hairs dorsally and light yellow hairs ventrally. Lateral postpronotal lobe with shiny and dirty orange spot. Scutum covered with dense brown pruinescence and sparse long black hairs. Scutellum black with sparse brown pruinescence, covered with dense long pale hairs admixed few black hairs basilally, hairs in anterior margin strongly proclinate. Postalar callus with long black hairs. Pleura black with thick brown pruinescence; anepisternum densely covered in long black hairs, hairs denser posteriorly and dorsally; katepisternum with sparse black and light yellow hairs on dorsal margin, anepimeron, katepimeron, and meron bare. Metanepisternum densely covered in light yellow tomentums and brownish black hairs in middle area, with sparse black hairs posterolaterally; metakatepisternum bare; katatergite densely covered in long black hairs; anatergite covered with dense light yellow pruinescence on dorsal margin.
Legs. Legs black, coxae covered in dense light yellow and white hairs, femora mostly covered in dense long black hairs, ventral face admixed with dense long light yellow hairs on basal 3/5. Dorsal face of hind femora admixed with dark orange and golden yellow hairs (
Figure 4c). Fore tibiae mostly covered in dense long black hairs admixed strong long golden yellow bristles, ventral face of fore tibia with dense short golden yellow hairs on apical 4/5, posterior face of fore tibia with white hairs on apical 1/5; anterior face of mid tibia admixed with long black, dark orangish, and white hairs, dorsal face of mid tibia with half black hairs basally and half white hairs apically, admixed with long yellow hairs, posterior face on hind tibia with dense long white hairs on basal 2/5 and dense golden yellow hairs on 3/5, admixed with long yellow hairs (
Figure 3f), ventral face of hind tibia with dense short golden yellow hairs. Ventral face of tarsi with dense short black and white hairs, tarsi with short black hairs admixed with dark orangish bristles and short white hairs. Fore tibia 2.7× longer than fore basitarsus, mid tibia 3.4× longer than mid basitarsus, hind tibia 3.1× longer than hind basitarsus.
Wings. Wing membrane hyaline with infuscated wing base, anterior margin, cell
br, apex, and posterior of cell
bm, areas around crossveins
r-m1,
r-m2, cell
r-m, and base of cell
m1. Haltere stem and knob brownish black (
Figure 13h).
Abdomen. Integumental color of tergites mostly black with a few dark blue metallic and sparse light pruinescence. Tergite 1 with dense long pale yellow hairs, laterally admixed with more white hairs, and anterolaterally covered in dense short black hairs; tergites 2–6 with dense long pale yellow and golden yellow hairs, laterally with dense long black hairs; tergites 7–8 with long black hairs, tergite 7 admixed with few pale yellow hairs (
Figure 13d). Sternites black with thick light yellow pruinescence, covered in long pale yellow hairs admixed with black hairs; sternite 1 with black hairs, admixed with pale yellow hairs, sternite 2 with black hairs, other sternites admixed with black and yellow hairs. Genitalia (
Figure 14a–e). Posterior margin of epandrium 1.5× longer than full length, the length between middle point of posterior and anterior margins 0.58× longer than full length. Basiphallus enlarged. Gonocoxite with large ventral extension on posterior half, trifurcated, blunt posteriorly, inner tapered. Dorsal aedeagal sheath trifurcated, middle branch extremely short.
Female. Body length 9–15 mm, wing length 15–20 mm.
Head. Head about 1.6× wider than high (frontal view) and 1.5× higher than long (lateral view, including face). Frons 1.2× length of ocellar tubercle, 2.7× as wide as ocellar tubercle. Ocellar tubercle with pale yellow to long white hairs. Occiput with thick pale pruinescence and dense long white hairs, admixed with long black hairs, ventral half with admixed dense long black and white hairs, black hairs denser in antroventral half. Scape 1.1× as long as wide, and 0.9× as long as pedicel; pedicel 1.4× as long as wide; flagellum 10× as long as wide, 2.3× as long as scape + pedicel, 5.0× as long as scape; stylus 0.2× as long as flagellum, apical segment 1.5× as long as basal segment.
Thorax. Antepronotum with long pale hairs; proepimeron densely covered in white hairs. Anepisternum densely covered in long black hairs dorsally and white hairs denser posteriorly; katepisternum with sparse pale hairs on dorsal margin, katatergite densely covered in long black and light yellow to white hairs.
Legs. Posterior face, anterior 4/5 of ventral face of femora with light yellow to white hairs, anterior 4/5 face of mid femora with white hairs (
Figure 4d). Posterior face of fore tibia with white hairs on apical 3/5 to 4/5; except ventral face of mid and hind tibia admixed with black and golden yellow hairs, other parts of mid and hind tibia mostly covered in long white hairs (
Figure 3d). Fore tibia 2.8× longer than fore basitarsus, mid tibia 3.3× longer than mid basitarsus, hind tibia 3.0× longer than hind basitarsus.
Wings. Anterior of wing membrane hyaline, especially cell
c (
Figure 13j).
Abdomen. Tergites 2–7 with dense long golen yellow to pale yellow hairs, laterally with dense long black hairs; tergite 8 with pale yellow hairs. Sternite 1 with pale yellow hairs. Genitalia. Acanthophorite spines located on plate above cerci with six spines on each side, on plate ventrolateral of cerci with four larger spines and several smaller spines (
Figure 14f).
Remarks. Apex of R4+5; some specimens slightly infuscated.
G. solarius sp. nov. is similar to G. aino but differs from it as follows: a dorsal face of hind femora with distinct orange hairs; male tergites with lighter hairs; and female katatergite is densely covered with long black hairs admixed with light yellow to white hairs.
Etymology. This species was named after its orange hairs on the anterior and dorsal face of its hind femora combined with its sun-dependent ecology. The conspicuous orange and white hairs evoke imagery of autumn landscapes bathed in golden sunlight. This fly is a solar-powered hunter, relying on daylight to pursue prey. The Latin epithet is “solarius” (meaning “solar” or “of the sun”).
Grypoctonus yongshani Zhou & Li sp. nov.
Chinese common name: 永善辅脉食虫虻
Type Materials. HOLOTYPE: ♂, CHINA: YUNNAN: Diqing [迪庆], Deqen [德钦], Baimang Snow Mt. [白芒雪山], 4250 m, 31.VIII.1981, Xuezhong Zhang (NACRC, IOZ) (IOZ(E)2059369). PARATYPES: CHINA: YUNNAN: ♀, Diqing [迪庆], Deqen [德钦], Baimang Snow Mt. [白芒雪山], 4250 m, 31.VIII.1981, Xuezhong Zhang (NACRC, IOZ) (IOZ(E)2059370); ♀, Diqing [迪庆], Deqen [德钦], Baimang Snow Mt. [白芒雪山], 4000 m, 29.VIII.1981, Shuyong Wang (NACRC, IOZ) (IOZ(E)2059371); 2 ♀♀, Diqing [迪庆], Shangri-La [香格里拉], Xiaozhongdian [小中甸], 3800 m, 1.VIII.1984, Shuyong Wang (NACRC, IOZ) (IOZ(E)2059374–IOZ(E)2059375). SICHUAN: ♀, Kangding [康定], Garzê [甘孜], Gonggar Temple [贡嘎寺], 3650–4000 m, 3.IX.1982, Shuyong Wang (NACRC, IOZ) (IOZ(E)2059372); ♂, Kangding [康定], Garzê [甘孜], Gonggar Mt. [贡嘎山], 3650–4200 m, 4.Ⅸ.1982, Xuezhong Zhang (NACRC, IOZ) (IOZ(E)2059373).
Diagnosis. Small-sized. Apical half of postpedicel expanded, with or without two bristles. Anterior edge of transverse suture, near the middle of scutum with subtriangle pale pruinescence, surrounding it with light depression; between the scutum middle strip and lateral postpronotal lobe with subtriangle pale pruinescence. Posterior margin of scutum with short and blurred pruinescence pattern. Hind leg with black and white hairs. Dorsal aedeagal sheath blunt. Ventral aedeagal sheath four-branched, with middle two longer than later two branches. Hypandrium mammillary processes fused. Female. Katepisternum with thick pale pruinescence dorsally and covered in white hairs on the dorsal middle area. Notopleuron with several yellow bristles.
Description. Male. Body length 10–11 mm, wing length 12–15 mm.
Head. Head about 1.6× wider than high (frontal view) (
Figure 15e) and 1.6× higher than long (lateral view, including face) (
Figure 15f), mostly black with pale pruinescence and covered in dense long black hairs with admixed long white hairs. Frons trapezoid with pale pruinescence, 1.6× length of ocellar tubercle, 2.5× as wide as ocellar tubercle, with black hairs (hairs relatively short and sparse compared to hairs on other parts of the head). Ocellar tubercle slightly raised, black with sparse pale pruinescence, with long black hairs. Face with thick pale pruinescence and denser with long black hairs (
Figure 15e,f). Mystax not distinguishable from facial hairs. Gena narrow, with sparse pale pruinescence. Clypeus with thick pale pruinescence and otherwise bare. Occiput with thick pale pruinescence and dense long black hairs, hairs denser in ventral half, hairs near the compound eyes forward bend. Antenna black with sparse light yellow pruinescence, uniform from base to apex, scape, and pedicel with dense long black hairs, flagellum with two hairs, anterior postpedicel expanded, apex of apical segment of stylus with short black hairs (
Figure 15g). Scape 1.5× as long as wide, and 1.5× as long as pedicel; pedicel 1.0× as long as wide; flagellum 7.3× as long as wide, 2.2× as long as scape + pedicel, 3.6× as long as scape; stylus 0.2× as long as flagellum, two-segmented, with apical seta-like sensory article; apical segment 5.0× as long as basal segment. Palpus clavate, black with fine black hairs, two-segmented. Proboscis black, only slightly compressed laterally, basal 2/3 with sparse pruinescence and dense long light yellow to pale hairs ventrally, apical 1/3 shinning, with short light yellow hairs.
Thorax. Integumental color of scutum mostly black, brownish gray with pale yellow pruinescence; scutum with black middle strip reaching posterior 4/5 of the scutum; anterior edge of transverse suture, near the middle of scutum with subtriangle pale pruinescence, surrounding it with light depression; between the scutum middle strip and lateral postpronotal lobe with subtriangle pale pruinescence. Posterior margin of scutum with short and blurred pruinescence pattern (
Figure 15i). Antepronotum with long black hairs; postpronotum covered in long black hairs laterally; proepimeron with thick pale pruinescence and densely covered in long white hairs. Lateral postpronotal lobe with shiny and dirty orange spot. Scutum covered with black, brownish gray with pale yellow pruinescence and sparse long black hairs. Scutellum black with admixed black and light yellow hairs. Postalar callus with admixed long black and light yellow hairs. Notopleuron with several yellow bristles. Pleura black with relatively thick pale pruinescence; anepisternum densely covered in long black hairs, hairs denser posteriorly and dorsally; katepisternum with thick pale pruinescence dorsally and covered with sparse white hairs gathered on the dorsal middle area, with 2–3 white hairs posteriorly and ventrally; meron with two long white hairs ventrally; anepimeron and katepimeron bare. Metanepisternum with thick pale pruinescence and densely covered in pale tomentums; metakatepisternum with thick pruinescence; katatergite densely covered with long black hairs anteriorly and posteriorly, covered in long white hairs medially; anatergite covered with dense light yellow pruinescence on dorsal margin.
Legs. Legs black with sparse gray pruinescence, coxae with dense pruinescence covered in dense light yellow to white hairs, femora mostly covered in dense long black and light yellow to white hairs, ventral face covered in dense light yellow to white hairs on basal 3/5 and black hairs on apical 2/5, apex of tibia with strong long orange bristles. Dorsal face of fore femora with long black hairs and mid femora with shorter black hairs, anterior face of fore and mid femora with several yellow bristles on middle area, ventral face of hind femora covered in light yellow hairs on basal 4/5 and black hairs on apical 1/5 (
Figure 4h). Fore tibiae mostly covered in dense long black hairs admixed strong long dark orange bristles, ventral face of fore tibia with dense short dark orange hairs on apical 8/9, anterior face of fore tibia with long black hairs with short dark orange bristles in a row; mid tibia denser with long black hairs admixed with many long yellow bristles, posterior face of hind tibia with dense pale hairs on basal 2/6 to 3/6 and apical 1/6, other face of hind tibia with black hairs admixed with yellow bristles (
Figure 3h). Fore tibia 3.7× longer than fore basitarsus, mid tibia 3.7× longer than mid basitarsus, hind tibia 3.5× longer than hind basitarsus.
Wings. Wing membrane hyaline with infuscated wing base, apex of cell
br, posterior of cell
m4, and crossveins
r-m1,
r-m2, and apex of cell
d. Haltere stem brownish black and knob orange (
Figure 15h).
Abdomen. Integumental color of tergites mostly black with dark blue metallic, covered with sparse long black hairs dorsally and dense long black hairs laterally. Tergites 2–6 with triangular white dense pruinescence on lateral posterior margin (
Figure 15d). Sternites black with sparse pale pruinescence, covered in long black hairs admixed with some light yellow hairs; sternites 1–2 covered in black hairs. Genitalia (
Figure 16a–e). Posterior margin of epandrium 1.3× longer than full length, the length between middle point of posterior and anterior margins 0.68× longer than full length. Hypandrium mammillary processes fused. Basiphallus enlarged. Lateral ejaculatory process small and fused within basiphallus. Gonocoxite with large ventral extension on posterior half, bifid, blunt posteriorly, inner slightly tapered. Outer apex of gonocoxite long. Dorsal aedeagal sheath blunt, ventral aedeagal sheath four-branched, with middle two longer than later two branches.
Female. Body length 10–12 mm, wing length 15–20 mm.
Head. Frons 2.0× length of ocellar tubercle, 2.2× as wide as ocellar tubercle. Flagellum bare. Scape 1.2× as long as wide, and 1.0× as long as pedicel; pedicel 1.2× as long as wide; flagellum 5.5× as long as wide, 4.0× as long as scape; stylus 0.6× as long as flagellum; apical segment 3.5× as long as basal segment.
Thorax. Posterior margin of scutum with relatively large triangular pale pruinescence. Anepisternum densely covered in long black hairs dorsally and admixed with black and white hairs posteriorly; katepisternum with thick pale pruinescence dorsally and covered in white hairs on the dorsal middle area; anepimeron, katepimeron, and meron bare. katatergite densely covered with long pale hairs, admixed with black hairs posteriorly.
Legs. Posterior face of fore femora with long black hairs admixed with long pale hairs. Fore tibia 2.7× longer than fore basitarsus, mid tibia 3.2× longer than mid basitarsus, hind tibia 3.2x longer than hind basitarsus.
Wings. Very similar to male.
Abdomen. Tergites 2–6 with white dense pruinescence on posterior margin and triangular in laterally (
Figure 15m). Tergites 1–6 laterally with dense long black and white hairs. Sternites 1 with covered in black and pale hairs. Acanthophorite spines located on plate above cerci with six spines on each side, on plate ventrolateral of cerci with four larger spines and several smaller spines.
Remarks. Morphological variations were observed in several specimens, particularly in antennal vestiture and thoracic patterns. Bristles were occasionally present on flagellomeres (IOZ(E)2059371: left flagellum with one yellow bristle; IOZ(E)2059373: right flagellum with one black bristle; IOZ(E)2059375: left flagellum with two black bristles) and rarely on pedicels (IOZ(E)2059371: ventral pedicel with one yellow bristle). Additionally, thoracic patterns appeared blurred in some specimens (IOZ(E)2059371, IOZ(E)2059372, IOZ(E)2059374, IOZ(E)2059375), likely due to dust accumulation or oil contamination.
The holotype was originally identified as
Cyrtopogon daimyo (=
Grypoctonus hatakeyamae) by Shi [
11]. Our examination revealed that this specimen does not belong to
C. daimyo but instead represents a new species, invalidating the previous record of
C. daimyo from Yunnan. While Shi [
11] reported three specimens (1 ♂, 2 ♀♀), only two (1 ♂, 1 ♀) were found from IOZ.
G. yongshani sp. nov. is similar to G. engli, but the dorsal face of the tibia does not have a reddish stripe, and the scutum has special patterns.
Etymology. This species is named after Dr. Yongshan Shi for his important contributions to the Chinese Asilidae taxonomy.