A “Sconce” Trap for Sampling Egg Masses of Spotted Lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
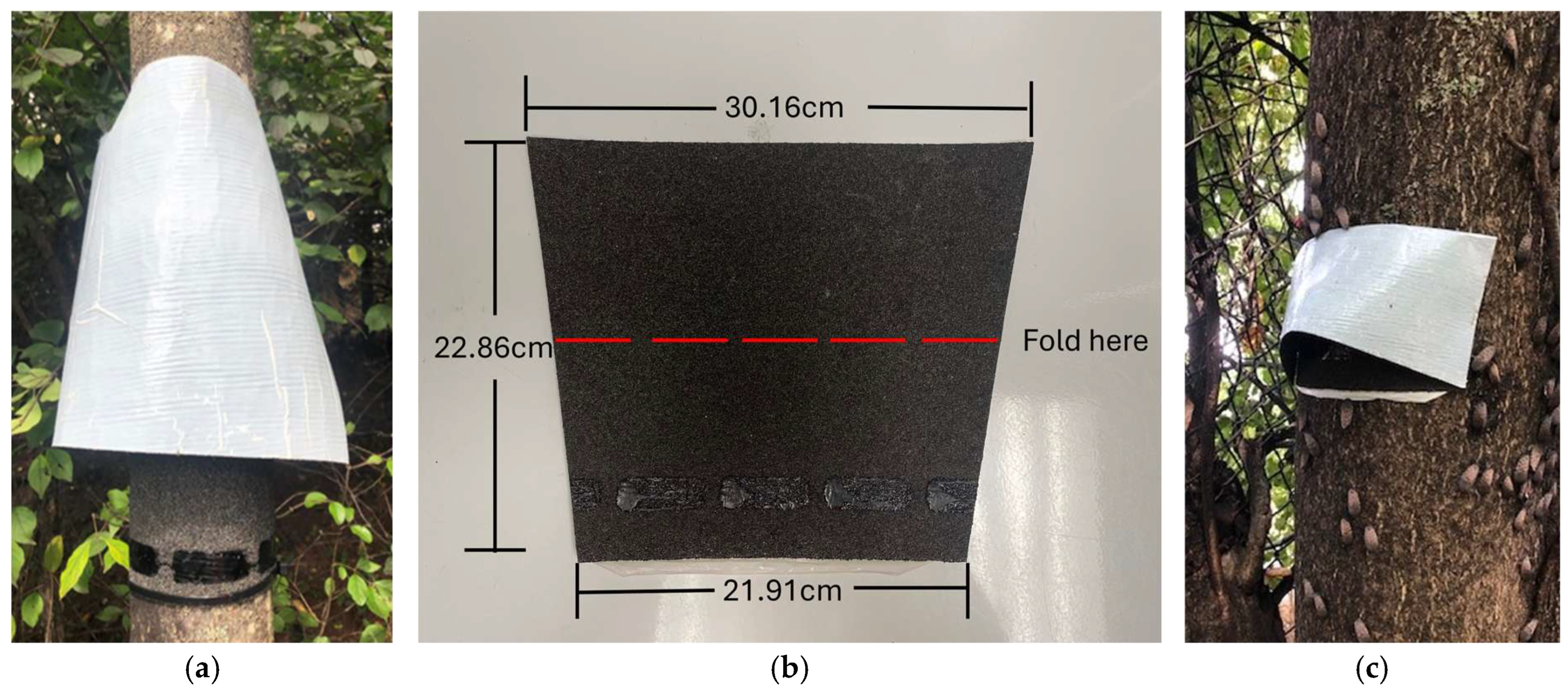
2.1. Egg Mass Traps
2.2. Trapping Assays
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SLF | Spotted lanternfly |
| DBH | Diameter at breast height |
| USDA | United States Department of Agriculture |
| APHIS | Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service |
| PPQ | Plant Protection and Quarantine |
| S&T | Science and Technology |
| FPML | Forest Pest Methods Laboratory |
References
- USDA APHIS PPQ. Spotted Lanternfly. Available online: https://www.aphis.usda.gov/plant-pests-diseases/slf (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Barringer, L.E.; Donovall, L.R.; Spichiger, S.E.; Henry, D. The first New World record of Lycorma delicatula (Insecta: Hemiptera: Fulgoridae). Entomol. News 2015, 125, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barringer, L.; Ciafre, C.M. Worldwide feeding host plants of the spotted lanternfly, with significant additions from North America. Enviorn. Entomol. 2020, 49, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francese, J.A.; Cooperband, M.F.; Murman, K.M.; Cannon, S.L.; Booth, E.G.; Devine, S.M.; Wallace, M.S. Developing traps for the spotted lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae). Environ. Entomol. 2020, 49, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nixon, L.J.; Leach, H.; Barnes, C.; Urban, J.; Kirkpatrick, D.M.; Ludwick, D.C.; Short, B.; Pfeiffer, D.G.; Leskey, T.C. Development of behaviorally based monitoring and bio-surveillance tools for the invasive spotted lanternfly (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae). Environ. Entomol. 2020, 49, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, J.A.; Hoover, K. Approach to surveying egg masses of the invasive spotted lanternfly (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae). Environ. Entomol. 2023, 52, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, P.; Davila-Flores, A.; Wallis, E. An effective trap for spotted lanternfly egg masses. Front. Insect Sci. 2023, 3, 1154510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- University of Massachusetts. Lampshade Trap Construction for Spotted Lanternfly Egg Masses. Available online: https://www.umass.edu/agriculture-food-environment/sites/ag.umass.edu/files/pdf,doc,ppt/lampshade_trap_for_slf_egg_masses_lewis_2022.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Cooperband, M.F.; Murman, K. Responses of adult spotted lanternflies to artificial aggregations composes of all males or females. Front. Insect Sci. 2022, 2, 981832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, J.M.; Storer, A.J.; Fraser, I.; Beachy, J.A.; Mastro, V.C. Effectiveness of differing trap types for the detection of emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae). Environ. Entomol. 2009, 38, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Hunter, M. Nondestructive sampling for spotted lanternfly (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae) egg masses in woodlands based on fixed-radius plots. J. Econ. Entomol. 2021, 114, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Trap Type | N | Tree DBH (cm) | Mean No. of Egg Masses Collected Per Trap (±S.E.) | Mean Trap Surface Area (cm2) Per Trap (±S.E.) 1 | Mean No. of Egg Masses Collected Per cm2 of Trap Surface (±S.E.) | Percentage of Traps Collecting Egg Masses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lampshade | 34 | 19.3 ± 1.1 | 46.6 ± 6.2 a | 3132.1 ± 952.3 | 0.017 ± 0.002 b | 97.1% |
| Sconce | 34 | 18.6 ± 1.2 | 14.9 ± 2.2 b | 595.2 | 0.025 ± 0.004 a | 94.1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Devine, S.M.; Booth, E.G.; Cooperband, M.F.; Franzen, E.K.L.; Lewis, P.A.; Murman, K.M.; Francese, J.A. A “Sconce” Trap for Sampling Egg Masses of Spotted Lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula. Insects 2025, 16, 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070689
Devine SM, Booth EG, Cooperband MF, Franzen EKL, Lewis PA, Murman KM, Francese JA. A “Sconce” Trap for Sampling Egg Masses of Spotted Lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula. Insects. 2025; 16(7):689. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070689
Chicago/Turabian StyleDevine, Sarah M., Everett G. Booth, Miriam F. Cooperband, Emily K. L. Franzen, Phillip A. Lewis, Kelly M. Murman, and Joseph A. Francese. 2025. "A “Sconce” Trap for Sampling Egg Masses of Spotted Lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula" Insects 16, no. 7: 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070689
APA StyleDevine, S. M., Booth, E. G., Cooperband, M. F., Franzen, E. K. L., Lewis, P. A., Murman, K. M., & Francese, J. A. (2025). A “Sconce” Trap for Sampling Egg Masses of Spotted Lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula. Insects, 16(7), 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070689





