Morphological and Ultrastructural Characteristics of Tea Mosquito Bug Antennae, Helopeltis theivora Waterhouse (Hemiptera: Miridae) from Hainan, China
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects
2.2. Observation of Antennae of H. theivora in the Laboratory
2.3. Determination of Morphological Characteristics of Antennae of H. theivora
2.3.1. Body Length and Antennal Length
2.3.2. Number and Length of Antennal Setae
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4.1. Sample Preparation
2.4.2. Sample Observation
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.5.1. Sample Preparation
2.5.2. Sample Observation
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
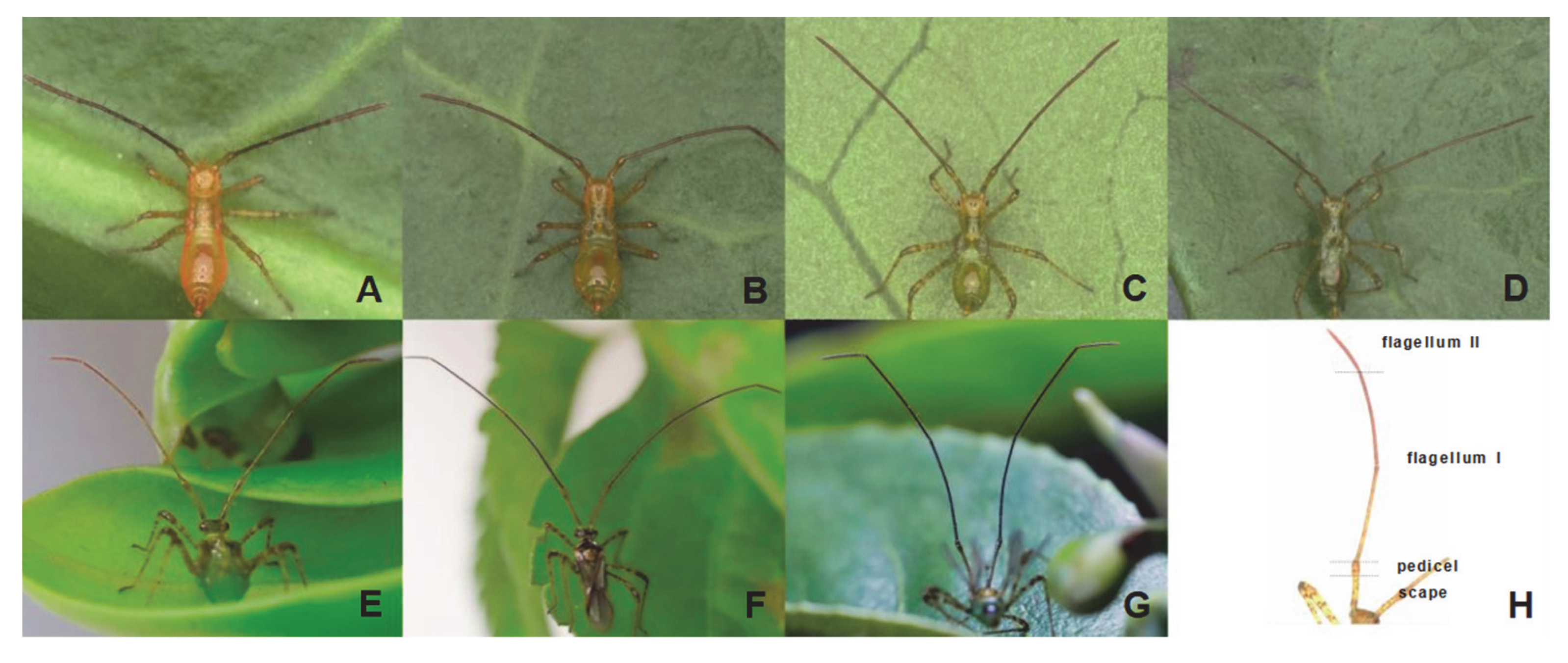
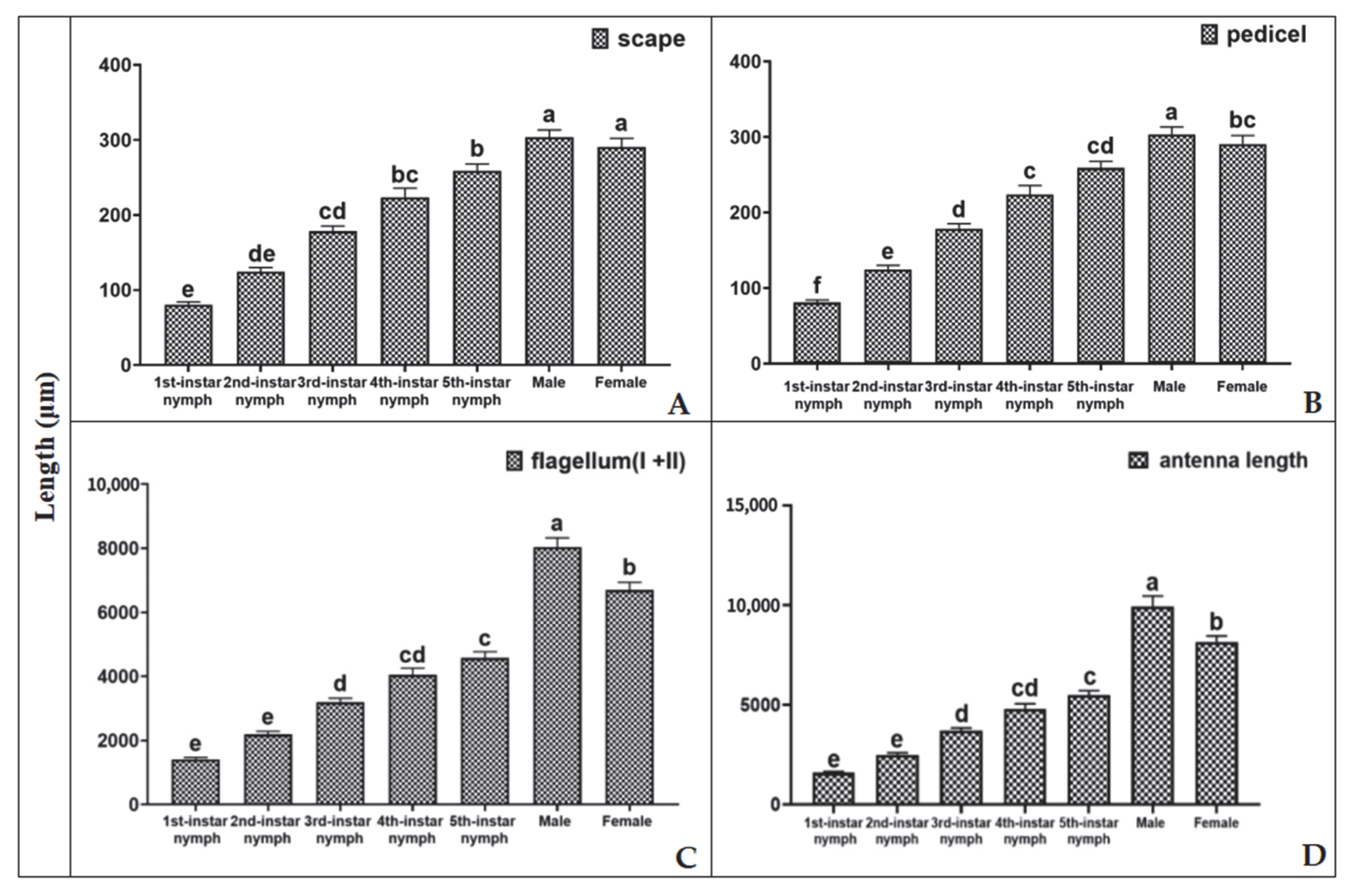
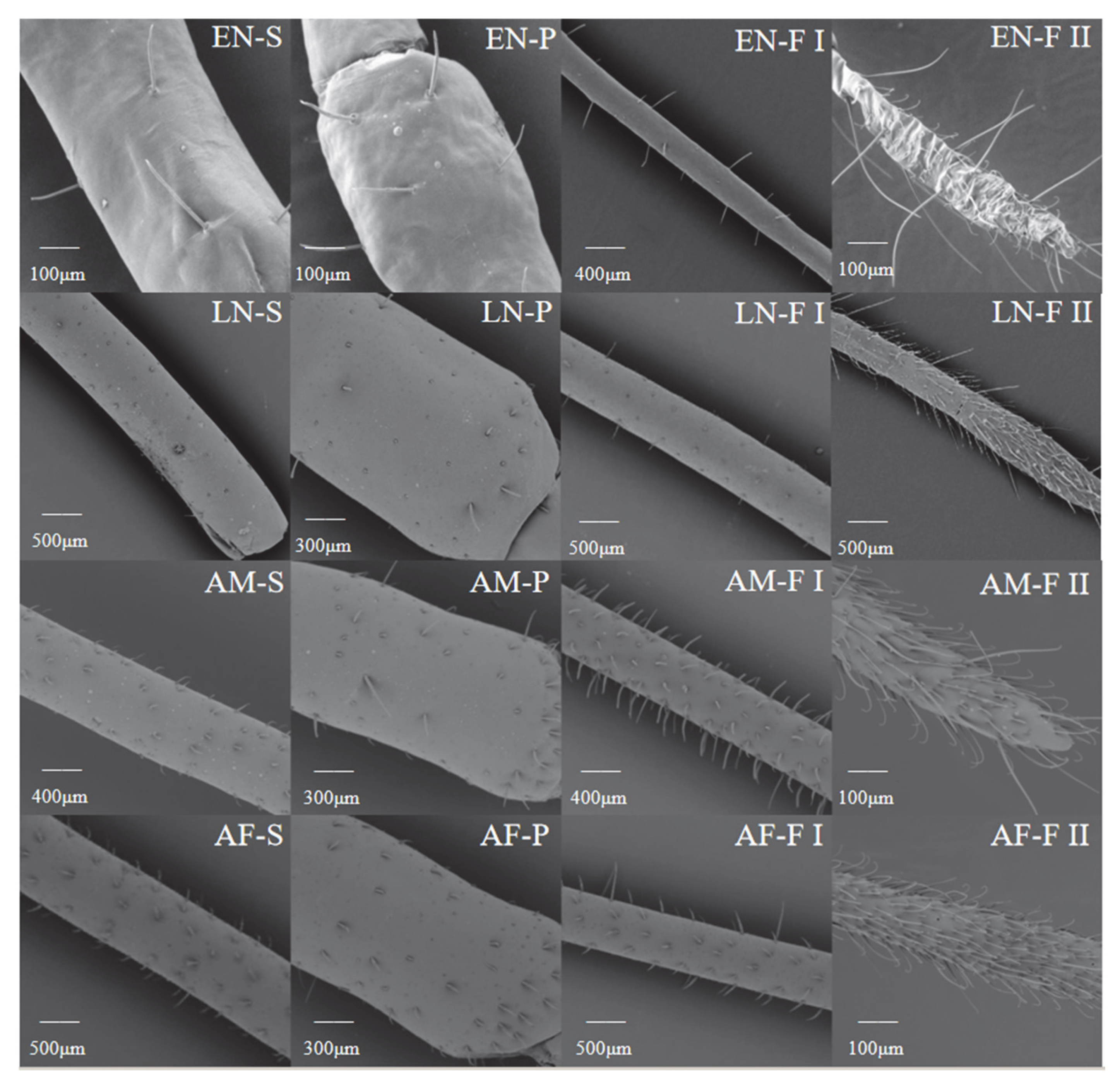
3.1. Development of H. theivora Antennae
3.2. Morphological Characteristics of H. theivora Antennae
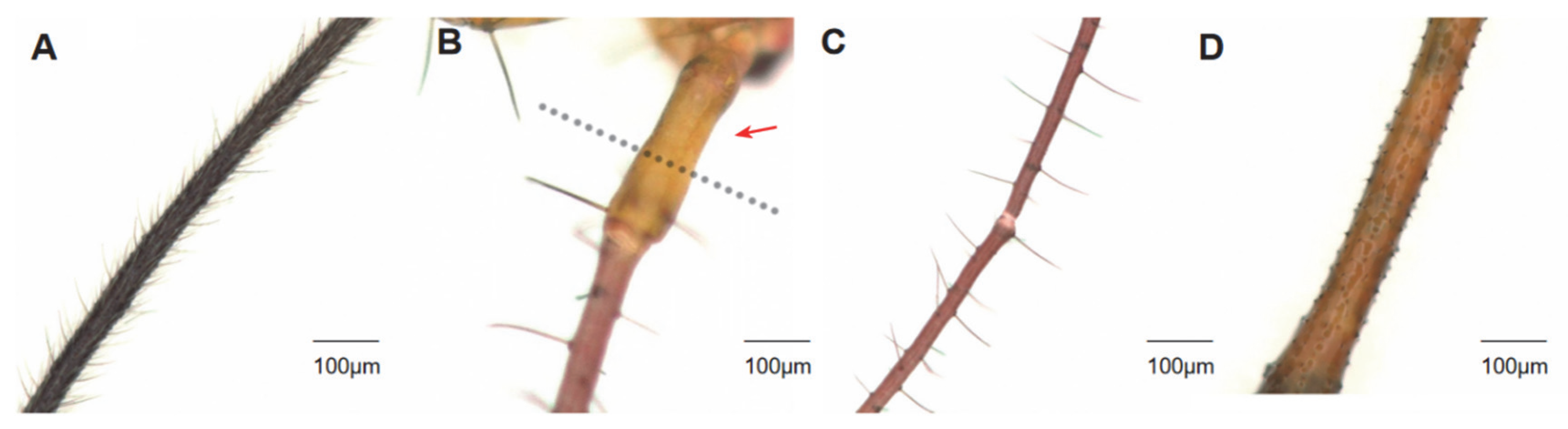
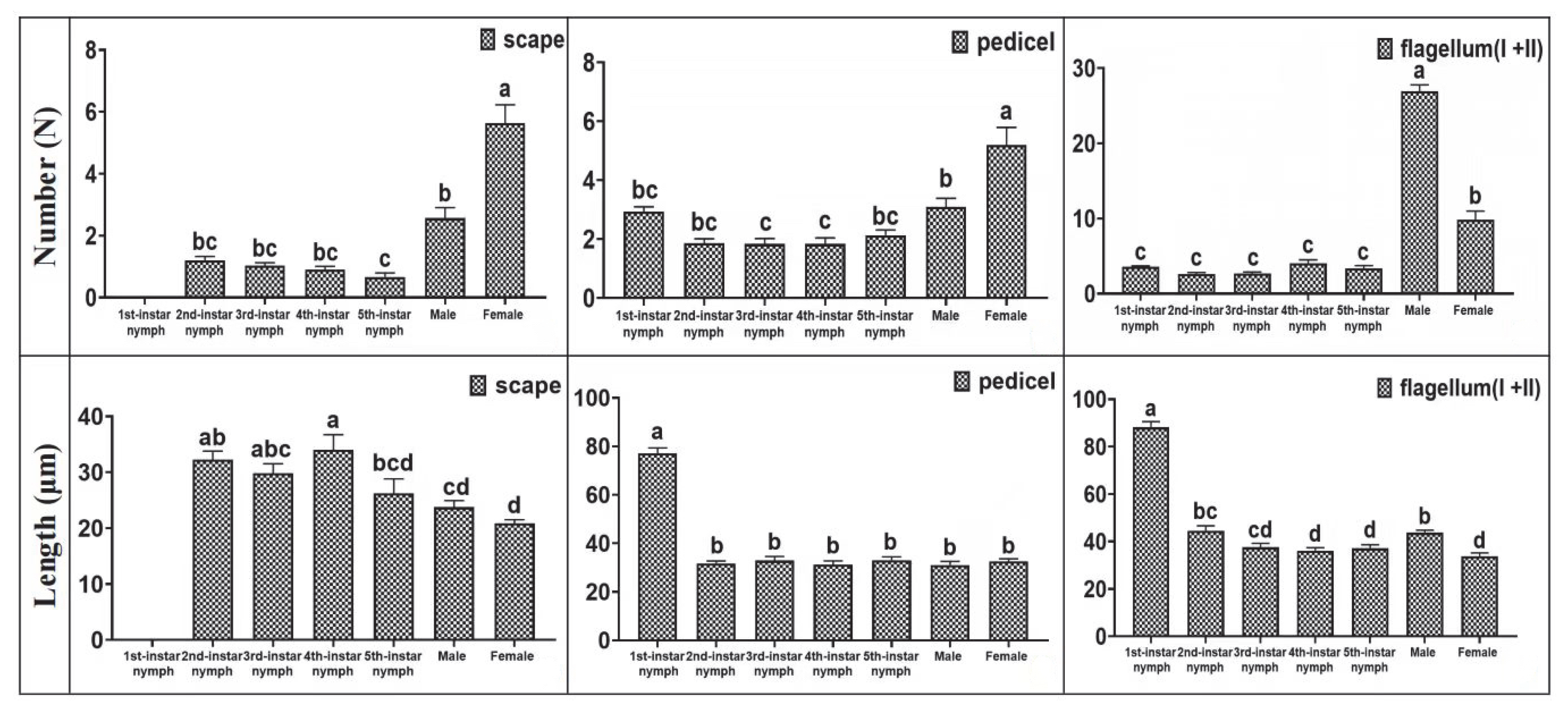
3.3. Distribution of Setae on H. theivora Antenna
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy on Antennae of H. theivora
3.4.1. Types of Sensilla on Antennae of H. theivora
3.4.2. Distribution of Sensilla on Antennae of H. theivora
3.4.3. Length of Sensilla on Antennae of H. theivora
3.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy on Sensilla of H. theivora
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bandyopadhyay, T.; Gohain, B.; Bharalee, R.; Gupta, S.; Bhorali, P.; Das, S.K.; Das, S. Molecular landscape of Helopeltis theivora induced transcriptome and defense gene expression in tea. Plant Mol. Biol. Report. 2015, 33, 1042–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, B.; Babu, A.; John Peter, A.M.T.; Pandey, A.K.; Kumhar, K.C.; Sarkar, S.; Talluri, V.R. Beauveria bassiana: As a potential microbial biocontrol agent for tea mosquito bug, Helopeltis theivora Waterhouse (Hemiptera: Miridae) in Dooars and Darjeeling, India. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2021, 31, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, N.S.; Mahendran, P.; Sujatha, K.; Ashokraj, S.; Rabeesh, T.P. Pathogenic potential of Metarhizium anisopliae and Lecanicillium longisporum on tea mosquito bug, Helopeltis theivora Waterhouse (Hemiptera: Miridae). J. Basic Appl. Zool. 2022, 83, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagiman, F.X.; Sari, N.M.; Wijonarko, A. The population structure and presence of helopeltis bradyi on the tea plant parts at various times during the day. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 686, 012062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magsi, F.H.; Cai, X.M.; Luo, Z.X. Identification, synthesis, and field evaluation of components of the female-produced sex pheromone of Helopeltis cinchonae (Hemiptera: Miridae), an emerging pest of tea. Pest Manag. Sci. 2024, 80, 4243–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Roy, S.; Handique, G.; Chakraborti, D.; Naskar, S.; Chakraborty, K.; Babu, A. Decoding defenses: Biochemical insights into insecticide resistance in tea mosquito bug, Helopeltis theivora Waterhouse (Hemiptera: Miridae) from tea plantations of Eastern India. Crop Prot. 2024, 184, 106802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.; Roy, S. Changing dimensions of IPM in the tea plantations of the north eastern sub-Himalayan region. In National Symposium on IPM Strategies to Combat Emerging Pest in the Current Scenario of Climate Change; Ramamurthy, V.V., Gupta, G.P., Puri, S.N., Eds.; Collage of Horticulture and Forestry, Central Agricultural University: Pasighat, Indian, 2009; Volume 791002, pp. 290–302. [Google Scholar]
- Sankarganesh, E.; Lavanya Sravani, B.; Rajeshwaran, B.; Mounika, M.N. Tea Mosquito Bug (Helopeltis spp.): A Pest of Economically Important Fruit and Plantation Crops: Its Status and Management Prospects. Plant Health Issues 2020, 1, 014–024. [Google Scholar]
- Samynathan, R.; Venkidasamy, B.; Shanmugam, A.; Khaled, J.M.; Chung, I.M.; Thiruvengadam, M. Investigating the impact of tea mosquito bug on the phytochemical profile and quality of Indian tea cultivars using HPLC and LC-MS-based metabolic profiling. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 204, 117278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Lin, Y.Z.; Qin, S.; Lin, Z.F.; Ji, X.C. Characterization of feeding damage by tea mosquito bug, Helopeltis theivora Waterhouse (Hemiptera: Miridae) on Hainan Dayezhong tea cultivar. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 15, 1529535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Mukhopadhyay, A. Insecticide-induced change in egg-laying strategy of Helopeltis theivora (Hemiptera: Miridae) on tea shoot (Camellia sinensis). Proc. Zool. Soc. Springer-Verl. 2011, 64, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W. Preliminary observations on the life habits of the tea capsid bug (Helopeltis theivora). China Tea 1983, 2, 30–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.W. Research on the Biological Characteristics and Control of Tea mosquito Bug on Tea Trees Natural Science. Nat. Sci. J. Hainan Univ. 1985, 1, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Yu, W.; Wu, X. Ultrastructure of sensilla on the maxillary and labial palps of three species (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae: Staphylininae). Entomol. Res. 2019, 49, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.N.; Xiang, S.S.; Zhu, H. Research Progress on Types and Functions of Insect Antennal Sensilla. J. Environ. Entomol. 2023, 45, 1197–1216. [Google Scholar]
- Bruce, T.J.A.; Pickett, J.A. Perception of plant volatile blends by herbivorous insects–finding the right mix. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 1605–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z. Identification and Expression Analysis of Olfactory Receptor Genes in Empoasca onukii. Ph.D. Thesis, Shandong Agricultural University, Taian, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.H.; Tong, Y.J.; Wu, K.M. Antennal sensilla of the green plant bug, Lygus lucorum Meyer-Dür (Heteroptera: Miridae) observed with scanning electron microscopy. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2007, 50, 863–867. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Meng, Q.Q.; Liu, A.Q.; Sang, L.W.; Sun, S.W.; Gou, Y.F.; Gao, S.F. Scanning Electron Microscopy Observation on Antennal Sensilla and Foreleg Sensilla of Helopeltis theivora. Trop. Crops Journa 2017, 38, 2165–2170. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.Y.; Zheng, L.X.; Zhang, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.J. The structure and morphologic changes of antennae of Cyrtorhinus lividipennis (Hemiptera: Miridae: Orthotylinae) in different instars. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Zhu, F.; Chen, L.Z.; Zhou, L.J.; Lei, Z.L. Scanning Electron Microscopy Observation on Antennal Sensilla of Adelphocoris suturalis. J. Insect Knowl. 2009, 6, 879–882. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, F.; Isobe, Y.; Oishi, T. The Types and Distribution of Setae on the Larval Legs of Neoperla geniculata in International Advances in the Ecology, Zoogeography, and Systematics of Mayflies and Stoneflies; Hauer, F.R., Stanford, J.A., Newell, R.L., Eds.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 355–368. [Google Scholar]
- Jansson, A.; Vuoristo, T. Significance of stridulation in larval Hydropsychidae (Trichoptera). Behaviour 1979, 71, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, F.; Isobe, Y.; Oishi, T. Comparative study of the morphology and distribution of setae and hairs on the larval legs of two families (Perlodidae, Perlidae) of Japanese Plecoptera. Aquat. Insects 2009, 31, 547–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, W.S. Odorant reception in insects: Roles of receptors, binding proteins, and degrading enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinta, S.; Dickens, J.C.; Baker, G.T. Morphology and distribution of antennal sensilla of the tarnished plant bug, Lygus lineolaris (Palisot de beauvois) (Hemiptera: Miridae). Int. J. Insect Morphol. Embryol. 1997, 26, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.H. Exploration and functional analysis of olfactory related genes in the lucerne plant bug, Adelphocoris lineolatus (Goeze). Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Xiao, H.J.; Gu, S.H. Perception of potential sex pheromones and host-associated volatiles in the cotton plant bug, Adelphocoris fasciaticollis (Hemiptera: Miridae): Morphology and electrophysiology. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2014, 49, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Bai, S.X.; Yao, C.C.; Gao, C.Q.; Feng, H.Z. Ultrastructural Observation on the Adult of Lygus pratensis. China Cotton 2022, 49, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.Z.; Wu, W.J.; Liang, G.W. Observation of the antennal sensilla of Campylomma chinensis (Hemiptera: Miridae) by environmental scanning electron microscope. J. South China Agric. Univ. 2006, 4, 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Cai, B. Scanning Electron Microscopy Observation on Antennal Sensilla of Pilophorus typicus. Bull. Biol. 2013, 48, 54–55+63. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.H.; Liao, Y.L.; Yang, T.H.; Ji, X.C.; Yao, Q. Morphological Development and Biological Characteristics of Helopeltis theivora Waterhouse in Hainan Tea Region. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2025, 46, 978–986. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Z.H.; Li, S.; Yang, W.; Zhou, Y.F. Mosquitoes in Tea Plantations—Tea Mosquitoes Bug. Chin. Tea 2020, 42, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, D. Insect antennae. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1964, 9, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Shi, X.H.; He, Y.R.; Xiao, Q.; Weng, X.J. Observation of antennal sensilla of Ectropis grisescens adults with Transmission Electron Microscope. China Plant Prot. 2020, 40, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, M.Q.; Hu, Y.; Chen, H.; Yin, C.H. Morphological structure of the antennal sensilla of Nesidiocoris tenuis observed with a scanning electron microscopy. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2012, 49, 631–635. [Google Scholar]
- Eguchi, E.; Tominaga, Y. Atlas of Arthropod Sensory Receptors. Dynamic Morphology in Relation to Function; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, F.; Isobe, Y.; Oishi, T. A comparative SEM study on the setae of larval legs in three species of Perlidae (PLECOPTERA). In Contemporary Aquatic Entomological Study in East Asia (AESEA); Wang, X., Liu, W., Ji, B., Eds.; Nankai University Press: Tianjin, China, 2008; pp. 111–122. [Google Scholar]
- Ronderos, D.; Smith, D. Diverse signaling mechanisms mediate volatile odorant detection in Drosophila. Fly 2009, 3, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Shi, W.; Wang, Y.E.; Liu, Q.; He, Q.J.; Yi, C.H. Scanning electron microscopic observation of antennal sensilla of Vespa velutina variana vander Vecht. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 34, 455–460. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Wyckhuys, K.A.; Wu, K. Pest status, bio-ecology, and area-wide management of Mirids in East Asia. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2014, 69, 393–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachin, J.P.; Selvasundaram, R.; Babu, A.; Muraleedharan, N. Behavioral and electroantennographic responses of the tea mosquito, Helopeltis theivora, to female sex pheromones. Environ. Entomol. 2018, 37, 1416–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, R.F. Mechanoreception. Chemoreception. In The Insects: Structure and Function, 4th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998; pp. 610–652. [Google Scholar]
- Altner, H.; Prillinger, L. Ultrastructure of invertebrate chemo-, thermo- and hygroreceptors and its functional significance. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1980, 6, 69–139. [Google Scholar]


| Scape | Pedicel | Flagellum I | Flagellum II | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early instar nymph | SCh-I | SCh-I | SCh-I | SCh-I, ST-I, ST-II |
| Late instar nymph | SCh-III, SCo, BB | SCh-II, SCh-III, SCo, BB | SCh-I, SCh-II, SCo, BB | SCh-I, SB-I, ST-I, ST-II |
| Adult male | SCh-III, SCo, SM, BB | SCh-I, SCh-II, SCh-III, SCo, SM, BB | SCh-I, SCh-II, SCh-III, SB-II, SCo, BB | SCh-I, SB-I, SB-III, ST-I, ST-II |
| Adult female | SCh-III, SCo, BB | SCh-II, SCh-III, SCo, BB | SCh-I, SCh-II, SCh-III, SCo, BB | SCh-I, SB-I, SB-III, ST-I, ST-II |
| Sensilla Length (μm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early Instar Nymph | Late Instar Nymph | Adult Male | Adult Female | |
| SCh-I | 96.38 ± 2.52 a | 72.65 ± 2.59 c | 82.74 ± 2.38 b | 68.42 ± 2.01 c |
| SCh-II | 31.66 ± 1.51 b | 31.73 ± 1.49 b | 41.23 ± 1.54 a | 41.13 ± 1.08 a |
| SCh-III | 10.6 ± 1.06 b | 10.60 ± 0.45 b | 19.44 ± 0.41 a | 20.68 ± 0.39 a |
| SB-I | 39.51 ± 4.74 b | 37.89 ± 1.4 9 b | 64.92 ± 2.47 a | 49.30 ± 1.88 b |
| SB-II | — | — | 37.09 ± 0.64 | — |
| SB-III | 13.03 ± 0.73 c | 12.53 ± 0.39 c | 16.54 ± 0.30 a | 15.13 ± 0.21 b |
| ST-I | 33.06 ± 1.68 b | 36.14 ± 1.44 b | 52.89 ± 1.57 a | 52.13 ± 1.24 a |
| ST-II | 29.75 ± 0.83 c | 36.31 ± 1.00 b | 52.49 ± 1.26 a | 50.27 ± 1.00 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Liao, Y.; Lin, Z.; Ji, X.; Yao, Q. Morphological and Ultrastructural Characteristics of Tea Mosquito Bug Antennae, Helopeltis theivora Waterhouse (Hemiptera: Miridae) from Hainan, China. Insects 2025, 16, 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070654
Li W, Liao Y, Lin Z, Ji X, Yao Q. Morphological and Ultrastructural Characteristics of Tea Mosquito Bug Antennae, Helopeltis theivora Waterhouse (Hemiptera: Miridae) from Hainan, China. Insects. 2025; 16(7):654. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070654
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wenhui, Yonglin Liao, Zhufeng Lin, Xuncong Ji, and Qi Yao. 2025. "Morphological and Ultrastructural Characteristics of Tea Mosquito Bug Antennae, Helopeltis theivora Waterhouse (Hemiptera: Miridae) from Hainan, China" Insects 16, no. 7: 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070654
APA StyleLi, W., Liao, Y., Lin, Z., Ji, X., & Yao, Q. (2025). Morphological and Ultrastructural Characteristics of Tea Mosquito Bug Antennae, Helopeltis theivora Waterhouse (Hemiptera: Miridae) from Hainan, China. Insects, 16(7), 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070654






