Enhancing the Survival of Ichneumonid Parasitoid Campoletis chlorideae (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) by Utilizing Haserpin-e Protein to Effectively Manage Lepidopteran Pests
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects and Haserpin-e
2.2. Effect of Haserpin-e on C. chlorideae
2.3. Effect of Haserpin-e on Encapsulations of Host
2.4. The Effect of Haserpin-e on Hemolymph In Vitro
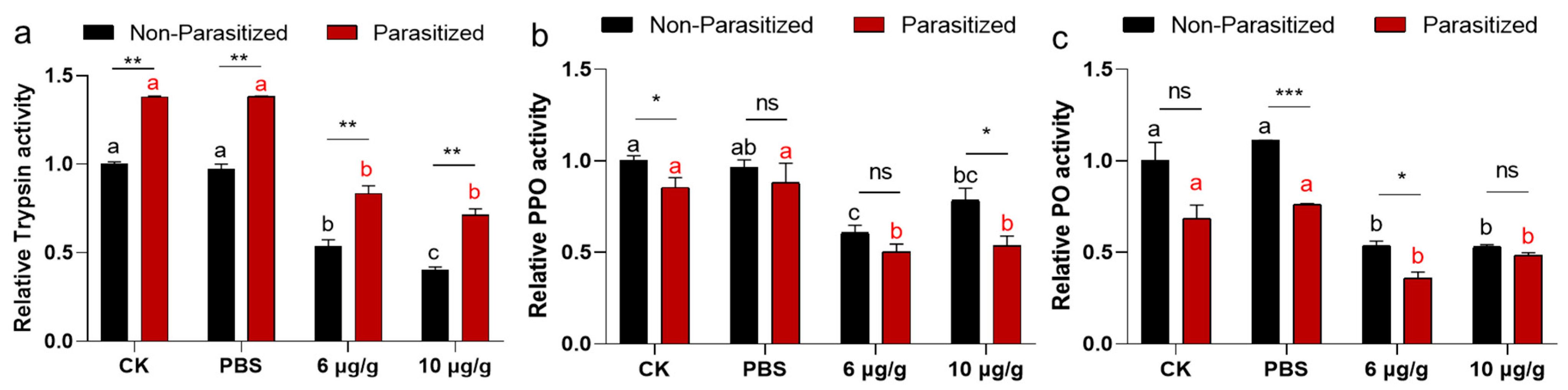
2.5. The Impacts of Haserpin-e on Enzyme Activities in Non-Parasitized and Parasitized H. armigera Larvae
2.6. Sample Preparation, cDNA Synthesis and Real-Time Quantitative PCR Analyses
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Impact of Haserpin-e on the Cocoon Production of C. chlorideae
3.2. The Impact of Haserpin-e on the Life History Traits of C. chlorideae
3.3. The Effects of Haserpin-e Protein on the Encapsulation of C. chlorideae in H. armigera
3.4. The Effects Haserpin-e Protein on Melanization of H. armigera Larvae Hemolymph In Vitro
3.5. The Effects Haserpin-e Protein on Melanization of H. armigera In Vivo
3.6. Haserpin-e Suppresses the Expression of AMPs Expression in H. armigera
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, S.G.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Wang, H.T.; Miao, L.; Qin, Q.L. Research progress in rearing of parasitoid wasp Campoletis chlorideae. Chin. J. Biol. Control. 2012, 28, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, M.K.; Sharma, H.C. Survival and development of Campoletis chlorideae on various insect and crop hosts: Implications for Bt-transgenic crops. J. Appl. Entomol. 2007, 131, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.S.; Lei, R.H.; Jiang, J.X.; BO, L.Y.; Xiao, Z.S. Bionomic of Campoletis chlorideae (Hym: Ichneumonidae) as a parasitoid of the cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera (Lep: Noctuidae). Insect Sci. 2002, 9, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhao, Q.; Keyhani, N.; Lei, X.F.; Liu, C.H.; Al Dhafer, H.M. Biocontrol performance and mass production potential of the larval endoparasitoid Campoletis chlorideae Uchida (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) against the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2024, 34, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Wang, C. Identification of Mythmna separata induced maize volatile synomones that attract the parasitoid Campoletis chlorideae. J. Appl. Entomol. 2006, 130, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolappan, B. Misuse of Pesticides to Blame for Disappearance of Pollinators. Available online: www.thehindu.com/news/national/tamil-nadu/misuse-of-pesticides-to-blame-for-disappearance-of-pollinators/article30814702.ece (accessed on 14 February 2020).
- Pandey, R.K.; Singh, G.R.; Tripathi, A. Effect of biopesticides (HaNPV) on larval population of Helicoverpa armigera on chickpea in eastern part of U.P under rainfed low-land ecosystem. National conference on role of bio-agents and bio-fertilizers for sustainable agriculture and horticulture. IISR-Lucknow 2004, 86, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.Q.; Shi, M.; Huang, J.H.; Chen, X.X. Parasitoid polydnaviruses and immune interaction with secondary hosts. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 83, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strad, M.R.; Clark, K.D. Plasmatocyte spreading peptide induces spreading of plasmatocytes but represses spreading of granulocytes. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1999, 42, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, M.R.; Pech, L.L. Immunological basis for compatibility in parasitoid-host relationships. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1995, 40, 31–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.Q.; Chen, Y.X.; Lu, W.X.; Wu, B.; Qi, P.Z. Transcriptome analysis of Mytilus coruscus hemocytes in response to Vibrio alginnolyficus infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 70, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalini, M.; Kim, Y. Transient expression of a polydnaviral gene, CpBV15beta, induces immune and developmental alterations of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2009, 100, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, M.W.; Martin, S.B.; Webb, B.A. Quantitative analysis of hemocyte morphological abnormalities associated with Campoletis sonorensis parasitization. J. Insect Sci. 2004, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, D.K.; Erickson, S.L.; Hersh, B.M.; Turnbull, M.W. Virus innexins induce alterations in insect cell and tissue function. J. Insect Physiol. 2017, 98, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, D.; Stoltz, D.B. Comparative serology of viruses isolated from Ichneumonid parasitoids. Virology 1983, 130, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelby, K.S.; Adeyeye, O.A.; Okot-Kotber, B.M.; Webb, B.A. Parasitism-linked block of host plasma melanization. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2000, 75, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, S.J.M.; Huguet, E.; Drezen, J.M. Polydnaviruses as Tools to Deliver Wasp Virulence Factors to Impair Lepidopteran Host Immunity. Insect Infection and Immunity: Evolution, Ecology, and Mechanisms; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 137–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappi, A.J.; Frey, F.; Carton, Y. Drosophila serpin 27A is a likely target for immune suppression of the blood cell-mediated melanotic encapsulation response. J. Insect Physiol. 2004, 51, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meekins, D.A.; Kanost, M.R.; Michel, K. Serpins in arthropod biology. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 62, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanost, M.R.; Gorman, M.J. Phenoloxidases in insect immunity. Insect Immunol. 2008, 1, 69–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shen, D.X.; Hong, F.; Wang, G.R.; An, C.J. Serine proteases SP1 and SP13 mediate the melanization response of asian corn borer, Ostrinia furnacalis, against entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 128, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Hong, F.; Liu, Q.Z.; An, C.J. Serine protease SP105 activates prophenoloxidase in Asian corn borer melanization and is regulated by serpin-3. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, H.; Kim, C.H.; Kwon, H.M.; Park, J.W.; Roh, K.B.; Lee, H.; Park, B.J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, J.H.; Söderhäll, K.; et al. Molecular control of phenoloxidase-induced melanin synthesis in an insect. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25316–25323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugumaran, M.; Barek, H. Critical analysis of the melanogenic pathway in insects and higher animals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Shin, S.W.; Alvarez, K.S.; Kokoza, V.; Raikhel, A.S. Distinct melanization pathways in the mosquito Aedes Aegypti. Immunity 2010, 32, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.F.; Xing, L.S.; Wang, M.L.; Wang, X.; Yin, M.Y.; Wang, Q.R. Inhibition of melanization by Serpin-5 and Serpin-9 promotes baculovirus infection in cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, M.; El Moussawi, L.; Saab, S.; Zhang, S.S.; Osta, M.A. CLIPB10 is a terminal protease in the regulatory network that controls melanization in the African malaria mosquito anopheles gambiae. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 585986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.R.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Qian, C.; Wei, G.Q.; Dai, L.S.; Li, J.; Zhu, B.J.; Liu, C.L. Serpin-15 from Bombyx mori inhibits prophenoloxidase activation and expression of antimicrobial peptides. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 51, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Ma, L.; Lin, Z.; Zou, Z.; Lu, Z.Q. Serpin-5 regulates prophenoloxidase activation and antimicrobial peptide pathways in the Silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 73, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Fu, H.; Zhang, L.; Guo, P.; Xia, Q. Silkworm serpin32 functions as a negative-regulator in prophenoloxidase activation. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 91, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yu, H.Z.; Ye, C.J.; Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, T.; Chen, F.S.; Xu, J.P. Bombyx Mori Serpin6 regulates prophenoloxidase activity and the expression of antimicrobial proteins. Gene 2017, 610, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Jiang, H.; Kanost, M.R. Identification of plasma proteases inhibited by Manduca sexta serpin-4 and serpin-5 and their association with components of the prophenoloxidase activation pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 14932–14942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.J.; Kanost, M.R. Manduca sexta serpin-5 regulates prophenoloxidase activation and the toll signaling pathway by inhibiting hemolymph proteinase HP6. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.J.; Ragan, E.J.; Kanost, M.R. Serpin-1 splicing isoform j inhibits the prospätzle-activating proteinase hp8 to regulate expression of antimicrobial hemolymph proteins in Manduca Sexta. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.W.; Xu, J.H.; Wang, L.L.; Guo, P.C.; Tang, Z.C.; Sun, X.T.; Tang, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.A.; Cao, Y.; et al. Serpin-1a and serpin-6 regulate the Toll pathway immune homeostasis by synergistically inhibiting the Spätzle-processing enzyme CLIP2 in silkworm, Bombyx mori. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 18, e1011740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Kim, E.H.; Gong, J.H.; Kwon, H.M.; Kim, C.H.; Ryu, K.H.; Park, J.W.; Kurokawa, K.; Zhang, J.H.; Gubb, D. Three pairs of protease serpin complexes cooperatively regulate the insect innate immune responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 35652–35658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.Y.; Shen, D.X.; Zhang, S.S.; Wang, L.; An, C.J. Serpin-4 facilitates baculovirus infection by inhibiting melanization in asian corn borer, Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée). Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 905357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.H.; Wei, J.Z.; Naing, Z.L.; Soe, E.T.; Liang, G.M. Endogenous serpin reduces toxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac against Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 175, 104837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.H.; Wei, J.Z.; Naing, Z.L.; Soe, E.T.; Tang, J.R.; Liang, G.M. Up-regulated serpin gene involved in Cry1Ac resistance in Helicoverpa armigera. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 188, 105269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.Y.; Yang, Y.; Xue, Y.Y.; Zhao, W.L.; Liu, X.G.; Du, M.F.; Yin, X.M.; Guan, R.B.; Wei, J.Z.; An, S.H. New insights on the effects of spinosad on the development of Helicoverpa armigera. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 221, 112452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.F.; Li, X.; Chen, X.X.; Cheng, J.A.; He, J.H. Interspecific competition between two endoparasitoids Cotesia vestalis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) and Oomyzus sokolowskii (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2011, 76, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.X.; Li, X.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Li, S.J.; Wang, K.; Tian, C.H.; Feng, H.Q.; Liu, X.G.; Yin, X.M.; Bai, S.F.; et al. Cyclosporin A acts as an insecticide candidate: Providing sustainable biocontrol potential for managing Mythimna separata. J. Pest Sci. 2023, 96, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.B.; Huang, L.Q.; Wang, C.Z. Host preference and suitability in the endoparasitoid Campoletis chlorideae is associated with its ability to suppress host immune responses. Ecol. Entomol. 2013, 38, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, X.Y.; Qin, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, S.P.; Li, M.W. The hemolymph melanization response is related to defence against the AcMNPV infection in Bombyx mori. Arch. Insect Biochem. 2020, 108, e21764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Z.; Li, T.; Yang, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, G.C.; Zhang, J. Transcriptomic analysis of interactions between Iymantria dispar larvae and carvacrol. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 181, 105012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Q.; Kong, F.; Ma, B.; Chen, D.S.; Ran, Z.S.; Ma, S.N.; Liao, K.; Cao, J.Y.; Zhang, L.; Yan, X.J.; et al. Effects of light on growth, feeding rate, digestion, and antioxidation in juvenile razor clams Sinonovacula constricta. Aquaculture 2023, 568, 739306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, P.; Deng, Z.Y.; Yin, X.M.; An, S.H.; Li, X.C. Functional assessment of cadherin as a shared mechanism for cross/dual resistance to Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab in Helicoverpa zea. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, 23, 1604–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.P.; Qi, H.P.; Liu, X.N.; Ren, X.W.; Li, J.S. Implementation of two-way nonparametric ANOVA in SPSS. Chin. J. Health Stat. 2013, 30, 913–914. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.H.; Gu, L.Q.; Wang, C.Z. Superparasitism behavior and host discrimination of Campoletis chlorideae (Ichneumonidae: Hymenoptera) toward Mythimna separata (Noctuidae: Lepidoptera). Environ. Entomol. 2010, 39, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, A.A.; Ross, P.A. Rates and patterns of laboratory adaptation in (mostly) insects. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.B.; Liu, C.X.; Xiao, Y.T.; Zhang, D.D.; Zhang, Y.D.; Li, X.C.; Tabashnik, B.E.; Wu, K.M. A toxin-binding alkaline phosphatase fragment synergizes Bt toxin Cry1Ac against susceptible and resistant Helicoverpa armigera. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.J.; Dong, S.; Hu, X.D.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, J.F.; Lu, L.N.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.M.; Liu, X.J. Roles of midgut cadherin from two moths in different Bacillus thuringiensis action mechanisms: Correlation among toxin binding, cellular toxicity, and synergism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13237–13246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Duan, Y.P.; Deng, Z.Y.; Zhao, W.L.; Wei, J.Z.; Li, X.C.; An, S.H. ATP synthase subunit α from Helicoverpa armigera acts as a receptor of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac and synergizes Cry1Ac toxicity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 6155–6163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.L.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.Y.; Gu, H.Y.; Li, F.C.; Li, B.; Wei, J. Parasitism by the tachinid parasitoid Exorista japonica leads to suppression of basal metabolism and activation of immune response in the host Bombyx mori. Insects 2022, 13, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Cao, X.L.; Zou, Z.; Lu, Z.Q.; Kanost, M.R.; Jiang, H.B. Hemolymph protease-5 links the melanization and Toll immune pathways in the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 23581–23587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qie, X.T.; Yan, X.Z.; Wang, W.T.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.J.; Hao, C.; Lu, Z.Q.; Ma, L. Serpin-4 Negatively Regulates Prophenoloxidase activation and antimicrobial peptide synthesis in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Treatments | F0 | F1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Life History Traits | CK | PBS | 6 μg/g | 10 μg/g | CK | PBS | 6 μg/g | 10 μg/g | |
| Rate of cocoon production (%) | 78.33 ± 3.33 cA | 80.83 ± 1.66 bcA | 84.99 ± 1.92 bA | 91.66 ± 6.38 aA | 75.00 ± 1.67 aB | 75.00 ± 5.00 aB | 71.11 ± 1.92 aB | 71.11 ± 1.92 aB | |
| Emergence rate (%) | 93.09 ± 3.94 aA | 96.23 ± 2.84 aA | 91.48 ± 7.87 aA | 93.60 ± 2.65 aA | 77.99 ± 12.49 aB | 79.15 ± 9.91 aB | 82.63 ± 5.00 aB | 79.93 ± 8.27 aB | |
| Sex ratio (%) | 47.72 ± 0.08 abA | 46.54 ± 4.59 abA | 51.78 ± 8.26 aA | 37.27 ± 4.78 bA | 26.71 ± 5.29 aB | 26.28 ± 2.28 aB | 21.05 ± 5.26 aB | 20.34 ± 3.03 aB | |
| Mating rate (%) | 55.40 ± 16.51 aB | 50.92 ± 19.28 aB | 58.09 ± 13.62 aB | 72.13 ± 6.11 aB | 76.38 ± 10.48 aA | 75.00 ± 5.00 aA | 76.944 ± 14.82 aA | 71.95 ± 5.57 aA | |
| Cocoon length (mm) | 7.54 ± 0.61 aA | 7.69 ± 0.00 a A | 6.97 ± 0.67 bA | 6.90 ± 0.61 bA | 6.77 ± 0.77 aB | 6.70 ± 0.43 aB | 6.79 ± 0.53 aB | 6.60 ± 0.70 aB | |
| Cocoon width (mm) | 2.56 ± 0.24 aA | 2.51 ± 0.28 aA | 2.50 ± 0.24 aA | 2.45 ± 0.22 aA | 2.40 ± 0.32 aB | 2.40 ± 0.23 aB | 2.42 ± 0.20 aB | 2.31 ± 0.25 AB | |
| Number of mature eggs * | 47.62 ± 17.10 aA | 53.88 ± 27.06 aA | 47.05 ± 17.314 aA | 45.88 ± 20.80 aA | 40.88 ± 18.55 aB | 38.38 ± 16.77 aB | 28.33 ± 15.77 aB | 35.33 ± 10.29 aB | |
| Tibial length of hind leg (mm) | 1.45 ± 0.05 aA | 1.44 ± 0.08 aA | 1.41 ± 0.07 abA | 1.39 ± 0.09 bA | 1.37 ± 0.11 aB | 1.33 ± 0.11 aB | 1.38 ± 0.7 aB | 1.35 ± 0.88 aB | |
| Male survival time (day) | 15.42 ± 5.67 aA | 15.50 ± 5.56 aA | 15.88 ± 8.44 aA | 14.52 ± 10.43 aA | 15.56 ± 9.53 abA | 13.71 ± 5.7 abA | 12.76 ± 5.7 bA | 16.43 ± 7.28 aA | |
| Female survival time (day) | 24.62 ± 7.41 aA | 25.18 ± 10.43 aA | 27.16 ± 12.99 aA | 27.88 ± 11.47 aA | 22.84 ± 9.31 aA | 27.80 ± 7.03 aA | 25.10 ± 3.78 aA | 25.26 ± 10.61 aA | |
| Ovarioles # | 36.06 ± 3.21 a | 36.00 ± 2.53 a | 36.06 ± 2.01 a | 35.33 ± 3.92 a | |||||
| Number of mature eggs ξ | 82.93 ± 13.48 a | 82.46 ± 11.74 a | 82.00 ± 18.93 a | 82.93 ± 15.64 a | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huo, L.; Yao, X.; Zhang, N.; Wang, S.; Bai, S.; Wang, Y.; Wei, J.; An, S. Enhancing the Survival of Ichneumonid Parasitoid Campoletis chlorideae (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) by Utilizing Haserpin-e Protein to Effectively Manage Lepidopteran Pests. Insects 2025, 16, 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050474
Huo L, Yao X, Zhang N, Wang S, Bai S, Wang Y, Wei J, An S. Enhancing the Survival of Ichneumonid Parasitoid Campoletis chlorideae (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) by Utilizing Haserpin-e Protein to Effectively Manage Lepidopteran Pests. Insects. 2025; 16(5):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050474
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuo, Liuming, Xue Yao, Ningbo Zhang, Shengyi Wang, Sufen Bai, Yanmei Wang, Jizhen Wei, and Shiheng An. 2025. "Enhancing the Survival of Ichneumonid Parasitoid Campoletis chlorideae (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) by Utilizing Haserpin-e Protein to Effectively Manage Lepidopteran Pests" Insects 16, no. 5: 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050474
APA StyleHuo, L., Yao, X., Zhang, N., Wang, S., Bai, S., Wang, Y., Wei, J., & An, S. (2025). Enhancing the Survival of Ichneumonid Parasitoid Campoletis chlorideae (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) by Utilizing Haserpin-e Protein to Effectively Manage Lepidopteran Pests. Insects, 16(5), 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050474




