Adding Fruit Fermentation Liquid Improves the Efficiency of the Black Soldier Fly in Converting Chicken Manure and Reshapes the Structure of Its Intestinal Microbial Community
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Design and Sample Collection
2.3. Analysis Methods
2.3.1. Measurement of BSFL Growth Performance and Nutritional Composition
2.3.2. Determination of Ammonia (NH3) and Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)
2.3.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing
2.3.4. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis of Data
3. Results
3.1. The Effect of the Addition of FFL on the Growth Performance of BSFL
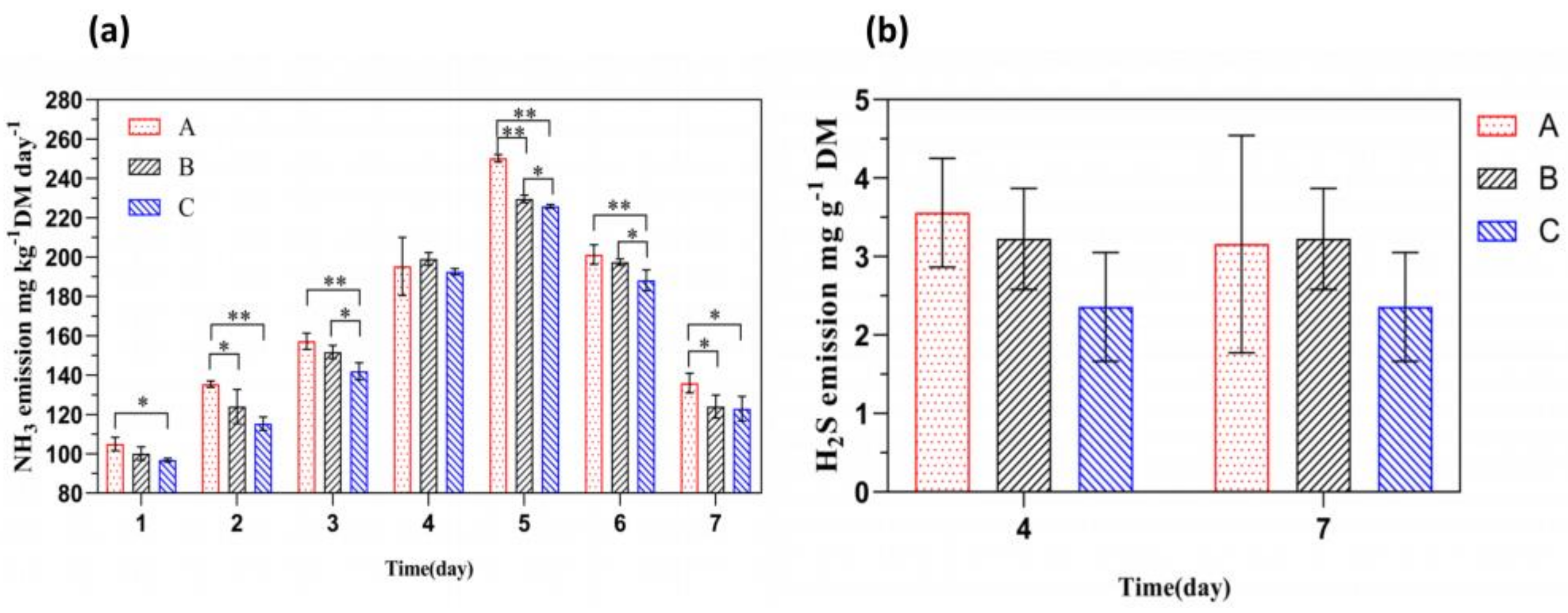
3.2. The Effect of Adding FFL on the Release of NH3 and H2S
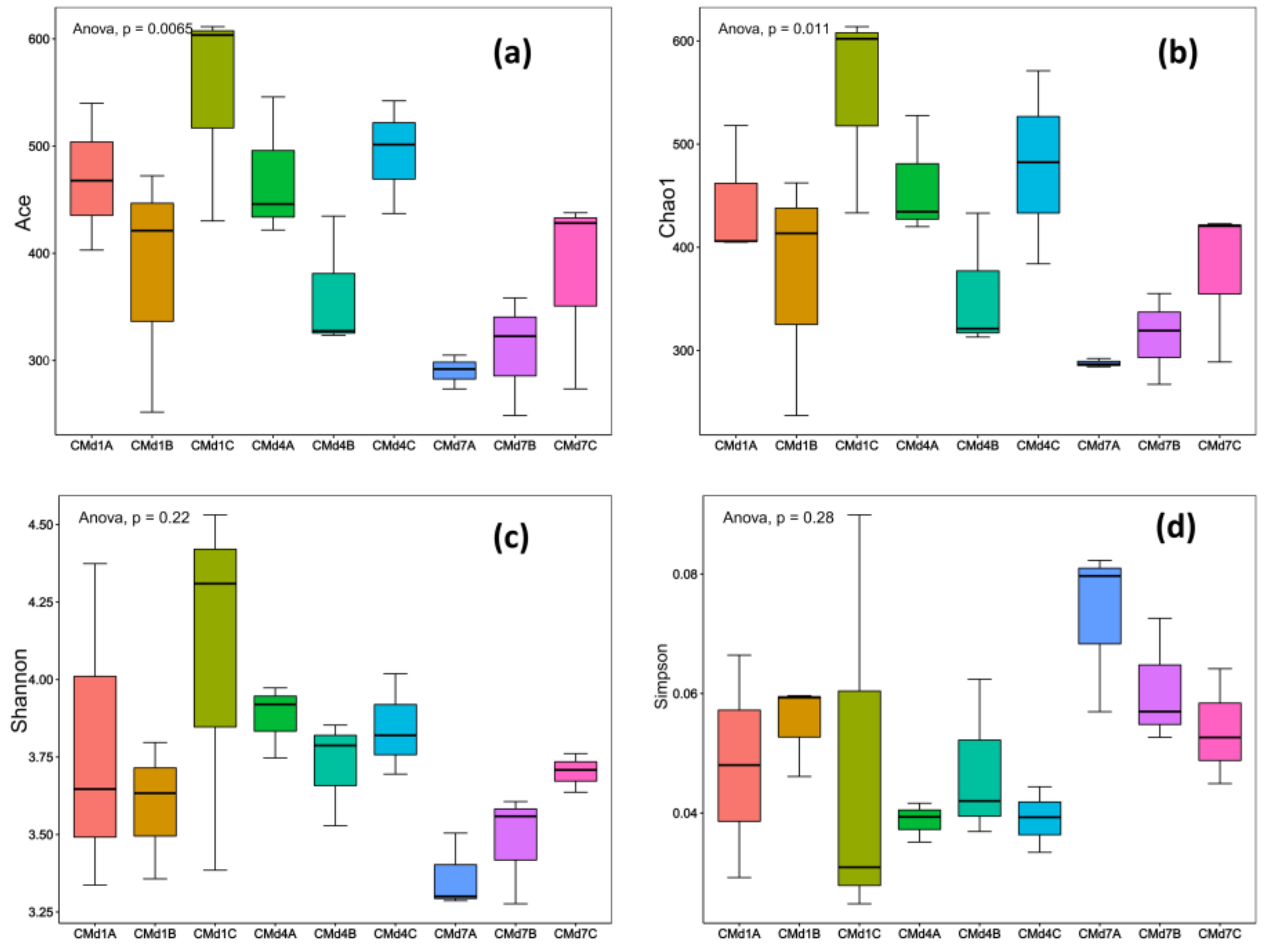
3.3. The Effect of Adding FFL on the Gut Microbiota of BSFL
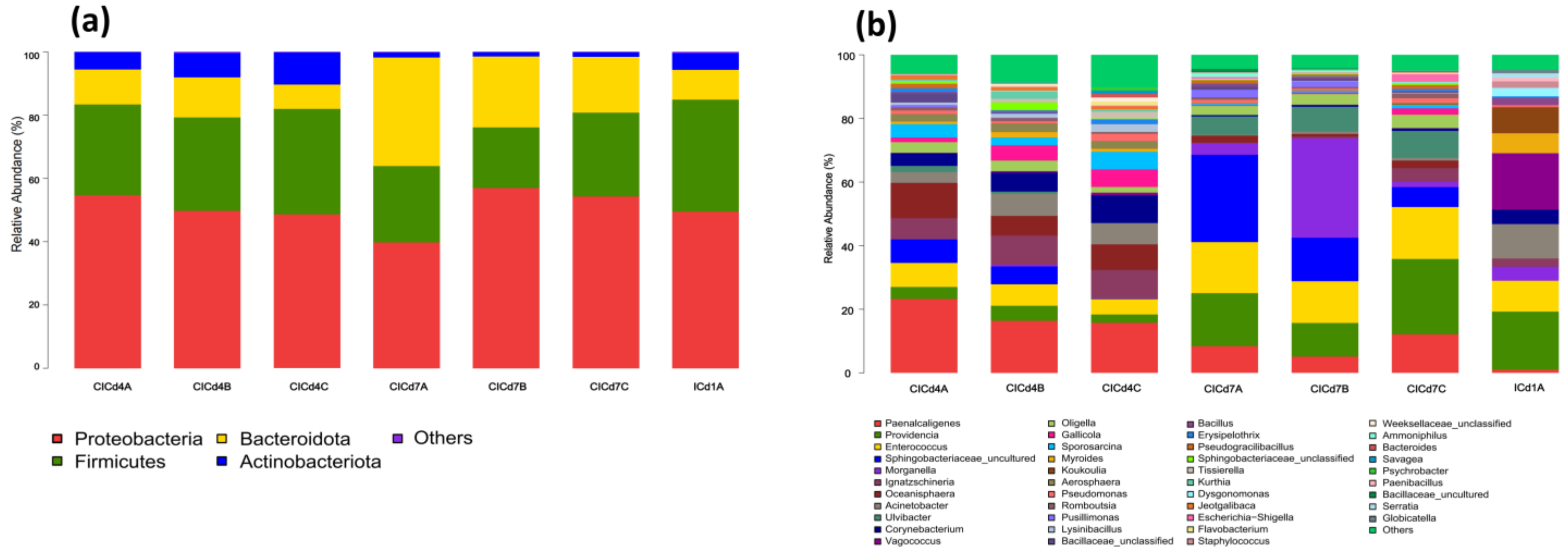
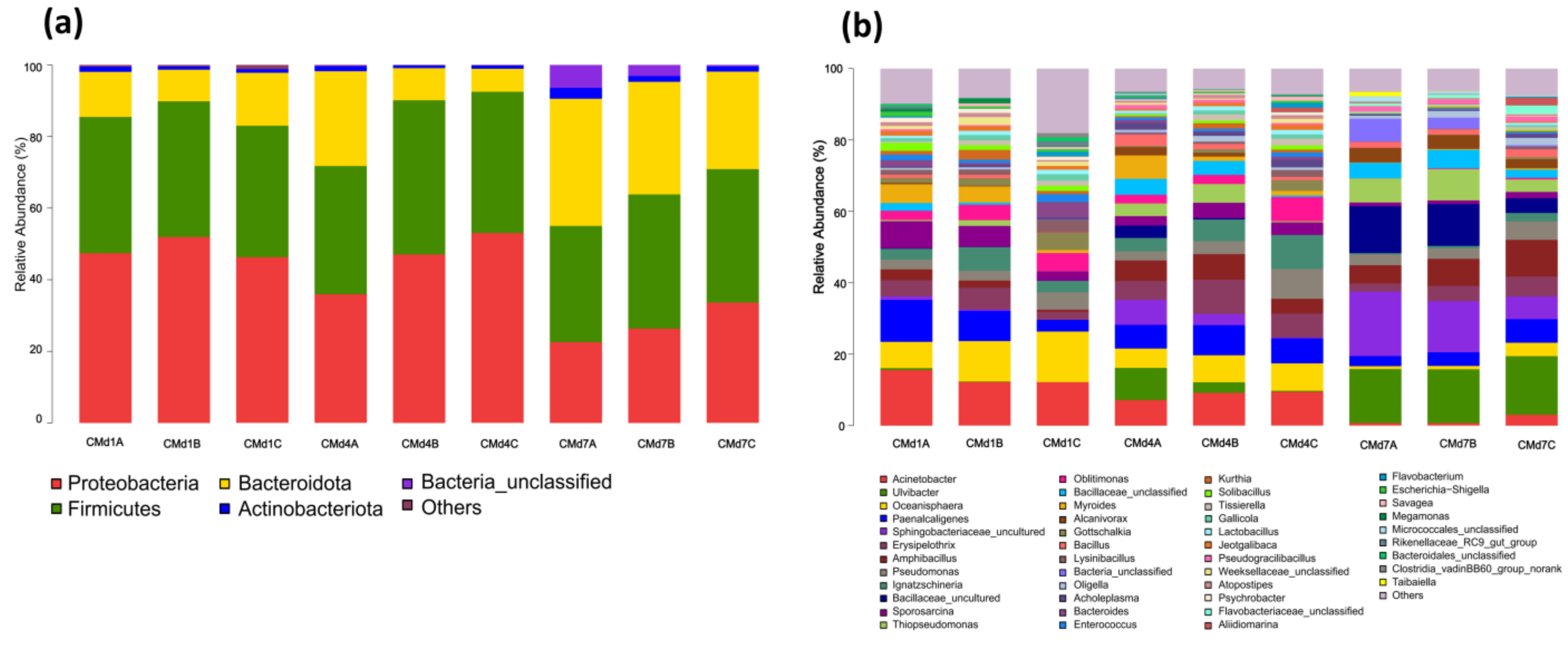
3.4. The Effect of Adding FFL on the Substrate Microbial Community
3.5. The Correlation Analysis of Environmental Parameters and the Abundance of Dominant Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Onwosi, C.O.; Igbokwe, V.C.; Odimba, J.N.; Eke, I.E.; Nwankwoala, M.O.; Iroh, I.N.; Ezeogu, L.I. Composting technology in waste stabilization: On the methods, challenges and future prospects. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 190, 140–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Geng, B.; Liu, X.; Ye, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, C.; Yuan, H. Characterization of bacterial consortium and its application in an ectopic fermentation system. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 139, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Hou, D.; Pang, W.; Nowar, E.E.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Hu, R.; Chen, H.; Xie, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.; et al. Effect of moisture content on greenhouse gas and NH3 emisions from pig manure converted by black soldier fly. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 133840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Lin, J.-G.; Zhang, N.; Cao, W. Biogas energy generated from livestock manure in China: Current situation and future trends. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Tang, J.; Sun, H.; Yao, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Ye, S. Straw waste promotes microbial functional diversity and lignocellulose degradation during the aerobic process of pig manure in an ectopic fermentation system via metagenomic analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Chen, L.; Xin, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Meng, X.; Zhang, W.; Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. Characteristics and Mechanism of Ammonia Nitrogen Removal by Heterotrophic Nitrification Bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae LCU1 and Its Application in Wastewater Treatment. Microorganisasms 2025, 13, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagos, K.; Zong, J.; Li, D.; Liu, C.; Lu, X. Anaerobic co-digestion process for biogas production: Progress, challenges and perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 1485–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, A.; Tian, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wennersten, R.; Sun, Q. Comparison between the Technologies for Food Waste Treatment. Energy Procedia 2017, 105, 3915–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Shi, H.; Liu, G.; Che, J.; Liu, B. Microbial community and function in nitrogen transformation of ectopic fermentation bed system for pig manure composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassauer, F.; Ferdous, J.; Pelletier, N. Manure Valorization Using Black Soldier Fly Larvae: A Review of Current Systems, Production Characteristics, Utilized Feed Substrates, and Bioconversion and Nitrogen Conversion Efficiencies. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Klammsteiner, T.; Dregulo, A.M.; Kumar, V.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Aisthi, M.K. Black soldier fly larvae for organic manure recycling and its potential for a circular bioeconomy: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raksasat, R.; Lim, J.W.; Kiatkittipong, W.; Kiatkittipong, K.; Ho, Y.C.; Lam, M.K.; Font-Palma, C.; Mohd Zaid, H.F.; Cheng, C.K. A review of organic waste enrichment for inducing palatability of black soldier fly larvae: Wastes to valuable resources. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyers, M.; Coudron, C.; Ravi, R.; Meers, E.; Bruun, S. Black soldier fly larvae as an alternative feed source and agro-waste disposal route—A life cycle perspective. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 192, 106917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froonickx, L.; Berrens, S.; Broeckx, L.; Van Miert, S. The potential of black soldier fly to recycle nitrogen from biowaste. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2023, 44, 100864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, X.; Weng, Y.; Nan, X.; Han, X.; Li, C.; Liu, B. Ingestion and biodegradation of disposable surgical masks by yellow mealworms Tenebrio molitor larvae: Differences in mask layers and effects on the larval gut microbiome. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magara, H.J.O.; Niassy, S.; Ayieko, M.A.; Mukundamago, M.; Egonyu, J.P.; Tanga, C.M.; Kimathi, E.K.; Ongere, J.O.; Fiaboe, K.K.M.; Hugel, S.; et al. Edible Crickets (Orthoptera) Around the World: Distribution, Nutritional Value, and Other Benefits—A Review. Front. Nutr. 2021, 7, 537915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, K.u.; Hollah, C.; Wiesotzki, K.; Rehman, R.u.; Rehman, A.U.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, L.; Nienaber, T.; Heinz, V.; Aganovic, K. Black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens as a potential innovative and environmentally friendly tool for organic waste management: A mini-review. Waste Manag. Res. J. A Sustain. Circ. Econ. 2022, 41, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, M.; Shang, R.; Xin, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, H.; Li, L. Evaluating Different Supplements on the Growth Performance and Bioconversion Efficiency of Kitchen Waste by Black Soldier Fly Larvae. Insects 2024, 16, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Xu, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, G.; Lu, W.; Liu, Z.; Shang, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, H.; et al. Effects of Different Defatting Methods of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Meal on the Metabolic Energy and Nutrient Digestibility in Young Laying Hens. Animals 2024, 14, 2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Xin, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, Y.; Song, H.; Fu, J.; Shang, R.; et al. Impact of Incorporating Defatted Black Soldier Fly Meal into Diet on Growth Performance, Serum Biochemical Parameters, Nutrient Digestibility, Morphology of the Intestinal Tract, and Immune Index of Brooding Laying Hens. Animals 2025, 15, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidini Lopes, I.; Wiklicky, V.; Ermolaev, E.; Lalander, C. Dynamics of black soldier fly larvae composting—Impact of substrate properties and rearing conditions on process efficiency. Waste Manag. 2023, 172, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohm, K.; Taylor, W.; Gyawali, P.; Pattis, I.; Gutiérrez Ginés, M.J. Black soldier fly-based bioconversion of biosolids: Microbial community dynamics and fate of antibiotic resistance genes. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 930, 172823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, M.; Cassar, C.M.; Zurbrügg, C.; Kreuzer, M.; Boulos, S.; Diener, S.; Mathys, A. Biowaste treatment with black soldier fly larvae: Increasing performance through the formulation of biowastes based on protein and carbohydrates. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Quan, J.; Cheng, X.; Li, C.; Yuan, Z. Relationship of black soldier fly larvae (BSFL) gut microbiota and bioconversion efficiency with properties of substrates. Waste Manag. 2024, 180, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlambo, V.; Dibakoane, S.R.; Mashiloane, T.; Mukwevho, L.; Wokadala, O.C.; Mnisi, C.M. Rethinking food waste: Exploring a black soldier fly larvae-based upcycling strategy for sustainable poultry production. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 199, 107284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, H.R.; Tomberlin, J.K. Microbial influence on reproduction, conversion, and growth of mass produced insects. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2021, 48, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somroo, A.A.; ur Rehman, K.; Zheng, L.; Cai, M.; Xiao, X.; Hu, S.; Mathys, A.; Gold, M.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Influence of Lactobacillus buchneri on soybean curd residue co-conversion by black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) for food and feedstock production. Waste Manag. 2019, 86, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Mazza, L.; Yu, Y.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Yu, J.; van Huis, A.; Yu, Z.; Fasulo, S.; et al. Efficient co-conversion process of chicken manure into protein feed and organic fertilizer by Hermetia illucens L. (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae and functional bacteria. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 217, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Li, C.; Yuan, Z. Revealing the effects of fermented food waste on the growth and intestinal microorganisms of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae. Waste Manag. 2023, 171, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yandi, I.; Öztürk, R.Ç.; Kocabas, M.; Kurtoglu, I.Z.; Altinok, I. Nutritional composition of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) reared on chicken waste meal, fruit & vegetable waste, and their mixture. J. Insects Food Feed 2023, 9, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Peña, E.I.; Parameswaran, P.; Kang, D.W.; Canul-Chan, M.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R. Anaerobic digestion and co-digestion processes of vegetable and fruit residues: Process and microbial ecology. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9447–9455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 6435-2014; Determination of Moisture in Feedstuffs. State Administration for Market Regulation, China National Standardization Administration Committee: Beijing, China, 2014.
- GB/T 6432-2018; Determination of Crude Protein in Feeds-Kjeldahl Method. State Administration for Market Regulation, China National Standardization Administration Committee: Beijing, China, 2018.
- GB/T 6433-2006; Determination of Crude Fat in Feeds. State Administration for Market Regulation, China National Standardization Administration Committee: Beijing, China, 2006.
- GB/T 6434-2006; Feeding Stuffs-Determination of Crud Fiber Content-Method with Intermediate Filtration. State Administration for Market Regulation, China National Standardization Administration Committee: Beijing, China, 2006.
- GB/T 6436-2018; Determination of Calcium in Feeds. State Administration for Market Regulation, China National Standardization Administration Committee: Beijing, China, 2018.
- GB/T 6437-2018; Determination of Phosphorus in Feeds-Spectrophotometry. State Administration for Market Regulation, China National Standardization Administration Committee: Beijing, China, 2018.
- GB/T 14679-1993; Air Quality—Determination of Ammonia—Sodium Salicylate-Sodium Hypochlorite Spectrophotometric Method. State Administration for Market Regulation, China National Standardization Administration Committee: Beijing, China, 1993.
- GB/T 14678-1993; Air Quality—Determination of Sulfuretted Hydrogen, Methyl Sulfhydryl, Dimethyl Sulfide and Dimethyl Disulfide—Gas Chromatography. State Administration for Market Regulation, China National Standardization Administration Committee: Beijing, China, 1993.
- Tessier, L.; Côté, O.; Bienzle, D. Sequence variant analysis of RNA sequences in severe equine asthma. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An Open Source Software for Exploring and Manipulating Networks. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–20 May 2009; Association for the Advancement of ArtificialIntelligence: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; Volume 3, pp. 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beskin, K.V.; Holcomb, C.D.; Cammack, J.A.; Crippen, T.L.; Knap, A.H.; Sweet, S.T.; Tomberlin, J.K. Larval digestion of different manure types by the black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) impacts associated volatile emissions. Waste Manag. 2018, 74, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Xia, M.; Yuan, W.; Ming, Y.; Zhang, Q. Bioconversion of sulfamethazine-contaminated chicken manure by black soldier fly larvae: Effects on antibiotic resistance genes and microbial communities. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.; Shahzadi, A.; Zheng, H.; Alam, F.; Nabi, G.; Dezhi, S.; Ullah, W.; Ammara, S.; Ali, N.; Bilal, M. Effect of different environmental conditions on the growth and development of Black Soldier Fly Larvae and its utilization in solid waste management and pollution mitigation. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Kong, C.-X.; Mei, Z.-L.; Li, J. A Review of the Anaerobic Digestion of Fruit and Vegetable Waste. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 183, 906–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, P.; Hammaz, F.; Morand-Laffargue, L.; Creton, B.; Halimi, C.; Sabatier, D.; Desmarchelier, C. Using black soldier fly larvae reared on fruits and vegetables waste as a sustainable dietary source of provitamin a carotenoids. Food Chem. 2021, 359, 129911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcel, K.K.; Abo, N.g.E.P.; Djakalia, B.; Guichard, B.L. Chemical Characterization of Some Fruits and Vegetables Used as Substrates for the Production of Black Soldier Fly Larvae. South Asian Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2022, 4, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jucker, C.; Erba, D.; Leonardi, M.G.; Lupi, D.; Savoldelli, S. Assessment of Vegetable and Fruit Substrates as Potential Rearing Media for Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae. Environ. Entomol. 2017, 46, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.L.; Jin, W.Z.; Tao, X.H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Feng, S.Y.; Xu, X.H.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, Z.J. Black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) strengthen the metabolic function of food waste biodegradation by gut microbiome. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 528–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klammsteiner, T.; Walter, A.; Bogataj, T.; Heussler, C.D.; Stres, B.; Steiner, F.M.; Schlick-Steiner, B.C.; Arthofer, W.; Insam, H. The Core Gut Microbiome of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Raised on Low-Bioburden Diets. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, P.; Moran, N.A. The gut microbiota of insects—Diversity in structure and function. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 699–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Zhao, S.; Hou, D.; Qin, W.; Zhu, X.; Luo, L.; Chen, D.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Electric field mitigates NH3 and N2O emissions during bioconversion of dairy manure by black soldier fly. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, A.; De Boer, I.J.M.; Gerrits, W.J.J.; Van Loon, J.J.A.; Heetkamp, M.J.W.; Van Schelt, J.; Bolhuis, J.E.; Van Zanten, H.H.E. Bioconversion efficiencies, greenhouse gas and ammonia emissions during black soldier fly rearing—A mass balance approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 271, 122488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, W.; Hou, D.; Chen, J.; Nowar, E.E.; Li, Z.; Hu, R.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Yu, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, S. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing carbon and nitrogen conversion in food wastes by the black soldier fly. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, N.; Sarmadi, K.; Goudarzi, G.; Babaei, A.A.; Bakhshoodeh, R.; Paydary, P. Attenuation of tetracyclines during chicken manure and bagasse co-composting: Degradation, kinetics, and artificial neural network modeling. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, A.; Gerrits, W.J.J.; Van Loon, J.J.A.; De Boer, I.J.M.; Aarnink, A.J.A.; Van Zanten, H.H.E. Black soldier fly rewered on pig manure: Bioconversion efficiencies, nutrients in the residual material, greenhouse gas and ammonia emissions. Waste Manag. 2021, 126, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Aisthi, M.K.; Chen, H.; Duan, Y.; Aisthi, S.K.; Zhang, Z. Performance of black soldier fly larvae (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) for manure composting and production of cleaner compost. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svane, S.; Sigurdarson, J.J.; Finkenwirth, F.; Eitinger, T.; Karring, H. Inhibition of urease activity by different compounds provides insight into the modulation and association of bacterial nickel import and ureolysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, H.; Zhang, T.; Li, R.; Zhai, B.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z. Apple pomace improves the quality of pig manure aerobic compost by reducing emissions of NH3 and N2O. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Yeung, M.; Xi, J. H2S Emission and Microbial Community of Chicken Manure and Vegetable Waste in Anaerobic Digestion: A Comparative Study. Fermentation 2023, 9, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Derlon, N.; Hu, S.; Yuan, Z. Modeling the pH effect on sulfidogeneswas in anaerobic sewer biofilm. Water Res. 2014, 49, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, F.; Fan, M.; Zheng, J.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Huang, F.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Enhanced protein degradation by black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens L.) and its gut microbes. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1095025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, D.; Bonelli, M.; De Filippis, F.; Di Lelio, I.; Tettamanti, G.; Casartelli, M.; Ercolini, D.; Caccia, S. The Intestinal Microbiota of Hermetia illucens Larvae was Affected by Diet and Shows a Diverse Composition in the Different Midgut Regions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01864-01818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhmood, A.; Wang, X.; Dong, R.; Wu, S. New insights into interactions of organic substances in poultry slurry with struvite formation: An overestimated concern? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, H.; Romano, N. Fruit, vegetable, and starch mixtures on the nutritional quality of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae and resulting frass. J. Insects Food Feed 2021, 7, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alciatore, G.; Peguero, D.A.; Gold, M.; Zurbrügg, C.; Niu, M.; Bargetze, F.; Mathys, A. Preservation of agri-food byproducts by acidification and fermentation in black soldier fly larvae bioconversion. Waste Manag. 2024, 186, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, L.; Shang, R.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J. Improvement in bioconversion efficiency and reduction of ammonia emission by introduction of fruit fermentation broth in a black soldier fly larvae and kitchen waste conversion system. Insect Sci. 2023, 30, 975–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, A.M.; Chandler, G.; Dunham, K.J.; Carlton, A.G. Data Gap: Air Quality Networks Miss Air Pollution from Concentrated Animal Feeding Operations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 20718–20725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Wang, G.; Song, H.; Yang, Q.; Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Sun, Y.; et al. Adding Fruit Fermentation Liquid Improves the Efficiency of the Black Soldier Fly in Converting Chicken Manure and Reshapes the Structure of Its Intestinal Microbial Community. Insects 2025, 16, 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050472
Chen L, Wang G, Song H, Yang Q, Fu J, Liu J, Sun H, Wang Y, Tian Q, Sun Y, et al. Adding Fruit Fermentation Liquid Improves the Efficiency of the Black Soldier Fly in Converting Chicken Manure and Reshapes the Structure of Its Intestinal Microbial Community. Insects. 2025; 16(5):472. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050472
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lifei, Guiying Wang, Hanhan Song, Qi Yang, Jiani Fu, Jiale Liu, Haoyang Sun, Yuxi Wang, Qile Tian, Yuting Sun, and et al. 2025. "Adding Fruit Fermentation Liquid Improves the Efficiency of the Black Soldier Fly in Converting Chicken Manure and Reshapes the Structure of Its Intestinal Microbial Community" Insects 16, no. 5: 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050472
APA StyleChen, L., Wang, G., Song, H., Yang, Q., Fu, J., Liu, J., Sun, H., Wang, Y., Tian, Q., Sun, Y., Sun, L., Xin, H., Xiao, Z., Wang, G., Zhang, Z., Zhao, Y., Yang, H., & Li, L. (2025). Adding Fruit Fermentation Liquid Improves the Efficiency of the Black Soldier Fly in Converting Chicken Manure and Reshapes the Structure of Its Intestinal Microbial Community. Insects, 16(5), 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050472





