Impact of Sulfoxaflor on Brown Marmorated Stink Bug: Developmental and Reproductive Effects
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Insects
2.2. Insecticide Formulation
2.3. Toxicity Test
2.4. Sublethal Effects of Sulfoxaflor on H. halys
2.5. Enzyme Assays
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Toxicity of Sulfoxaflor Against H. halys
3.2. Sublethal Effects of Sulfoxaflor on Nymph Development of H. halys
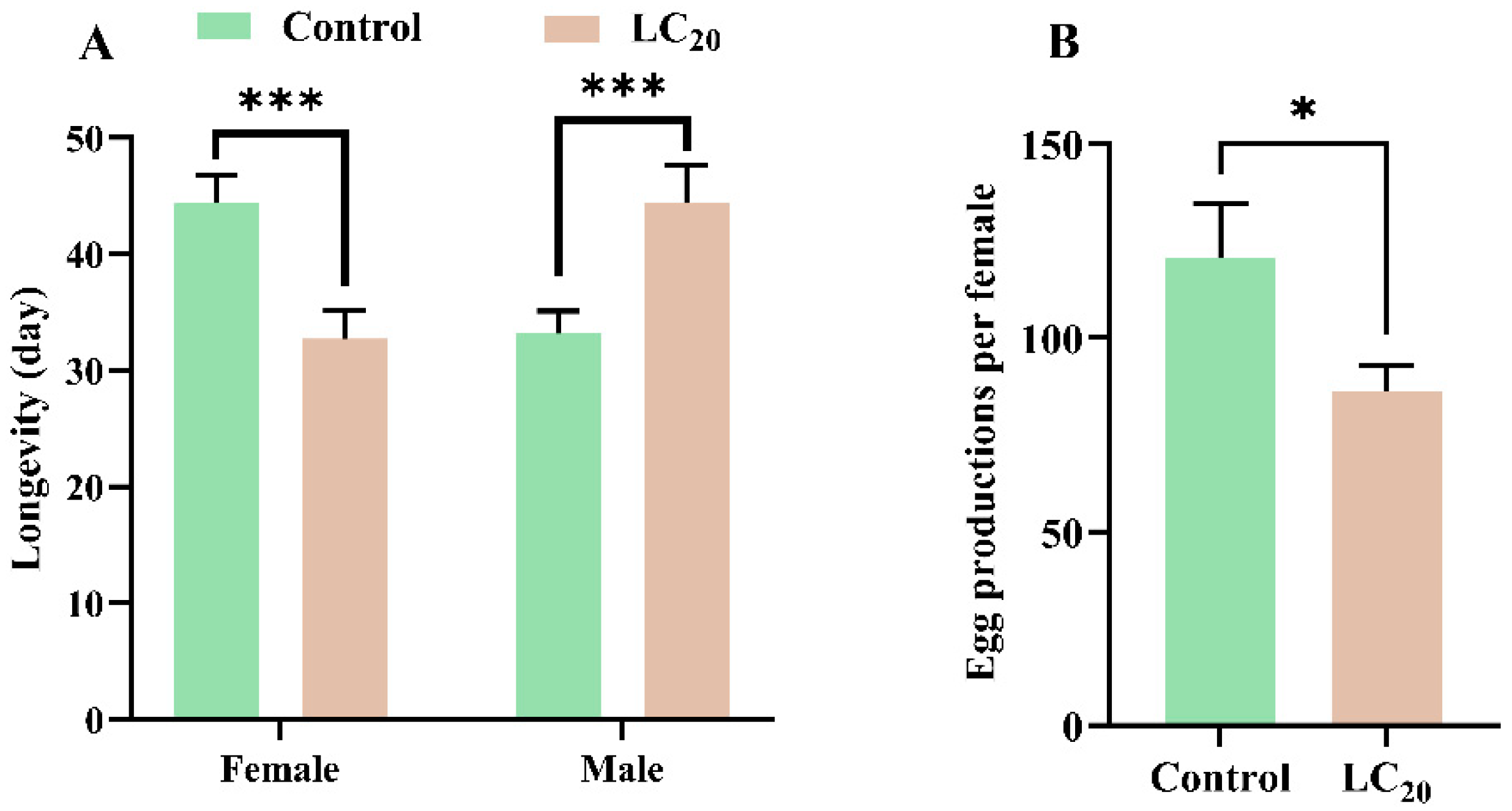
3.3. Effects of Sulfoxaflor on Longevity and Reproduction of Adults
3.4. Effects of Sulfoxaflor on Life Table Parameter of H. halys
3.5. Effects of Sulfoxaflor on Enzymatic Activity of H. halys
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pajač Beus, M.; Lemić, D.; Skendžić, S.; Čirjak, D.; Pajač Živković, I. The brown marmorated stink bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae)—A major challenge for global plant production. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznik, S.Y.; Dolgovskaya, M.Y.; Karpun, N.N.; Zakharchenko, V.Y.; Saulich, A.K.; Musolin, D.L. The invasive Caucasian populations of the brown marmorated stink bug Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) rapidly adapt their ecophysiological traits to the local environmental conditions. Insects 2023, 14, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leskey, T.C.; Nielsen, A.L. Impact of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug in North America and Europe: History, biology, ecology, and management. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 63, 599–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H. Current status of research progress on the biology and management of Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) as an invasive species. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2015, 50, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, K.B.; Bergh, C.J.; Bergmann, E.J.; Biddinger, D.J.; Dieckhoff, C.; Dively, G.; Fraser, H.; Gariepy, T.; Hamilton, G.; Haye, T.; et al. Biology, ecology, and management of brown marmorated stink bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2014, 5, A1–A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Li, W.J.; Li, J.J.; Yao, C.C.; Ma, G.; Shi, S.S.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.P. Identifying damage inflicted by Halyomorpha halys on kiwifruit crops. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2022, 59, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cira, T.M.; Burkness, E.C.; Koch, R.L.; Hutchison, W.D. Halyomorpha halys mortality and sublethal feeding effects following insecticide exposure. J. Pest Sci. 2017, 90, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alford, A.; Kuhar, T.P.; Hamilton, G.C.; Jentsch, P.; Krawczyk, G.; Walgenbach, J.F.; Welty, C. Baseline Toxicity of the insecticides bifenthrin and thiamethoxam on Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) Collected From the Eastern United States. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskey, T.C.; Lee, D.H.; Short, B.D.; Wright, S.E. Impact of Insecticides on the invasive Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae): Analysis of insecticide lethality. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 1726–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doo-Hyung, L.; Brent, D.S.; Anne, L.N.; Tracy, C.L. Impact of organic insecticides on the survivorship and mobility of Halyomorpha halys (Stål) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in the laboratory. Fla. Entomol. 2014, 97, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, I.W.R.; Poling, B.; Leskey, T.C. The consequences of sublethal exposure to insecticide on the survivorship and mobility of Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, Z.Y.; Xi, Y.Q.; Su, L.J.; An, S.H.; Yin, X.M. Sublethal and lethal concentrations of deltamethrin suppresses the population growth of Bactrocera dorsalis. Entomol. Gen. 2025, 45, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Güncan, A.; Abbas, A.; Gul, H.; Guedes, R.N.C.; Zhang, Z.J.; Huang, J.; Khan, K.A.; Ghramh, H.A.; Chavarín-Gómez, L.E.; et al. Sublethal effects of neonicotinoids on insect pests. Entomol. Gen. 2024, 44, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Loso, M.R.; Watson, G.B.; Sparks, T.C.; Rogers, R.B.; Huang, J.X.; Gerwick, B.C.; Babcock, J.M.; Kelley, D.; Hegde, V.B.; et al. Discovery and characterization of sulfoxaflor, a novel insecticide targeting sap-feeding pests. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2950–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babcock, J.M.; Gerwick, C.B.; Huang, J.X.; Loso, M.R.; Nakamura, G.; Nolting, S.P.; Rogers, R.B.; Sparks, T.C.; Thomas, J.; Watson, G.B.; et al. Biological characterizatio-n of sulfoxaflor, a novel insecticide. Pest Manage. Sci. 2011, 67, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, G.B.; Loso, M.R.; Babcock, J.M.; Hasler, J.M.; Letherer, T.J.; Young, C.D.; Zhu, Y.; Casida, J.E.; Sparks, T.C. Novel nicotinic action of the sulfoximine insecticide sulfoxaflor. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, T.; Kong, X.; Jiang, C.; Li, Z.; Zou, Z.; Xia, B. Reproductive and detoxifying responses of Panonychus citri (Acari: Tetranychidae) to sulfoxaflor stress. Crop Prot. 2025, 190, 107100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Koo, H.N.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, G.H. Analysis of the feeding behavior and life table of Nilaparvata lugens and Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) under sublethal concentrations of imidacloprid and sulfoxaflor. Insects 2022, 13, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangfu, N.B.; Guo, L.X.; Shang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, K.X.; Li, D.Y.; Gao, X.K.; Zhu, X.Z.; Ji, J.C.; Luo, J.Y.; et al. Hormetic dose response induced by sublethal-dose sulfoxaflor leads to reproductive stimulation of Aphis gossypii. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 204, 106061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.N. Indoor toxicity test of different insecticides against Halyomorpha halys. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2020, 18, 95–96. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.W.; Han, Z.J. Fitness costs of laboratory-selected imidacloprid resistance in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stål. Pest Manag. Sci. 2006, 62, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhar, T.P.; Kamminga, K. Review of the chemical control research on Halyomorpha halys in the USA. J. Pest Sci. 2017, 90, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.L.; Shearer, P.W.; Hamilton, G.C. Toxicity of insecticides to Halymnorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) using glass-vial bioassays. J. Econ. Entomol. 2008, 101, 1439–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IRAC. Mode of Action Classification of Insectcides (Version 10.4). Insecticide Resistance Action Committee (IRAC). 2025. Available online: https://irac-online.org (accessed on 16 January 2025).
- Zhen, C.A.; Miao, L.; Gao, X.W. Sublethal effects of sulfoxaflor on biological characteristics and vitellogenin gene (AlVg) expression in the mirid bug, Apolygus lucorum (Meyer-Dür). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 144, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.W.; Zhang, Z.y.; Xia, S.; Zhang, H. Biofunctional analysis of vitellogenin and vitellogenin receptor in citrus red mites, Panonychus citri by RNA interference. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhai, Y.H.; Zhu, J.S.; Wang, Q.Q.; Ji, X.J.; Wang, W.J.; Yuan, H.Z.; Rui, C.H.; Cui, L. Sulfoxaflor adversely influences the biological characteristics of Coccinella septempunctata by suppressing vitellogenin expression and predation activity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 447, 130787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Song, Y.Y.; Zeng, R.S. The role of cytochrome P450-mediated detoxification in insect adaptation to xenobiotics. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2021, 43, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koirala, B.K.S.; Moural, T.; Zhu, F. Functional and structural diversity of insect glutathione S-transferases in xenobiotic adaptation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 5713–5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.H.; Li, M.; Li, T.; Liu, N.N. Molecular and functional characterization of three novel carboxylesterases in the detoxification of permethrin in the mosquito, Culex quinquefasciatus. Insect Sci. 2022, 29, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.G.; Ruan, Y.W.; Gong, C.W.; Xiang, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.M.; Shen, L.T. Transcriptome analysis of Sogatella furcifera (Homoptera: Delphacidae) in response to sulfoxaflor and functional verification of resistance-related P450 genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.; Jin, R.H.; Zhang, X.L.; Ali, E.; Mao, K.K.; Xu, P.F.; Li, J.H.; Wan, H. Characterization of sulfoxaflor resistance in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 1646–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.S.; Tang, Q.L.; Zhang, B.Z.; Liang, P.; Wang, B.M.; Gao, X.W. Overexpression of multiple cytochrome P450 genes asso-ciated with sulfoxaflor resistance in Aphis gossypii Glover. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 157, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pym, A.; Umina, P.A.; Reidy-Crofts, J.; Troczka, B.J.; Matthews, A.; Gardner, J.; Hunt, B.J.; van Rooyen, A.R.; Edwards, O.R.; Bass, C. Overexpression of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase and cytochrome P450 enzymes confers resistance to sulfoxaflor in field populations of the aphid, Myzus persicae. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 143, 103743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Number | Slope ± SE a | χ2 (df) b | LC20 (95% CI c) (mg/L) | LC50 (95% CI c) (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 270 | 1.95 ± 0.33 | 4.32 (3) | 7.75 (0.95–14.520) | 20.97 (9.75–45.16) |
| Life Stage | Sulfoxaflor | Control | p-Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Developmental Duration (Day) | Longest Period (Day) | Shortest Period (Day) | Number | Developmental Duration (Day) | Longest Period (Day) | Shortest Period (Day) | ||
| 2nd instar | 125 | 10.82 ± 0.11 | 13 | 9 | 125 | 8.68 ± 0.12 | 12 | 6 | <0.0001 |
| 3rd instar | 125 | 7.26 ± 0.11 | 12 | 6 | 124 | 6.85 ± 0.11 | 11 | 4 | 0.011 |
| 4th instar | 124 | 6.86 ± 0.22 | 13 | 4 | 124 | 7.19 ± 0.14 | 14 | 4 | 0.216 |
| 5th instar | 120 | 10.24 ± 0.24 | 13 | 7 | 114 | 10.45 ± 0.17 | 14 | 6 | 0.495 |
| Total nymph stage (except 1st instar) | 120 | 34.91 ± 0.36 | 54 | 29 | 114 | 32.97 ± 0.30 | 27 | 47 | <0.0001 |
| Developmental Period | LC20 | CK |
|---|---|---|
| Preoviposition period (days) | 14.98 ± 0.67 b | 19.51 ± 0.78 a |
| Oviposition period (days) | 19.53 ± 2.83 b | 29.00 ± 2.40 a |
| Parameter | LC20 | Control |
|---|---|---|
| N0 | 175 | 134 |
| Sr1 (survival rate from 2nd to 3rd instar) | 0.76 | 0.93 |
| Sr2 (survival rate from 3rd to 5th instar) | 0.90 | 0.93 |
| Er (emergence rate) | 0.87 | 0.96 |
| Fr (female ratio) | 0.61 | 0.55 |
| Cr (Copulation rate, %) | 0.79 | 0.93 |
| Fd (Fecundity, eggs per female) | 90.61 | 87.82 |
| Ha (Hatchability, %) | 0.75 | 0.95 |
| N (predicted number of offspring) | 3453.52 | 4711.19 |
| I (population trend index) | 19.73 | 35.19 |
| Relative fitness | 0.56 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F.; Su, T.; Qiao, G.; Wang, S. Impact of Sulfoxaflor on Brown Marmorated Stink Bug: Developmental and Reproductive Effects. Insects 2025, 16, 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050465
Li R, Wang Z, Yang F, Su T, Qiao G, Wang S. Impact of Sulfoxaflor on Brown Marmorated Stink Bug: Developmental and Reproductive Effects. Insects. 2025; 16(5):465. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050465
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ren, Zehua Wang, Fan Yang, Tao Su, Guanghang Qiao, and Shanning Wang. 2025. "Impact of Sulfoxaflor on Brown Marmorated Stink Bug: Developmental and Reproductive Effects" Insects 16, no. 5: 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050465
APA StyleLi, R., Wang, Z., Yang, F., Su, T., Qiao, G., & Wang, S. (2025). Impact of Sulfoxaflor on Brown Marmorated Stink Bug: Developmental and Reproductive Effects. Insects, 16(5), 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050465






