Physiological and Biochemical Mechanisms of Aoria nigripes (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae) Adaption to Flavonoid-Rich Plant Nekemias grossedentata
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects
2.2. Host Plants
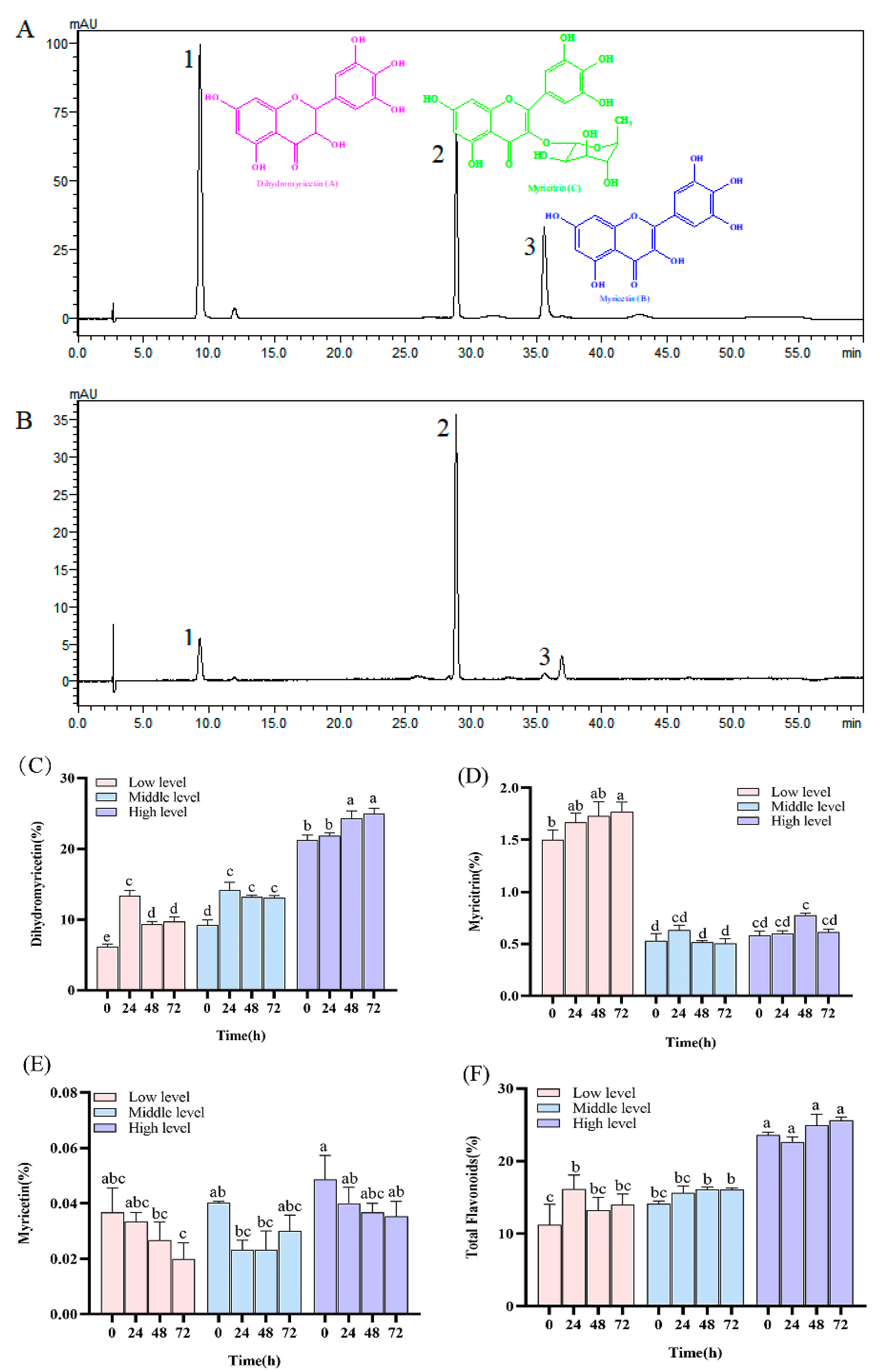
2.3. Determination of Secondary Metabolite Contents of N. grossedentata
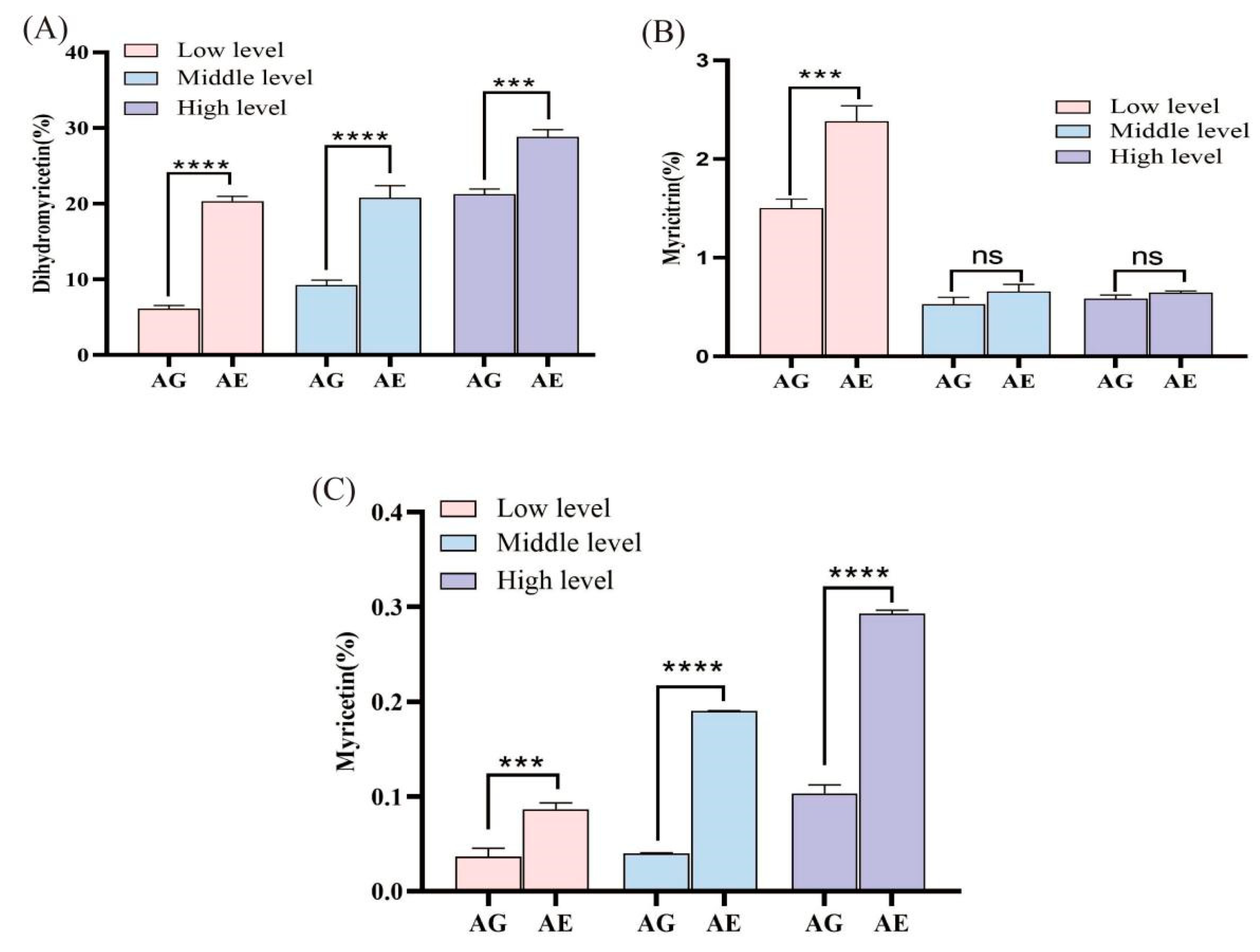
2.4. Determination of Flavonoid Compounds in Insect Excreta
2.5. Measurement of Protective and Detoxifying Enzyme Activities in A. nigripes Adults
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Secondary Metabolites Contents in Host Plant
3.2. Three Protective and Four Detoxifying Enzyme Activities
3.2.1. Superoxide Dismutase Activity
3.2.2. Peroxidase Activity
3.2.3. CAT Activity
3.2.4. CarE Activity
3.2.5. AchE Activity
3.2.6. GST Activity
3.2.7. CYP450 Activity
3.3. Relationship Between A. nigripes Enzyme Activity and Secondary Metabolite Content in Host Plant Leaves
3.4. Metabolic Accumulation of Major N. grossedentata Flavonoids in Insects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, C.Y.; Kang, Z.J.; Shi, X.Y.; Gao, X.W. Metabolic adaptation mechanisms of insects to plant secondary metabolites and their implications for insecticide resistance of insects. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2015, 58, 1126–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.S.; Yuan, Y.F.; Wu, L.; Chen, M. Effects of host plants on the feeding behavior and detoxification enzyme activities in Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae) larvae. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2018, 61, 232–239. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, D.Z. Defensive Responses of Camellia sinensis to Colaspoides femoralis Feeding. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.B.; Cao, P.R.; Liu, C.Y.; Zhou, Y.H. The effect on the component contents in fresh leaves of Lingtou Danzong tea plant by moderate damage of Basilepta melanopus. J. South China Agric. Univ. 2005, 26, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Aal, E.S.M.; Hucl, P.; Sosulski, F.W.; Graf, R.; Gillott, C.; Pietrzak, L. Screening spring wheat for midge resistance in relation to ferulic acid content. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2001, 49, 3559–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.J.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.H.; Zhao, J.M. Effects of the major nutritional substances and micro-structure of rice plants on the host preference of the small brown plant hopper, Laodelphax striatellus. J. Plant Prot. 2009, 36, 200–206. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Tian, T.W.; Guo, X.R.; Li, W.Z.; Yan, F.M. Study on the relationship between the occurrence quantity of Rhopalosiphum maidis (Fitch) and main biochemical substance contents in maize. J. Henan Agric. Uni. 2016, 50, 364–369. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Gao, H.; Zhang, G.J.; Zhu, K.Y.; Cheng, W.N. Effects of secondary metabolites in wheat kernels on activities of three detoxifying enzymes and related gene expression in Sitodiplosis mosellena. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2020, 53, 4204–4214. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Y.; Niu, H.; Jin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, P. Effects of Honeysuckle Varieties on Protective and Detoxifying Enzyme Activities in Heterolocha Jinyinhuaphaga Chu (Lepidoptera: Geometridae) Larvae. J. Chem. Ecol. 2023, 49, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.D. Studies on Life-History Characteristics of Plagiodera versicolora and Clostera anastomosis and Their Behavioral Response to the Alkaloids from Sophora alopecuroids. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.H.; Chen, Y.P.; Zhou, A.C.; He, S.Q.; Li, H.; Bao, Y.Y.; Cui, F.R. Effects of multi-generation feeding with different host plants on activities of enzyme in Spodoptera frugiperda larvae. J. Environ. Entomol. 2020, 42, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Chertemps, T.; Goff, G.; Maïbèchea, M.; Hilliou, F. Detoxification gene families in Phylloxera: Endogenous functions and roles in response to the environment. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 40, 100867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. Study on effects of three secondary metabolites and cyanobromonamide on P450 and GST in Lymantria dispar. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Ge, Z.; Liu, D.; Cui, X.; Huang, X.; Wang, D. Effects of Host Plants on Activities of Detoxificatoin Enzymes in Different Genotypes of Cereal Aphid Sitobion avenae. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2018, 27, 283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Lindroth, R.L. Host plant alteration of detoxification enzyme in Papilio glaucus glaucus. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1989, 50, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigsby, C.M.; Showalter, D.N.; Herms, D.A.; Koch, J.L.; Bonello, P.; Cipollini, D. Physiological responses of emerald ash borer larvae to feeding on different ash species reveal putative resistance mechanisms and insect counter-adaptations. J. Insect Physiol. 2015, 78, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Bahadur, M. Effect of host plants on fitness traits and detoxifying enzymes activity of Helopeltis theivora, a major sucking insect pest of tea. Phytoparasitica 2012, 40, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Xia, X.M.; Liu, T.X. Influence of three diets on susceptibility of selected insecticides and activities of detoxification esterases of Helicoverpa assulta (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2010, 96, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Feng, H.L.; Li, K.B.; Cao, Y.Z. Effects of host plants on the activities of some detoxification enzymes and protective enzymes in the meadow moth. Plant Prot. 2012, 38, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.T.; Shi, C.H.; Cheng, J.X.; Zhang, Y.J. Effects of feeding on different host plants on development, reproduction and protective enzymes of Bradysia odoriphaga. Plant Prot. 2017, 43, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.K.; Wang, W.X.; Fu, Q.; Lai, F.X.; Luo, J. Effects of host plants on activities of detoxification and protective enzymes in three rice plant hoppers. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2011, 25, 659–666. [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby, M. Descriptions of new genera and species of phytophagous Coleoptera. Zoology 1885, 53, 925–929. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, L.Z. List of Chinese Insects: Second Volume; Zhongshan (Sun Yat-sen) University Press: Guangzhou, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, R.H.; Ou, X.H.; Situ, Y.X. A New Pest Harming Parthenocisus himalayana: Aoria nigripes; Yunnan Forestry: Kunming, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Zhou, H.Z. Fauna Sinica Insects: Fortieth Volume; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016; pp. 206–215. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.X.; Bai, M.Q.; Ai, Z.X.; Zhao, A.Q. Occurrence rule and green prevention and control technology of Aoria nigripes on crystal grape in Sandu county. Guizhou Agric. Sci. 2015, 43, 62–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Liu, W.W.; Qin, W.T.; Yuan, H.Z.; Yang, S.L.; Li, H. Occurrence and control of the grape pest, Aoria nigripes, in Wenshan of Yunnan Province. Plant Prot. 2011, 37, 178–180. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Jiang, C.; Wu, S.; Feng, X.; Yu, Z. The complete mitochondrial genome of Aoria nigripes (Coleoptera, Eumolpidae, Eumolpinae) and its phylogenetic status. Biodivers. Data J. 2022, 10, e93591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, L.; Chen, Q.; Chen, M.; Wei, Y.; Yu, Z. Biological Characteristics and Occurrence of Aoria nigripes (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) in Ampelopsis grossedentata. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2023, 52, 94–102. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.Y. Effects of Karst Habitat on the Physiological and Biochemical Properties of Ampelopsis grossedentata and Its Generalization. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.X.; Hong, Z.S.; Yang, K.; Zeng, C.H. Research progress of dihydromyricetin in Ampelopsis grossedentata. J. Shenyang Pharm. Univ. 2020, 37, 569–576. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.K.; Li, J.; Huang, D.; Ou, Y.W.; Yao, R. Research progress on chemical constituents and anti- infective effects of the traditional Chinese medicine vine tea (Ampelopsis grossedentata). Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. Mater. Medica World Sci. Technol. 2021, 23, 2012–2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.J.; Xiao, H.; Zeng, Z.; Sun, Z.W.; Lei, C.; Dong, J.Z.; Wang, Y. Composition and serum antioxidation of the main flavonoids from fermented vine tea (Ampelopsis grossedentata). J. Funct. Foods 2014, 9, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Cui, X.M.; Liu, D.Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.X.; Yang, X.Y.; Qu, Y. Research progress of chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Ampelopsis grossedentata. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2016, 44, 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.J.; Gao, X.W.; Lei, M.Q.; Zheng, B.Z. Effects of tannic acid on glutathione S-transferases in Helicoverpa armigera (Hüb-ner). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2003, 46, 684–690. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, R.S.; Wen, Z.M.; Niu, G.D.; Schuler, M.A.; Berenbaum, M.R. Allelochemical induction of cytochrome P450 monooxygenases and amelioration of xenobiotic toxicity in Helicoverpa zea. J. Chem. Ecol. 2007, 33, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.P.; Luo, M.; Wang, X.Y.; He, X.Z.; Lu, W.; Zheng, X.L. Pathogenicity of Beauveria bassiana PfBb and Immune Responses of a Non-Target Host, Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Insects 2022, 13, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.C.; Shen, Y.D.; Sun, J.C.; Li, X.X.; Huang, Y.; Dong, Y.C.; Cao, H.Q. Effect of chlorantraniliprole and emamectin benzoate on toxicity and detoxification enzymes activity in Spodoptera frugiperda larva. J. Environ. Entomol. 2019, 41, 961–967. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, S.F.; Xue, Y.N.; Du, R.S.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.T.; Wang, Y.W.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.H.; Xia, X.M. Toxicity and sublethal effects of triflumezopyrim on the development and detoxification enzymatic activities in the small brown planthopper (SBPH), Laodelphax striatellus (Fallen). Crop Prot. 2021, 150, 105813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Ni, X.; Li, X. Identification of the Flavone-Inducible Counter-Defense Genes and Their cis-Elements in Helicoverpa armigera. Toxins 2023, 15, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; He, S.; Guo, J.; Chen, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, H.; Xie, Q.; Gui, F. Effects of host plants on activities of three groups of enzymes in Spodoptera frugiperda (Smith) larvae. J. South. Agric. 2020, 51, 2461–2469. [Google Scholar]
- Giraudo, M.; Hilliou, F.; Fricaux, T.; Audant, P.; Feyereisen, R.; Le Goff, G. Cytochrome P450s from the fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda): Responses to plant allelochemicals and pesticides. Insect Mol. Biol. 2015, 24, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.Q.; Kang, Z.Y.; Ren, F.; Guo, P. Effects of Quercetin on the Growth and Expression of Immune-Pathway-Related Genes in Silkworm (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). J. Insect Sci. 2020, 20, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskorski, R.; Dorn, S. How the oligophage codling moth Cydia pomonella survives on walnut despite its secondary metabolite juglone. J. Insect Physiol. 2011, 57, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, G.W.; Summers, C.B. Antioxidant systems in insects. Arch. Insect Biochem. 1995, 29, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Oberley, L.W.; Murhammer, D.W. Antioxidant defense systems of two lipidopteran insect cell lines. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 30, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.C.; Ning, Q.; Dai, Y.J.; Wang, L.H.; Li, G.Y.; Peng, Y. Cloning and expression analysis of glutathione S-transferase gene in Pardosa pseudoannulata. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 35, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Lü, C.J.; Han, J.C.; Liu, H.; Ren, Y.X.; Ma, L. Influence of host plants to detoxification enzymes and susceptibilities to insecticides on Aphis citricola von der Goot. J. Plant Prot. 2007, 34, 534–538. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, J.H.; Bi, J.R.; Ma, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.K.; Shi, S.S. Effects of host plants on digestive enzymes and detoxification enzyme activities in the midgut of Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky). J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2018, 40, 551–556. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.P.; Song, D.L.; Shi, X.Y.; Liang, P.; Gao, X.W. Effects of three alleochemcals on the carboxylesterase activity and its susceptibility to insecticides in Bemisia tabaci Biotype, B. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2008, 10, 292–296. [Google Scholar]
- Erb, M.; Robert, C.A. Sequestration of plant secondary metabolites by insect herbivores: Molecular mechanisms and ecological consequences. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2016, 14, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, H.; Sharma, A.; Trivedi, P.K. The role of flavonols in insect resistance and stress response. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2023, 73, 102353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, M.S.J. Flavonoid-insect interactions: Recent advances in our knowledge. Phytochemistry 2003, 64, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Enzyme | t/h | Host Plant | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Level | Middle Level | High Level | ||
| Acetylcholinesterase (U/g), AchE | 0 | 89.76 ± 3.29 e | 89.76 ± 3.29 e | 89.76 ± 3.29 e |
| 24 | 135.98 ± 2.53 d | 160.55 ± 3.32 c | 176.06 ± 3.38 b | |
| 48 | 102.17 ± 4.97 e | 182.32 ± 22.22 b | 178.81 ± 2.21 b | |
| 72 | 67.96 ± 1.38 f | 141.73 ± 1.56 d | 200.28 ± 1.83 a | |
| Carboxylesterase (U/g), CarE | 0 | 27.46 ± 1.89 gh | 27.46 ± 1.89 gh | 27.46 ± 1.89 gh |
| 24 | 33.21 ± 2.28 fg | 55.20 ± 4.58 b | 40.83 ± 2.15 de | |
| 48 | 49.56 ± 4.14 bc | 39.42 ± 2.80 ef | 47.16 ± 3.38 cd | |
| 72 | 20.80 ± 3.36 h | 38.06 ± 6.31 ef | 71.22 ± 4.33 a | |
| Glutathione S-transferase (U/g), GST | 0 | 722.69 ± 79.50 f | 722.69 ± 79.50 f | 722.69 ± 79.50 f |
| 24 | 1238.20 ± 3.51 cd | 1119.04 ± 3.91 cde | 1475.75 ± 48.71 ab | |
| 48 | 1313.40 ± 132.93 bc | 1013.06 ± 92.68 e | 1307.39 ± 146.88 bc | |
| 72 | 1043.91 ± 101.74 de | 1183.89 ± 176.17 cde | 1676.28 ± 141.90 a | |
| Cytochrome P450 (ng/g), CYP450 | 0 | 14.95 ± 0.88 d | 14.95 ± 0.88 d | 14.95 ± 0.88 d |
| 24 | 12.47 ± 0.45 e | 16.96 ± 0.81 b | 15.46 ± 0.54 cd | |
| 48 | 15.05 ± 0.56 cd | 15.70 ± 1.04 bcd | 18.55 ± 0.21 a | |
| 72 | 16.45 ± 1.04 bc | 19.04 ± 0.13 a | 19.38 ± 0.61 a | |
| Peroxidase (U/g), POD | 0 | 53.92 ± 8.61 g | 53.92 ± 8.61 g | 53.92 ± 8.61 g |
| 24 | 117.47 ± 5.81 f | 182.14 ± 4.34 ab | 173.79 ± 0.46 b | |
| 48 | 109.05 ± 9.05 f | 194.12 ± 16.19 a | 137.65 ± 7.48 de | |
| 72 | 147.55 ± 6.48 cd | 122.94 ± 2.00 ef | 155.00 ± 6.67 c | |
| Superoxide Dismutase (U/g), SOD | 0 | 163.03 ± 15.41 c | 163.03 ± 15.41 c | 163.03 ± 15.41 c |
| 24 | 187.58 ± 7.45 ab | 172.05 ± 7.69 bc | 188.42 ± 5.41 ab | |
| 48 | 189.68 ± 4.44 ab | 199.36 ± 13.99 a | 162.31 ± 2.72 c | |
| 72 | 170.28 ± 12.73 bc | 154.80 ± 18.20 c | 187.44 ± 6.39 ab | |
| Catalase (U/g), CAT | 0 | 253.18 ± 15.37 c | 253.18 ± 15.37 c | 253.18 ± 15.37 c |
| 24 | 349.05 ± 15.7 b | 404.33 ± 18.86 a | 418.49 ± 17.96 a | |
| 48 | 274.96 ± 18.55 c | 396.13 ± 15.45 a | 327.70 ± 0.92 b | |
| 72 | 318.82 ± 8.49 b | 331.52 ± 25.78 b | 284.07 ± 3.37 c | |
| Enzyme | Secondary Metabolites | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Flavonoids | Dihydromyricetin | Myricitrin | Myricetin | |
| Acetylcholinesterase (U/g), AchE | 0.583 ** | 0.633 ** | −0.797 ** | 0.251 |
| Carboxylesterase (U/g), CarE | 0.563 ** | 0.561 ** | −0.407 * | 0.201 |
| Glutathione S-transferase (U/g), GST | 0.722 ** | 0.689 ** | −0.143 | 0.370 |
| Cytochrome P450 (ng/g), CYP450 | 0.525 ** | 0.579 ** | −0.526 ** | −0.047 |
| Peroxidase (U/g), POD | 0.178 | 0.208 | −0.527 ** | 0.121 |
| Superoxide dismutase (U/g), SOD | 0.060 | 0.051 | 0.189 | 0.027 |
| Catalase (U/g), CAT | −0.033 | −0.123 | −0.496 ** | 0.183 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Z.; Yang, C.; Xie, L.; Yang, F.; Yuan, Y. Physiological and Biochemical Mechanisms of Aoria nigripes (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae) Adaption to Flavonoid-Rich Plant Nekemias grossedentata. Insects 2025, 16, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040399
Yu Z, Yang C, Xie L, Yang F, Yuan Y. Physiological and Biochemical Mechanisms of Aoria nigripes (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae) Adaption to Flavonoid-Rich Plant Nekemias grossedentata. Insects. 2025; 16(4):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040399
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Zhengwen, Chenju Yang, Lian Xie, Feng Yang, and Yuyu Yuan. 2025. "Physiological and Biochemical Mechanisms of Aoria nigripes (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae) Adaption to Flavonoid-Rich Plant Nekemias grossedentata" Insects 16, no. 4: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040399
APA StyleYu, Z., Yang, C., Xie, L., Yang, F., & Yuan, Y. (2025). Physiological and Biochemical Mechanisms of Aoria nigripes (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae) Adaption to Flavonoid-Rich Plant Nekemias grossedentata. Insects, 16(4), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040399





