Species Delimitation and Cryptic Diversity in Rheotanytarsus Thienemann & Bause, 1913 (Diptera: Chironomidae) Based on DNA Barcoding
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
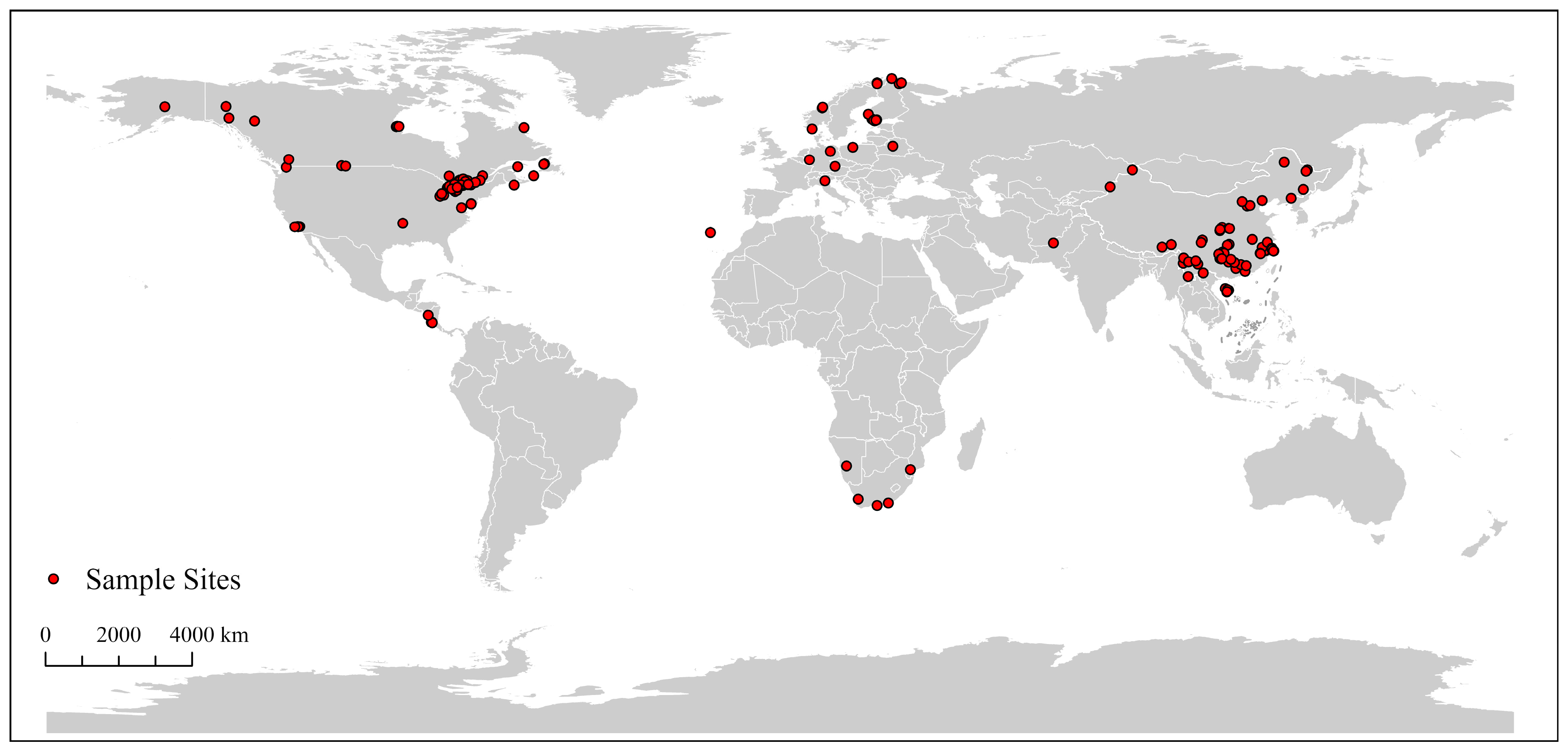
3.1. Dataset Characteristics and Global Distribution
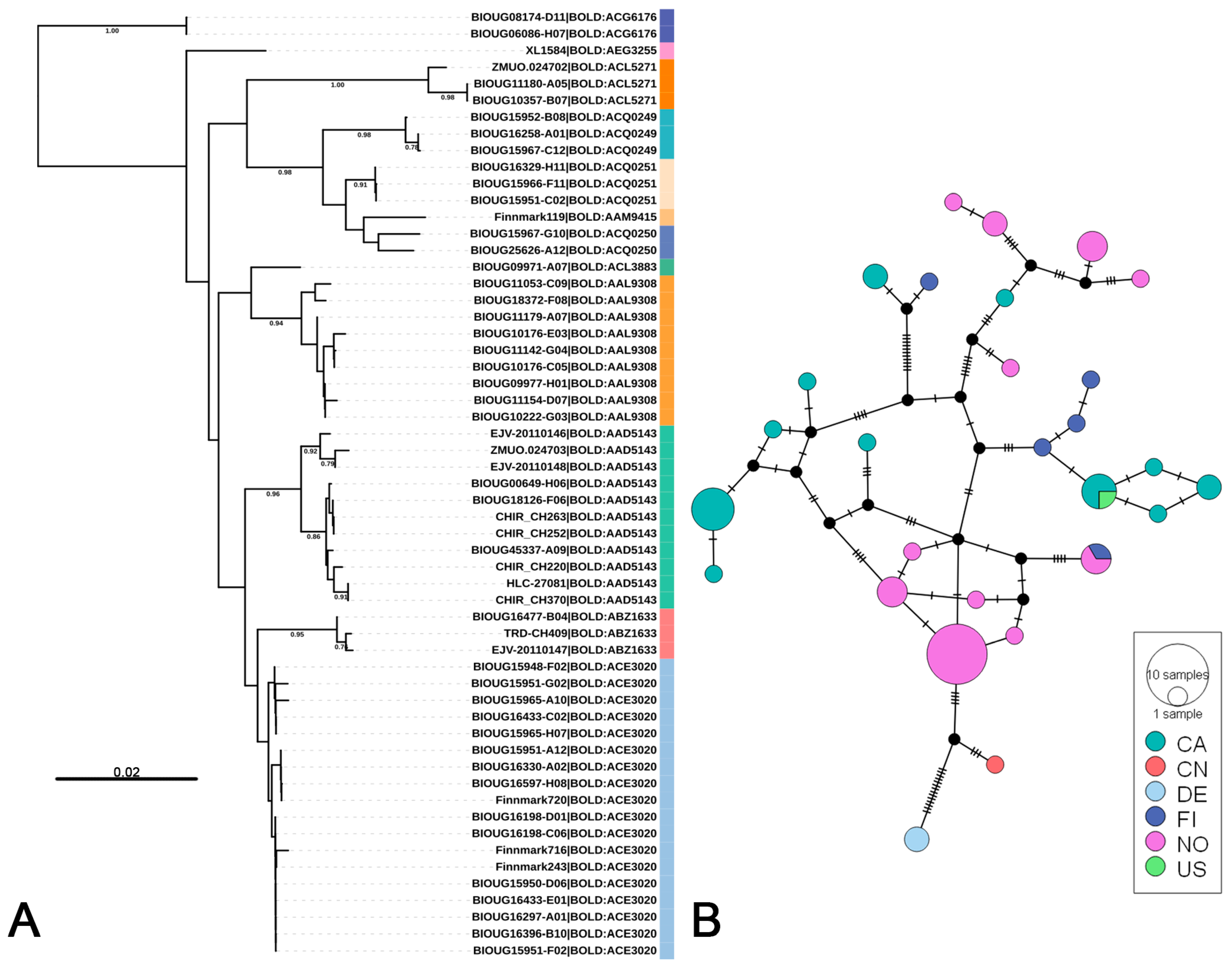
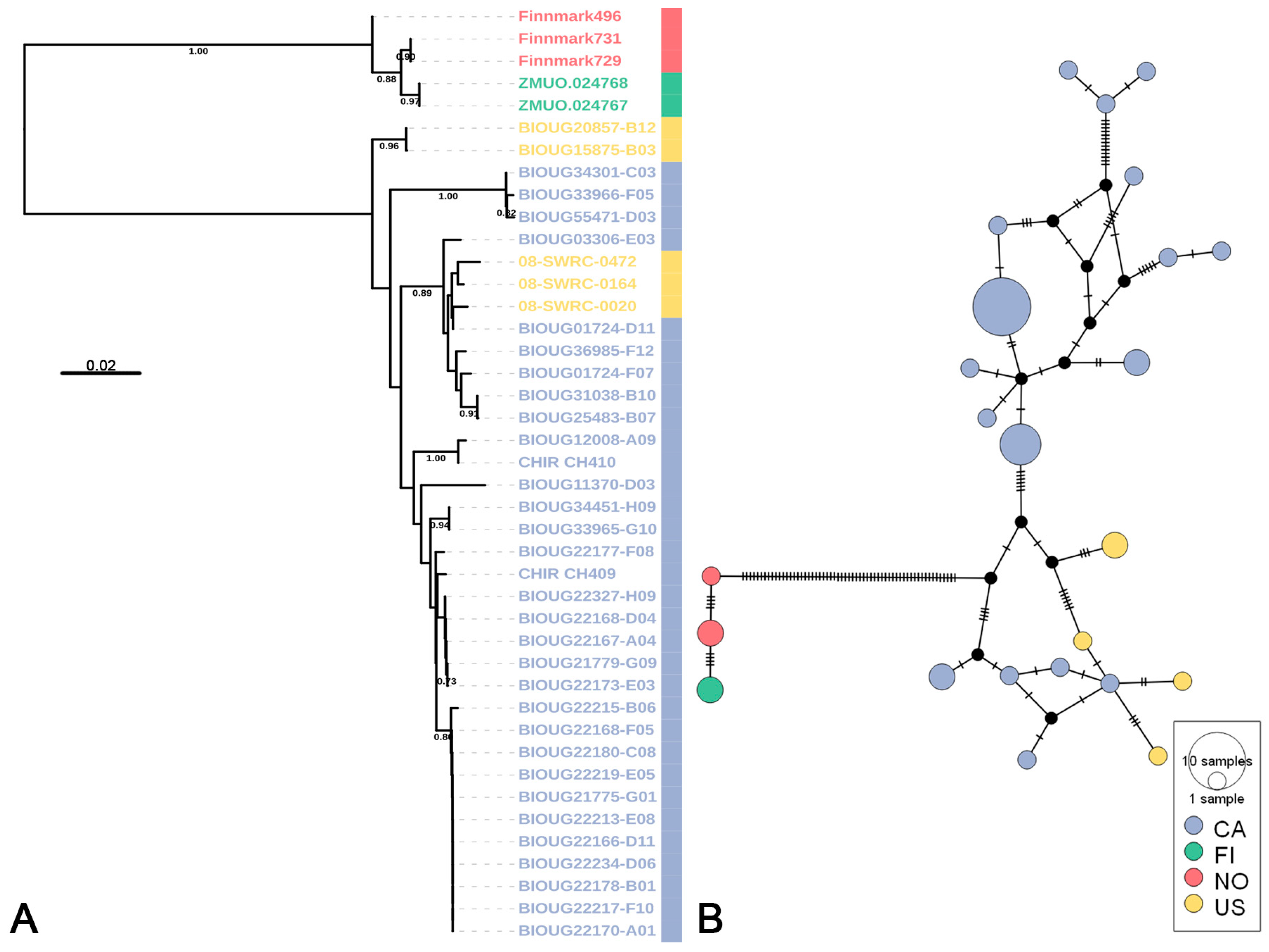
3.2. Putative Species Delimitation and Genetic Divergence
3.3. Life-Stage Association and Distribution
4. Discussion
4.1. Appropriate Delimitation Methods and Threshold Value
4.2. Cryptic Species Diversity
4.3. Summary and Outlook
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pape, T.; Blagoderov, V.; Mostovski, M.B. Order Diptera Linnaeus, 1758. In: Zhang, Z.-Q.(Ed.) Animal biodiversity: An outline of higher-level classification and survey of taxonomic richness. Zootaxa 2011, 3148, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, G.W.; Pape, T.; Skevington, J.H.; Sinclair, B.J. Biodiversity of diptera. In Insect Biodiversity: Science and Society; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 229–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, N.; Saha, G.K.; Mazumdar, A.; Chaudhuri, P.K. Records of chironomids of the tribe Pentaneurini (Diptera: Chironomidae) in the Eastern Himalayas of India. Ann. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 2011, 47, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicacio, G.; Juen, L. Chironomids as indicators in freshwater ecosystems: An assessment of the literature. Insect Conserv. Divers. 2015, 8, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrington, L.C. Global diversity of non-biting midges (Chironomidae; Insecta-Diptera) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 2008, 595, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayford, B.L.; Sublette, J.E.; Herrmann, S.J. Distribution of Chironomids (Diptera: Chironomidae) and Ceratopogonids (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) along a Colorado Thermal Spring Effluent. J. Kansas Entomol. Soc. 1995, 68, 77–92. [Google Scholar]
- Karima, Z. Chironomidae: Biology, ecology and systematics. In Wonders Diptera—Charact Divers Significance World’s Ecosyst; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, P.D.; Cranston, P.S.; Pinder, L.C.V. The Chironomidae: Biology and Ecology of Non-Biting Midges; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1995; 572p. [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell, M.L.; Sherbot, D.M.; Pollock, C.M. Ecosystem response to solar ultraviolet-B radiation: Influence of trophic-level interactions. Science 1994, 265, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobinske, R.J.; Cichra, C.E.; Ali, A. Predation by bluegill (Lepomis macrochirus) on larval Chironomidae (Diptera) in relation to midge standing crop in two central Florida lake. Fla. Entomol. 2002, 85, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, M.S.; Pasmans, F.; Adriaensen, C.; Du Laing, G.; Janssens, G.P.J.; Martel, A. Chironomidae Bloodworms Larvae as Aquatic Amphibian Food. Zoo. Biol. 2014, 33, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raunio, J.; Heino, J.; Paasivirta, L. Non-biting midges in biodiversity conservation and environmental assessment: Findings from boreal freshwater ecosystems. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Bogan, M.T.; Lytle, D.A.; Prat, N. Are Chironomidae (Diptera) good indicators of water scarcity? Dryland streams as a case study. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 71, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molineri, C.; Tejerina, E.G.; Torrejón, S.E.; Pero, E.J.; Hankel, G.E. Indicative value of different taxonomic levels of Chironomidae for assessing the water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencioni, V.; Cranston, P.S.; Makarchenko, E. Recent advances in the study of Chironomidae: An overview. J. Limnol. 2018, 77, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyerematen, R.A.; Andersen, T. Rheotanytarsus Thienemann et Bause (Diptera: Chironomidae) from Central America and Mexico. Stud. Neotrop. Fauna E 2002, 37, 23–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyerematen, R.A.; Andersen, T.; Saether, O.A. A review of Oriental Rheotanytarsus Thienemann & Bause, with descriptions of some new species (Insecta, Diptera, Chironomidae). Spixiana 2000, 23, 225–258. [Google Scholar]
- Kyerematen, R.A.; Sæther, O.A. A review of Afrotropical Rheotanytarsus Thienemann et Bause, 1913 (Diptera: Chironomidae). Tijdschr Ent 2000, 143, 27–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moubayed-Breil, J.; Kettani, K. Description of Rheotanytarsus langtoni sp. n. from the Rif of north-western Morocco [Diptera, Chironomidae, Tanytarsini]. Ephemera 2018, 19, 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Cranston, P.S. Revision of Australian Rheotanytarsus Thienemann & Bause (Diptera: Chironomidae), with emphasis on immature stages. Invertebr. Syst. 1997, 11, 705–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-B.; Yao, Y.; Chang, T.; Yan, C.-C.; Lin, X.-L. Contribution to the knowledge of Rheotanytarsus pellucidus species group from China (Diptera, Chironomidae): Three new and one newly recorded species. Zootaxa 2022, 5188, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sæther, O.A.; Kyerematen, R.A. Towards phylogeny and zoogography of the genus Rheotanytarsus Thienemann et Bause, 1913 (Diptera: Chironomidae). Tijdschrift voor Entomologie 2001, 144, 73–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortelezzi, A.; Simoy, M.V.; Siri, A.; Donato, M.; Cepeda, R.E.; Marinelli, C.B.; Berkunsky, I. New insights on bioindicator value of Chironomids by using occupancy modelling. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prat, N. A case of phoresis of midges on Zygoptera. CHIRONOMUS J. Chironomidae Res. 2022, 35, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosdall, L.; Mason, P.; Lehmkuhl, D. First records of phoretic Chironomidae (Diptera) associated with nymphs of Pteronarcys dorsata (Say)(Plecoptera: Pteronarcyidae). Can. Entomol. 1986, 118, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, R.-H.; Yao, Y.; Sun, B.-J.; Lin, X.-L. Review of the Rheotanytarsus acerbus species group from China (Diptera: Chironomidae). Zool. Syst. 2024, 49, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langton, P.H.A.; Patrick, D. Rheotanytarsus rioensis (Diptera: Chironomidae), a new species of the pentapoda group from the Canary Islands. Br. J. Entomol. Nat. Hist. 1995, 8, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.-L.; Stur, E.; Ekrem, T. Exploring genetic divergence in a species-rich insect genus using 2790 DNA barcodes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, J.C. Biodiversity of aquatic insects. In Insect Biodiversity: Science and Society; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 205–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; DeWaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.; Ratnasingham, S.; De Waard, J.R. Barcoding animal life: Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergences among closely related species. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, S96–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, P.D.; Stoeckle, M.Y.; Zemlak, T.S.; Francis, C.M. Identification of birds through DNA barcodes. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSalle, R.; Egan, M.G.; Siddall, M. The unholy trinity: Taxonomy, species delimitation and DNA barcoding. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1905–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Ratnasingham, S.; Zakharov, E.V.; Telfer, A.C.; Levesque-Beaudin, V.; Milton, M.A.; Pedersen, S.; Jannetta, P.; Dewaard, J.R. Counting animal species with DNA barcodes: Canadian insects. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimeno, C.; Hausmann, A.; Schmidt, S.; Raupach, M.J.; Doczkal, D.; Baranov, V.; Hübner, J.; Höcherl, A.; Albrecht, R.; Jaschhof, M.; et al. Peering into the darkness: DNA barcoding reveals surprisingly high diversity of unknown species of Diptera (Insecta) in Germany. Insects 2022, 13, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivathsan, A.; Ang, Y.; Heraty, J.M.; Hwang, W.S.; Jusoh, W.F.; Kutty, S.N.; Puniamoorthy, J.; Yeo, D.; Roslin, T.; Meier, R. Convergence of dominance and neglect in flying insect diversity. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 7, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D. A DNA-based registry for all animal species: The Barcode Index Number (BIN) system. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Li, K.; Liu, X. Comprehensive DNA barcode reference library and optimization of genetic divergence threshold facilitate the exploration of species diversity of green lacewings (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). Insect Sci. 2024, 31, 613–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X. Elevational diversity patterns of green lacewings (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae) uncovered with DNA barcoding in a biodiversity hotspot of Southwest China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 778686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.-L.; Yu, H.-J.; Wang, Q.; Bu, W.-J.; Wang, X.-H. DNA barcodes and morphology confirm a new species of Rheocricotopus (Psilocricotopus) orientalis group (Diptera: Chironomidae). Zootaxa 2020, 4768, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meusnier, I.; Singer, G.A.; Landry, J.-F.; Hickey, D.A.; Hebert, P.D.; Hajibabaei, M. A universal DNA mini-barcode for biodiversity analysis. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajibabaei, M.; Smith, M.A.; Janzen, D.H.; Rodriguez, J.J.; Whitfield, J.B.; Hebert, P.D. A minimalist barcode can identify a specimen whose DNA is degraded. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucklin, A.; Steinke, D.; Blanco-Bercial, L. DNA barcoding of marine metazoa. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2011, 3, 471–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willyard, A.; Cronn, R.; Liston, A. Reticulate evolution and incomplete lineage sorting among the ponderosa pines. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2009, 52, 498–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuis, J.R.; Roe, A.D.; Sperling FA, H. Multi-locus species delimitation in closely related animals and fungi: One marker is not enough. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 4422–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satler, J.D.; Carstens, B.C.; Hedin, M. Multilocus Species Delimitation in a Complex of Morphologically Conserved Trapdoor Spiders (Mygalomorphae, Antrodiaetidae, Aliatypus). Syst. Biol. 2013, 62, 805–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prebus, M.M. Phylogenomic species delimitation in the ants of the Temnothorax salvini group (Hymenoptera: Formicidae): An integrative approach. Syst. Entomol. 2021, 46, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Taylor, A.T.; Near, T.J. Phylogenomics and species delimitation of the economically important Black Basses (Micropterus). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gostel, M.R.; Kress, W.J. The expanding role of DNA barcodes: Indispensable tools for ecology, evolution, and conservation. Diversity 2022, 14, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, L.; Gibbs, J.; Sheffield, C.; Hanner, R. DNA barcoding and the mediocrity of morphology. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberlet, P.; Bonin, A.; Zinger, L.; Coissac, E. Environmental DNA: For Biodiversity Research and Monitoring; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virgilio, M.; Backeljau, T.; Nevado, B.; De Meyer, M. Comparative performances of DNA barcoding across insect orders. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D. BOLD: The Barcode of Life Data System (http://www.barcodinglife.org). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaneto, D.; Flot, J.-F.; Tang, C.Q. Guidelines for DNA taxonomy, with a focus on the meiofauna. Mar. Biodivers. 2015, 45, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Wei, C.; Chan, D.; Agda, J.; Agda, J.; Ballesteros-Mejia, L.; Boutou, H.A.; El Bastami, Z.M.; Ma, E.; Manjunath, R.; et al. BOLD v4: A Centralized Bioinformatics Platform for DNA-Based Biodiversity Data. In DNA Barcoding. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2744th ed.; DeSalle, R., Ed.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 403–441. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.-L.; Stur, E.; Ekrem, T. DNA barcodes and morphology reveal unrecognized species in Chironomidae (Diptera). Insect Syst. Evol. 2018, 49, 329–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Lin, X.-L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.-H. DNA barcodes successfully delimit morphospecies in a superdiverse insect genus. Zool. Scr. 2018, 47, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.-L.; Mo, L.-D.; Bu, W.-J.; Wang, X.-H. The first comprehensive DNA barcode reference library of Chinese Tanytarsus (Diptera: Chironomidae) for environmental DNA metabarcoding. Divers. Distrib. 2021, 27, 1932–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Chen, G.; Wang, L.; Lei, T.; Qi, X. DNA Barcoding Supports “Color-Pattern’’-Based Species of Stictochironomus from China (Diptera: Chironomidae). Insects 2024, 15, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, H.-F.; Li, C.-H.; Zhang, H.-X.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Sun, B.-J.; Lin, X.-L. Towards a Comprehensive DNA Barcode Library of Stenochironomus Kieffer, 1919 (Diptera: Chironomidae) from China. Diversity 2024, 16, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Yao, Y.; Liu, W.-B.; Yan, C.-C.; Wang, X.-H.; Lin, X.-L. Review of the Rheotanytarsus muscicola species group from China (Diptera: Chironomidae). Diversity 2022, 14, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-Y.; Yao, Y.; Sun, L.; Ling, H.-N.; Jin, W.-D.; Lin, X.-L. DNA barcodes and morphology reveal new species within the Rheotanytarsus guineensis species group from China (Diptera: Chironomidae). Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 114, e22060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sæther, O.A. Some Nearctic Podonominae, Diamesinae, and Orthocladiinae (Diptera: Chironomidae). In Bulletin of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada; Fisheries Research Board of Canada: Vancouver, BC, USA, 1969; Volume 170, pp. 1–154. Available online: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=1jAntAEACAAJ (accessed on 12 January 2025).
- Wang, X.-H.; Guo, Y.-H. A review of the genus Rheotanytarsus Thienemann & Bause from China (Diptera: Chironomidae: Tanytarsini). Zootaxa 2004, 650, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moubayed-Breil, J.; Langton, P.H.; Ashe, P. Rheotanytarsus dactylophoreus, a new mountain species from streams in the Eastern Pyrenees and Corsica (Diptera: Chironomidae). Fauna Nor. 2012, 31, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liu, W.-B.; Wang, X.-H.; Lin, X.-L. Rheotanytarsus baihualingensis and R. diaoluoensis (Diptera: Chironomidae), Two New Species from Oriental China. Ann. Zool. Fenn. 2022, 59, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: A maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol. 1981, 17, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puillandre, N.; Lambert, A.; Brouillet, S.; Achaz, G. ABGD, Automatic Barcode Gap Discovery for primary species delimitation. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1864–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapli, P.; Lutteropp, S.; Zhang, J.; Kobert, K.; Pavlidis, P.; Stamatakis, A.; Flouri, T. Multi-rate Poisson tree processes for single-locus species delimitation under maximum likelihood and Markov chain Monte Carlo. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 1630–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, J.; Barraclough, T.G.; Gomez-Zurita, J.; Cardoso, A.; Duran, D.P.; Hazell, S.; Kamoun, S.; Sumlin, W.D.; Vogler, A.P. Sequence-Based Species Delimitation for the DNA Taxonomy of Undescribed Insects. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouckaert, R.; Vaughan, T.G.; Barido-Sottani, J.; Duchêne, S.; Fourment, M.; Gavryushkina, A.; Heled, J.; Jones, G.; Kühnert, D.; De Maio, N.; et al. BEAST 2.5: An advanced software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, 1006650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior Summarization in Bayesian Phylogenetics Using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer HE, L. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence Polymorphism Analysis of Large Data Sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyerematen, R.A.; Sæther, O.A.; Andersenn, T. A review of the Rheotanytarsus pellucidus group (Diptera: Chironomidae). In Proceedings of the Late 20th Century Research on Chironomidae: An Anthology from the 13th International Symposium on Chironomidae, Freiburg, Germany, 5–9 September 1997; Shaker: Maastricht, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Puillandre, N.; Brouillet, S.; Achaz, G. ASAP: Assemble species by automatic partitioning. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Wang, L.; Lei, T.; Qi, X. New Color-Patterned Species of Microtendipes Kieffer, 1913 (Diptera: Chironomidae) and a Deep Intraspecific Divergence of Species by DNA Barcodes. Insects 2023, 14, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, M.T.; Wild, R.; Elliot, M.; Fujisawa, T.; Balke, M.; Inward, D.J.; Lees, D.C.; Ranaivosolo, R.; Eggleton, P.; Barraclough, T.G.; et al. Accelerated Species Inventory on Madagascar Using Coalescent-Based Models of Species Delineation. Syst. Biol. 2009, 58, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, M.R.; Behan-Pelletier, V.M.; Hebert PD, N. Revealing the Hyperdiverse Mite Fauna of Subarctic Canada through DNA Barcoding. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e0048755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Hu, Y.; Shao, Z.-K.; Yao, L.-F.; Li, N.; Hebert PD, N.; Xue, X.-F. Factors affecting the accuracy of molecular delimitation in minute herbivorous mites (Acari: Eriophyoidea). Zool. Scr. 2023, 52, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Rannala, B. Bayesian species identification under the multispecies coalescent provides significant improvements to DNA barcoding analyses. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 3028–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havermans, C.; Nagy, Z.T.; Sonet, G.; De Broyer, C.; Martin, P. DNA barcoding reveals new insights into the diversity of Antarctic species of Orchomene sensu lato (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Lysianassoidea). Deep. Sea Res. Part. II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2011, 58, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Schmid-Egger, C.; Morinière, J.; Haszprunar, G.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA barcoding largely supports 250 years of classical taxonomy: Identifications for Central European bees (Hymenoptera, Apoidea partim). Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 985–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, M.T.; Balke, M.; Gregory, T.R.; Vogler, A.P. DNA-based species delineation in tropical beetles using mitochondrial and nuclear markers. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1925–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, J.M.; Jacobus, L.M.; Funk, D.H.; Zhou, X.; Kondratieff, B.; Geraci, C.J.; DeWalt, R.E.; Baird, D.J.; Richard, B.; Phillips, I.; et al. A DNA Barcode Library for North American Ephemeroptera: Progress and Prospects. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e0038063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlebec, D.; Sivec, I.; Podnar, M.; Kučinić, M. DNA barcoding for biodiversity assessment: Croatian stoneflies (Insecta: Plecoptera). PeerJ 2022, 10, 13213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzelu, C.O.; Cáceres, A.G.; Arrunátegui-Jiménez, M.J.; Lañas-Rosas, M.F.; Yañez-Trujillano, H.H.; Luna-Caipo, D.V.; Holguín-Mauricci, C.E.; Katakura, K.; Hashiguchi, Y.; Kato, H. DNA barcoding for identification of sand fly species (Diptera: Psychodidae) from leishmaniasis-endemic areas of Peru. Acta Trop. 2015, 145, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauls, S.U.; Blahnik, R.J.; Zhou, X.; Wardwell, C.T.; Holzenthal, R.W. DNA barcode data confirm new species and reveal cryptic diversity in Chilean Smicridea (Smicridea) (Trichoptera:Hydropsychidae). J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2010, 29, 1058–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagna, M.; Mereghetti, V.; Lencioni, V.; Rossaro, B. Integrated Taxonomy and DNA Barcoding of Alpine Midges (Diptera: Chironomidae). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.J.; Baek, M.J.; Kang, J.H.; Bae, Y.J. Diversity and DNA Barcode Analysis of Chironomids (Diptera: Chironomidae) from Large Rivers in South Korea. Insects 2022, 13, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadawski, P.; Montagna, M.; Rossaro, B.; Giłka, W.; Pešić, V.; Grabowski, M.; Magoga, G. DNA barcoding of Chironomidae from the Lake Skadar region: Reference library and a comparative analysis of the European fauna. Divers. Distrib. 2022, 28, 2838–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, N.I.; Ueno, R.; Ohbayashi, K.; Golygina, V.V.; Takamura, K. DNA barcoding supports reclassification of Japanese Chironomus species (Diptera: Chironomidae). Entomol. Sci. 2016, 19, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vences, M.; Miralles, A.; Dufresnes, C. Next-generation species delimitation and taxonomy: Implications for biogeography. J. Biogeogr. 2024, 51, 1709–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickford, D.; Lohman, D.J.; Sodhi, N.S.; Ng, P.K.; Meier, R.; Winker, K.; Ingram, K.K.; Das, I. Cryptic species as a window on diversity and conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimeno, C.; Rulik, B.; Manfrin, A.; Kalinkat, G.; Hölker, F.; Baranov, V. Facing the infinity: Tackling large samples of challenging Chironomidae (Diptera) with an integrative approach. PeerJ 2023, 11, 15336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, R. Two new species of subgenus Tripodura Towns (Diptera, Chironomidae, Polypedilum) from Oriental China. Zootaxa 2021, 5072, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.-B.; Yao, Y.; Yan, C.-C.; Wang, X.-H.; Lin, X.-L. A New Species of Polypedilum (Cerobregma) (Diptera, Chironomidae) from Oriental China. ZooKeys 2021, 1011, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, J. Revision der europäischen Arten (Imagines♂♂ und Puppen♂♂) der Gattung Rheotanytarsus BAUSE (Diptera, Chironomidae). Zool. Anz. 1970, 185, 343–378. [Google Scholar]
- Slatkin, M. Gene Flow and the Geographic Structure of Natural Populations. Science 1987, 236, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, P.Y.; Bourlat, S.J.; Ferguson, C.; Korlevic, P.; Zhao, L.; Ekrem, T.; Meier, R.; Lawniczak, M.K. Future of DNA-based insect monitoring. Trends Genet. 2023, 39, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.L.; Grames, E.M.; Forister, M.L.; Berenbaum, M.R.; Stopak, D. Insect decline in the Anthropocene: Death by a thousand cuts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2023989118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.K.; Didham, R.K. Global meta-analysis reveals overall higher nocturnal than diurnal activity in insect communities. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raitif, J.; Roussel, J.-M.; Olmos, M.; Piscart, C.; Plantegenest, M. Assessing spatial deposition of aquatic subsidies by insects emerging from agricultural streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.-J.; Sing, K.-W.; Floyd, R.M.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA Barcodes and Insect Biodiversity. In Insect Biodiversity; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 575–592. [Google Scholar]
- Moritz, C.; Cicero, C. DNA Barcoding: Promise and Pitfalls. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e0020354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, J.A.M.; Cocchiararo, B.; Verdelhos, T.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Pestana, J.L.T.; Nowak, C. Population genetic structure and hybridization patterns in the cryptic sister species Chironomus riparius and Chironomus piger across differentially polluted freshwater systems. Ecotox Environ. Safe 2017, 141, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailova, P. Cytogenetic analysis of a hybrid, Glyptotendipes pallens Mg. ×Glyptotendipes glaucus Mg. (Diptera, Chironomidae): Evolutionary considerations. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 1998, 36, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polukonova, N.V.; Beljanina, S.I. On the Possibility of Hybridogenesis in the Origin of Midge Chironomus usenicus Loginova et Beljanina (Chironomidae, Diptera). Russ. J. Genet. 2002, 38, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, M.T.; Balke, M.; Pons, J.; Vogler, A.P. Beyond barcodes: Complex DNA taxonomy of a South Pacific Island radiation. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 273, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Bai, M.; Rivas-González, I.; Li, C.; Liu, S.; Tong, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, G.; Xie, D.; Sears, K.E.; et al. Incomplete lineage sorting and phenotypic evolution in marsupials. Cell 2022, 185, 1646–1660.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, R.A.; Cruickshank, R.H. The seven deadly sins of DNA barcoding. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 13, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.M.; Gonçalves, L.T. Getting science priorities straight: How to increase the reliability of specimen identification? Biol. Lett. 2021, 17, 20200874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadawski, P. Species Diversity and Origin of Non-Biting Midges (Chironomidae) from a Geologically Young Lake and Its Old Spring System. PhD Thesis, University of Lodz, Łódź, Poland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Bock, D.G.; Prosser, S.W.J. Interrogating 1000 insect genomes for NUMTs: A risk assessment for estimates of species richness. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartop, E.; Srivathsan, A.; Ronquist, F.; Meier, R. Towards Large-Scale Integrative Taxonomy (LIT): Resolving the Data Conundrum for Dark Taxa. Syst. Biol. 2022, 71, 1404–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Klink, R.; August, T.; Bas, Y.; Bodesheim, P.; Bonn, A.; Fossøy, F.; Høye, T.T.; Jongejans, E.; Menz, M.H.; Miraldo, A.; et al. Emerging technologies revolutionise insect ecology and monitoring. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2022, 37, 872–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milošević, D.; Milosavljević, A.; Predić, B.; Medeiros, A.S.; Savić-Zdravković, D.; Piperac, M.S.; Kostić, T.; Spasić, F.; Leese, F. Application of deep learning in aquatic bioassessment: Towards automated identification of non-biting midges. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 135160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Order * | Species Identification | Specimens | Total Countries | Total BINs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | Rheotanytarsus pellucidus | 37 | 2 | 6 |
| 3 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 2 | 55 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | Rheotanytarsus pentapoda | 57 | 6 | 12 |
| 5 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 3 | 35 | 3 | 3 |
| 6 | Rheotanytarsus ringei | 195 | 3 | 1 |
| 7 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 8 | Rheotanytarsus ashei | 17 | 1 | 3 |
| 9 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 5XL | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 10 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 5 | 51 | 1 | 2 |
| 11 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 6 | 38 | 1 | 1 |
| 12 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 13 | Rheotanytarsus yamamotoi | 20 | 1 | 7 |
| 14 | Rheotanytarsus diaoluoensis | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 15 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 11XL | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 16 | Rheotanytarsus baihualingensis | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| 17 | Rheotanytarsus muscicola | 45 | 5 | 2 |
| 18 | Rheotanytarsus curtistylus | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 19 | Rheotanytarsus oss | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 20 | Rheotanytarsus vallenduuki | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 21 | Rheotanytarsus ferringtoni | 5 | 1 | 1 |
| 22 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 19XL | 28 | 1 | 1 |
| 23 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 3XL | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 24 | Rheotanytarsus guoae | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 25 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 6XL | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 26 | Rheotanytarsus fluminis | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 27 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 2XL | 11 | 4 | 1 |
| 28 | Rheotanytarsus photophilus | 5 | 1 | 1 |
| 29 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 17XL | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 30 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 13XL | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| 31 | Rheotanytarsus yueqingensis | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 32 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 9XL | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 33 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 12XL | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 34 | Rheotanytarsus miaoae | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 35 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 20XL | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 36 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 14XL | 9 | 1 | 1 |
| 37 | Rheotanytarsus cangshanensis | 8 | 1 | 1 |
| 38 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 21XL | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 39 | Rheotanytarsus illiesi | 6 | 1 | 3 |
| 40 | Rheotanytarsus qiangi | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 41 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 24XL | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| 42 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 8XL | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 43 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 16XL | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 44 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 23XL | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 45 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 15XL | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 46 | Rheotanytarsus adjectus | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 47 | Rheotanytarsus guanacastensis | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 48 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 3TE | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 49 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 2TE | 5 | 2 | 1 |
| 50 | Rheotanytarsus pellucidus | 13 | 1 | 2 |
| 51 | Rheotanytarsus sp. TE01 | 40 | 1 | 1 |
| 52 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 8 | 38 | 2 | 2 |
| 53 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 9 | 45 | 2 | 1 |
| 54 | Rheotanytarsus exiguus group sp. | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 55 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 7XL | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 56 | Rheotanytarsus sp. TE-2006 | 31 | 2 | 1 |
| 57 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 10 | 6 | 2 | 1 |
| 58 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 11 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 59 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 22XL | 5 | 2 | 1 |
| 60 | Rheotanytarsus cf. ringei | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 61 | Rheotanytarsus yui | 5 | 1 | 1 |
| 62 | Rheotanytarsus pinderi | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 63 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 4XL | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 64 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 1XL | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 65 | Rheotanytarsus falcipedius | 5 | 1 | 1 |
| 66 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 18XL | 4 | 1 | 2 |
| 67 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 10XL | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 68 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 12 | 18 | 1 | 2 |
| 69 | Rheotanytarsus sp. 13 | 5 | 1 | 3 |
| Total | 911 | 15 | 109 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, Y.; Chen, J.-Y.; Gong, X.-L.; Li, C.-H.; Liu, Z.; Lin, X.-L. Species Delimitation and Cryptic Diversity in Rheotanytarsus Thienemann & Bause, 1913 (Diptera: Chironomidae) Based on DNA Barcoding. Insects 2025, 16, 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040370
Yao Y, Chen J-Y, Gong X-L, Li C-H, Liu Z, Lin X-L. Species Delimitation and Cryptic Diversity in Rheotanytarsus Thienemann & Bause, 1913 (Diptera: Chironomidae) Based on DNA Barcoding. Insects. 2025; 16(4):370. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040370
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Yuan, Jia-Yu Chen, Xiao-Ling Gong, Chen-Hong Li, Zheng Liu, and Xiao-Long Lin. 2025. "Species Delimitation and Cryptic Diversity in Rheotanytarsus Thienemann & Bause, 1913 (Diptera: Chironomidae) Based on DNA Barcoding" Insects 16, no. 4: 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040370
APA StyleYao, Y., Chen, J.-Y., Gong, X.-L., Li, C.-H., Liu, Z., & Lin, X.-L. (2025). Species Delimitation and Cryptic Diversity in Rheotanytarsus Thienemann & Bause, 1913 (Diptera: Chironomidae) Based on DNA Barcoding. Insects, 16(4), 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040370






