An Overview of the Adverse Impacts of Old Combs on Honeybee Colonies and Recommended Beekeeping Management Strategies
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biological Functions of Combs
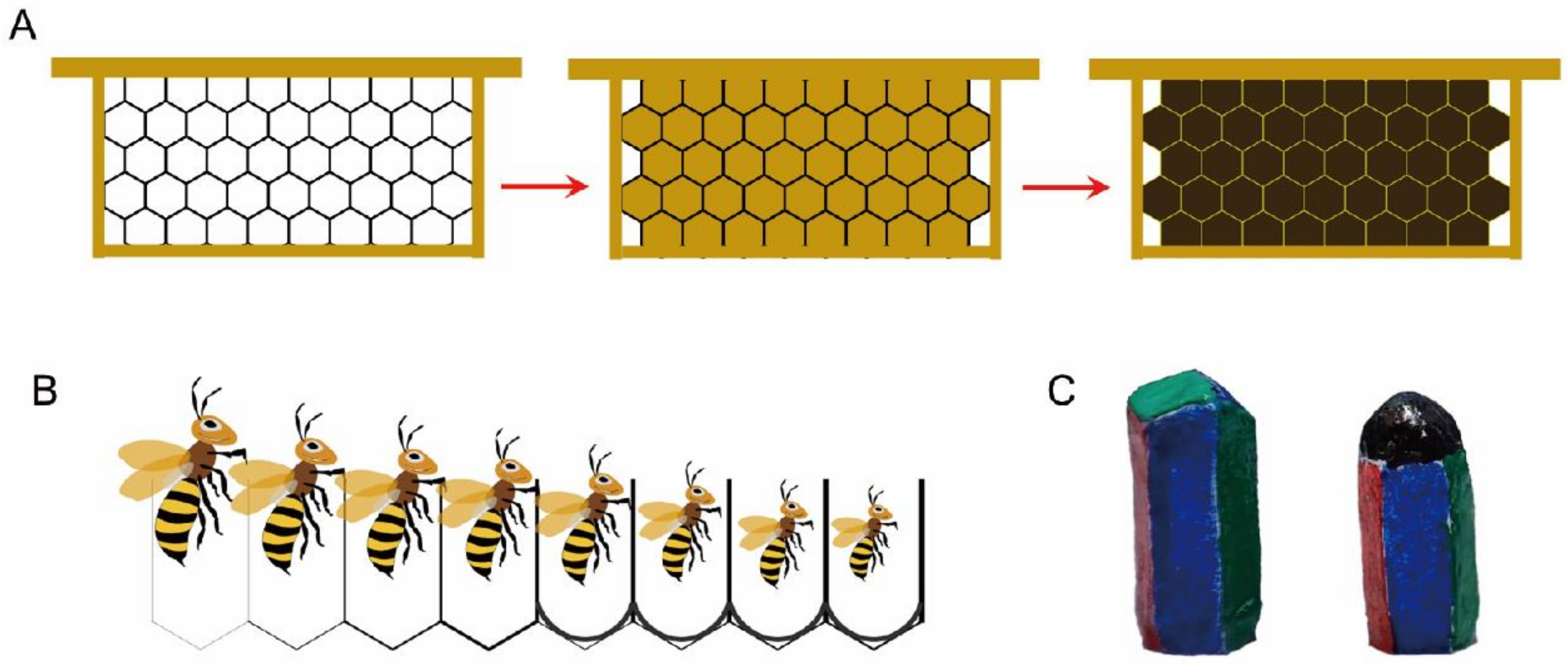
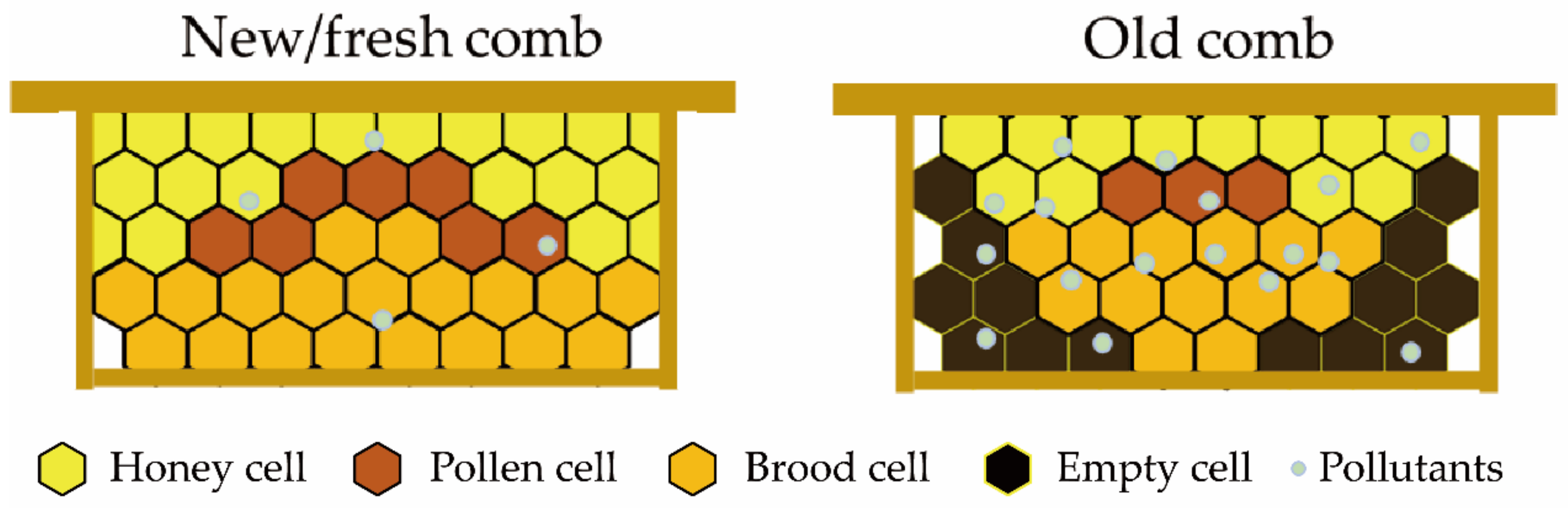
3. Aging Process of the Comb
3.1. Color Changes in the Comb
3.2. Structural Changes in the Comb Cells
3.3. Effects of Old Combs on the External Morphological Traits of the Workers
3.4. Impact of Old Combs on Colony Strength and Production Performance
3.5. Impact of Old Combs on the Quality of Bee Products
3.6. Accumulation of Environmental Pollutants in Old Combs
4. Bee Adaptations in Old Combs
4.1. Behavioral Adaptations to Structural Degradation
4.2. Molecular Mechanisms of Pollutant Detoxification
5. Beekeeping Management Practices
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khalifa, S.A.M.; Elshafiey, E.H.; Shetaia, A.A.; El-Wahed, A.A.A.; Algethami, A.F.; Musharraf, S.G.; AlAjmi, M.F.; Zhao, C.; Masry, S.H.D.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; et al. Overview of bee pollination and its economic value for crop production. Insects 2021, 12, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hepburn, H.R.; Pirk, C.W.W.; Duangphakdee, O. Honeybee Nests; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Fattah, M.A.A.-W.A.; Ibrahim, Y.Y.; Haggag, M.I. Some biological aspects of honey bee colonies in relation to the age of beeswax combs. J. Apic. Res. 2021, 60, 405–413. [Google Scholar]
- Taha, E.-K.A.; Rakha, O.M.; Elnabawy, E.-S.M.; Hassan, M.M.; Shawer, D.M.B. Comb age significantly influences the productivity of the honeybee (Apis mellifera) colony. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2021, 33, 101436. [Google Scholar]
- Hepburn, H.R.; Kurstjens, S.P. The combs of honeybees as composite materials. Apidologie 1988, 19, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Schmickl, T.; Crailsheim, K. Inner nest homeostasis in a changing environment with special emphasis on honey bee brood nursing and pollen supply. Apidologie 2004, 35, 249–263. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.J.F.; Paxton, R.J. The conservation of bees: A global perspective. Apidologie 2009, 40, 410–416. [Google Scholar]
- Feldhaar, H.; Otti, O. Pollutants and their interaction with diseases of social Hymenoptera. Insects 2020, 11, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassona, N.M.; El-Wahed, A.A.A. Heavy metal concentrations of beeswax (Apis mellifera L.) at different ages. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2023, 111, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Ravoet, J.; Reybroeck, W.; de Graaf, D.C. Pesticides for apicultural and/or agricultural application found in Belgian honey bee wax combs. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 94, 543–548. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Yang, S.; Huang, R.; Yang, L.; Xun, L.; Tian, Y.; Gong, X.; Wang, J.; Kuang, H.; Zhao, W.; et al. The significance of Apis cerana cerana (Hymenoptera: Apidae) gnawing off the old brood cells. Apidologie 2023, 54, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Duan, H.; Karihaloo, B.L.; Wang, J. Hierarchical, multilayered cell walls reinforced by recycled silk cocoons enhance the structural integrity of honeybee combs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9502–9506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dizaji, A.A.; Alishah, H.M.; Shaddel, A.-A.; Sis, N.M. Effects of comb wax age on the brood and honey product performance in honey bee. Asian J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2008, 3, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, E.-K.; Elsanat, S. Effect of combs age on honey production and its physical and chemical properties. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference of the Entomological Society of Egypt, Giza, Egypt, 8–11 December 2007; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Huang, R.; Li, H.; Gong, X.; Yue, D.; Jiang, W.; Tian, Y.; Dong, K. Analysis of comb-gnawing behavior in Apis cerana cerana (Hymenoptera: Apidae). J. Insect Sci. 2024, 24, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepburn, H.R.; Bernard, R.T.F.; Davidson, B.C.; Muller, W.J.; Lloyd, P.; Kurstjens, S.P.; Vincent, S.L. Synthesis and secretion of beeswax in honeybees. Apidologie 1991, 22, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeder, R.; Schwabe, D. The upward tilt of honeycomb cells increases the carrying capacity of the comb and is not to prevent the outflow of honey. Apidologie 2020, 52, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortis, G.; Frizzera, D.; Seffin, E.; Annoscia, D.; Nazzi, F. Honeybees use various criteria to select the site for performing the waggle dances on the comb. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2019, 73, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, K. Natural supersedure of queens in honey bee colonies. Bee World 2010, 87, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Deng, S.; Kuang, H.; Zhou, D.; Gong, X.; Dong, K. Evaluating and comparing the natural cell structure and dimensions of honey bee comb cells of Chinese bee, Apis cerana cerana (hymenoptera: Apidae) and Italian bee, Apis mellifera ligustica (hymenoptera: Apidae). J. Insect Sci. 2021, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, M.L. The Biology of the Honey Bee; Harvard University Press: London, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.; Huang, W. Apiculture in the new China. Bee World 1981, 62, 163–166. [Google Scholar]
- Fratini, F.; Cilia, G.; Turchi, B.; Felicioli, A. Beeswax: A minireview of its antimicrobial activity and its application in medicine. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svečnjak, L.; Chesson, L.A.; Gallina, A.; Maia, M.; Martinello, M.; Mutinelli, F.; Muz, M.N.; Nunes, F.M.; Saucy, F.; Tipple, B.J.; et al. Standard methods for Apis mellifera beeswax research. J. Apic. Res. 2019, 58, 1–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Meng, Q.; Zhi, D.; Deng, S.; Zhao, W.; Tian, Y.; Gong, X.; Dong, K. Comb cell structure and morphological characteristics of the Chinese honey bee, Apis cerana cerana (Hymenoptera: Apidae), under successive generations. J. Econ. Entomol. 2023, 116, 352–358. [Google Scholar]
- Bonvehi, J.S.; Orantes-Bermejo, F.J. Discoloration and adsorption of acaricides from beeswax. J. Food Process Eng. 2017, 40, e12344. [Google Scholar]
- Maia, M.; Nunes, F.M. Authentication of beeswax (Apis mellifera) by high-temperature gas chromatography and chemometric analysis. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bogdanov, S. Beeswax: Production, Properties, Composition, Control. In Beeswax Book; Bee Product Science Publishing: Muehlethurnen, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jay, S.C. The development of honeybees in their cells. J. Apic. Res. 1963, 2, 117–134. [Google Scholar]
- Jay, S.C. The cocoon of the honey bee, Apis mellifera L. Can. Entomol. 1964, 96, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, B.A.; Busby, M.K. Slumber in a cell: Honeycomb used by honey bees for food, brood, heating… and sleeping. PeerJ 2020, 5, e9583. [Google Scholar]
- Hepburn, H.R.; Muerrle, T.; Radloff, S.E. The cell bases of honeybee combs. Apidologie 2007, 38, 268–271. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, J.M. The Hive and the Honey Bee; Dadant & Sons: Hamilton, IL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Elnabawy, E.M.; Mousa, K.M.; Ueno, T.; Shawer, M.B. Impact of different comb age on morphological and biological characteristics of honeybee workers (Apis Mellifera L.). J.-Fac. Agric. Kyushu Univ. 2020, 65, 277–282. [Google Scholar]
- Ruttner, F. Biogeography and Taxonomy of Honeybees; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, F.G. The races of honeybees in Africa. Bee World 1961, 42, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Dutton, R.W.; Ruttner, F.; Berkeley, A.; Manley, M.J.D. Observations on the morphology, relationships and ecology of Apis Mellifera of Oman. J. Apic. Res. 1981, 20, 201–214. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.S.; Kaushik, H.D.; Rohilla, H.R. Nesting behaviour of the rock bee, Apis dorsata at Hisar, India: II-height and directional preferences for comb building. Indian Bee J. 2007, 69, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Starr, C.K. Encyclopedia of Social Insects; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Free, J.B. Biology and behaviour of the honeybee Apis Florea, and possibilities for beekeeping. Bee World 1981, 62, 46–59. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Shao, L.; Raza, M.F.; Han, R.; Li, W. The effect of comb cell size on the development of Apis mellifera drones. Life 2024, 14, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Deng, S.; Meng, Q.; Yang, S.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, W.; Tian, Y.; Dong, K.; Gong, X. Impact of Apis cerana cerana (Hymenoptera: Apidae) body size on newly built cell size. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2024, 27, 102277. [Google Scholar]
- Volosevich, A.P.; Kulzhinskaya, K.P. Improved rearing of bees by changing the feeding conditions. Bee World 1957, 38, 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Abdellatif, M. Comb cell size and its effect on the body weight of the worker bee, Apis mellifera L. Am. Bee J. 1965, 105, 86–87. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, J.A.; Delaplane, K.S. Effects of comb age on honey bee colony growth and brood survivorship. J. Apic. Res. 2001, 40, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sipos, T.; DonkÓ, T.; CsÓka, Á.; Kiss, T.; Keszthelyi, S. Comparative micro-computed tomographic analysis of the structure of brood cells and its effect on the development of the pupae of honey bee (Apis mellifera). Eur. J. Entomol. 2023, 120, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- AL-Kahtani, S.N. Morphometric characteristics of carniolan honeybee workers in relation to age of comb. Sci. J. King Faisal Univ. (Basic Appl. Sci.) 2018, 19, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Nazzi, F. The hexagonal shape of the honeycomb cells depends on the construction behavior of bees. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28341. [Google Scholar]
- AlKahtani, S.N.; Taha, E.A. Morphometric study of Yemeni (Apis mellifera jemenitica) and Carniolan (A. m. carnica) honeybee workers in Saudi Arabia. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247262. [Google Scholar]
- Dizaji, A.A.; Sis, N.M.; Tili, A.S.; Golshani, A.A. Effect of comb wax age on brood performance or population of honey bee, Apis melifera. Agroecol. J. 2009, 5, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Taha, E.; Al-Kahtani, S.N. The relationship between comb age and performance of honey bee (Apis mellifera) colonies. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 27, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapla, U.M.; Solayman, M.; Alam, N.; Khalil, M.I.; Gan, S.H. 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) levels in honey and other food products: Effects on bees and human health. Chem. Cent. J. 2018, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miquelena, E.; Piccirillo, G.; Rodriguez, B. Influence of comb age on some physical-chemical properties of honeys produced by African bees. Rev. De La Fac. De Agron. 2010, 27, 626–638. [Google Scholar]
- Taha, E.-K.A.; Manosur, H.M.; Shawer, M.B. The relationship between comb age and the amounts of mineral elements in honey and wax. J. Apic. Res. 2010, 49, 202–207. [Google Scholar]
- Fröhlich, B.; Tautz, J.; Riederer, M. Chemometric classification of comb and cuticular waxes of the honeybee Apis mellifera carnica. J. Chem. Ecol. 2000, 26, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Khan, N. Does adoption of honeybee pollination promote the economic value of kiwifruit farmers? Evidence from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eeraerts, M.; DeVetter, L.W.; Batáry, P.; Ternest, J.J.; Mallinger, R.; Arrington, M.; Benjamin, F.E.; Blaauw, B.R.; Campbell, J.W.; Cavigliasso, P.; et al. Synthesis of highbush blueberry pollination research reveals region-specific differences in the contributions of honeybees and wild bees. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 60, 2528–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Nowak, I. Review of harmful chemical pollutants of environmental origin in honey and bee products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 5094–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinello, M.; Manzinello, C.; Dainese, N.; Giuliato, I.; Gallina, A.; Mutinelli, F. The honey bee: An active biosampler of environmental pollution and a possible warning biomarker for human health. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Huang, R.; Yang, S.; Li, H.; Yue, D.; Gong, X.; Zhao, W.; Tian, Y.; Dong, K. Impact of brood cell cocoons on metal accumulation and CYP450 detoxification gene expression in Apis cerana cerana. Toxics 2024, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Latorre, C.; Barciela-García, J.; García-Martín, S.; Peña-Crecente, R.M. The use of honeybees and honey as environmental bioindicators for metals and radionuclides: A review. Environ. Rev. 2017, 25, 463–480. [Google Scholar]
- Bargańska, Ż.; Ślebioda, M.; Namieśnik, J. Honey bees and their products: Bioindicators of environmental contamination. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 235–248. [Google Scholar]
- Gajger, I.T.; Kosanović, M.; Oreščanin, V.; Kos, S.; Bilandžić, N. Mineral content in honeybee wax combs as a measurement of the impact of environmental factors. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 103, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scivicco, M.; Nolasco, A.; Esposito, L.; Ariano, A.; Squillante, J.; Esposito, F.; Cirillo, T.; Severino, L. Effects of COVID-19 pandemic lockdown and environmental pollution assessment in Campania region (Italy) through the analysis of heavy metals in honeybees. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizaw, G.; Kim, Y.; Moon, K.; Choi, J.B.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, J.K. Effect of environmental heavy metals on the expression of detoxification-related genes in honey bee Apis mellifera. Apidologie 2020, 51, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Long, H.; Ma, X.; Shariati, K.; Webb, J.; Guo, L.; Pan, Y.; Ma, M.; Deng, C.; et al. Global honeybee health decline factors and potential conservation techniques. Food Secur. 2023, 15, 855–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkassab, A.T.; Bischoff, G.; Thorbahn, D.; Frommberger, M.; Pistorius, J. Transfer of xenobiotics from contaminated beeswax into different bee matrices under field conditions and the related exposure probability. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135615. [Google Scholar]
- Wallner, K. Varroacides and their residues in bee products. Apidologie 1999, 30, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medici, S.K.; Castro, A.; Sarlo, E.G.; Marioli, J.M.; Eguaras, M.J. The concentration effect of selected acaricides present in beeswax foundation on the survival of Apis mellifera colonies. J. Apic. Res. 2012, 51, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Таранoв, Г.Φ. Биoлoгия Пчелинoй Семьи; 1961, Сельхoзиздат: Гoссельхoзиздат. 1-331. Available online: https://tochok.info/files/file/121-%D1%82%D0%B0%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B2-%D0%B3-%D1%84-%D0%B1%D0%B8%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%B8%D1%8F-%D0%BF%D1%87%D0%B5%D0%BB%D0%B8%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B9-%D1%81%D0%B5%D0%BC%D1%8C%D0%B8-1961/ (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Gong, Y.; Diao, Q. Current knowledge of detoxification mechanisms of xenobiotic in honey bees. Ecotoxicology 2017, 26, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Zhang, W.; Liu, F.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Xu, B. Characterization of an Apis cerana cerana cytochrome P450 gene (AccCYP336A1) and its roles in oxidative stresses responses. Gene 2016, 584, 120–128. [Google Scholar]
- Rand, E.E.d.; Smit, S.; Beukes, M.; Apostolides, Z.; Pirk, C.W.W.; Nicolson, S.W. Detoxification mechanisms of honey bees (Apis mellifera) resulting in tolerance of dietary nicotine. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11779. [Google Scholar]
- Amezian, D.; Nauen, R.; Le Goff, G. Transcriptional regulation of xenobiotic detoxification genes in insects—An overview. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 174, 104822. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, J.D.; Graham, J.R.; Mortensen, A. Standard methods for wax moth research. J. Apic. Res. 2013, 52, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Kwadha, C.A.; Ong’amo, G.O.; Ndegwa, P.N.; Raina, S.K.; Fombong, A.T. The biology and control of the greater wax moth, Galleria mellonella. Insects 2017, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Hortal, M.D.; Orantes-Bermejo, F.J.; Sánchez-González, C.; Varela-López, A.; Giampieri, F.; Torres Fernández-Piñar, C.; Serra-Bonvehí, J.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Reboredo-Rodríguez, P.; Llopis, J.; et al. Industrial-scale decontamination procedure effects on the content of acaricides, heavy metals and antioxidant capacity of beeswax. Molecules 2019, 24, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, A.; Alonso, R.; Cutillas, V.M.; Ferrer, C.M.; Gómez-Ramos, M.J.; Hernando, D.; Valverde, A.; Flores, J.M.; Fernández-Alba, A.R.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Removal of pesticide residues from beeswax using a methanol extraction-based procedure: A pilot-scale study. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101606. [Google Scholar]

| Honeybee Species | Average Cell Diameter (mm) | Citation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Worker | Drone | |||
| Apis mellifera | A. m. carnica | 5.51 | 6.91 | Ruttner, 1988 [35] |
| A. m. ligustica | 5.49 | 6.62 | Yang et al., 2021 [20] | |
| A. m. scutellata | 4.80 | 6.15 | Smith et al., 1961 [36] | |
| A. m. jemenitica | 4.75 | 6.19 | Dutton et al., 1981 [37] | |
| A. m. litorea | 4.62 | 6.15 | Ruttner, 1988 [35] | |
| Apis cerana | A. c. cerana | 4.82 | 5.62 | Yang et al., 2021 [20] |
| A. c. japonica | 4.78 | / | Ruttner, 1988 [35] | |
| A. c. indica | 4.37 | / | Ruttner, 1988 [35] | |
| Apis dorsata | 5.32 | / | Khan et al., 2007 [38] | |
| Apis laboriosa | 6.3 | / | Starr, 2021 [39] | |
| Apis florea | 2.7–3.1 | 4.2–4.8 | Free, 1981 [40] | |
| Apis andreniformis | 2.8 | 4.2 | Starr, 2021 [39] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, Q.; Huang, R.; Yang, S.; Jiang, W.; Tian, Y.; Dong, K. An Overview of the Adverse Impacts of Old Combs on Honeybee Colonies and Recommended Beekeeping Management Strategies. Insects 2025, 16, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040351
Meng Q, Huang R, Yang S, Jiang W, Tian Y, Dong K. An Overview of the Adverse Impacts of Old Combs on Honeybee Colonies and Recommended Beekeeping Management Strategies. Insects. 2025; 16(4):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040351
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Qingxin, Rong Huang, Shunhua Yang, Wutao Jiang, Yakai Tian, and Kun Dong. 2025. "An Overview of the Adverse Impacts of Old Combs on Honeybee Colonies and Recommended Beekeeping Management Strategies" Insects 16, no. 4: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040351
APA StyleMeng, Q., Huang, R., Yang, S., Jiang, W., Tian, Y., & Dong, K. (2025). An Overview of the Adverse Impacts of Old Combs on Honeybee Colonies and Recommended Beekeeping Management Strategies. Insects, 16(4), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040351







