Abundance of the Dominant Endosymbiont Rickettsia and Fitness of the Stored-Product Pest Liposcelis bostrychophila (Psocoptera: Liposcelididae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect
2.2. Metagenomic Sequencing
2.2.1. DNA Extraction
2.2.2. Library Preparation for Sequencing
2.2.3. Data Assessment and Quality Control
2.2.4. Metagenome Assembly and Binning
2.2.5. Gene Prediction and Non-Redundant Gene Set Construction
2.2.6. Species Annotations
2.3. Construction of Diverse Rickettsia Abundance System
2.4. Fitness of L. bostrychophila at Varying Levels of Rickettsia Abundance
2.5. Data Statistics and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dominant Symbiotic Bacterial Species in L. bostrychophila
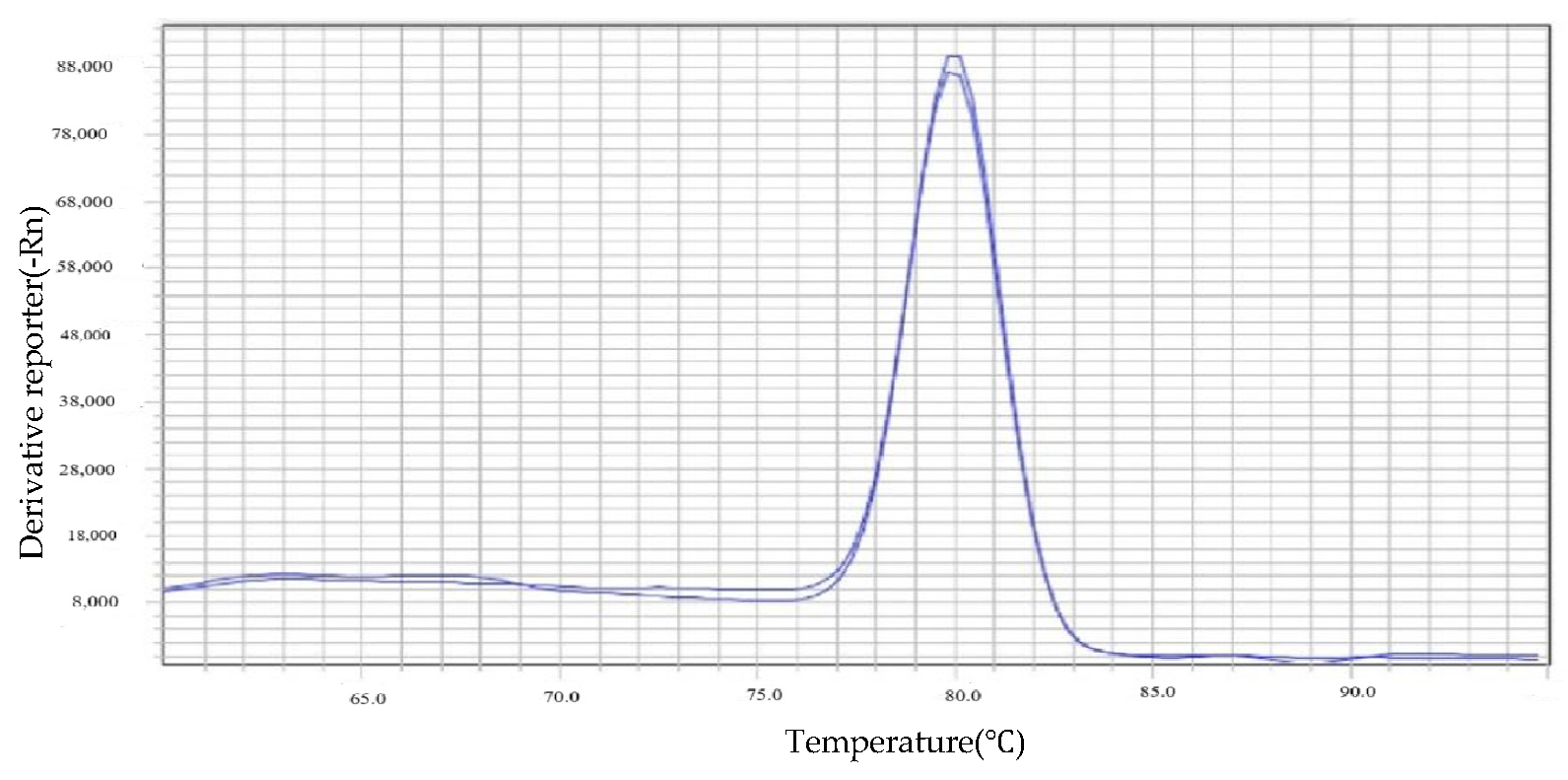
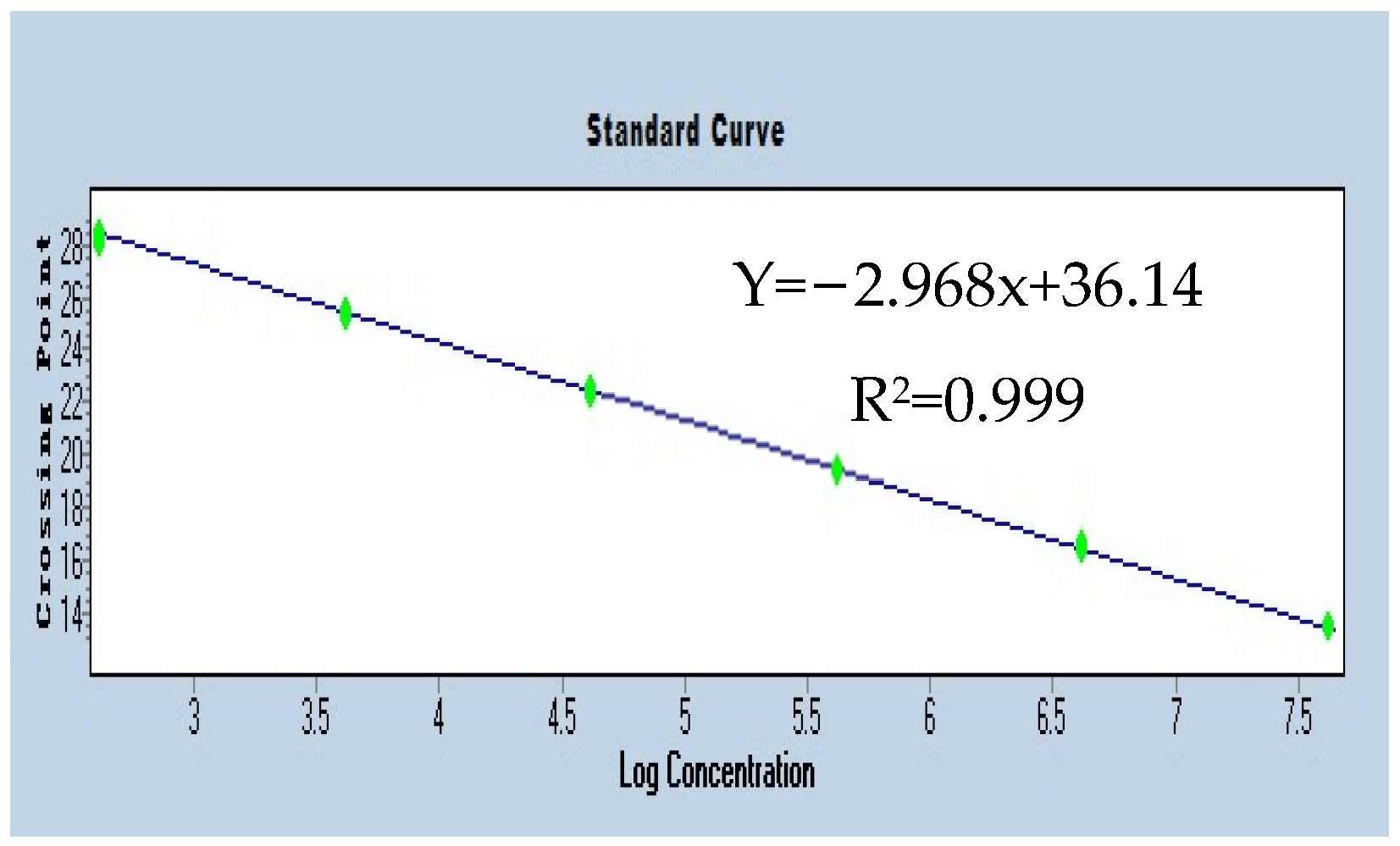
3.2. Quantification of Rickettsia
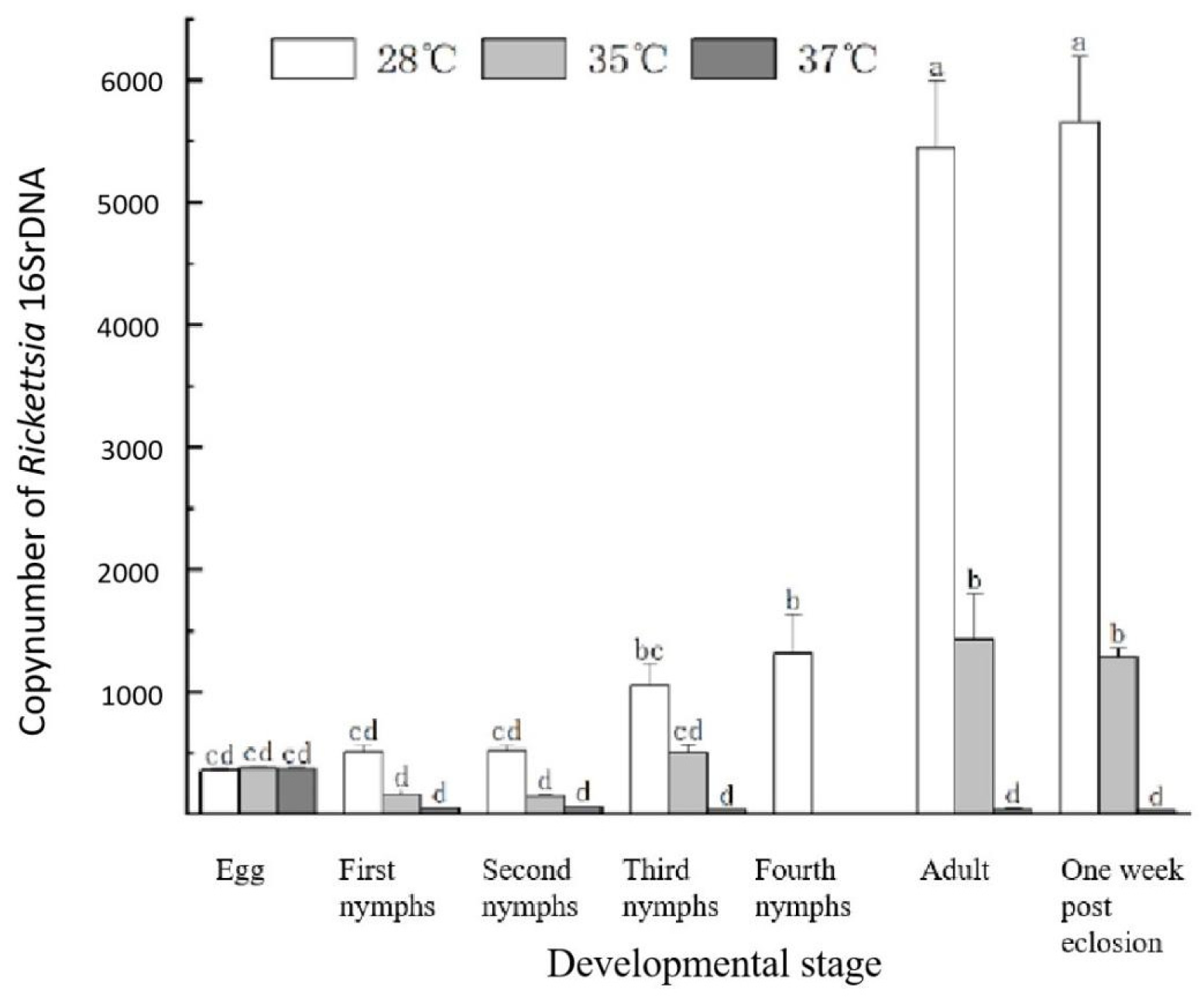
3.3. Diverse Rickettsia Abundance System
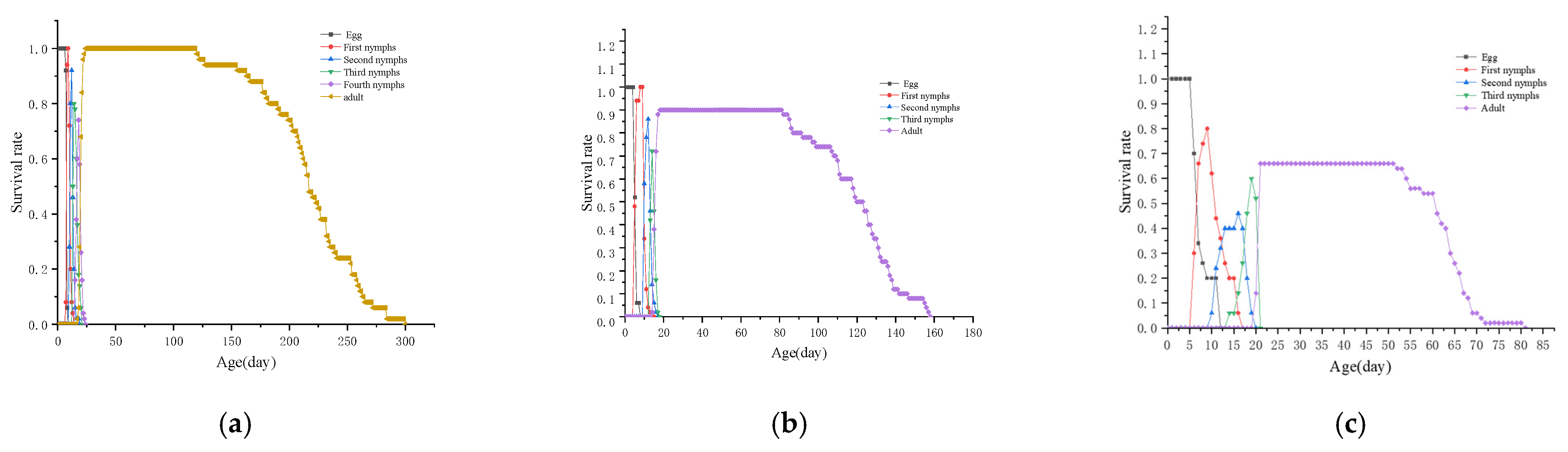
3.4. Life Table Parameters of L. bostrychophila at Varying Levels of Rickettsia Abundance
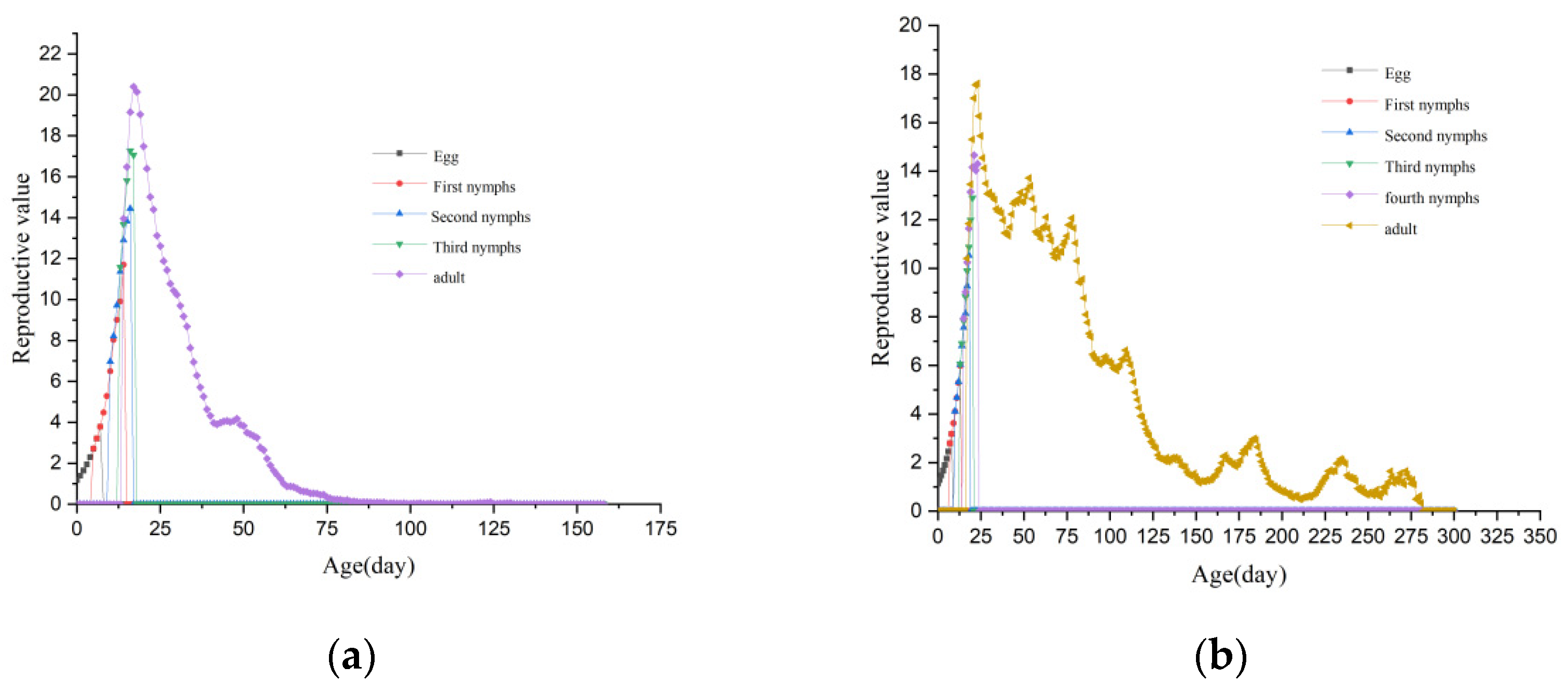
3.5. Population Parameters of L. bostrychophila at Varying Levels of Rickettsia Abundance
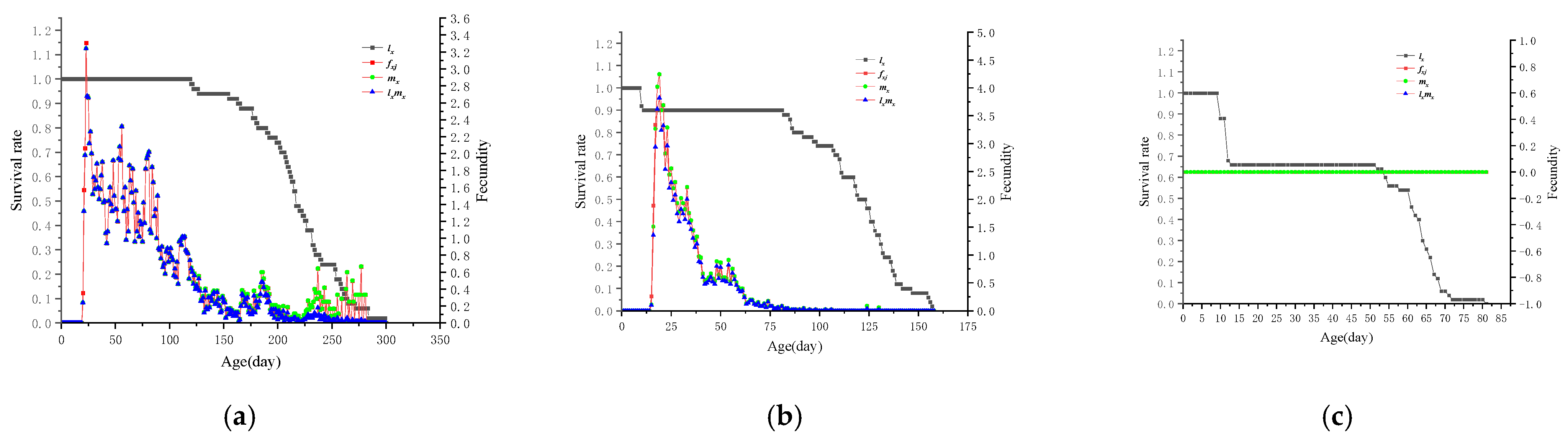
3.6. Sxj of L. bostrychophila at Varying Levels of Rickettsia Abundance
3.7. lx and mx of L. bostrychophila at Varying Levels of Rickettsia Abundance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abu El-Hassan, G.M.M.; Alfarraj, S.A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Atiya, N.H. Survey of insect pests in the manuscripts library of Coptic museum in Egypt. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 5061–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Gu, A.; Wei, L. Regularity in distribution, and control, of pests in the hall of mental cultivation, the Forbidden City, Beijing, China. Herit. Sci. 2021, 9, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmedani, M.S.; Shagufta, N.; Muhammad, A.; Hussnain, A. Psocid: A new risk for global food security and safety. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2010, 45, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kučerová, Z. Weight losses of wheat grain caused by psocid infestation (Liposcelis bostrychophila: Liposcelididae: Psocoptera). Plant Prot. Sci. 2002, 38, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, M.K.; Collins, P.J.; Throne, J.E.; Wang, J.J. Biology and management of psocids infesting stored products. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2014, 59, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.D.; Maude-Roxby, H. Starvation survival of the stored product pest L. bostrychophila Badonnel (Psocoptera, Liposcelidae). J. Stored Prod. Res. 1988, 24, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukutomi, Y.; Kawakami, Y.; Taniguchi, M.; Saito, A.; Fukuda, A.; Yasueda, H.; Nakazawa, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Nakamura, H.; Akiyama, K. Allergenicity and cross-reactivity of booklice (Liposcelis bostrichophila): A common household insect pest in Japan. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 157, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediannikov, O.; Bechah, Y.; Amanzougaghene, N.; Lepidi, H.; Bassene, H.; Sambou, M.; Lienhard, C.; Benkacimi, L.; Dieme, C.; Sokhna, C. Booklice L. bostrychophila naturally infected by Rickettsia felis cause fever and experimental pneumonia in mammals. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 226, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, O.; Sakuragi, K.; Fukutomi, Y.; Kawakami, Y.; Kamata, Y.; Sakurai, M.; Nakayama, S.; Uchiyama, H.; Kobayashi, H.; Kojima, H. Lip b 1 is a novel allergenic protein isolated from the booklouse, L. bostrychophila. Allergy 2017, 72, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.-D.; He, W.; Miao, Z.Q.; Tu, Y.Q.; Wang, L.; Dou, W.; Wang, J.J. Characterization of esterase genes involving malathion detoxification and establishment of an RNA interference method in L. bostrychophila. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoso, T.; Sunjaya, S.; Dharmaputra, O.; Halid, H.; Hodges, R. Pest management of psocids in milled rice stores in the humid tropics. Int. J. Pest Manag. 1996, 42, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, Z.; Lizé, A. Insect behaviour and the microbiome. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 9, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, J.P. The genomics and cell biology of host-beneficial intracellular infections. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 37, 115–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, N.; Baumann, P. Phylogenetics of cytoplasmically inherited microorganisms of arthropods. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1994, 9, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, N.A.; McCutcheon, J.P.; Nakabachi, A. Genomics and evolution of heritable bacterial symbionts. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 165–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, C.; Moran, N.A. Molecular interactions between bacterial symbionts and their hosts. Cell 2006, 126, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, P. Biology of bacteriocyte-associated endosymbionts of plant sap-sucking insects. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 59, 155–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, A.E. Multiorganismal insects: Diversity and function of resident microorganisms. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2015, 60, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukasik, P.; Kolasa, M.R. With a little help from my friends: The roles of microbial symbionts in insect populations and communities. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2024, 379, 20230122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, E.; Mercer, D.R.; Dobson, S.L. Life-shortening Wolbachia infection reduces population growth of Aedes aegypti. Acta Trop. 2017, 172, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.Q.; Montllor, C.B.; Purcell, A.H. Fitness effects of two facultative endosymbiotic bacteria on the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum, and the blue alfalfa aphid, A. kondoi. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2000, 95, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickin, M.L.; Kakumanu, M.L.; Schal, C. Effects of Wolbachia Elimination and B-Vitamin Supplementation on Bed Bug Development and Reproduction. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgini, M.; Bernardo, U.; Monti, M.; Nappo, A.; Gebiola, M. Rickettsia symbionts cause parthenogenetic reproduction in the parasitoid wasp Pnigalio soemius (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2589–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Hayatsu, M.; Hosokawa, T.; Nagayama, A.; Tago, K.; Fukatsu, T. Symbiont-mediated insecticide resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8618–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brumin, M.; Kontsedalov, S.; Ghanim, M. Rickettsia influences thermotolerance in the Whitefly Bemisia tabaci B biotype. Insect Sci. 2011, 18, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, S.L.; Giordano, R.; Colbert, A.; Karr, T.L.; Robertson, H.M. 16S rRNA phylogenetic analysis of the bacterial endosymbionts associated with cytoplasmic incompatibility in insects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 2699–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, H.S.; Singh, A.; Popli, S.; Pandey, N.; Rajagopal, R. Infection of bacterial endosymbionts in insects: A comparative study of two techniques viz PCR and FISH for detection and localization of symbionts in Whitefly, Bemisia tabaci. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyomar, C.; Legeai, F.; Jousselin, E.; Mougel, C.; Lemaitre, C.; Simon, J.C. Multi-scale characterization of symbiont diversity in the pea aphid complex through metagenomic approaches. Microbiome 2018, 6, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellappan, M.; Ranjith, M.T. Metagenomic approaches for insect symbionts. In Microbial Approaches for Insect Pest Management; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 271–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedoluzhko, A.V.; Sharko, F.S.; Tsygankova, S.V.; Boulygina, E.S.; Sokolov, A.S.; Rastorguev, S.M.; Kadnikov, V.V.; Mardanov, A.V.; Ravin, N.V.; Mazur, A.N. Metagenomic analysis of microbial community of a parasitoid wasp Megaphragma amalphitanum. Genom. Data 2017, 11, 87–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethu, S.; Jayaprakas, C.A.; Harish, E.R. Metagenomic DNA analysis of bacterial communities associated with striped mealy bugs, Ferrisia virgata (Cockerell) (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae) infesting Cassava. J. Entomol. Res. 2023, 47, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, K.; Humińska, K.; Wojciechowicz, J.; Tryjanowski, P. Metagenomic survey of bacteria associated with the invasive ladybird Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2017, 114, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, H.J.; Ramos Aguila, L.C.; Akutse, K.S.; Ilyas, M.; Abbasi, A.; Li, X.; Wang, L. Comparative microbiome analysis of Diaphorina citri and its associated parasitoids Tamarixia radiata and Diaphorencyrtus aligarhensis reveals Wolbachia as a dominant endosymbiont. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 1638–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, M.; Turner, B.S.; Whitfield, P.J.; Miles, R.J.; Pacey, J.A. Electron microscopical evidence of a vertically transmitted Wolbachia-like parasite in the parthenogenetic, stored-product pest L. bostrychophila Badonnel (Psocoptera). J. Stored Prod. Res. 2000, 36, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, M.; Turner, B. Characterisation of Wolbachia-like bacteria isolated from the parthenogenetic stored-product pest psocid L. bostrychophila (Badonnel) (Psocoptera). J. Stored Prod. Res. 2004, 40, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikac, K.M. PCR Confirms Multiple Wolbachia Strain Infection in Australian and International Populations of the Invasive Stored-Product Psocid L. bostrychophila Badonnel. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2007, 43, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y. The Symbiotic Relationship of Several Psocid Species and Their Endosymbionts. Ph.D. Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Dong, P.; Xiao, L.S.; Dou, W. Effects of removal of Cardinium infection on fitness of the stored-product pest L. bostrychophila (Psocoptera: Liposcelididae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2008, 101, 1711–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perotti, M.A.; Clarke, H.K.; Turner, B.D.; Braig, H.R. Rickettsia as obligate and mycetomic bacteria. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 2372–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behar, A.; McCormick, L.J.; Perlman, S.J. Rickettsia felis Infection in a Common Household Insect Pest, L. bostrychophila (Psocoptera: Liposcelidae). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2280–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Kavousi, A.; Gharekhani, G.; Atlıhan, R.; Özgökçe, M.; Güncan, A.; Gökçe, A.; Smith, C.; Benelli, G.; Guedes, R.N.; et al. Advances in theory, data analysis, and application of the age-stage, two-sex life table for demographic research, biological control, and pest management. Entomol. Gen. 2023, 43, 705–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Güncan, A.; Kavousi, A.; Gharakhani, G.; Atlihan, R.; Özgökçe, M.S.; Shirazi, J.; Amir-Maafi, M.; Maroufpoor, M.; Taghizadeh, R. TWOSEX-MSChart: The key tool for life table research and education. Entomol. Gen. 2022, 42, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H. Life-table analysis incorporating both sexes and variable development rates among individuals. Environ. Entomol. 1988, 17, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; You, M.; Atlıhan, R.; Smith, C.L.; Kavousi, A.; Özgökçe, M.S.; Güncan, A.; Tuan, S.-J.; Fu, J.-W.; Xu, Y.-Y.; et al. Age-stage, two-sex life table: An introduction to theory, data analysis, and application. Entomol. Gen. 2020, 40, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Liu, H. Two new methods for the study of insect population ecology. Bull. Inst. Zool. Acad. Sin. 1985, 24, 225–240. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, F.X. Effect of Continuous High-Temperature Stress on the Symbiosis Rate of Wolbachia and Population Fitness in Liposcelis tricolor. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Throne, J.E.; Flinn, P.W. Distribution of Psocids (Psocoptera) in Temperature Gradients in Stored Wheat. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2013, 55, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shi, P.; An, X.; Qiu, B.L. Effects of the endosymbiont Rickettsia on the biological characteristics of whiteflies. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2020, 57, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.; He, Z.Q.; Wen, Q.; Chen, X.-Y.; Khan, M.M.; Osman, M.; Mandour, N.S.; Qiu, B.-L. Rickettsia Infection Benefits Its Whitefly Hosts by Manipulating Their Nutrition and Defense. Insects 2022, 13, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiel, E.; Inbar, M.; Mozes-Daube, N.; White, J.; Hunter, M.; Zchori-Fein, E. Assessments of Fitness Effects by the Facultative Symbiont Rickettsia in the Sweet potato Whitefly (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2009, 102, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurlovs, A.H.; Li, J.; Cheng, D.; Zhong, J. Ixodes pacificus Ticks Maintain Embryogenesis and Egg Hatching After Antibiotic Treatment of Rickettsia Endosymbiont. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagimori, T.; Abe, Y.; Date, S.; Miura, K. The first finding of a Rickettsia bacterium associated with parthenogenesis induction among insects. Curr. Microbiol. 2006, 52, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.Y.; Guo, C.L.; Chu, D. Research progress on the factors affecting microbial diversity in insects. J. Biol. Saf. 2019, 28, 170–176. [Google Scholar]

| Levels of Rickettsia Abundance | Developmental Periods (d) | Longevity (d) | Adult Preoviposition Period (d) | Oviposition Period (d) | Fecundity (Eggs/Female) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Egg (d) | First Nymphs (d) | Second Nymphs (d) | Third Nymphs (d) | Fourth Nymphs (d) | Nymph Period (d) | |||||
| LBhp | 7.98 ± 0.05 a | 3.06 ± 0.13 a | 2.78 ± 0.16 a | 3.42 ± 0.22 a | 2.94 ± 0.15 a | 12.2 ± 0.17 a | 217.4 ± 5.70 a | 1.54 ± 0.12 a | 176.66 ± 5.59 a | 155.56 ± 3.87 a |
| LBmp | 5.64 ± 0.11 b | 4.9 ± 0.18 b | 3.22 ± 0.14 a | 1.98 ± 0.12 b | — | 10.11 ± 0.19 b | 121.98 ± 3.00 b | 0.84 ± 0.14 b | 55.42 ± 2.87 b | 72.71 ± 2.06 b |
| LBlp | 6.87 ± 0.14 c | 5.8 ± 0.38 c | 4.45 ± 0.35 b | 3.18 ± 0.29 a | — | 13.88 ± 0.14 c | 63.88 ± 1.03 c | 0.00 ± 0.00 c | 0.00 ± 0.00 c | 0.00 ± 0.00 c |
| Parameter | Levels of Rickettsia Abundance | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| LBhp | LBmp | LBlp | |
| T | 39.27 ± 0.50 a | 25.11 ± 0.21 b | — |
| R0 | 155.56 ± 3.84 a | 65.44 ± 3.59 b | — |
| r | 0.13 ± 0.002 b | 0.17 ± 0.003 a | — |
| λ | 1.14 ± 0.002 b | 1.18 ± 0.003 a | — |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, C.; Duan, Y.; Zhao, C.; Yan, L.; Suthisut, D.; Lü, J.; Bai, Y.; Zeng, F.; Zhang, M. Abundance of the Dominant Endosymbiont Rickettsia and Fitness of the Stored-Product Pest Liposcelis bostrychophila (Psocoptera: Liposcelididae). Insects 2025, 16, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040349
Bai C, Duan Y, Zhao C, Yan L, Suthisut D, Lü J, Bai Y, Zeng F, Zhang M. Abundance of the Dominant Endosymbiont Rickettsia and Fitness of the Stored-Product Pest Liposcelis bostrychophila (Psocoptera: Liposcelididae). Insects. 2025; 16(4):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040349
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Chunqi, Yiwen Duan, Chao Zhao, Lei Yan, Duangsamorn Suthisut, Jianhua Lü, Yueliang Bai, Fangfang Zeng, and Meng Zhang. 2025. "Abundance of the Dominant Endosymbiont Rickettsia and Fitness of the Stored-Product Pest Liposcelis bostrychophila (Psocoptera: Liposcelididae)" Insects 16, no. 4: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040349
APA StyleBai, C., Duan, Y., Zhao, C., Yan, L., Suthisut, D., Lü, J., Bai, Y., Zeng, F., & Zhang, M. (2025). Abundance of the Dominant Endosymbiont Rickettsia and Fitness of the Stored-Product Pest Liposcelis bostrychophila (Psocoptera: Liposcelididae). Insects, 16(4), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040349






