Faunal and Ecological Analysis of Gamasid Mites (Acari: Mesostigmata) Associated with Small Mammals in Yunnan Province, Southwest China
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas
2.2. Collection and Identification of Gamasid Mites and Their Hosts
2.3. Statistics on Constituent Ratios and Community Indexes
2.4. Analysis of the Relationship Between Gamasid Mites and Their Hosts
2.5. Analyses of the Ecological Niches of Gamasid Mites
2.6. Analyses of the Interspecific Relationships of Gamasid Mites
2.7. Faunal Similarity Analysis
2.8. Estimation of Total Species
3. Results
3.1. Species Diversity and Faunal Distribution of Small Mammal Hosts
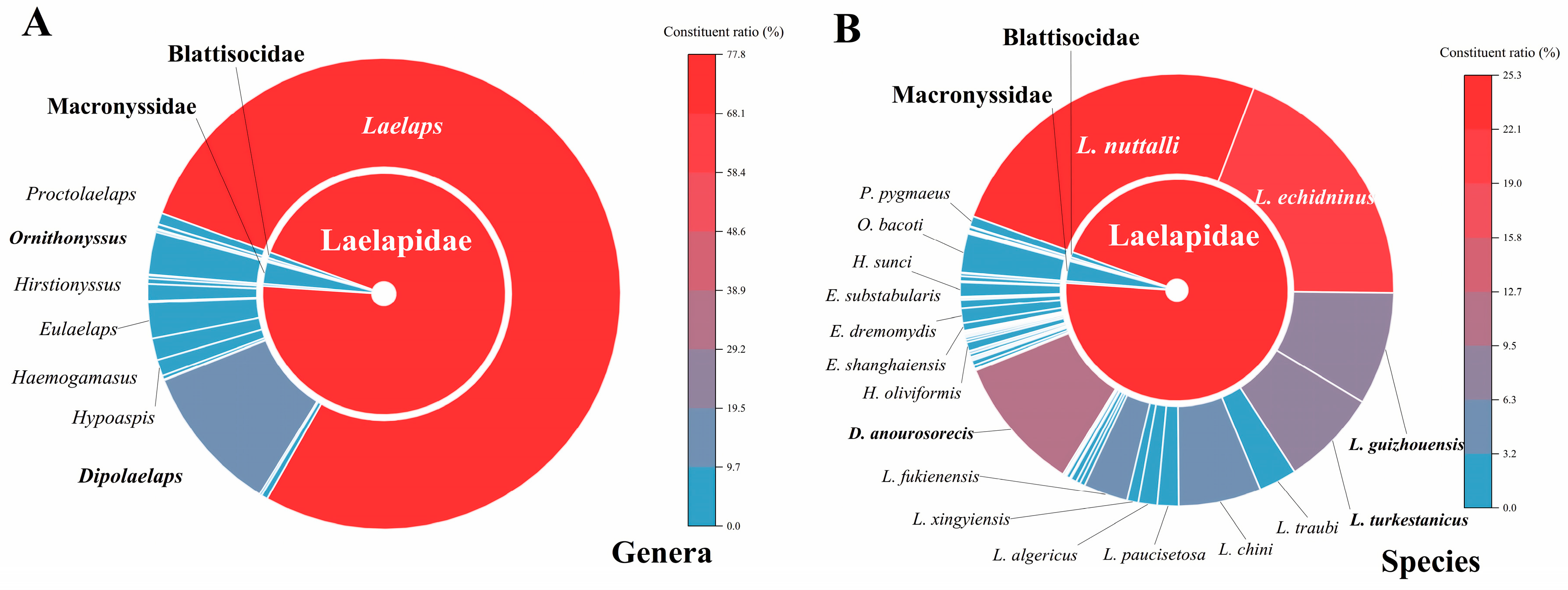
3.2. Species Diversity and Faunal Distribution of Gamasid Mites
3.3. Relationship Between Gamasid Mites and Their Hosts
3.4. Ecological Niches of Gamasid Mites
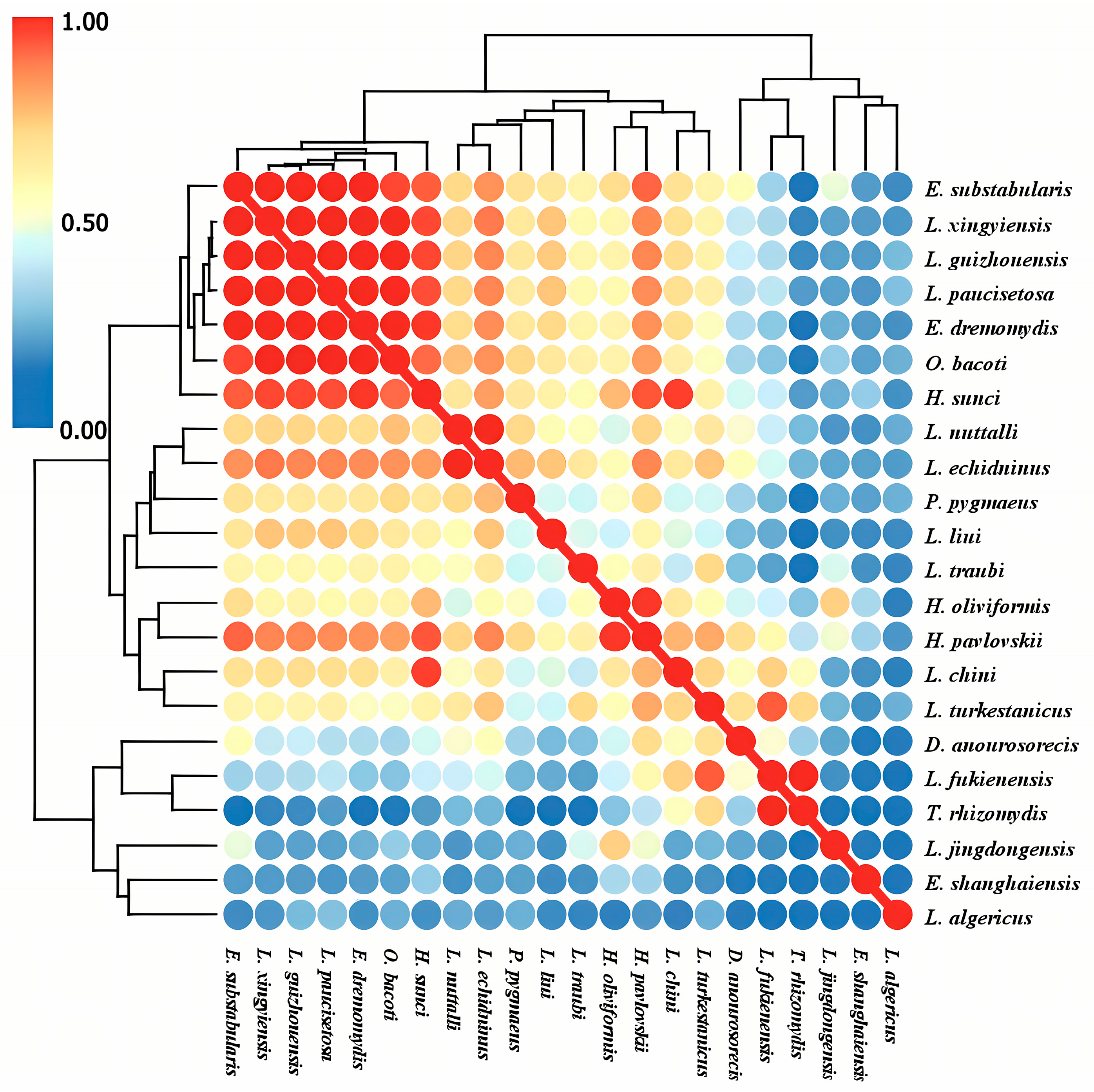
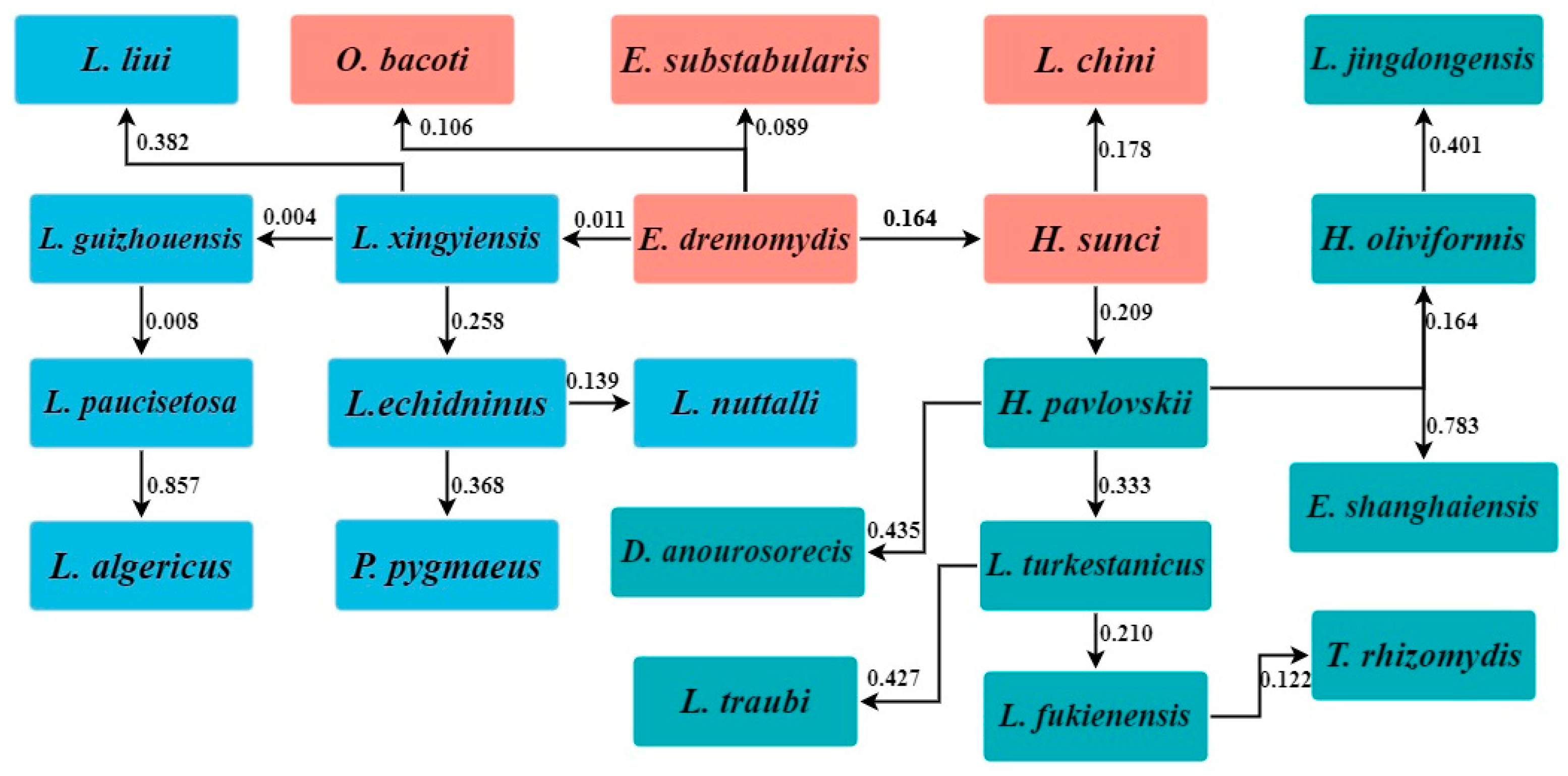
3.5. Interspecific Relationships of Gamasid Mites
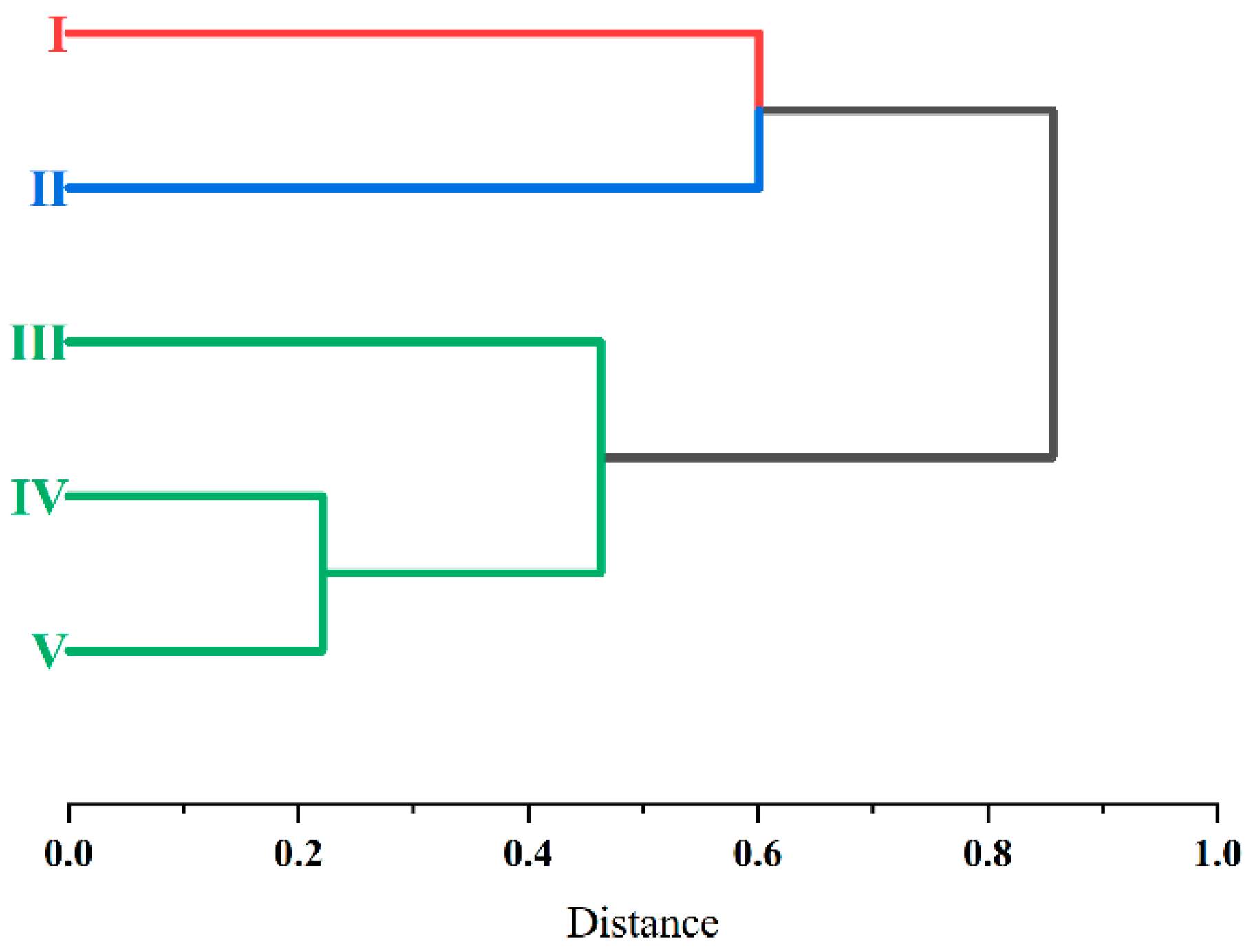
3.6. Distribution of Gamasid Mites in Different Geographical Landscapes and Habitats
3.7. Estimation of Total Number of Gamasid Mite Species
4. Discussion
4.1. General Faunal Characteristics of Gamasid Mites in Yunnan of Southwest China
4.2. Faunal Similarity of Gamasid Mites in Different Zoogeographical Microregions
4.3. Distribution of Gamasid Mites in Different Geographical Landscapes and Habitats
4.4. Estimation of Total Species of Gamasid Mites
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
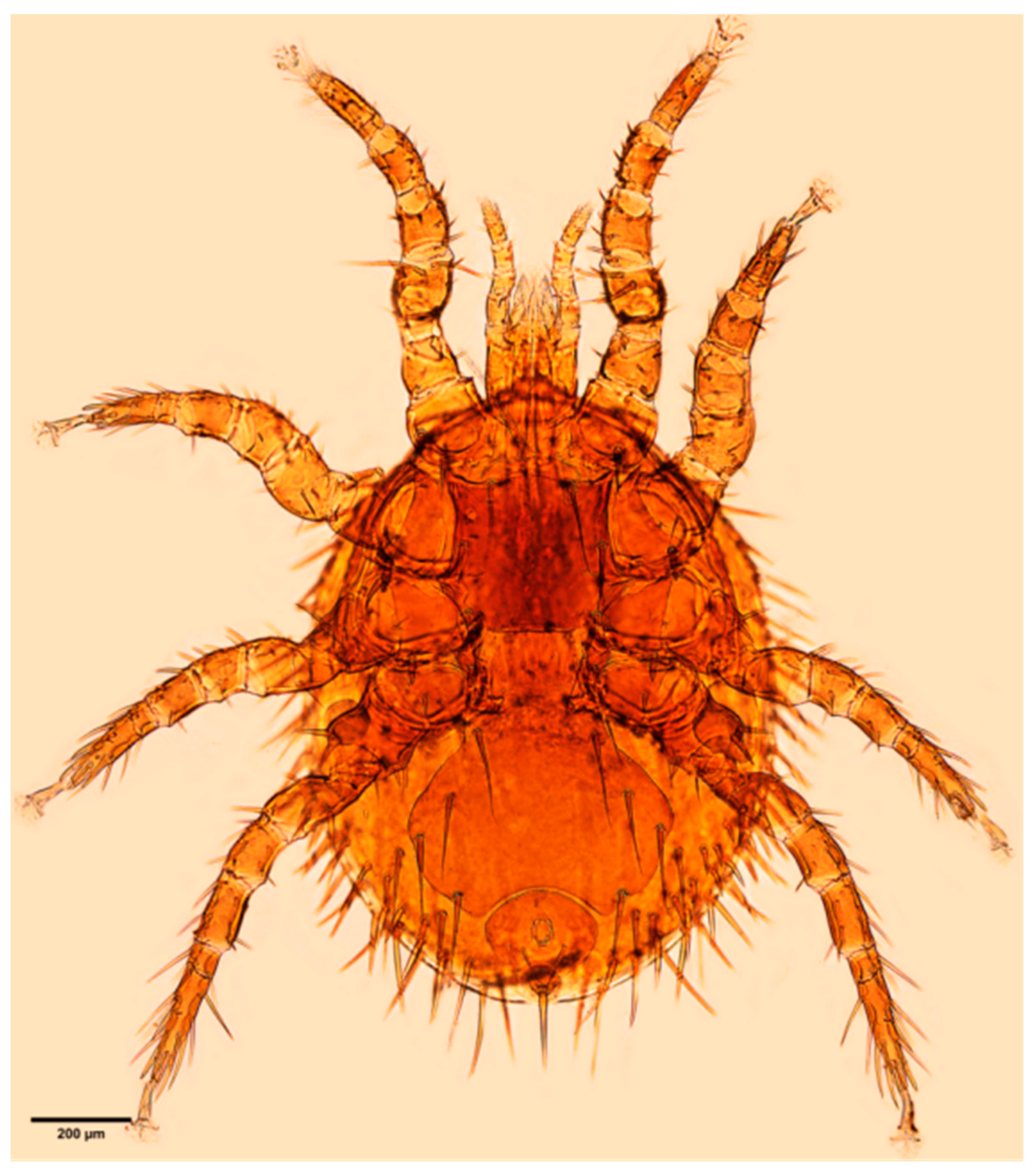
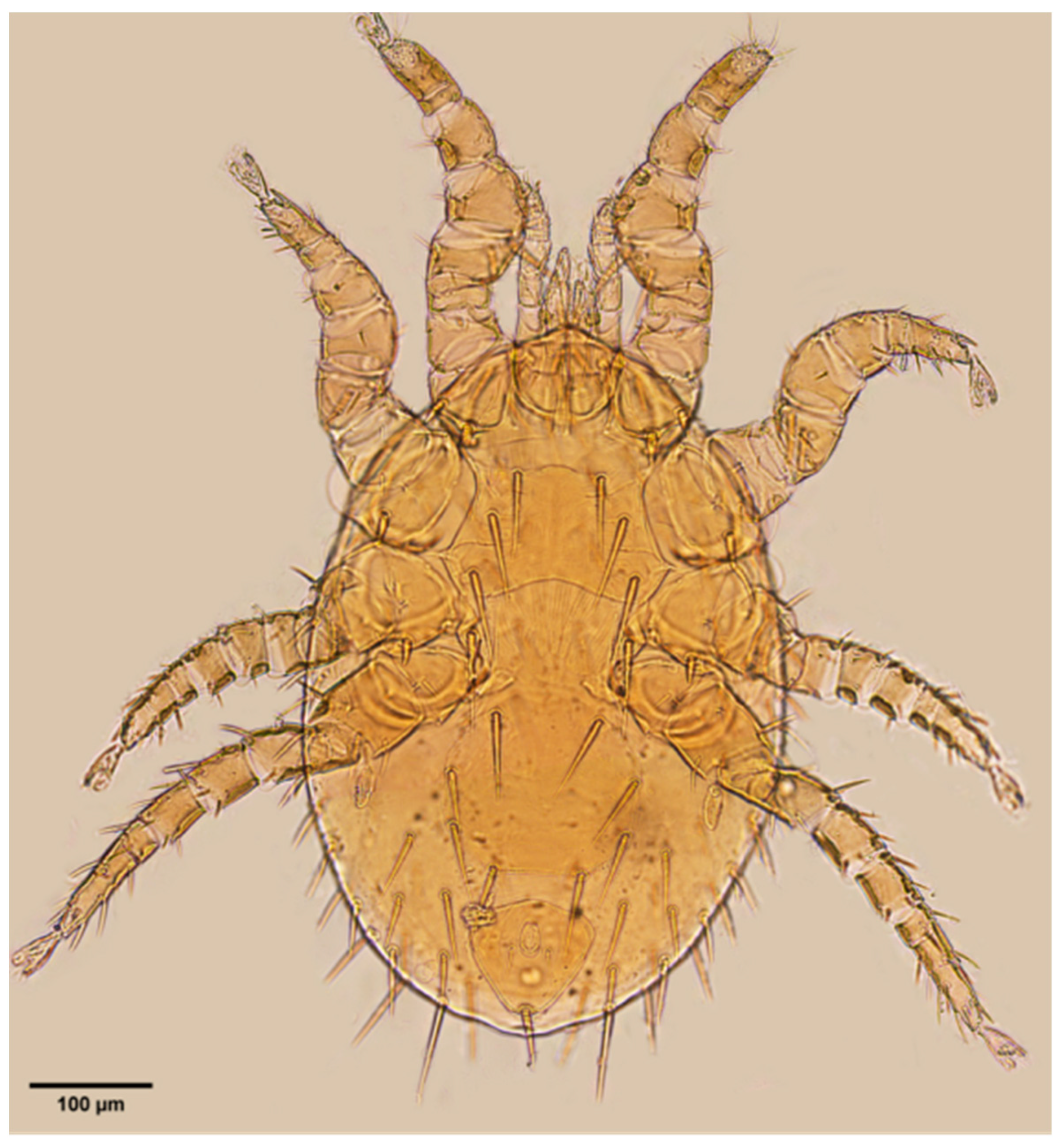
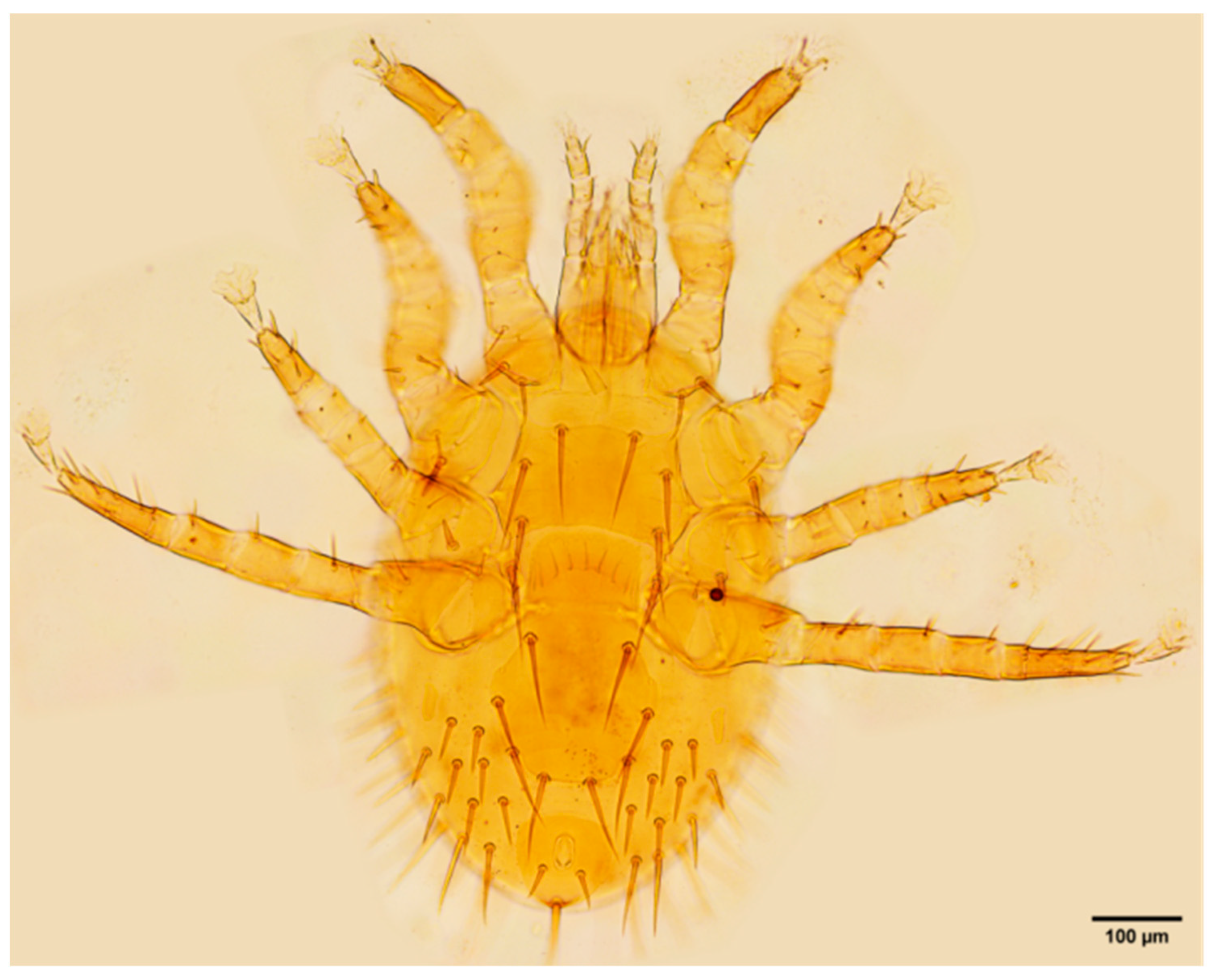
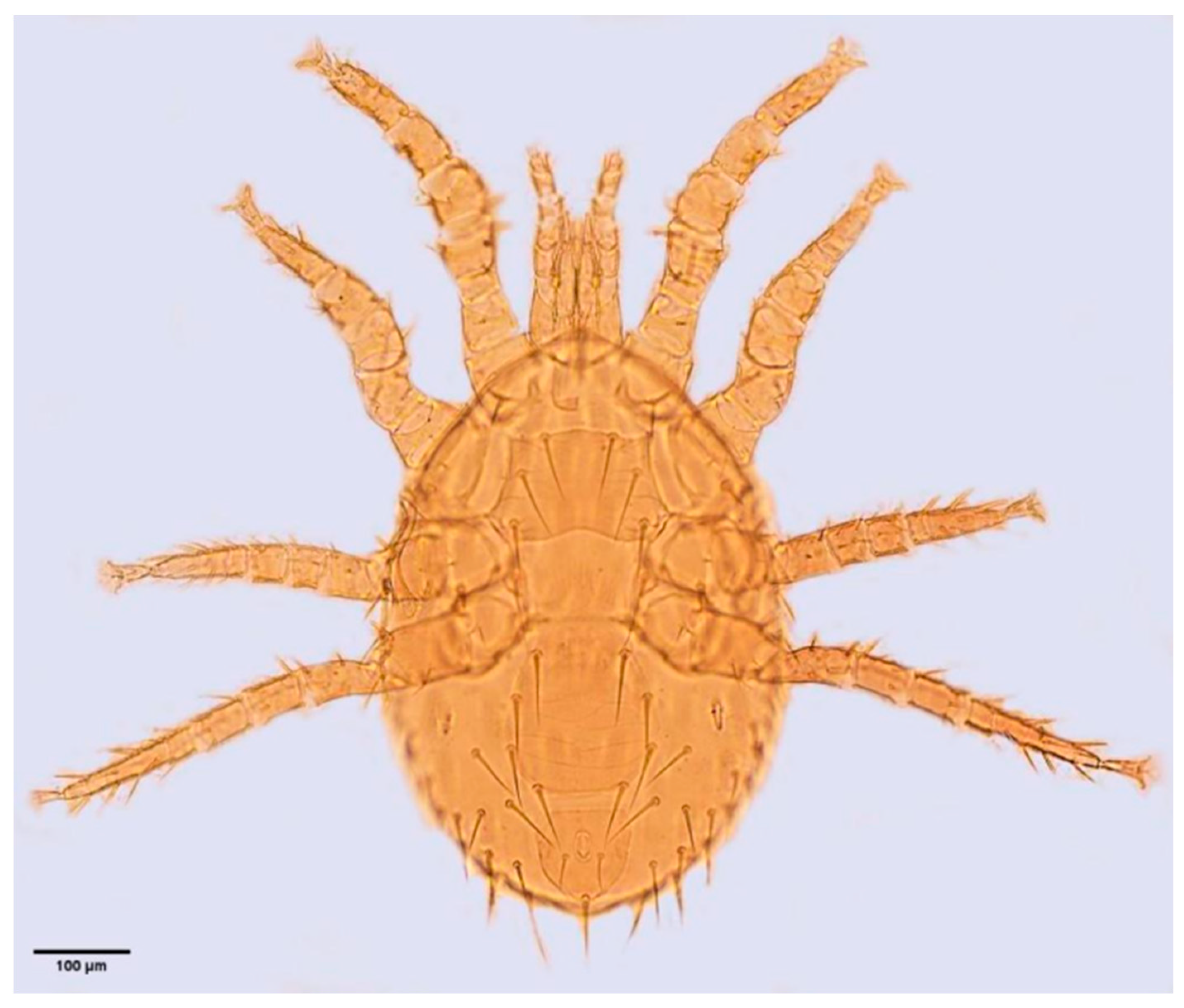





References
- Krantz, G.W. A Manual of Acarology, 2nd ed.; Oregon State University Book Stores: Corvallis, OR, USA, 1978; pp. 1–509. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, P.W.; Guo, X.G.; Song, W.Y.; Dong, W.G.; Lv, Y.; Jin, D.C. The on-Site Monitoring and Specimen-Making of Ectoparasites on Rodents and Other Small Mammals. Bio-Protocol 2024, 14, e5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guo, X.G.; Fan, R.; Zhao, C.F.; Mao, K.Y.; Zhang, Z.W.; Zhao, Y. Ecological analysis of gamasid mites on the body surface of Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus) in Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Biologia 2019, 75, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.Y.; Guo, X.G.; Jin, D.C.; Dong, W.G.; Qian, T.J.; Qin, F.; Yang, Z.H. Species abundance distribution and ecological niches of chigger mites on small mammals in Yunnan province, southwest China. Biologia 2017, 72, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.W.; Guo, X.G.; Jin, D.C.; Fan, R.; Zhao, C.F.; Zhang, Z.W.; Huang, X.B.; Mao, K.Y. Distribution and Host Selection of Tropical Rat Mite, Ornithonyssus bacoti, in Yunnan Province of Southwest China. Animals 2021, 11, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Mares, A.; Guzman-Cornejo, C.; Ulloa-Garcia, A.; Cordoba-Aguilar, A.; Silva-de la Fuente, M.C.; Suzan, G. Mites, rodents, and pathogens: A global review for a multi-species interaction in disease ecology. Acta Trop. 2022, 232, 106509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hande, B.; Öztoprak, N. Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (Hantaviruses). J. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 4, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Pavelkina, V.F.; Uskova, Y.G. Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome: Clinical, pathogenetic and therapeutic aspects. Mordovia Univ. Bull. 2017, 27, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengis, R.G.; Leighton, F.A.; Fischer, J.R.; Artois, M.; Morner, T.; Tate, C.M. The role of wildlife in emerging and re-emerging zoonoses. Rev. Sci. Tech.-Off. Int. Epizoot. 2004, 23, 497–512. [Google Scholar]
- Zhijun, W.; Young, S.S. Differences in bird diversity between two swidden agricultural sites in mountainous terrain, Xishuangbanna, Yunnan, China. Biol. Conserv. 2003, 110, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.W.; Yu, Y.; Liu, P.; Tang, R.C.; Dai, Y.C.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Identifying climate refugia and its potential impact on small population of Asian elephant (Elephas maximus) in China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 19, e00664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.M.; Tian, K.; Hao, J.M.; Pei, S.J.; Yang, Y.X. Biodiversity and biodiversity conservation in Yunnan, China. Biodivers. Conserv. 2004, 13, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.C.; Wilkes, A. Biodiversity impact analysis in northwest Yunnan, southwest China. Biodivers. Conserv. 2004, 13, 959–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.J.; Weng, C.Y.; Guo, J.Q.; Dai, L.; Zhou, Z.Z. Vegetation responses to late Quaternary climate change in a biodiversity hotspot, the Three Parallel Rivers region in southwestern China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2018, 491, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, E.O.; Mayden, R.L. Species and speciation in phylogenetic systematics, with examples from the North American fish fauna. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 1985, 72, 596–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avise, J.C. Molecular population structure and the biogeographic history of a regional fauna: A case history with lessons for conservation biology. Oikos 1992, 63, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreft, H.; Jetz, W. A framework for delineating biogeographical regions based on species distributions. J. Biogeogr. 2010, 37, 2029–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krantz, G.W.; Walter, D.E. A Manual of Acarology, 3rd ed.; Texas Tech University Press: Lubbock, TX, USA, 2009; pp. 124–233. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, S.G.; Bei, N.X.; Chen, W.P. Soil Gamasida from Northeast China; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2013. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.L. The fauna of gamasid mites in Ningxia. Sichuan J. Zool. 1990, 9, 14–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.L.; Yan, L.M.; Wu, X.L.; Wei, H.; Qi, R.J. Composition and distribution and harm of gamasid mites in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region. J. Med. Pest Control 2009, 25, 487–493. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.L.; Ma, L.M. Investigations on mesostigmatic mites from Ningxia and neighboring Provinces (Acari) (2). Bull. Dis. Control Prev. (China) 2013, 28, 13–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.A.; Liu, J.S.; Zhang, Z.C.; She, J.J.; Nian, Q.F. The fauna of gamasid mites in Shaanxi Province. J. Med. Pest Control 1995, 11, 313–317. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.S.; Li, M.L.; Yang, X.Z. The fauna of the parasitic mites in Qinghai Province. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 1996, 33, 105–107. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tao, J.W.; Liu, Y.R.; Yang, Z.Q. Analysis on fauna of gamasid mites in Hubei Province China. Chin. J. Vector Biol. Control 2005, 16, 294–296. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.G.; Qian, T.J. Fauna investigation of gamasid mites from the GaoligongMountain and the Dandanglika Mountain. Bull. Dis. Control Prev. (China) 1998, 13, 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Skorupski, M.; Luxton, M. Mesostigmatid mites (Acari: Parasitiformes) associated with yew (Taxus baccata) in England and Wales. J. Nat. Hist. 1998, 32, 419–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coja, T.; Bruckner, A. Soil microhabitat diversity of a temperate Norway spruce (Picea abies) forest does not influence the community composition of gamasid mites (Gamasida, Acari). Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2003, 39, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, O.L. Gamasid mites (Parasitiformes, Mesostigmata) dwelling in bracket fungi at the pechoro-ilychskii reserve (Republic of Komi). Zool. Zhurnal 2004, 83, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar]
- Mašán, P.; Stanko, M. Mesostigmatic mites (Acari) and fleas (Siphonaptera) associated with nests of mound-building mouse, Mus spicilegus Petényi, 1882 (Mammalia, Rodentia). Acta Parasitol. 2005, 50, 228–234. [Google Scholar]
- Gwiazdowicz, D.J.; Coulson, S.J. High-Arctic gamasid mites (Acari, Mesostigmata): Community composition on Spitsbergen, Svalbard. Polar Res. 2011, 30, 8311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, O.L. A review of gamasid mites (Parasitiformes, Mesostigmata) dwelling in the taiga of the Pechoro-Ilychskii Nature Reserve (northern Cis-Ural Region) with analysis of their assemblages in spruce forests. Entomol. Rev. 2011, 91, 915–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonovich, S.A.; Dimov, I. Sense organs on palps and fore tarsi of gamasid mites (Parasitiformes, Rhinonyssidae), parasites of the nasal cavity of the Great Tit, the Rock Dove, and the Eurasian Coot. Entomol. Rev. 2012, 92, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova, M.V.; Orlov, O.L.; Kshnyasev, I.A. Changes in the abundance of parasitic gamasid mite Macronyssus corethroproctus (Oudemans, 1902) during the overwintering period of its host, the pond bat Myotis dasycneme (Boie, 1825). Russ. J. Ecol. 2012, 43, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.Y.; Zeng, J.F. The Siphonaptera of Yunnan; Yunnan Science and Technology Press: Kunming, China, 2000. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.P.; Guo, X.G.; Qian, T.J.; Wu, D.; Men, X.Y.; Dong, W.G. Distribution of gamasid mites on small mammals in Yunnan Province, China. Insect Sci. 2007, 14, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.Y.; Cheng, J.L.; Wen, Z.X.; Feijó, A.; Xia, L.; Yang, Q.S. A protocol for field collection and specimen preparation of glires. Bio-101 2021, e1010667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.F.; Teng, K.F. Economic Insect Fauna of China Fasc. 40 Acari: Dermanyssoidese; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1993. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.W.; Deng, G.F. Economic Insect Fauna of China. Fasc 17, Acari: Gamasina; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1980. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Margolis, L.; Esch, G.W.; Holmes, J.C.; Kuris, A.M.; Schad, G.A. The use of ecological terms in parasitology (report of an ad hoc committee of the American Society of Parasitologists). J. Parasitol. 1982, 68, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, A.O.; Lafferty, K.D.; Lotz, J.M.; Shostak, A.W. Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms. J. Parasitol. 1997, 83, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, X.Y.; Guo, X.G.; Dong, W.G.; Niu, A.Q.; Qian, T.J.; Wu, D. Ectoparasites of Chevrier’s field mouse, Apodemus chevrieri, in a focus of plague in southwest China. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2007, 21, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E.; Weaver, W. The Mathematical Theory of Communication; University of Illinois Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Magurran, A.E. Measuring richness and evenness. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1998, 13, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margalef, R. Perspectives in Ecological Theory; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez, D.P.; Stevens, R.D. The latitudinal gradient in niche breadth: Concepts and evidence. Am. Nat. 2004, 164, E1–E19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexton, J.P.; Montiel, J.; Shay, J.E.; Stephens, M.R.; Slatyer, R.A. Evolution of ecological niche breadth. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2017, 48, 183–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurlbert, S.H. The measurement of niche overlap and some relatives. Ecology 1978, 59, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatzmann, E.; Gerrard, R.; Barbour, A.D. Measures of niche overlap, I. Math. Med. Biol. J. IMA 1986, 3, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, P. Some comments on measuring niche overlap. Ecology 1980, 61, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.T. Quantitative Ecology, 3rd ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Krasnov, B.R.; Vinarski, M.V.; Korallo-Vinarskaya, N.P.; Mouillot, D.; Poulin, R. Inferring associations among parasitic gamasid mites from census data. Oecologia 2009, 160, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, A. Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand. J. Stat. 1984, 11, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, P.Y.; Guo, X.G.; Song, W.Y.; Hou, P.; Zou, Y.J.; Fan, R. Ectoparasitic chigger mites on large oriental vole (Eothenomys miletus) across southwest, China. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.P. Medical Acarology; Peoples Military Medical Press: Beijing, China, 2006. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.P. Medical Arthropodology; People’s Health Press: Beijing, China, 2009. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.J.; Tesh, R.B. The Role of Mites in the Transmission and Maintenance of Hantaan Virus (Hantavirus: Bunyaviridae). J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 1693–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.C.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhu, L.; Dong, L.Y.; Zhang, Z.T.; Hao, B.; Yang, F.; Liu, W.B.; Deng, Y. Meteorological factors affect the epidemiology of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome via altering the breeding and hantavirus-carrying states of rodents and mites: A 9 years’ longitudinal study. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2017, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Zou, Y.; Fu, Z.F.; Plyusnin, A. Hantavirus infections in humans and animals, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avšič-Županc, T.; Saksida, A.; Korva, M. Hantavirus infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 21, e6–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnov, B.R.; Vinarski, M.V.; Korallo-Vinarskaya, N.P.; Khokhlova, I.S. Ecological correlates of body size in gamasid mites parasitic on small mammals: Abundance and niche breadth. Ecography 2013, 36, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korallo-Vinarskaya, N.P.; Krasnov, B.R.; Vinarski, M.V.; Shenbrot, G.I.; Mouillot, D.; Poulin, R. Stability in abundance and niche breadth of gamasid mites across environmental conditions, parasite identity and host pools. Evol. Ecol. 2009, 23, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnov, B.R.; Korallo-Vinarskaya, N.P.; Vinarski, M.V.; Shenbrot, G.I.; Mouillot, D.; Poulin, R. Searching for general patterns in parasite ecology: Host identity versus environmental influence on gamasid mite assemblages in small mammals. Parasitology 2008, 135, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowling, A.P. Mesostigmatid mites as parasites of small mammals: Systematics, ecology, and the evolution of parasitic associations. In Micromammals and Macroparasites: From Evolutionary Ecology to Management; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2006; p. 103. [Google Scholar]
- Korzikov, V.A.; Vasilyeva, O.L.; Korallo-Vinarskaya, N.P.; Medvedev, S.G. Gamasid Mites (Gamasina) Associated with Small Terrestrial Vertebrates in the South of Non-Chernozem Center of Russia (Kaluga Province). Entomol. Rev. 2021, 101, 1441–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.X.; Guo, X.G.; Song, W.Y.; Zhao, C.F.; Zhang, Z.W.; Fan, R.; Chen, T.; Lv, Y.; Yin, P.W.; Jin, D.C. Preliminary Study on Species Diversity and Community Characteristics of Gamasid Mites on Small Mammals in Three Parallel Rivers Area of China. Animals 2022, 12, 3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balashov, Y.S. Types of parasitism of acarines and insects on terrestrial vertebrates. Entomol. Rev. 2006, 86, 957–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Meng, F.; Che, T.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Ji, Y.; Fan, Z.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, B.; et al. Mapping the distributions of blood-sucking mites and mite-borne agents in China: A modeling study. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2022, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairawita, M.; Mursyid, A.; Dahelmi, D.; Diniyati, F.; Lidia, D.; Putri, N.; Arifa, M.M.; Jefrial, J.; Maulana, R.M. Co-occurrence of ectoparasites on wild rodents in Sipora Island, Mentawai, Indonesia with the zoonotic potential review. Biodiversitas J. Biol. Divers. 2023, 24, 6369–6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra-Santos, M.A.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Benelli, G.; Otranto, D. Emerging parasites and vectors in a rapidly changing world: From ecology to management. Acta Trop. 2023, 238, 106746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Wei, Y.W.; Li, C.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.Q.; Yang, N.; Ma, Y.J. Cluster analysis of gamasid mites in Qinghai Province, China. Chin. J. Zoonoses 2014, 30, 67–72. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.H.; Deng, Y.Q.; Li, S.Y.; Wang, L.L. Supplementary records of Dermanyssoid mites(Acari:Parasitiformes)in Fujian province. Chin. J. Vector Biol. Control 2012, 23, 467–469. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.N.; Wang, Y.; Feng, B.; Ma, L.M. Gamasid mites in Heilongjiang Province. Chin. J. Vector Biol. Control 1996, 7, 477–480. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.H.; Xiang, Y.Q.; Li, Y.G. Study on the composition and geographical Distribution of gamasid mites in Hebei Province. Chin. J. Vector Biol. Control 1992, 3, 391–392. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.Z.; Wang, Z.; Huang, W.C.; Li, P.; Yin, G.Q.; Wen, Y.; Cheng, X.H.; Xue, J. Survey of gamasid mite species and evaluation of gamasid mite controlefficacy in military camps in Shandong province, China. Chin. J. Vector Biol. Control 2013, 24, 535–537. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.Z.; Zhang, Y.X.; Chen, X.; Lin, S.; Yang, J.; Xiang, D.; Sun, L.; Ma, L.M. Investigation of free living gamasid mites in China (XIII) (Acari: Mesostigmata). Wuyi Sci. J. 2020, 36, 119–135. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.Z.; Dai, W.A.; Zhang, Y.X.; Lin, S.; Chen, X.; Sun, L.; Ma, L.M. Investigation of free living gamasid mites in China (XII) (Acari: Mesostigmata). Wuyi Sci. J. 2019, 35, 127–134. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.H.; Liu, J.X.; Li, C.P. Species and ecological characteristics of gamasid mites in storage. J. Environ. Health 2015, 32, 737. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bush, A.O. Parasitism: The Diversity and Ecology of Animal Parasites; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Maleki-Ravasan, N.; Solhjouy-Fard, S.; Beaucournu, J.; Laudisoit, A.; Mostafavi, E. The fleas (Siphonaptera) in Iran: Diversity, host range, and medical importance. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahondère, C. Recent advances in insect thermoregulation. J. Exp. Biol. 2023, 226, jeb245751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbi, M.; Darghouth, M.A. A review of Hyalomma scupense (Acari, Ixodidae) in the Maghreb region: From biology to control. Parasite 2014, 21, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnov, B.R.; Shenbrot, G.I.; Khokhlova, I.S.; Stanko, M.; Morand, S.; Mouillot, D. Assembly rules of ectoparasite communities across scales: Combining patterns of abiotic factors, host composition, geographic space, phylogeny and traits. Ecography 2015, 38, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnov, B.R.; Mouillot, D.; Shenbrot, G.I.; Khokhlova, I.S.; Poulin, R. Deconstructing spatial patterns in species composition of ectoparasite communities: The relative contribution of host composition, environmental variables and geography. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2010, 19, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domatskiy, V.N.; Sivkova, E.I. The influence of climatogeographic conditions on the expansion of the range of ixodes ticks. Entomol. Appl. Sci. Lett. 2023, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnov, B.R.; Shenbrot, G.I.; Khokhlova, I.S.; Vinarski, M.; Korallo-Vinarskaya, N.; Poulin, R. Geographical patterns of abundance: Testing expectations of the ‘abundance optimum’model in two taxa of ectoparasitic arthropods. J. Biogeogr. 2008, 35, 2187–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanko, M.; Miklisová, D.; Goüy de Bellocq, J.; Morand, S. Mammal density and patterns of ectoparasite species richness and abundance. Oecologia 2002, 131, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmane, I.; Brumelis, G. Species list and habitat preference of Mesostigmata mites (Acari, Parasitiformes) in Latvia. Acarologia 2010, 50, 373–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, G.O.; Till, W.M. Mesostigmatic mites of Britain and Ireland (Chelicerata: Acari-Parasitiformes): An introduction to their external morphology and classification. Trans. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1979, 35, 139–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.N.; Shao, R.F.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, W.; Xue, X.F. Mitochondrial genome reorganization characterizes various lineages of mesostigmatid mites (Acari: Parasitiformes). Zool. Scr. 2019, 48, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, R.; Guo, X.G.; Zhao, C.F.; Fan, R.; Mao, K.Y.; Zhang, Z.W.; Huang, X.B. Infestation and distribution of gamasid mites on Himalayan field rat (Rattus nitidus) in Yunnan Province of Southwest China. Biologia 2021, 76, 1763–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korallo, N.P.; Vinarski, M.V.; Krasnov, B.R.; Shenbrot, G.I.; Mouillot, D.; Poulin, R. Are there general rules governing parasite diversity? Small mammalian hosts and gamasid mite assemblages. Divers. Distrib. 2007, 13, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.Q.; Guo, X.G.; Speakman, J.R.; Dong, W.G. Analysis of gamasid mites (Acari: Mesostigmata) associated with the Asian house rat, Rattus tanezumi (Rodentia: Muridae) in Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 1967–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.Q.; Guo, X.G.; Wu, D.; Zhou, D.H. Distribution and ecological niches of gamasid mites (Acari: Mesostigmata) on small mammals in Southwest China. Psyche J. Entomol. 2010, 2010, 934508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.W.; Guo, X.G.; Jin, D.C.; Song, W.Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, C.F.; Fan, R.; Zhang, Z.W.; Mao, K.Y. Infestation and Seasonal Fluctuation of Gamasid Mites (Parasitiformes: Gamasida) on Indochinese Forest Rat, Rattus andamanensis (Rodentia: Muridae) in Southern Yunnan of China. Biology 2021, 10, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicek, H.; Stanyukovich, M.; Yağci, S.; Aktaş, M.; Karaer, Z. Gamasine mite (Parasitiformes: Mesostigmata) infestations of small mammals (mammalia: Rodentia, Insectivora) in Turkey. Türkiye Parazitoloji Derg. 2008, 32, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.G. Host-specificity and host-selection of gamasid mites (Acari: Gamasina). Syst. Appl. Acarol. 1998, 3, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinarski, M.V.; Korallo, N.P.; Krasnov, B.R.; Shenbrot, G.I.; Poulin, R. Decay of similarity of gamasid mite assemblages parasitic on Palaearctic small mammals: Geographic distance, host-species composition or environment. J. Biogeogr. 2007, 34, 1691–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.H.N.A. Important vector-borne diseases with their zoonotic potential: Present situation and future perspective. Bangladesh J. Vet. Med. 2015, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmana, H.; Granjon, L.; Diagne, C.; Davoust, B.; Fenollar, F.; Mediannikov, O. Rodents as hosts of pathogens and related zoonotic disease risk. Pathogens 2020, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sianturi, L.A.; Hutagalung, S.V.; Lubis, S.M. Identification of mites in wild rats in Simpang Limun traditional wet market area, Medan-Indonesia. J. Endocrinol. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2024, 6, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.C.; Lee, P.L.; Wang, H.C. Molecular detection of Rickettsia species and host associations of Laelaps mites (Acari: Laelapidae) in Taiwan. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2020, 81, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, W.K.; Loftis, A.D.; Szumlas, D.E.; Abbassy, M.M.; Helmy, I.M.; Hanafi, H.A.; Dasch, G.A. Rickettsial pathogens in the tropical rat mite Ornithonyssus bacoti (Acari: Macronyssidae) from Egyptian rats (Rattus spp.). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2007, 41, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiente Moro, C.; Chauve, C.; Zenner, L. Vectorial role of some dermanyssoid mites (Acari, Mesostigmata, Dermanyssoidea). Parasite 2005, 12, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, P.J.; Nath, A.J. Record of Tropical Rat Mite, Ornithonyssus bacoti (Acari: Mesostigmata: Macronyssidae) from Domestic and Peridomestic Rodents (Rattus rattus) in Nilgiris, Tamil Nadu, India. J. Arthropod-Borne Dis. 2016, 10, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, G. Epidemiological progresses of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in China. Chinese Med. J. 1999, 112, 472–477. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, F.F.; Xu, Q.; Chen, J.J.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, W.H.; Fan, Z.W.; Zhao, G.P.; Jiang, B.G.; Shi, T.X.; Fang, L.Q. A dataset of distribution and diversity of blood-sucking mites in China. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.G.; Qian, T.J. Sex ratio and age structure of gamasid mites from small mammals in western Yunnan, China. Insect Sci. 2001, 8, 166–174. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.Y.; Lv, Y.; Yin, P.W.; Yang, Y.Y.; Guo, X.G. Potential distribution of Leptotrombidium scutellare in Yunnan and Sichuan Provinces, China, and its association with mite-borne disease transmission. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Guo, X.G.; Jin, D.C.; Song, W.Y.; Fan, R.; Zhao, C.F.; Zhang, Z.W.; Mao, K.Y.; Peng, P.Y.; Lin, H.; et al. Host selection and seasonal fluctuation of Leptotrombidium deliense (Walch, 1922) (Trombidiformes: Trombiculidae) at a localized area of southern Yunnan, China. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2019, 24, 2253–2271. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.Z. Zoogeography of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2011. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Tan, Y.H. Flora and vegetation of Yunnan, Southwestern China: Diversity, origin and evolution. Diversity 2022, 14, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.B.; He, Y.L.; Cai, Y.; Qu, X.X.; Cui, X.L. Relationship between extreme climate indices and spatiotemporal changes of vegetation on Yunnan Plateau from 1982 to 2019. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 31, e01813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Li, X.; Kang, L.H.; Brunson, K.; Liu, H.G.; Dong, W.M.; Li, H.M.; Min, R.; Liu, X.; Dong, G.H. Human paleodiet and animal utilization strategies during the Bronze Age in northwest Yunnan Province, southwest China. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Ye, P.C.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Ling, Y.C. Geographical division of terrestrial mammals in China based on species composition characteristics. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 35, 1123–1130. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.M.; Gong, T.; Liu, W.J.; Chen, H.; Fei, Y.F. Community structure of soil mites under different crops and its response to environmental factors in the buffer zone of Shibing Karst World Natural Heritage. Environ. Res. Commun. 2023, 5, 065004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, A.H.; Liu, L.; Lin, J.Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.P.; Zhang, J.; Cen, G.Z.; Lu, C.C. Advancements in research on sustainable ecosystem development in the Three Parallel Rivers region based on bibliometric analysis. In Proceedings of the 2024 12th International Conference on Agro-Geoinformatics (Agro-Geoinformatics), Novi Sad, Serbia, 15–18 July 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, A.E.; Wijeratne, A.J.; Sweet, A.D.; Hernandes, F.A.; Toews, D.P.; Boves, T.J. Dispersal-limited symbionts exhibit unexpectedly wide variation in host specificity. Syst. Biol. 2023, 72, 802–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymkowiak, P.; Górski, G.; Bajerlein, D. Passive dispersal in arachnids. Biol. Lett. 2007, 44, 75–101. [Google Scholar]
- Beasley, E.M. Host traits explain more variation in occupancy of generalists than specialists due to strong host preferences among generalists. J. Parasitol. 2024, 110, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, E.; Rossetti, M.R.; Moreno, M.L.; Bernaschini, M.L.; Cagnolo, L.; Musicante, M.L.; Salvo, A.; Valladares, G. Habitat loss and fragmentation in Chaco forests: A review of the responses of insect communities and consequences for ecosystem processes. In Insect Decline and Conservation in the Neotropics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 129–162. [Google Scholar]
- Krasnov, B.R.; Vinarski, M.V.; Korallo-Vinarskaya, N.P.; Khokhlova, I.S.; Grabovsky, V. Parasite traits, host traits, and environment as determinants of dark diversity affinity in flea and gamasid mite assemblages from the Palearctic. Parasitol. Res. 2024, 123, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, D.I.; Nichols, J.D.; Sutton, N.; Kawanishi, K.; Bailey, L.L. Improving inferences in population studies of rare species that are detected imperfectly. Ecology 2005, 86, 1101–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Wu, C.Z.; Gu, W.; Ye, R.Z.; Zhang, H.B.; Qi, P.; Wang, S.Q.; Zhou, S.Y.; Wei, Y.J.; Cai, Y.H. The biogeographical distribution of tree species-abundance and its relation to climatic factors in mass islands. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2017, 36, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, M.B.; Guisan, A. Five (or so) challenges for species distribution modelling. J. Biogeogr. 2006, 33, 1677–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
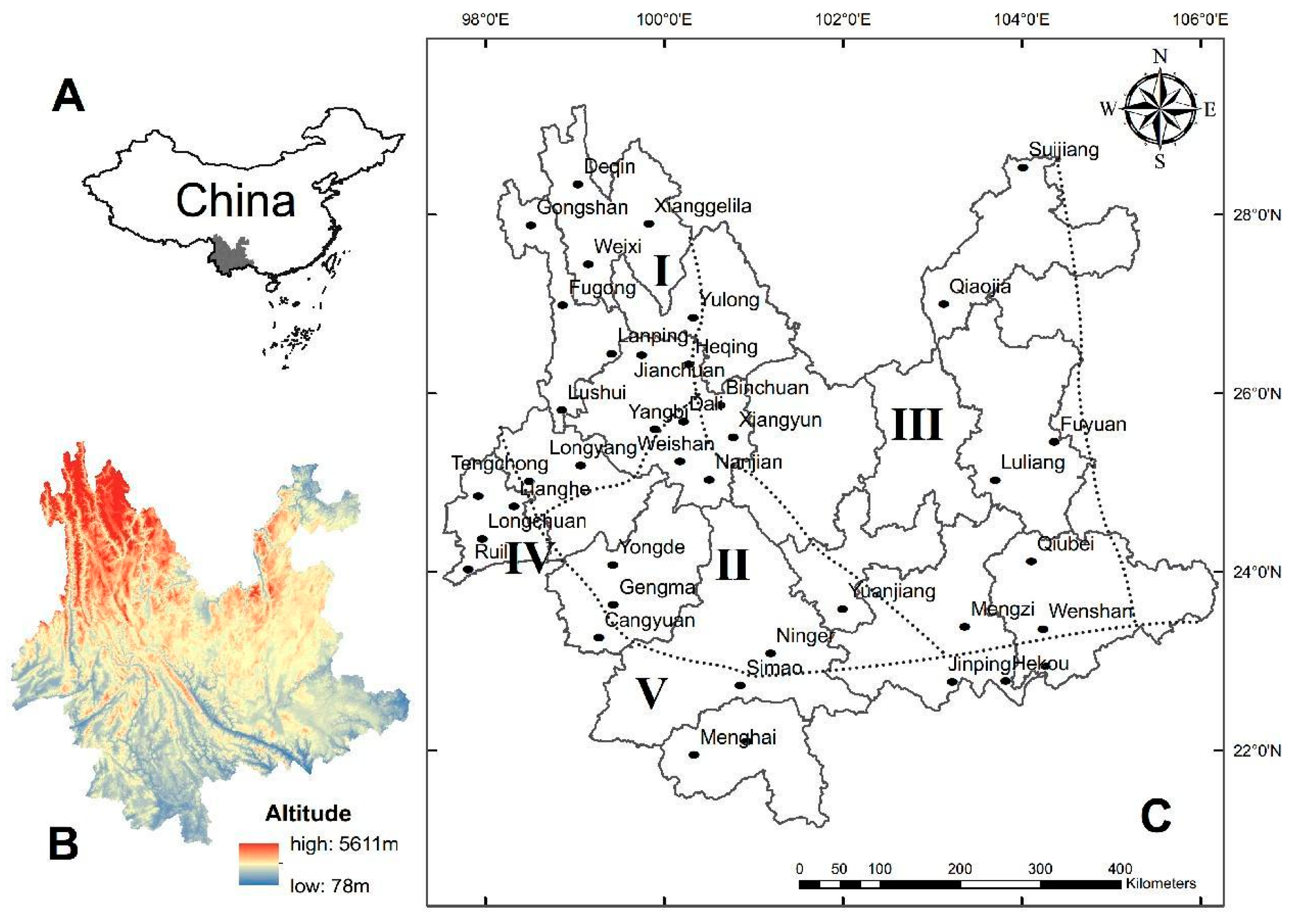
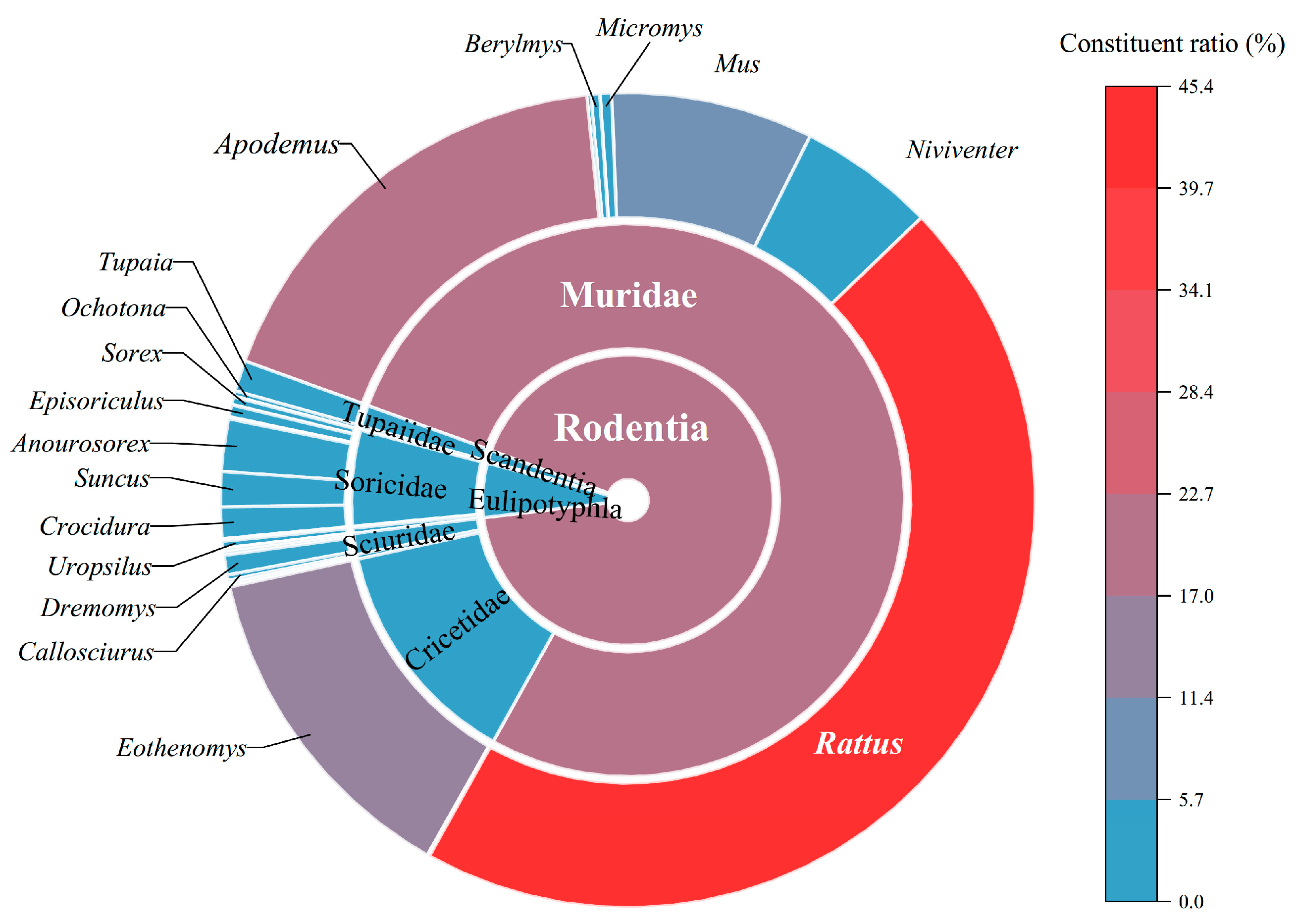
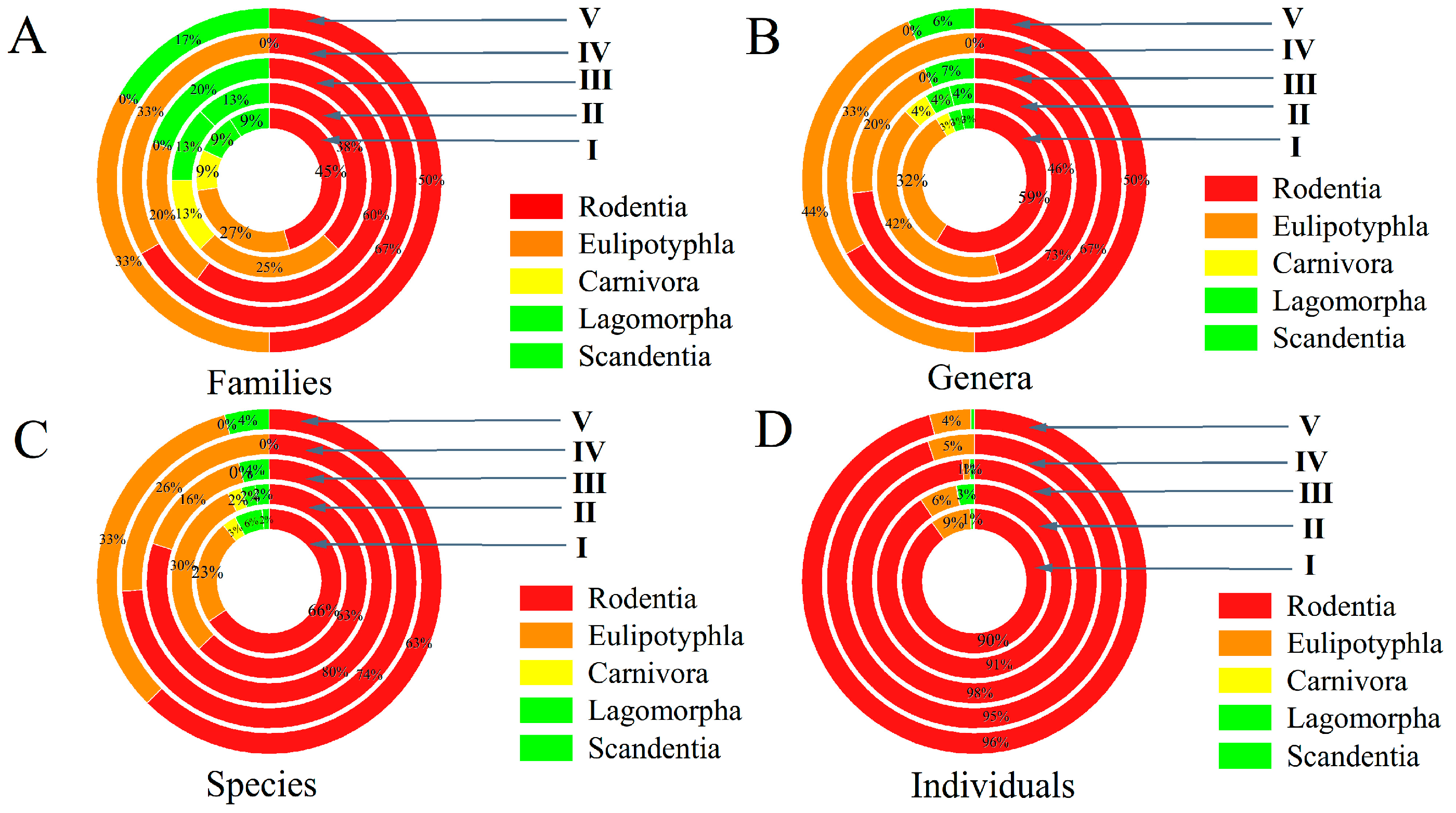


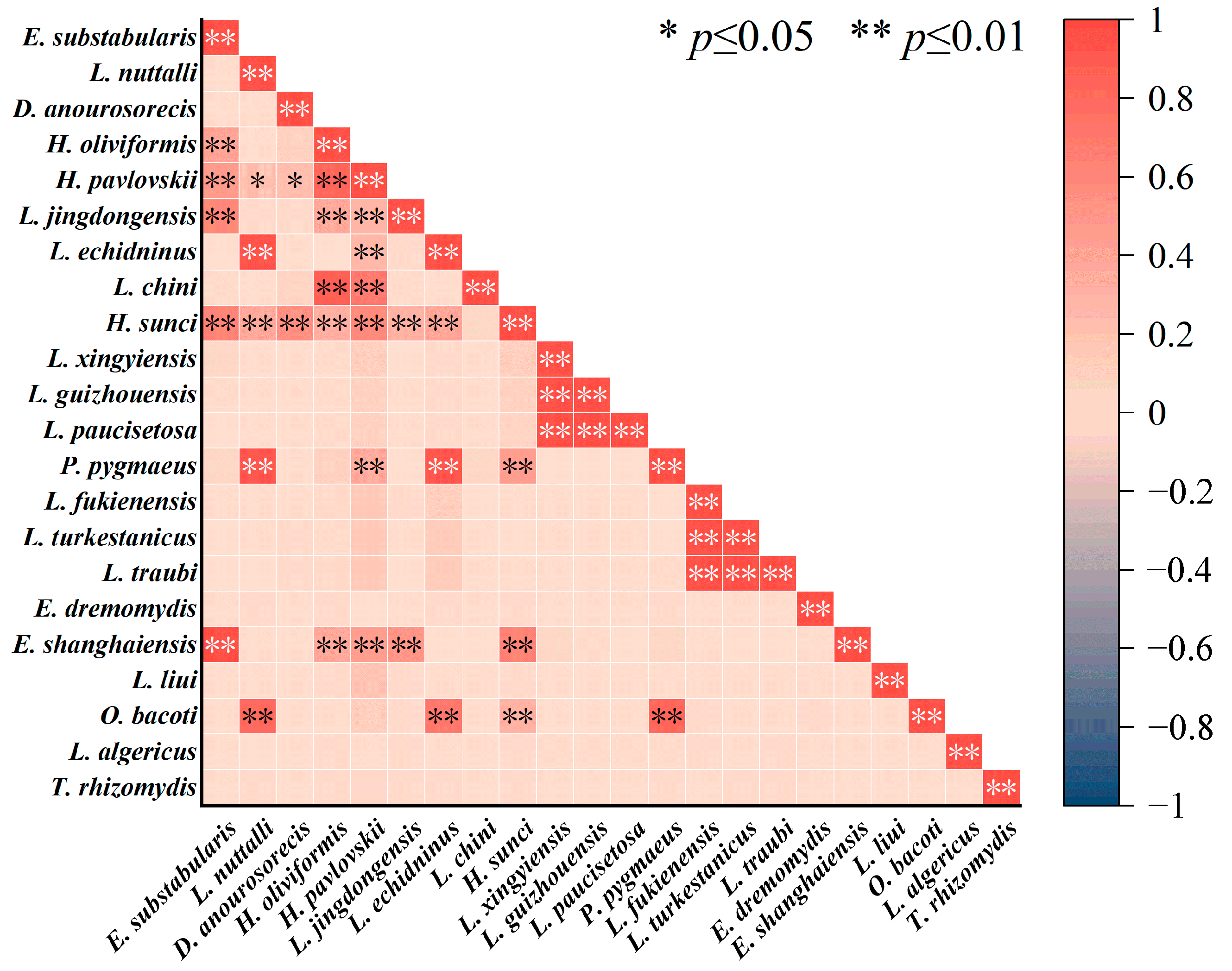
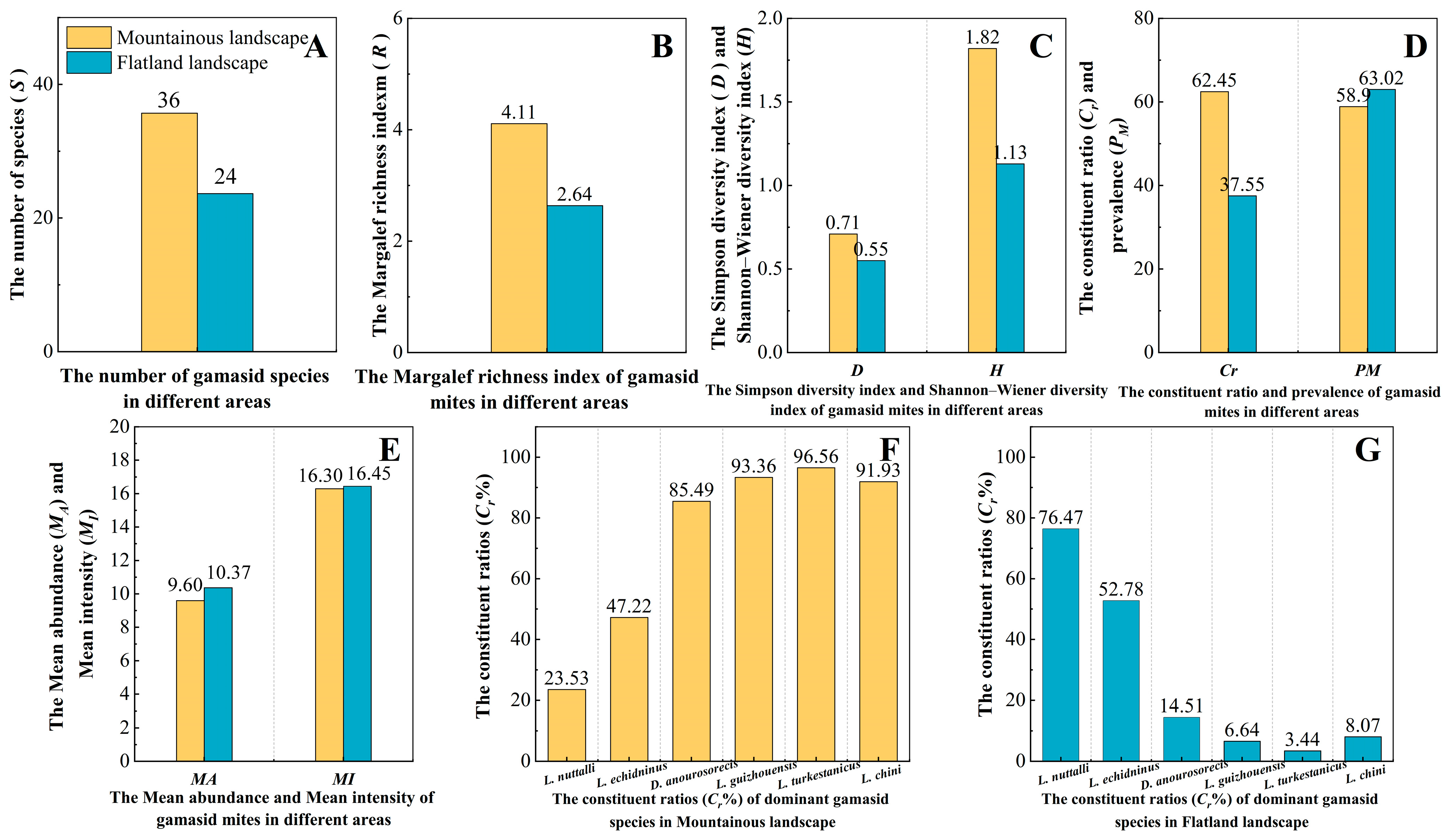
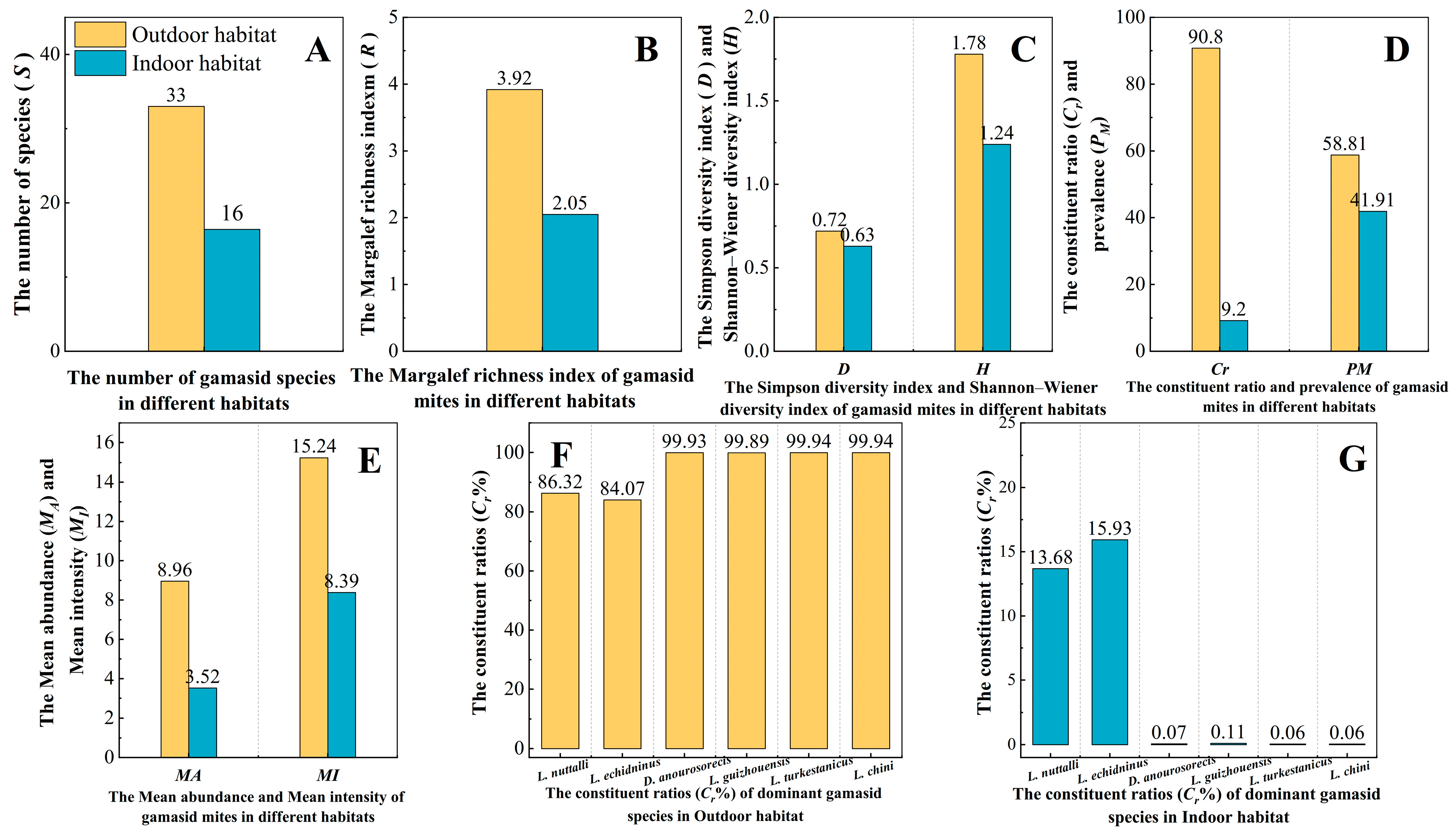
| Realm and Subrealm | Regions | Subregions | Microregions | Names of Survey Sites |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sino-Indian Subrealm in Oriental Realm | Southwest China Region | Southwest Mountain Subregion | I—Middle Microregion of Hengduan Mountains | Gongshan, Jianchuan, Yulong, Xianggelila Lanping, Weixi, Deqin, Lushui, Fugong, Heqing, Yangbi, Longyang, and Tengchong |
| II—Southern Microregion of Hengduan Mountains | Gengma, Yongde, Ninger, Yuanjiang, Dali, Weishan, and Nanjian | |||
| III—Eastern Plateau Microregion of Yunnan | Luliang, Fuyuan, Suijiang, Wenshan, Qiaojia, Mengzi, Binchuan, Xiangyun, and Qiubei | |||
| South China Region | Southern Yunnan Mountain Subregion | IV—Western Plateau Microregion of Yunnan | Longchuan, Lianghe, Ruili, and Yingjiang | |
| V—Southern Mountainous Microregion of Yunnan | Hekou, Simao, Maguan, Menghai, Jinghong, Jinping, and Cangyuan |
| Taxonomic Taxa of Small Mammal Hosts | Collected Species and Individuals of Small Mammal Hosts (the Figures in the Brackets Are the Collected Individuals for Each Host Species). |
|---|---|
| Rodentia | Total hosts: 16,714 individuals; 50 species; 22 genera; 5 families |
| Muridae | Apodemus chevrieri (2216); A. ilex (566); A. latronum (341); A. peninsulae (94); A. draco (2); A. agrarius (4); Bandicota indica (28); Berylmys bowersi (57); B. berdmorei (3); B. manipulus (1); Hapalomys delacouri (1); Leopoldamys edwardsi (1); Micromys erythrotis (81); Mus pahari (739); M. caroli (489); M. musculus (223); Niviventer confucianus (582); N. fulvescens (288); N. andersoni (65); N. eha (36); N. excelsior (6); Rattus tanezumi (5387); R. norvegicus (1452); R. nitidus (998); R. andamanensis (348); Vernaya fulva (1) |
| Cricetidae | Neodon clarkei (15); Eothenomys miletus (2175); E. custos (105); E. eleusis (79); E. proditor (23); E. cachinus (19); E. melanogaster (12); E. olitor (7) |
| Pteromyidae | Hylopetes alboniger (6); Petaurista caniceps (5); P. xanthotis (5); P. philippensis (4); Pteromys volans (11); Trogopterus xanthipes (18) |
| Sciuridae | Callosciurus erythraeus (32); C. quinquestriatus (6); Dremomys pernyi (132); D. lokriah (5); D. rufigenis (3); Rupestes forresti (19); Sciurotamias davidianus (4); Tamiops swinhoei (18) |
| Spalacidae | Rhizomys pruinosus (1); R. sinensis (1) |
| Eulipotyphla | Total hosts: 1084 individuals; 21 species; 13 genera; 3 families |
| Talpidae | Parascaptor leucura (4); Scaptonyx fusicaudus (3); Uropsilus gracilis (32); U. investigator (17) |
| Erinaceidae | Neotetracus sinensis (12); Hylomys suillus (6) |
| Soricidae | Anourosorex squamipes (375); Blarinella wardi (9); B. quadraticauda (3); Crocidura attenuata (205); C. dracula (18); C. vorax (1); Chimarrogale styani (1); C. himalayica (1); Episoriculus caudatus (51); E. leucops (23); E. macrurus (11); Nectogale elegans (4); Suncus murinus (252); Sorex excelsus (36); S. bedfordiae (20); |
| Carnivora | Total hosts: 5 individuals; 2 species; 1 genus; 1 family |
| Mustelidea | Mustela kathiah (4); M. sibirica (1) |
| Lagomorpha | Total hosts: 38 individuals; 4 species; 1 genus; 1 family |
| Ochotonidae | Ochotona forresti (18); O. thibetana (11); O. gaoligongensis (8); O. roylii (1) |
| Scandentia | Total hosts: 222 individuals; 1 species; 1 genus; 1 family |
| Tupaiidae | Tupaia belangeri (222) |
| Zoogeographical Microregions | Species and Individuals of Small Mammal Hosts | Average Community Indexes of Small Mammal Hosts | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Species | Individuals | |||||
| I | 65 | 5541 | 15.09 | 2.26 | 0.70 | 1.68 |
| II | 43 | 6345 | 10.31 | 1.51 | 0.50 | 1.14 |
| III | 25 | 2327 | 12.60 | 1.88 | 0.73 | 1.67 |
| IV | 23 | 1394 | 13.00 | 1.97 | 0.57 | 1.30 |
| V | 24 | 2456 | 11.20 | 1.65 | 0.34 | 0.84 |
| Total | 78 | 18,063 | - | - | - | - |
| Microregions | Names of Dominant Hosts | Numbers and Constituent Ratios (Cr) of Hosts | Microregions | Names of Dominant Hosts | Numbers and Constituent Ratios (Cr) of Hosts | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Cr, % | No. | Cr, % | ||||
| I | A. chevrieri | 1206 | 21.77 | IV | R. tanezumi | 833 | 59.76 |
| E. miletus | 747 | 13.48 | E. miletus | 162 | 11.62 | ||
| R. tanezumi | 622 | 11.23 | V | R. tanezumi | 1848 | 75.24 | |
| A. ilex | 566 | 10.21 | |||||
| II | R. tanezumi | 1593 | 25.11 | Total | R. tanezumi | 5387 | 29.82 |
| E. miletus | 1209 | 19.05 | (I–V) | A. chevrieri | 2216 | 12.27 | |
| A. chevrieri | 782 | 12.32 | E. miletus | 2175 | 12.04 | ||
| III | R. norvegicus | 670 | 28.79 | R. norvegicus | 1452 | 8.04 | |
| R. tanezumi | 491 | 21.1 | |||||
| Mus caroli | 248 | 10.66 | |||||
| Taxonomic Taxa of Gamasid Mites | Collected Species and Individuals of Gamasid Mites (the Figures in the Brackets Are the Collected Individuals for Each Mite Species). |
|---|---|
| Laelapidae | 135,110 individuals; 107 species; 17 genera. |
| Laelaps | L. nuttalli (35,683); L. echidninus (27,482); L. guizhouensis (11,985); L. turkestanicus (10,196); L. traubi (4025); L. chini (8706); L. paucisetosa (2231); L. algericus (1998); L. xingyiensis (1190); L. fukienensis (4679); L. liui (533); L. jettmari (425); L. hongaiensis (2); L. jingdongensis (622); L. extremi (14); L. clethrionomydis (17); L. taingueni (2); L. hilaris (96); L. micromydis (7); L. sedlaceki (1) |
| Haemolaelaps | H. glasgowi (404); H. casalis (50); H. petauristae (5); H. anomalis (1); H. chinensis (11); H. traubi (83); H. cordatus (12); H. semidesertus (2); H. orientalis (27); H. liae (2); H. triangular (6) |
| Androlaelaps | A. singularis (177); A. hsui (29); A. subpavlovskii (6); A. singuloides (7) |
| Dipolaelaps | D. anourosorecis (14,317); D. jiangkouensis (98); D. longisetosus (4); D. chimmarogalis (7); Dipolaelaps hoi (5) |
| Hyperlaelaps | H. microti (72) |
| Neocypholaelaps | N. indica (2) |
| Tricholaelaps | T. myonysognathus (384) |
| Hypoaspis | H. pavlovskii (545); H. miles (143); H. lubrica (166); H. chianensis (61); H. praesternalis (20); H. concinna (356); H. aculeifer (2); H. ovatus (238); H. digitalis (5); H. tengi (9); H. chelaris (1); H. hrdyi (13); H. haiyuanensis (1); H. qinghaiensis (5); H. lecae (16); H. sorecis (12); H. vacua (2) |
| Ololaelaps | O. Veneta (1) |
| Haemogamasus | H. oliviformis (914); H. dorsalis (271); H. gongshanensis (259); H. monticola (150); H. sexsetosus (123); H. pontiger (40); H. multidentis (69); H. quadrisetatus (17); H. yunlongensis (3); H. paradauricus (36); H. sanxiaensis (110); H. hodosi (4); H. trifurcisetus (41); H. quadratus (4); H. szechwanensis (19); H. nidiformis (8); H. dauricus (2); H. gui (6); H. nidi (4); H. emeiensis (20); H. parascaptoris (11) |
| Eulaelaps | E. stabularis (43); E. shanghaiensis (815); E. dremomydis (1524); E. substabularis (911); E. huzhuensis (164); E. silvestris (6); E. dongfangis (3); E. tsinghaiensis (5); E. novus (12) |
| Gymnolaelaps | G. sinensis (4); G. weishanensis (46) |
| Cosmolaelaps | C. retirugi (34); C. yeruiyuae (71) |
| Hirstionyssus | H. sunci (1497); H. callosciuri (31); H. neosinicus (8); H. qinghaiensis (1); H. microti (4); H. isabellinus (11); H. musculi (64); H. hupehensis (1); H. phodopi (2) |
| Mysolaelaps | M. cunicularis (1) |
| Qinghailaelaps | Q. gui (7) |
| Tylolaelaps | T. rhizomydis (523) |
| Dermanyssidae | 388 individuals; 2 species; 2 genera |
| Liponyssoides | L. muris (295) |
| Echinonyssus | E. nasatus (93) |
| Macronyssidae | 4135 individuals; 2 species; 2 genera |
| Ornithonyssus | O. bacoti (4134) |
| Macronyssus | M. hongheensis (1) |
| Aceosejidae | 207 individuals; 14 species; 1 genus |
| Lasioseius | L. medius (97); L. trifurcipilus (19); L. qinghaiensis (38); L. multispathus (1); L. liaohaorongae (8); L. chenpengi (1); L. analis (12); L. praevius (17); L. jilinensis (6); L. paucispathus (1); L. confusus (4); Lasioseius spatulus (1); L. sugawari (1); L. daanensis (1) |
| Ameroseiidae | 8 individuals; 3 species; 2 genera |
| Ameroseius | A. taoerhensis (3); A. denticulatus (3) |
| Sinoseius | S. lobatus (2) |
| Parasitidae | 90 individuals; 12 species; 3 genera |
| Parasitus | P. consanguineus (33); P. wangdunqingi (8); P. baoshanensis (1); P. wentinghuani (5); P. fragilis (1); P. quadrichaetus (2) |
| Vulgarogamasus | V. xiphoideus (2); V. oudemansi (1); V. xinjiangensis (4); V. radialis (1); V. plumosus (31) |
| Amblygamasus | A. shennongjiaensis (1) |
| Phytoseiidae | 1 individual; 1 species; 1 genus |
| Amblyseius | A. ishizuchiensis (1) |
| Ascidae | 6 individuals; 3 species; 3 genera |
| Asca | A. idiobasis (4) |
| Antennoseius | A. sinicus (1) |
| Paraproctolaelaps | P. zhongweiensis (1) |
| Parholaspidae | 6 individuals; 4 species; 2 genera |
| Parholaspis | P. wuhanensis (1) |
| Gamasholaspis | G. eothenomydis (2); G. concavus (2); G. imiteothenomydis (1) |
| Macrochelidae | 447 individuals; 10 species; 3 genera |
| Macrocheles | M. liguizhenae (389); M. muscaedomesticae (37); M. sinicus (4); M. plateculus (1); M. glaber (8); M. plumiventris (2); M. merdarius (1); M. nataliae (3) |
| Glyptholaspis | G. wuhouyongi (1) |
| Holostaspella | H. ornata (1) |
| Pachylaelaptidae | 17 individuals; 3 species; 1 genus |
| Pachylaelaps | P. badongensis (1); P. nuditectus (14); P. xizangensis (2) |
| Rhodacaridae | 2 individuals; 2 species; 2 genera |
| Euryparasitus | E. laxiventralis (1) |
| Rhodacarellus | R. liuzhiyingi (1) |
| Eviphididae | 1 individual; 1 species; 1 genus |
| Eviphis | E. wanglangensis (1) |
| Blattisocidae | 1093 individuals; 3 species; 1 genus |
| Proctolaelaps | P. pygmaeus (1079); P. yinchuanensis (1); P. pistilli (13) |
| Names of Vector Gamasid Mite Species | Numbers and Constituent Ratios (Cr,) of the Mites | Number of Host Species (Host Range) | Distribution in Different Microregions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Cr% | |||
| Laelapsechidninus | 27,482 | 59.79 | 25 | I, II, III, IV, V |
| L.turkestanicus | 10,196 | 22.18 | 35 | I, II, III, IV, V |
| L. algericus | 1998 | 4.35 | 7 | I, II, III, IV, V |
| L. jettmari | 425 | 0.92 | 10 | I, II, III |
| L. clethrionomydis | 17 | 0.04 | 5 | I, II, III |
| Haemolaelaps glasgowi | 404 | 0.88 | 14 | I, II, III, V |
| H. casalis | 50 | 0.11 | 13 | I, II, III, IV, V |
| Tricholaelaps myonysognathus | 384 | 0.84 | 12 | I, II, III, IV, V |
| Haemogamasus nidi | 4 | 0.01 | 3 | I, II, V |
| Eulaelaps stabularis | 43 | 0.09 | 10 | I, II, III, V |
| E. shanghaiensis | 815 | 1.77 | 11 | I, II, III |
| Hirstionyssus isabellinus | 11 | 0.02 | 5 | I, II, III, V |
| Ornithonyssus bacoti | 4134 | 8.99 | 15 | I, II, III, IV, V |
| Total | 45,963 | 100.00 | - | - |
| Names of Vector Gamasid Mites | Rickettsial Pox | HFRS | TBE | LCM | Psittacosis | Endemic Typhus | Q Fever | North-Asian Tick-Borne Typhus | Scrub Typhus | Tularemia | Plague | Leptospirosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L.echidninus | # | ▲ | # | # | # | |||||||
| L.turkestanicus | # | |||||||||||
| L. algericus | # | # | ||||||||||
| L. jettmari | ||||||||||||
| L. clethrionomydis | # | # | ||||||||||
| H. glasgowi | #▲◯ | # | # | ▲ | # | #▲ | ||||||
| H. casalis | # | # | # | |||||||||
| T. myonysognathus | #▲ | # | ||||||||||
| H. nidi | # | # | #▲ | ▲ | # | |||||||
| E. stabularis | #▲◯ | # | ||||||||||
| E. shanghaiensis | ||||||||||||
| H. isabellinus | # | ▲ | # | # | ◯ | |||||||
| O. bacoti | #◯ | #▲ | ▲ | #◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ▲ |
| Different Groups of Gamasid Mites | No. of Species and Constituent Ratio (Cr, %) of Gamasid Mites | No. of Individuals and Constituent Ratio (Cr, %) of Gamasid Mites | Corresponding Families of Gamasid Mites in Zoological Taxonomy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Cr, % | No. | Cr, % | ||
| Ectoparasitic group | 129 | 77.25 | 140,738 | 99.46 | Laelapidae, Dermanyssidae, Macronyssidae, Ameroseiidae, Ascidae, Parholaspidae, Rhodacaridae, Blattisocidae |
| Free-living group | 38 | 22.75 | 763 | 0.54 | Macrochelidae, Parasitidae, Phytoseiidae, Aceosejidae, Pachylaelaptidae, Eviphididae |
| Total | 167 | 100 | 141,501 | 100 | 14 families |
| Zoogeographical Microregions | The Numbers of Species and Individuals of Gamasid Mites | The Average Number of Species , Average Margalef Richness Index , Average Simpson Diversity Index , and Average Shannon–Wiener Diversity Index () | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Species | Individuals | |||||
| I | 108 | 34,932 | 31.73 | 3.98 | 0.77 | 1.97 |
| II | 105 | 50,413 | 30.62 | 3.69 | 0.66 | 1.62 |
| III | 72 | 14,523 | 27.60 | 3.34 | 0.78 | 1.89 |
| IV | 49 | 15,760 | 28.00 | 3.13 | 0.74 | 1.62 |
| V | 77 | 25,873 | 28.00 | 3.15 | 0.63 | 1.34 |
| Total | 167 | 141,501 | - | - | - | - |
| Microregions | Names of Dominant Gamasid Mites | Numbers and Constituent Ratios (Cr)% of Gamasid Mites | Microregions | Names of Dominant Gamasid Mites | Numbers and Constituent Ratios (Cr)% of Gamasid Mites | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Cr, % | No. | Cr, % | ||||
| I | D.anourosorecis | 8622 | 24.68 | IV | L.nuttalli | 3341 | 21.20 |
| L.nuttalli | 7410 | 21.21 | D.anourosorecis | 2906 | 18.44 | ||
| L.echidninus | 5115 | 14.64 | L.echidninus | 2318 | 14.71 | ||
| II | L.nuttalli | 11,092 | 22.00 | V | L.nuttalli | 11,357 | 43.90 |
| L.echidninus | 8767 | 17.39 | L.echidninus | 8066 | 31.18 | ||
| L.guizhouensis | 8615 | 17.09 | Total (I–V) | L.nuttalli | 35,683 | 25.22 | |
| III | L.echidninus | 3216 | 22.14 | L.echidninus | 27,482 | 19.42 | |
| L.nuttalli | 2483 | 17.10 | D.anourosorecis | 14,317 | 10.12 | ||
| L.turkestanicus | 1916 | 13.19 | L.guizhouensis | 11,985 | 8.47 | ||
| Names of Gamasid Mites | Individuals of Gamasid Mites | Constituent Ratio (Cr) % of Gamasid Mites | Spatial Niches (Bi) of Gamasid Mites | Host Niches (Bi) and Host Ranges of Gamasid Mites | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi | Numbers of Collected Sites | Bi | Host Ranges | |||
| L.nuttalli * | 35,683 | 25.22 | 27.08 | 37 | 3.49 | 32 |
| L.echidninus * | 27,482 | 19.42 | 28.95 | 37 | 4.73 | 25 |
| D.anourosorecis * | 14,317 | 10.12 | 6.46 | 14 | 1.60 | 29 |
| L.guizhouensis * | 11,985 | 8.47 | 4.87 | 18 | 1.44 | 21 |
| L.turkestanicus * | 10,196 | 7.21 | 22.95 | 22 | 3.13 | 35 |
| L.chini * | 8706 | 6.15 | 12.32 | 24 | 1.74 | 34 |
| L. fukienensis | 4679 | 3.31 | 10.74 | 13 | 2.83 | 19 |
| O. bacoti | 4134 | 2.92 | 11.77 | 27 | 2.98 | 15 |
| L. traubi | 4025 | 2.84 | 12.68 | 16 | 3.50 | 27 |
| L. paucisetosa | 2231 | 1.58 | 5.36 | 14 | 1.41 | 11 |
| L. algericus | 1998 | 1.41 | 4.27 | 13 | 1.45 | 7 |
| E. dremomydis | 1524 | 1.08 | 3.03 | 8 | 1.42 | 14 |
| H. sunci | 1497 | 1.06 | 12.96 | 30 | 8.41 | 31 |
| L.xingyiensis | 1190 | 0.84 | 4.58 | 17 | 1.64 | 11 |
| P. pygmaeus | 1079 | 0.76 | 26.07 | 29 | 6.18 | 25 |
| H. oliviformis | 914 | 0.65 | 21.52 | 19 | 5.05 | 29 |
| E. substabularis | 911 | 0.64 | 7.88 | 13 | 2.24 | 21 |
| E. shanghaiensis | 815 | 0.58 | 6.57 | 11 | 1.52 | 11 |
| L. jingdongensis | 622 | 0.44 | 7.95 | 5 | 4.59 | 12 |
| H. pavlovskii | 545 | 0.39 | 23.04 | 34 | 11.57 | 26 |
| L. liui | 533 | 0.38 | 12.32 | 10 | 1.34 | 3 |
| T. rhizomydis | 523 | 0.37 | 2.50 | 1 | 1.28 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, P.-W.; Peng, P.-Y.; Guo, X.-G.; Song, W.-Y.; Ren, T.-G.; Zhao, Y.-F.; Dong, W.-G.; Jin, D.-C. Faunal and Ecological Analysis of Gamasid Mites (Acari: Mesostigmata) Associated with Small Mammals in Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Insects 2025, 16, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16030305
Yin P-W, Peng P-Y, Guo X-G, Song W-Y, Ren T-G, Zhao Y-F, Dong W-G, Jin D-C. Faunal and Ecological Analysis of Gamasid Mites (Acari: Mesostigmata) Associated with Small Mammals in Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Insects. 2025; 16(3):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16030305
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Peng-Wu, Pei-Ying Peng, Xian-Guo Guo, Wen-Yu Song, Tian-Guang Ren, Ya-Fei Zhao, Wen-Ge Dong, and Dao-Chao Jin. 2025. "Faunal and Ecological Analysis of Gamasid Mites (Acari: Mesostigmata) Associated with Small Mammals in Yunnan Province, Southwest China" Insects 16, no. 3: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16030305
APA StyleYin, P.-W., Peng, P.-Y., Guo, X.-G., Song, W.-Y., Ren, T.-G., Zhao, Y.-F., Dong, W.-G., & Jin, D.-C. (2025). Faunal and Ecological Analysis of Gamasid Mites (Acari: Mesostigmata) Associated with Small Mammals in Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Insects, 16(3), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16030305







