20-Hydroxyecdysone Regulates the Expression of 30 Genes Specifically Expressed in Larval Digestive Tube of the Silkworm, Bombyx mori
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals and 20-Hydroxyecdysone Treatment
2.2. Identification of the 30 Genes
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Reverse Transcription PCR and Reverse Transcription–Quantitative PCR Analysis
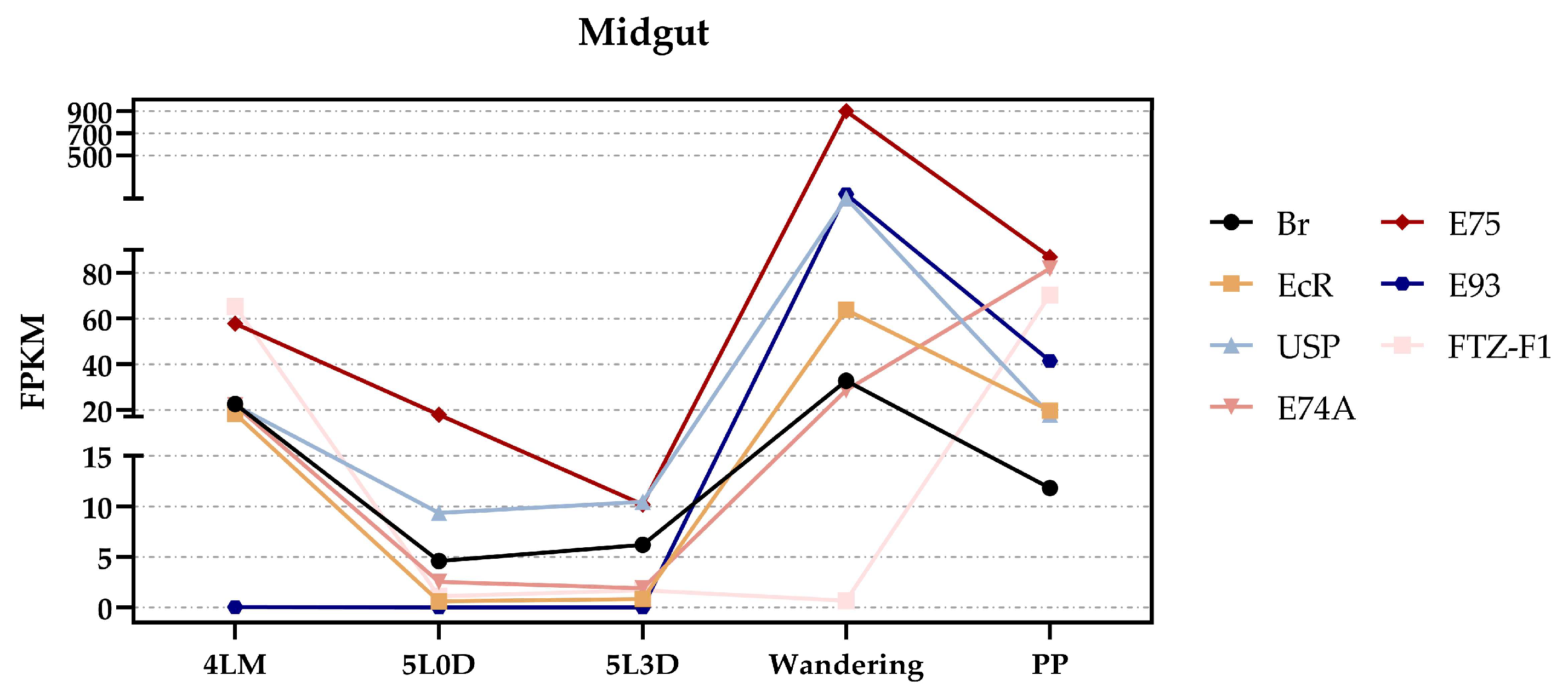
2.5. Expression Pattern Analysis of 20E Signaling Pathway
2.6. Trypsin Activity Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Expression Analysis in Digestive Tube
3.2. Developmental Expression Profile of Each Gene from Day 3 of Fourth Instar to Wandering Period
3.3. Regulation of Expression of Each Gene by 20E Treatment
3.4. The Potential Regulatory Mechanism of Each Gene by 20E in Midgut
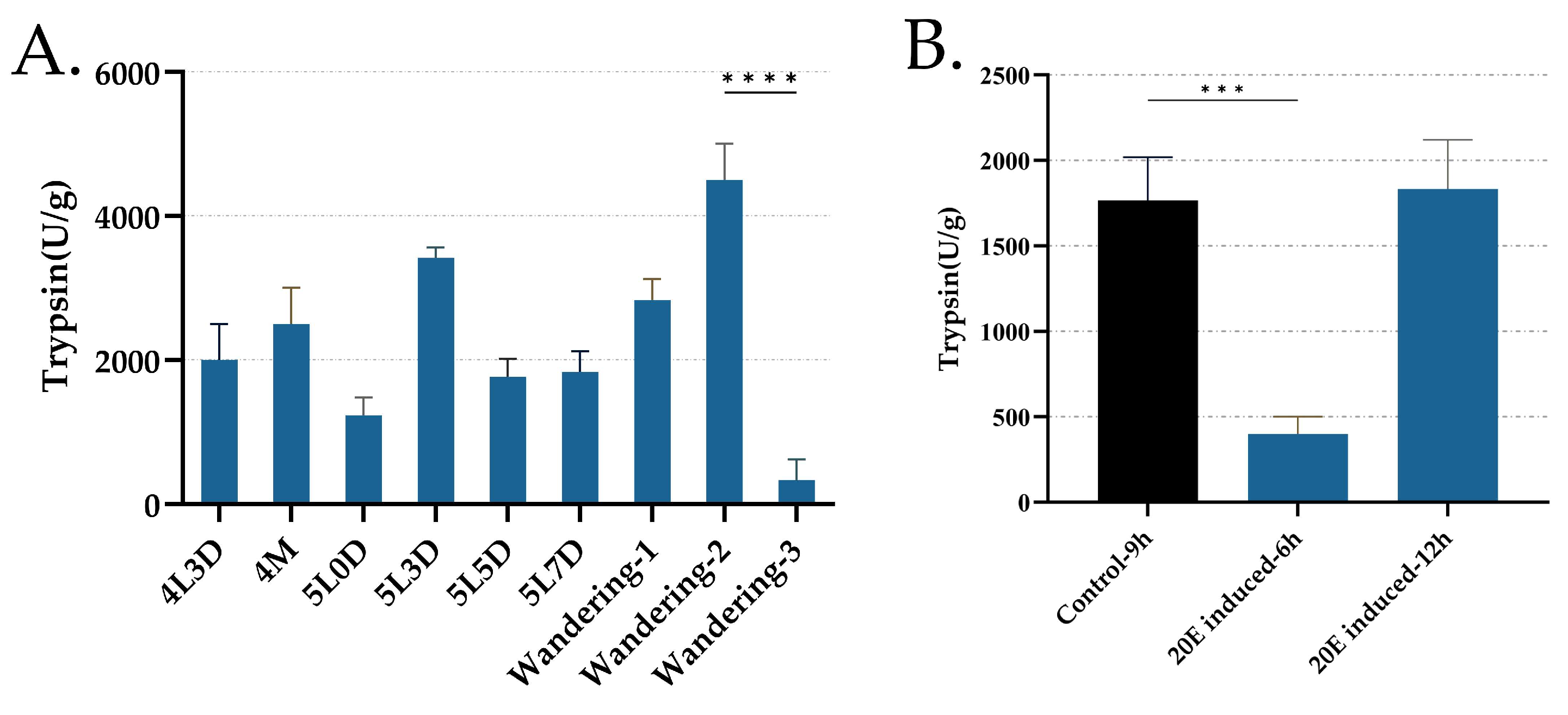
3.5. Trypsin Activity from Day 3 of the Fourth Instar to the Wandering Period and Its Regulation by 20E Treatment in Midgut
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldsmith, M.R.; Shimada, T.; Abe, H. The genetics and genomics of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2005, 50, 71–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Q.; Cheng, D.; Duan, J.; Wang, G.; Cheng, T.; Zha, X.; Liu, C.; Zhao, P.; Dai, F.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Microarray-based gene expression profiles in multiple tissues of the domesticated silkworm, Bombyx mori. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhang, M.; Qian, P.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y. iTRAQ-Based Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Digestive Juice across the First 48 Hours of the Fifth Instar in Silkworm Larvae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, X.F.; He, Y.Q.; Shuai, J.B.; Chen, X.M.; Ling, E.J. Expression of antimicrobial peptide genes in Bombyx mori gut modulated by oral bacterial infection and development. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cymborowski, B.; Bogus, M.; Beckage, N.E.; Williams, C.M.; Riddiford, L.M. Juvenile hormone titres and metabolism during starvation-induced supernumerary larval moulting of the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta L. J. Insect Physiol. 1982, 28, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Gu, S.H. Stage-dependent effects of starvation on the growth, metamorphosis, and ecdysteroidogenesis by the prothoracic glands during the last larval instar of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J. Insect Physiol. 2006, 52, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtof, M.; Lenaerts, C.; Cullen, D.; Vanden Broeck, J. Extracellular nutrient digestion and absorption in the insect gut. Cell Tissue Res. 2019, 377, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehane, M.J.; Blakemore, D.; Williams, S.; Moffatt, M.R. Regulation of digestive enzyme levels in insects. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 110, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truman, J.W.; Hiruma, K.; Allee, J.P.; MacWhinnie, S.G.B.; Champlin, D.T.; Riddiford, L.M. Juvenile hormone is required to couple imaginal disc formation with nutrition in insects. Science 2006, 312, 1385–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaidina, M.; Delanoue, R.; Gronke, S.; Partridge, L.; Leopold, P. A Drosophila Insulin-like Peptide Promotes Growth during Nonfeeding States. Dev. Cell 2009, 17, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, A.; Nijhout, H.F. A Switch in the Control of Growth of the Wing Imaginal Disks of Manduca sexta. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layalle, S.; Arquier, N.; Leopold, P. The TOR Pathway Couples Nutrition and Developmental Timing in Drosophila. Dev. Cell 2008, 15, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Iwami, M. Ecdysteroid ingestion suppresses carbohydrate hydrolysis in larvae of the silkworm Bombyx mori. Sci. Nat. 2020, 107, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Iwami, M. Sequential changes in the regulatory mechanism of carbohydrate digestion in larvae of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2021, 191, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Sakurai, S.; Iwami, M. Steroidal regulation of hydrolyzing activity of the dietary carbohydrates in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J. Insect Physiol. 2011, 57, 1282–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizoguchi, A.; Ohashi, Y.; Hosoda, K.; Ishibashi, J.; Kataoka, H. Developmental profile of the changes in the prothoracicotropic hormone titer in hemolymph of the silkworm Bombyx mori: Correlation with ecdysteroid secretion. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2001, 31, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzelak, K. Control of expression of silk protein genes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 110, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Wei, Z.; Luo, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhang, G.; Xia, Q.; Wang, Y. SilkDB 3.0: Visualizing and exploring multiple levels of data for silkworm. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D749–D755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L.; Tosatto, S.C.E.; Paladin, L.; Raj, S.; Richardson, L.J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D412–D419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.X.; Ueda, H.; Hirose, S. MBF2 is a tissue- and stage-specific coactivator that Is regulated at the step of nuclear transport in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Dev. Biol. 2000, 225, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafino, S.; Giannios, P.; Casanova, J.; Martín, D.; Franch-Marro, X. Antagonistic role of the BTB-zinc finger transcription factors Chinmo and Broad-Complex in the juvenile/pupal transition and in growth control. eLife 2023, 12, e84648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.-Z.; Ding, Y.; Wang, X.; Zou, Z.; Raikhel, A.S. E93 confers steroid hormone responsiveness of digestive enzymes to promote blood meal digestion in the midgut of the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 134, 103580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caccia, S.; Casartelli, M.; Tettamanti, G. The amazing complexity of insect midgut cells: Types, peculiarities, and functions. Cell Tissue Res. 2019, 377, 505–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napoleao, T.H.; Albuquerque, L.P.; Santos, N.D.L.; Nova, I.C.V.; Lima, T.A.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Pontual, E.V. Insect midgut structures and molecules as targets of plant-derived protease inhibitors and lectins. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 1212–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terra, W.R.; Ferreira, C. Chapter 74—Digestive System. In Encyclopedia of Insects, 2nd ed.; Resh, V.H., Cardé, R.T., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Stoffolano, J.G., Jr.; Haselton, A.T. The adult Dipteran crop: A unique and overlooked organ. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 205–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Huang, W.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Beerntsen, B.T.; Song, H.; Ling, E. Analysis of gene expression in the midgut of Bombyx mori during the larval molting stage. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigg, H.N.; Svoboda, J.A.; Thompson, M.J.; Dutky, S.R.; Kaplanis, J.N.; Robbins, W.E. Ecdysome 20-hydroxylase from the midgut of the tobacco hornworm (Manduca sexta L.). Experientia 1976, 32, 438–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.A.; Weirich, G.F. Ecdysone 20-hydroxylation and 3-epimerization in larvae of the gypsy moth, Lymantria dispar L.: Tissue distribution and developmental changes. J. Insect Physiol. 1997, 43, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, T.; Obara, Y.; Iwami, M.; Sakurai, S. Commencement of pupal commitment in late penultimate instar and its hormonal control in wing imaginal discs of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J. Insect Physiol. 2004, 50, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnuvel, K.M.; Nithya, K.; Sirigineedi, S.; Awasthi, A.K.; Yamakawa, M. In vitro antiviral activity of an alkaline trypsin from the digestive juice of Bombyx mori larvae against nucleopolyhedrovirus. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2012, 81, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.D.; Dong, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, K.Y.; Guo, P.C.; Zhao, P.; Xia, Q.Y. Proteomics Provides Insight into the Interaction between Mulberry and Silkworm. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 2472–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Li, H.; Hao, F.; Li, N.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H. Developmental Changes for the Hemolymph Metabolome of Silkworm (Bombyx mori L.). J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 2331–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzetti, E.; Casartelli, M.; D’Antona, P.; Montali, A.; Romanelli, D.; Cappellozza, S.; Caccia, S.; Grimaldi, A.; de Eguileor, M.; Tettamanti, G. Midgut epithelium in molting silkworm: A fine balance among cell growth, differentiation, and survival. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2016, 45, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungreis, A.M.; Wyatt, G.R. Sugar release and penetration in insect fat body: Relations to regulation of haemolymph trehalose in developing stages of Hyalophora cecropia. Biol. Bull. 1972, 143, 367–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, O.; Sumida, M.; Hasegawa, K. Developmental changes in midgut trehalase activity and its localization in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J. Insect Physiol. 1974, 20, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, Y.; Iwami, M.; Osanai, M.; Sakurai, S. Dynamics of haemolymph sorbitol-6-phosphate and its control by ecdysteroid in the larvae of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1997, 27, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smagghe, G.J.; Elsen, K.; Loeb, M.J.; Gelman, D.B.; Blackburn, M. Effects of a fat body extract on larval midgut cells and growth of lepidoptera. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 2003, 39, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smagghe, G.; Vanhassel, W.; Moeremans, C.; De Wilde, D.; Goto, S.; Loeb, M.J.; Blackburn, M.B.; Hakim, R.S. Stimulation of midgut stem cell proliferation and differentiation by insect hormones and peptides. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1040, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzetti, E.; Romanelli, D.; Caccia, S.; Cappellozza, S.; Congiu, T.; Rajagopalan, M.; Grimaldi, A.; de Eguileor, M.; Casartelli, M.; Tettamanti, G. The midgut of the silkmoth Bombyx mori is able to recycle molecules derived from degeneration of the larval midgut epithelium. Cell Tissue Res. 2015, 361, 509–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
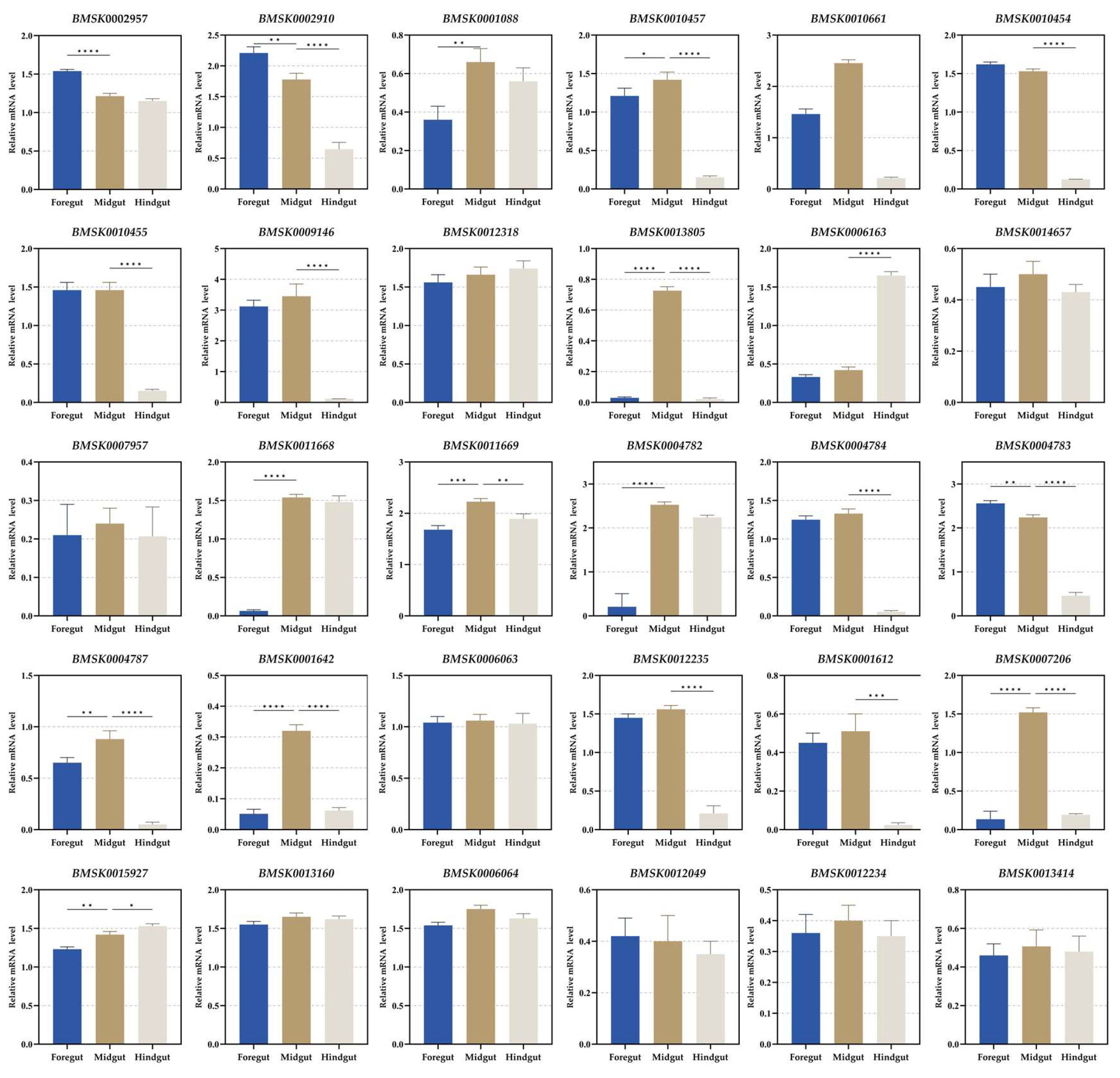
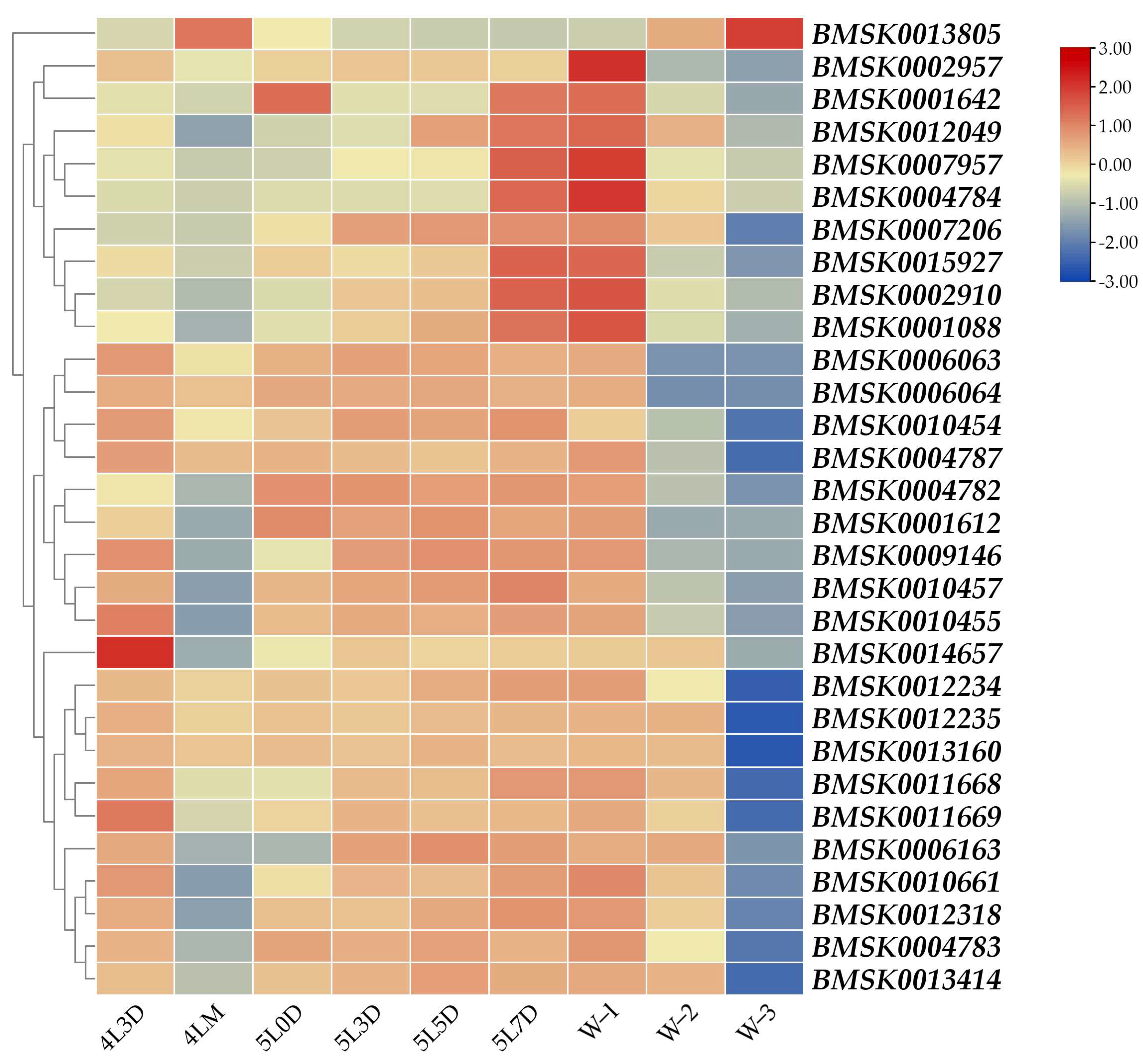
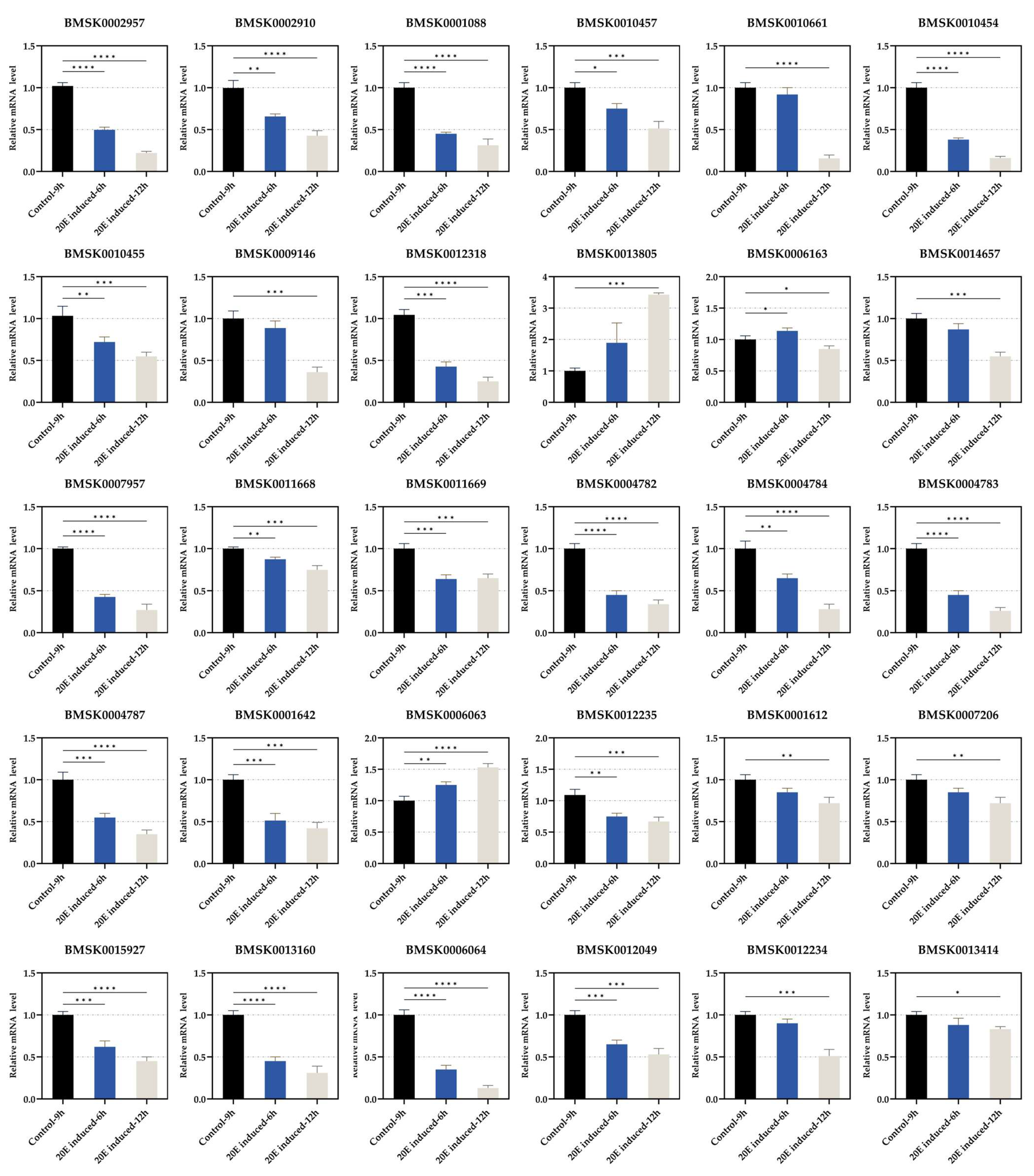
| SilkDB 3.0 ID | SilkDB 2.0 ID | Description | Location (Chr.) | Pfam | KOG | GO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMSK0002957 | BGIBMGA003604 | trypsin, alkaline C | 5 | PF00089 | KOG3627 | 0005615; 0004252 |
| BMSK0002910 | BGIBMGA003568 | trypsin, alkaline A | 5 | PF00089 | KOG3627 | 0005615; 0004252 |
| BMSK0001088 | BGIBMGA007377 | collagenase-like | 3 | PF00089 | KOG3627 | 0004175; 0004252; 0006508 |
| BMSK0010457 | BGIBMGA008281 | ovochymase-2-like | 18 | PF00089 | KOG3627 | 0005615; 0004252 |
| BMSK0010661 | BGIBMGA008514 | transmembrane protease serine 9-like | 18 | PF00089 | KOG3627 | 0005615; 0004252; 0030574 |
| BMSK0010454 | BGIBMGA008279 | ovochymase-2-like | 18 | PF00089 | KOG3627 | 0005615; 0004252 |
| BMSK0010455 | BGIBMGA008280 | chymotrypsin-2 | 18 | PF00089 | KOG3627 | 0005615; 0004252 |
| BMSK0009146 | BGIBMGA012791 | transmembrane protease serine 9 | 16 | PF00089 | KOG3627 | 0005576; 0004252; 0030574 |
| BMSK0012318 | BGIBMGA007183 | kallikrein-1 | 21 | PF00089 | - | - |
| BMSK0014657 | BGIBMGA004830 | carboxypeptidase B | 25 | PF00246 | KOG2650 | 0005576; 0004181; 0008270 |
| BMSK0007957 | BGIBMGA009477 | zinc carboxypeptidase | 14 | PF00246 | KOG2650 | 0005576; 0004181; 0008270 |
| BMSK0004782 | BGIBMGA008060 | aminopeptidase N-1 | 9 | PF01433 | KOG1046 | 0031225; 0005886; 0004177 |
| BMSK0004784 | BGIBMGA008062 | membrane alanyl aminopeptidase-like | 9 | PF01433 | KOG1046 | 0031225; 0005886; 0004177; 0008237; 0008270 |
| BMSK0004783 | BGIBMGA008061 | aminopeptidase N-3 | 9 | PF01433 | KOG1046 | 0031225; 0005886; 0004177; 0008237; 0008270 |
| BMSK0004787 | BGIBMGA008017 | aminopeptidase N-7 | 9 | PF01433 | KOG1046 | 0031225; 0005886; 0004177; 0008237; 0008270 |
| BMSK0006063 | BGIBMGA001640 | metallopeptidase family M24 | 11 | PF00557 | KOG2413 | 0005829; 0046872; 0070006; 0006508 |
| BMSK0007206 | BGIBMGA010349 | serine carboxypeptidase-like 51 | 12 | PF00450 | - | 0005794; 0016021; 0004185; 0006915; 0030448; 0075307 |
| BMSK0006064 | BGIBMGA001639 | creatinase | 11 | PF01321 | KOG2413 | 0005829; 0046872; 0070006; 0006508 |
| BMSK0001642 | BGIBMGA006066 | maltase A1 | 4 | PF00128 | KOG0471 | 0004558; 0032450 |
| BMSK0012235 | BGIBMGA001569 | sucrase-isomaltase, intestinal-like | 21 | PF01055 | KOG1066 | 0005783; 0031160; 0090599; 0030246; 0016052 |
| BMSK0015927 | BGIBMGA013757 | polysaccharide deacetylase | 28 | PF01522 | - | - |
| BMSK0013805 | BGIBMGA008141 | alpha-esterase 49 precursor | 24 | PF00135 | KOG1516 | 80030 |
| BMSK0006163 | BGIBMGA011895 | pancreatic triacylglycerol lipase | 11 | PF00151 | - | 0005576; 0046872; 0016042 |
| BMSK0001612 | BGIBMGA008818 | alkaline phosphatase | 3 | PF00245 | KOG4126 | 0031225; 0005886; 0004035; 0046872 |
| BMSK0011668 | BGIBMGA004286 | transcription activator MBF2 | 20 | PF15868 | - | - |
| BMSK0011669 | BGIBMGA004285 | ACN81326.1, Bm122 | 20 | PF15868 | - | - |
| BMSK0013160 | BGIBMGA011074 | gamma interferon-inducible lysosomal thiol reductase | 23 | PF03227 | - | - |
| BMSK0012049 | BGIBMGA002366 | uncharacterized protein LOC101742057 | 21 | - | - | - |
| BMSK0012234 | BGIBMGA001568 | lysosomal alpha-glucosidase-like | 21 | - | - | - |
| BMSK0013414 | BGIBMGA011598 | uncharacterized protein OBRU01 20501, partial | 23 | - | - | - |
| Cluster | Functional Annotation | No. of Genes | Pfam | Name of Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Protein digestion | 18 | PF00089 | BMSK0002957, BMSK0002910, BMSK0001088, BMSK0010457, BMSK0010661, BMSK0010454, BMSK0010455, BMSK0009146, BMSK0012318 |
| PF01433 | BMSK0004782, BMSK0004783, BMSK0004784, BMSK0004787 | |||
| PF00246 | BMSK0014657, BMSK0007957 | |||
| PF00557 | BMSK0006063 | |||
| PF00450 | BMSK0007206 | |||
| PF01321 | BMSK0006064 | |||
| 2 | Carbohydrate digestion | 3 | PF00128 | BMSK0001642 |
| PF01055 | BMSK0012235 | |||
| PF01522 | BMSK0015927 | |||
| 3 | Lipid digestion | 2 | PF00135 | BMSK0013805 |
| PF00151 | BMSK0006163 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Xia, M.; Huang, S.; Zhang, G.; Tang, Y.; Xu, P.; Zhang, M. 20-Hydroxyecdysone Regulates the Expression of 30 Genes Specifically Expressed in Larval Digestive Tube of the Silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insects 2025, 16, 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16030291
Li J, Xia M, Huang S, Zhang G, Tang Y, Xu P, Zhang M. 20-Hydroxyecdysone Regulates the Expression of 30 Genes Specifically Expressed in Larval Digestive Tube of the Silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insects. 2025; 16(3):291. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16030291
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiahao, Mulin Xia, Songyao Huang, Guangxie Zhang, Yuncheng Tang, Pingzhen Xu, and Meirong Zhang. 2025. "20-Hydroxyecdysone Regulates the Expression of 30 Genes Specifically Expressed in Larval Digestive Tube of the Silkworm, Bombyx mori" Insects 16, no. 3: 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16030291
APA StyleLi, J., Xia, M., Huang, S., Zhang, G., Tang, Y., Xu, P., & Zhang, M. (2025). 20-Hydroxyecdysone Regulates the Expression of 30 Genes Specifically Expressed in Larval Digestive Tube of the Silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insects, 16(3), 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16030291





