Gut Microbiome Diversity in European Honeybees (Apis mellifera L.) from La Union, Northern Luzon, Philippines
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
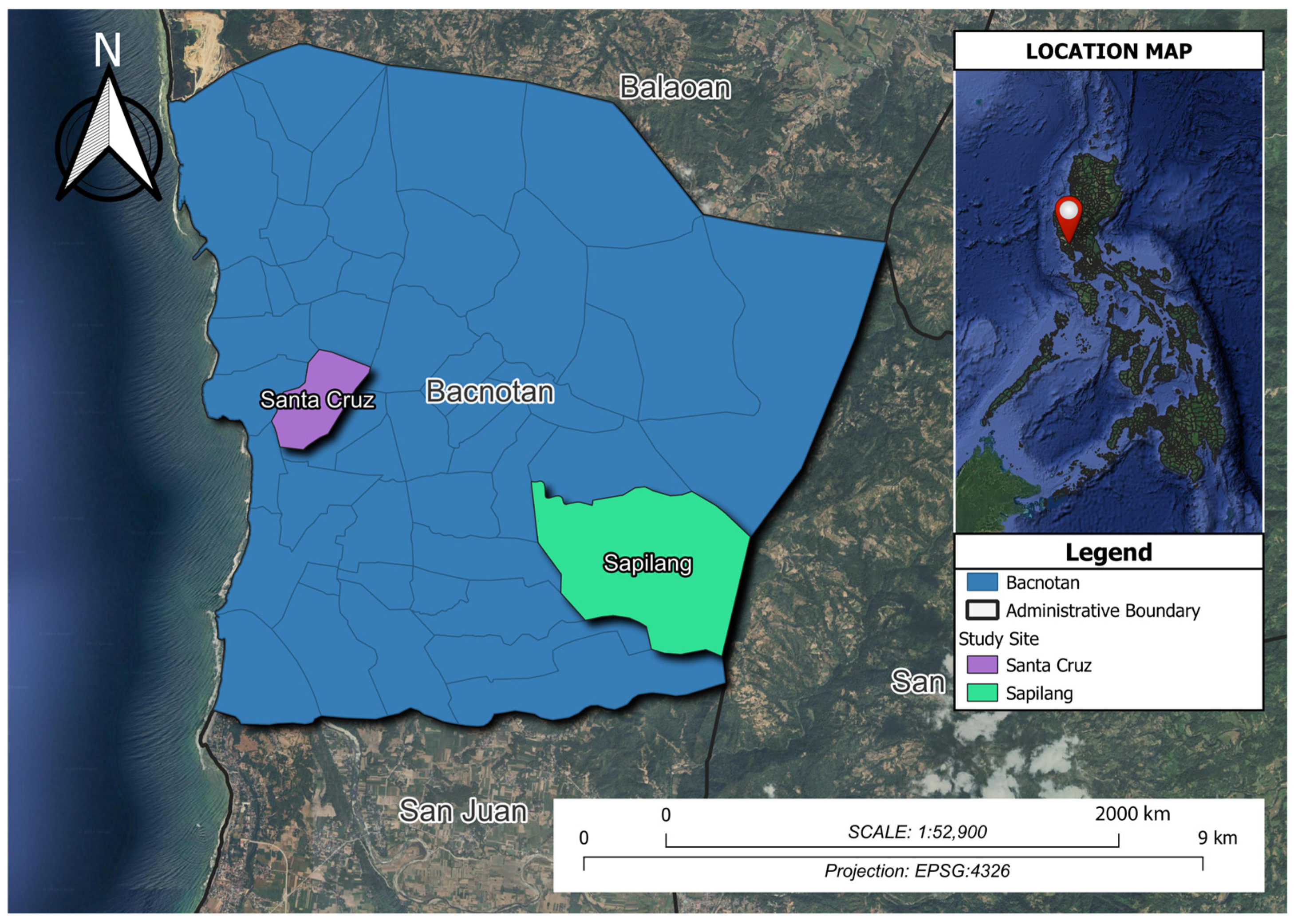
2.1. Honeybee Sample Collection and Site Description
2.2. Sample Preparation and Genomic DNA Extraction
2.3. Bacterial 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon and Fungal ITS Gene Amplicon Sequencing
2.4. Bioinformatic and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Sequence Read Curation
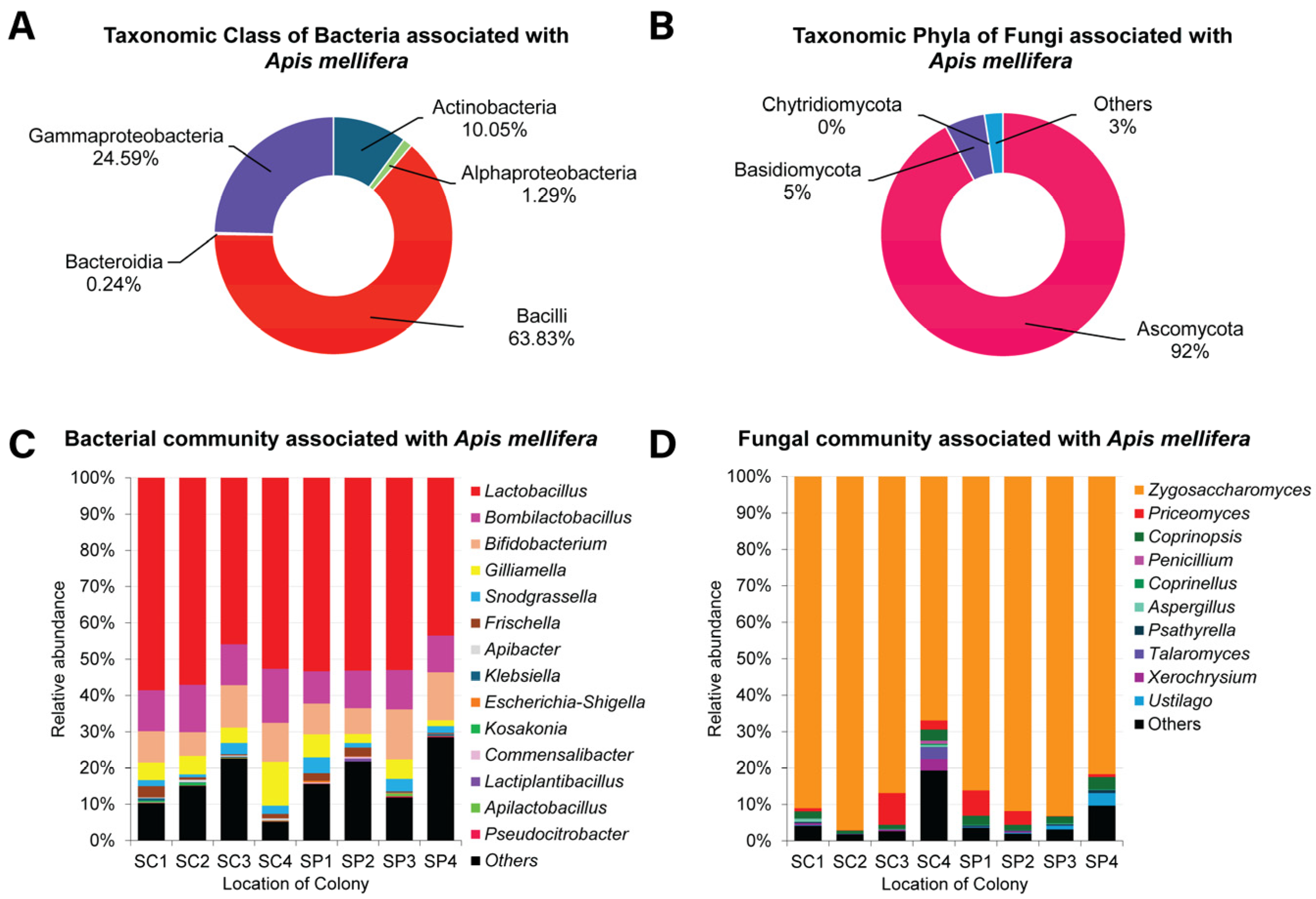
3.2. The Gut Bacteriota of Apis mellifera
3.3. The Gut Mycobiota of Apis mellifera
3.4. Differences in Diversity Across Site Locations
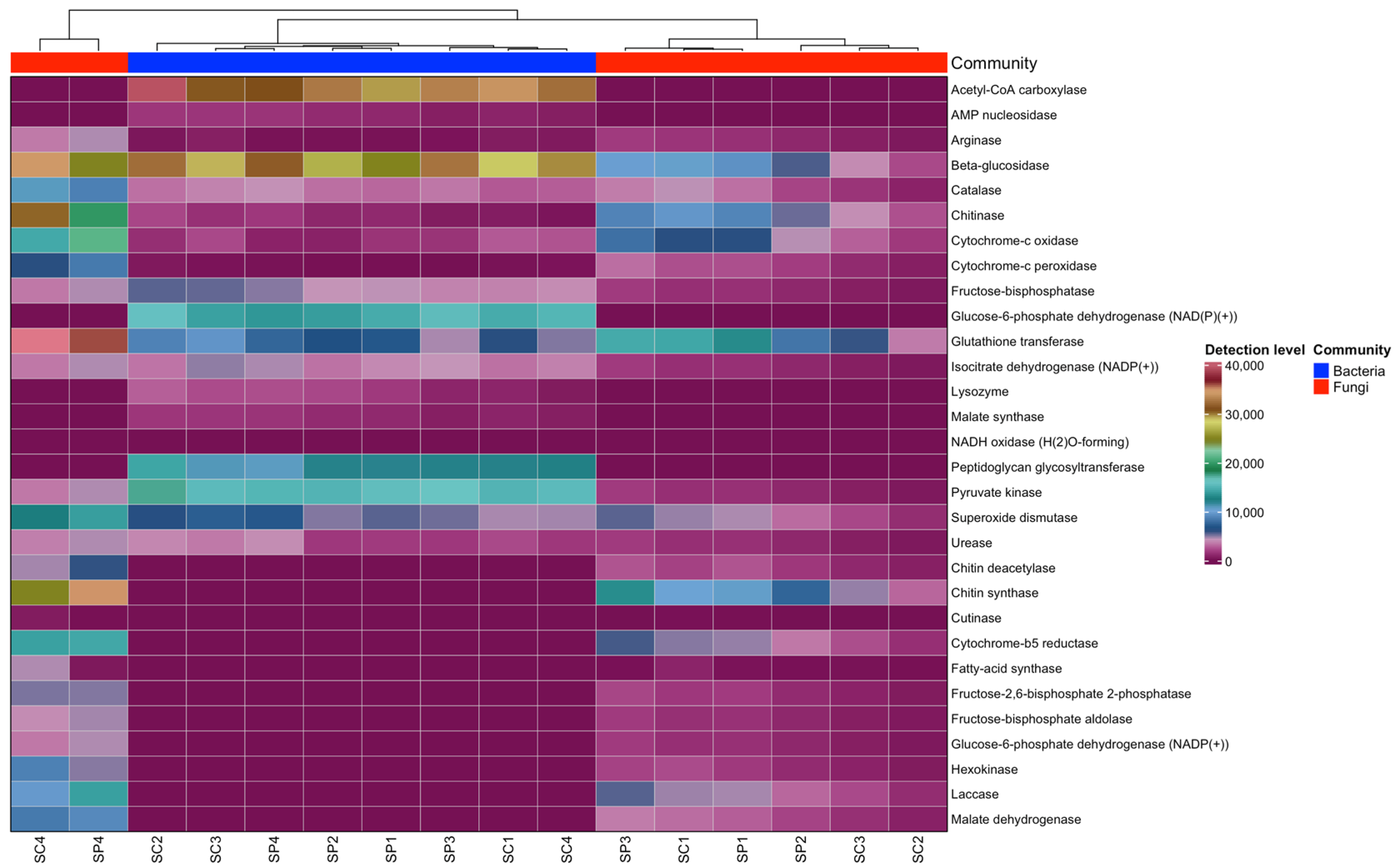
3.5. Functional Properties of the Gut Microbiome of Honeybee, Apis mellifera
3.6. Correlations of Bacterial and Fungal Microbiome
4. Discussion
4.1. Environmental Factors Shape Microbial Community Similarities Between Sites
4.2. Characterization of the Core Gut Microbiome and Fungal Diversity in Apis mellifera
4.3. Ecological and Geographical Factors Contributing to Gut Microbiome Similarity
4.4. Predicted Functional Enzymes and Their Roles in Honeybee Health
4.5. Microbial Association Network Support the Bee’s Immune Defense
4.6. Building Baseline Data for Honeybee Microbiome in a Unique Environment in the Philippines
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aizen, M.A.; Garibaldi, L.A.; Cunningham, S.A.; Klein, A.M. Long-Term Global Trends in Crop Yield and Production Reveal No Current Pollination Shortage but Increasing Pollinator Dependency. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 1572–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, K.-L.J.; Kingston, J.M.; Albrecht, M.; Holway, D.A.; Kohn, J.R. The Worldwide Importance of Honey Bees as Pollinators in Natural Habitats. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20172140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouda, M.N.R.; Subramanian, S.; Kumar, A.; Ramakrishnan, B. Microbial Ensemble in the Hives: Deciphering the Intricate Gut Ecosystem of Hive and Forager Bees of Apis mellifera. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barathan, M.; Ng, S.L.; Lokanathan, Y.; Ng, M.H.; Law, J.X. The Profound Influence of Gut Microbiome and Extracellular Vesicles on Animal Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymann, K.; Moran, N.A. The Role of the Gut Microbiome in Health and Disease of Adult Honey Bee Workers. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2018, 26, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, W.K.; Mancenido, A.L.; Moran, N.A. Immune System Stimulation by the Native Gut Microbiota of Honey Bees. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, W.K.; Medina, L.A.; Koch, H.; Sing, K.-W.; Soh, E.J.Y.; Ascher, J.S.; Jaffé, R.; Moran, N.A. Dynamic Microbiome Evolution in Social Bees. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1600513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, N.A.; Hansen, A.K.; Powell, J.E.; Sabree, Z.L. Distinctive Gut Microbiota of Honey Bees Assessed Using Deep Sampling from Individual Worker Bees. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, W.K.; Moran, N.A. Gut Microbial Communities of Social Bees. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, P.; Martinson, V.G.; Moran, N.A. Functional Diversity within the Simple Gut Microbiota of the Honey Bee. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11002–11007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kešnerová, L.; Mars, R.A.T.; Ellegaard, K.M.; Troilo, M.; Sauer, U.; Engel, P. Disentangling Metabolic Functions of Bacteria in the Honey Bee Gut. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2003467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, F.J.; Miller, K.I.; McKinlay, J.B.; Newton, I.L.G. Differential Carbohydrate Utilization and Organic Acid Production by Honey Bee Symbionts. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Perreau, J.; Powell, J.E.; Han, B.; Zhang, Z.; Kwong, W.K.; Tringe, S.G.; Moran, N.A. Division of Labor in Honey Bee Gut Microbiota for Plant Polysaccharide Digestion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 25909–25916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, C.; Balloi, A.; Essanaa, J.; Crotti, E.; Gonella, E.; Raddadi, N.; Ricci, I.; Boudabous, A.; Borin, S.; Manino, A.; et al. Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis and Honeybee Health. J. Appl. Entomol. 2011, 135, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, E.V.S.; Raymann, K.; Moran, N.A. Glyphosate Perturbs the Gut Microbiota of Honey Bees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 10305–10310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Colmenero, M.; Baroja-Careaga, I.; Kovačić, M.; Filipi, J.; Puškadija, Z.; Kezić, N.; Estonba, A.; Büchler, R.; Zarraonaindia, I. Differences in Honey Bee Bacterial Diversity and Composition in Agricultural and Pristine Environments—A Field Study. Apidologie 2020, 51, 1018–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callegari, M.; Crotti, E.; Fusi, M.; Marasco, R.; Gonella, E.; De Noni, I.; Romano, D.; Borin, S.; Tsiamis, G.; Cherif, A.; et al. Compartmentalization of Bacterial and Fungal Microbiomes in the Gut of Adult Honeybees. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakumanu, M.L.; Reeves, A.M.; Anderson, T.D.; Rodrigues, R.R.; Williams, M.A. Honey Bee Gut Microbiome Is Altered by In-Hive Pesticide Exposures. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaurepaire, A.; Piot, N.; Doublet, V.; Antunez, K.; Campbell, E.; Chantawannakul, P.; Chejanovsky, N.; Gajda, A.; Heerman, M.; Panziera, D.; et al. Diversity and Global Distribution of Viruses of the Western Honey Bee, Apis mellifera. Insects 2020, 11, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosch, C.; Manigk, A.; Streicher, T.; Tehel, A.; Paxton, R.J.; Tragust, S. The Gut Microbiota Can Provide Viral Tolerance in the Honey Bee. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandel, M.; Paxton, R.J.; Al Naggar, Y. Nationwide Screening for Bee Viruses in Apis mellifera Colonies in Egypt. Insects 2023, 14, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantawannakul, P.; de Guzman, L.I.; Li, J.; Williams, G.R. Parasites, Pathogens, and Pests of Honeybees in Asia. Apidologie 2016, 47, 301–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshiyama, M.; Kimura, K. Bacteria in the Gut of Japanese Honeybee, Apis cerana japonica, and Their Antagonistic Effect against Paenibacillus larvae, the Causal Agent of American Foulbrood. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2009, 102, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bovo, S.; Ribani, A.; Utzeri, V.J.; Schiavo, G.; Bertolini, F.; Fontanesi, L. Shotgun Metagenomics of Honey DNA: Evaluation of a Methodological Approach to Describe a Multi-Kingdom Honey Bee Derived Environmental DNA Signature. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Kong, K.; Yao, Y.; Huang, Z.; Shi, S.; Liu, P.; Huang, Y.; Abbas, N.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Y. Community Composition, Bacterial Symbionts, Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities of Honeybee-Associated Fungi. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.A.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Ghramh, H.A.; Ansari, M.J.; Ali, H.; Alamri, S.A.; Al- Kahtani, S.N.; Adgaba, N.; Qasim, M.; Hafeez, M. Structural Diversity and Functional Variability of Gut Microbial Communities Associated with Honey Bees. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 138, 103793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, D.; Weston, M.; Vannette, R.L. Bees Just Wanna Have Fungi: A Review of Bee Associations with Nonpathogenic Fungi. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2023, 99, fiad077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervancia, C.R. Management and Conservation of Philippine Bees. In Asian Beekeeping in the 21st Century; Chantawannakul, P., Williams, G., Neumann, P., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 307–321. ISBN 978-981-10-8222-1. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, M.H.; Harpur, B.A. Genetic Past, Present, and Future of the Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) in the United States of America. Apidologie 2021, 52, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, P.; Neov, B.; Shumkova, R.; Palova, N. Significance of Apoidea as Main Pollinators. Ecological and Economic Impact and Implications for Human Nutrition. Diversity 2020, 12, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Pauli, N.; Biggs, E.; Barbour, L.; Boruff, B. Why Bees Are Critical for Achieving Sustainable Development. Ambio 2021, 50, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, G.; Maier, R.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Karabagias, I.K.; Plutino, M.; Bianchetto, E.; Aromolo, R.; Pignatti, G.; Ambrogio, A.; et al. The Honey Bee Apis mellifera: An Insect at the Interface between Human and Ecosystem Health. Biology 2022, 11, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Guzman, L.I.; Simone-Finstrom, M.; Cervancia, C.; Tokarz, P.; Frake, A.M. Tropilaelaps Species Identification and Viral Load Evaluation of Tropilaelaps and Varroa Mites and Their Apis mellifera Hosts in Palawan, Philippines. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2020, 170, 107324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortsch, S.; Timberlake, T.P.; Cirtwill, A.R.; Sapkota, S.; Rokoya, M.; Devkota, K.; Roslin, T.; Memmott, J.; Saville, N. Decline in Honeybees and Its Consequences for Beekeepers and Crop Pollination in Western Nepal. Insects 2024, 15, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phiri, B.J.; Fèvre, D.; Hidano, A. Uptrend in Global Managed Honey Bee Colonies and Production Based on a Six-Decade Viewpoint, 1961–2017. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licuanan, W.Y.; Cabreira, R.W.; Aliño, P.M. Chapter 23—The Philippines. In World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation, 2nd ed.; Sheppard, C., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 515–537. ISBN 978-0-08-100853-9. [Google Scholar]
- Prado, S.G.; Collazo, J.A.; Marand, M.H.; Irwin, R.E. The Influence of Floral Resources and Microclimate on Pollinator Visitation in an Agro-Ecosystem. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 307, 107196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, E.L.; Ribiere, C.; Frei, W.; Kenny, D.; Coffey, M.F.; O’Toole, P.W. Geographical and Seasonal Analysis of the Honeybee Microbiome. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 85, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Jing, Z.; Diao, Q.; He, J.-Z.; Liu, Y.-J. Host Species and Geography Differentiate Honeybee Gut Bacterial Communities by Changing the Relative Contribution of Community Assembly Processes. mBio 2021, 12, e0075121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellegaard, K.M.; Engel, P. Genomic Diversity Landscape of the Honey Bee Gut Microbiota. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-X.; Huo, Q.-B.; Wen, T.; Wang, X.-Y.; Zhao, M.-Y.; Du, Y.-Z. Mechanisms of Fungal Community Assembly in Wild Stoneflies Moderated by Host Characteristics and Local Environment. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2022, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Kent, J. Biodiversity Hotspots for Conservation Priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez, A.F.L.; Tirador, A.D.G.; Villorente, Z.M.; Bagarinao, C.F.; Sollesta, J.V.N.; Dumancas, G.G.; Sun, Z.; Zhan, Z.Q.; Saludes, J.P.; Dalisay, D.S. The Isorhamnetin-Containing Fraction of Philippine Honey Produced by the Stingless Bee Tetragonula Biroi Is an Antibiotic against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Molecules 2021, 26, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvez, J.P.F.; Lagrimas, R.D.; Gonzales, R.M.C.; Constante, J.L.; Galay, R.L. Diagnosis and Management of Varroosis in European Honey Bees, Apis mellifera L., (Hymenoptera: Apidae) in an Apiary. Philipp. J. Vet. Med. 2020, 57, 118–123. [Google Scholar]
- Pakwan, C.; Kaltenpoth, M.; Weiss, B.; Chantawannakul, P.; Jun, G.; Disayathanoowat, T. Bacterial Communities Associated with the Ectoparasitic Mites Varroa destructor and Tropilaelaps mercedesae of the Honey Bee (Apis mellifera). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fix160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claesson, M.J.; Wang, Q.; O’Sullivan, O.; Greene-Diniz, R.; Cole, J.R.; Ross, R.P.; O’Toole, P.W. Comparison of Two Next-Generation Sequencing Technologies for Resolving Highly Complex Microbiota Composition Using Tandem Variable 16S rRNA Gene Regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardes, M.; Bruns, T.D. ITS Primers with Enhanced Specificity for Basidiomycetes—Application to the Identification of Mycorrhizae and Rusts. Mol. Ecol. 1993, 2, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.J.W.T.; Taylor, J. Amplification and Direct Sequencing of Fungal Ribosomal RNA Genes for Phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. ISBN 978-0-12-372180-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unterseher, M.; Jumpponen, A.; Öpik, M.; Tedersoo, L.; Moora, M.; Dormann, C.F.; Schnittler, M. Species Abundance Distributions and Richness Estimations in Fungal Metagenomics—Lessons Learned from Community Ecology. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleine Bardenhorst, S.; Vital, M.; Karch, A.; Rübsamen, N. Richness Estimation in Microbiome Data Obtained from Denoising Pipelines. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abarenkov, K.; Zirk, A.; Piirmann, T.; Pöhönen, R.; Ivanov, F.; Nilsson, R.H.; Kõljalg, U. Full UNITE+INSD Dataset for Fungi; UNITE Community: Boston, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of Diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Losada, M.; Narayanan, D.B.; Kolbe, A.R.; Ramos-Tapia, I.; Castro-Nallar, E.; Crandall, K.A.; Domínguez, J. Comparative Analysis of Metagenomics and Metataxonomics for the Characterization of Vermicompost Microbiomes. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 854423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.C.; Fruciano, C.; Marchant, J.; Hildebrand, F.; Forslund, S.; Bork, P.; Engel, P.; Hughes, W.O.H. The Gut Microbiome Is Associated with Behavioural Task in Honey Bees. Insect. Soc. 2018, 65, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for Prediction of Metagenome Functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; RStudio, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2020; Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An Open Source Software for Exploring and Manipulating Networks. Proc. Int. AAAI Conf. Web Social. Media 2009, 3, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S.P. Exact Sequence Variants Should Replace Operational Taxonomic Units in Marker-Gene Data Analysis. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2639–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Gregory Caporaso, J. Optimizing Taxonomic Classification of Marker-Gene Amplicon Sequences with QIIME 2’s Q2-Feature-Classifier Plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, R.H.; Larsson, K.-H.; Taylor, A.F.S.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Jeppesen, T.S.; Schigel, D.; Kennedy, P.; Picard, K.; Glöckner, F.O.; Tedersoo, L.; et al. The UNITE Database for Molecular Identification of Fungi: Handling Dark Taxa and Parallel Taxonomic Classifications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D259–D264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beekman, M.; Ratnieks, F.L.W. Long-Range Foraging by the Honey-Bee, Apis mellifera L. Funct. Ecol. 2000, 14, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, H.; McFrederick, Q.S.; Philpott, S.M. Environment Shapes the Microbiome of the Blue Orchard Bee, Osmia lignaria. Microb. Ecol. 2020, 80, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.E.; Sheehan, T.H.; Mott, B.M.; Maes, P.; Snyder, L.; Schwan, M.R.; Walton, A.; Jones, B.M.; Corby-Harris, V. Microbial Ecology of the Hive and Pollination Landscape: Bacterial Associates from Floral Nectar, the Alimentary Tract and Stored Food of Honey Bees (Apis mellifera). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; Franz, C.M.A.P.; Harris, H.M.B.; Mattarelli, P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Pot, B.; Vandamme, P.; Walter, J.; et al. A Taxonomic Note on the Genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 Novel Genera, Emended Description of the Genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and Union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Hu, J.; Su, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Du, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Han, B.; Tang, J.; Guo, L.; et al. A Review on Recent Taxonomic Updates of Gut Bacteria Associated with Social Bees, with a Curated Genomic Reference Database. Insect Sci. 2024, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellegaard, K.M.; Suenami, S.; Miyazaki, R.; Engel, P. Vast Differences in Strain-Level Diversity in the Gut Microbiota of Two Closely Related Honey Bee Species. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 2520–2531.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disayathanoowat, T.; Young, J.P.W.; Helgason, T.; Chantawannakul, P. T-RFLP Analysis of Bacterial Communities in the Midguts of Apis mellifera and Apis cerana Honey Bees in Thailand. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 79, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tola, Y.H.; Waweru, J.W.; Hurst, G.D.D.; Slippers, B.; Paredes, J.C. Characterization of the Kenyan Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) Gut Microbiota: A First Look at Tropical and Sub-Saharan African Bee Associated Microbiomes. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, J.-H.; Jung, M.-J.; Kim, P.S.; Bae, J.-W. Social Status Shapes the Bacterial and Fungal Gut Communities of the Honey Bee. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacinto-Castillo, D.F.; Canto, A.; Medina-Medina, L.A.; O’Connor-Sánchez, A. Living in Honey: Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Honey of Sympatric Populations of Apis mellifera and the Stingless Bee Melipona beecheii, in Yucatan, Mexico. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachance, M.-A.; Starmer, W.T.; Rosa, C.A.; Bowles, J.M.; Barker, J.S.F.; Janzen, D.H. Biogeography of the Yeasts of Ephemeral Flowers and Their Insects. FEMS Yeast Res. 2001, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliam, M. Identification and Roles of Non-Pathogenic Microflora Associated with Honey Bees. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1997, 155, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disayathanoowat, T.; Li, H.; Supapimon, N.; Suwannarach, N.; Lumyong, S.; Chantawannakul, P.; Guo, J. Different Dynamics of Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Hive-Stored Bee Bread and Their Possible Roles: A Case Study from Two Commercial Honey Bees in China. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribière, C.; Hegarty, C.; Stephenson, H.; Whelan, P.; O’Toole, P.W. Gut and Whole-Body Microbiota of the Honey Bee Separate Thriving and Non-Thriving Hives. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 78, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, K.; Fazio, G.; Jensen, A.B.; Hughes, W.O.H. The Distribution of Aspergillus Spp. Opportunistic Parasites in Hives and Their Pathogenicity to Honey Bees. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 169, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.C.; Fruciano, C.; Hildebrand, F.; Al Toufalilia, H.; Balfour, N.J.; Bork, P.; Engel, P.; Ratnieks, F.L.; Hughes, W.O. Gut Microbiota Composition Is Associated with Environmental Landscape in Honey Bees. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinson, V.G.; Danforth, B.N.; Minckley, R.L.; Rueppell, O.; Tingek, S.; Moran, N.A. A Simple and Distinctive Microbiota Associated with Honey Bees and Bumble Bees. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahl, M.; Zhu, H.; Tautz, J.; Zhang, S. Large Scale Homing in Honeybees. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danihlík, J.; Aronstein, K.; Petřivalský, M. Antimicrobial Peptides: A Key Component of Honey Bee Innate Immunity: Physiology, Biochemistry, and Chemical Ecology. J. Apic. Res. 2015, 54, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dampc, J.; Kula-Maximenko, M.; Molon, M.; Durak, R. Enzymatic Defense Response of Apple Aphid Aphis Pomi to Increased Temperature. Insects 2020, 11, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmolz, E.; Dewitz, R.; Schricker, B.; Lamprecht, I. Energy Metabolism of European (Apis mellifera Carnica) and Egyptian (A. M. Lamarckii) Honeybees. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2001, 65, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunieda, T.; Fujiyuki, T.; Kucharski, R.; Foret, S.; Ament, S.A.; Toth, A.L.; Ohashi, K.; Takeuchi, H.; Kamikouchi, A.; Kage, E.; et al. Carbohydrate Metabolism Genes and Pathways in Insects: Insights from the Honey Bee Genome. Insect Mol. Biol. 2006, 15, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauers, L.A.; Bassingthwaite, T.; Sierra-Rivera, B.; Hampton, K.J.; Duffield, K.R.; Gore, H.; Ramirez, J.L.; Sadd, B.M. Membership Robustness but Structural Change of the Native Gut Microbiota of Bumble Bees upon Systemic Immune Induction. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e00861-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau-Del Valle, C.; Fernández, J.; Solá, E.; Montoya-Castilla, I.; Morillas, C.; Bañuls, C. Association between Gut Microbiota and Psychiatric Disorders: A Systematic Review. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1215674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.; Jung, S.-C.; Kwak, K.; Kim, J.-S. The Role of Prebiotics in Modulating Gut Microbiota: Implications for Human Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liao, C.; Li, Z.; Shi, X.; Wu, X. Synergistic Resistance of Honeybee (Apis mellifera) and Their Gut Microorganisms to Fluvalinate Stress. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 201, 105865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, B.P. Prospects for Industrial Entomology in the Philippines. Philipp. Ent 1980, 4, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, C.H. The Italian Bees at Alabang, Rizal. Phil. Agric. Rev. 1913, 6, 335–339. [Google Scholar]
- Otanes, F.Q. Beekeeping in the Philippines. Plant Ind. Dig. 1950, 13, 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Deyto, R.; Manila-Fajardo, A.; Cervancia, C. Pollen Contents of Apis mellifera Linn. Honey from Davao City, Philippines. J. Nat. Stud. 2012, 11, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Cervancia, C.; Duangphakdee, O.; Disayathanoowat, T.; Dinh, Q.; Baroga-Barbecho, J.; Cortez, M.; Locsin, A.; Merillo, M.; Avante, L.; Jamparat, W.; et al. Diversity of Bees and Wild Pollinators in the Philippines, Thailand, and Viet Nam; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2023; pp. 1–139. [Google Scholar]
- Basconcillo, J.; Aquino, K.; Malabanan, L.; Bagulbagul, V.A.; Bangquiao, N.; Ison, C.; Baldomero, M.; Miranda, N.; Au, P.; Badrina, R.; et al. 2023 PAGASA Annual Climate Bulletin; Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration: Senator Miriam P. Defensor—Santiago Avenue, Philippines, 2024; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, K.E.; Copeland, D.C. The Honey Bee “Hive” Microbiota: Meta-Analysis Reveals a Native and Aerobic Microbiota Prevalent throughout the Social Resource Niche. Front. Bee Sci. 2024, 2, 1410331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricigliano, V.A.; Williams, S.T.; Oliver, R. Effects of Different Artificial Diets on Commercial Honey Bee Colony Performance, Health Biomarkers, and Gut Microbiota. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castillo, D.; Abella, E.; Sinpoo, C.; Phokasem, P.; Chantaphanwattana, T.; Yongsawas, R.; Cervancia, C.; Baroga-Barbecho, J.; Attasopa, K.; Noirungsee, N.; et al. Gut Microbiome Diversity in European Honeybees (Apis mellifera L.) from La Union, Northern Luzon, Philippines. Insects 2025, 16, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16020112
Castillo D, Abella E, Sinpoo C, Phokasem P, Chantaphanwattana T, Yongsawas R, Cervancia C, Baroga-Barbecho J, Attasopa K, Noirungsee N, et al. Gut Microbiome Diversity in European Honeybees (Apis mellifera L.) from La Union, Northern Luzon, Philippines. Insects. 2025; 16(2):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16020112
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastillo, Diana, Evaristo Abella, Chainarong Sinpoo, Patcharin Phokasem, Thunyarat Chantaphanwattana, Rujipas Yongsawas, Cleofas Cervancia, Jessica Baroga-Barbecho, Korrawat Attasopa, Nuttapol Noirungsee, and et al. 2025. "Gut Microbiome Diversity in European Honeybees (Apis mellifera L.) from La Union, Northern Luzon, Philippines" Insects 16, no. 2: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16020112
APA StyleCastillo, D., Abella, E., Sinpoo, C., Phokasem, P., Chantaphanwattana, T., Yongsawas, R., Cervancia, C., Baroga-Barbecho, J., Attasopa, K., Noirungsee, N., & Disayathanoowat, T. (2025). Gut Microbiome Diversity in European Honeybees (Apis mellifera L.) from La Union, Northern Luzon, Philippines. Insects, 16(2), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16020112








