Transgenerational Consequences of Imidacloprid Larval Diet Contamination in the Sheep Blowfly Lucilia sericata (Diptera: Calliphoridae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
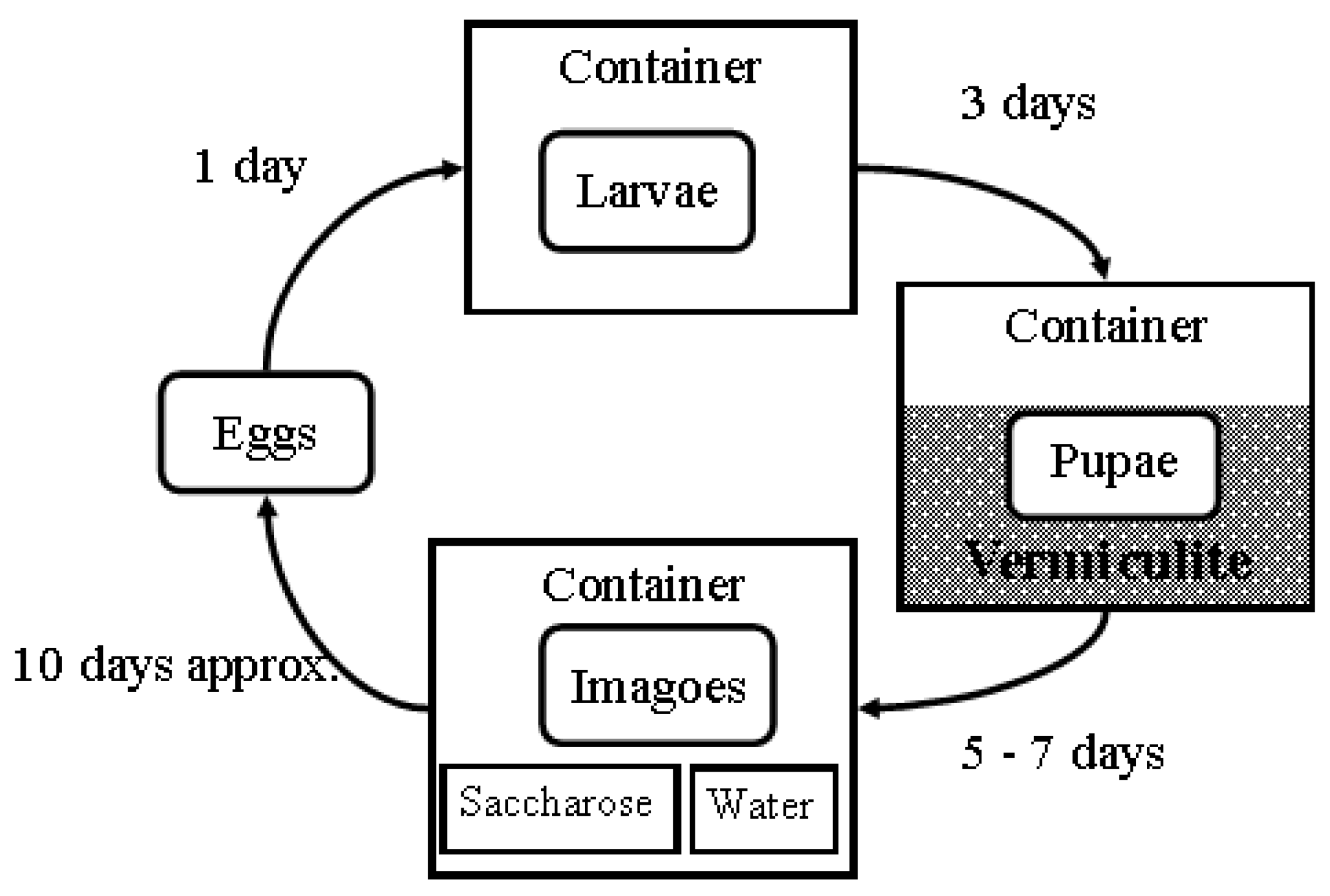
2.1. Insects
2.2. Rearing Conditions and Diet
2.3. Measurements and Statistics
3. Results
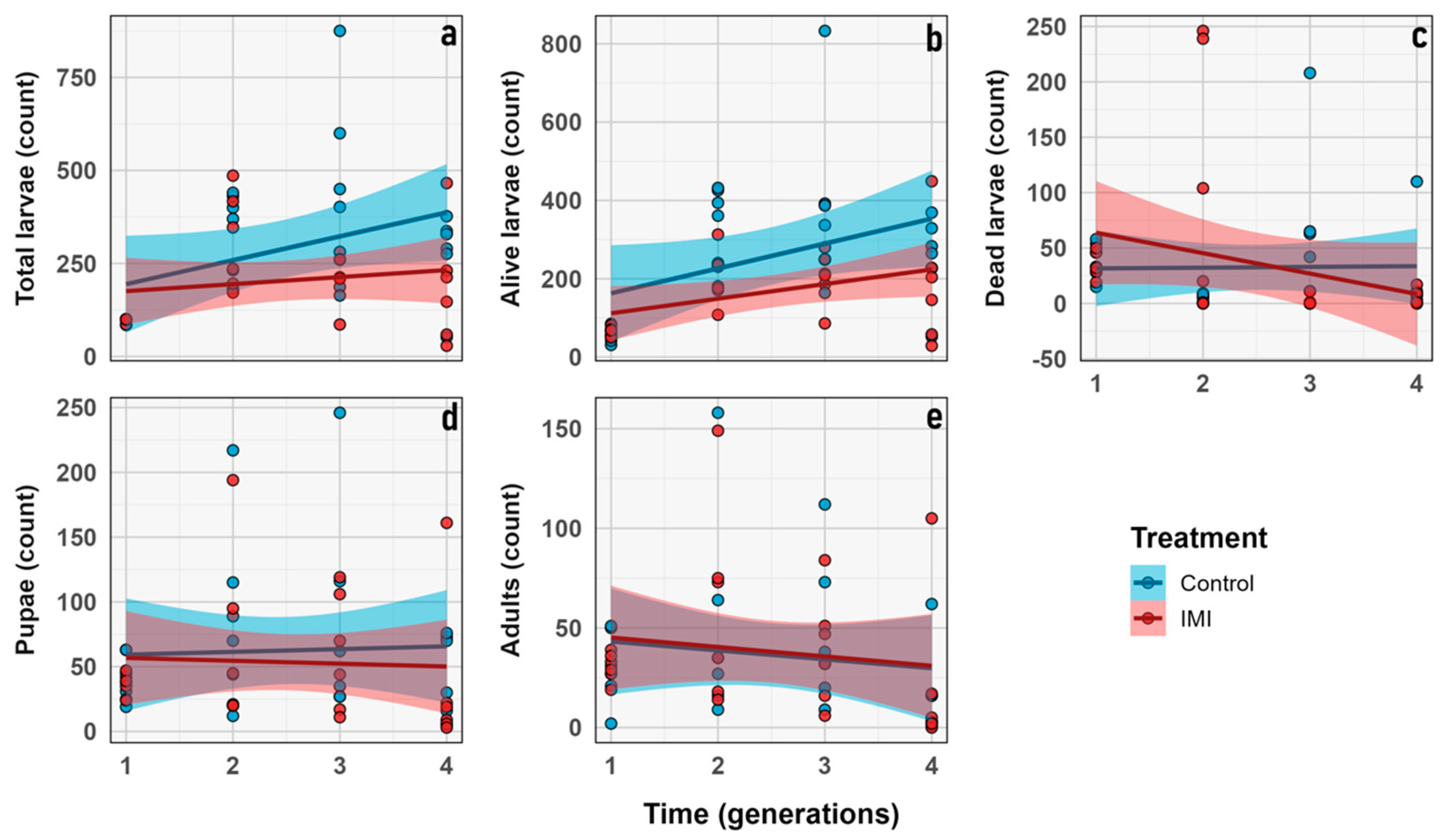
3.1. Morphological Traits
3.2. Demographic Traits
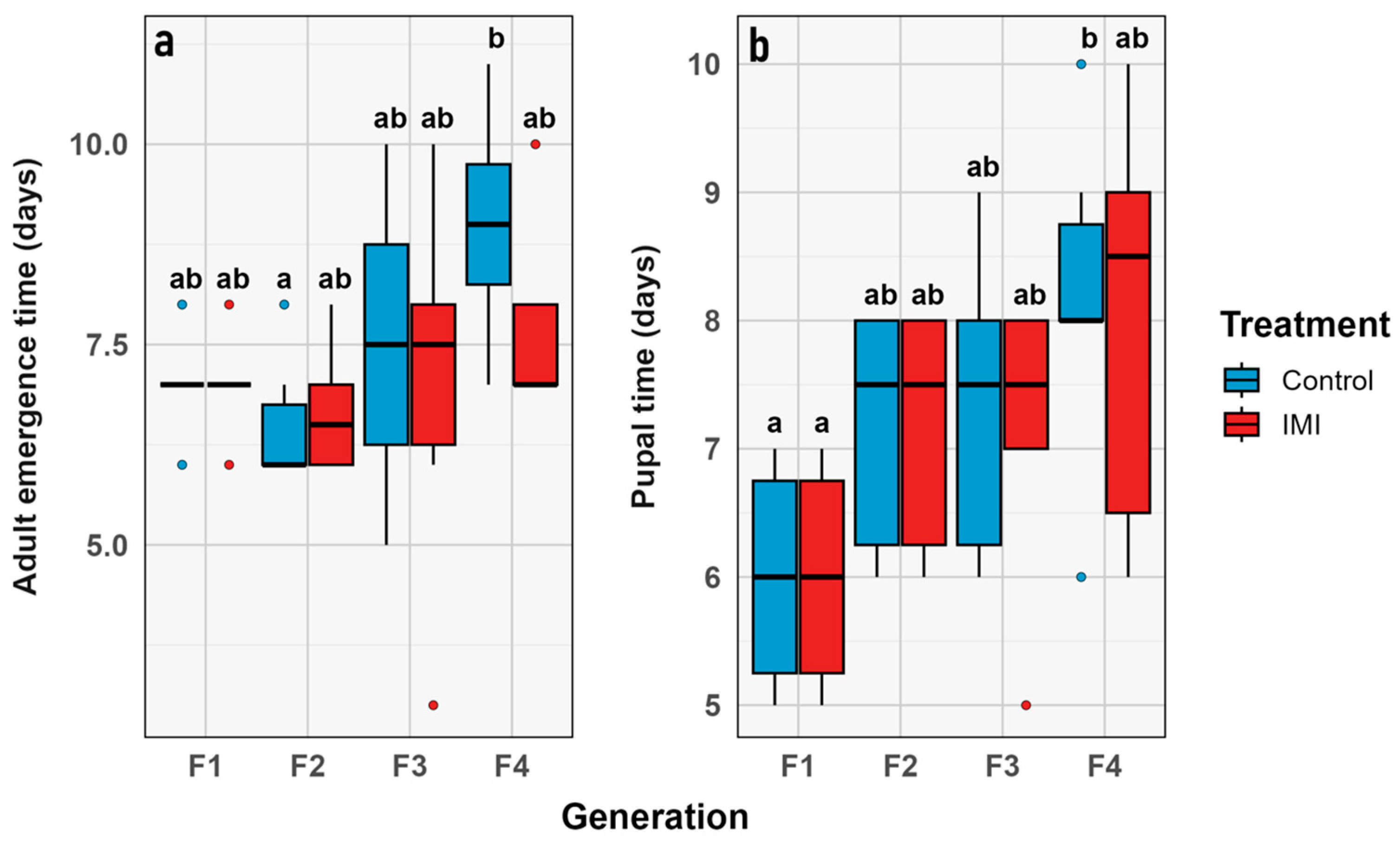
3.3. Phenological Traits
3.4. Proportional Traits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ballantyne, B.; Marrs, T.C. Pesticides: An Overview of Fundamentals. In Pesticide Toxicology and International Regulation; Marrs, T.C., Ballantyne, B., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 1–23. ISBN 978-0-471-49644-1. [Google Scholar]
- Geiger, F.; Bengtsson, J.; Berendse, F.; Weisser, W.W.; Emmerson, M.; Morales, M.B.; Ceryngier, P.; Liira, J.; Tscharntke, T.; Winqvist, C.; et al. Persistent Negative Effects of Pesticides on Biodiversity and Biological Control Potential on European Farmland. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2010, 11, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syromyatnikov, M.Y.; Isuwa, M.M.; Savinkova, O.V.; Derevshchikova, M.I.; Popov, V.N. The Effect of Pesticides on the Microbiome of Animals. Agriculture 2020, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.R.; Fitsanakis, V.; Westerink, R.H.S.; Kanthasamy, A.G. Neurotoxicity of Pesticides. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 138, 343–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baena-Díaz, F.; Martínez-M, I.; Gil-Pérez, Y.; González-Tokman, D. Trans-Generational Effects of Ivermectin Exposure in Dung Beetles. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chick, A.; Cassella, J.P.; Terrell-Nield, C. Study of The Effects of Common Insecticides on The Colonisation and Decomposition of Carrion by Invertebrates. Glob. Forensic Sci. Today Sci. Investig. Tech. 2008, 18–26. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, D.S.; Georgin, J.; Villarreal Campo, L.A.; Mayoral, M.A.; Goenaga, J.O.; Fruto, C.M.; Neckel, A.; Oliveira, M.L.; Ramos, C.G. The Environmental Pollution Caused by Cemeteries and Cremations: A Review. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 136025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdjoub, H.; Blanckenhorn, W.U.; Lüpold, S.; Roy, J.; Gourgoulianni, N.; Khelifa, R. Fitness Consequences of the Combined Effects of Veterinary and Agricultural Pesticides on a Non-Target Insect. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Warchol, K.M.; Callahan, R.A. In Situ Replication of Honey Bee Colony Collapse Disorder. Bull. Insectology 2012, 65, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Basley, K.; Davenport, B.; Vogiatzis, K.; Goulson, D. Effects of Chronic Exposure to Thiamethoxam on Larvae of the Hoverfly Eristalis tenax (Diptera, Syrphidae). PeerJ 2018, 6, e4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, D.F.; Tufail, M.S.; Howse, E.T.; Voss, S.C.; Foley, J.; Norrish, B.; Delroy, N. Pollination of Enclosed Avocado Trees by Blow Flies (Diptera: Calliphoridae) and a Hover Fly (Diptera: Syrphidae). Insects 2025, 16, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, L. Collapse of Terrestrial Biodiversity. In Capitalism and Environmental Collapse; Marques, L., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 247–273. ISBN 978-3-030-47527-7. [Google Scholar]
- Sud, M. Managing the Biodiversity Impacts of Fertiliser and Pesticide Use: Overview and Insights from Trends and Policies Across Selected OECD Countries; OECD Environment Working Papers; OECD: Paris, France, 2020; Volume 155. [Google Scholar]
- Vanbergen, A.J.; Aizen, M.A.; Cordeau, S.; Garibaldi, L.A.; Garratt, M.P.D.; Kovács-Hostyánszki, A.; Lecuyer, L.; Ngo, H.T.; Potts, S.G.; Settele, J.; et al. Chapter Six-Transformation of Agricultural Landscapes in the Anthropocene: Nature’s Contributions to People, Agriculture and Food Security. In Advances in Ecological Research; Bohan, D.A., Vanbergen, A.J., Eds.; The Future of Agricultural Landscapes, Part I; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 63, pp. 193–253. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi, N. Chapter 12. Adverse Effects of Pesticides on Regional Biodiversity and Their Mechanisms. In Risks and Regulation of New Technologies; Matsuda, T., Wolff, J., Yanagawa, T., Eds.; Springer & Kobe University: Kobe, Japan, 2021; pp. 235–247. [Google Scholar]
- Jeschke, P.; Nauen, R. Neonicotinoids—From Zero to Hero in Insecticide Chemistry. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 1084–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbert, A.; Haas, M.; Springer, B.; Thielert, W.; Nauen, R. Applied Aspects of Neonicotinoid Uses in Crop Protection. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Kaur, J. Advantages of Neonicotinoids Over Other Classes of Pesticides. In Neonicotinoids in the Environment: Emerging Concerns to the Human Health and Biodiversity; Singh, R., Singh, V.K., Kumar, A., Tripathi, S., Bhadouria, R., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 15–27. ISBN 978-3-031-45343-4. [Google Scholar]
- Mota, Z.L.; Díaz, I.A.; Martínez-Ávila, A.E.; Otero-Olvera, M.; Leyva-Ruíz, D.; Aponte-Pineda, L.S.; Rangel-Duarte, S.G.; Pacheco-Aguilar, J.R.; Amaro-Reyes, A.; Campos-Guillén, J.; et al. A Review of the Adverse Effects of Neonicotinoids on the Environment. Environments 2024, 11, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Chang, C.-H.; Palmer, C.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Q. Neonicotinoid Residues in Fruits and Vegetables: An Integrated Dietary Exposure Assessment Approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3175–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mencke, N.; Jeschke, P. Therapy and Prevention of Parasitic Insects in Veterinary Medicine Using Imidacloprid. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2002, 2, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedrizzi, G.; Altafini, A.; Armorini, S.; Al-Qudah, K.M.; Roncada, P. LC–MS/MS Analysis of Five Neonicotinoid Pesticides in Sheep and Cow Milk Samples Collected in Jordan Valley. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 102, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botías, C.; David, A.; Horwood, J.; Abdul-Sada, A.; Nicholls, E.; Hill, E.; Goulson, D. Neonicotinoid Residues in Wildflowers, a Potential Route of Chronic Exposure for Bees. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12731–12740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botías, C.; David, A.; Hill, E.M.; Goulson, D. Contamination of Wild Plants near Neonicotinoid Seed-Treated Crops, and Implications for Non-Target Insects. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulson, D. An Overview of the Environmental Risks Posed by Neonicotinoid Insecticides. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 50, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Meng, R.; Liu, G.; Yu, W.; Jin, H. Neonicotinoid Pesticide Residues in Bottled Water: A Worldwide Assessment of Distribution and Human Exposure Risks. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2025, 27, 1960–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Gao, M.; Damgaard, C.; Zhu, D.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, N.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Dai, W. Elevated Temperature Magnifies the Toxicity of Imidacloprid in the Collembolan, Folsomia candida. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 374, 126260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallmann, C.A.; Foppen, R.P.B.; Van Turnhout, C.A.M.; De Kroon, H.; Jongejans, E. Declines in Insectivorous Birds Are Associated with High Neonicotinoid Concentrations. Nature 2014, 511, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisa, L.W.; Amaral-Rogers, V.; Belzunces, L.P.; Bonmatin, J.M.; Downs, C.A.; Goulson, D.; Kreutzweiser, D.P.; Krupke, C.; Liess, M.; Mcfield, M.; et al. Effects of Neonicotinoids and Fipronil on Non-Target Invertebrates. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 22, 68–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.-X.; Milne, R.I.; Cui, P.; Gu, W.-J.; Hu, M.-F.; Liu, X.-Y.; Song, Y.-Q.; Cao, J.; Zha, H.-G. Comparing the Contents, Functions and Neonicotinoid Take-up between Floral and Extrafloral Nectar within a Single Species (Hemerocallis citrina Baroni). Ann. Bot. 2022, 129, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbrother, A.; Purdy, J.; Anderson, T.; Fell, R. Risks of Neonicotinoid Insecticides to Honeybees. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, M.; Bonchev, G.; Zehirov, G.; Vasileva, V.; Vassileva, V. Neonicotinoid Insecticides Exert Diverse Cytotoxic and Genotoxic Effects on Cultivated Sunflower. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 53193–53207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, E.E.; Meese, R.J.; Holyoak, M. Neonicotinoid Exposure in Tricolored Blackbirds (Agelaius tricolor). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 15392–15399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolás de Francisco, O.; Ewbank, A.C.; de la Torre, A.; Sacristán, I.; Jordana, I.A.; Planella, A.; Grau, O.; Garcia Ferré, D.; Olmo-Vidal, J.M.; García-Fernández, A.J.; et al. Environmental Contamination by Veterinary Medicinal Products and Their Implications in the Conservation of the Endangered Pyrenean Capercaillie (Tetrao urogallus Aquitanicus). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 288, 117299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatjina, F.; Papaefthimiou, C.; Charistos, L.; Dogaroglu, T.; Bouga, M.; Emmanouil, C.; Arnold, G. Sublethal Doses of Imidacloprid Decreased Size of Hypopharyngeal Glands and Respiratory Rhythm of Honeybees in Vivo. Apidologie 2013, 44, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Haleem, D.R.; Genidy, N.A.; Fahmy, A.R.; Abu-El Azm, F.S.M.; Ismail, N.S.M. Comparative Modelling, Toxicological and Biochemical Studies of Imidacloprid and Thiamethoxam Insecticides on the House Fly, Musca domestica L. (Diptera: Muscidae). Egypt. Acad. J. Biol. Sci. Entomol. 2018, 11, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maloney, E.M.; Liber, K.; Headley, J.V.; Peru, K.M.; Morrissey, C.A. Neonicotinoid Insecticide Mixtures: Evaluation of Laboratory-Based Toxicity Predictions under Semi-Controlled Field Conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1727–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, D.; Morrissey, C.; Mineau, P. A Review of the Direct and Indirect Effects of Neonicotinoids and Fipronil on Vertebrate Wildlife. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladosu, J.I.; Flaws, J.A. The Impact of Neonicotinoid Pesticides on Reproductive Health. Toxicol. Sci. 2025, 203, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawal, A.; Lüpold, S.; Gossner, M.M.; Blanckenhorn, W.U. Neonicotinoids Negatively Affect Life-History Traits in Widespread Dung Fly Species. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 383, 126763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elhakim, Y.M.; Abu-Zeid, E.H.; Ibrahim, D.; Alhallag, K.A.; Wagih, E.; Abdelaty, A.I.; Khamis, T.; Metwally, M.M.M.; Ismail, T.A.; Eldoumani, H. Moringa Oleifera Leaves Powder Mitigates Imidacloprid-Induced Neurobehavioral Disorders and Neurotoxic Reactions in Broiler Chickens by Regulating the Caspase-3/Hsp70/PGC-1α Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 8040–8053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Lu, S. Human Exposure to Neonicotinoids and the Associated Health Risks: A Review. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Dong, F.; Xu, J.; Phung, D.; Liu, Q.; Li, R.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; He, M.; Zheng, Y. Characteristics of Neonicotinoid Imidacloprid in Urine Following Exposure of Humans to Orchards in China. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 105079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallaro, M.C.; Hladik, M.L.; McMurry, R.S.; Hittson, S.; Boyles, L.K.; Hoback, W.W. Neonicotinoid Exposure Causes Behavioral Impairment and Delayed Mortality of the Federally Threatened American Burying Beetle, Nicrophorus Americanus. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0314243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurita, A.; Abu Hassan, A. Comparative Performance of Two Commercial Neonicotinoid Baits against Filth Flies under Field Conditions. Trop. Biomed. 2010, 27, 559–565. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera-Miranda, T.S.; Hans, K.R. Impact of Bifenthrin and Clothianidin on Blow Fly (Diptera: Calliphoridae) Oviposition Patterns under Laboratory and Field Conditions. J. Forensic Sci. 2025, 70, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, T.R.; Scott, F.B.; Verocai, G.G.; Souza, C.P.; Fernandes, J.I.; Melo, R.M.P.S.; Vieira, V.P.C.; Ribeiro, F.A. Larvicidal Efficacy of Nitenpyram on the Treatment of Myiasis Caused by Cochliomyia hominivorax (Diptera: Calliphoridae) in Dogs. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 173, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devine, J.A.; Wright, P.J.; Pardoe, H.E.; Hussein, M.A. Fisheries-Induced Rates of Contemporary Evolution: Comparing Haldanes and Darwins. 2010. Available online: https://ices-library.figshare.com/articles/conference_contribution/Fisheries-induced_rates_of_contemporary_evolution_comparing_haldanes_and_darwins/25132874 (accessed on 8 December 2025).
- Dobzhansky, T. Genetics and the Origin of Species; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1937. [Google Scholar]
- Gingerich, P.D. Rates of Evolution. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2009, 40, 657–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingerich, P.D. Quantification and Comparison of Evolutionary Rates. Am. J. Sci. 1993, 293, 453–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, M.; Sánchez-Villagra, M.R. Similar Rates of Morphological Evolution in Domesticated and Wild Pigs and Dogs. Front. Zool. 2018, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendry, A.P.; Farrugia, T.J.; Kinnison, M.T. Human Influences on Rates of Phenotypic Change in Wild Animal Populations. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendry, A.P.; Kinnison, M.T. Perspective: The pace of modern life: Measuring rates of contemporary microevolution. Evolution 1999, 53, 1637–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.A.; Ross, P.A. Rates and Patterns of Laboratory Adaptation in (Mostly) Insects. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruna, W.; Guarderas, P.; Donoso, D.A.; Barragán, Á. Life Cycle of Lucilia Sericata (Meigen 1826) Collected from Andean Mountains. Neotropical. Biodivers. 2019, 5, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, C.R.; Llanos, L.; Oses, C.; Elgueta, M. Calliphoridae from Chile: Key to the Genera and Species (Diptera: Oestroidea). An. Inst. Patagon. 2017, 45, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, H.K.; Denecke, S.M.; Robin, C.; Fournier-Level, A. Sublethal Larval Exposure to Imidacloprid Impacts Adult Behaviour in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Evol. Biol. 2020, 33, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.K. How to Choose a Sampling Technique and Determine Sample Size for Research: A Simplified Guide for Researchers. Oral Oncol. Rep. 2024, 12, 100662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrício Macedo, M.; Arantes, L.C.; Tidon, R. Sexual Size Dimorphism in Three Species of Forensically Important Blowflies (Diptera: Calliphoridae) and Its Implications for Postmortem Interval Estimation. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 293, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salanitro, L.B.; Massaccesi, A.C.; Urbisaglia, S.; Pería, M.E.; Centeno, N.D.; Chirino, M.G. Calliphora vicina (Diptera: Calliphoridae): Growth Rates, Body Length Differences, and Implications for the Minimum Post-Mortem Interval Estimation. Rev. Soc. Entomológica Argent. 2022, 81, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, F.; Alkuriji, M.; AlReshaidan, S.; Alajmi, R.; Metwally, D.M.; Almutairi, B.; Alorf, M.; Haddadi, R.; Ahmed, A. Body Size and Cuticular Hydrocarbons as Larval Age Indicators in the Forensic Blow Fly, Chrysomya albiceps (Diptera: Calliphoridae). J. Med. Entomol. 2021, 58, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathy, H.; Attia, R.; Yones, D.; Eldeek, H.; Tolba, M.; Shaheen, M. Effect of Codeine Phosphate on Developmental Stages of Forensically Important Calliphoride Fly: Chrysomya albiceps. Mansoura J. Forensic Med. Clin. Toxicol. 2008, 16, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyoti, S.; Maddheshiya, R. Effect of Geranyl Acetate on the Third Instar Larvae of Latrine Blow Fly, Chrysomya megacephala (Fabricius, 1794) (Diptera: Calliphoridae). J. Exp. Zool. India 2023, 26, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.H.D.; Von Zuben, C.J. Demographic Aspects of Chrysomya megacephala (Diptera, Calliphoridae) Adults Maintained under Experimental Conditions: Reproductive Rate Estimates. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2006, 49, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.H.; Castner, J.L. Forensic Entomology: The Utility of Arthropods in Legal Investigations, 2nd ed.; CRC press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-8493-9215-3. [Google Scholar]
- Gennard, D.E. Forensic Entomology: An Introduction; Wiley: England, UK, 2007; ISBN 978-0-470-01478-3. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.; Kumar Garg, R.; Gaur, J.R. Various Methods for the Estimation of the Post Mortem Interval from Calliphoridae: A Review. Egypt. J. Forensic Sci. 2015, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kökdener, M.; Gündüz, N.E.A.; Zeybekoğlu, Ü.; Aykut, U.; Yılmaz, A.F. The Effect of Different Heavy Metals on the Development of Lucilia sericata (Diptera: Calliphoridae). J. Med. Entomol. 2022, 59, 1928–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, H.; Nguyen, B.; Morimoto, J.; Lundback, I.; Kumar, S.S.; Ponton, F. Transgenerational Effects of Parental Diet on Offspring Development and Disease Resistance in Flies. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 606993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öst, A.; Lempradl, A.; Casas, E.; Weigert, M.; Tiko, T.; Deniz, M.; Pantano, L.; Boenisch, U.; Itskov, P.M.; Stoeckius, M.; et al. Paternal Diet Defines Offspring Chromatin State and Intergenerational Obesity. Cell 2014, 159, 1352–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonduriansky, R.; Head, M. Maternal and Paternal Condition Effects on Offspring Phenotype in Telostylinus angusticollis (Diptera: Neriidae). J. Evol. Biol. 2007, 20, 2379–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valtonen, T.M.; Kangassalo, K.; Pölkki, M.; Rantala, M.J. Transgenerational Effects of Parental Larval Diet on Offspring Development Time, Adult Body Size and Pathogen Resistance in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, J.D.; Banks, J.E. Population-Level Effects Of Pesticides And Other Toxicants On Arthropods. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2003, 48, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, G.W. Effects of Pesticides on Nontarget Organisms. In Residue Reviews; Gunther, F.A., Gunther, J.D., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 173–201. ISBN 978-1-4612-6109-4. [Google Scholar]
- Costantini, D.; Metcalfe, N.B.; Monaghan, P. Ecological Processes in a Hormetic Framework. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 1435–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Urquiza, A.; Vergara-Ortiz, A.; Santiago-Álvarez, C.; Quesada-Moraga, E. Insecticidal and Sublethal Reproductive Effects of Metarhizium anisopliae Culture Supernatant Protein Extract on the Mediterranean Fruit Fly. J. Appl. Entomol. 2010, 134, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deans, C.; Hutchison, W.D. Hormetic and Transgenerational Effects in Spotted-Wing Drosophila (Diptera: Drosophilidae) in Response to Three Commonly-Used Insecticides. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, G.C. Insects, Insecticides and Hormesis: Evidence and Considerations for Study. Dose-Response 2013, 11, 154–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matute, D.R. The Role of Founder Effects on the Evolution of Reproductive Isolation. J. Evol. Biol. 2013, 26, 2299–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, R.J.; Gaugler, R. Genetic Adaptation and Founder Effect in Laboratory Populations of the Entomopathogenic Nematode Steinernema glaseri. Can. J. Zool. 1996, 74, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, B.S.; Long, S.M.; Pettigrove, V.J.; Hoffmann, A.A. The Parthenogenetic Cosmopolitan Chironomid, Paratanytarsus grimmii, as a New Standard Test Species for Ecotoxicology: Culturing Methodology and Sensitivity to Aqueous Pollutants. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 95, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.; Beukeboom, L.W.; Zwaan, B.J. Inbreeding and Outbreeding Depression in Wild and Captive Insect Populations. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2025, 70, 271–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoglou, A. Phenotypic Plasticity: From Microevolution to Macroevolution. In Handbook of Evolutionary Thinking in the Sciences; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 285–318. ISBN 978-94-017-9013-0. [Google Scholar]
- Gowri, V.; Monteiro, A. Inheritance of Acquired Traits in Insects and Other Animals and the Epigenetic Mechanisms That Break the Weismann Barrier. J. Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malook, S.U.; Arora, A.K.; Wong, A.C.N. The Role of Microbiomes in Shaping Insecticide Resistance: Current Insights and Emerging Paradigms. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2025, 69, 101346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, N.; Chen, J.T.; Waterman, P.D.; Kosheleva, A.; Beckfield, J. History, Haldanes and Health Inequities: Exploring Phenotypic Changes in Body Size by Generation and Income Level in the US-Born White and Black Non-Hispanic Populations 1959–1962 to 2005–2008. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, X.; Yu, C.; Liu, F.; Mu, W. Sublethal and Transgenerational Effects of Thiamethoxam on the Demographic Fitness and Predation Performance of the Seven-Spot Ladybeetle Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Chemosphere 2019, 216, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Sun, T.; He, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, L.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, X. Sublethal Toxicity, Transgenerational Effects, and Transcriptome Expression of the Neonicotinoid Pesticide Cycloxaprid on Demographic Fitness of Coccinella septempunctata. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 842, 156887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collotta, M.; Bertazzi, P.A.; Bollati, V. Epigenetics and Pesticides. Toxicology 2013, 307, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, J.; Chi, B.; Chen, P.; Liu, Y. Sublethal and Transgenerational Effects of Six Insecticides on Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2021, 24, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, I.L. An inside View on Pesticide Policy. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 920–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kummu, M.; Heino, M.; Taka, M.; Varis, O.; Viviroli, D. Climate Change Risks Pushing One-Third of Global Food Production Outside the Safe Climatic Space. One Earth 2021, 4, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahat, N.M.; Zyaan, O.; Khaled, A.S.; Hussein, M.A. Toxic and Biochemical Effects of Imidacloprid and Tannic Acid on the Culex pipiens Larvae (Diptera: Culicidae). Int. J. Mosq. Res. 2018, 5, 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Eggleton, P. The State of the World’s Insects. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2020, 45, 61–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.-M.; Hendrix, S.D.; Clough, Y.; Scofield, A.; Kremen, C. Interacting Effects of Pollination, Water and Nutrients on Fruit Tree Performance. Plant Biol. 2015, 17, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donley, N. The USA Lags behind Other Agricultural Nations in Banning Harmful Pesticides. Environ. Health 2019, 18, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
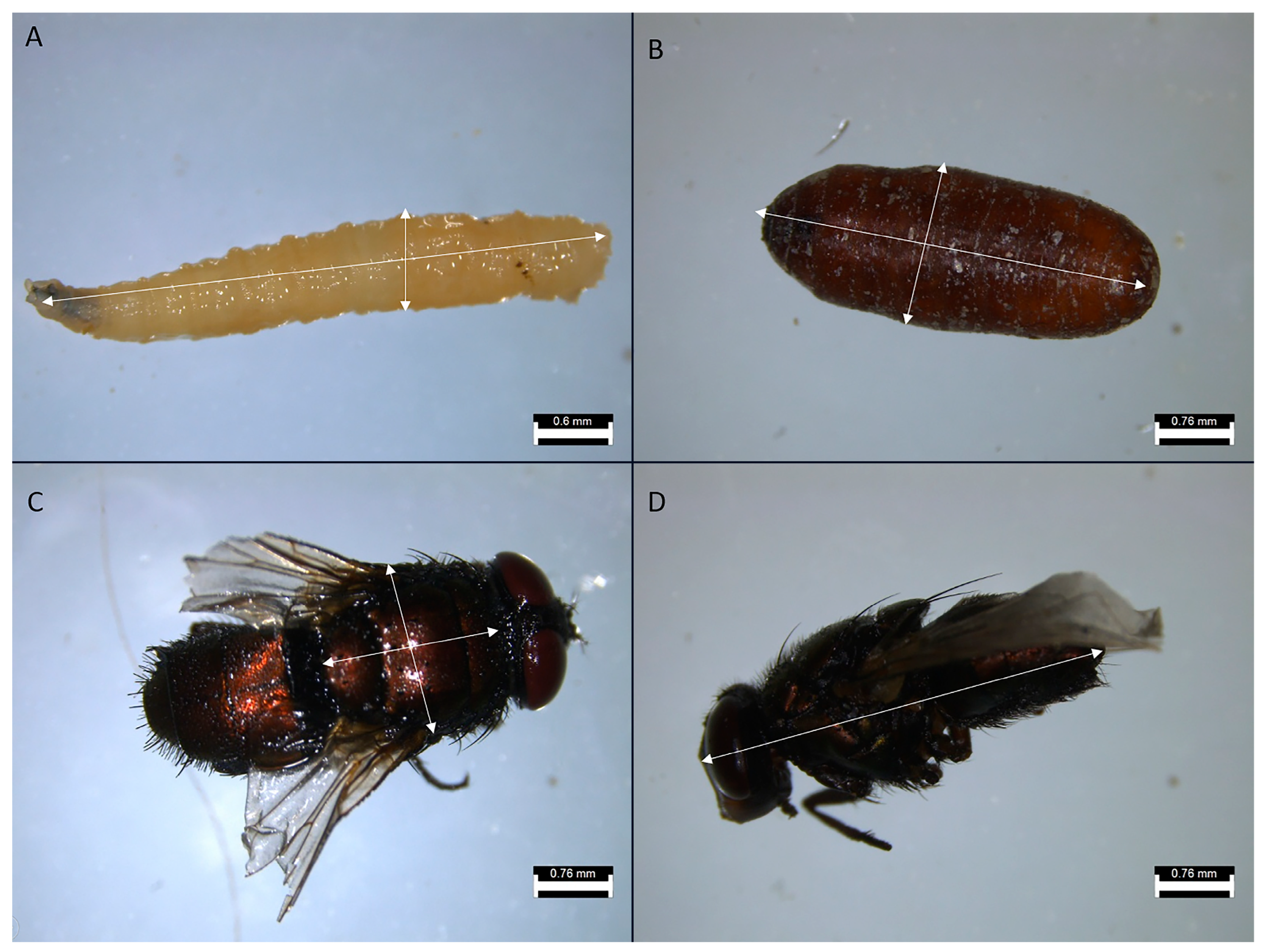







| Generation | Treatment | Replicate | Larvae | Pupae | Imagoes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | Control | 1 | 85 | 19 | 2 |
| 2 | 100 | 38 | 31 | ||
| 3 | 100 | 31 | 27 | ||
| 4 | 100 | 25 | 21 | ||
| 5 | 100 | 63 | 50 | ||
| 6 | 100 | 63 | 51 | ||
| Exposed | 1 | 86 | 24 | 19 | |
| 2 | 100 | 45 | 39 | ||
| 3 | 100 | 42 | 33 | ||
| 4 | 100 | 47 | 36 | ||
| 5 | 100 | 35 | 27 | ||
| 6 | 100 | 39 | 29 | ||
| F2 | Control | 1 | 181 | 12 | 9 |
| 2 | 400 | 217 | 158 | ||
| 3 | 370 | 70 | 35 | ||
| 4 | 431 | 20 | 16 | ||
| 5 | 440 | 115 | 64 | ||
| 6 | 232 | 44 | 27 | ||
| Exposed | 1 | 172 | 21 | 18 | |
| 2 | 486 | 89 | 73 | ||
| 3 | 417 | 194 | 149 | ||
| 4 | 347 | 45 | 35 | ||
| 5 | 196 | 95 | 75 | ||
| 6 | 236 | 20 | 14 | ||
| F3 | Control | 1 | 187 | 35 | 32 |
| 2 | 600 | 246 | 112 | ||
| 3 | 450 | 116 | 73 | ||
| 4 | 402 | 27 | 20 | ||
| 5 | 164 | 27 | 9 | ||
| 6 | 875 | 62 | 38 | ||
| Exposed | 1 | 260 | 70 | 51 | |
| 2 | 213 | 119 | 84 | ||
| 3 | 209 | 44 | 32 | ||
| 4 | 281 | 17 | 16 | ||
| 5 | 86 | 11 | 6 | ||
| 6 | 261 | 106 | 47 | ||
| F4 | Control | 1 | 337 | 5 | 1 |
| 2 | 290 | 30 | 16 | ||
| 3 | 377 | 73 | 16 | ||
| 4 | 329 | 16 | 3 | ||
| 5 | 52 | 70 | 3 | ||
| 6 | 276 | 76 | 62 | ||
| Exposed | 1 | 147 | 22 | 17 | |
| 2 | 231 | 9 | 5 | ||
| 3 | 466 | 161 | 105 | ||
| 4 | 213 | 6 | 2 | ||
| 5 | 29 | 19 | 0 | ||
| 6 | 59 | 3 | 2 |
| Trait | Treatment | Generation | Mean | SD | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pupal size | Control | F1 | 20.91 | 3.84 | 6 |
| F4 | 11.14 | 1.35 | 6 | ||
| Imidacloprid | F1 | 23.17 | 0.91 | 6 | |
| F4 | 12.89 | 3.95 | 6 | ||
| Imago size | Control | F1 | 31.78 | 7.38 | 6 |
| F4 | 9.34 | 1.47 | 6 | ||
| Imidacloprid | F1 | 29.41 | 3.31 | 6 | |
| F4 | 9.55 | 3.08 | 6 |
| Trait | Haldane Mean Control | Haldane Mean IMI | t | d.f. | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average larvae size | −1.60 | −0.72 | −1.90 | 9.50 | 0.0876 |
| Pupae size | −2.54 | −11.24 | 4.90 | 5.06 | 0.0043 |
| Average imago size | −3.04 | −6.01 | 6.94 | 4.36 | 0.0017 |
| Imago body length | −1.48 | −2.66 | 2.29 | 4.80 | 0.0729 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olivares-Castro, G.; Schapheer, C.; Guerrero-Bosagna, C.; Acuña-Rodríguez, I.S.; Villagra, C. Transgenerational Consequences of Imidacloprid Larval Diet Contamination in the Sheep Blowfly Lucilia sericata (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Insects 2025, 16, 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16121265
Olivares-Castro G, Schapheer C, Guerrero-Bosagna C, Acuña-Rodríguez IS, Villagra C. Transgenerational Consequences of Imidacloprid Larval Diet Contamination in the Sheep Blowfly Lucilia sericata (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Insects. 2025; 16(12):1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16121265
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlivares-Castro, Gabriela, Constanza Schapheer, Carlos Guerrero-Bosagna, Ian S. Acuña-Rodríguez, and Cristian Villagra. 2025. "Transgenerational Consequences of Imidacloprid Larval Diet Contamination in the Sheep Blowfly Lucilia sericata (Diptera: Calliphoridae)" Insects 16, no. 12: 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16121265
APA StyleOlivares-Castro, G., Schapheer, C., Guerrero-Bosagna, C., Acuña-Rodríguez, I. S., & Villagra, C. (2025). Transgenerational Consequences of Imidacloprid Larval Diet Contamination in the Sheep Blowfly Lucilia sericata (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Insects, 16(12), 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16121265







