Effect of Bt-Cry1Ab Maize Commercialization on Arthropod Community Biodiversity in Southwest China
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plants
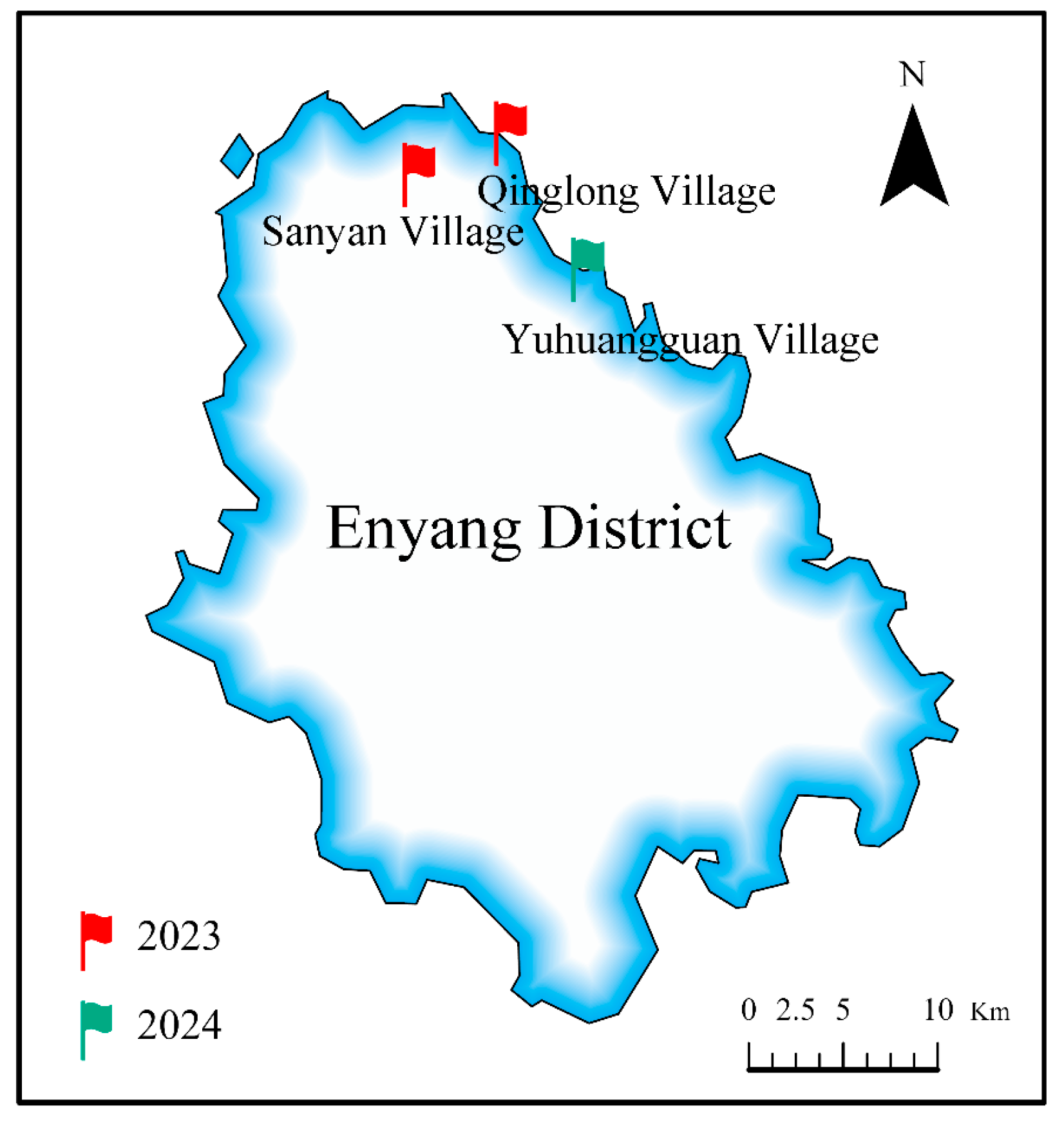
2.2. Sampling Site
2.3. Arthropod Community Species and Population Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
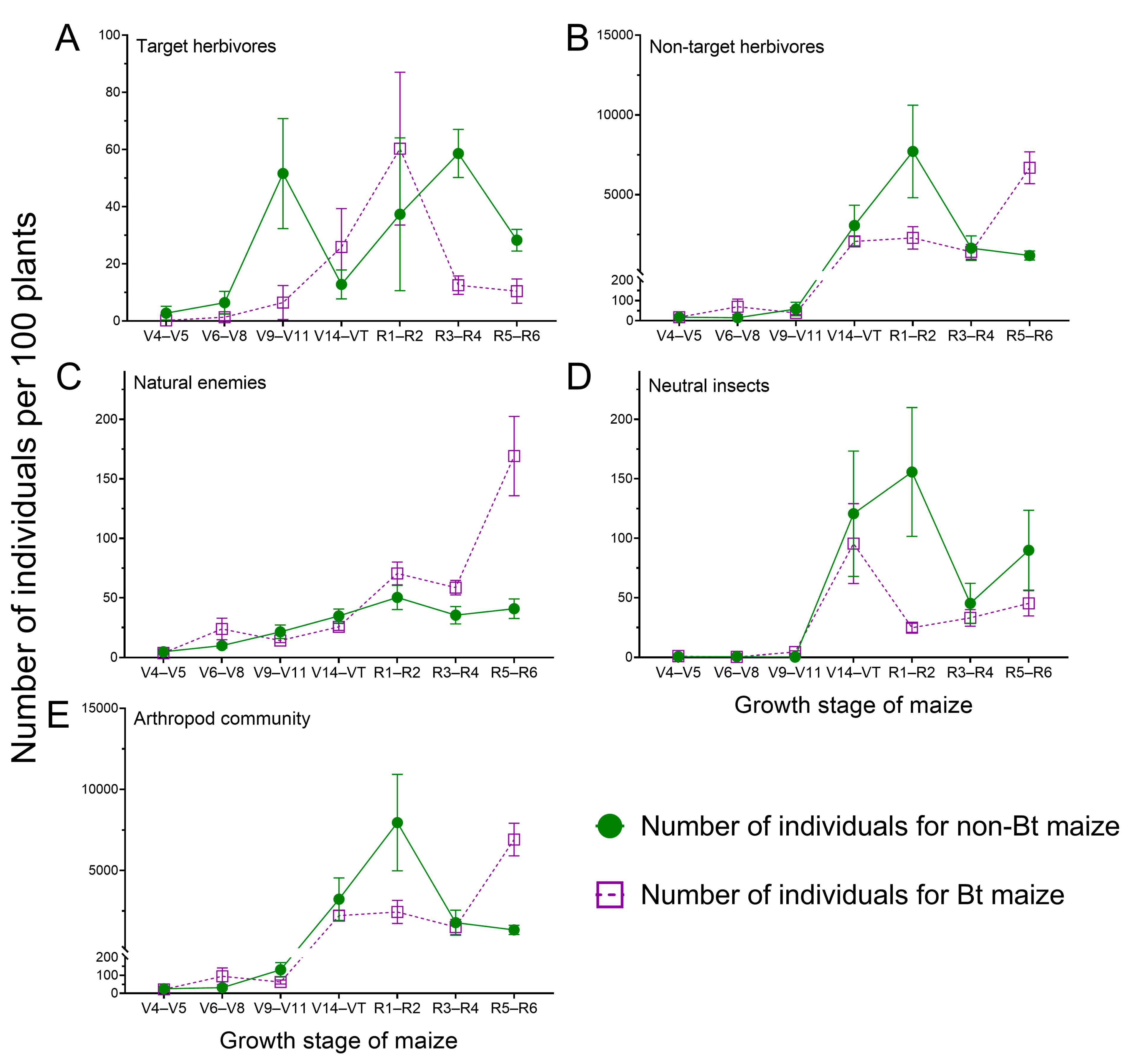
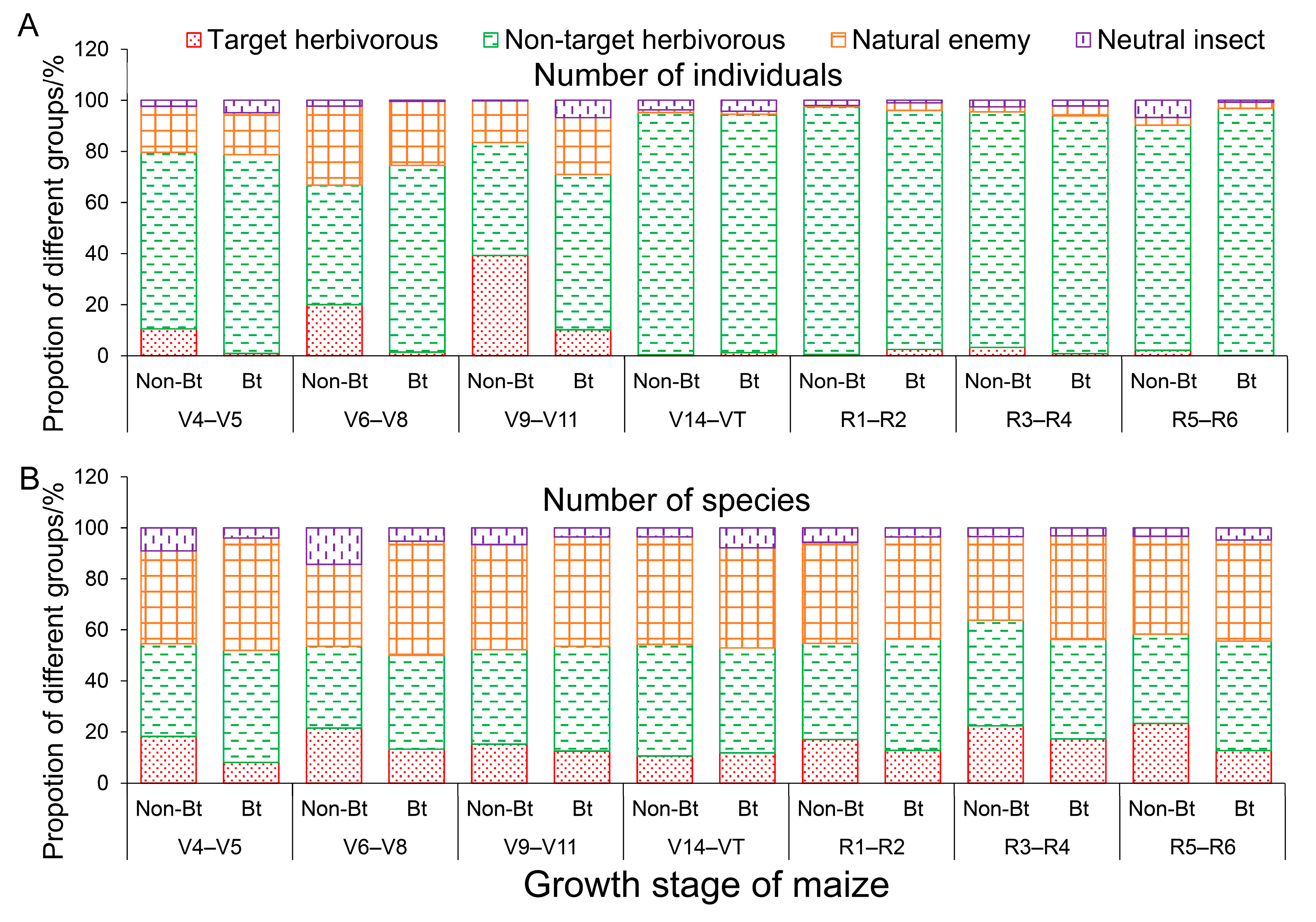
3.1. Arthropod Community Structure in Bt and Non-Bt Maize Fields
3.2. Arthropod Community Diversity in Bt and Non-Bt Maize Fields
3.3. Similarity of the Arthropod Community in Bt and Non-Bt Maize Fields
3.4. Stability of the Arthropod Community in Bt and Non-Bt Maize Fields
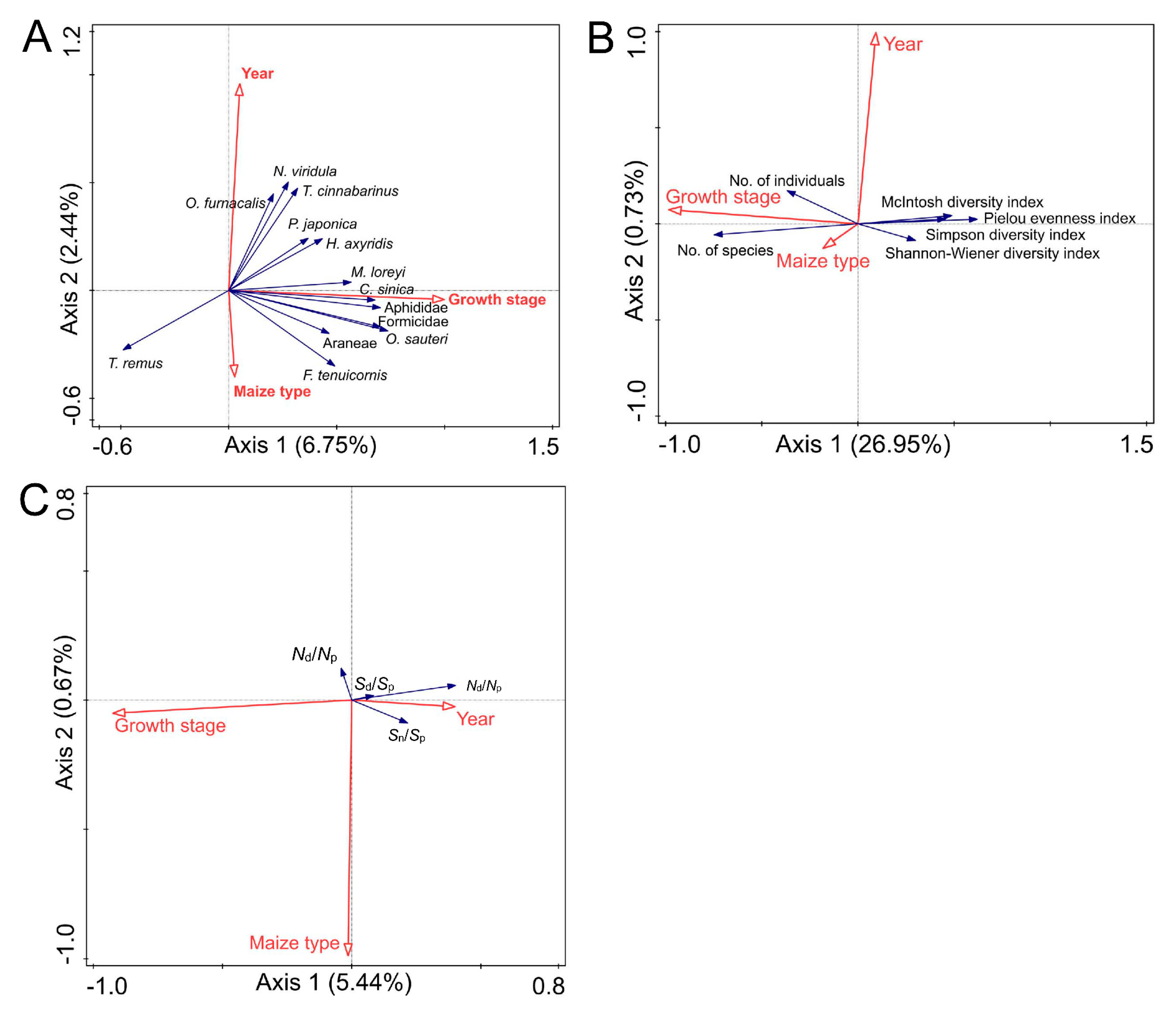
3.5. Correlation Analysis Between Environmental Factors and Arthropod Diversity or Stability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pardo-López, L.; Soberón, M.; Bravo, A. Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal three-domain Cry toxins: Mode of action, insect resistance and consequences for crop protection. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmacio, S.C.; Lugod, T.R.; Serrano, E.M.; Munkvold, G.P. Reduced incidence of bacterial rot on transgenic insect-resistant maize in the Philippines. Plant Dis. 2007, 91, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgerton, M.D.; Fridgen, J.; Anderson, J.R., Jr.; Ahlgrim, J.; Criswell, M.; Dhungana, P.; Gocken, T.; Li, Z.; Mariappan, S.; Pilcher, C.D.; et al. Transgenic insect resistance traits increase corn yield and yield stability. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, W.D.; Burkness, E.C.; Mitchell, P.D.; Moon, R.D.; Leslie, T.W.; Fleischer, S.J.; Abrahamson, M.; Hamilton, K.L.; Steffey, K.L.; Gray, M.E.; et al. Areawide suppression of European corn borer with Bt maize reaps savings to non-Bt maize growers. Science 2010, 330, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wu, K. Commercial strategy of transgenic insect-resistant maize in China. J. Plant. Prot. 2022, 49, 17–32. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, L.; Yang, Q.; Liang, G.; Wu, K. Control efficacy of Bt-Cry1Ab maize (event DBN9936) against Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée) in Sichuan Province, China. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2025, 81, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissle, M.; Naranjo, S.E.; Romeis, J. Does the growing of Bt maize change abundance or ecological function of non-target animals compared to the growing of non-GM maize? A systematic review. Environ. Evid. 2022, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. Development Trends of Global Agricultural Transgenic Industry. Available online: http://www.moa.gov.cn/ztzl/zjyqwgz/ckzl/202411/t20241126_6466932.htm (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Sanahuja, G.; Banakar, R.; Twyman, R.M.; Capell, T.; Christou, P. Bacillus thuringiensis: A century of research, development and commercial applications. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2011, 9, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Hallerman, E.; Peng, Y.; Li, Y. Development of Bt rice and Bt maize in China and their efficacy in target pest control. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Z. Development and application of transgenic crops in globe. Mod. Agrochem. 2023, 22, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, J. Future perspective of China’s feed demand and supply during its fast transition period of food consumption. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, L. Reasearch progress in maize pests. Guizhou Agric. Sci. 2018, 46, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, T.; Jiang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Wang, Y. Occurrence characteristics of main maize diseases and pests in China in 2020. China Plant Prot. 2021, 41, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, T.; Zhu, W.; Pang, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dong, J. Influence of the damage of cotton bollworm and corn borer to ear rot in corn. J. Maize Sci. 2013, 21, 116–118, 123. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X. Current status and management strategies for corn pests and diseases in China. Plant Prot. 2019, 45, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Shi, J.; Huang, C.; Guo, J.; He, K.; Wang, Z. Asian corn borer (Ostrinia furnacalis) infestation increases Fusarium verticillioides infection and Fumonisin Contamination in maize and reduces the yield. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckel, D.G. Insecticide resistance after silent spring. Science 2012, 337, 1612–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, B.; Pan, L.; Xing, S.; Xiao, N.; Guan, X. Impact of transgenic insect-resistant maize HGK60 with Cry1Ah gene on biodiversity of arthropods in the fields. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 7360–7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, K.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Desneux, N. Widespread adoption of Bt cotton and insecticide decrease promotes biocontrol services. Nature 2012, 487, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollerton, J. Pollinator diversity: Distribution, ecological function, and conservation. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2017, 48, 353–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, W.; Deng, X.; Van Der Werf, W.; Lu, Y.; Wu, K.; Rosegrant, M.W. Uncovering the economic value of natural enemies and true costs of chemical insecticides to cotton farmers in China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 064027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. Approval List for Agricultural Genetically Modified Organisms Safety Certificate in 2020 (II). Available online: http://www.kjs.moa.gov.cn/gzdt/202101/t20210113_6359909.htm (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. Approval List for Agricultural Genetically Modified Organisms Safety Certificate in 2023 (III). Available online: http://www.moa.gov.cn/ztzl/zjyqwgz/spxx/202401/t20240118_6446121.htm (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. Approval List for Agricultural Genetically Modified Organisms Safety Certificate in 2024 (III). Available online: http://www.moa.gov.cn/ztzl/zjyqwgz/spxx/202412/t20241231_6468714.htm (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Wu, K.; Lu, Y.; Feng, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, J. Suppression of cotton bollworm in multiple crops in China in areas with Bt toxin-containing cotton. Science 2008, 321, 1676–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Huang, J.; Ji, T.; Tian, C.; Zhao, X.; Feng, H. Baseline susceptibility and resistance allele frequency in Ostrinia furnacalis related to Cry1 toxins in the Huanghuaihai summer corn region of China. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 4311–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, D.; Zhao, S.; Wang, C.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, D.; Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, L.; et al. Expression profiles of Cry1Ab protein and its insecticidal efficacy against the invasive fall armyworm for Chinese domestic GM maize DBN9936. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 792–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, S.; Wu, K. Susceptibilities of the invasive fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) to the insecticidal proteins of Bt maize in China. Toxins 2022, 14, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noriega, J.A.; Hortal, J.; Azcárate, F.M.; Berg, M.P.; Bonada, N.; Briones, M.J.I.; Del Toro, I.; Goulson, D.; Ibanez, S.; Landis, D.A.; et al. Research trends in ecosystem services provided by insects. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2018, 26, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeis, J.; Bartsch, D.; Bigler, F.; Candolfi, M.P.; Gielkens, M.M.C.; Hartley, S.E.; Hellmich, R.L.; Huesing, J.E.; Jepson, P.C.; Layton, R.; et al. Assessment of risk of insect-resistant transgenic crops to nontarget arthropods. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolt, J.D.; Keese, P.; Raybould, A.; Fitzpatrick, J.W.; Burachik, M.; Gray, A.; Olin, S.S.; Schiemann, J.; Sears, M.; Wu, F. Problem formulation in the environmental risk assessment for genetically modified plants. Transgenic Res. 2009, 19, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masehela, T.S.; Maseko, B.; Barros, E.; Pessoa De Miranda, M.; Chaurasia, A.; Hawksworth, D.L. Impact of GM Crops on Farmland Biodiversity; GMOs; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2020; pp. 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Arias-Martín, M.; García, M.; Luciáñez, M.J.; Ortego, F.; Castañera, P.; Farinós, G.P. Effects of three-year cultivation of Cry1Ab-expressing Bt maize on soil microarthropod communities. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 220, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szénási, Á.; Pálinkás, Z.; Zalai, M.; Schmitz, O.J.; Balog, A. Short-term effects of different genetically modified maize varieties on arthropod food web properties: An experimental field assessment. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, Z.; He, K.; Wang, Z. Impacts of transgenic corn with cry1Ie gene on arthropod biodiversity in the fields. Acta Phytophylacica Sin. 2014, 41, 482–489. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Ren, M.; Pan, L.; Liu, B.; Guan, X.; Tao, J. Impact of transgenic insect-resistant maize HGK60 with Cry1Ah gene on community components and biodiversity of arthropods in the fields. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Yang, M.; He, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, B.; Xue, K. Transgenic maize has insignificant effects on the diversity of arthropods: A 3-year study. Plants 2022, 11, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; He, K.; Hellmich, R.L.; Bai, S.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y.; Ahmed, T.; Wang, Z. Field trials to evaluate the effects of transgenic cry1Ie maize on the community characteristics of arthropod natural enemies. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Li, G.; Liu, B.; Gao, Y.; Wu, K.; Feng, H.; Scott, M. Field evaluation the effect of two transgenic Bt maize events on predatory arthropods in the Huang-Huai-Hai summer maize-growing region of China. Environ. Entomol. 2024, 53, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Guo, Y. Principles and Methods of Community Ecology; Chongqing Branch of Science and Technology Document Press: Chongqing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Magurran, A.E. Measuring Biological Diversity; Blackwell Press: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, R. Principles of Animal Ecology; Beijing Normal University Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, K.; Liu, C.; Liu, M. Measurement methods for biodiversity of biological communities: II measurement methods for β diversity. Chin. Biodivers. 1995, 3, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z. Studies on the influence of the closed forest on the structure, diversity and stability of insect community. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1992, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Wan, N.; Ji, X.; Dan, J. Diversity and stability of arthropod community in peach orchard under effects of ground cover vegetation. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 22, 2303–2308. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q. DPS Data Processing System: Experimental Desin, Statistical Analysis and Data Mining; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ter Braak, C.J.F.; Smilauer, P. Canoco 5, Windows release (5.00); Software for Mutivariate Data Exploration, Testing, and Summarization; Biometris, Plant Research International: Wageningen, Holland, 2012.
- Yang, B.; Ge, F. The applications of multivariate analysis in arthropod community analysis. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 50, 1178–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Comas, C.; Lumbierres, B.; Pons, X.; Albajes, R. No effects of Bacillus thuringiensis maize on nontarget organisms in the field in southern Europe: A meta-analysis of 26 arthropod taxa. Transgenic Res. 2013, 23, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeis, J.; Hellmich, R.L.; Candolfi, M.P.; Carstens, K.; De Schrijver, A.; Gatehouse, A.M.R.; Herman, R.A.; Huesing, J.E.; Mclean, M.A.; Raybould, A.; et al. Recommendations for the design of laboratory studies on non-target arthropods for risk assessment of genetically engineered plants. Transgenic Res. 2010, 20, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kort, H.; Prunier, J.G.; Ducatez, S.; Honnay, O.; Baguette, M.; Stevens, V.M.; Blanchet, S. Life history, climate and biogeography interactively affect worldwide genetic diversity of plant and animal populations. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, Y. Geographical Distribution of Agricultural and Forestry Insects in China; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Priestley, A.L.; Brownbridge, M. Field trials to evaluate effects of Bt-transgenic silage corn expressing the Cry1Ab insecticidal toxin on non-target soil arthropods in northern New England, USA. Transgenic Res. 2008, 18, 425–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awmack, C.S.; Leather, S.R. Host plant quality and fecundity in herbivorous insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2002, 47, 817–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, T.; Chen, Y.; Ge, S.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Wu, K. Larval diet affects development and reproduction of East Asian strain of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; He, L.; Zhao, S.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Wu, K. Suitability of common crop- and non-crop plants for Spodoptera frugiperda development in tropical Asia. Pest Manag. Sci. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Zhao, S.; He, W.; Wu, K. Pollen and nectar have different effects on the development and reproduction of noctuid moths. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 976987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J.; Chang, H.; Wu, K. Host plants and pollination regions for the long-distance migratory noctuid moth, Hadula trifolii Hufnagel in China. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e8819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenn, H.W. Feeding mechanisms of adult Lepidoptera: Structure, function, and evolution of the mouthparts. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 307–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dively, G.P.; Venugopal, P.D.; Bean, D.; Whalen, J.; Holmstrom, K.; Kuhar, T.P.; Doughty, H.B.; Patton, T.W.; Cissel, W.; Hutchison, W.D. Regional pest suppression associated with widespread Bt maize adoption benefits vegetable growers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3320–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, T.H.; Potting, R.P.J.; Denholm, I.; Poppy, G.M. Parasitoid behaviour and Bt plants. Nature 1999, 400, 825–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Peng, Y. Research progress in chemical communication among insect-resistant genetically modified plants, insect pests and natural enemies. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 25, 2431–2439. [Google Scholar]
- Altieri, M.A. The myth of coexistence: Why transgenic crops are not compatible with agroecologically based systems of production. Bull. Sci. Technol. Soc. 2005, 25, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabashnik, B.E.; Fabrick, J.A.; Carrière, Y.; Wu, Y. Global patterns of insect resistance to transgenic Bt crops: The first 25 years. J. Econ. Entomol. 2023, 116, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Difonzo, C.; Hennessy, D.A.; Zhao, J.; Wu, F.; Conley, S.P.; Gassmann, A.J.; Hodgson, E.W.; Jensen, B.; Knodel, J.J.; et al. Too much of a good thing: Lessons from compromised rootworm Bt maize in the US Corn Belt. Science 2025, 387, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, K.; Jiang, Y.; Xia, B.; Li, P.; Feng, H.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Guo, Y. Mirid bug outbreaks in multiple crops correlated with wide-scale adoption of Bt cotton in China. Science 2010, 328, 1151–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flachs, A.; Stone, G.D.; Hallett, S.; Kranthi, K.R. GM crops and the Jevons paradox: Induced innovation, systemic effects and net pesticide increases from pesticide-decreasing crops. J. Agrar. Change 2025, 25, e70006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, N.; Xie, Y.; Liang, J.; Li, F. Progress on the effect of transgenic insect-resistant maize on biodiversity of arthropods. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2022, 38, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar]


| Year | Growth Stage of Maize | Arthropod Community | Target Herbivores | Non-Target Herbivores | Natural Enemies | Neutral Insects |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | V4–V5 | 0.44 | 0.50 | 0.46 | 0.31 | 1.00 |
| V6–V8 | 0.55 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.50 | 0.40 | |
| V9–V11 | 0.75 | 0.77 | 0.67 | 0.84 | 0.67 | |
| V14–VT | 0.85 | 0.75 | 0.88 | 0.90 | 0.50 | |
| R1–R2 | 0.83 | 0.89 | 0.80 | 0.87 | 0.67 | |
| R3–R4 | 0.75 | 0.86 | 0.73 | 0.69 | 1.00 | |
| R5–R6 | 0.84 | 0.86 | 0.75 | 0.93 | 0.67 | |
| 2024 | V4–V5 | 0.27 | - | 0.33 | 0.33 | - |
| V6–V8 | 0.55 | - | 0.67 | 0.67 | - | |
| V9–V11 | 0.32 | - | 0.40 | 0.33 | - | |
| V14–VT | 0.67 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.80 | 1.00 | |
| R1–R2 | 0.67 | 0.57 | 0.63 | 0.70 | 1.00 | |
| R3–R4 | 0.77 | 0.80 | 0.63 | 0.84 | 1.00 | |
| R5–R6 | 0.64 | 0.50 | 0.63 | 0.67 | 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, L.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, W.; Cong, S.; Tan, Y.; He, W.; Liang, G.; Wu, K. Effect of Bt-Cry1Ab Maize Commercialization on Arthropod Community Biodiversity in Southwest China. Insects 2025, 16, 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111132
He L, Wang L, Zhou Y, Wu W, Cong S, Tan Y, He W, Liang G, Wu K. Effect of Bt-Cry1Ab Maize Commercialization on Arthropod Community Biodiversity in Southwest China. Insects. 2025; 16(11):1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111132
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Limei, Ling Wang, Yatao Zhou, Wenxian Wu, Shengbo Cong, Yanni Tan, Wei He, Gemei Liang, and Kongming Wu. 2025. "Effect of Bt-Cry1Ab Maize Commercialization on Arthropod Community Biodiversity in Southwest China" Insects 16, no. 11: 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111132
APA StyleHe, L., Wang, L., Zhou, Y., Wu, W., Cong, S., Tan, Y., He, W., Liang, G., & Wu, K. (2025). Effect of Bt-Cry1Ab Maize Commercialization on Arthropod Community Biodiversity in Southwest China. Insects, 16(11), 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111132






