The Cercal Sensilla of the Praying Mantis Hierodula patellifera and Statilia maculata: A New Partition Based on the Cerci Ultrastructure
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Collection and Preparation
2.2. Sample Preparation for Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
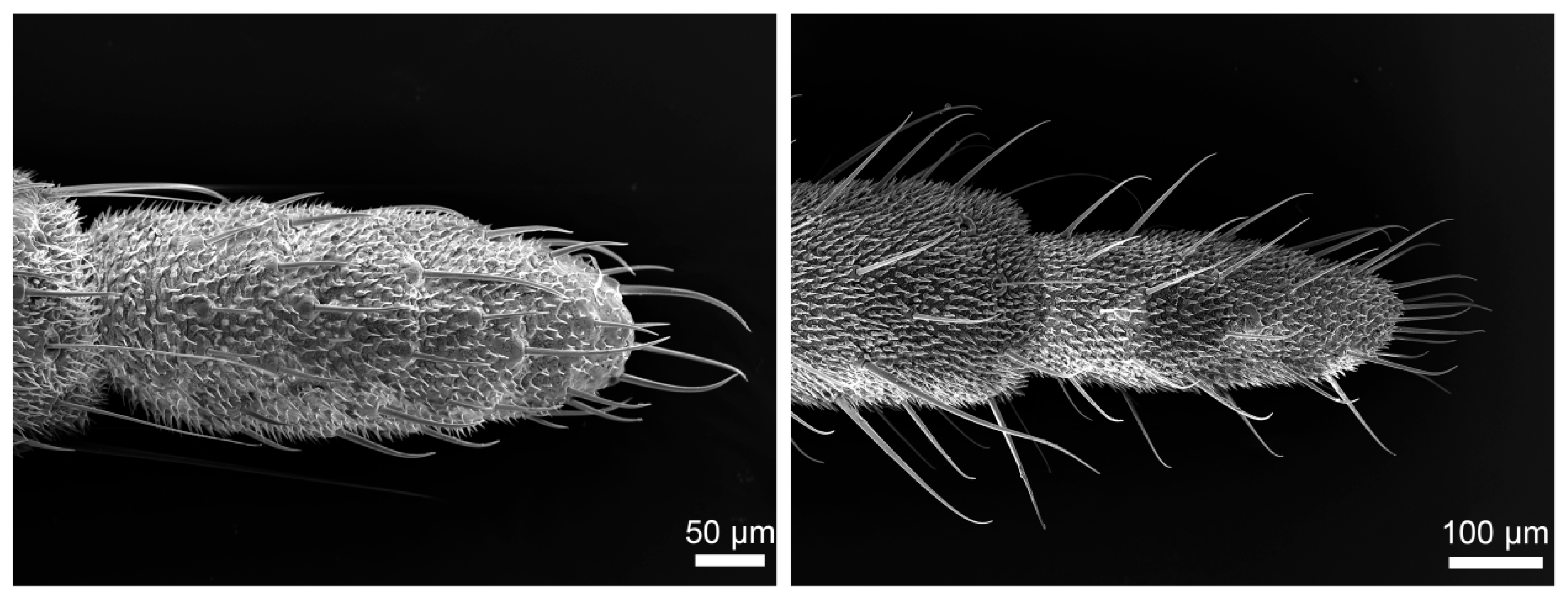
3.1. Gross Morphology
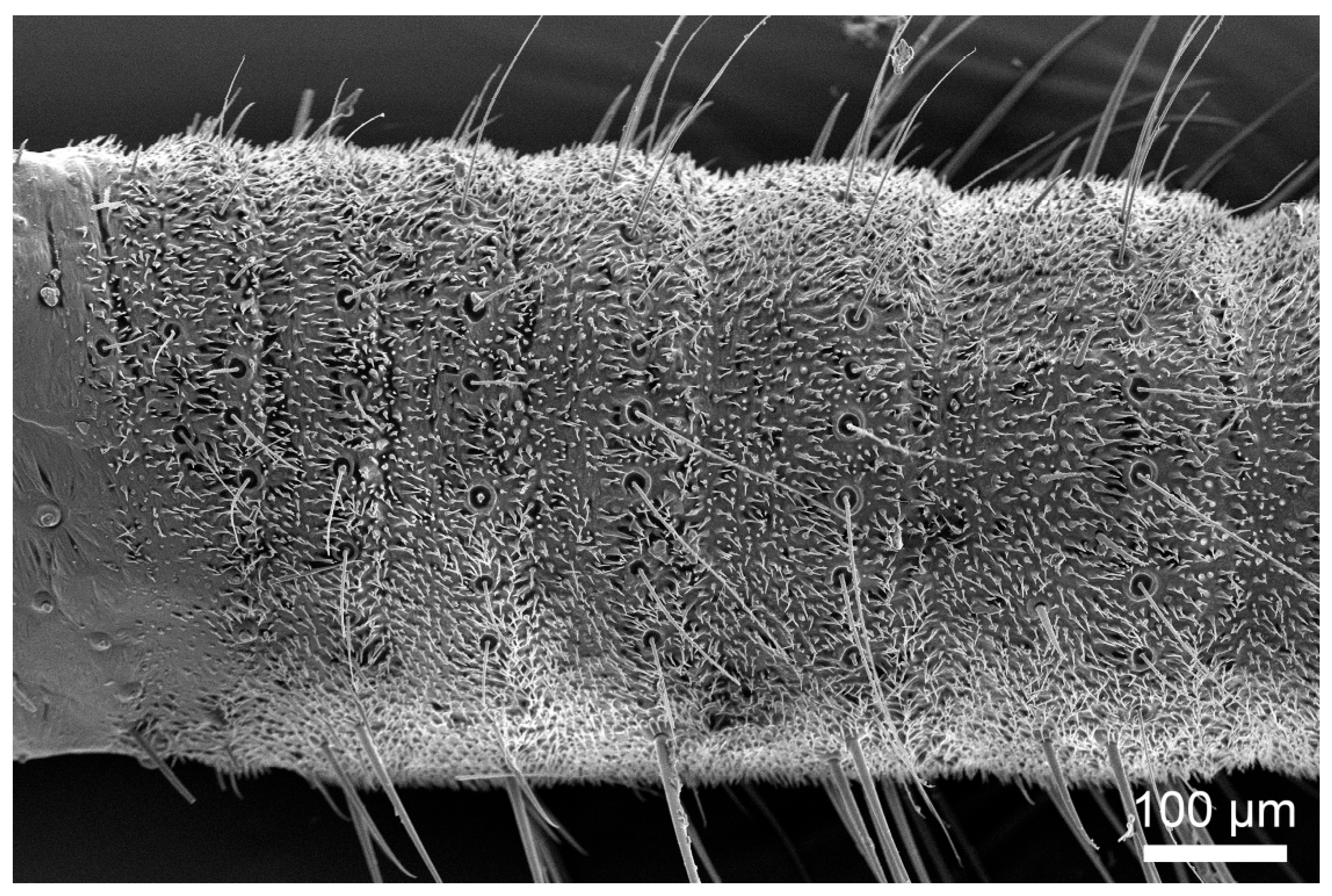
3.2. Types and Characteristics of Sensilla
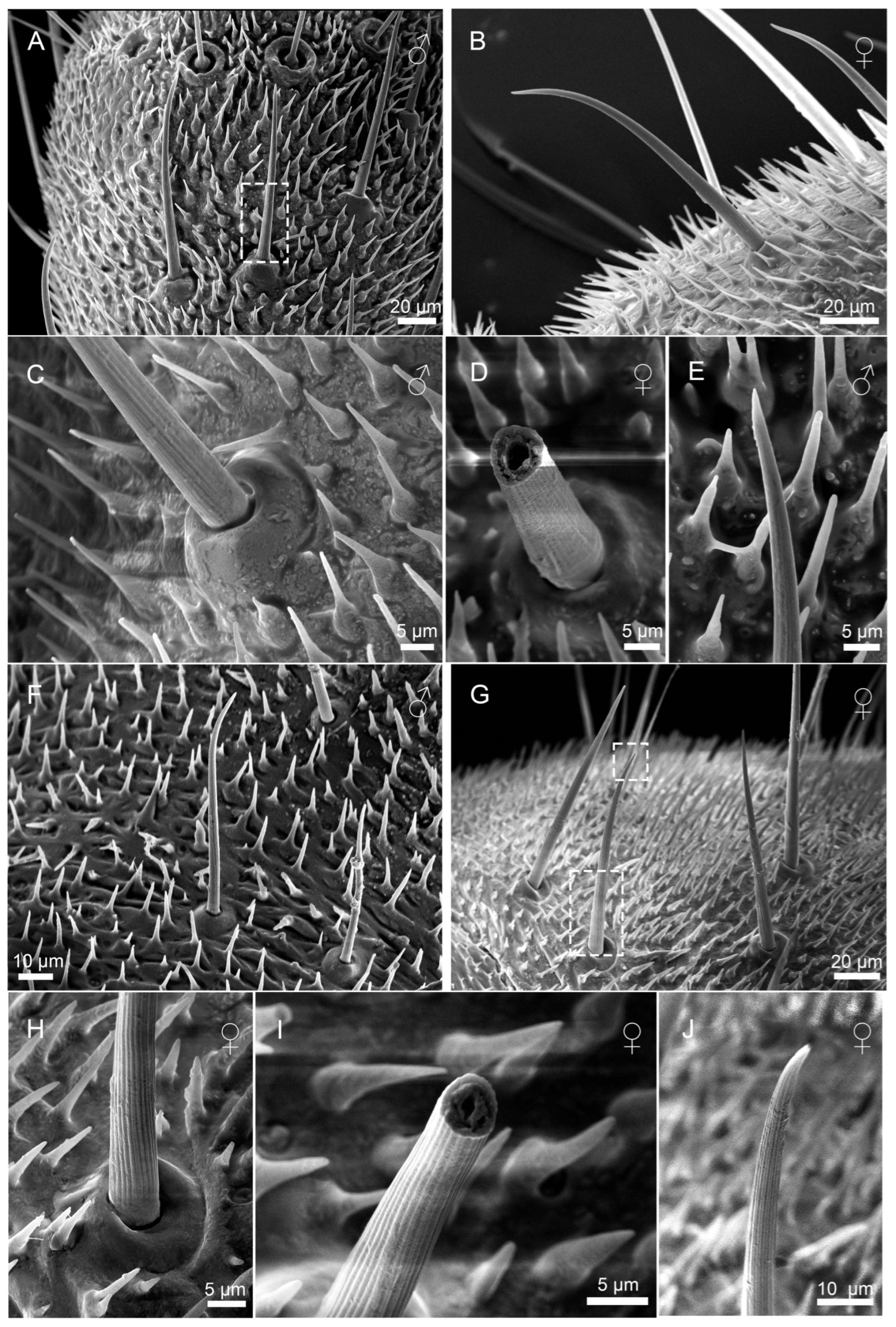
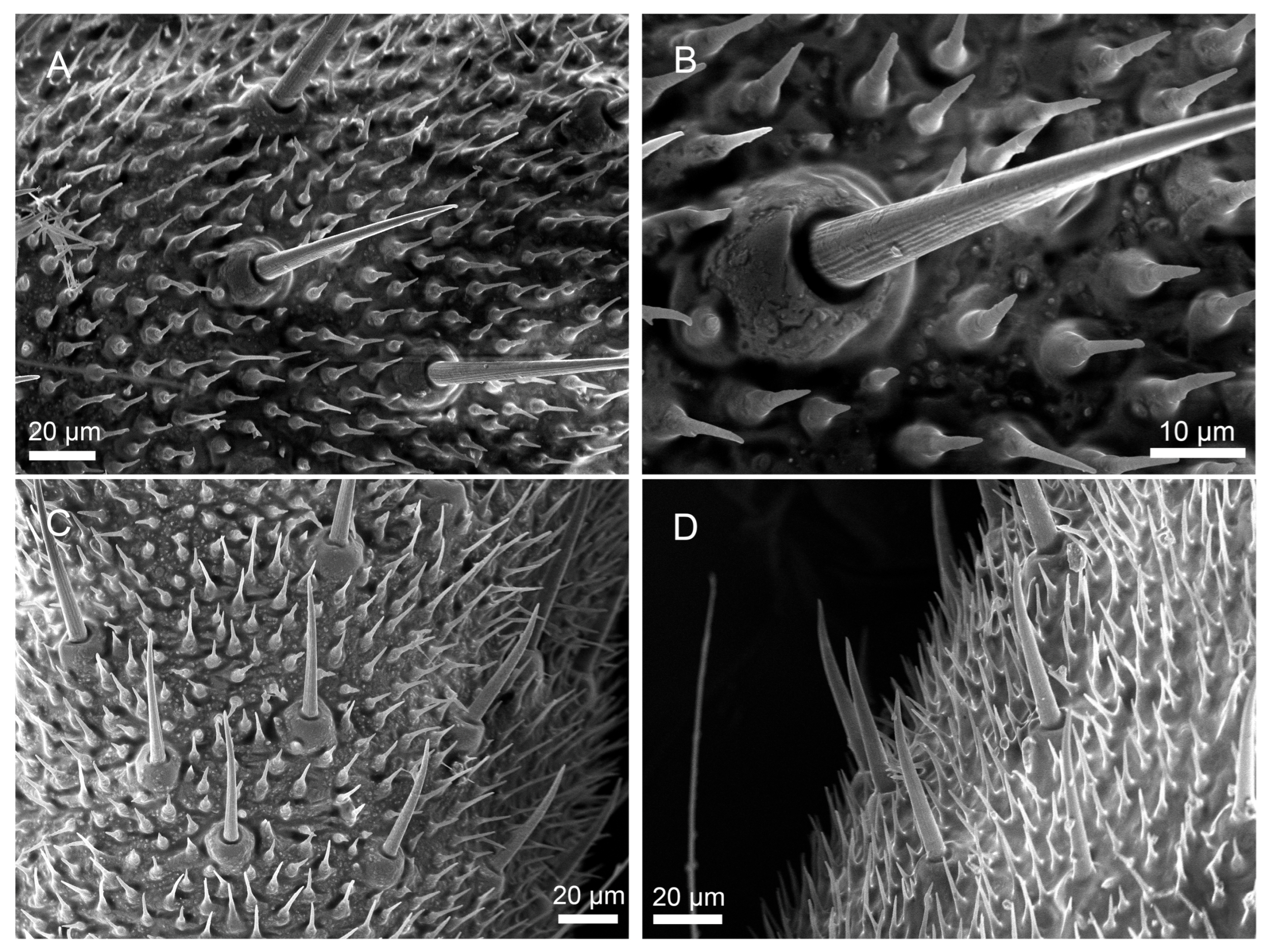
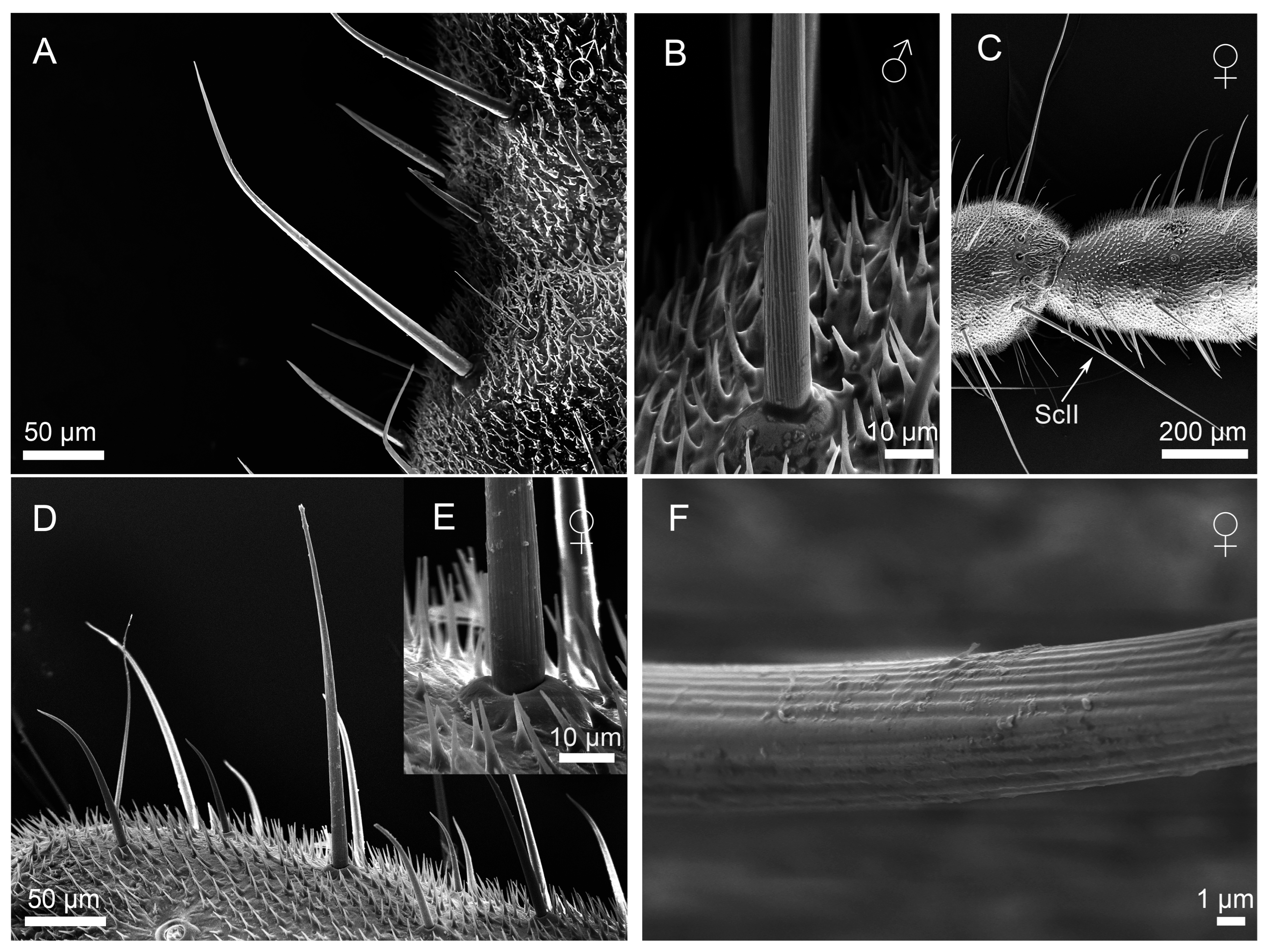
3.2.1. Sensilla Filiformia (Sf)
3.2.2. Sensilla Chaetica (Sc)
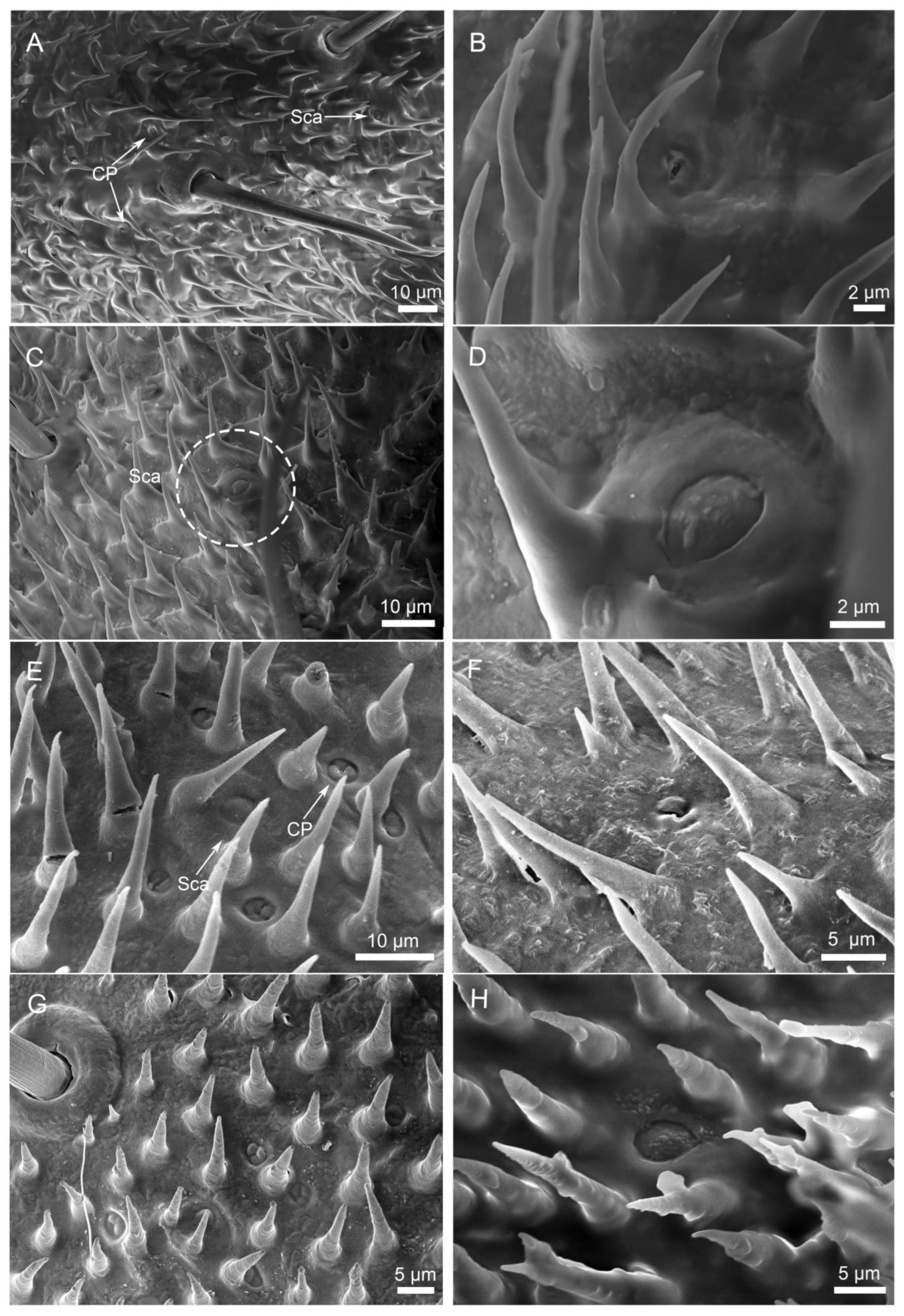
3.2.3. Sensilla Campaniformia (Sca)
3.2.4. Cuticular Pore (CP)
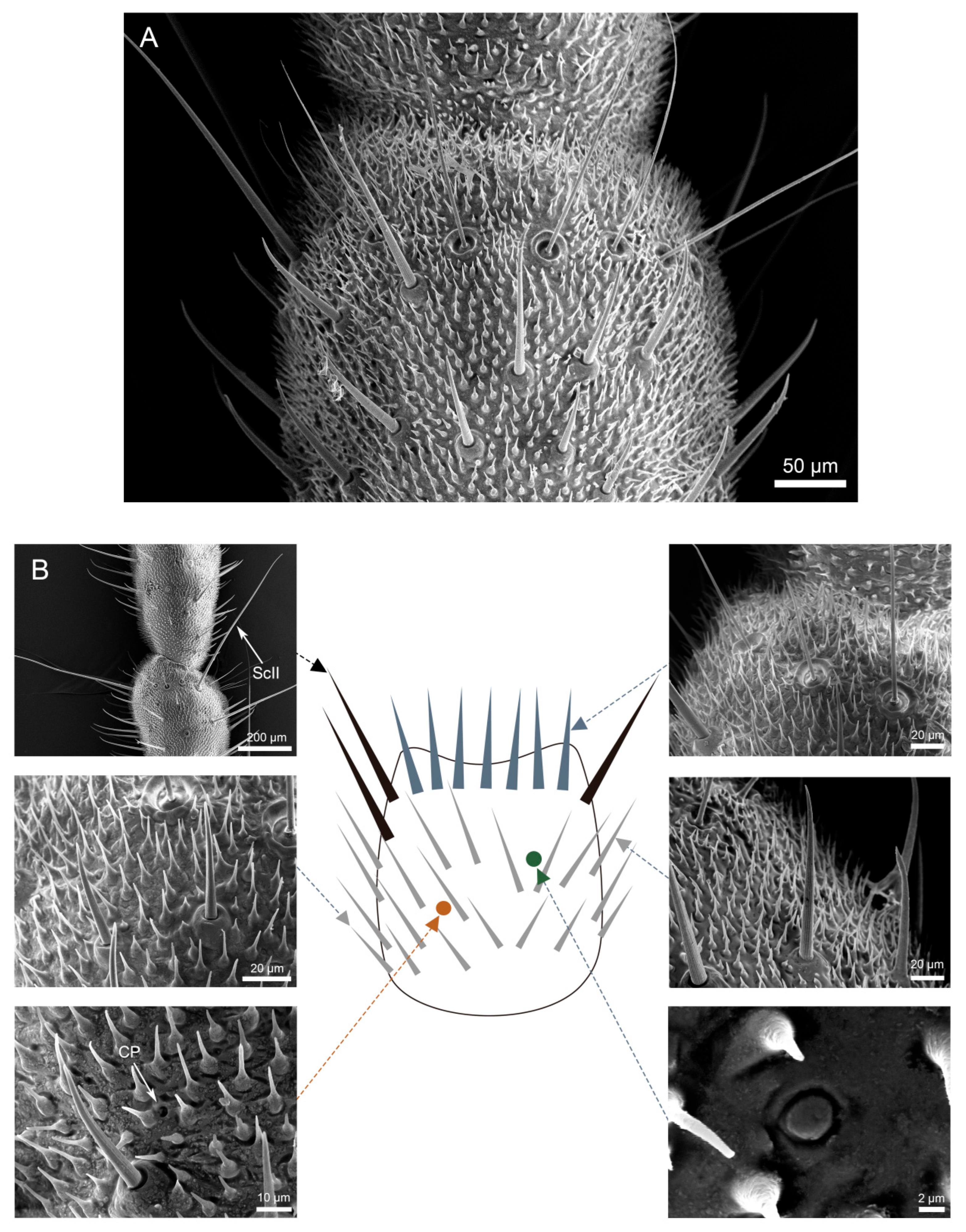
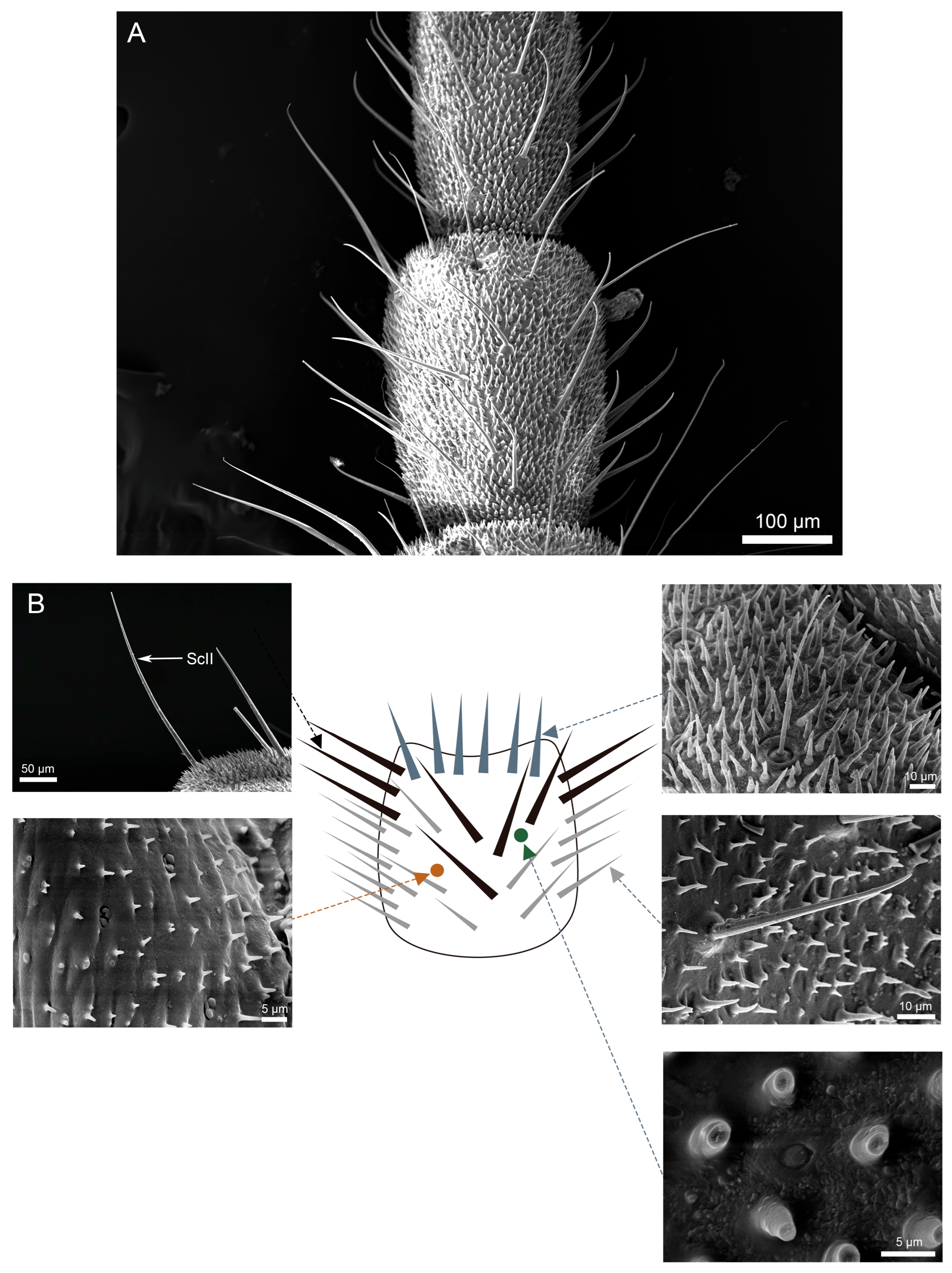
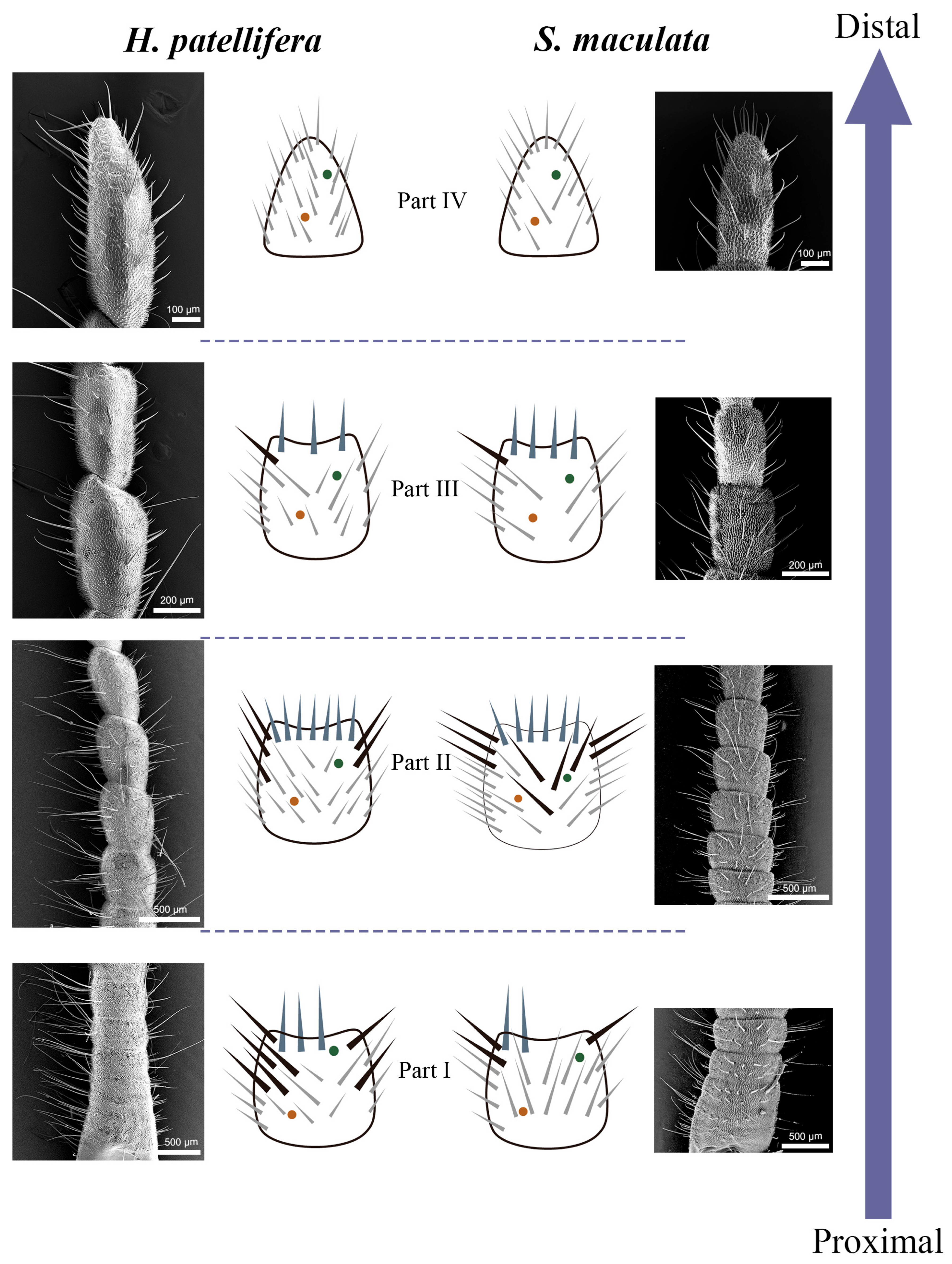
3.3. Density and Distribution Pattern of the Cercal Sensilla
3.3.1. Part I: Proximal Basic Perception Zone
3.3.2. Part II: Central Comprehensive Perception Zone
3.3.3. Part III: Distal Fine Perception Transition Zone
3.3.4. Part IV: Terminal Specialized Perception Zone
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chapman, R.F. The Insects: Structure and Function, 5th ed.; Simpson, S.J., Douglas, A.E., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 738–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullan, P.J.; Cranston, P.S. The Insects: An Outline of Entomology, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 125–130. Available online: https://www.wiley-vch.de/en/areas-interest/natural-sciences/life-sciences-11ls/entomology-11lsc/the-insects-978-1-118-84615-5 (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Rose, R.K.; Hurd, L.E. Coexistence of two congeneric praying mantids: A 7-year field study of reproductive success and failure. Environ. Entomol. 2016, 45, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, C.J.; Ehrmann, R. A new genus and species of bark mantis from Thailand, with an updated key to the bark mantis genera of the Oriental region (Insecta: Mantodea). Zootaxa 2017, 4291, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, D.F.; Wang, G.L.; Liu, J.W.; Wu, Q.Y.; Zhu, Y.P. Antennal morphology and sensilla of Asian multicolored ladybird beetles, Harmonia axyridis Pallas (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Entomol. News 2009, 120, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, S.L.; Oh, H.W.; Park, K.C. Antennal sensillum morphology and electrophysiological responses of olfactory receptor neurons in trichoid sensilla of the diamondback moth (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Fla. Entomol. 2016, 99, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altner, H.; Prillinger, L. Ultrastructure of Invertebrate Chemo-, Thermo-, and Hygroreceptors and Its Functional Significance. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1980, 67, 69–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altner, H.; Loftus, R. Ultrastructure and Function of Insect Thermo- and Hygroreceptors. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1985, 30, 273–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merivee, E.; Rahi, M.; Bresciani, J.; Ravn, H.P.; Luik, A. Antennal sensilla of the click beetle, Limonius aeruginosus (Olivier) (Coleoptera: Elateridae). Int. J. Insect Morphol. Embryol. 1998, 27, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIver, S.B. Structure of cuticular mechanoreceptors of arthropods. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1975, 20, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnatzy, W.; Tautz, J. Ultrastructure and mechanical properties of an insect mechanoreceptor: Stimulus-transmitting structures and sensory apparatus of the cereal filiform hairs of Gryllus. Cell Tissue Res. 1980, 213, 441–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desutter-Grandcolas, L.; Blanchet, E.; Robillard, T.; Magal, C.; Vannier, F.; Dangles, O. Evolution of the cercal sensory system in a tropical cricket clade (Orthoptera: Grylloidea: Eneopterinae): A phylogenetic approach. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2010, 99, 614–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.-Q.; Zhang, S.; Lv, L.; Wang, M.-Q. Insight into the ultrastructure of antennal sensilla of Mythimna separata (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Insect Sci. 2015, 15, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, T.; Zhang, T.-T.; Wang, Z.-Y.; He, K.-L.; Bai, S.-X. Morphology and ultrastructure of antennal sensilla of Macrocentrus cingulum Brischke (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) and their probable functions. Micron 2013, 50, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, F.; Svenson, G.J. Biodiversity of Mantodea. In Insect Biodiversity: Science and Society; Foottit, R.G., Adler, P.H., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 2, pp. 389–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackledge, T.A.; Eliason, C.M. Functionally independent components of prey capture are architecturally constrained in spider orb webs. Biol. Lett. 2007, 3, 456–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrette, B.J. Prey capture in the praying mantis Tenodera aridifolia sinensis: Coordination of the capture sequence and strike movements. J. Exp. Biol. 1990, 148, 147–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, F. Observations on the Micromorpholopy of Circus of Gryllus bimaculatus and Study on the Projection of Ganglion Impar Neurous. Master’s Thesis, Shenyang Normal University, Shenyang, China, 2011. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD2011&filename=1011084292.nh (accessed on 2 November 2024).
- Gnatzy, W. The ultrastructure of the thread-hairs on the cerci of the cockroach Periplaneta americana: The intermoult phase. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1976, 54, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, F.; Nel, A.; Svenson, G.J.; Robillard, T.; Pellens, R.; Grandcolas, P. Phylogeny of Dictyoptera: Dating the origin of cockroaches, praying mantises and termites with molecular data and controlled fossil evidence. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battiston, R.; Picciau, L.; Fontana, P.; Marshall, J. The Mantids of the Euro-Mediterranean Area; WBA Handbooks: Verona, Italy, 2010; Volume 2, Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/215988183_The_Mantids_of_the_Euro-Mediterranean_Area (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- Schwarz, C.J.; Roy, R. The systematics of Mantodea revisited: An updated classification incorporating multiple data sources (Insecta: Dictyoptera). Ann. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 2019, 55, 101–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, C.J.; Roy, R. Some taxonomic and nomenclatural changes in Mantodea (Dictyoptera). Bull. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 2018, 123, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D. Insect antennae. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1964, 9, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.; Gnatzy, W. Die Feinstruktur der Sinneshaare auf den Cerci von Gryllus bimaculatus Deg. (Saltatoria, Gryllidae). III. Die kurzen Borstenhaare. Z. Zellforsch. Mikrosk. Anat. 1972, 126, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, J.M.; Federle, W. The effect of surface roughness on claw and adhesive hair performance in the dock beetle Gastrophysa viridula. Insect Sci. 2010, 18, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liang, A.-P. Ultrastructure of the tarsus in Oides decempunctatus (Billberg) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 2013, 86, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonhoven, L.; Simmonds, M.; Blaney, W. Changes in the responsiveness of the maxillary styloconic sensilla of Spodoptera littoralis to inositol and sinigrin correlate with feeding behaviour during the final larval stadium. J. Insect. Physiol. 1991, 37, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acebes, A.; Cobb, M.; Ferveur, J.-F. Species-specific effects of single sensillum ablation on mating position in Drosophila. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 3095–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, L.E.; Barry, K.L.; Holwell, G.I. Mate location and antennal morphology in the praying mantid Hierodula majuscula. Aust. J. Entomol. 2012, 51, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carle, T.; Toh, Y.; Yamawaki, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Yokohari, F. The antennal sensilla of the praying mantis Tenodera aridifolia: A new flagellar partition based on the antennal macro-, micro-and ultrastructures. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2014, 43, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wan, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Liu, Y. Ultrastructure of the antennal sensilla of the praying mantis Creobroter nebulosa Zheng (Mantedea: Hymenopodidae). PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0301445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faucheux, M.J. Sensory and glandular structures on the antennae of Mantis religiosa, Iris oratoria and Rivetina baetica: Sexual dimorphism, physiological implications (Mantodea: Mantidae). Bull. Inst. R. Sci. Nat. Belg. Entomol. 2009, 79, 231–242. Available online: https://docslib.org/doc/7048492/sensory-and-glandular-structures-on-the-antennae-of-mantis-religiosa (accessed on 25 December 2024).
- Feng, X.; Huang, S.; Luo, C. Ultrastructure of cerci of karst cave species Tachycines lalinus (Orthoptera: Rhaphidophoridae: Aemodogryllinae). J. Northwest A&F Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 50, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanou, M.; Shimozawa, T. A threshold analysis of cricket cercal interneurons by an alternating air-current stimulus. J. Comp. Physiol. A 1984, 154, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, S.; Horseman, G.; Cokl, A. Directional sensitivity of wind-sensitive giant interneurons in the cave cricket Troglophilus neglectus. J. Exp. Zool. 2002, 292, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, P.S.M.; Wells, H. Sound generation in Mantis religiosa (Mantodea: Mantidae): Stridulatory structures and acoustic signal. J. Orthoptera Res. 2007, 16, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yager, D.D.; Hoy, R.R. The cyclopean ear: A new sense for the praying mantis. Science 1986, 231, 727–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kämper, G.; Vedenina, V. Frequency-intensity characteristics of cricket cercal interneurons: Units with high-pass functions. J. Comp. Physiol. A 1998, 182, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozhkova, G.; Vedenina, V.; Kämper, G. Frequency-intensity characteristics of cricket cercal interneurons: Broadband units. J. Comp. Physiol. A 1999, 184, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, M.; Yokohari, F.; Ishibashi, T. The antennal thermoreceptor of the camel cricket, Tachycines asynamorus. J. Insect Physiol. 1985, 31, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharuk, R.Y. Ultrastructure and function of insect chemosensilla. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1980, 25, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, D.; Higgins, R.; Ramaswamy, S. Antennal morphology of the soybean stemborer Dectes texanus texanus LeConte (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 2003, 76, 397–405. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262950451_Antennal_morphology_of_the_soybean_Stemborer_Dectes_texanus_texanus_LeConte_Coleoptera_Cerambycidae (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- Agrawal, S.; Grimaldi, D.; Fox, J.L. Haltere morphology and campaniform sensilla arrangement across Diptera. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2017, 46, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Qin, D. Fine morphology of the antennae and mouthparts of Dentatissus damnosa (Chou & Lu) (Hemiptera: Issidae). Zool. Anz. 2017, 268, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cônsoli, F.L.; Kitajima, E.W.; Parra, J.R.P. Sensilla on the antenna and ovipositor of the parasitic wasps Trichogramma galloi Zucchi and T. pretiosum Riley (Hym., Trichogrammatidae). Microsc. Res. Tech. 1999, 45, 313–324. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10383124/ (accessed on 15 March 2025). [CrossRef]
- Lastra-Valdés, J.; da-Silva, J.R.M.C.; Duarte, M. Morphology and histology of vom Rath’s organ in brush-footed butterflies (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, B.; Deora, T.; Mohren, T.; Daniel, T. Neural evidence supports a dual sensory-motor role for insect wings. Proc. R. Soc. B 2017, 284, 20170969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frantsevich, L.; Gorb, S.; Radchenko, V.; Gladun, D.; Polilov, A.; Cherney, L.; Browdy, V.; Kovalev, M. Lehr’s fields of campaniform sensilla in beetles (Coleoptera): Functional morphology. II. Wing reduction and the sensory field. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2015, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heusslein, R.; Gnatzy, W. Central projections of campaniform sensilla on the cerci of crickets and cockroaches. Cell Tissue Res. 1987, 247, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.; Palka, J. The cerci and abdominal giant fibres of the house cricket, Acheta domesticus. I. Anatomy and physiology of normal adults. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 1974, 185, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walthall, W.; Murphey, R. Positional information, compartments, and the cercal sensory system of crickets. Dev. Biol. 1986, 113, 182–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Type of Sensilla | Species | Diameter (μm) | Length (μm) | Outer Wall of Sensillar Hair | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Sex | ||||
| Sensilla filiformia | H. patellifera | male | 18.1 ± 1.7 aA | 113.2 ± 50.3 aA | Shallow grooved |
| female | 23.0 ± 2.0 aA | 125.6 ± 49.3 aA | Shallow grooved | ||
| S. maculata | male | 20.2 ± 2.8 aA | 155.2 ± 75.3 aA | Shallow grooved | |
| female | 22.2 ± 2.2 aA | 148.2 ± 66.0 aA | Shallow grooved | ||
| Sensilla chaetica I | H. patellifera | male | 15.2 ± 2.4 aA | 62.9 ± 20.4 bB | Deeply grooved |
| female | 17.8 ± 4.1 aA | 78.2 ± 32.6 aB | Deeply grooved | ||
| S. maculata | male | 16.8 ± 1.2 aA | 94.4 ± 24.2 bA | Deeply grooved | |
| female | 17.3 ± 3.1 aA | 116.0 ± 22.9 aA | Deeply grooved | ||
| Sensilla chaetica II | H. patellifera | male | 21.5 ± 3.0 aA | 274.0 ± 66.6 bA | Deeply grooved |
| female | 24.5 ± 3.4 aA | 477.2 ± 76.0 aA | Deeply grooved | ||
| S. maculata | male | 17.0 ± 2.2 bB | 220.3 ± 12.7 bB | Deeply grooved | |
| female | 20.0 ± 3.3 aB | 250.5 ± 29.4 aB | Deeply grooved | ||
| Sensilla campaniformia | H. patellifera | male | 7.6 ± 1.0 aA | — | — |
| female | 7.6 ± 1.2 aA | — | — | ||
| S. maculata | male | 8.1 ± 0.7 aA | — | — | |
| female | 7.4 ± 1.0 aA | — | — | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Ding, X.; Li, H.; Liu, Y. The Cercal Sensilla of the Praying Mantis Hierodula patellifera and Statilia maculata: A New Partition Based on the Cerci Ultrastructure. Insects 2025, 16, 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111093
Wang Y, Ding X, Li H, Liu Y. The Cercal Sensilla of the Praying Mantis Hierodula patellifera and Statilia maculata: A New Partition Based on the Cerci Ultrastructure. Insects. 2025; 16(11):1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111093
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yang, Xiaoqun Ding, Huan Li, and Yang Liu. 2025. "The Cercal Sensilla of the Praying Mantis Hierodula patellifera and Statilia maculata: A New Partition Based on the Cerci Ultrastructure" Insects 16, no. 11: 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111093
APA StyleWang, Y., Ding, X., Li, H., & Liu, Y. (2025). The Cercal Sensilla of the Praying Mantis Hierodula patellifera and Statilia maculata: A New Partition Based on the Cerci Ultrastructure. Insects, 16(11), 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111093






