Artificial Diet Assay Screening of Candidate RNAi Effectors Against Myzus persicae (Hemiptera)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Aphid Culture
2.2. M. persicae Genes Targeted for RNAi Bioassays
2.3. In Vitro Transcription of dsRNA Effectors
2.4. Aphid Artificial Diet Feeding Bioassay
2.5. Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (qRT–qPCR)
2.6. Graphs and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Artificial Diet Bioassays
3.1.1. Aphid Mortality Counts Fed dsRNA Effectors Individually
3.1.2. Relative Gene Expression (RGE)
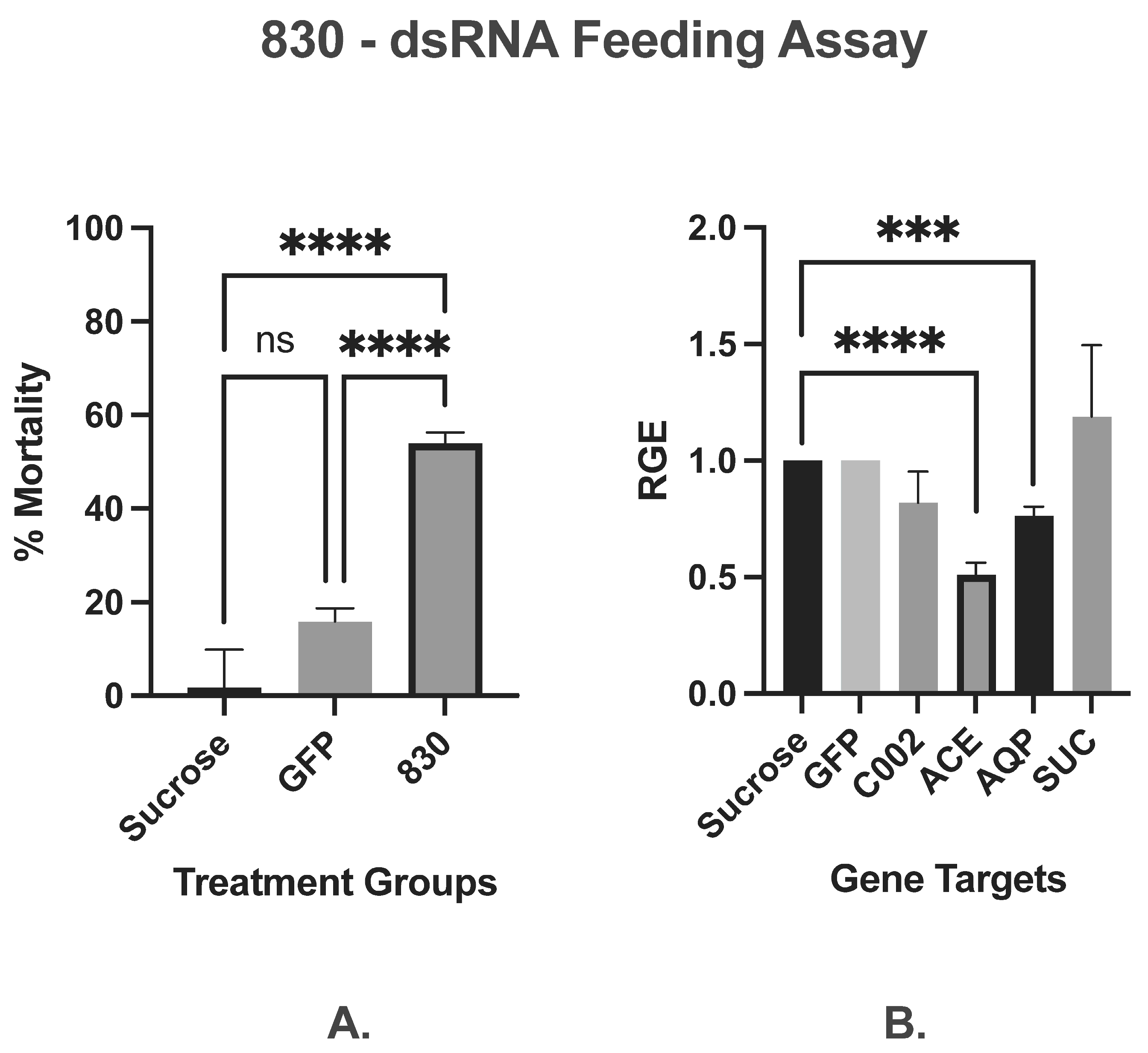
3.1.3. dsRNA Effector Combinations
3.1.4. Stacked Construct
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bass, C.; Puinean, A.M.; Zimmer, C.T.; Denholm, I.; Field, L.M.; Foster, S.P.; Gutbrod, O.; Nauen, R.; Slater, R.; Williamson, M.S. The evolution of insecticide resistance in the peach potato aphid, Myzus persicae. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 51, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ffrench-Constant, R.H.; Daborn, P.J.; Goff, G.L. The genetics and genomics of insecticide resistance. Trends Genet. 2004, 20, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndakidemi, B.; Mtei, K.; Ndakidemi, P.A. Impacts of synthetic and botanical pesticides on beneficial insects. Agric. Sci. 2016, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Agudo, M.; González-Cabrera, J.; Picó, Y.; Calatayud-Vernich, P.; Urbaneja, A.; Dicke, M.; Tena, A. Neonicotinoids in excretion product of phloem-feeding insects kill beneficial insects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 16817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunstone, T.; Cornelisse, T.; Klein, K.; Dubey, A.; Donley, N. Pesticides and soil invertebrates: A hazard assessment. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 643847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Rossi, J. RNAi mechanisms and applications. Biotechniques 2008, 44, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitchen, J.H.; Beachy, R.N. Genetically engineered protection against viruses in transgenic plants. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1993, 47, 739–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Shimura, H.; Masuta, C. Advancing toward commercial application of RNA silencing-based strategies to protect plants from viral diseases. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2019, 85, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wohlhueter, R.; Zhang, H. Genetically modified foods: A critical review of their promise and problems. Food Sci. Human Well. 2016, 5, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Miguel, K.; Scott, J.G. The next generation of insecticides: dsRNA is stable as a foliar-applied insecticide. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degnan, R.M.; Shuey, L.S.; Radford-Smith, J.; Gardiner, D.M.; Carroll, B.J.; Mitter, N.; McTaggart, A.R.; Sawyer, A. Double-stranded RNA prevents and cures infection by rust fungi. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Dean, R.A. Movement of small RNAs in and between plants and fungi. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 21, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Thomas, N.; Jin, H. Cross-kingdom RNA trafficking and environmental RNAi for powerful innovative pre- and post-harvest plant protection. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 38, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Weiberg, A.; Lin, F.-M.; Thomma, B.P.H.J.; Huang, H.-D.; Jin, H. Bidirectional cross-kingdom RNAi and fungal uptake of external RNAs confer plant protection. Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 16151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitter, N.; Worrall, E.A.; Robinson, K.E.; Li, P.; Jain, R.G.; Taochy, C.; Fletcher, S.J.; Carroll, B.J.; Lu, G.Q.; Xu, Z.P. Clay nanosheets for topical delivery of RNAi for sustained protection against plant viruses. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 16207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitter, N.; Worrall, E.A.; Robinson, K.E.; Xu, Z.P.; Carroll, B.J. Induction of virus resistance by exogenous application of double-stranded RNA. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 26, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worrall, E.A.; Bravo-Cazar, A.; Nilon, A.T.; Fletcher, S.J.; Robinson, K.E.; Carr, J.P.; Mitter, N. Exogenous application of RNAi-inducing double-stranded RNA inhibits aphid-mediated transmission of a plant virus. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, A.; Sarmah, N.; Kaldis, A.; Perdikis, D.; Voloudakis, A. Plant insects and mites uptake double-stranded RNA upon its exogenous application on tomato leaves. Planta 2017, 246, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Qiao, L.; Wang, M.; He, B.; Lin, F.M.; Palmquist, J.; Huang, S.D.; Jin, H. Plants send small RNAs in extracellular vesicles to fungal pathogen to silence virulence genes. Science 2018, 360, 1126–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbian, Y.; Maori, E.; Kalev, H.; Shafir, S.; Sela, I. Bidirectional transfer of RNAi between honey bee and Varroa destructor: Varroa gene silencing reduces Varroa population. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1003035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutti, N.S.; Park, Y.; Reese, J.C.; Reeck, G.R. RNAi knockdown of a salivary transcript leading to lethality in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. J. Insect Sci. 2006, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Yang, W.-J.; Tian, Y.; Fan, J.-Y.; Ye, C.; Shang, F.; Ding, B.-Y.; Zhang, J.; An, X.; Yang, L.; et al. Topical dsRNA delivery induces gene silencing and mortality in the pea aphid. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 2873–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacques, S.; Reidy-Crofts, J.; Sperschneider, J.; Kamphuis, L.G.; Gao, L.L.; Edwards, O.R.; Singh, K.B. An RNAi supplemented diet as a reverse genetics tool to control bluegreen aphid, a major pest of legumes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, J.; Zeng, F. Feeding-based RNA interference of a gap gene is lethal to the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, A.D.; Mugford, S.T.; Hogenhout, S.A. Silencing of aphid genes by dsRNA feeding from plants. In Management of Insect Pests to Agriculture: Lessons Learned from Deciphering Their Genome, Transcriptome and Proteome; Czosnek, H., Ghanim, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 245–251. [Google Scholar]
- Pitino, M.; Coleman, A.D.; Maffei, M.E.; Ridout, C.J.; Hogenhout, S.A. Silencing of aphid genes by dsRNA feeding from plants. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzin, V.; Yang, X.; Jing, X.; Zhang, K.; Jander, G.; Douglas, A.E. RNA interference against gut osmoregulatory genes in phloem-feeding insects. J. Insect Physiol. 2015, 79, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiaens, O.; Swevers, L.; Smagghe, G. DsRNA degradation in the pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum) associated with lack of response in RNAi feeding and injection assay. Peptides 2014, 53, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodke, A.B.; Good, R.T.; Golz, J.F.; Russell, D.A.; Edwards, O.; Robin, C. Extracellular endonucleases in the midgut of Myzus persicae may limit the efficacy of orally delivered RNAi. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-S.; Tian, H.-g.; McMullen, J.G.; Chung, S.H.; Douglas, A.E. Candidate genetic determinants of intraspecific variation in pea aphid susceptibility to RNA interference. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 123, 103408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.G.; Fletcher, S.J.; Manzie, N.; Robinson, K.E.; Li, P.; Lu, E.; Brosnan, C.A.; Xu, Z.P.; Mitter, N. Foliar application of clay-delivered RNA interference for whitefly control. Nat. Plants 2022, 8, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karley, A.J.; Ashford, D.A.; Minto, L.M.; Pritchard, J.; Douglas, A.E. The significance of gut sucrase activity for osmoregulation in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. J. Insect Physiol. 2005, 51, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.W.; Liu, F.H.; Tian, H.G.; Zhang, M.; Guo, S.S.; Liu, T.X. Evaluation of the reference genes for expression analysis using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae. Insect Sci. 2017, 24, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, H. Selection of reference genes for the normalization of RT-qPCR data in gene expression studies in insects: A systematic review. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.-P.; Singh, S.K.; Gao, Y.; Lassiter, T.L.; Mishra, R.K.; Zhu, K.Y.; Brimijoin, S. Selective and irreversible inhibitors of aphid acetylcholinesterases: Steps toward human-safe insecticides. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Song, X.; Wang, G.; Yang, K.; Wang, Y.; Niu, L.; Chen, X.; Fang, R. Plant-generated artificial small RNAs mediated aphid resistance. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakesby, A.J.; Wallace, I.S.; Isaacs, H.V.; Pritchard, J.; Roberts, D.M.; Douglas, A.E. A water-specific aquaporin involved in aphid osmoregulation. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrus, A.M.; Frolov, M.V. The diverse roles of RNA helicases in RNAi. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 3500–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.H.; Jing, X.; Luo, Y.; Douglas, A.E. Targeting symbiosis-related insect genes by RNAi in the pea aphid-Buchnera symbiosis. Insect Bioch. Mol. Biol. 2018, 95, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.C.; Sun, W.; Spencer, J.L.; Pittendrigh, B.R.; Seufferheld, M.J. Differential effects of RNAi treatments on field populations of the western corn rootworm. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2014, 110, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willow, J.; Taning, C.N.T.; Cook, S.M.; Sulg, S.; Silva, A.I.; Smagghe, G.; Veromann, E. RNAi targets in agricultural pest insects: Advancements, knowledge gaps, and IPM. Front. Agron. 2021, 3, 794312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.G.; Robinson, K.E.; Asgari, S.; Mitter, N. Current scenario of RNAi-based hemipteran control. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 2188–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.; An, X.; Jiang, Y.-D.; Ding, B.-Y.; Shang, F.; Christiaens, O.; Taning, C.N.T.; Smagghe, G.; Niu, J.; Wang, J.-J. Induction of RNAi core machinery’s gene expression by exogenous dsRNA and the effects of pre-exposure to dsRNA on the gene silencing efficiency in the Pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum). Front. Physiol. 2019, 9, 01906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.; Jiang, Y.-D.; An, X.; Yang, L.; Shang, F.; Niu, J.; Wang, J.-J. Effects of RNAi-based silencing of chitin synthase gene on moulting and fecundity in pea aphids (Acyrthosiphon pisum). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapountzis, P.; Duport, G.; Balmand, S.; Gaget, K.; Jaubert-Possamai, S.; Febvay, G.; Charles, H.; Rahbé, Y.; Colella, S.; Calevro, F. New insight into the RNA interference response against cathepsin-L gene in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum: Molting or gut phenotypes specifically induced by injection or feeding treatments. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 51, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Luo, L.; Lu, H.; Chen, S.; Kang, L.; Cui, F. Angiotensin-converting enzymes modulate aphid–plant interactions. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.Y.; Shang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Yang, Q.; Niu, J.Z.; Smagghe, G.; Wang, J.J. Silencing of two insulin receptor genes disrupts nymph-adult transition of alate brown citrus aphid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.H.; Yu, X.R.; Shang, Q.L.; Shi, X.Y.; Gao, X.W. Oral delivery mediated RNA interference of a carboxylesterase gene results in reduced resistance to organophosphorus insecticides in the cotton Aphid, Aphis gossypii Glover. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebijith, K.B.; Asokan, R.; Hande, H.R.; Kumar, N.K.; Krishna, V.; Vinutha, J.; Bakthavatsalam, N. RNA interference of odorant-binding protein 2 (OBP2) of the Cotton Aphid, Aphis gossypii (Glover), resulted in altered electrophysiological responses. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 178, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Pan, Y.; Yang, C.; Gao, X.; Xi, J.; Wu, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhu, E.; Xin, X.; Zhan, C.; et al. Over-expression of CYP6A2 is associated with spirotetramat resistance and cross-resistance in the resistant strain of Aphis gossypii. Glover. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2016, 126, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Down, R.E.; Gatehouse, A.M.R.; Hamilton, W.D.O.; Gatehouse, J.A. Snowdrop lectin inhibits development and decreases fecundity of the Glasshouse Potato Aphid (Aulacorthum solani) when administered in vitro and via transgenic plants both in laboratory and glasshouse trials. J. Insect Physiol. 1996, 42, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Maiti, M.K.; Basu, A.; Sen, S.; Ghosh, A.K.; Sen, S.K. Transgenic expression of onion leaf lectin gene in Indian mustard offers protection against aphid colonization. Crop Sci. 2006, 46, 2022–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Feng, Z.J.; Chen, Z.S.; Zhang, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.X. Use of tyrosine hydroxylase RNAi to study Megoura viciae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) sequestration of its host’s l-DOPA for body melanism. J. Insect Physiol. 2019, 114, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulot, M.; Boissinot, S.; Monsion, B.; Rastegar, M.; Clavijo, G.; Halter, D.; Bochet, N.; Erdinger, M.; Brault, V. Comparative analysis of RNAi-based methods to down-regulate expression of two genes expressed at different levels in Myzus persicae. Viruses 2016, 8, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, V.; Bhattacharya, R. Host-mediated RNA interference targeting a cuticular protein gene impaired fecundity in the green peach aphid Myzus persicae. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 2059–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, K.; Ali, A.; Davies, T.G.E.; Naz, E.; Naz, L.; Sohail, S.; Hou, M.; Ullah, F. RNA interference-mediated knockdown of voltage-gated sodium channel (MpNav) gene causes mortality in peach-potato aphid, Myzus persicae. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, A.D.; Wouters, R.H.M.; Mugford, S.T.; Hogenhout, S.A. Persistence and transgenerational effect of plant-mediated RNAi in aphids. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Lu, Y.H.; Shang, Q.L.; Song, D.L.; Gao, X.W. Gene silencing of two acetylcholinesterases reveals their cholinergic and non-cholinergic functions in Rhopalosiphum padi and Sitobion avenae. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Z.; Ma, K.S.; Liu, J.J.; Lu, L.Y.; Chen, X.L.; Zhang, S.P.; Gao, X.W. Differential expression of genes in greenbug (Schizaphis graminum Rondani) treated by imidacloprid and RNA interference. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 1726–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Sparks, C.; Jones, H.; Riley, M.; Francis, F.; Du, W.; Xia, L. Silencing an essential gene involved in infestation and digestion in grain aphid through plant-mediated RNA interference generates aphid-resistant wheat plants. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 852–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Xu, L.; Liu, G.; Pang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; You, M.; Ni, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Liang, R. Plant-mediated gene silencing of an essential olfactory-related Gqα gene enhances resistance to grain aphid in common wheat in greenhouse and field. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 1718–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Zhao, Z. Influence of catalase gene silencing on the survivability of Sitobion avenae. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2014, 86, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
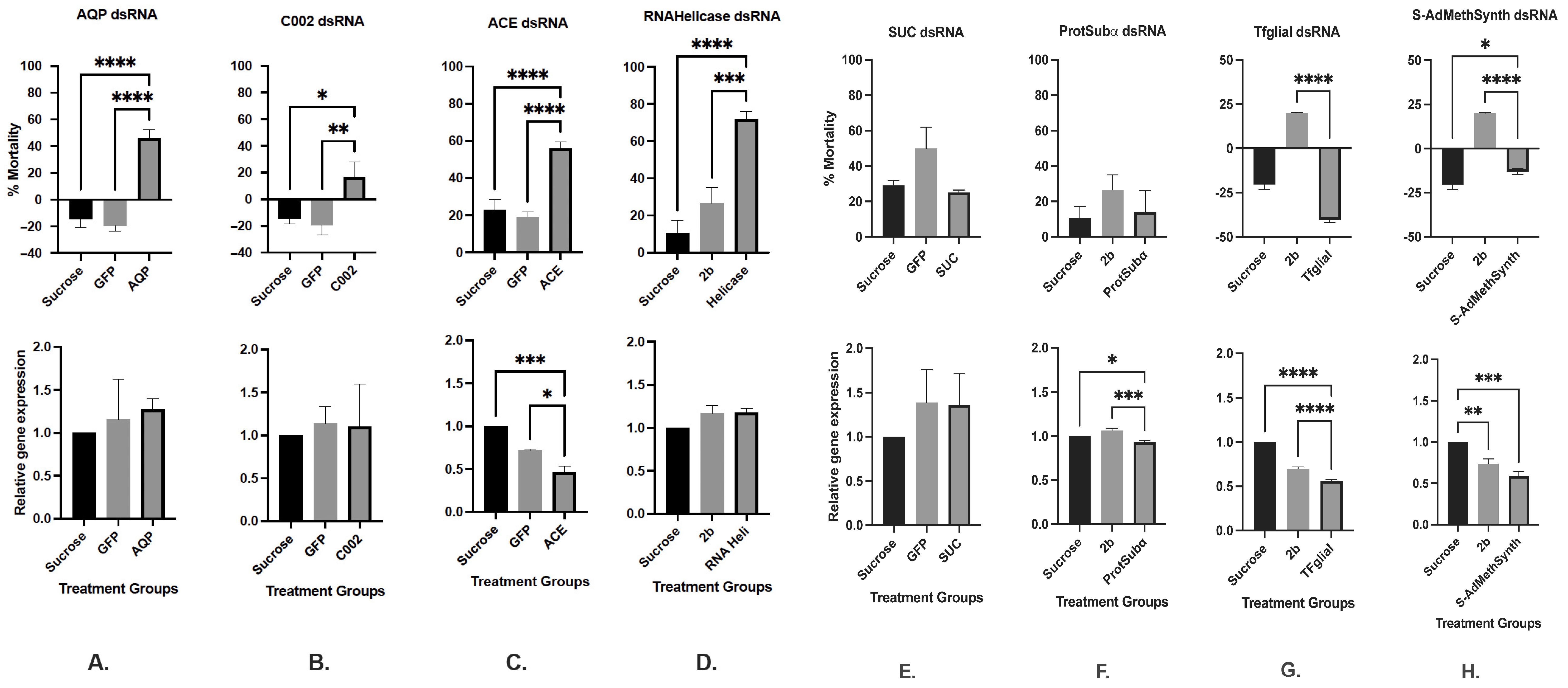

| Target Gene | Name | Function | Position | Length (bp) | Sequence ID a | % Mortality in AD b | % Relative Gene Expression c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aquaporin | AQP | Osmoregulatory | 331–830 | 500 | KR047100 | 45.8% d | +24% |
| Sucrose transporter | SUC | Osmoregulatory | 1334–1683 | 350 | KR047101 | 25% | +36% |
| Acetylcholinesterase | ACE | Neuronal functioning | 1600–1999 | 400 | KJ561353 | 56% | −53.7% |
| Salivary gland | C002 | Feeding/Probing | 391–890 | 500 | EC389531.1 | 16.7% d | +14% |
| Transcription factor glial cells missing | Tfglial | Neuronal functioning | 588–853 | 266 | XM 022324935 | −4.38% | −44% |
| S-adenosylmethionine synthase | S-AdMethSynth | Nucleic acid metabolism | 622–871 | 250 | XM 022314690 | −13.02% | −41% |
| Proteasome subunit alpha type | ProtSubAlpha | Protein metabolism | 260–569 | 310 | XM 022311085 | 13.84% | −6.3% |
| ATP-dependent RNA helicase | RNAHelicase | Nucleic acid metabolism | 667–994 | 328 | XM 022316612 | 71.76% | −18.3% |
| Stacked (AQP, C002, ACE, SUC) | 830 | Osmoregulatory, Neuronal function, Feeding/Probing | 830 (166 bp each) | 54% | −24%, −17.7%, −49%, +19.3% | ||
| Combination I (AQP/ACE) | Combination I | AQP/ACE | As Above | As Above | As Above | 78.7% | −5.5%, −13.5% |
| Combination II (AQP/C002) | Combination II | AQP/C002 | “ | “ | “ | 85.2% | −59.7%, −33.7% |
| Combination III (ACE/C002) | Combination III | ACE/C002 | “ | “ | “ | 79.4% | −35.3%, −36.7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghodke, A.B.; Fletcher, S.J.; Jain, R.G.; Manzie, N.; Mitter, N.; Robinson, K.E. Artificial Diet Assay Screening of Candidate RNAi Effectors Against Myzus persicae (Hemiptera). Insects 2025, 16, 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111086
Ghodke AB, Fletcher SJ, Jain RG, Manzie N, Mitter N, Robinson KE. Artificial Diet Assay Screening of Candidate RNAi Effectors Against Myzus persicae (Hemiptera). Insects. 2025; 16(11):1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111086
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhodke, Amol Bharat, Stephen J. Fletcher, Ritesh G. Jain, Narelle Manzie, Neena Mitter, and Karl E. Robinson. 2025. "Artificial Diet Assay Screening of Candidate RNAi Effectors Against Myzus persicae (Hemiptera)" Insects 16, no. 11: 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111086
APA StyleGhodke, A. B., Fletcher, S. J., Jain, R. G., Manzie, N., Mitter, N., & Robinson, K. E. (2025). Artificial Diet Assay Screening of Candidate RNAi Effectors Against Myzus persicae (Hemiptera). Insects, 16(11), 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111086






