Response of Chironomids (Diptera, Chironomidae) to Environmental Factors at Different Spatial Scales
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
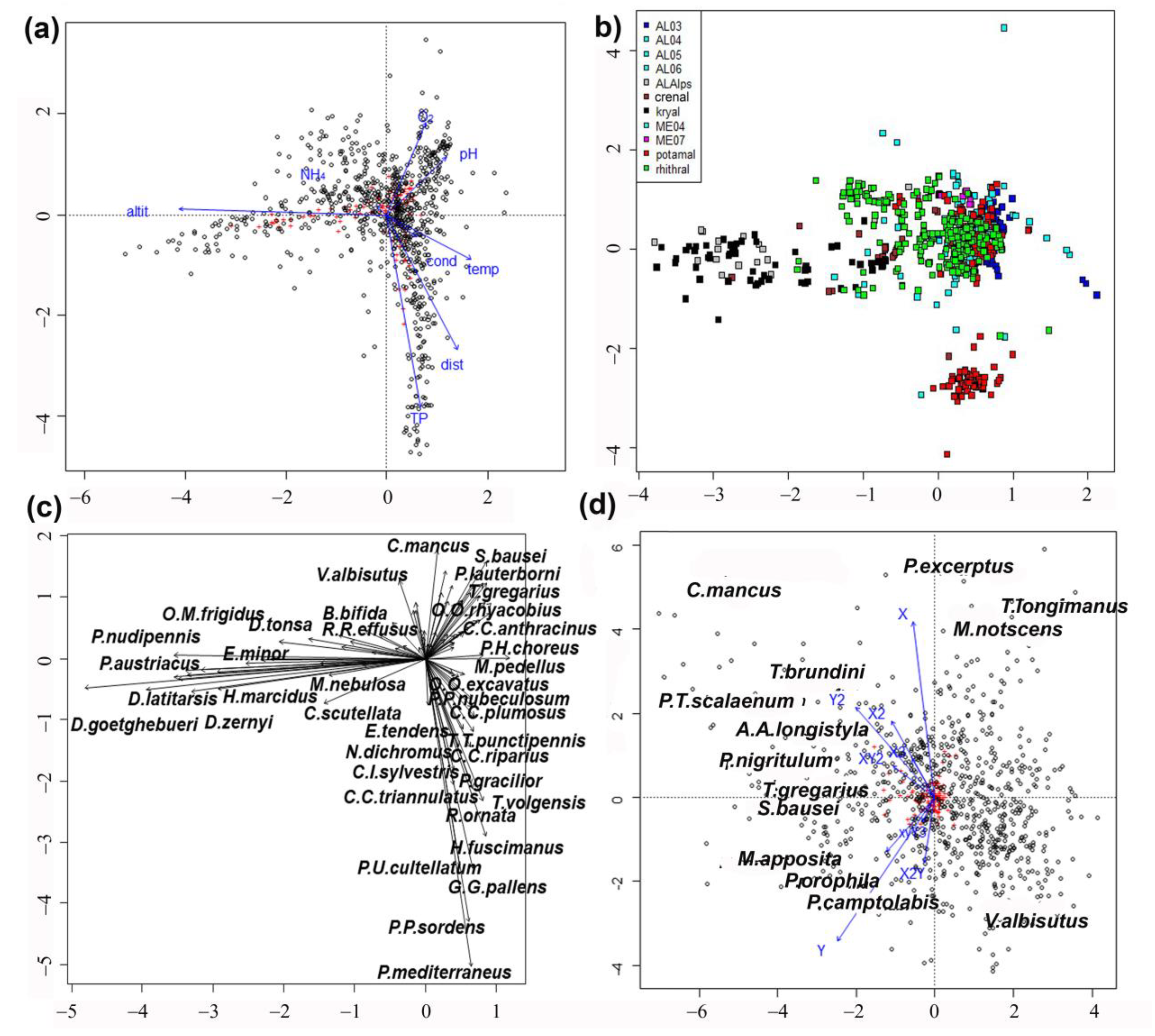
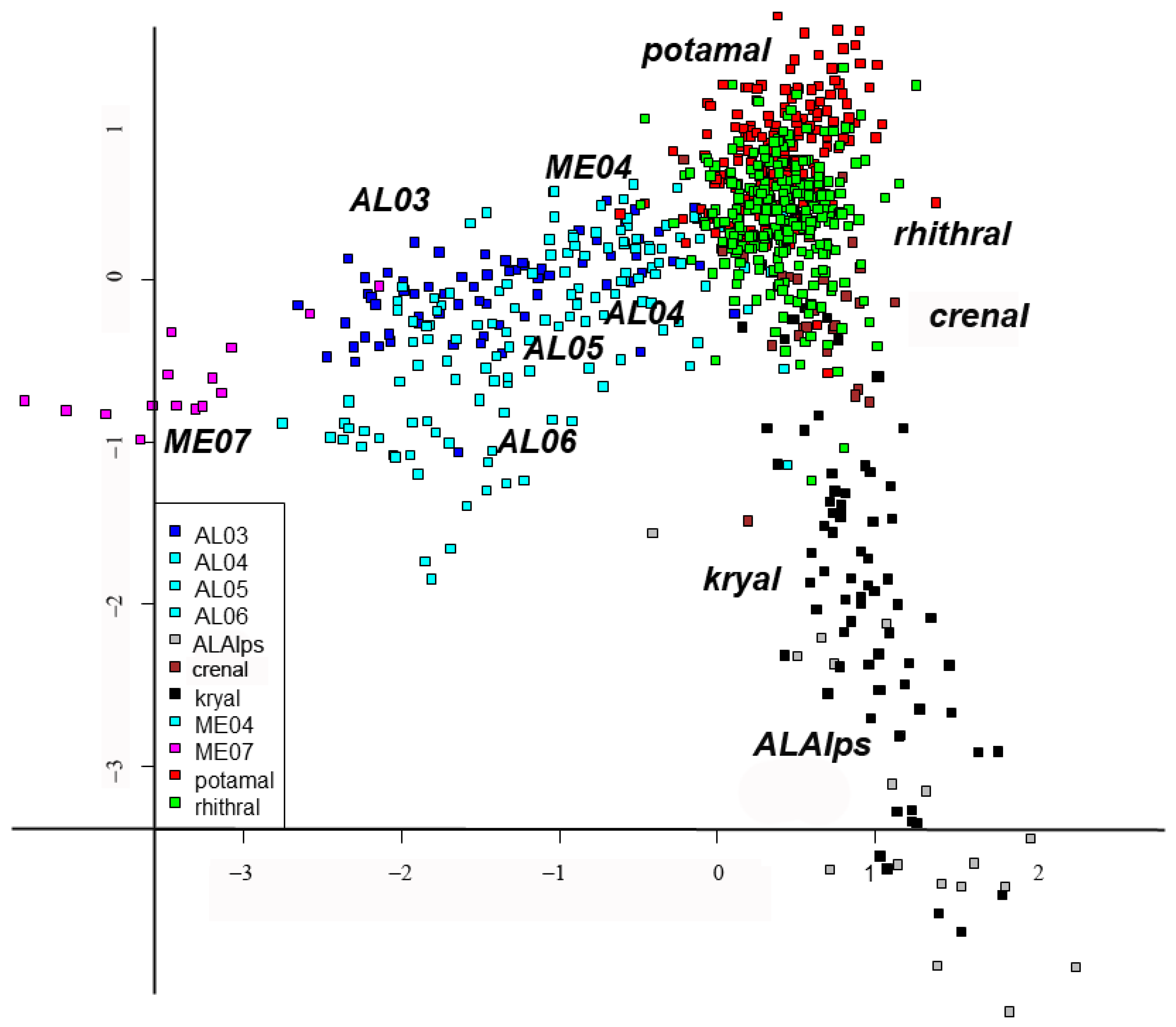
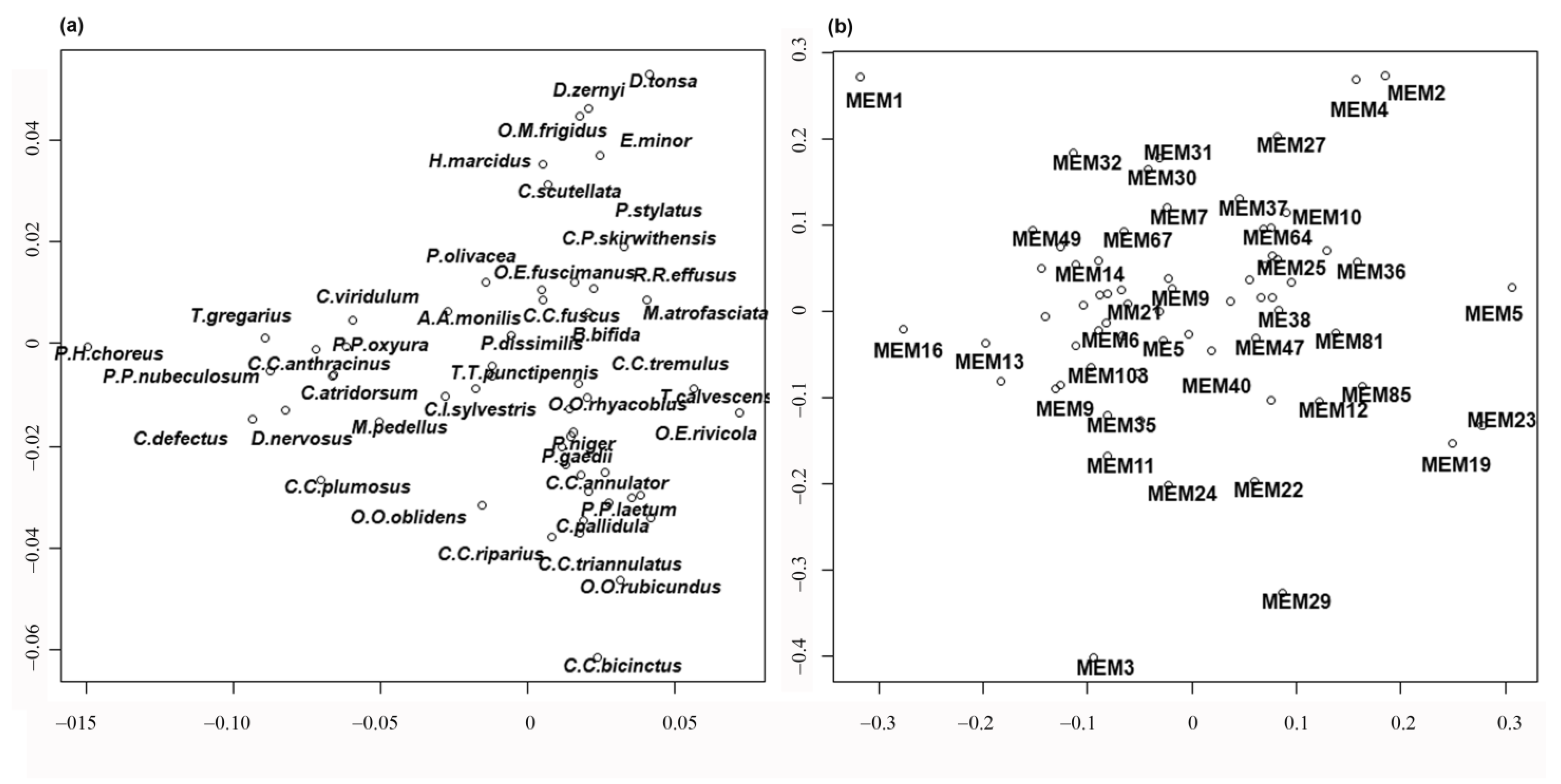
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armitage, P.; Cranston, P.; Pinder, C. (Eds.) The Chironomidae: Biology and Ecology of Non-Biting Midges; XII; Chapman Hall: London, UK; Glasgow, Scotland; Weinheim, Germany; New York NY, USA; Melbourne, VC, Australia; Madras, India, 1995; ISBN 041245260X. [Google Scholar]
- Rossaro, B.; Marziali, L.; Boggero, A. Response of Chironomids to Key Environmental Factors: Perspective for Biomonitoring. Insects 2022, 13, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flory, E.A.; Milner, A.M. The Role of Competition in Invertebrate Community Development in a Recently Formed Stream in Glacier Bay National Park, Alaska. Aquat. Ecol. 1999, 33, 175–184. Available online: https://link.springer.com/journal/10452/volumes-and-issues/33-2 (accessed on 1 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Bonada, N.; Resh, V.H. Mediterranean-Climate Streams and Rivers: Geographically Separated but Ecologically Comparable Freshwater Systems. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonada, N.; Dolédec, S.; Statzner, B. Taxonomic and Biological Trait Differences of Stream Macroinvertebrate Communities between Mediterranean and Temperate Regions: Implications for Future Climatic Scenarios. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2007, 13, 1658–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brundin, L. Transantarctic Relationships and Their Significance, as Evidenced by Chironomid Midges: With a Monograph of the Subfamilies Podonominae and Aphroteniinae and the Austral Heptagyiae. K. Sven. Vetenskapsakad Handl. 1966, 134, 433. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:129593839 (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Bonada, N.; Múrria, C.; Zamora-Muñoz, C.; El Alami, M.; Poquet, J.M.; Puntí, T.; Moreno, J.L.; Bennas, N.; Alba-Tercedor, J.; Ribera, C.; et al. Using Community and Population Approaches to Understand How Contemporary and Historical Factors Have Shaped Species Distribution in River Ecosystems. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2009, 18, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossaro, B.; Marziali, L.; Montagna, M.; Magoga, G.; Zaupa, S.; Boggero, A. Factors Controlling Morphotaxa Distributions of Diptera Chironomidae in Freshwaters. Water 2022, 14, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menge, B.A.; Olson, A.M. Role of scale and environmental factors in regulation of community structure. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1990, 5, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feld, C.K.; Hering, D. Community Structure or Function: Effects of Environmental Stress on Benthic Macroinvertebrates at Different Spatial Scales. Freshwat. Biol. 2007, 52, 1380–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leszczynska, J.; Glowacki, L.; Grzybkowska, M.; Przybylski, M. Chironomid Riverine Assemblages at the Regional Temperate Scale—Compositional Distance and Species Diversity. Eur. Zool. J. 2021, 88, 731–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leszczynska, J.; Grzybkowska, M.; Glowacki, L.; Dukowska, M. Environmental Variables Influencing Chironomid Assemblages (Diptera: Chironomidae) in Lowland Rivers of Central Poland. Environ. Ent. 2019, 48, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dray, S.; Pélissier, R.; Couteron, P.; Fortin, M.J.; Legendre, P.; Peres-Neto, P.R.; Bellier, E.; Bivand, R.; Blanchet, F.G.; De Cáceres, M.; et al. Community Ecology in the Age of Multivariate Multiscale Spatial Analysis. Ecol. Monogr. 2012, 82, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illies, J.; Botosaneanu, L. Problème et Méthodes de La Classification et de La Zonation Écologique Des Eaux Courantes, Considérées Surtout Du Point de Vue Faunistique. Mit. Intern. Ver. Limnol. 1963, 12, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buraschi, E.; Salerno, F.; Monguzzi, C.; Barbiero, G.; Tartari, G. Characterization of the Italian Lake-Types and Identification of Their Reference Sites Using Anthropogenic Pressure Factors. J. Limnol. 2005, 64, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartari, G.; Buraschi, E.; Legnani, E.; Previtali, L.; Pagnotta, R.; Marchetto, A. Tipizzazione Dei Laghi Italiani Secondo Il Sistema B Della Direttiva 2000/60/CE. In Documento Presentato al Ministero Dell’Ambiente e Della Tutela Del Territorio e Del Mare; CNR IRSA: Roma, Italy, 2006; pp. 1–20. Available online: https://www.irsa.cnr.it/wp/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/notiz2008_NS.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Free, G.; Solimini, A.; Rossaro, B.; Marziali, L.; Giacchini, R.; Paracchini, B.; Ghiani, M.; Vaccaro, S.; Gawlik, B.; Fresner, R.; et al. Modelling Lake Macroinvertebrate Species in the Shallow Sublittoral: Relative Roles of Habitat Lake Morphology Aquatic Chemistry and Sediment Composition. Hydrobiologia 2009, 633, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossaro, B.; Boggero, A.; Crozet, B.L.; Free, G.; Lencioni, V.; Marziali, L. A Comparison of Different Biotic Indices Based on Benthic Macroinvertebrates in Italian Lakes. J. Limnol. 2011, 70, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lods-Crozet, B. Long-Term Biomonitoring of Invertebrate Neozoans in Lake Geneva. Arch. Sci. 2014, 67, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadawski, P.; Montagna, M.; Rossaro, B.; Giłka, W.; Pešić, V.; Grabowski, M.; Magoga, G. DNA Barcoding of Chironomidae from the Lake Skadar Region: Reference Library and a Comparative Analysis of the European Fauna. Divers. Distrib. 2022, 28, 2838–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntitslidou, C.; Rossaro, B.; Lazaridou, M.; Bobori, D.C. What Drives Benthic Macroinvertebrate Dispersal in Different Lake Substrata? The Case of Three Mediterranean Lakes. Aquat. Ecol. 2021, 55, 1033–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulaaba, S.; Zrelli, S.; Boumaiza, M.; Rossaro, B. Relationships between Physical and Chemical Factors and Aquatic Macroinvertebrates in Perennial Streams in the Arid Northern Mountain Basin El Batina. J. Entomol. Acarol. Res. 2014, 46, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zerguine, K.; Samraoui, B.; Rossaro, B. A Survey of Chironomids from Seasonal Ponds of Numidia Northeastern Algeria. Boll. Zool. Agrar. E Bachic. 2009, 41, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QGIS.org QGIS Geographic Information System. Open Source Geospatial Foundation Project. 2009. Available online: https://www.qgis.org/it/site/ (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Borcard, D.; Gillet, F.; Legendre, P. Numerical Ecology with R; Use R! 2nd ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 9783319714035. [Google Scholar]
- Griffith, D.A. Spatial Autocorrelation and Eigenfunctions of the Geographic Weights. Can. Geogr. 1996, 40, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jombart, T.; Dray, S.; Dufour, A.-B. Finding Essential Scales of Spatial Variation in Ecological Data: A Multivariate Approach. Ecography 2009, 32, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauman, D.; Drouet, T.; Fortin, M.J.; Dray, S. Optimizing the Choice of a Spatial Weighting Matrix in Eigenvector-Based Methods. Ecology 2018, 99, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stéphane Dray Moran’s Eigenvector Maps and Related Methods for the Spatial Multiscale Analysis of Ecological Data 2023. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/adespatial/vignettes/tutorial.html (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Rossaro, B. Chironomids and Water Temperature. Aquat. Insects 1991, 13, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marziali, L.; Rossaro, B. Quantitative Response of Chironomid Species to Water Temperature: Effects on Species Distribution in Specific Habitats. J. Entomol. Acarol. Res. 2013, 45, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomisto, H. A Diversity of Beta Diversities: Straightening up a Concept Gone Awry. Part 1. Defining Beta Diversity as a Function of Alpha and Gamma Diversity. Ecography 2010, 33, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, J.H. Diversity in Tropical Rain Forests and Coral Reefs. Science 1978, 199, 1302–1310. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/1745369 (accessed on 1 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Coffman, W.P.; Cummins, K.W.; Wuycheck, J.C. Energy Flow in a Woodland Stream Ecosystem: I. Tissue Support Trophic Structure of the Autumnal Community. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1971, 68, 232–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belle, S.; Goedkoop, W. Functional Diversity of Chironomid Communities in Subarctic Lakes across Gradients in Temperature and Catchment Characteristics. Limnology 2021, 22, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resh, V.H.; Hildrew, A.G.; Statzner, B.; Townsend, C.R. Theoretical Habitat Templets, Species Traits, and Species Richness: A Synthesis of Long-term Ecological Research on the Upper Rhône River in the Context of Concurrently Developed Ecological Theory. Freshw. Biol. 1994, 31, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, S.R.Q.; Graça, M.A.S.; Dolédec, S.; Feio, M.J. Chironomidae of the Holarctic Region: A Comparison of Ecological and Functional Traits between North America and Europe. Hydrobiologia 2017, 794, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykrä, H.; Heino, J.; Muotka, T. Scale-related Patterns in the Spatial and Environmental Components of Stream Macroinvertebrate Assemblage Variation. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2007, 16, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marziali, L.; Pirola, N.; Schiavon, A.; Rossaro, B. Response of Chironomidae (Diptera) to DDT, Mercury, and Arsenic Legacy Pollution in Sediments of the Toce River (Northern Italy). Insects 2024, 15, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Water Bodies | Code | Habitat Description | Number of Sites |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lakes | AL03 | Large lakes with 100 km2 surface, maximum depth above 120 m, below 800 m a.s.l. altitude, including littoral, sublittoral and profundal zones | 68 |
| AL04 | Lakes with maximum depth < 15 m, below 800 m a.s.l. altitude, polymictic, without a clear thermal stratification | 8 | |
| AL05 | Lakes similar to AL04, but with thermal stratification, with littoral, sublittoral and profundal zone | 53 | |
| AL06 | Lakes similar to AL05, but with depth above 15 m, with littoral, sublittoral and profundal zone | 53 | |
| ALAlps | Small alpine lakes, including types AL01, AL02, AL07, AL08, AL09, AL10 described in [15,16], all above 800 m a.s.l., with a calcareous or siliceous substrate | 18 | |
| ME04 | Lakes collected in the Mediterranean area, except for the volcanic lakes ME07 | 22 | |
| ME07 | Volcanic lakes in Central Italy | 15 | |
| Streams and rivers | Crenal | Springs | 45 |
| Kryal | Glacial streams or cold springs near glacial streams | 70 | |
| Rhithral | Wadable streams | 259 | |
| Potamal | Large, not wadable rivers | 177 |
| Abbreviations | Species | Author | n |
|---|---|---|---|
| T. T. punctipennis | Tanypus (Tanypus) punctipennis | Meigen, 1818 | 83 |
| P. H. choreus | Procladius (Holotanypus) choreus | (Meigen, 1804) | 255 |
| M. nebulosa | Macropelopia nebulosi | (Meigen, 1804) | 68 |
| A. A. longistyla | Ablabesmyia (Ablabesmyia) longistyla | Fittkau, 1962 | 68 |
| A. A. monilis | Ablabesmyia (Ablabesmyia) monilis | (Linnaeus, 1758) | 94 |
| T. longimanus | Trissopelopia longimanus | (Stäger, 1839) | 31 |
| Z. barbatipes | Zavrelimyia barbatipes | (Kieffer, 1911) | 63 |
| C. pallidula | Conchapelopia pallidula | (Meigen, 1818) | 349 |
| R. ornata | Rheopelopia ornate | (Meigen, 1838) | 73 |
| P. branickii | Pseudodiamesa branickii | (Nowicki, 1873) | 72 |
| D. bertrami | Diamesa bertrami | Edwards, 1935 | 58 |
| D. goetghebueri | Diamesa goetghebueri | Pagast, 1947 | 21 |
| D. latitarsis | Diamesa latitarsis | (Goetghebuer, 1921) | 48 |
| D. cinerella | Diamesa cinerella | Meigen in Gistl, 1835 | 29 |
| D. tonsa | Diamesa tonsa | (Walker, 1856) | 184 |
| D. zernyi | Diamesa zernyi | Edwards, 1933 | 85 |
| S. spinifera | Sympotthastia spinifera | Serra-Tosio, 1968 | 61 |
| P. gaedii | Potthastia gaedii | (Meigen, 1838) | 90 |
| P. longimanus | Potthastia longimanus | (Kieffer, 1922) | 52 |
| P. olivacea | Prodiamesa olivacea | (Meigen, 1818) | 173 |
| B. bifida | Brillia bifida | (Kieffer, 1909) | 152 |
| B. longifurca | Brillia longifurca | Kieffer, 1921 | 53 |
| T. calvescens | Tvetenia calvescens | (Edwards, 1929) | 310 |
| E. ilkleyensis | Eukiefferiella ilkleyensis | (Edwards, 1929) | 109 |
| E. minor | Eukiefferiella minor | (Edwards, 1929) | 124 |
| E. brevicalcar | Eukiefferiella brevicalcar | (Kieffer, 1911) | 57 |
| E. claripennis | Eukiefferiella claripennis | (Lundbeck, 1898) | 241 |
| P. P. sordidellus | Psectrocladius (Psectrocladius) sordidellus | (Zetterstedt, 1838) | 53 |
| P. P. oxyura | Psectrocladius (Psectrocladius) oxyura | Langton, 1985 | 120 |
| R. P. chalybeatus | Rheocricotopus (Psilocricotopus) chalybeatus | (Edwards, 1929) | 136 |
| R. R. effusus | Rheocricotopus (Rheocricotopus) effusus | (Walker, 1856) | 121 |
| R. R. fuscipes | Rheocricotopus (Rheocricotopus) fuscipes | Kieffer, 1909 | 210 |
| P. niger | Paracricotopus niger | (Kieffer, 1913) | 95 |
| N. dichromus | Nanocladius dichromus | (Kieffer, 1906) | 89 |
| P. nudipennis | Parorthocladius nudipennis | (Kieffer, 1908) | 42 |
| S. semivirens | Synorthocladius semivirens | (Kieffer, 1909) | 244 |
| O. E. fuscimanus | Orthocladius (Eudactylocladius) fuscimanus | (Kieffer in K. & Thien., 1908) | 82 |
| O. E. rivicola | Orthocladius (Euorthocladius) rivicola | Kieffer, 1921 | 294 |
| O. M. frigidus | Orthocladius (Mesorthocladius) frigidus | (Zetterstedt, 1838) | 147 |
| O. O. excavatus | Orthocladius (Orthocladius) excavatus | Brundin, 1947 | 179 |
| O. O. oblidens | Orthocladius (Orthocladius) oblidens | (Walker, 1856) | 184 |
| O. O. rhyacobius | Orthocladius (Orthocladius) rhyacobius | Kieffer, 1911 | 164 |
| O. O. rubicundus | Orthocladius (Orthocladius) rubicundus | (Meigen, 1818) | 217 |
| C. P. skirwithensis | Cricotopus (Paratrichocladius) skirwithensis | (Edwards, 1929) | 100 |
| C. P. rufiventris | Cricotopus (Paratrichocladius) rufiventris | (Meigen, 1830) | 304 |
| C. C. fuscus | Cricotopus (Cricotopus) fuscus | (Kieffer, 1909) | 80 |
| C. C. tremulus | Cricotopus (Cricotopus) tremulus | (Linnaeus, 1756) | 179 |
| C. C. annulator | Cricotopus (Cricotopus) annulator | Goetghebuer, 1927 | 193 |
| C. C. triannulatus | Cricotopus (Cricotopus) triannulatus | (Macquart, 1826) | 138 |
| C. C. bicinctus | Cricotopus (Cricotopus) bicinctus | (Meigen, 1818) | 326 |
| C. C. trifascia | Cricotopus (Cricotopus) trifascia | Edwards, 1929 | 97 |
| C. I. sylvestris | Cricotopus (Isocladius) sylvestris | (Fabricius, 1794) | 218 |
| C. I. intersectus | Cricotopus (Isocladius) intersectus | (Stäger, 1839) | 33 |
| C. dentiforceps | Chaetocladius dentiforceps | (Edwards, 1929) | 46 |
| P. excerptus | Paratrissocladius excerptus | (Walker, 1856) | 21 |
| H. marcidus | Heterotrissocladius marcidus | (Walker, 1856) | 64 |
| P. stylatus | Parametriocnemus stylatus | (Kieffer, 1924) | 181 |
| P. bathophila | Parakiefferiella bathophila | (Kieffer, 1912) | 52 |
| H. serratosioi | Heleniella serratosioi | Ringe, 1976 | 45 |
| C. lobata | Corynoneura lobata | Edwards, 1924 | 28 |
| C. scutellata | Corynoneura scutellata | Winnertz, 1846 | 118 |
| S. bausei | Stempellina bausei | (Kieffer, 1911) | 45 |
| T. brundini | Tanytarsus brundini | Lindeberg, 1963 | 44 |
| T. gregarius | Tanytarsus gregarius | Kieffer, 1909 | 123 |
| T. volgensis | Tanytarsus volgensis | Miseiko, 1967 | 58 |
| V. albisutus | Virgatanytarsus albisutus | (Santos-Abreu, 1918) | 53 |
| C. atridorsum | Cladotanytarsus atridorsum | Kieffer, 1924 | 100 |
| C. mancus | Cladotanytarsus mancus | (Walker, 1856) | 32 |
| R. rhenanus | Rheotanytarsus rhenanus | Klink, 1983 | 74 |
| P. austriacus | Paratanytarsus austriacus | (Kieffer, 1924) | 26 |
| P. dissimilis | Paratanytarsus dissimilis | (Johannsen, 1905) | 88 |
| P. lauterborni | Paratanytarsus lauterborni | (Kieffer, 1909) | 62 |
| P. mediterraneus | Paratanytarsus mediterraneus | Reiss & Säwedal, 1981 | 60 |
| M. atrofasciata | Micropsectra atrofasciata | (Kieffer, 1911) | 395 |
| M. apposita | Micropsectra apposita | (Walker, 1856) | 15 |
| M. notescens | Micropsectra notescens | (Walker, 1856) | 45 |
| P. prasinatus | Pseudochironomus prasinatus | (Stäger, 1839) | 62 |
| P. albimanus | Paratendipes albimanus | (Meigen, 1818) | 143 |
| M. pedellus | Microtendipes pedellus | (De Geer, 1776) | 205 |
| P. orophila | Pagastiella orophila | (Edwards, 1929) | 35 |
| P. flavipes | Phaenopsectra flavipes | (Meigen, 1818) | 134 |
| P. P. sordens | Polypedilum (Pentapedilum) sordens | (van der Wulp, 1874) | 81 |
| P. P. laetum | Polypedilum (Polypedilum) laetum | (Meigen, 1818) | 171 |
| P. P. nubeculosum | Polypedilum (Polypedilum) nubeculosum | (Meigen, 1804) | 320 |
| P. T. scalaenum | Polypedilum (Tripodura) scalaenum | (Schrank, 1803) | 34 |
| P. U. convictum | Polypedilum (Uresipedilum) convictum | (Walker, 1856) | 65 |
| P. U. cultellatum | Polypedilum (Uresipedilum) cultellatum | Goetghebuer, 1931 | 70 |
| E. tendens | Endochironomus tendens | (Fabricius, 1775) | 89 |
| C. C. anthracinus | Chironomus (Chironomus) anthracinus | Zetterstedt, 1860 | 101 |
| C. C. riparius | Chironomus (Chironomus) riparius | Meigen, 1804 | 237 |
| C. C. plumosus | Chironomus (Chironomus) plumosus | (Linnaeus, 1758) | 196 |
| D. nervosus | Dicrotendipes nervosus | (Stäger, 1839) | 182 |
| G. G. pallens | Glyptotendipes (Glyptotendipes) pallens | (Meigen, 1804) | 106 |
| C. viridulum | Cladopelma viridulum | (Linnaeus, 1767) | 115 |
| M. tener | Microchironomus tener | (Kieffer, 1918) | 35 |
| P. gracilior | Parachironomus gracilior | (Kieffer, 1918) | 109 |
| P. camptolabis | Paracladopelma camptolabis | (Kieffer, 1913) | 57 |
| P. nigritulum | Paracladopelma nigritulum | (Goetghebuer, 1942) | 17 |
| H. fuscimanus | Harnischia fuscimanus | (Kieffer, 1921) | 58 |
| C. defectus | Cryptochironomus defectus | (Kieffer, 1913) | 156 |
| D. vulneratus | Demicryptochironomus vulneratus | (Zetterstedt, 1838) | 52 |
| (a) pCCA | ||
| Partitioning of scaled chi-square | Inertia | Proportion |
| Total | 7.5026 | 1.0000 |
| Conditioned | 0.3442 | 0.0459 |
| Constrained | 0.8090 | 0.1078 |
| Unconstrained | 6.3494 | 0.8463 |
| (b) pCCAi | ||
| Partitioning of scaled chi-square | Inertia | Proportion |
| Total | 7.5026 | 1.0000 |
| Conditioned | 0.8742 | 0.1165 |
| Constrained | 0.2790 | 0.0372 |
| Unconstrained | 6.3494 | 0.8463 |
| (a) pCCA | |||||||
| CCA1 | CCA2 | CCA3 | CCA4 | CCA5 | CCA6 | CCA7 | |
| Eigenvalue | 0.39553 | 0.18411 | 0.07284 | 0.05362 | 0.04247 | 0.02286 | 0.02073 |
| Proportion explained | 0.05525 | 0.02572 | 0.01018 | 0.00749 | 0.00593 | 0.00319 | 0.00290 |
| Cumulative proportion | 0.05525 | 0.08097 | 0.09115 | 0.09864 | 0.10457 | 0.10777 | 0.11066 |
| (b) pCCAi | |||||||
| CCA1 | CCA2 | CCA3 | CCA4 | CCA5 | CCA6 | CCA7 | |
| Eigenvalue | 0.07832 | 0.06361 | 0.05698 | 0.03346 | 0.02045 | 0.01039 | 0.00783 |
| Proportion explained | 0.01182 | 0.00960 | 0.00860 | 0.00505 | 0.00309 | 0.00157 | 0.00118 |
| Cumulative proportion | 0.01182 | 0.02141 | 0.03001 | 0.03506 | 0.03814 | 0.03971 | 0.04089 |
| Habitat | AL03 | AL04 | AL05 | AL06 | Alalp | Crenal | Kryal | ME04 | ME07 | Potamal | Rhithral | Original |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AL03 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 68 |
| AL04 | 0 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 8 |
| AL05 | 3 | 1 | 38 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 53 |
| AL06 | 8 | 1 | 4 | 38 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 53 |
| AlAlps | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 18 |
| Crenal | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 10 | 45 |
| Kryal | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 70 |
| ME04 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 22 |
| ME07 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 15 |
| Potamal | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 148 | 26 | 177 |
| Rhithral | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 244 | 259 |
| Predicted | 71 | 8 | 44 | 41 | 19 | 36 | 61 | 25 | 15 | 160 | 308 |
| Order | Variables | R2 | R2Cum | AdjR2Cum | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MEM1 | 0.0271 | 0.0271 | 0.0234 | 0.01 |
| 2 | MEM5 | 0.0255 | 0.0526 | 0.0453 | 0.01 |
| 3 | MEM23 | 0.0190 | 0.0716 | 0.0609 | 0.01 |
| 4 | MEM16 | 0.0183 | 0.0899 | 0.0758 | 0.01 |
| 5 | MEM19 | 0.0172 | 0.1071 | 0.0898 | 0.01 |
| 6 | MEM3 | 0.0164 | 0.1235 | 0.1031 | 0.01 |
| 7 | MEM4 | 0.0159 | 0.1395 | 0.1160 | 0.01 |
| 8 | MEM2 | 0.0157 | 0.1552 | 0.1287 | 0.01 |
| 9 | MEM13 | 0.0128 | 0.1679 | 0.1385 | 0.01 |
| 10 | MEM29 | 0.0113 | 0.1792 | 0.1468 | 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rossaro, B.; Marziali, L. Response of Chironomids (Diptera, Chironomidae) to Environmental Factors at Different Spatial Scales. Insects 2024, 15, 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15040272
Rossaro B, Marziali L. Response of Chironomids (Diptera, Chironomidae) to Environmental Factors at Different Spatial Scales. Insects. 2024; 15(4):272. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15040272
Chicago/Turabian StyleRossaro, Bruno, and Laura Marziali. 2024. "Response of Chironomids (Diptera, Chironomidae) to Environmental Factors at Different Spatial Scales" Insects 15, no. 4: 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15040272
APA StyleRossaro, B., & Marziali, L. (2024). Response of Chironomids (Diptera, Chironomidae) to Environmental Factors at Different Spatial Scales. Insects, 15(4), 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15040272








