Effects of Diet on the Gut Bacterial Community of Aldrichina grahami (Diptera: Calliphoridae) across Developmental Stages
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fly Stock and Rearing
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. DNA Extraction and Sequencing Library Construction
2.4. High-Throughput Sequencing Data Analysis
2.5. Alpha Diversity and Beta Diversity
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing Data
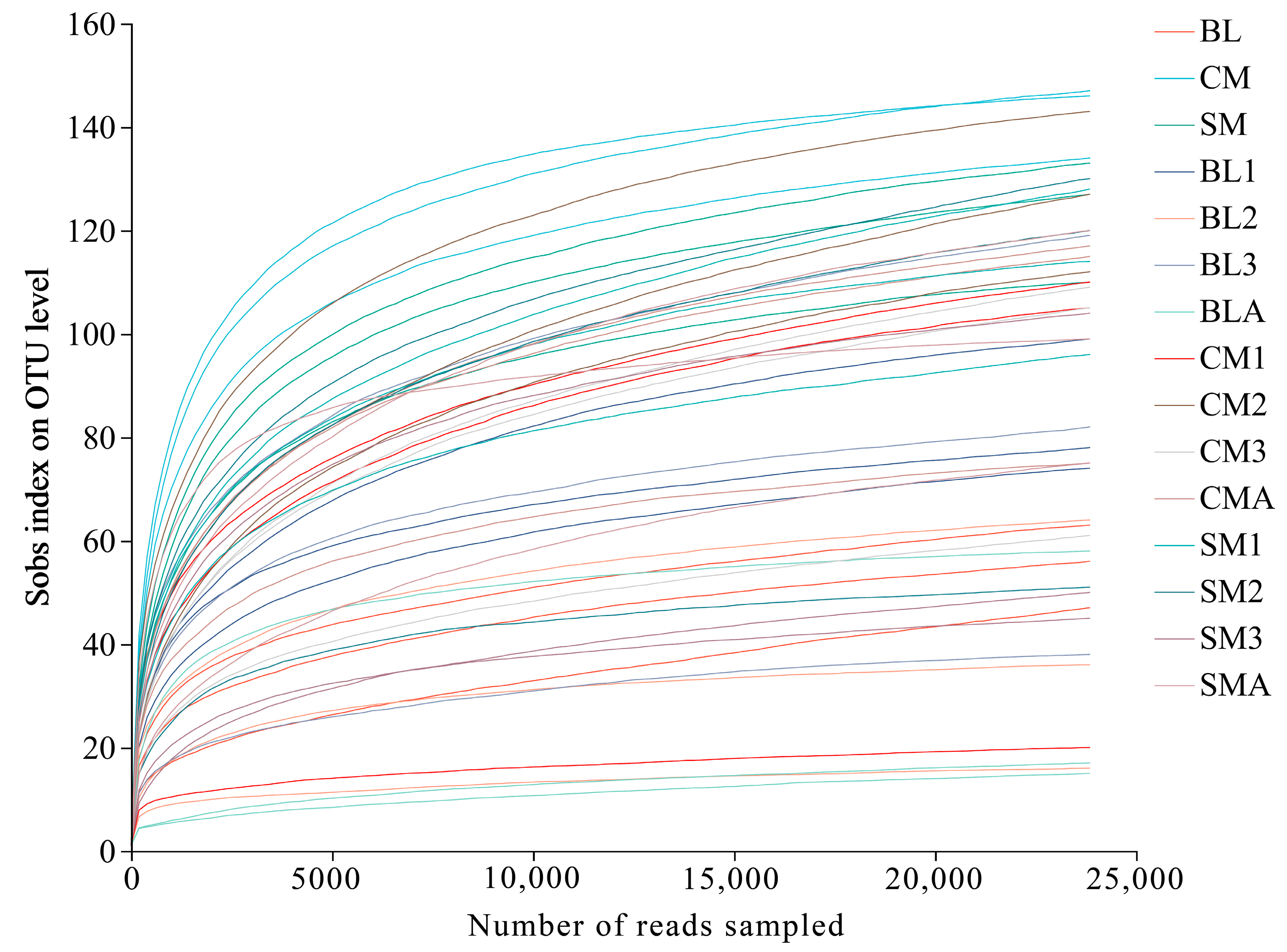
3.2. Species Richness and Diversity
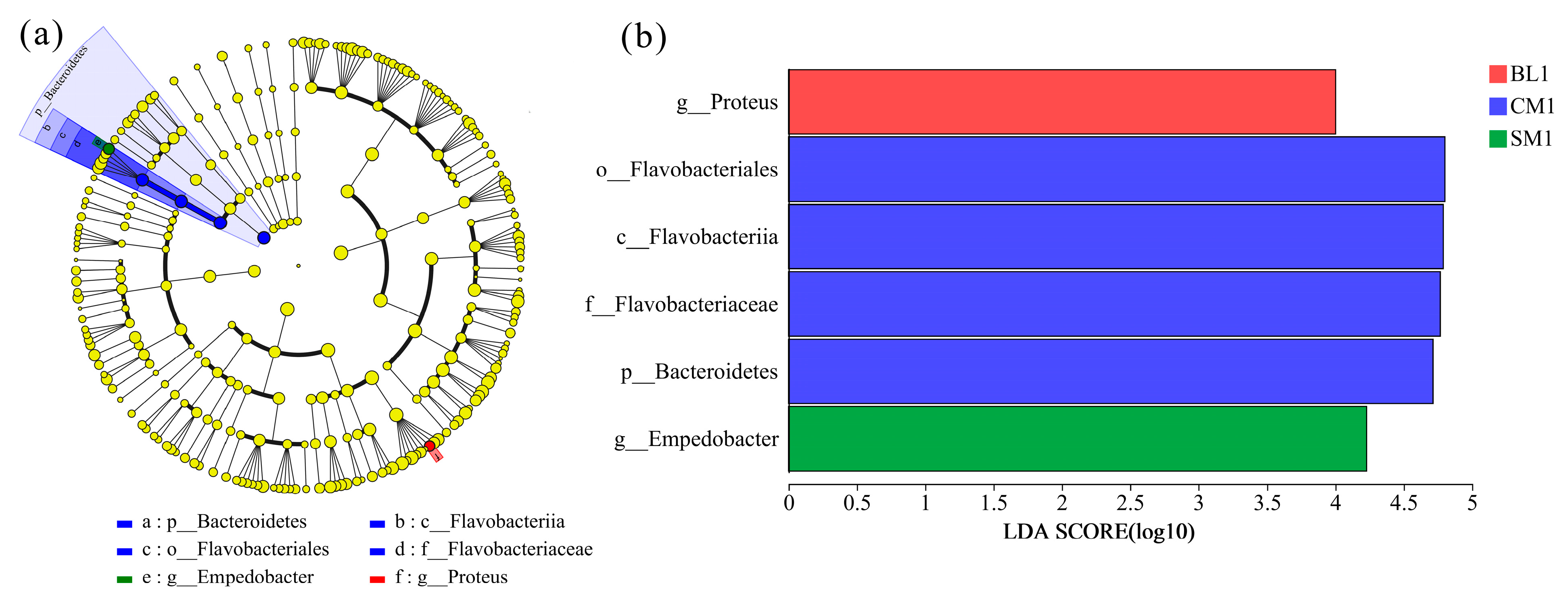
3.3. Comparison of Bacteral Communities

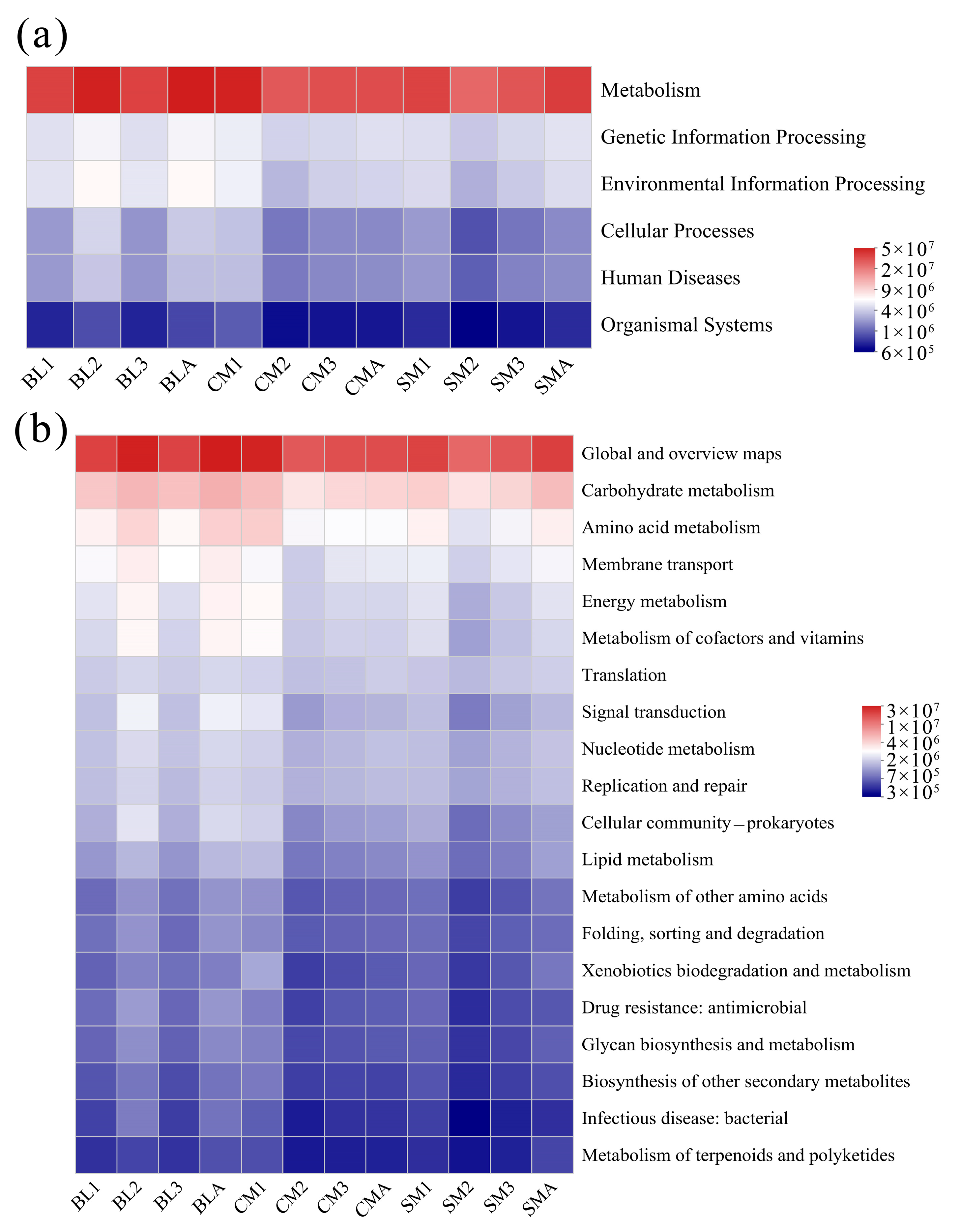
3.4. Functional Predictions of the Gut Microbiome of A. grahami
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vences, M.; Lyra, M.L.; Kueneman, J.G.; Bletz, M.C.; Archer, H.M.; Canitz, J.; Handreck, S.; Randrianiaina, R.D.; Struck, U.; Bhuju, S.; et al. Gut bacterial communities across tadpole ecomorphs in two diverse tropical anuran faunas. Sci. Nat. 2016, 103, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.N.; Liu, C.; Hu, G.L.; Wang, M.; Yang, L.J.; Chu, J.; Wang, J.F. Development of Aldrichina grahami (Diptera: Calliphoridae) at constant temperatures. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 1402–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Yang, L.; Ren, L.; Shang, Y.; Wang, S.; Guo, Y. Impact of constant versus fluctuating temperatures on the development and life history parameters of Aldrichina grahami (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Insects 2019, 10, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.F.; Hu, C.; Chen, Y.C.; Min, J.X.; Li, J.T. Application of the pupal morphogenesis of Aldrichina grahami (Aldrich) to the deduction of postmortem interval. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2002, 45, 696–699. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Chen, W.; Ren, L.; Ling, J.; Shang, Y.; Guo, Y. Effects of methamphetamine on the development and its determination in Aldrichina grahami (Diptera: Calliphoridae). J. Med. Entomol. 2020, 57, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceja-Navarro, J.A.; Vega, F.E.; Karaoz, U.; Hao, Z.; Jenkins, S.; Lim, H.C.; Kosina, P.; Infante, F.; Northen, T.R.; Brodie, E.L. Gut microbiota mediate caffeine detoxification in the primary insect pest of coffee. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thong-On, A.; Suzuki, K.; Noda, S.; Inoue, J.; Kajiwara, S.; Ohkuma, M. Isolation and characterization of anaerobic bacteria for symbiotic recycling of uric acid nitrogen in the gut of various termites. Microb. Environ. 2012, 27, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalappa, D.M.; Subramani, P.A.; Basavanna, S.K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Sundaramurthy, V.; Uragayala, S.; Tiwari, S.; Anvikar, A.R.; Valecha, N. Influence of midgut microbiota in Anopheles stephensi on Plasmodium berghei infections. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásquez, A.; Forsgren, E.; Fries, I.; Paxton, R.J.; Flaberg, E.; Szekely, L.; Olofsson, T.C. Symbionts as major modulators of insect health: Lactic acid bacteria and honeybees. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Liu, J.; Bai, P.; Ma, B.; Liu, W. Pathogenic Fungi-induced susceptibility is mitigated by mutual Lactobacillus plantarum in the Drosophila melanogaster model. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharon, G.; Segal, D.; Ringo, J.M.; Hefetz, A.; Zilber-Rosenberg, I.; Rosenberg, E. Commensal bacteria play a role in mating preference of Drosophila Melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20051–20056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Mota, M.; Vieira, P.; Butcher, R.A.; Sun, J. Interspecific communication between pinewood nematode, its insect vector, and associated microbes. Trends Parasitol. 2014, 30, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Yao, Z.; Li, Y.; Xi, Z.; Bourtzis, K.; Zhao, Z.; Bai, S.; Zhang, H. Intestinal probiotics restore the ecological fitness decline of bactrocera dorsalis by irradiation. Evol. Appl. 2018, 11, 1946–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, B.L.; Wang, J.; Aksoy, S. Tsetse immune system maturation requires the presence of obligate symbionts in larvae. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1000619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymann, K.; Moran, N.A. The role of the gut microbiome in health and disease of adult honey bee workers. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2018, 26, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinker, K.A.; Ottesen, E.A. The core gut microbiome of the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana, is stable and resilient to dietary shifts. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 6603–6610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, T.J.; Janzen, D.H.; Hallwachs, W.; Jaffe, S.P.; Fierer, N. Caterpillars lack a resident gut microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 9641–9646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, J.H.; Roh, S.W.; Whon, T.W.; Jung, M.J.; Kim, M.S.; Park, D.S.; Yoon, C.; Nam, Y.D.; Kim, Y.J.; Choi, J.H.; et al. Insect gut bacterial diversity determined by environmental habitat, diet, developmental stage, and phylogeny of host. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5254–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.N.A.; Ng, P.; Douglas, A.E. Low-diversity bacterial community in the gut of the fruitfly Drosophila melanogaster. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiede, J.; Scherber, C.; Mutschler, J.; McMahon, K.D.; Gratton, C. Gut microbiomes of mobile predators vary with landscape context and species identity. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 8545–8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, J.G.; Łukasik, P.; Frederickson, M.E.; Russell, J.A.; Koga, R.; Knight, R.; Pierce, N.E. Dramatic differences in gut bacterial densities correlate with diet and habitat in rainforest ants. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2017, 57, 705–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagna, M.; Chouaia, B.; Mazza, G.; Prosdocimi, E.M.; Crotti, E.; Mereghetti, V.; Vacchini, V.; Giorgi, A.; De Biase, A.; Longo, S.; et al. Effects of the diet on the microbiota of the red palm weevil (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Huang, Z.; Wan, Q.; Zhang, Z. Comparative analysis of gut bacterial communities in housefly larvae fed different diets using a high-throughput sequencing approach. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnz126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Teh, B.S.; Sun, C.; Hu, S.; Lu, X.; Boland, W.; Shao, Y. Biodiversity and activity of the gut microbiota across the life history of the insect herbivore Spodoptera littoralis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinton, H.E. The origin and function of the pupal stage. Proc. R. Entomol. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Gen. Entomol. 1963, 38, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, T.J.; Moran, N.A. Links between metamorphosis and symbiosis in holometabolous insects. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B. 2019, 374, 20190068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolff, J.; Johnston, P.R.; Reynolds, S. Complete metamorphosis of insects. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B. 2019, 374, 20190063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truman, J.W. The Evolution of insect metamorphosis. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, R1252–R1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, P.; Moran, N.A. The gut microbiota of insects-diversity in structure and function. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 699–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Li, W.; Luo, J.; Zhang, L.; Ji, J.; Zhu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Cui, J. Biodiversity of the microbiota in Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Pan, Q.; Tian, H.; Douglas, A.E.; Liu, T. Bacteria abundance and diversity of different life stages of Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae), revealed by bacteria culture-dependent and PCR-DGGE methods. Insect Sci. 2015, 22, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate otu sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junqueira, A.C.M.; Ratan, A.; Acerbi, E.; Drautz-Moses, D.I.; Premkrishnan, B.N.V.; Costea, P.I.; Linz, B.; Purbojati, R.W.; Paulo, D.F.; Gaultier, N.E.; et al. The microbiomes of blowflies and houseflies as bacterial transmission reservoirs. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Crippen, T.L.; Zheng, L.; Fields, A.T.; Yu, Z.; Ma, Q.; Wood, T.K.; Dowd, S.E.; Flores, M.; Tomberlin, J.K.; et al. A metagenomic assessment of the bacteria associated with Lucilia sericata and Lucilia cuprina (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 869–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomberlin, J.K.; Crippen, T.L.; Tarone, A.M.; Chaudhury, M.F.B.; Singh, B.; Cammack, J.A.; Meisel, R.P. A review of bacterial interactions with blow flies (Diptera: Calliphoridae) of medical, veterinary, and forensic importance. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2017, 110, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguenon, J.M.; Travanty, N.; Zhu, J.; Carr, A.; Denning, S.; Reiskind, M.H.; Watson, D.W.; Michael Roe, R.; Ponnusamy, L. Exogenous and endogenous microbiomes of wild-caught Phormia regina (Diptera: Calliphoridae) flies from a suburban farm by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klammsteiner, T.; Walter, A.; Bogataj, T.; Heussler, C.D.; Stres, B.; Steiner, F.M.; Schlick-Steiner, B.C.; Arthofer, W.; Insam, H. The core gut microbiome of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae raised on low-bioburden diets. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jonge, N.; Michaelsen, T.Y.; Ejbye-Ernst, R.; Jensen, A.; Nielsen, M.E.; Bahrndorff, S.; Nielsen, J.L. Housefly (Musca domestica L.) associated microbiota across different life stages. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, N.A.; Raffa, K.F.; Goodman, R.M.; Handelsman, J. Census of the bacterial community of the gypsy moth larval midgut by using culturing and culture-independent methods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayatri Priya, N.; Ojha, A.; Kajla, M.K.; Raj, A.; Rajagopal, R. Host plant induced variation in gut bacteria of Helicoverpa armigera. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erkosar, B.; Yashiro, E.; Zajitschek, F.; Friberg, U.; Maklakov, A.A.; Van Der Meer, J.R.; Kawecki, T.J. Host diet mediates a negative relationship between abundance and diversity of Drosophila gut microbiota. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 9491–9502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, A.; Lu, M.; Xu, L. Variation of gut microbiota caused by an imbalance diet is detrimental to bugs’ survival. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 144880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, Z.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Xu, H. Comparison of gut bacterial communities and their associations with host diets in four fruit borers. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Sun, S.; Yang, X.; Cheng, J.; Wei, H.; Li, Z.; Michaud, J.P.; Liu, X. Variability of gut microbiota across the life cycle of Grapholita molesta (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, J.S.; Naaz, N.; Prabhakar, C.S.; Das, B.; Singh, A.K.; Bhatt, B.P. High taxonomic and functional diversity of bacterial communities associated with melon fly, Zeugodacus cucurbitae (Diptera: Tephritidae). Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Zhu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, K.; Li, D.; Ji, J.; Niu, L.; Wu, C.; Gao, X.; Luo, J.; et al. Gut bacterial diversity in different life cycle stages of Adelphocoris suturalis (Hemiptera: Miridae). Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 670383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Luo, J.; Han, R.; Xu, L. Composition and diversity of gut bacterial community in different life stages of a leaf beetle Gastrolina depressa. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 86, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Jin, W.; Tao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Feng, S.; Xu, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z. Black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) strengthen the metabolic function of food waste biodegradation by gut microbiome. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 528–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Yue, C.; Ma, N.; Yan, G. Effects of Diet on the Gut Bacterial Community of Aldrichina grahami (Diptera: Calliphoridae) across Developmental Stages. Insects 2024, 15, 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15030181
Li Z, Yue C, Ma N, Yan G. Effects of Diet on the Gut Bacterial Community of Aldrichina grahami (Diptera: Calliphoridae) across Developmental Stages. Insects. 2024; 15(3):181. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15030181
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhen, Chao Yue, Na Ma, and Guanjie Yan. 2024. "Effects of Diet on the Gut Bacterial Community of Aldrichina grahami (Diptera: Calliphoridae) across Developmental Stages" Insects 15, no. 3: 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15030181
APA StyleLi, Z., Yue, C., Ma, N., & Yan, G. (2024). Effects of Diet on the Gut Bacterial Community of Aldrichina grahami (Diptera: Calliphoridae) across Developmental Stages. Insects, 15(3), 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15030181





