Effect of Guanylate Cyclase-22-like on Ovarian Development of Orius nagaii (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Total RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.4. OnGCY Gene Cloning
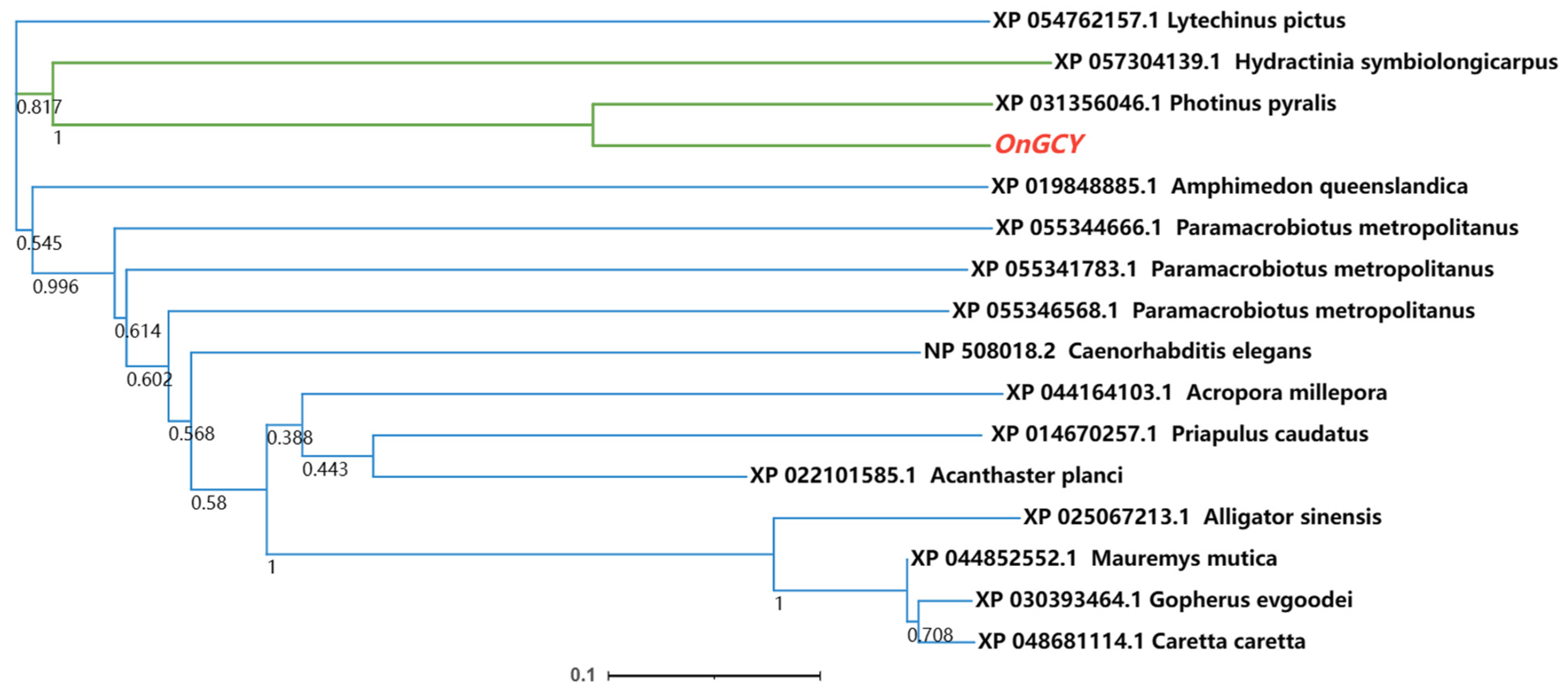
2.5. OnGCY Genetic Analysis
2.6. OnGCY Expression in Different Developmental Stages and Tissues
2.7. Double-Stranded RNA Synthesis
2.8. RNAi
2.9. Bioassay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sequence Identification and Characteristics of OnGCY
3.2. Prediction of OnGCY Protein Domains
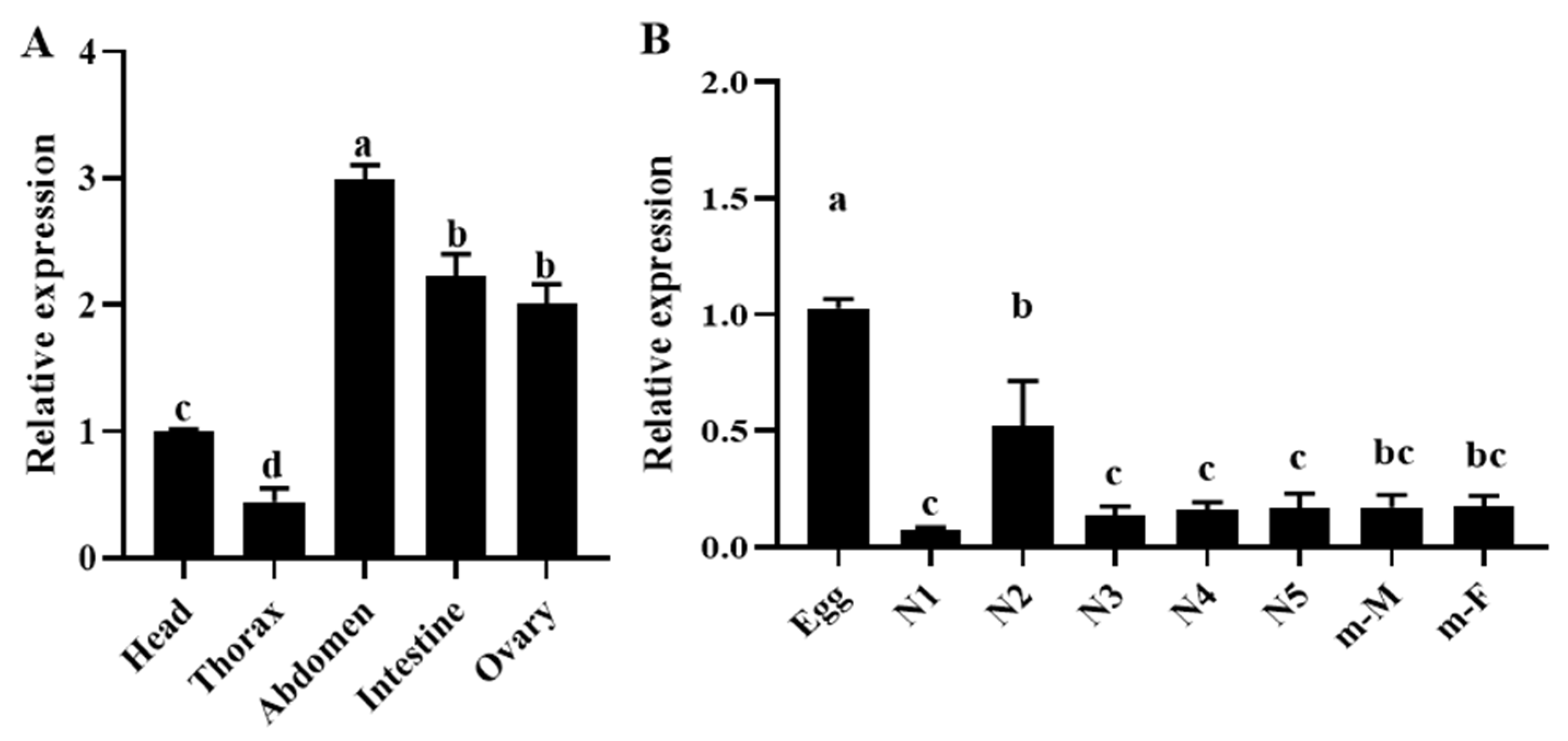
3.3. OnGCY Expression in Different Developmental Stages and Tissues
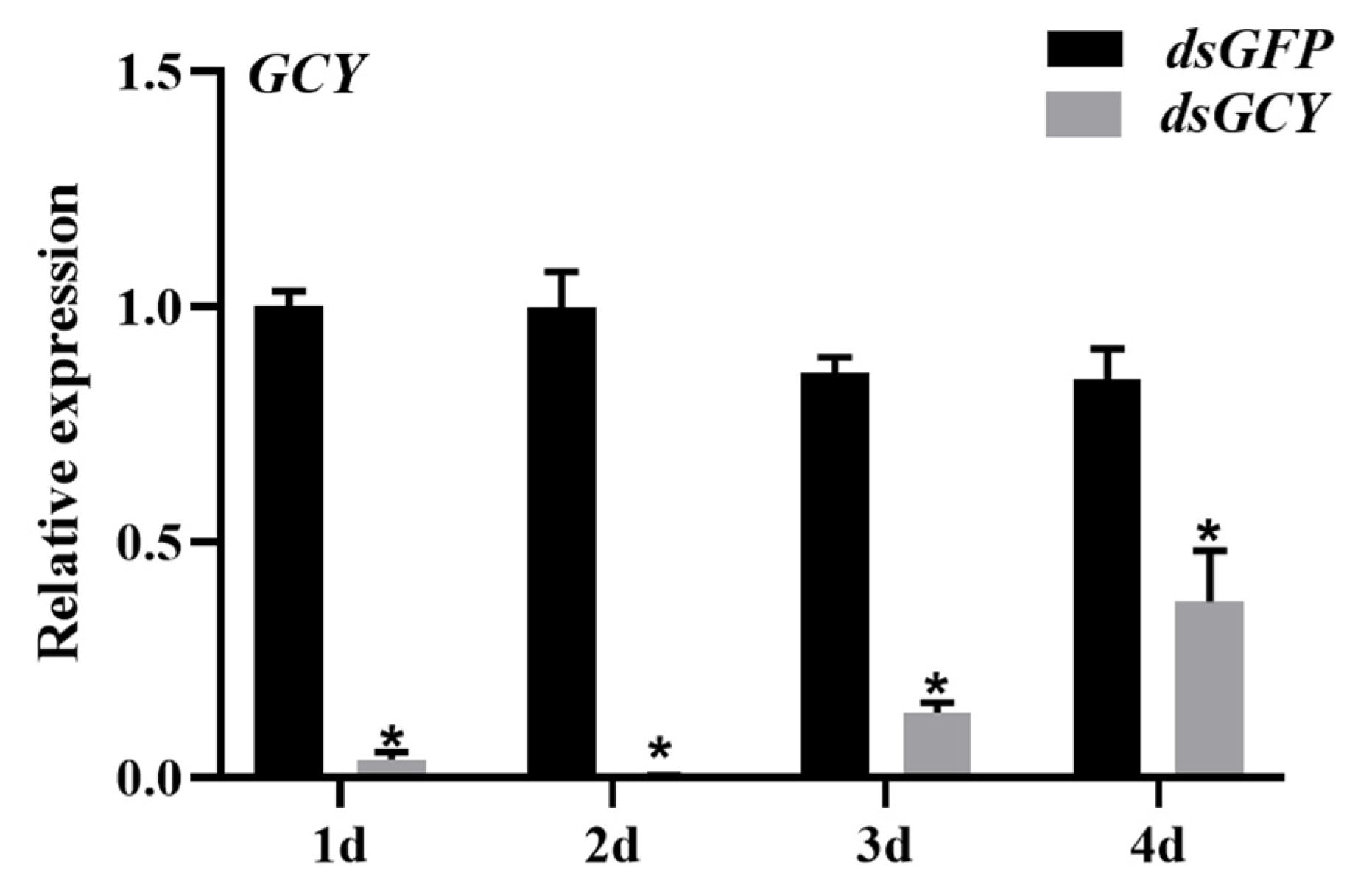
3.4. Effects of RNAi Silencing on OnGCY Gene Expression in Adult Female O. nagaii
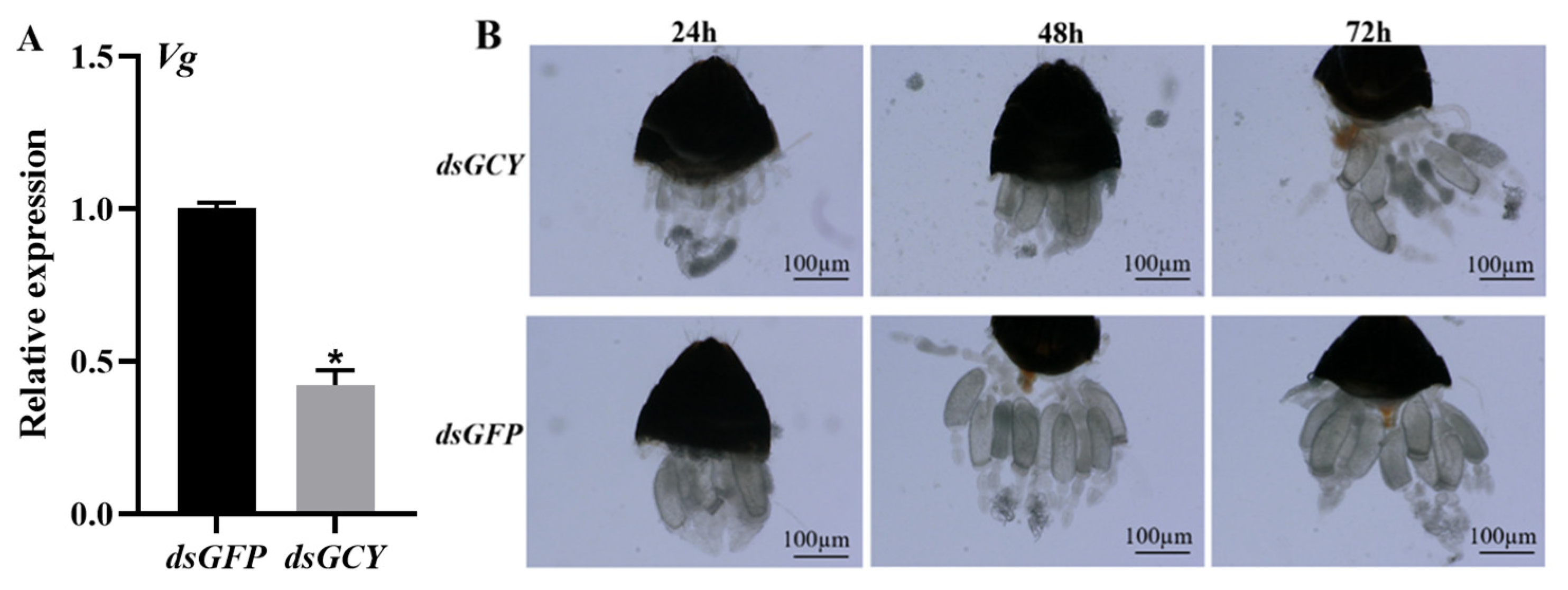
3.5. Effect of Silencing of OnGCY on Reproduction of O. nagaii Females
3.6. Effect of Silencing of OnGCY on Ovarian Development of O. nagaii Female Adults
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maeda, T.; Fujiwara-Tsujii, N.; Yasui, H.; Matsuyama, S. Female Sex Pheromone in Trails of the Minute Pirate Bug, Orius minutus (L). J. Chem. Ecol. 2016, 42, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, T.; Maeda, T.; Shimoda, M.; Fujiwara-Tsujii, N.; Yasui, H. Identification and Characterization of the Pheromones in the Minute Pirate Bug Orius sauteri (Heteroptera: Anthocoridae). J. Chem. Ecol. 2019, 45, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Camara, I.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, L.; Xing, Y.; Li, A.; Shi, W. Predation of Aphis craccivora (Hemiptera: Aphididae) by Orius sauteri (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) under different temperatures. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 2599–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.P.; Souza, I.L.; Marucci, R.C.; Guzman-Martine, M. Doru luteipes (Dermaptera: Forficulidae) and Orius insidiosus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) as Nocturnal and Diurnal Predators of Thrips. Neotrop. Entomol. 2023, 52, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, P.; Ma, C.; Yasir Ali, M.; Gao, G.; Lu, Z.; Zalucki, M.P. Is Orius sauteri Poppius a promising biological control agent for Walnut aphids? An assessment from the laboratory to field. Insects 2021, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Guo, X.; Tan, X.; Desneux, N.; Zappala, L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S. Using Calendula officinalis as a floral resource to enhance aphid and thrips suppression by the flower bug Orius sauteri (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). Pest. Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qin, Z.; Liu, P.; Yin, Y.; Felton, G.W.; Shi, W. Influence of Plant Physical and Anatomical Characteristics on the Ovipositional Preference of Orius sauteri (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). Insects 2021, 12, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Sarker, S.; Ham, E.; Lee, J.S.; Lim, U.T. Development and Fecundity of Orius minutus (Hemiptera: An-thocoridae) and O. laevigatus Reared on Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 1735–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, S.; Chinkers, M.; Garbers, D.L. The guanylate cyclase/receptor family of proteins. FASEB J. 1989, 3, 2026–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, S.; Singh, S.; Bellet, R.A.; Singh, G.; Tubb, D.J.; Chin, H.; Garbers, D.L. The primary structure of a plasma membrane guanylate cyclase demonstrate diversity within this new receptor family. Cell 1989, 58, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.S.; Lowe, D.G.; Lewis, M.; Hellmiss, R.; Chen, E.; Goeddel, D.V. Differential activation of atrial and brain natriuretic peptides of two receptor guanylate cyclases. Nature 1989, 341, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, S.; Green, C.K.; Yuen, P.S.; Garbers, D.L. Guanylyl cyclase is a heat-stable enterotoxin receptor. Cell 1990, 63, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sauvage, F.J.; Camerato, T.R.; Goeddel, D.V. Primary structure and functional expression of the human receptor for Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 17912–17918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Singh, G.; Meim, J.M.; Gerzer, R. Isolation and expression of a guanylate cyclase-coupled heat stable enterotoxin receptor cDNA from a human colonic cell line. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 179, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinkers, M.; Garbers, D.L.; Chang, M.-S.; Lowe, D.G.; Chin, H.; Goeddel, D.V.; Schulz, S. A membrane form of guanylate cyclase is an atrial natriuretic peptide receptor. Nature 1989, 338, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bold, A.J. Atrial natruiuretic factor: A hormone produced by the heart. Science 1985, 230, 767–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, K.J.; Lowe, D.G.; Bennet, G.L.; Minamino, N.; Kangawa, K.; Matsuo, H.; Goeddel, D.V. Selective activation of the B natriuretic peptide receptor by C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP). Science 1991, 252, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Lowe, D.G.; Thorp, D.S.; Rodriguez, H.; Kuang, W.J.; Dangott, L.J.; Chinkers, M.; Goeddel, D.V.; Garbers, D.L. Membrane guanylate cyclase is a cell surface receptor with homology to protein kinases. Nature 1988, 334, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Sha, W. Signaling pathways of enzyme-linked receptors. Biol. Teach. 2008, 33, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Mok, C.A.; Healey, M.P.; Shekhar, T.; Leroux, M.R.; Héon, E.; Zhen, M. Mutations in a guanylate cyclase GCY-35/GCY-36 modify Bardet-Biedl syndrome-associated phenotypes in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abergel, R.; Livshits, L.; Shaked, M.; Shaked, M.; Chatterjee, A.K.; Gross, E. Synergism between soluble guanylate cyclase signaling and neuropeptides extends lifespan in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Aging Cell 2017, 16, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallem, E.A.; Spencer, W.C.; McWhirter, R.D.; Zeller, G.; Hemz, S.R.; Rätsch, G.; Miller, D.M.; Horvitz, H.R. Receptor-type guanylate cyclase is required for carbon dioxide sensation by Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; van der Kooy, D. Mutations in the guanylate cyclase gcy-28 neuronally dissociate naïve attraction and memory retrieval. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 48, 3367–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Burght, S.N.; Rademakers, S.; Johnson, J.L.; Li, C.; Kremers, G.J.; Houtsmuller, A.B.; Leroux, M.R.; Jansen, G. Ciliary Tip Signaling Compartment Is Formed and Maintained by Intraflagellar Transport. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 4299–4306.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆CT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollas, M.A.; Ben Aissa, M.; Lee, S.H.; Gordon-Blake, J.M.; Thatcher, G.R.J. Pharmacological manipulation of cGMP and NO/cGMP in CNS drug discovery. Nitric Oxide 2019, 82, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friebe, A.; Sandner, P.; Schmidtko, A. cGMP: A unique 2nd messenger molecule-recent developments in cGMP research and development. N-S Arch. Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgunder, J.M.; Cheung, P.T. Expression of soluble guanylyl cyclase gene in adult rat brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1994, 6, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanjal, J.K.; Malik, V.; Radhakrishnan, N.; Sigar, M.; Kumari, A.; Sundar, D. Computational protein engineering approaches for effective design of new molecules. In Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology; Shoba, R., Michael, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 3, pp. 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, E.A.; Darlison, M.G.; Seeburg, P. Molecular biology of the GABAA receptor: The receptor/channel superfamily. Trends Neurosci. 1987, 10, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Gai, S.Y.; Zhang, W.H.; Huang, X.T.; Ma, S.M.; Huo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tu, H.; Pin, J.-P.; Rondard, P.; et al. The GABA receptor mediates neuroprotection by coupling to G13. Sci. Signal 2021, 14, eaaz4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H. Proteolytic Cleavage of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, F. The cGMP system: Components and function. Biol. Chem. 2020, 401, 447–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chiu, Y.L.; Chen, C.-J.; Ho, Y.-Y.; Shinzato, C.; Shikina, S.; Chang, C.-F. Discovery of a receptor guanylate cyclase expressed in the sperm flagella of stony corals. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Junior, N.C.; Crestani, C.C.; Lagatta, D.C.; Resstel, L.B.M.; Correa, F.M.A.; Alves, F.H.F. Nitric oxide in the insular cortex modulates baroreflex responses in a cGMP-independent pathway. Brain Res. 2020, 1747, 147037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montfort, W.R. Per-ARNT-Sim Domains in Nitric Oxide Signaling by Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase. J. Mol. Biol. 2023, 168235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantley, L.C. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 2002, 296, 1655–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Tian, P.; Tang, Y.; Yang, L.; Qiu, L.; He, H.; Ding, W.; Li, Z.; Li, Y. Molecular Characterization of Vitellogenin and Its Receptor in Sogatella furcifera, and Their Function in Oocyte Maturation. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amdam, G.V.; Simões, Z.L.; Hagen, A.; Norberg, K.; Schrøder, K.; Mikkelsen, Ø.; Kirkwood, T.B.; Omholt, S.W. Hormonal control of the yolk precursor vitellogenin regulates immune function and longevity in honeybees. Exp. Gerontol. 2004, 39, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amdam, G.V.; Norberg, K.; Hagen, A.; Omholt, S.W. Social exploitation of vitellogenin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1799–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Shu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, M.; Yao, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, W. Molecular characterization and RNA interference analysis of vitellogenin receptor from Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). J. Insect Physiol. 2015, 73, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, S.K.; Singh, H.; Dixit, S.; Mendu, V.; Verma, P.C. Molecular Characterization of Vitellogenin and Vitellogenin Receptor of Bemisia tabaci. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.W.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Xia, S.; Zhang, H. Biofunctional analysis of Vitellogenin and Vitellogenin receptor in citrus red mites, Panonychus citri by RNA interference. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, M.; Hosokawa, T.; Tanahashi, M.; Nikoh, N.; Fukatsu, T. Suppression of Bedbug’s Reproduction by RNA Interference of Vitellogenin. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleede, J.; Blair, S.S. The Gyc76C Receptor Guanylyl Cyclase and the Foraging cGMP-Dependent Kinase Regulate Extracellular Matrix Organization and BMP Signaling in the Developing Wing of Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, U.; Davies, S.A.; Myat, M.M. Receptor-type guanylyl cyclase Gyc76C is required for development of the Drosophila embryonic somatic muscle. Biol. Open 2012, 1, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tonoki, A.; Nagai, S.; Yu, Z.; Yue, T.; Lyu, S.; Hou, X.; Onuki, K.; Yabana, K.; Takahashi, H.; Itoh, M. Nitric oxide-soluble guanylyl cyclase pathway as a contributor to age-related memory impairment in Drosophila. Aging Cell 2022, 21, e13691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowański, S.; Walkowiak-Nowicka, K.; Winkiel, M.; Marciniak, P.; Urbański, A.; Pacholska-Bogalska, J. Insulin-like peptides and cross-talk with other factors in the regulation of insect metabolism. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 701203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.; Cat, A.; Montezano, A.; Salt, I.; Touyz, R. Activators of amp-activated protein kinase regulate adipocyte aldosterone secretion and mineralocorticoid receptor signalling. Endocr. Abstr. 2015, 37, OC5.3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, T.; Mendes, C.C.; Mirth, C.K. Mechanisms regulating nutrition-dependent developmental plasticity through organ-specific effects in insects. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smykal, V.; Raikhel, A.S. Nutritional control of insect reproduction. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 11, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Experiment | Primer | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| RACE | On-GCY-F | ATGGGGCCAGAACTGAGGTA |
| On-GCY-R | TTAAAGGATAGAGTCGATGTTAAC | |
| GCY-3′RACE-f1 | AAGCATCGGAGTTGGTGGAA | |
| GCY-3′RACE-f2-1 | TCCGTTCAGATGGACGACAC | |
| GCY-3′RACE-f2-2 | GCTTCGCCAAAGAACACCGT | |
| GCY-5′RACE-rt-r | ATGAACCATCCGAATCTCCC | |
| GCY-5′RACE-r1 | CGACTTCATCCCTTTCTTGG | |
| GCY-5′RACE-r2-1 | TCCTGTCCGTCACTCCCAAT | |
| GCY-5′RACE-r2-2 | CTTTTTGGGTTGACCTCTGG | |
| dsRNA synthesis | T7-GCY-F | TAATACGACTCATATAGGGGCGCTTAGCTATCTGGCTGA |
| T7-GCY-R | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGGACGATGGAACTGACGGTGT | |
| T7-GFP-F | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCACAAGTTCAGCGTGTCCG | |
| T7-GFP-R | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGGTTCACCTTGATGCCGTTC | |
| GCY-F | GCGCTTAGCTATCTGGCTGA | |
| GCY-R | GACGATGGAACTGACGGTGT | |
| GFP-F | CACAAGTTCAGCGTGTCCG | |
| GFP-R | GTTCACCTTGATGCCGTTC | |
| qPCR | GCY-F | GGTCGCCGTTGCTGTTAAAA |
| GCY-R | TGCAGACTCCAAGAAGCTGG | |
| Vg-F | AGCCTGTTGACTGTCGGAAG | |
| Vg-R | CGAAGGTCCAACCACTCGAT | |
| actin-F | CAGAAGGACTCGTACGTCGG | |
| actin-R | CATGTCGTCCCAGTTGGTGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, H.; Wang, R.; Dai, X.; Yin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Su, L.; Chen, H.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, L.; Dong, X.; et al. Effect of Guanylate Cyclase-22-like on Ovarian Development of Orius nagaii (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). Insects 2024, 15, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15020110
Du H, Wang R, Dai X, Yin Z, Liu Y, Su L, Chen H, Zhao S, Zheng L, Dong X, et al. Effect of Guanylate Cyclase-22-like on Ovarian Development of Orius nagaii (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). Insects. 2024; 15(2):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15020110
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Huiling, Ruijuan Wang, Xiaoyan Dai, Zhenjuan Yin, Yan Liu, Long Su, Hao Chen, Shan Zhao, Li Zheng, Xiaolin Dong, and et al. 2024. "Effect of Guanylate Cyclase-22-like on Ovarian Development of Orius nagaii (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae)" Insects 15, no. 2: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15020110
APA StyleDu, H., Wang, R., Dai, X., Yin, Z., Liu, Y., Su, L., Chen, H., Zhao, S., Zheng, L., Dong, X., & Zhai, Y. (2024). Effect of Guanylate Cyclase-22-like on Ovarian Development of Orius nagaii (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). Insects, 15(2), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15020110






