Effect of Acetamiprid, a Neonicotinoid Insecticide, on Locomotor Activity of the American Cockroach
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
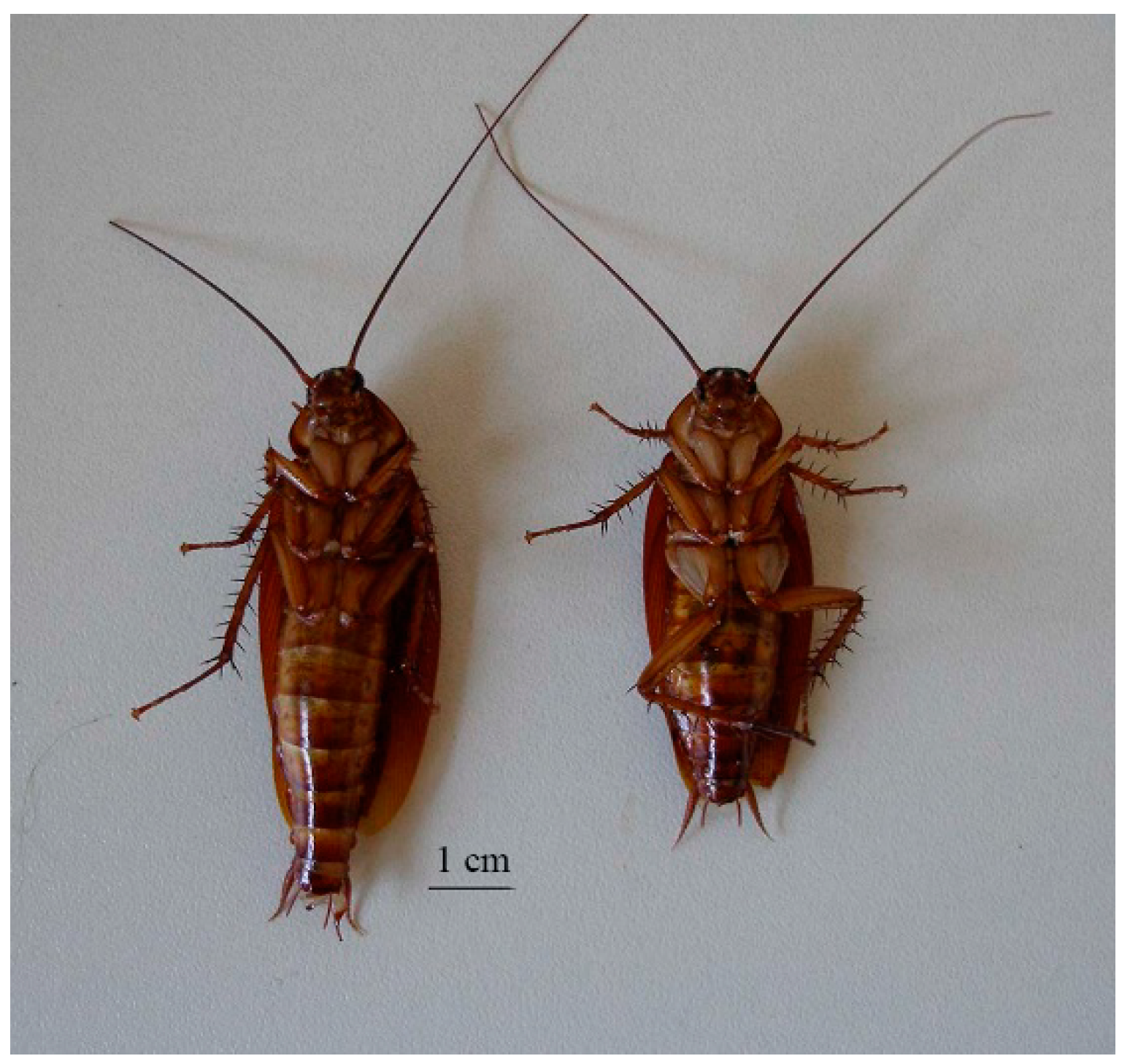
2.1. Animals
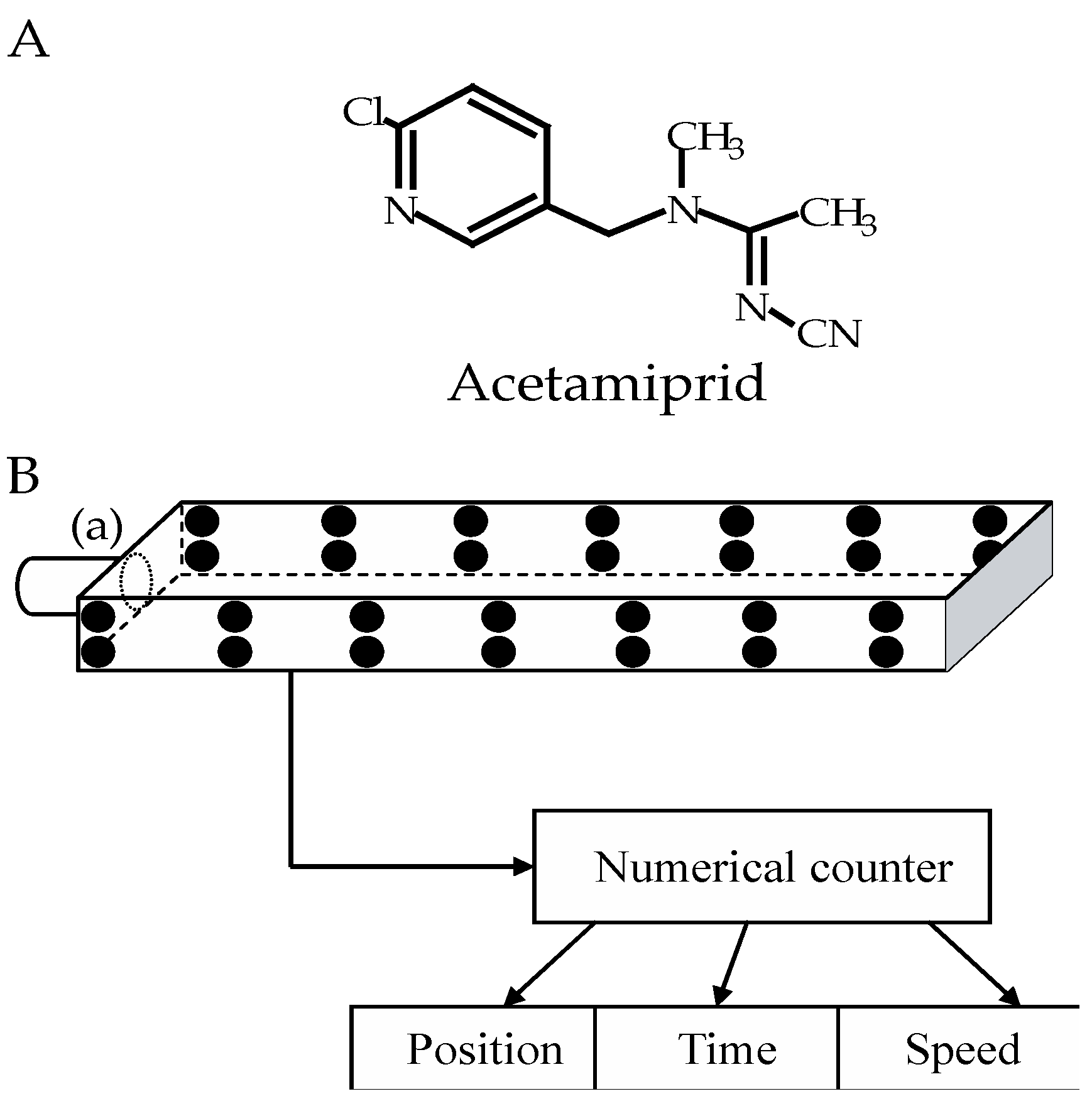
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Exposure Protocol
2.4. Evaluation of Locomotor Activity
2.5. Evaluation of Cockroaches’ Mortality
2.6. Mannitol-Gap Recordings
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
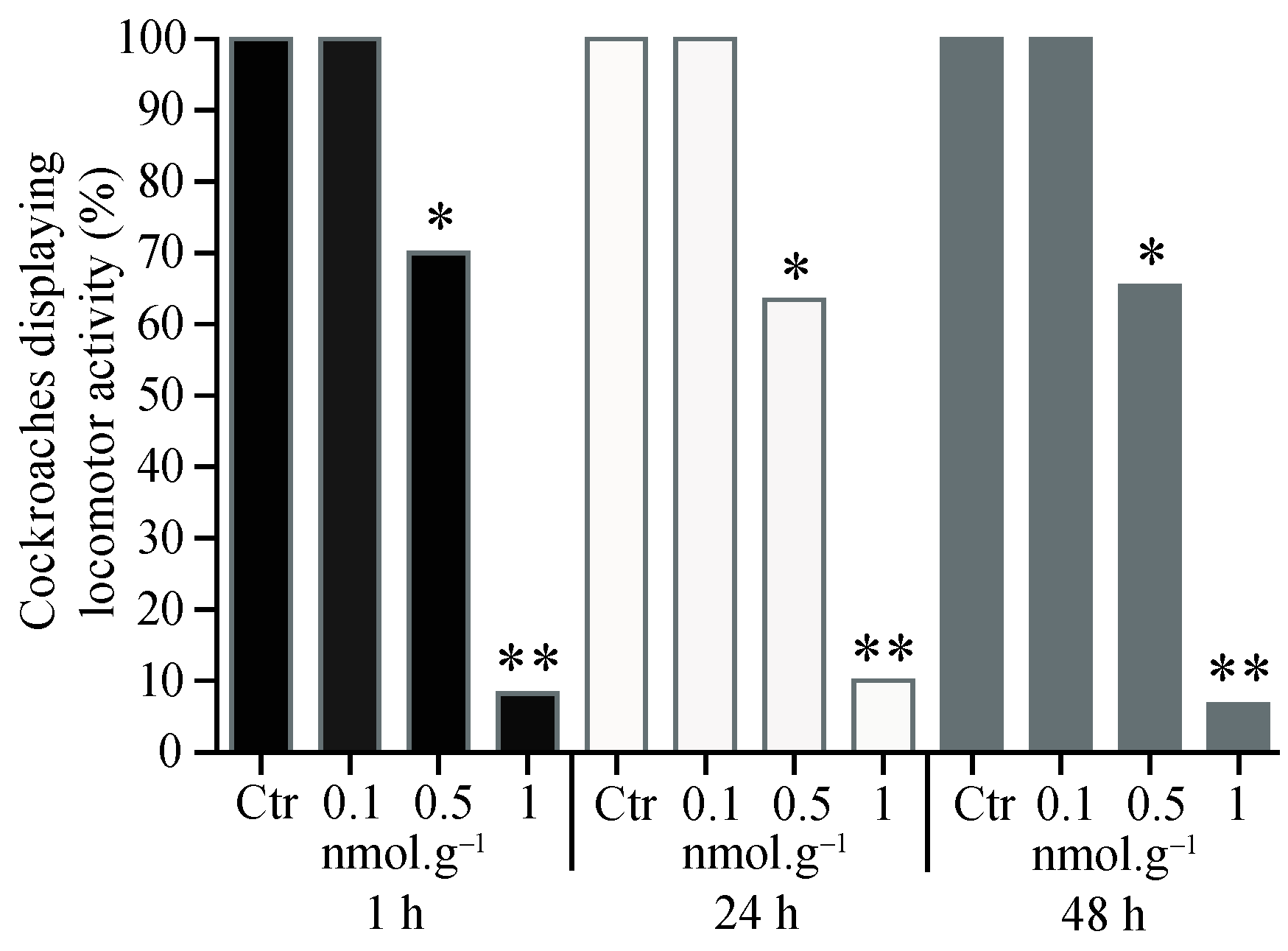
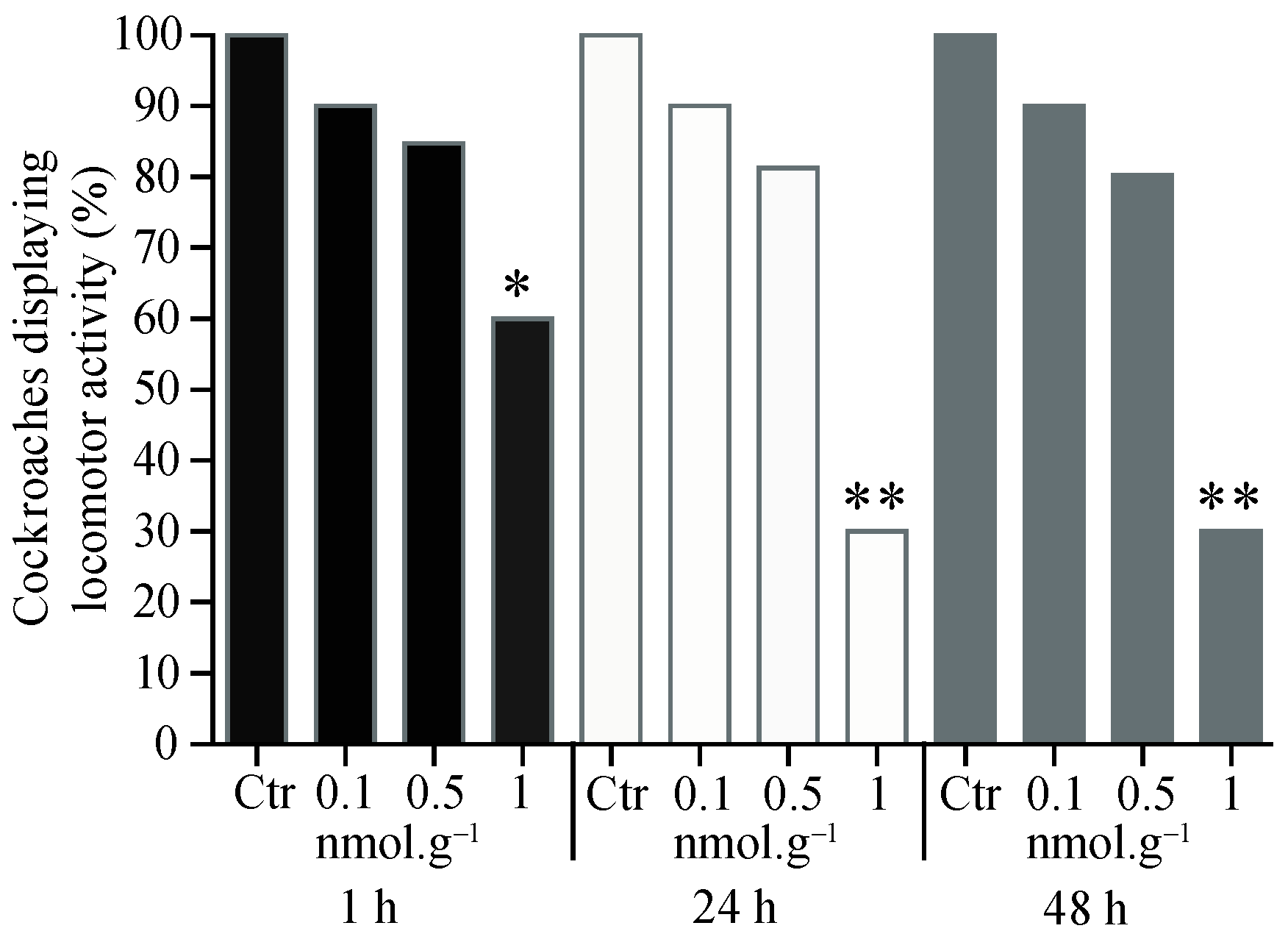
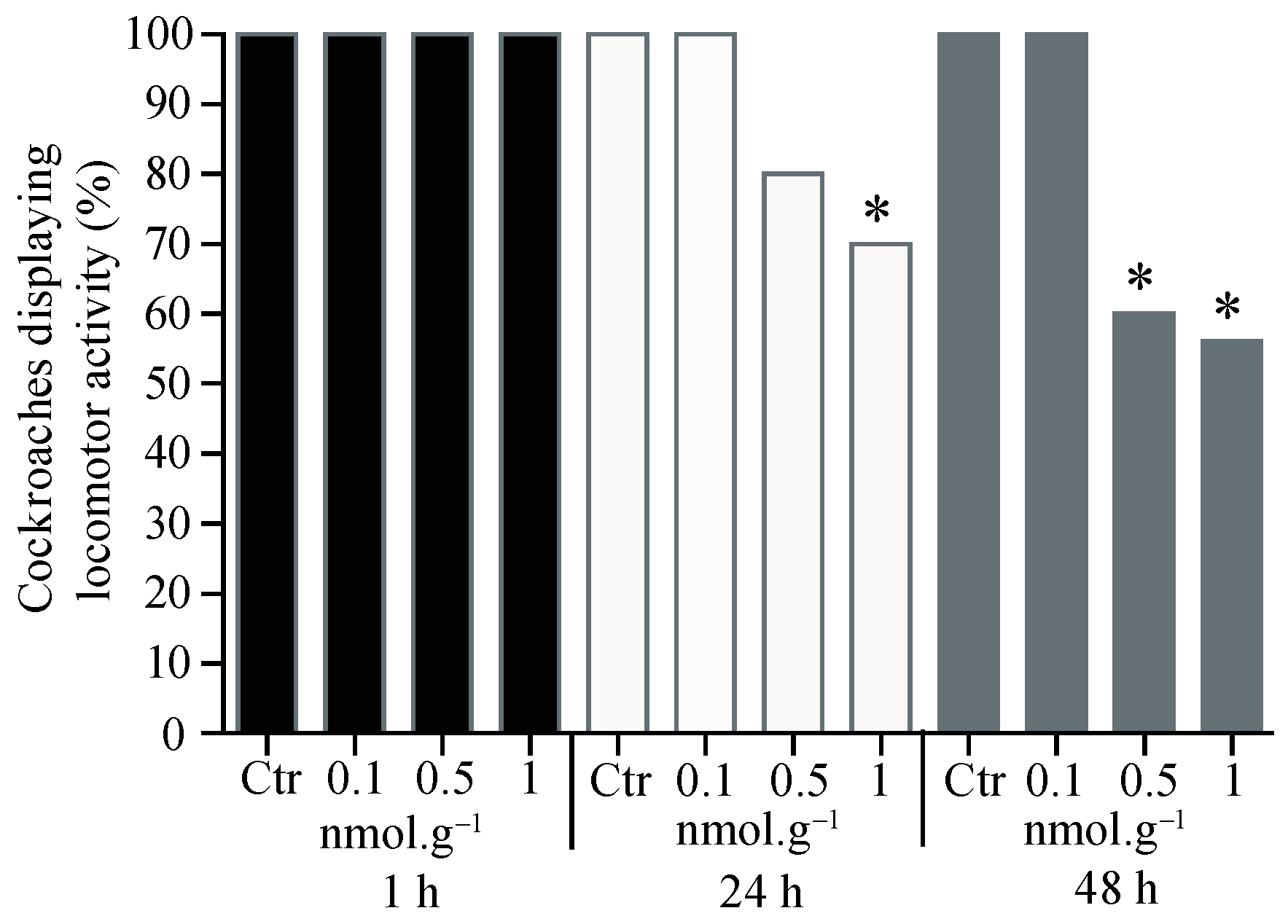
3.1. Percentage of Cockroaches Displaying Locomotor Activity
3.2. Cockroach Mortality after Acetamiprid Application
3.3. Characterization of Cockroach Locomotor Activity: Immobility and Time of Exploration
3.4. Effect of Acetamiprid on Cockroach Sixth Abdominal Ganglion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, Y.; Long, C.; Bai, X.; Liu, W.; Rong, M.; Lai, R.; An, S. Two new types of allergens from the cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Allergy 2015, 70, 1674–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, J.C.; Schal, C. Cockroach allergen biology and mitigation in the indoor environment. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 439–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagabu, S.; Ishihara, R.; Hieda, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Naruse, Y. Insecticidal and neuroblocking potencies of variants of the imidazolidine moiety of imidacloprid-related neonicotinoids and the relationship to partition coefficient and charge density on the pharmacophore. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagabu, S.K.C.; Nishimura, K. Insecticidal and neuroblocking activities toward American cockroach (Periplaneta americana L.) of imidacloprid metabolites, 5-hydroxy-, 4,5-dihydroxy- and 4,5-dehydroimidacloprid. J. Pestic. Sci. 2004, 29, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kagabu, S.M.N.; Hibino, R.; Hanzawa, M.; Nishimura, K. Insecticidal and neuroblocking activities of thiamethoxam-type compounds in the American cockroach (Periplaneta americana L.). J. Pestic. Sci. 2005, 30, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiriyama, K.; Nishiwaki, H.; Nakagawa, Y.; Nishimura, K. Insecticidal activity and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor binding of dinotefuran and its analogues in the housefly, Musca domestica. Pest Manag. Sci. 2003, 59, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Galligan, J.J.; Hollingworth, R.M. Agonist actions of neonicotinoids on nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed by cockroach neurons. Neurotoxicology 2007, 28, 829–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, M.; Casida, J.E. Neonicotinoid insecticide toxicology: Mechanisms of selective action. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2005, 45, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeschke, P.; Nauen, R. Neonicotinoids-from zero to hero in insecticide chemistry. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 1084–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeschke, P.; Nauen, R.; Beck, M.E. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists: A milestone for modern crop protection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 9464–9485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casida, J.E. Neonicotinoids and other insect nicotinic receptor competitive modulators: Progress and prospects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 63, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, H.; Tomizawa, M.; Casida, J.E. Insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: Neonicotinoid binding site specificity is usually but not always conserved with varied substituents and species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3365–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, M.; Casida, J.E. Minor structural changes in nicotinoid insecticides confer differential subtype selectivity for mammalian nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 127, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomizawa, M.; Lee, D.L.; Casida, J.E. Neonicotinoid insecticides: Molecular features conferring selectivity for insect versus mammalian nicotinic receptors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 6016–6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thany, S.H.; Lenaers, G.; Raymond-Delpech, V.; Sattelle, D.B.; Lapied, B. Exploring the pharmacological properties of insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 28, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, K.; Ihara, M.; Sattelle, D.B. Neonicotinoid insecticides: Molecular targets, resistance, and toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 60, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Takahashi, H.; Hatano, R. A novel insecticide, acetamiprid. In Nicotinoid Insecticides and the Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor; Yamamoto, L., Casida, J.E., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 1999; pp. 149–176. [Google Scholar]
- Le Questel, J.Y.; Graton, J.; Ceron-Carrasco, J.P.; Jacquemin, D.; Planchat, A.; Thany, S.H. New insights on the molecular features and electrophysiological properties of dinotefuran, imidacloprid and acetamiprid neonicotinoid insecticides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 7623–7634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodereau-Dubois, B.; List, O.; Calas-List, D.; Marques, O.; Communal, P.Y.; Thany, S.H.; Lapied, B. Transmembrane potential polarization, calcium influx, and receptor conformational state modulate the sensitivity of the imidacloprid-insensitive neuronal insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptor to neonicotinoid insecticides. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 341, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maienfisch, P.; Huerlimann, H.; Rindlisbacher, A.; Gsell, L.; Dettwiler, H.; Haettenschwiler, J.; Sieger, E.; Walti, M. The discovery of thiamethoxam: A second-generation neonicotinoid. Pest Manag. Sci. 2001, 57, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, H.; Tomizawa, M.; Casida, J.E. Neo-nicotinoid metabolic activation and inactivation established with coupled nicotinic receptor-CYP3A4 and -aldehyde oxidase systems. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 161, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzidane, Y.; Touinsi, S.; Motte, E.; Jadas-Hecart, A.; Communal, P.Y.; Leduc, L.; Thany, S.H. Effect of thiamethoxam on cockroach locomotor activity is associated with its metabolite clothianidin. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, P.L.; Ritzmann, R.E. Descending influences on escape behavior and motor pattern in the cockroach. J. Neurobiol. 2001, 49, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, S.; Lapied, B.; Corronc, H.; Sattelle, F. Imidacloprid actions on insect neuronal acetylcholine receptors. J. Exp. Biol. 1997, 200, 2685–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, L.A.; Glusman, J.G.; Libersat, F. Octopamine partially restores walking in hypokinetic cockroaches stung by the parasitoid wasp Ampulex compressa. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 4411–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lambin, M.; Armengaud, C.; Raymond, S.; Gauthier, M. Imidacloprid-induced facilitation of the proboscis extension reflex habituation in the honeybee. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2001, 48, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, C.F.; Tilton, E.W. Tests with Acaricides against the Brown Wheat Mite. J. Econ. Entomol. 1955, 48, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callec, J.J.; Sattelle, D.B. A simple technique for monitoring the synaptic actions of pharmacological agents. J. Exp. Biol. 1973, 59, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callec, J.J.; Sattelle, D.B.; Hue, B.; Pelhate, M. Central synaptic actions of pharmacological agents in insects: Oil-gap and mannitol-gap studies. In Neurotox 79; Sherwood, M., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Thany, S.H. Agonist actions of clothianidin on synaptic and extrasynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed on cockroach sixth abdominal ganglion. Neurotoxicology 2009, 30, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thany, S.H. Thiamethoxam, a poor agonist of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed on isolated cell bodies, acts as a full agonist at cockroach cercal afferent/giant interneuron synapses. Neuropharmacology 2011, 60, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihaka, R.G.R. R: A language for data analysis and graphics. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1996, 5, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Feng, Q.; Lai, K.; Huang, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, Q.X. Toxic effects of indoxacarb enantiomers on the embryonic development and induction of apoptosis in zebrafish larvae (Danio rerio). Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliouane, Y.; El Hassani, A.K.; Gary, V.; Armengaud, C.; Lambin, M.; Gauthier, M. Subchronic exposure of honeybees to sublethal doses of pesticides: Effects on behavior. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauen, R.; Salgado, V.; Kaussmann, M. Thiamethoxam is a neonicotinoid precursor converted to clothianidin in insects and plants. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2003, 76, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, K.; Kanda, Y.; Okazawa, A.; Ueno, T. relationship between insecticidal and neurophysiological activities of imidacloprid and related compounds. Pest Biochel. Physiol. 1994, 50, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, M.; Casida, J.E. Selective toxicity of neonicotinoids attributable to specificity of insect and mammalian nicotinic receptors. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2003, 48, 339–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troczka, B.J.; Homem, R.A.; Reid, R.; Beadle, K.; Kohler, M.; Zaworra, M.; Field, L.M.; Williamson, M.S.; Nauen, R.; Bass, C.; et al. Identification and functional charcterisation of a novel N-cyanoamidine neonicotinoid metabolising cytochrome P450, CYP9Q6, from the buff-tailed bumblebee Bombus terrestris. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 111, 103171–103178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beadle, K.; Singh, K.S.; Troczka, B.J.; Randall, E.; Zaworra, M.; Zimmer, C.T.; Hayward, A.; Reid, R.; Kor, L.; Kohler, M.; et al. Genomic insight into neonicotinoid sensitivity in the solitary bee Osmia bicornis. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1007903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjon, C.; Troczka, B.J.; Zaworra, M.; Beadle, K.; Randall, E.; Hertlein, G.; Singh, K.S.; Zimmer, C.T.; Homem, R.A.; Lueke, B.; et al. Unravelling the molecular determinants of bee sensitivity to neonicotinoid insecticides. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Salgado, V.L.; Hollingworth, R.M. Neural actions of imidacloprid and their involvement in resistance in the Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Say). Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzidane, Y.; Goven, D.; Abd-Ella, A.A.; Deshayes, C.; Lapied, B.; Raymond, V. Subchronic exposure to sublethal dose of imidacloprid changes electrophysiological properties and expression pattern of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes in insect neurosecretory cells. Neurotoxicology 2017, 62, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houchat, J.N.; Taillebois, E.; Thany, S.H. Effects of the DAG analogue 1,2-dioctanoyl-sn-glycerol (DiC8) on nicotine- and clothianidin-evoked currents through alpha-bungarotoxin-insensitive nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed on cockroach neurosecretory cells. Neurotoxicology 2020, 78, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, V.L. Antagonist pharmacology of desensitizing and non-desensitizing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in cockroach neurons. Neurotoxicology 2016, 56, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bantz, A.; Goven, D.; Siegwart, M.; Maugin, S.; Raymond, V. Exposure to a sublethal dose of imidacloprid induces cellular and physiological changes in Periplaneta americana: Involvement of α2 nicotinic acetylcholine subunit in imidacloprid sensitivity. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 181, 105014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihara, M.; Matsuda, K.; Shimomura, M.; Sattelle, D.B.; Komai, K. Super agonist actions of clothianidin and related compounds on the SAD β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2004, 68, 761–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, J.A.; Pitman, R.M. The pharmacology of alpha-bungarotoxin-resistant acetylcholine receptors on an identified cockroach motoneurone. J. Comp. Physiol. 1993, 172, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, V.L.; Saar, R. Desensitizing and non-desensitizing subtypes of alpha-bungarotoxin-sensitive nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in cockroach neurons. J. Insect Physiol. 2004, 50, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

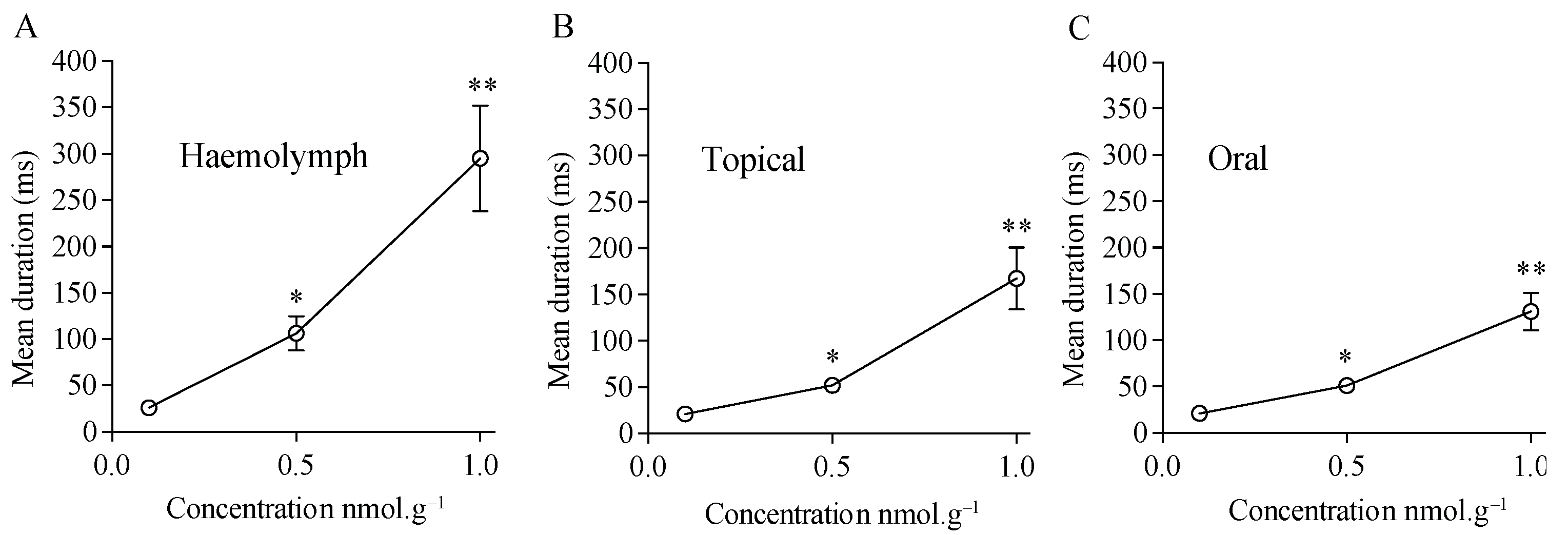
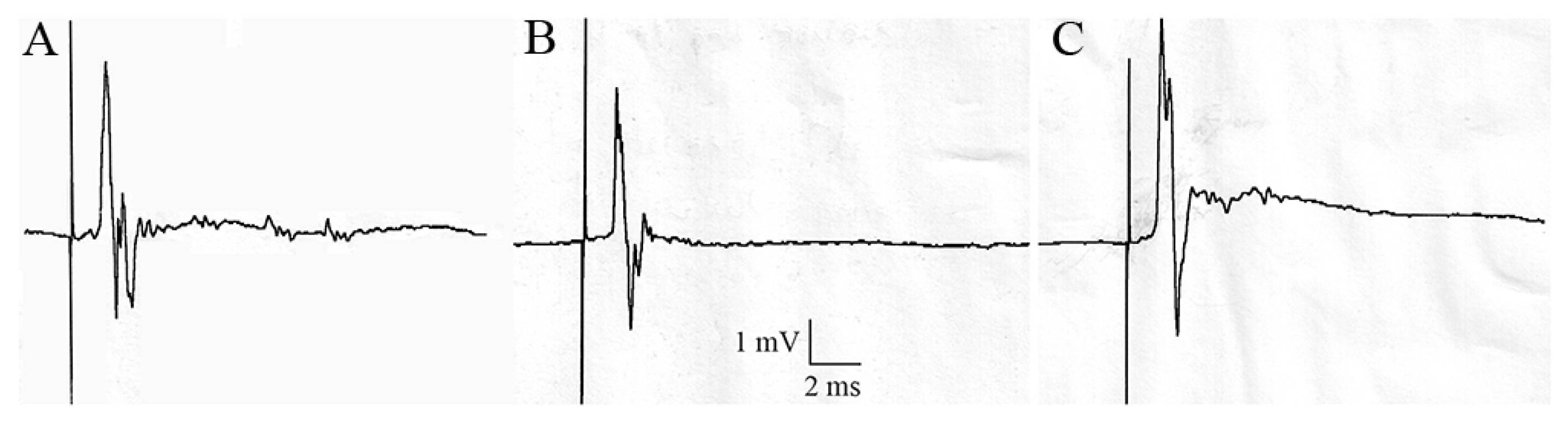
| Exposure Method | Control | Acetamiprid (nmol.g−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.5 | 1 | ||
| Haemolymph injection | 6.2 ± 0.7 s | 6.4 ± 1.7 s | 129.3 ± 25.0 s | 319.0 ± 67.0 s |
| Topical application | 5.9 ± 2.1 s | 6.4 ± 2.5 s | 74.4 ± 2.0 s | 189.0 ± 3.0 s |
| Oral application | 6.1 ± 1.7 s | 6.0 ± 2.0 s | 73.4 ± 17.0 s | 137.7 ± 38.0 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taillebois, E.; Cartereau, A.; Thany, S.H. Effect of Acetamiprid, a Neonicotinoid Insecticide, on Locomotor Activity of the American Cockroach. Insects 2024, 15, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15010054
Taillebois E, Cartereau A, Thany SH. Effect of Acetamiprid, a Neonicotinoid Insecticide, on Locomotor Activity of the American Cockroach. Insects. 2024; 15(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15010054
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaillebois, Emiliane, Alison Cartereau, and Steeve H. Thany. 2024. "Effect of Acetamiprid, a Neonicotinoid Insecticide, on Locomotor Activity of the American Cockroach" Insects 15, no. 1: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15010054
APA StyleTaillebois, E., Cartereau, A., & Thany, S. H. (2024). Effect of Acetamiprid, a Neonicotinoid Insecticide, on Locomotor Activity of the American Cockroach. Insects, 15(1), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15010054






