Comparison of Predatory Performance among Three Ladybird Species, Harmonia axyridis, Coccinella septempunctata and Hippodamia variegata, Feeding on Goji Berry Psyllid, Bactericera gobica
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing
2.2. Functional Response
2.3. Intraspecific Interactions
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Functional Response
2.4.2. Intraspecific Interactions
3. Results
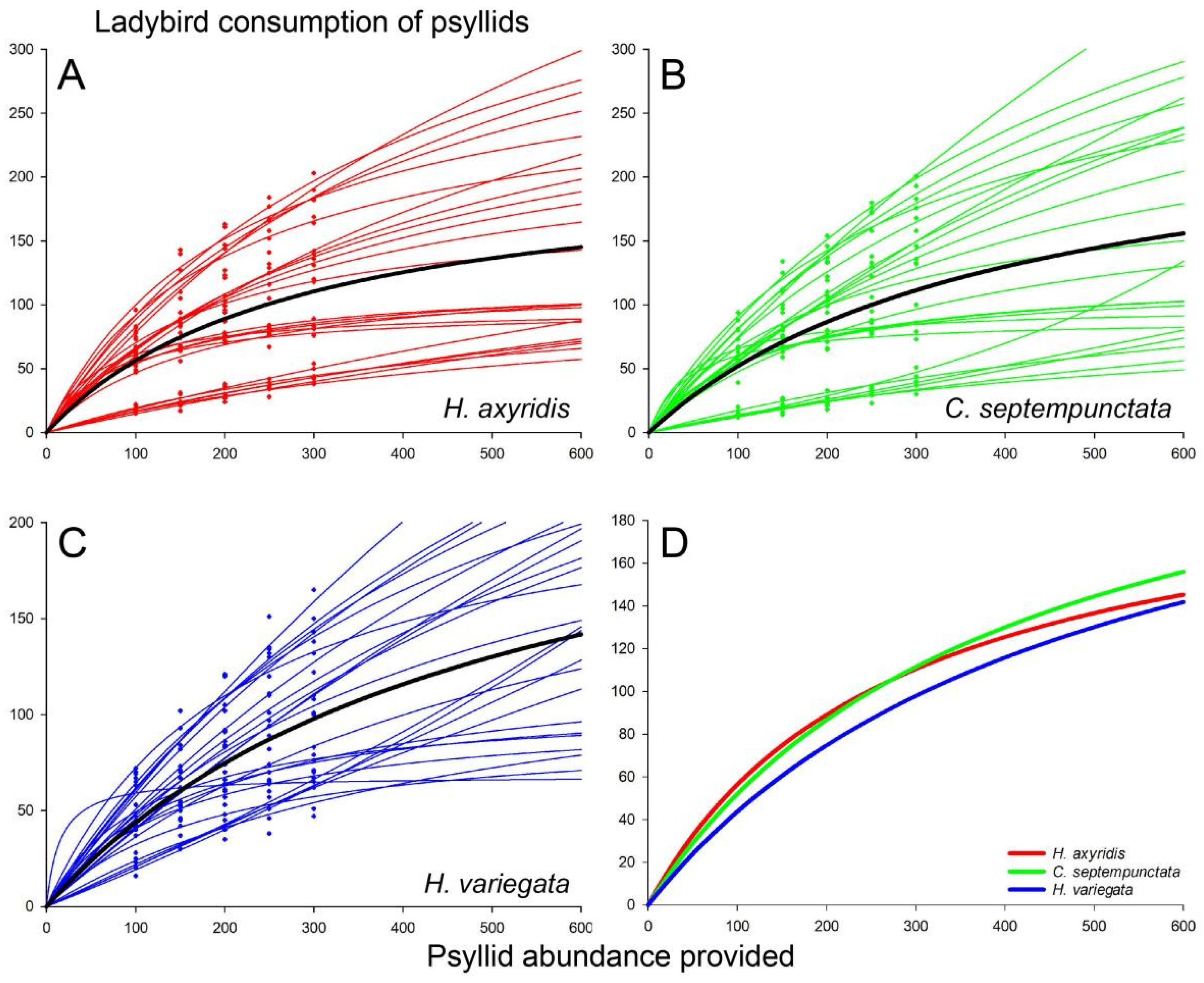
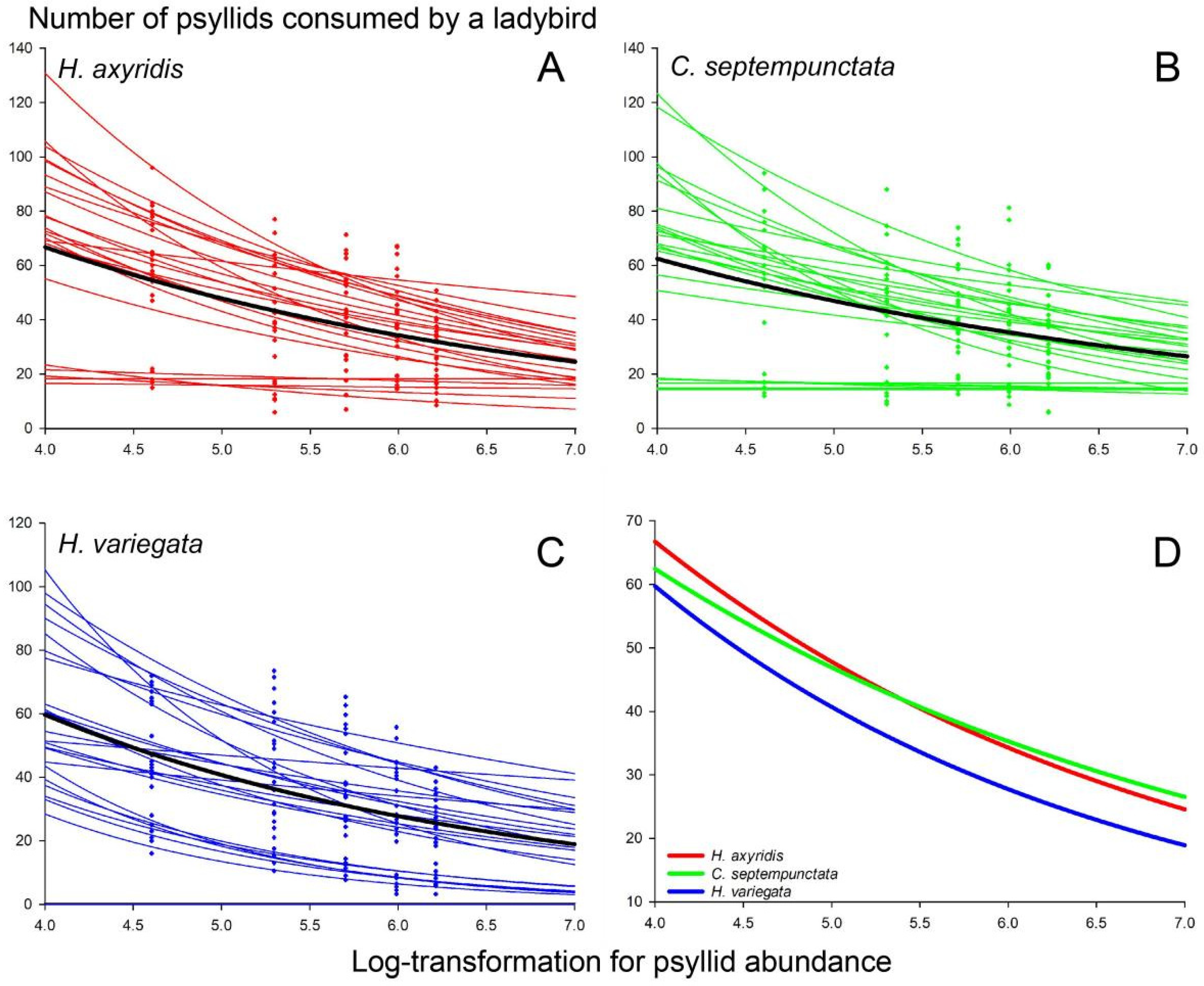
3.1. Functional Response
3.2. Intraspecific Interactions
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vidovi, B.B.; Milini, D.D.; Mareti, M.D.; Djuri, J.D.; Ilic, T.D.; Kosti, A.; Pesic, M.B. Health benefits and applications of goji berries in functional food products development: A review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhaes, V.; Silva, B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Silva, A.R.; Dias, A.C.P. Comparative studies on the anti-neuroinflammatory and antioxidant activities of black and red goji berries. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 92, 105038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, T.; Yu, X.M.; Badwal, T.S.; Xu, B.J. Comparative studies on phenolic profiles, antioxidant capacities and carotenoid contents of red goji berry (Lycium barbarum) and black goji berry (Lycium ruthenicum). Chem. Cent. J. 2017, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Yan, Y.M.; Zhang, L.T.; Mi, J.; Yu, L.M.; Zhang, F.F.; Lu, L.; Luo, Q.; Li, X.Y.; Zhou, X.; et al. A comprehensive review of goji berry processing and utilization. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 7445–7457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Y.; Shen, S.; Zhi, H.; Li, W. Pesticides residues on Goji berry: A characteristic minor crop in China. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 120, 105342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Gupta, R.; Sharma, S. Impact of chemical- and bio-pesticides on bacterial diversity in rhizosphere of Vigna radiata. Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.K.A.; Pratt, J.A.P.; Nelson, F.R.S. Compatability of Metarhizium Anisopliae Var. Anisopliae with chemical pesticides. Mycopathologia 1987, 99, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.D.; Biever, K.D.; Ignoffo, C.M. Contact toxicity of some chemical and biological pesticides to several insect parasitoids and predators. Entomophaga 1975, 20, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.X.; Ma, B.X.; Wu, F.M.; Ouyang, H.Y.; Fan, J.Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, R.Z. The hyperparasitoid Marietta picta mediates the coexistence of primary parasitoids of goji berry psyllid. Entomol. Gen. 2020, 2, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Smith, O.M.; Chen, W.; Liu, P.; Yuan, Q.; Kang, C.; Wang, T.; Sun, J.; Yan, B.; Liu, X.; et al. Morphological characterization and sexual dimorphism of the antennal sensilla in Bactericera gobica Loginova (Hemiptera: Psyllidae)—A scanning and transmission electron microscopic study. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.X.; Ma, B.X.; Wu, F.M.; Xu, J.; Zhang, R.Z. The endoparasitoid Psyllaephagus arenarius benefits from the ectoparasitic venom via multiparasitism with the ectoparasitoid Tamarixia lyciumi. Insect Sci. 2020, 27, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, G.; Burckhardt, D.; Lee, S. First record from Korea of the jumping plant-louse Bactericera gobica (Loginova) (Hemiptera: Triozidae), a pest on Lycium chinense Mill., with comments on psyllids associated with Lycium (Solanaceae). J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2016, 19, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.X.; Ge, Y.; He, J.; Haseeb, M.; Zhang, R.Z. Positive Interactions between Aceria pallida and Bactericera gobica on Goji Berry Plants. Insects 2022, 13, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Gupta, R.; Sharma, S. Impact of pesticides on plant growth promotion of Vigna radiata and non-target microbes: Comparison between chemical- and bio-pesticides. Ecotoxicology 2014, 23, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, N.A.; Margie, P.; Lois, S.G. Nature’s chemicals and synthetic chemicals: Comparative toxicology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 7782–7786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmann, K.P.; Minghua, Z.; Grant, J.A. Does Use of Pesticides Known to Harm Natural Enemies of Spider Mites (Acari: Tetranychidae) Result in Increased Number of Miticide Applications? An Examination of California Walnut Orchards. J. Econ. Entomol. 2011, 104, 1496–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smilanich, A.M.; Dyer, L.A. Effects of Banana Plantation Pesticides on the Immune Response of Lepidopteran Larvae and Their Parasitoid Natural Enemies. Insects 2012, 3, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.X.; Ouyang, H.Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, R.; He, J.; Zhang, R.Z. Predation of Poratrioza sinica Yang & Li by the adults of Coccinella septempunctata. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 3712–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.X.; Ouyang, H.Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, R.; He, J.; Zhang, R.Z. Predation of Paratrioza sinica Yang & Li by adult Hippodamia variegata (Goeze). Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2016, 53, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.X.; Ma, B.X.; Xu, J.; He, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, R.Z. Predation of Poratrioza sinica Yang & Li by Harmonia axyridis adults. Acta Phytophy. Sin. 2017, 44, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliano, S.A. Nonlinear curve fitting: Predation and functional response curves. In Design and Analysis of Ecological Experiments, 2nd ed.; Scheiner, S.M., Gurevitch, J., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 178–196. [Google Scholar]
- Timms, J.E.; Oliver, T.H.; Straw, N.A.; Leather, S.R. The effects of host plant on the coccinellid functional response: Is the conifer specialist Aphidecta obliterata (L.) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) better adapted to spruce than the generalist Adalia bipunctata (L.) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae)? Biol. Control 2008, 47, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Fadamiro, H.Y. Functional responses and prey-stage preferences of three species of predacious mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae) on citrus red mite, Panonychus citri (Acari: Tetranychidae). Biol. Control 2010, 53, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.F.; Matos, C.H.; de Oliveira, C.R.; Da Silva, T.G.; Lima Neto, I.F. Functional and numerical responses of Stethorus tridens Gordon (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) preying on Tetranychus bastosi Tuttle, Baker & Sales (Acari: Tetranychidae) on physic nut (Jatropha curcas). Biol. Control 2017, 111, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathipour, Y.; Karimi, M.; Farazmand, A.; Talebi, A.A. Age-specific functional response and predation rate of Amblyseius swirskii (Phytoseiidae) on two-spotted spider mite. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2017, 22, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M.A.; Tirry, L.; De Clercq, P. Effect of temperature on the functional response of Adalia bipunctata to Myzus persicae. BioControl 2010, 55, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Clercq, P.; Mohaghegh, J.; Tirry, L. Effect of host plant on the functional response of the predator Podisus nigrispinus (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Biol. Control 2000, 18, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, A.E.; Stillman, R.A.; Watson, H.K.; Norris, K.J. Searching efficiency and the functional response of a pause-travel forage. Funct. Ecol. 2007, 21, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, R.P.; Chandra, G.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Ghosh, A. Effect of temperature and search area on the functional response of Anisops sardea (Hemiptera: Notonectidae) against Anopheles stephensi in laboratory bioassay. Acta Trop. 2017, 166, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassell, M.P. A Population model for the interaction between Cyzenis albicans (Fall.) (Tachinidae) and Operophtera brumata (L.) (Geometridae) at Wytham, Berkshire. J. Anim. Ecol. 1969, 38, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.C.; Milroy, S.P.; Xu, W. Development and reproduction of a native generalist predator, Coccinella transversalis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), on the tomato potato psyllid, Bactericera cockerelli, with a greenhouse assay of biocontrol potential. Biol. Control 2022, 176, 105108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.D.; Qureshi, J.; Zhou, X.M.; Pu, Z.X.; Chen, G.Q.; Yu, J.H.; Zhang, H.Y. Predation and functional response of the multi-coloured Asian ladybeetle Harmonia axyridis on the adult Asian citrus psyllid Diaphorina citri. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2019, 29, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayntz, D.; Raubenheimer, D.; Salomon, M.; Toft, S.; Simpson, S. Nutrient-specific foraging in invertebrate predators. Science 2005, 307, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilder, S.M.; Holway, D.A.; Suarez, A.V.; Eubanks, M.D. Macronutrient content of plant-based food affects growth of a carnivorous arthropod. Ecology 2011, 92, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denno, R.F.; Fagan, W.F. Might nitrogen limitation promote omnivory among carnivorous arthropods? Ecology 2003, 84, 2522–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.M.; Sebastian, P.; Wilder, S.M.; Rypstra, A.L. The nutritional content of prey affects the foraging of a generalist arthropod predator. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.; Mayntz, D.; Toft, S.; Clissold, F.J.; Hunt, J.; Raubenheimer, D.; Raubenheimer, D.; Simpson, S.J. Optimal foraging for specific nutrients in predatory beetles. Proc. R. Soc. B 2012, 279, 2212–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.Z.; Yi, L.; Lu, Z.J. Silencing of Chitin-Binding Protein with PYPV-Rich Domain Impairs Cuticle and Wing Development in the Asian Citrus Psyllid, Diaphorina citri. Insects 2022, 13, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, E.D.; Hall, D.G.; Shatters, R.G. Ultrastructure and development of the new stylets inside pre-molting first instar nymphs of the asian citrus psyllid Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Liviidae). Fla. Entomol. 2015, 98, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkaczenko, G.K.; Fischer, A.C.; Weterings, R. Prey preference of the Common House Geckos Hemidactylus frenatus and Hemidactylus platyurus. Herpetol Notes 2014, 7, 483–488. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, D.O.; Dickman, C.R. Diets of insectivorous marsupials in arid Australia: Selection for prey type, size or hardness? J. Arid Environ. 1993, 25, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.X.; Ma, B.X.; Shuo, Y.; Xu, J.; He, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, R.Z. Protective effects of the egg stalk of Paratrioza sinica (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) at various angles and spacings against three predaceous coccinellids, Harmonia axyridis, Coccinella septempunctata and Hippodamia variegate (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhoudi, F.; Allahyari, H.; Tabadkani, S.M.; Gholizadeh, M. Prey preference of Aphidoletes aphidimyza on Acyrthosiphon pisum: Effect of Prey Color and Size. J. Insect Behav. 2014, 27, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayeh, A.; Hufbauer, R.A.; Estoup, A.; Ravigne, V.; Frachon, L.; Facon, B. Biological invasion and biological control select for different life histories. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klarner, D.; Barth, F.G. Vibratory signals and prey capture in orb-weaving spiders (Zygiella x-notata, Nephila clavipes; Araneidae). J. Comp. Physiol. 1982, 148, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergenroder, R.; Barth, F.G. Vibratory signals and spider behavior: How do the sensory inputs from the eight legs interact in orientation? J. Comp. Physiol. 1983, 152, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.X.; He, J.; Dong, H.; Zhang, R.Z. Functional response and intraspecific competition of three ladybird species feeding on aphids on goji berry plants in laboratory and semi-field conditions. Insects 2023, 14, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, Z. Effect of alfalfa habitat change on dispersal behavior of Harmonia axyridis Pallas and Hippodamia variegata Goeze (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2021, 24, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfadyen, S.; Davies, A.P.; Zalucki, M.P. Assessing the impact of arthropod natural enemies on crop pests at the field scale. Insect Sci. 2015, 22, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattingh, V.; Samways, M.J. Absence of intraspecific interference during feeding by the predatory ladybirds Chilocorus spp. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Ecol. Entomol. 1990, 15, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaviezo, T.; Soares, A.O.; Grez, A.A. Interspecific exploitative competition between Harmonia axyridis and other coccinellids is stronger than intraspecific competition. Biol. Control 2019, 131, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, A.G.; Ransijn, J.; Ravn, H.P. A sublethal effect on native Anthocoris nemoralis through competitive interactions with invasive Harmonia axyridis. Ecol. Entomol. 2015, 40, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondoni, G.; Ielo, F.; Ricci, C.; Conti, E. Intraguild predation responses in two aphidophagous coccinellids identify differences among juvenile stages and aphid densities. Insects 2014, 5, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsanis, A.; Babendreier, D.; Nentwig, W.; Kenis, M. Intraguild predation between the invasive ladybird Harmonia axyridis and non-target European coccinellid species. BioControl 2013, 58, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, N.E.; Milonas, P.G.; Demiris, N.; Papachristos, D.P.; Matsinos, Y.G. Digestion limits the functional response of an aphidophagous coccinellid. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2014, 107, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.X.; Zhang, J.; Haseeb, M.; Yan, S.; Kanga, L.; Zhang, R.Z. Functional responses and intraspecific competition in the ladybird Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) provided with Melanaphis sacchari (Homoptera: Aphididae) as prey. Eur. J. Entomol. 2018, 115, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gils, J.A.; Piersma, T. Digestively constrained predators evade the cost of interference competition. J. Anim. Ecol. 2004, 73, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, N.E.; Nikos, D.; Milonas, P.G.; Simon, P.; Theodore, K. Does mutual interference affect the feeding rate of aphidophagous coccinellids? A modeling perspective. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, J.P. Numerical response of Olla v-nigrum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) to infestations of Asian citrus psyllid, (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) in Florida. Fla. Entomol. 2001, 84, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, J.P. Biological control of Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) in Florida: A preliminary report. Entomol. News 2002, 113, 216–222. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neil, R.J. Functional response and search strategy of Podisus maculiventris (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) attacking Colorado potato beetle (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Environ. Entomol. 1997, 26, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, V.; Araya, J.E. Functional response of Nabis punctipennis Blanchard to Acyrthosiphon pisum Harris in the laboratory. Chil. J. Agric. Anim. Sci. 2017, 33, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.Q.; Wang, S.L.; Ren, Q.; Jin, Z.; Wu, Y.P. Effects of time delay and space on herbivore dynamics: Linking inducible defenses of plants to herbivore outbreak. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maupin, J.; Riechert, S. Superfluous killing in spiders: A consequence of adaptation to food-limited environments? Behav. Ecol. 2001, 12, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noriyuki, S.; Osawa, N. Intrinsic prey suitability in specialist and generalist Harmonia ladybirds: A test of the trade-off hypothesis for food specialization. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2012, 144, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zhang, L.; Qin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Tan, S.; Fu, Z.; Smith, O.M.; Shi, W.P. Different predation capacities and mechanisms of Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) on two morphotypes of pear psylla Cacopsylla chinensis (Hemiptera: Psyllidae). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.M.; Tao, Y.L.; Chi, H.; Wan, F.H.; Chu, D. Adaptability of small brown planthopper to four rice cultivars using life table and population projection method. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, P.; He, J.; Ge, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, R. Comparison of Predatory Performance among Three Ladybird Species, Harmonia axyridis, Coccinella septempunctata and Hippodamia variegata, Feeding on Goji Berry Psyllid, Bactericera gobica. Insects 2024, 15, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15010019
Wu P, He J, Ge Y, Liu Z, Zhang R. Comparison of Predatory Performance among Three Ladybird Species, Harmonia axyridis, Coccinella septempunctata and Hippodamia variegata, Feeding on Goji Berry Psyllid, Bactericera gobica. Insects. 2024; 15(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Pengxiang, Jia He, Yang Ge, Zhanghui Liu, and Runzhi Zhang. 2024. "Comparison of Predatory Performance among Three Ladybird Species, Harmonia axyridis, Coccinella septempunctata and Hippodamia variegata, Feeding on Goji Berry Psyllid, Bactericera gobica" Insects 15, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15010019
APA StyleWu, P., He, J., Ge, Y., Liu, Z., & Zhang, R. (2024). Comparison of Predatory Performance among Three Ladybird Species, Harmonia axyridis, Coccinella septempunctata and Hippodamia variegata, Feeding on Goji Berry Psyllid, Bactericera gobica. Insects, 15(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15010019




